Metagenomic Analysis Revealing the Impact of Water Contents on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities and the Distribution of Major Ecological Functional Genes in Poyang Lake Wetland Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sampling
2.2. Measurement of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Data Processing
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Soil Samples
3.2. Taxonomic Composition of Microbial Communities
3.3. Microbial Carbon Fixation Genes
3.4. Microbial Methane Cycling Genes
3.5. Microbial N Cycling Genes
3.6. Microbial Antibiotic Resistance Genes
3.7. The Correlation Between C/N-Cycle Functional Genes and Physicochemical Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. The Difference in Moisture Content Results in Differences in the Physicochemical Properties of Wetland Soil
4.2. The Difference in Soil Physicochemical Properties Results in Differences in Soil Microbial Community Structure
4.3. The Differences in Soil Microbial Community Structure Result in Differences in Ecological Function Distribution
4.4. The Differences in Soil Microbial Community Structure Result in Differences in Antibiotic Resistance Distribution
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nybo, S.E.; Khan, N.E.; Woolston, B.M.; Curtis, W.R. Metabolic engineering in chemolithoautotrophic hosts for the production of fuels and chemicals. Metab. Eng. 2015, 30, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.L.; Cabezas, A.; Marzorati, M.; Friedrich, M.W.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Microbial community analysis of anodes from sediment microbial fuel cells powered by rhizodeposits of living rice plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2002–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, S.; Liang, R.; Shen, J. Effects of root exudates on denitrifier gene abundance, community structure and activity in a micro-polluted constructed wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 15, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Hu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Lv, X. Progress in research methods of soil microbial structure and diversity in wetlands. Chin. J. Soil. Sci. 2016, 47, 758–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Yan, Z.; Li, M.; Kang, E.; Yan, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, A.; et al. Changes in precipitation regime lead to acceleration of the N cycle and dramatic N2O emission. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 20, 152140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, T.; Yu, C. A review of factors affecting the soil microbial community structure in wetlands. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 46760–46768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, N.; de Jong, A.E.; Li, Y.; Trubl, G.; Xue, Y.; Dove, N.C. Metagenomic tools in microbial ecology research. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 67, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Ogawa, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Saito, M. Molecular approaches to studying microbial communities: Targeting the 16S ribosomal RNA gene. J. UOEH 2016, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Miller, S.A. Clinical metagenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Tan, P.; Zhang, R.; Li, J. mNGS in clinical microbiology laboratories: On the road to maturity. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 668–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougoulias, C.; Clark, J.M.; Shaw, L.J. The role of soil microbes in the global carbon cycle: Tracking the below-ground microbial processing of plant-derived carbon for manipulating carbon dynamics in agricultural systems. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2362–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, S.; Almuktar, S.A.; Scholz, M. Impact of climate change on wetland ecosystems: A critical review of experimental wetlands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 15, 112160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Megonigal, J.P. Tidal wetland stability in the face of human impacts and sea-level rise. Nature 2013, 504, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgham, S.D.; Cadillo-Quiroz, H.; Keller, J.K.; Zhuang, Q. Methane emissions from wetlands: Biogeochemical, microbial, and modeling perspectives from local to global scales. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 1325–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.L.; Ni, C.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Song, P.F.; Zhang, Z.B. Effect of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake estuary on microbial communities structure base on Mi-seq sequencing. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 3475–3486. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, W.; Zhang, J.; Lu, X.; Ma, Y.; Mou, X.; Wu, L. Identification of bacterial communities in sediments of Poyang Lake, the largest freshwater lake in China. Springerplus 2016, 1, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Deng, S.; Ji, H.; Liang, F. Assessing habitat quality at Poyang Lake based on InVEST and Geodetector modeling. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Zhou, L.; Miao, L.; Zhang, J. Water level has higher influence on soil organic carbon and microbial community in Poyang Lake Wetland than vegetation type. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Yang, W.; Jian, M.; Hu, Q. A comparison of metric scoring and health status classification methods to evaluate benthic macroinvertebrate-based index of biotic integrity performance in Poyang Lake wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Yu, Z.; Yang, G.; Wan, R. Role of flooding patterns in the biomass production of vegetation in a typical herbaceous wetland, Poyang Lake Wetland, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 521358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Ma, Y.T.; He, S.Y.; Mou, X.; Wu, L. Dynamics of bacterioplankton community structure in response to seasonal hydrological disturbances in Poyang Lake, the largest wetland in China. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, G.; Wan, R.; Lai, X.; Wagner, P.D. Impacts of hydrological alteration on ecosystem services changes of a large river-connected lake (Poyang Lake), China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 310, 114750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.W.; Jorge, G.M.; Lin, L.S.; Min, Z.; Zhao, S.W.; Huan, Z.; Jun, X. Drivers and changes of the Poyang Lake wetland ecosystem. Wetlands 2019, 39, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, X.; Kuyper, T.W.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. High microbial diversity stabilizes the responses of soil organic carbon decomposition to warming in the subsoil on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moomaw, W.R.; Chmura, G.L.; Davies, G.T.; Finlayson, C.M.; Middleton, B.A.; Natali, S.M.; Perry, J.E.; Roulet, N.; Sutton-Grier, A.E. Wetlands in a changing climate: Science, Policy and Management. Wetlands 2018, 38, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Yu, X.; Gutknecht, J.L.