The Degradation Characteristics and Soil Remediation Capabilities of the Butachlor-Degrading Strain DC-1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pharmaceuticals and Culture Media
2.2. Enrichment and Isolation of Bacteria
2.3. Identification of Microbial Strains
2.4. Study on the Growth and Butachlor Degradation Capability of Bacterial Strains
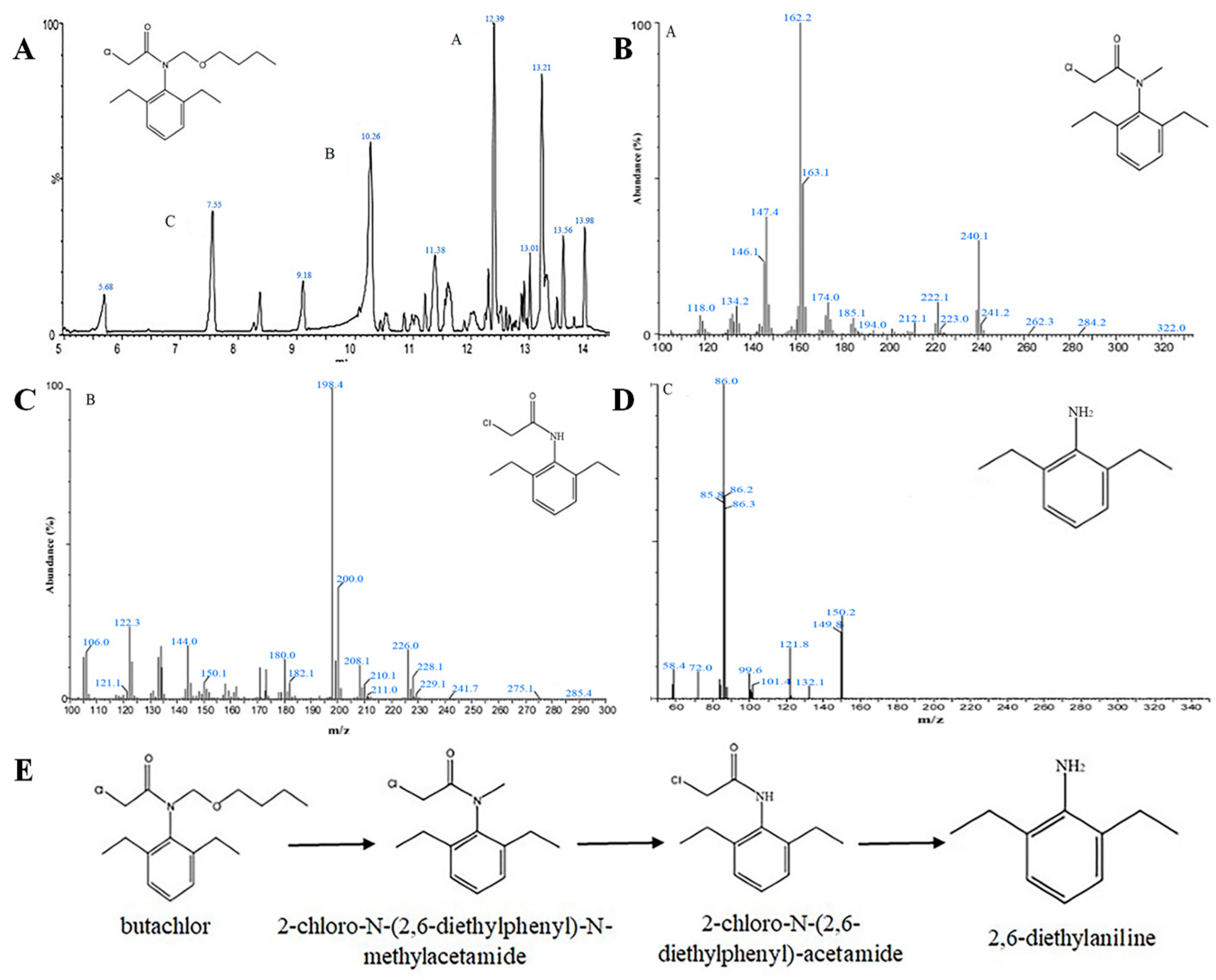
2.5. Degradation Product Analysis
2.6. Soil Remediation
2.7. Soil Microbial Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
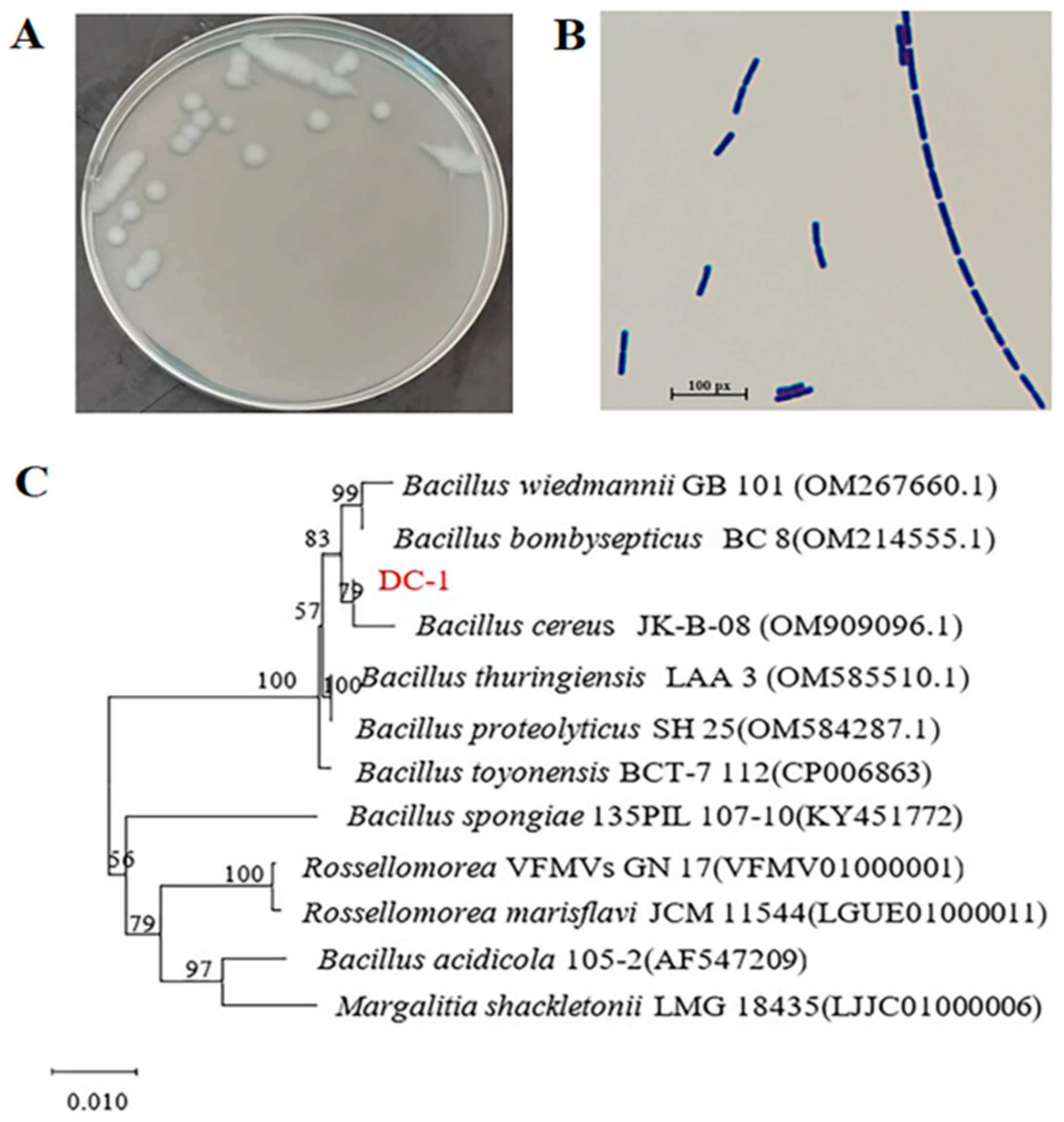
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Strain DC-1
