TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings and Inactivation of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm—Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract
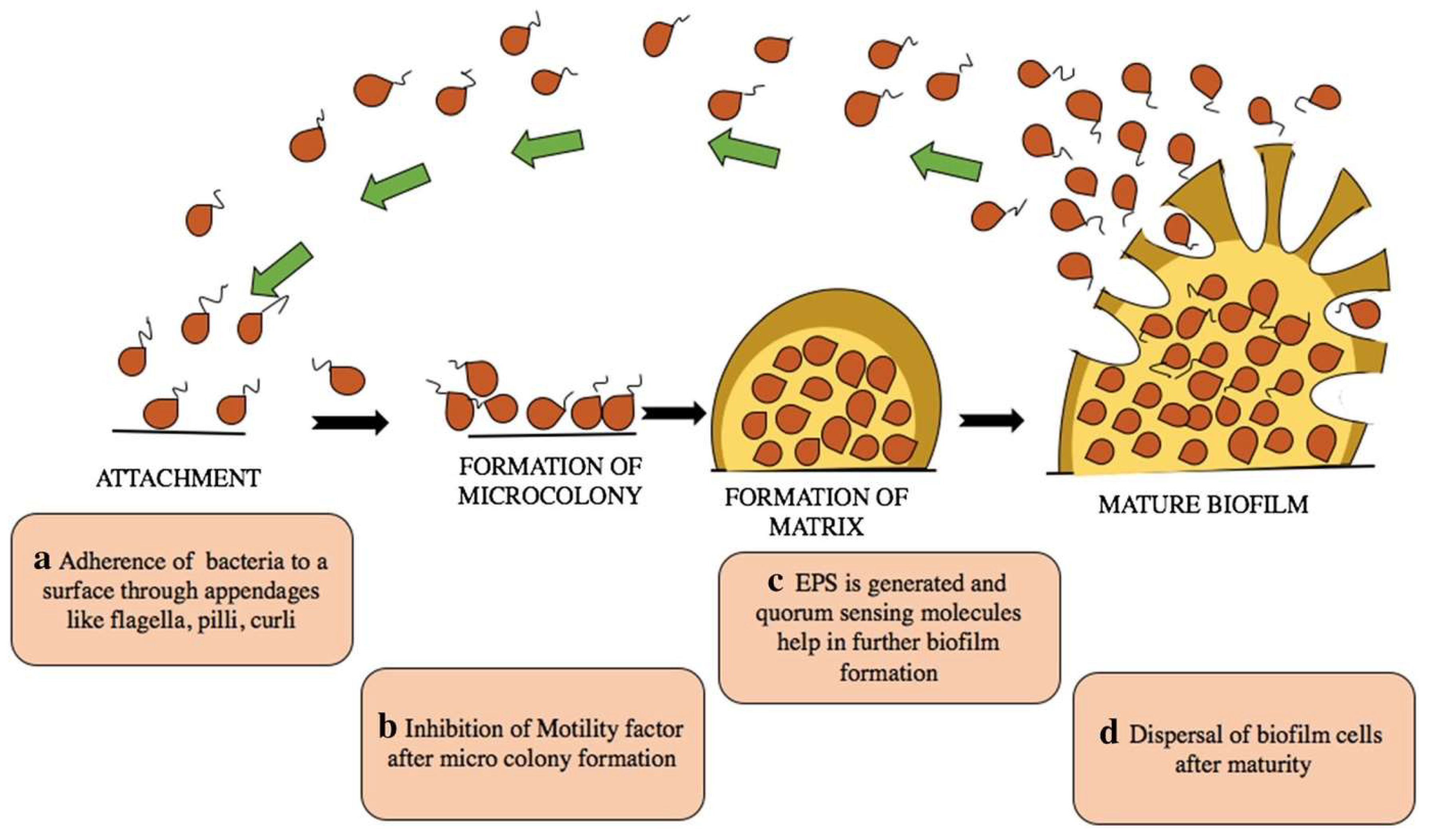
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Studies on MDR Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm
3.2. Studies on Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effects of TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings
| Study | Country | Type of Study | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alipanahpour Dil E et al., 2019 [53] | Iran | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coating |
| Araújo BF et al., 2018 [64] | Brazil | Cross-sectional | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Aslam M et al., 2021 [62] | Malaysia | Review | TiO2 nanoparticles |
| Bai J et al., 2023 [77] | China | Cross-sectional | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Banerjee D et al., 2019 [28] | India | Review | Biofilms, TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Barani M et al., 2022 [95] | Iran | Review | Biofilms, nanocomposite coating |
| Bevacqua E et al., 2023 [60] | Italy | Review | TiO2 nanoparticles |
| Bode-Aluko et al., 2021 [40] | South Africa | Experimental study | Biofilms, nanocomposite coating |
| Booq RY et al., 2022 [68] | Saudi Arabia | Cross-sectional | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Bonan RF et al., 2019 [113] | Brazil | Experimental study | Biofilms, nanocomposite coating |
| Bourigault et al., 2018 [10] | France | Experimental study | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Brunke MS et al., 2022 [7] | Germany | Case control | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Cai Y et al., 2013 [101] | Sweden | Experimental study | Biofilms, TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Centeleghe I et al., 2023 [94] | UK | Experimental study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Costa DM et al., 2019 [90] | Brazil | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Dan B et al., 2023 [8] | China | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| D’Apolito D et al., 2020 [69] | Italy | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Dey D et al., 2016 [76] | India | Experimental study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Fasciana T et al., 2021 [16] | Italy | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Fetyan NAH et al., 2024 [61] | Egypt | Experimental study | TiO2 nanoparticles |
| Folliero V et al., 2021 [80] | Italy | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Hebeish AA et al., 2013 [98] | Egypt | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Horváth E et al., 2020 [42] | Switzerland | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Hu H et al., 2015 [91] | Australia | Cross-sectional | Biofilm |
| Jones RN, 2010 [84] | USA | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Joya YF et al., 2012 [106] | UK | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Kerbauy G et al., 2016 [74] | Brazil | Experimental study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Kumar A et al., 2017 [56] | India | Review | Biofilms |
| Kumaravel V et al., 2021 [39] | Ireland | Review | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Kiran ASK et al., 2018 [97] | India | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Ledwoch K et al., 2018 [89] | UK | Multicenter study | Biofilms |
| Liu Y et al., 2017 [70] | China | Experimental study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Lin Y et al., 2021 [102] | China | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Mahmud ZH et al., 2022 [71] | Bangladesh | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Melsen WG et al., 2011 [86] | Netherlands | Systematic review | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Mohammadi M et al., 2023 [87] | Iran | Cohort study | Biofilms, KPC-Kp |
| Moongraksathum B et al., 2019 [99] | Taiwan | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Motay M et al., 2020 [55] | France | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Mousavi SM et al., 2023 [59] | Iran | Experimental study | Biofilms, TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Naik K et al., 2013 [112] | India | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Nica IC et al., 2017 [107] | Romania | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Nica IC et al., 2017 [108] | Romania | Experimental study | Biofilms, TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Noreen et al., 2019 [105] | Pakistan | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Nosrati et al., 2017 [103] | Iran | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Ochońska et al., 2021 [83] | Poland | Experimental study | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Ohko et al., 2009 [110] | Japan | Experimental study | Biofilms, TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Palacios et al., 2022 [75] | Spain | Experimental study | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, biofilms |
| Pandya et al., 2024 [63] | India | Review | TiO2 nanoparticles |
