Comparative Analysis of Hindgut Microbiota Variation in Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae across Diverse Farms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Sampling
2.2. DNA Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics and Sequencing Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Information and Sample Sequencing
3.2. Diversity Analyses and Gut Microbial Community
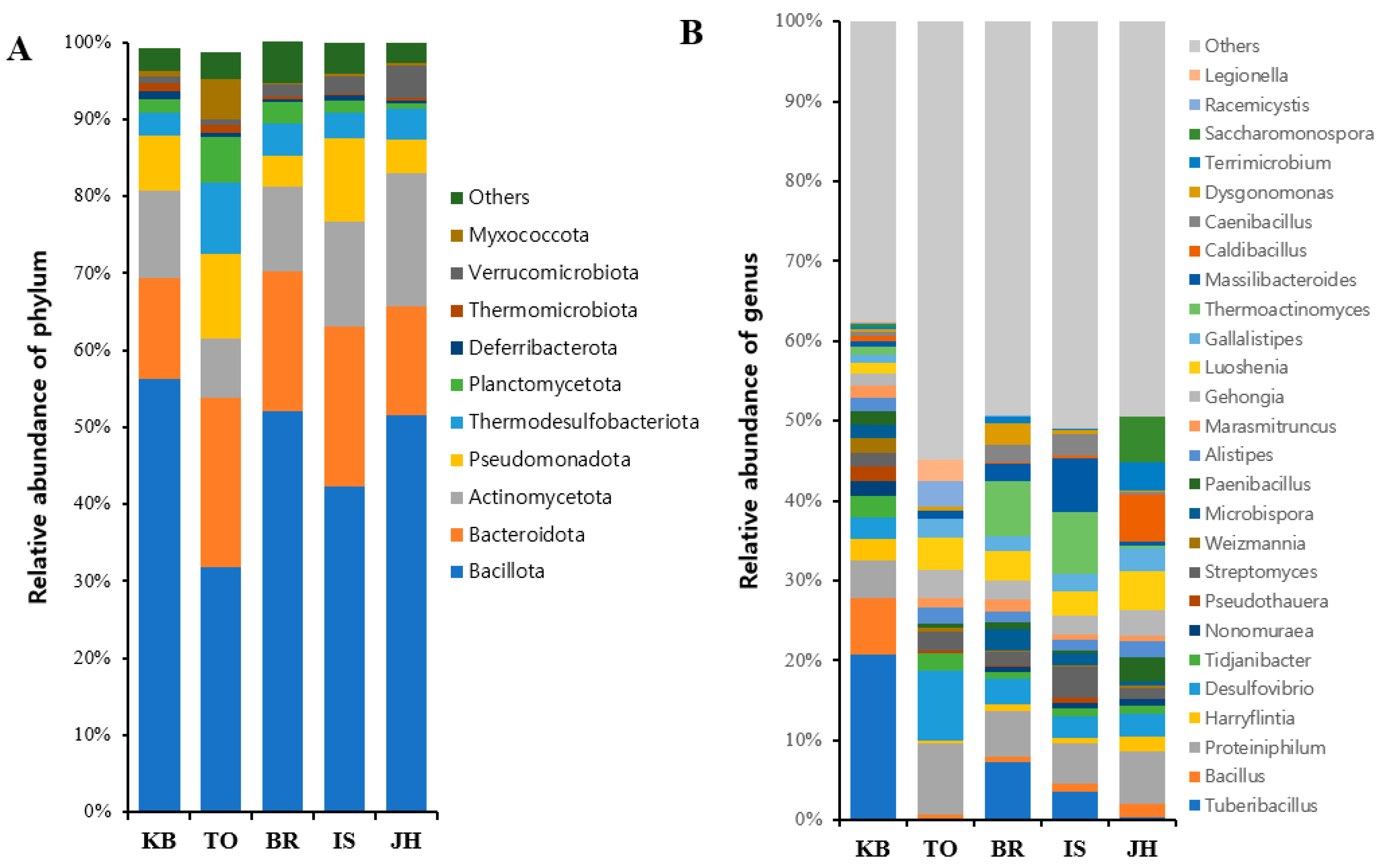
3.3. Analysis of Microbial Abundance and Composition
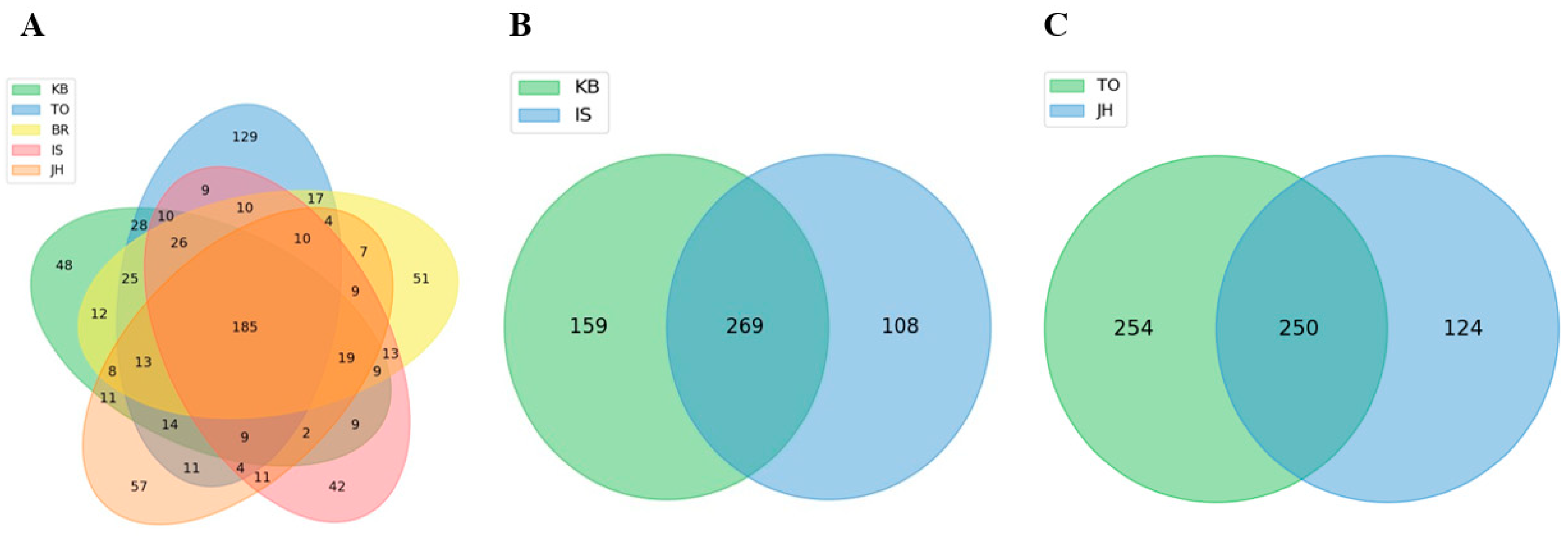
3.4. Shared and Unique Microbial Populations
3.5. Differential Bacterial Abundance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Huis, A. Edible insects contributing to food security? Agric. Food Secur. 2015, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makkar, H.P.S.; Tran, G.; Heuzé, V.; Ankers, P. State-of-the-art on use of insects as animal feed. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.S.; Choi, M.K. Recognition, purchase, and consumption of edible insects in Korean adults. J. Nutr. Health 2020, 53, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Shin, J.T.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, Y.W. An overview of the South Korean edible insect food industry: Challenges and future pricing/promotion strategies. Entomol. Res. 2017, 47, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, T.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Influence of Trap Color, Type, and Placement on Capture Efficacy for Protaetia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.K.; Kim, S.W.; Song, D.H.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, I.S. Nutritional Composition of White-Spotted Flower Chafer (Protaetia brevitarsis) Larvae Produced from Commercial Insect Farms in Korea. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 416–427. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.K.; Weaver, C.M.; Choi, M.K. Proximate composition and mineral content of five edible insects consumed in Korea. CyTA J. Food 2017, 15, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, H.; Youn, K.; Kim, M.; Yun, E.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Jeong, W.S.; Jun, M. Fatty Acid Composition and Volatile Constituents of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2013, 18, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkhah, A.; Van Haute, S.; Jovanovic, V.; Jung, H.; Dewulf, J.; Cirkovic Velickovic, T.; Ghnimi, S. Life cycle assessment of edible insects (Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis larvae) as a future protein and fat source. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.M.; Min, N.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.R.; Kwon, O. The effects of feed materials on the nutrient composition of Protaetia brevitarsis larvae. Entomol. Res. 2020, 50, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Ha, Y.J.; Kim, S.W.; Bang, W.Y.; Bang, K.H.; Gal, S.W.; Kim, I.S.; Cho, Y.S. Functional Chemical Components in Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae: Impact of Supplementary Feeds. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.M.; Myung, N.Y.; Jung, H.A.; Kim, S.J. The ameliorative effect of Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae in HFD-induced obese mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1177–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.M.; Noh, E.M.; Lee, H.Y.; Shin, D.Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Kang, Y.G.; Na, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Ki, M.J.; et al. Anti-diabetic effects of Protaetia brevitarsis in pancreatic islets and a murine diabetic model. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 7508–7515. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.S.; Shin, N.R.; Nam, H.H.; Song, J.H.; Moon, B.C.; Choi, G.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, J.S. Effects of larval extracts from identified Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis against benign prostatic hyperplasia induced by testosterone in rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, R.Y.; Kim, I.W.; Ji, M.; Paik, M.J.; Ban, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Kweon, H.; Seo, M. Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis larvae ethanol extract inhibits RANKL-stimulated osteoclastogenesis and ameliorates bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 165, 115112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Seo, Y.H.; Song, J.H.; Kim, W.J.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, B.C.; Ang, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, C.; Lee, J.; et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis’ Water Extract on Trimethyltin-Induced Seizures and Hippocampal Neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, A.; Alhanout, K.; Duval, R.E. Bacteriocins, Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacterial Origin: Overview of Their Biology and Their Impact against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Cao, D.; Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Shu, C.; Liu, R. Prediction and bioactivity of small-molecule antimicrobial peptides from Protaetia brevitarsis Lewis larvae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1124672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, W.; Kim, M.A.; Hwang, J.S.; Na, M.; Bae, J.S. Inhibition of platelet aggregation and thrombosis by indole alkaloids isolated from the edible insect Protaetia brevitarsis seulensis (Kolbe). J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, K.; Engel, P. Mechanisms underlying gut microbiota-host interactions in insects. J. Exp. Biol. 2021, 224, 207696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barko, P.C.; McMichael, M.A.; Swanson, K.S.; Williams, D.A. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Review. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.S.B.; Raes, J.; Bork, P. The Human Gut Microbiome: From Association to Modulation. Cell 2018, 172, 1198–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. The role of the gut microbiome in health and disease of adult honey bee workers. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Nguyen, S.G.; Guevarra, R.B.; Lee, I.; Unno, T. Analysis of swine fecal microbiota at various growth stages. Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, T.J.; Moran, N.A. Links between metamorphosis and symbiosis in holometabolous insects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20190068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, B.; Xuan, H.; Geng, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, W.; Liu, R.; Shu, C. Microflora for improving the Auricularia auricula spent mushroom substrate for Protaetia brevitarsis production. ISC 2022, 25, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gao, P.; Geng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Shu, C. Lignocellulose degradation in Protaetia brevitarsis larvae digestive tract: Refining on a tightly designed microbial fermentation production line. Microbiome 2022, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, H.; Gao, P.; Du, B.; Geng, L.; Wang, K.; Huang, K.; Zhang, J.; Huang, T.; Shu, C. Characterization of Microorganisms from Protaetia brevitarsis Larva Frass. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Patil, M.P.; Kim, J.O.; Woo, H.E.; Kim, K. Diversity of Microbial Communities in Sediment from Yeosu Bay, Republic of Korea, as Determined by 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e0036322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, W.; Zewide, I. Review on Agricultural waste utilization British. J. Earth Sci. Res. 2022, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Harshwardhan, K.; Upadhyay, K. Effective utilization of agricultural waste: Review. J. Fundam. Renew. Energy Appl. 2017, 7, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, T.; Geng, L.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Liu, F.; Liu, C.; Song, F.; Zhang, J.; Shu, C. Protaetia brevitarsis larvae can efficiently convert herbaceous and ligneous plant residues to humic acids. Waste Manag. 2019, 83, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, P.; Li, Y.; Lai, D.; Geng, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Shu, C.; Liu, R. Protaetia brevitarsis larvae can feed on and convert spent mushroom substrate from Auricularia auricula and Lentinula edodes cultivation. Waste Manag. 2020, 114, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.Y.; Song, F.P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R.M.; Zhang, X.P.; Duan, J.Y.; Shu, C.L. Diversity of gut bacteria in larval Protaetia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Scarabaedia) fed on corn stalk. Acta. Entomol. Sin. 2017, 60, 632–641. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M.; Li, H.; Gu, J.; Tuo, X.; Sun, W.; Qian, X.; Wang, X. Effects of biochar on reducing the abundance of oxytetracycline, antibiotic resistance genes, and human pathogenic bacteria in soil and lettuce. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.P.; Hu, H.W.; Zhang, J.; Shu, C.; He, J.Z. Alteration of Manure Antibiotic Resistance Genes via Soil Fauna Is Associated with the Intestinal Microbiome. mSystems 2022, 7, e0052922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Farm Name | Farm Location | Feed | Main Ingredients | * Larval Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB | Gyeongsangbuk-do | commercial | oak sawdust | 2.71 ± 0.31 |
| TO | Gyeongsangbuk-do | homemade | oak sawdust | 2.29 ± 0.15 |
| BR | Incheon | commercial | spent mushroom substrate | 2.66 ± 0.36 |
| IS | Incheon | commercial | oak sawdust | 2.48 ± 0.21 |
| JH | Chungcheongnam-do | homemade | oak sawdust | 2.03 ± 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, N.; Min, J.G.; Cammayo-Fletcher, P.L.T.; Nguyen, B.T.; Yim, D. Comparative Analysis of Hindgut Microbiota Variation in Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae across Diverse Farms. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030496
Min N, Min JG, Cammayo-Fletcher PLT, Nguyen BT, Yim D. Comparative Analysis of Hindgut Microbiota Variation in Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae across Diverse Farms. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030496
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Namkyong, Jean Geung Min, Paula Leona T. Cammayo-Fletcher, Binh T. Nguyen, and Dongjean Yim. 2024. "Comparative Analysis of Hindgut Microbiota Variation in Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae across Diverse Farms" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030496
APA StyleMin, N., Min, J. G., Cammayo-Fletcher, P. L. T., Nguyen, B. T., & Yim, D. (2024). Comparative Analysis of Hindgut Microbiota Variation in Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae across Diverse Farms. Microorganisms, 12(3), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030496