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, S.; Ma, K. Soil microbial responses to warming and increased precipitation and their implications for ecosystem C cycling. Oecologia 2013, 173, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, L.; Zeng, K.; Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Ji, X. Microbial-driven carbon fixation in natural wetland. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, J.T.; Nguyễn-Thùy, D.; Phạm, T.M.; Drobniak, A.; Tạ, P.H.; Phạm, N.D.; Streil, T.; Webster, K.D.; Schimmelmann, A. Microbial contributions to subterranean methane sinks. Geobiology 2017, 15, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, S.D.; Anthony, T.L.; Silver, W.L.; Eichelmann, E.; Hemes, K.S.; Oikawa, P.Y.; Sturtevant, C.; Szutu, D.J.; Verfaillie, J.G.; Baldocchi, D.D. Soil properties and sediment accretion modulate methane fluxes from restored wetlands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4107–4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zheng, P.; Wang, L.; Hu, B. Salinity causes differences in stratigraphic methane sources and sinks. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2023, 19, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Malfatti, S.A.; McFarland, J.W.; Anderson, F.E.; Pati, A.; Huntemann, M.; Tremblay, J.; Glavina, D.R.T.; Waldrop, M.P.; Windham-Myers, L.; et al. Patterns in wetland microbial community composition and functional gene repertoire associated with methane emissions. MBio 2015, 19, e00066-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramond, J.B.; Jordaan, K.; Díez, B.; Heinzelmann, S.M.; Cowan, D.A. Microbial biogeochemical cycling of nitrogen in arid ecosystems. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2022, 86, e0010921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, M.; Bosch, J.; Coclet, C.; Johnson, J.; Lebre, P.; Salawu-Rotimi, A.; Vikram, S.; Makhalanyane, T.; Cowan, D. Microbial nitrogen cycling in antarctic soils. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Yu, K. Application of microbial gene databases in the annotation of nitrogen cycle functional genes. Microbiol. China 2020, 47, 3021–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Jiang, L.; Song, Y.Y.; Sun, L.; Song, C.C.; Hou, A.X.; Gao, J.L.; Du, Y. Effects of temperature and moisture changes on functional gene abundance of soil nitrogen cycle in permafrost peatland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 6707–6717. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Achmon, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Siame, B.A.; Leung, K.Y. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Qu, J.H.; Wang, Y.K.; Mai, W.N.; Wan, D.J.; Lu, X.Y. Responses of microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes to co-existence of chloramphenicol and salinity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 7683–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, K.L. Wetlands and global climate change: The role of wetland restoration in a changing world. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 17, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wei, X.; Huang, H.; Lü, T. Poyang Lake basin: A successful, large-scale integrated basin management model for developing countries. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shen, H.; Wang, D. Water level fluctuations influence microbial communities and mercury methylation in soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 68, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, T.L.; Silver, W.L. Mineralogical associations with soil carbon in managed wetland soils. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 6555–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adomako, M.O.; Xue, W.; Tang, M.; Du, D.L.; Yu, F.H. Synergistic effects of soil microbes on solidago canadensis depend on water and nutrient availability. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Feng, D.; Yang, G.; Deng, Z.; Rui, J.; Chen, H. Soil water content and pH drive archaeal distribution patterns in sediment and soils of water-level-fluctuating zones in the East Dongting Lake wetland, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 29127–29137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Z.G.; Xiao, H.X.; Li, Y.F.; Peng, W.X. Changes of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen, and enzyme activities in East Dongting Lake wetlands at different water levels. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2021, 32, 2958–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil microbiomes and climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, D.A.; Jansson, J.K.; Remais, J.V.; Rich, V.I.; Singh, B.K.; Trivedi, P. Climate change microbiology—Problems and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, O.; Liu, F. Spatial variation in bacterial community in natural wetland-river-sea ecosystems. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, M.K.; Wong, C.K.; Chu, K.H.; Kwan, H.S. Community structure, dynamics and interactions of bacteria, archaea and fungi in subtropical coastal wetland sediments. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Meng, H.; Liu, Y.; Gu, J.D.; Li, M. Stratified bacterial and archaeal community in mangrove and intertidal wetland mudflats revealed by high throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Cao, X.; Qi, W.; Peng, J.; Liu, H.; Qu, J. The influence of wet-to-dry season shifts on the microbial community stability and nitrogen cycle in the Poyang Lake sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Kong, Z.; Feinstein, L.M.; Ding, X.; Ge, G.; Wu, L. Bacterial and fungal community composition and functional activity associated with lake wetland water level gradients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Liu, X.; Mou, X.Z.; Wu, L. Research status of microorganisms in a large, shallow lake Poyang Lake wetland. Microbiol. China 2019, 46, 3453–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, A.; Zhang, Y.; Gajaraj, S.; Brown, P.B.; Hu, Z. Toward the development of microbial indicators for wetland assessment. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1711–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado, M.; Vera, J. Microorganisms that participate in biochemical cycles in wetlands. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, O. Constructed wetlands revisited: Microbial diversity in the -omics era. Microb. Ecol. 2017, 73, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Milo, R. The global mass and average rate of rubisco. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, Y.; Yokota, A. “Green-like” and “red-like” RubisCO cbbL genes in Rhodobacter azotoformans. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Leu, A.O.; Xie, G.J.; Guo, J.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Tyson, G.W.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, S. A methanotrophic archaeon couples anaerobic oxidation of methane to Fe(III) reduction. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leu, A.O.; Cai, C.; McIlroy, S.J.; Southam, G.; Orphan, V.J.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, S.; Tyson, G.W. Anaerobic methane oxidation coupled to manganese reduction by members of the Methanoperedenaceae. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturini, A.M.; Dias, N.M.S.; Gontijo, J.B.; Yoshiura, C.A.; Paula, F.S.; Meyer, K.M.; Nakamura, F.M.; França, A.G.D.; Borges, C.D.; Barlow, J.; et al. Increased soil moisture intensifies the impacts of forest-to-pasture conversion on methane emissions and methane-cycling communities in the Eastern Amazon. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Z.; Ma, J.; Xu, H.; Jia, Z. Differential contributions of ammonia oxidizers and nitrite oxidizers to nitrification in four paddy soils. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C.F. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Wen, D. Characterization of antibiotic resistance across Earth’s microbial genomes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

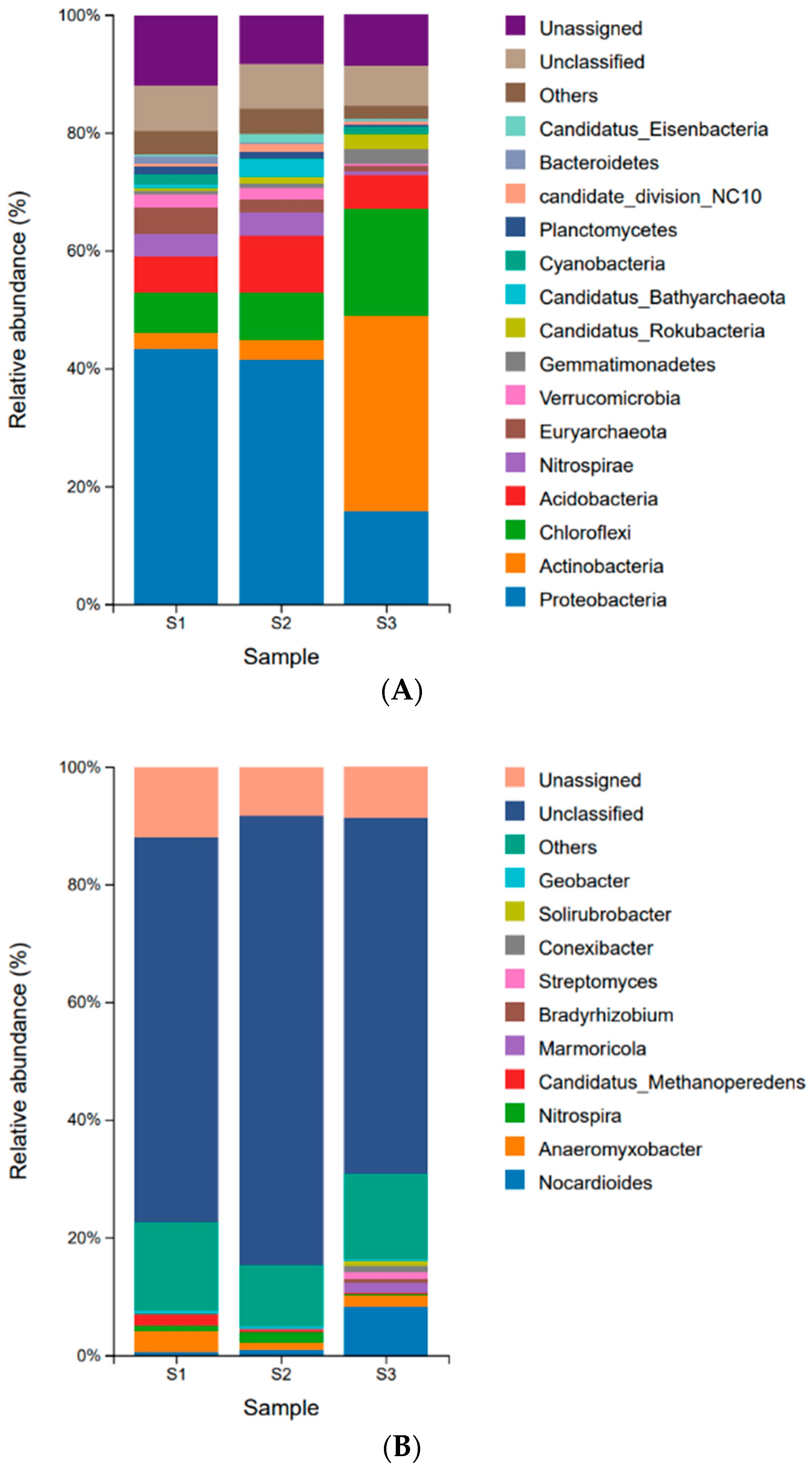



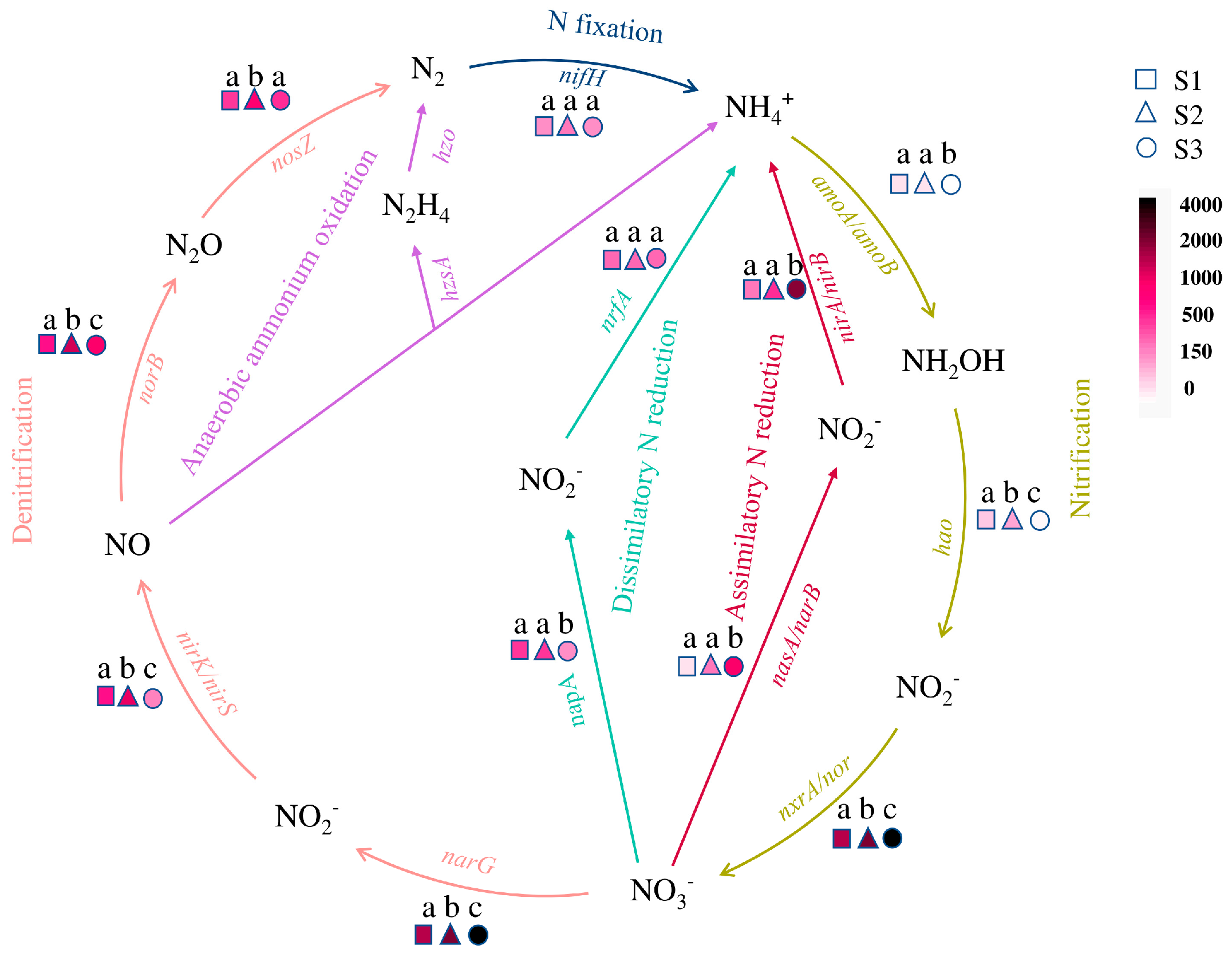


| Sample | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physicochemical Property | ||||
| WC (%) | 25.25 ± 1.05 (c) | 11.05 ± 1.35 (b) | 3.75 ± 0.65 (a) | |
| pH | 6.34 ± 0.1 (ab) | 6.55 ± 0.23 (b) | 6.01 ± 0.27 (a) | |
| NH4+-N (mg/kg) | 5.64 ± 0.99 (a) | 2.27 ± 0.69 (a) | 3.42 ± 1.22 (a) | |
| NO3-N (mg/kg) | 1.46 ± 0.12 (a) | 10.55 ± 1.52 (c) | 6.01 ± 1.15 (b) | |
| NO2-N (mg/kg) | 0.07 ± 0.01 (ab) | 0.09 ± 0.01 (b) | 0.05 (a) | |
| TN (g/kg) | 0.19 ± 0.06 (a) | 1.64 ± 0.02 (c) | 0.49 ± 0.09 (b) | |
| TC (g/kg) | 1.73 ± 0.57 (a) | 21.38 ± 0.34 (c) | 4.77 ± 1.2 (b) | |
| SOC (g/kg) | 1.59 ± 0.52 (a) | 20.56 ± 0.84 (c) | 4.08 ± 0.98 (b) | |
| EC (us/cm) | 23.80 ± 7.17 (a) | 163.75 ± 35.65 (b) | 70.42 ± 11.10 (a) | |
| C/N | 9.16 ± 0.49 (a) | 13.10 ± 0.28 (b) | 9.17 ± 1.00 (a) | |
| Sample | Observed Species | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Pielou |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 10,755 (687.89) | 10,759.98 (687.44) | 10,757.22 (687.65) | 6.28 (0.17) | 0.99 (0.002) | 0.68 (0.016) |
| S2 | 13,403.33 (458.68) | 13,413.72 (457.42) | 13,407.63 (458.28) | 6.23 (0.01) | 0.99 | 0.64 (0.002) |
| S3 | 13,279 (83.48) | 13,284.83 (83.59) | 13,281.72 (83.05) | 5.99 (0.02) | 0.98 (0.001) | 0.63 (0.002) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Peng, X.; Yang, H.; Ni, H.; Zou, L.; Long, Z. Metagenomic Analysis Revealing the Impact of Water Contents on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities and the Distribution of Major Ecological Functional Genes in Poyang Lake Wetland Soil. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122569
Long Y, Zhang X, Peng X, Yang H, Ni H, Zou L, Long Z. Metagenomic Analysis Revealing the Impact of Water Contents on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities and the Distribution of Major Ecological Functional Genes in Poyang Lake Wetland Soil. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122569
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Yuxin, Xiaomei Zhang, Xuan Peng, Huilin Yang, Haiyan Ni, Long Zou, and Zhong’er Long. 2024. "Metagenomic Analysis Revealing the Impact of Water Contents on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities and the Distribution of Major Ecological Functional Genes in Poyang Lake Wetland Soil" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122569
APA StyleLong, Y., Zhang, X., Peng, X., Yang, H., Ni, H., Zou, L., & Long, Z. (2024). Metagenomic Analysis Revealing the Impact of Water Contents on the Composition of Soil Microbial Communities and the Distribution of Major Ecological Functional Genes in Poyang Lake Wetland Soil. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2569. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122569