| Papalini et al., 2020 [73] | Italy | Experimental study | KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, biofilms |
| Pourmehdiabadi et al., 2023 [26] | Iran | Experimental study | KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, biofilms |
| Prasad et al., 2019 [100] | India | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Rafiq et al., 2016 [37] | India | Experimental study | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Rahman et al., 2021 [114] | Pakistan | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Rani et al., 2021 [104] | India | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Sabenca et al., 2023 [81] | Portugal | Experimental study | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, biofilms |
| Shadkam et al., 2021 [38] | Iran | Experimental study | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae, biofilms |
| Snyder et al., 2020 [9] | USA | Review | Biofilms |
| Silva et al., 2021 [72] | Brazil | Experimental study | KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Singha et al., 2023 [54] | Bangladesh | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Stallbaum et al., 2021 [65] | Brazil | Cross-sectional study | Biofilms |
| Tahir et al., 2016 [111] | China | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Taylor et al., 2011 [96] | USA | Review | Biofilms |
| Thakur et al., 2019 [109] | India | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Thorarinsdottir et al., 2020 [82] | Sweden | Observational study | Biofilms |
| Veltri et al., 2019 [47] | Italy | Descriptive study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Vickery et al., 2012 [88] | Australian | Experimental study | Biofilms |
| Yazgan et al., 2018 [67] | Turkey | Experimental study | Biofilms |
| Zhang et al., 2019 [43] | UK | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
| Zheng et al., 2020 [50] | Singapore | Experimental study | Biofilms |
| Zhou C et al., 2023 [79] | China | Experimental study | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| Zhou H et al., 2021 [48] | China | Experimental study | TiO2 nanocomposite coatings |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHL | Acyl homoserine lactose inducer |
| Ag | Silver |
| Au | Gold |
| BC | Bacterial cellulose |
| Cu | Copper |
| CuO | Copper oxide |
| CVC | Central venous catheter |
| CRKP | Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| CS | Chitosan |
| DSB | Dry surface biofilms |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| ICU KP | Intensive care unit Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| KPC | Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| MBC | Minimum bactericidal concentration |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| PDR | Pandrug-resistant |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SiO2 | Silicon dioxide |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| VAP | Ventilator-associated pneumonia |
| XDR | Extensively drug-resistant |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
| ZOI | Zone of inhibition |
References
- Suay-García, B.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Present and Future of Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Infections. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bhadury, P.; Mitra, S.; Naha, S.; Saha, B.; Dutta, S.; Basu, S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Causing Neonatal Bloodstream Infections: Emergence of NDM-1-Producing Hypervirulent ST11-K2 and ST15-K54 Strains Possessing pLVPK-Associated Markers. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04121-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Peghin, M. How to manage KPC infections. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 2049936120912049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe 2017. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/surveillance-antimicrobial-resistance-europe-2017 (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Carbapenem- and/or Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae in Greece: Molecular Follow-Up Survey 2022. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/carbapenem-andor-colistin-resistant-klebsiella-pneumoniae-greece-molecular-follow (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Reyes, J.; Aguilar, A.C.; Caicedo, A. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Microbiology Key Points for Clinical Practice. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2019, 12, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunke, M.S.; Konrat, K.; Schaudinn, C.; Piening, B.; Pfeifer, Y.; Becker, L.; Schwebke, I.; Arvand, M. Tolerance of biofilm of a carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae involved in a duodenoscopy-associated outbreak to the disinfectant used in reprocessing. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, B.; Dai, H.; Zhou, D.; Tong, H.; Zhu, M. Relationship Between Drug Resistance Characteristics and Biofilm Formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, G.M. Introduction to Transmission of Infection: Potential Agents Transmitted by Endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N Am. 2020, 30, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourigault, C.; Le Gallou, F.; Bodet, N.; Musquer, N.; Juvin, M.-E.; Corvec, S.; Ferronniere, N.; Wiesel, S.; Gournay, J.; Birgand, G.; et al. Duodenoscopy: An amplifier of cross-transmission during a carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae outbreak in a gastroenterology pathway. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 99, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastmeier, P.; Vonberg, R.P. Klebsiella spp. in endoscopy-associated infections: We may only be seeing the tip of the iceberg. Infection 2014, 42, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, R.M.; Yang, S.; Kim, S.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Russell, D.; Trout, A.M.; Zaroda, T.; Cheng, Q.J.; Aldrovandi, G.; Uslan, D.Z.; et al. Duodenoscope-Related Outbreak of a Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Identified Using Advanced Molecular Diagnostics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioutis, C.; Eichel, V.M.; Mutters, N.T. Transmission of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: The role of infection control. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76 (Suppl. S1), i4–i11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vintila, B.I.; Arseniu, A.M.; Morgovan, C.; Butuca, A.; Sava, M.; Bîrluțiu, V.; Rus, L.L.; Ghibu, S.; Bereanu, A.S.; Codru, I.R.; et al. A Pharmacovigilance Study Regarding the Risk of Antibiotic-Associated Clostridioides difficile Infection Based on Reports from the EudraVigilance Database: Analysis of Some of the Most Used Antibiotics in Intensive Care Units. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, W.; Dasti, J.I.; Andrews, S.C. Draft genome sequence of a carbapenemase-producing (NDM-1) and multidrug-resistant, hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 isolate from Pakistan, with a non-hypermucoviscous phenotype associated with rmpA2 mutation. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasciana, T.; Ciammaruconi, A.; Gentile, B.; Di Carlo, P.; Virruso, R.; Tricoli, M.R.; Palma, D.M.; Pitarresi, G.L.; Lista, F.; Giammanco, A. Draft Genome Sequence and Biofilm Production of a Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (KpR405) Sequence Type 405 Strain Isolated in Italy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Burns, K.; Baño, J.R.; Borg, M.; Daikos, G.; Dumpis, U.; Lucet, J.C.; Moro, M.L.; Tacconelli, E.; Simonsen, G.S.; et al. Infection prevention and control measures and tools for the prevention of entry of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae into healthcare settings: Guidance from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facility Guidance for Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE): November 2015 Update—CRE Toolkit. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/79104 (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Health Care Facilities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Bassetti, M.; Giacobbe, D.; Giamarellou, H.; Viscoli, C.; Daikos, G.; Dimopoulos, G.; De Rosa, F.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.; Rossolini, G.; Righi, E.; et al. Management of KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, M.; Carnelutti, A.; Peghin, M. Patient specific risk stratification for antimicrobial resistance and possible treatment strategies in gram-negative bacterial infections. Expt. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2017, 15, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasoo, S.; Barreto, J.N.; Tosh, P.K. Emerging issues in gram-negative bacterial resistance: An update for the practicing clinician. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Global Dissemination of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Genetic Context, Treatment Options, and Detection Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Ou, Q.; Zheng, L.; Chen, X.; Mao, G.; Fang, J.; Jin, D.; Tang, X. Carbapenem-resistant hypermucoviscous Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates from a tertiary hospital in China: Antimicrobial susceptibility, resistance phenotype, epidemiological characteristics, microbial virulence, and risk factors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegan, A.; Totan, M.; Antonescu, E.; Bumbu, A.G.; Pantis, C.; Furau, C.; Urducea, C.B.; Grigore, N. Prevalence of Urinary Tract Infections in Children and Changes in Sensitivity to Antibiotics of E. coli Strains. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 3788–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmehdiabadi, A.; Nobakht, M.S.; Hajjam Balajorshari, B.; Yazdi, M.R.; Amini, K. Investigating the effects of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the formation of biofilm and persister cells in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Gautam, P.K.; Misra, K.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. A Review on Basic Biology of Bacterial Biofilm Infections and Their Treatments by Nanotechnology-Based Approaches. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 90, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, M.; Lee, J. Recent Nanotechnology Approaches for Prevention and Treatment of Biofilm-Associated Infections on Medical Devices. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1851242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Maiti, P.; Dey, R.; Kundu, A.; Dey, R. Biofilms on indwelling urologic devices: Microbes and antimicrobial management prospect. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2014, 4, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codru, I.R.; Sava, M.; Vintilă, B.I.; Bereanu, A.S.; Bîrluțiu, V. A Study on the Contributions of Sonication to the Identification of Bacteria Associated with Intubation Cannula Biofilm and the Risk of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia. Medicina 2023, 59, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; He, J. Biofilms: The Microbial “Protective Clothing” in Extreme Environments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.Y. The emerging problems of Klebsiella pneumoniae infections: Carbapenem resistance and biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, H.A.; Malekabad, E.S.; Dadashi, A.-R.; Takei, E.; Keikha, M.; Kazemian, H.; Karami-Zarandi, M. Correlation between biofilm formation and carbapenem resistance among clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2019, 29, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Samanta, I.; Banerjee, J.; Habib; Dutta, T.K.; Dutt, T. Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Biofilm-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Healthy Cattle and Cattle with Diarrhea. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.-F.; Purmal, K.; Chin, S.; Chan, X.-Y.; Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Chan, K.-G. N-acyl homoserine lactone production by Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from human tongue surface. Sensors 2012, 12, 3472–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiq, Z.; Sam, N.; Vaidyanathan, R. Whole genome sequence of Klebsiella pneumoniae U25, a hypermucoviscous, multidrug resistant, biofilm producing isolate from India. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2016, 111, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadkam, S.; Goli, H.R.; Mirzaei, B.; Gholami, M.; Ahanjan, M. Correlation between antimicrobial resistance and biofilm formation capability among Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated from hospitalized patients in Iran. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2021, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaravel, V.; Nair, K.M.; Mathew, S.; Bartlett, J.; Kennedy, J.E.; Manning, H.G.; Whelan, B.J.; Leyland, N.S.; Pillai, S.C. Antimicrobial TiO2 nanocomposite coatings for surfaces, dental and orthopaedic implants. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 416, 129071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode-Aluko, C.A.; Pereao, O.; Kyaw, H.H.; Al-Naamani, L.; Al-Abri, M.Z.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Rossouw, A.; Fatoba, O.; Petrik, L.; Dobretsov, S. Photocatalytic and antifouling properties of electrospun TiO2 polyacrylonitrile composite nanofibers under visible light. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 264, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, K.; Gutarowicz, M.; Mierzejewska, J.; Parzuchowski, P. Antimicrobial films of poly(2-aminoethyl methacrylate) and its copolymers doped with TiO2 and CaCO3. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, E.; Rossi, L.; Mercier, C.; Lehmann, C.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Forró, L. Photocatalytic Nanowires-Based Air Filter: Towards Reusable Protective Masks. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Gadd, G.M.; Zhao, Q. Advanced titanium dioxide-polytetrafluorethylene (TiO2-PTFE) nanocomposite coatings on stainless steel surfaces with antibacterial and anti-corrosion properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 490, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Su, X.; Zhang, S.; Song, W.; Wang, S.; Ning, G.; Ye, J.; Lin, Y.; Gong, W. Antibacterial characteristics of electroless plating Ni-P-TiO2 coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 274, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Geng, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhao, Q. Mechanisms of the enhanced antibacterial effect of Ag-TiO2 coatings. Biofouling 2018, 34, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Geng, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Q. Reduction of bacterial adhesion on Ag-TiO2 coatings. Mater. Lett. 2018, 218, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veltri, S.; Palermo, A.M.; De Filpo, G.; Xu, F. Subsurface treatment of TiO2 nanoparticles for limestone: Prolonged surface photocatalytic biocidal activities. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; He, F.J. Copper Modified Titania Nanocomposites with a High Photocatalytic Inactivation of Escherichia coli. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 5486–5492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Nieto, I.; Caudillo-Flores, U.; Fernández-García, M.; Kubacka, A. Sunlight-Operated TiO2-Based Photocatalysts. Molecules 2020, 25, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Li, S.; Jing, L.; Chen, P.Y.; Xie, J. Synergistic Antimicrobial Titanium Carbide (MXene) Conjugated with Gold Nanoclusters. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e2001007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagay, B.E.; Dini, C.; Cordeiro, J.M.; Ricomini-Filho, A.P.; de Avila, E.D.; Rangel, E.C.; da Cruz, N.C.; Barao, V.A.R. Visible-Light-Induced Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activity of TiO2 Codoped with Nitrogen and Bismuth: New Perspectives to Control Implant-Biofilm-Related Diseases. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18186–18202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Yin, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Song, Y. Gallium–Carbenicillin Framework Coated Defect-Rich Hollow TiO2 as a Photocatalyzed Oxidative Stress Amplifier against Complex Infections. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipanahpour Dil, E.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Mehrabi, F.; Bazrafshan, A.A.; Tayebi, L. Synthesis and application of Ce-doped TiO2 nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon for ultrasound-assisted adsorption of Basic Red 46 dye. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, S.K.; Hoque, S.M.; Das, H.; Alim, M.A. Evaluation of chitosan-Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite for the enhancement of shelf life of chili and banana fruits. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motay, M.; Martel, D.; Vileno, B.; Soraru, C.; Ploux, L.; Méndez-Medrano, M.G.; Colbeau-Justin, C.; Decher, G.; Keller, N. Virtually Transparent TiO2/Polyelectrolyte Thin Multilayer Films as High-Efficiency Nanoporous Photocatalytic Coatings for Breaking Down Formic Acid and for Escherichia coli Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55766–55781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Alam, A.; Rani, M.; Ehtesham, N.Z.; Hasnain, S.E. Biofilms: Survival and defense strategy for pathogens. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 307, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulaz, S.; Vitale, S.; Quinn, L.; Casey, E. Nanoparticle-Biofilm Interactions: The Role of the EPS Matrix. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, S.; Rampazzo, E.; Hiebner, D.; Devlin, H.; Quinn, L.; Prodi, L.; Casey, E. Interaction between Engineered Pluronic Silica Nanoparticles and Bacterial Biofilms: Elucidating the Role of Nanoparticle Surface Chemistry and EPS Matrix. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 34502–34512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Mousavi, S.M.A.; Moeinizadeh, M.; Aghajanidelavar, M.; Rajabi, S.; Mirshekar, M. Evaluation of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles effects on expression levels of virulence and biofilm-related genes of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevacqua, E.; Occhiuzzi, M.A.; Grande, F.; Tucci, P. TiO2-NPs Toxicity and Safety: An Update of the Findings Published over the Last Six Years. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetyan, N.A.H.; Essa, T.A.; Salem, T.M.; Taha, A.A.; Elgobashy, S.F.; Tharwat, N.A.; Elsakhawy, T. Promising Eco-Friendly Nanoparticles for Managing Bottom Rot Disease in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa var. longifolia). Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 196–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Rafatullah, M. Recent Development in the Green Synthesis of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Plant-Based Biomolecules for Environmental and Antimicrobial Applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, P.; Ghosh, S. Biogenic TiO2 Nanoparticles for Advanced Antimicrobial and Antiviral Applications. In Nanoparticles in Modern Antimicrobial and Antiviral Applications. Nanotechnology in the Life Sciences; Kokkarachedu, V., Sadiku, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, B.F.; Ferreira, M.L.; de Campos, P.A.; Royer, S.; Gonçalves, I.R.; Batistão, D.W.d.F.; Fernandes, M.R.; Cerdeira, L.T.; de Brito, C.S.; Lincopan, N.; et al. Hypervirulence and biofilm production in KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae CG258 isolated in Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallbaum, L.R.; Pruski, B.B.; Amaral, S.C.; de Freitas, S.B.; Wozeak, D.R.; Hartwig, D.D. Phenotypic and molecular evaluation of biofilm formation in Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) isolates obtained from a hospital of Pelotas, RS, Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70, 001451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, A.J.; Burgos-Garay, M.L.; Kartforosh, L.; Mazher, M.; Donlan, R.M. Bacteriophage treatment of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a multispecies biofilm: A potential biocontrol strategy for healthcare facilities. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazgan, B.; Türkel, I.; Güçkan, R.; Kılınç, K.; Yıldırım, T. Comparison of biofilm formation and efflux pumps in ESBL and carbapenemase producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booq, R.Y.; Abutarboush, M.H.; Alolayan, M.A.; Huraysi, A.A.; Alotaibi, A.N.; Alturki, M.I.; Alshammari, M.K.; Bakr, A.A.; Alquait, A.A.; Tawfik, E.A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Plasmids and Genes from Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Makkah Province, Saudi Arabia. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’apolito, D.; Arena, F.; Conte, V.; De Angelis, L.H.; Di Mento, G.; Carreca, A.P.; Cuscino, N.; Russelli, G.; Iannolo, G.; Barbera, F.; et al. Phenotypical and molecular assessment of the virulence potential of KPC-3-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST392 clinical isolates. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 240, 126551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, P.P.; Wang, L.H.; Wei, D.D.; Wan, L.G.; Zhang, W. Capsular Polysaccharide Types and Virulence-Related Traits of Epidemic KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in a Chinese University Hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmud, Z.H.; Uddin, S.Z.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Ali, S.; Hossain, M.; Islam, T.; Costa, D.T.D.; Islam, M.R.; Islam, S.; Hassan, Z.; et al. Healthcare Facilities as Potential Reservoirs of Antimicrobial Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: An Emerging Concern to Public Health in Bangladesh. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, N.B.S.; Alves, P.G.V.; Marques, L.D.A.; Silva, S.F.; Faria, G.D.O.; de Araújo, L.B.; Pedroso, R.D.S.; Penatti, M.P.A.; Menezes, R.D.P.; Röder, D.V.D.D.B. Quantification of biofilm produced by clinical, environment and hands’ isolates Klebsiella species using colorimetric and classical methods. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 185, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papalini, C.; Sabbatini, S.; Monari, C.; Mencacci, A.; Francisci, D.; Perito, S.; Pasticci, M.B. In vitro antibacterial activity of ceftazidime/avibactam in combination against planktonic and biofilm carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from blood. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbauy, G.; Vivan, A.C.; Simões, G.C.; Simionato, A.S.; Pelisson, M.; Vespero, E.C.; Costa, S.F.; Andrade, C.G.D.J.; Barbieri, D.M.; Mello, J.C.; et al. Effect of a Metalloantibiotic Produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa on Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC)-producing K. pneumoniae. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Palacios, P.; Gual-De-Torrella, A.; Delgado-Valverde, M.; Oteo-Iglesias, J.; Hidalgo-Díaz, C.; Pascual, Á.; Fernández-Cuenca, F. Transfer of plasmids harbouring blaOXA-48-like carbapenemase genes in biofilm-growing Klebsiella pneumoniae: Effect of biocide exposure. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 254, 126894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, D.; Ghosh, S.; Ray, R.; Hazra, B. Polyphenolic Secondary Metabolites Synergize the Activity of Commercial Antibiotics against Clinical Isolates of β-Lactamase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, J.; Song, Y.; Yin, D.; Wang, S.; Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Duan, J. Antibiotic resistance and virulence characteristics of four carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains coharbouring blaKPC and blaNDM based on whole genome sequences from a tertiary general teaching hospital in central China between 2019 and 2021. Microb Pathog. 2023, 175, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larcher, R.; Laffont-Lozes, P.; Naciri, T.; Bourgeois, P.-M.; Gandon, C.; Magnan, C.; Pantel, A.; Sotto, A. Continuous infusion of meropenem-vaborbactam for a KPC-3-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infection in a critically ill patient with augmented renal clearance. Infection 2023, 51, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, B.; Lin, Y.; Shen, F. Within-Host Resistance and Virulence Evolution of a Hypervirulent Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST11 Under Antibiotic Pressure. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7255–7270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folliero, V.; Franci, G.; Dell’annunziata, F.; Giugliano, R.; Foglia, F.; Sperlongano, R.; De Filippis, A.; Finamore, E.; Galdiero, M. Evaluation of Antibiotic Resistance and Biofilm Production among Clinical Strain Isolated from Medical Devices. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 9033278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabença, C.; Costa, E.; Sousa, S.; Barros, L.; Oliveira, A.; Ramos, S.; Igrejas, G.; Torres, C.; Poeta, P. Evaluation of the Ability to Form Biofilms in KPC-Producing and ESBL-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Clinical Samples. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorarinsdottir, H.R.; Kander, T.; Holmberg, A.; Petronis, S.; Klarin, B. Biofilm formation on three different endotracheal tubes: A prospective clinical trial. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochońska, D.; Ścibik, Ł.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M. Biofilm Formation of Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated from Tracheostomy Tubes and Their Association with Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence and Genetic Diversity. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.N. Microbial etiologies of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51 (Suppl. S1), S81–S87, Erratum in Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Thoracic Society; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Guidelines for the management of adults with hospital-acquired, ventilator-associated, and healthcare-associated pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 171, 388–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melsen, W.G.; Rovers, M.M.; Koeman, M.; Bonten, M.J.M. Estimating the attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia from randomized prevention studies. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 2736–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Saffari, M.; Siadat, S.D.; Hejazi, S.H.; Shayestehpour, M.; Motallebi, M.; Eidi, M. Isolation, characterization, therapeutic potency, and genomic analysis of a novel bacteriophage vB_KshKPC-M against carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae strains (CRKP) isolated from Ventilator-associated pneumoniae (VAP) infection of COVID-19 patients. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, K.; Deva, A.; Jacombs, A.; Allan, J.; Valente, P.; Gosbell, I.B. Presence of biofilm containing viable multiresistant organisms despite terminal cleaning on clinical surfaces in an intensive care unit. J. Hosp. Infect. 2012, 80, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledwoch, K.; Dancer, S.; Otter, J.; Kerr, K.; Roposte, D.; Rushton, L.; Weiser, R.; Mahenthiralingam, E.; Muir, D.; Maillard, J.-Y. Beware biofilm! Dry biofilms containing bacterial pathogens on multiple healthcare surfaces; a multi-centre study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2018, 100, e47–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Johani, K.; Melo, D.; Lopes, L.; Lima, L.L.; Tipple, A.; Hu, H.; Vickery, K. Biofilm contamination of high-touched surfaces in intensive care units: Epidemiology and potential impacts. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Johani, K.; Gosbell, I.; Jacombs, A.; Almatroudi, A.; Whiteley, G.; Deva, A.; Jensen, S.; Vickery, K. Intensive care unit environmental surfaces are contaminated by multidrug-resistant bacteria in biofilms: Combined results of conventional culture, pyrosequencing, scanning electron microscopy, and confocal laser microscopy. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 91, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, Q.; Abulaila, S.; Jaradat, Z. Isolation of extensively drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from environmental surfaces inside intensive care units. Am. J. Infect. Control 2022, 50, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, J.Y.; Centeleghe, I. How biofilm changes our understanding of cleaning and disinfection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2023, 12, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centeleghe, I.; Norville, P.; Hughes, L.; Maillard, J.Y. Klebsiella pneumoniae survives on surfaces as a dry biofilm. Am. J. Infect. Control 2023, 51, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, M.; Fathizadeh, H.; Arkaban, H.; Kalantar-Neyestanaki, D.; Akbarizadeh, M.R.; Turki Jalil, A.; Akhavan-Sigari, R. Recent Advances in Nanotechnology for the Management of Klebsiella pneumoniae-Related Infections. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, E.; Webster, T.J. Reducing infections through nanotechnology and nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, A.S.K.; Kumar, T.S.S.; Sanghavi, R.; Doble, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Antibacterial and Bioactive Surface Modifications of Titanium Implants by PCL/TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebeish, A.A.; Abdelhady, M.M.; Youssef, A.M. TiO2 nanowire and TiO2 nanowire doped Ag-PVP nanocomposite for antimicrobial and self-cleaning cotton textile. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moongraksathum, B.; Chien, M.Y.; Chen, Y.W. Antiviral and Antibacterial Effects of Silver-Doped TiO2 Prepared by the Peroxo Sol-Gel Method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 7356–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.S.; Dutt, V.G.V.; Kumar, K.K.P.; Atchuta, S.R.; Anbazhagan, V.; Sakthivel, S. A functional Ag-TiO2 nanocomposite solar selective absorber with antimicrobial activity by photochemical reduction process. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2019, 199, 111626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Strømme, M.; Welch, K. Photocatalytic antibacterial effects are maintained on resin-based TiO2 nanocomposites after cessation of UV irradiation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Visible-Light-Driven Photocatalysis-Enhanced Nanozyme of TiO2Nanotubes@MoS2 Nanoflowers for Efficient Wound Healing Infected with Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Small 2021, 17, e2103348, Erratum in Small 2022, 18, e2201184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, R.; Olad, A.; Shakoori, S. Preparation of an antibacterial, hydrophilic and photocatalytically active polyacrylic coating using TiO2 nanoparticles sensitized by graphene oxide. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 80, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Dehiya, B.S. Magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@TiO2nanocomposites for broad spectrum antibacterial applications. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 15, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, Z.; Khalid, N.R.; Abbasi, R.; Javed, S.; Ahmad, I.; Bokhari, H. Visible light sensitive Ag/TiO2/graphene composite as a potential coating material for control of Campylobacter jejuni. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 98, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joya, Y.F.; Liu, Z.; Joya, K.S.; Wang, T. Preparation and antibacterial properties of laser-generated silver-anatase nanocomposite film against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 495708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nica, I.C.; Stan, M.S.; Popa, M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Lazar, V.; Dumitrescu, I.; Diamandescu, L.; Feder, M.; Baibarac, M.; et al. Interaction of New-Developed TiO2-Based Photocatalytic Nanoparticles with Pathogenic Microorganisms and Human Dermal and Pulmonary Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nica, I.C.; Stan, M.S.; Popa, M.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Pircalabioru, G.G.; Lazar, V.; Dumitrescu, I.; Diamandescu, L.; Feder, M.; Baibarac, M.; et al. Development and Biocompatibility Evaluation of Photocatalytic TiO2/Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Nanoparticles Designed for Self-Cleaning Purposes. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, B.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, D. Green synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and evaluation of their antibacterial activity. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 124, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohko, Y.; Nagao, Y.; Okano, K.; Sugiura, N.; Fukuda, A.; Yang, Y.; Negishi, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Hanada, S. Prevention of Phormidium tenue Biofilm Formation by TiO2 Photocatalysis. Microbes Environ. 2009, 24, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, K.; Ahmad, A.; Li, B.; Nazir, S.; Khan, A.U.; Nasir, T.; Khan, Z.U.H.; Naz, R.; Raza, M. Visible light photo catalytic inactivation of bacteria and photo degradation of methylene blue with Ag/TiO2 nanocomposite prepared by a novel method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2016, 162, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, K.; Chatterjee, A.; Prakash, H.; Kowshik, M. Mesoporous TiO2 nanoparticles containing Ag ion with excellent antimicrobial activity at remarkable low silver concentrations. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonan, R.F.; Mota, M.F.; Farias, R.M.D.C.; da Silva, S.D.; Bonan, P.R.F.; Diesel, L.; Menezes, R.R.; Perez, D.E.D.C. In vitro antimicrobial and anticancer properties of TiO2 blow-spun nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 109876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.U.; Ferreira-Neto, E.P.; Rahman, G.U.; Parveen, R.; Monteiro, A.S.; Rahman, G.; Van Le, Q.; Domeneguetti, R.R.; Ribeiro, S.J.; Ullah, S. Flexible bacterial cellulose-based BC-SiO2-TiO2-Ag membranes with self-cleaning, photocatalytic, antibacterial and UV-shielding properties as a potential multifunctional material for combating infections and environmental applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bereanu, A.-S.; Vintilă, B.I.; Bereanu, R.; Codru, I.R.; Hașegan, A.; Olteanu, C.; Săceleanu, V.; Sava, M. TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings and Inactivation of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm—Opportunities and Challenges. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040684
Bereanu A-S, Vintilă BI, Bereanu R, Codru IR, Hașegan A, Olteanu C, Săceleanu V, Sava M. TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings and Inactivation of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm—Opportunities and Challenges. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(4):684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040684
Chicago/Turabian StyleBereanu, Alina-Simona, Bogdan Ioan Vintilă, Rareș Bereanu, Ioana Roxana Codru, Adrian Hașegan, Ciprian Olteanu, Vicențiu Săceleanu, and Mihai Sava. 2024. "TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings and Inactivation of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm—Opportunities and Challenges" Microorganisms 12, no. 4: 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040684
APA StyleBereanu, A.-S., Vintilă, B. I., Bereanu, R., Codru, I. R., Hașegan, A., Olteanu, C., Săceleanu, V., & Sava, M. (2024). TiO2 Nanocomposite Coatings and Inactivation of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm—Opportunities and Challenges. Microorganisms, 12(4), 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12040684