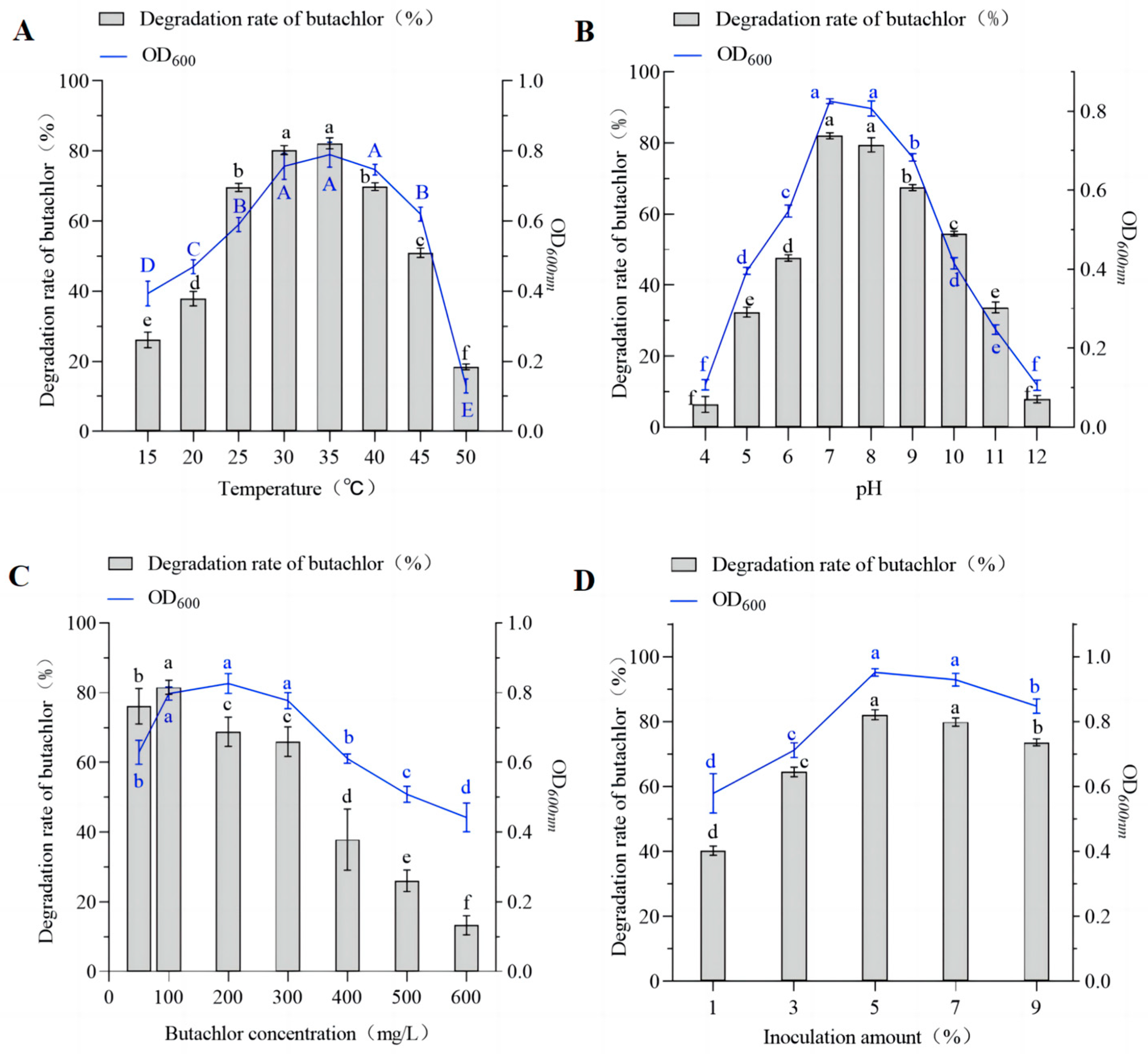
3.2. Effects of Environmental Factors on Growth and Biodegradation
3.3. Optimization of Butachlor Degradation Conditions by Strain DC-1
3.4. Analysis of Degradation Pathways by Strain DC-1
3.5. Bioremediation of Butachlor-Contaminated Soil
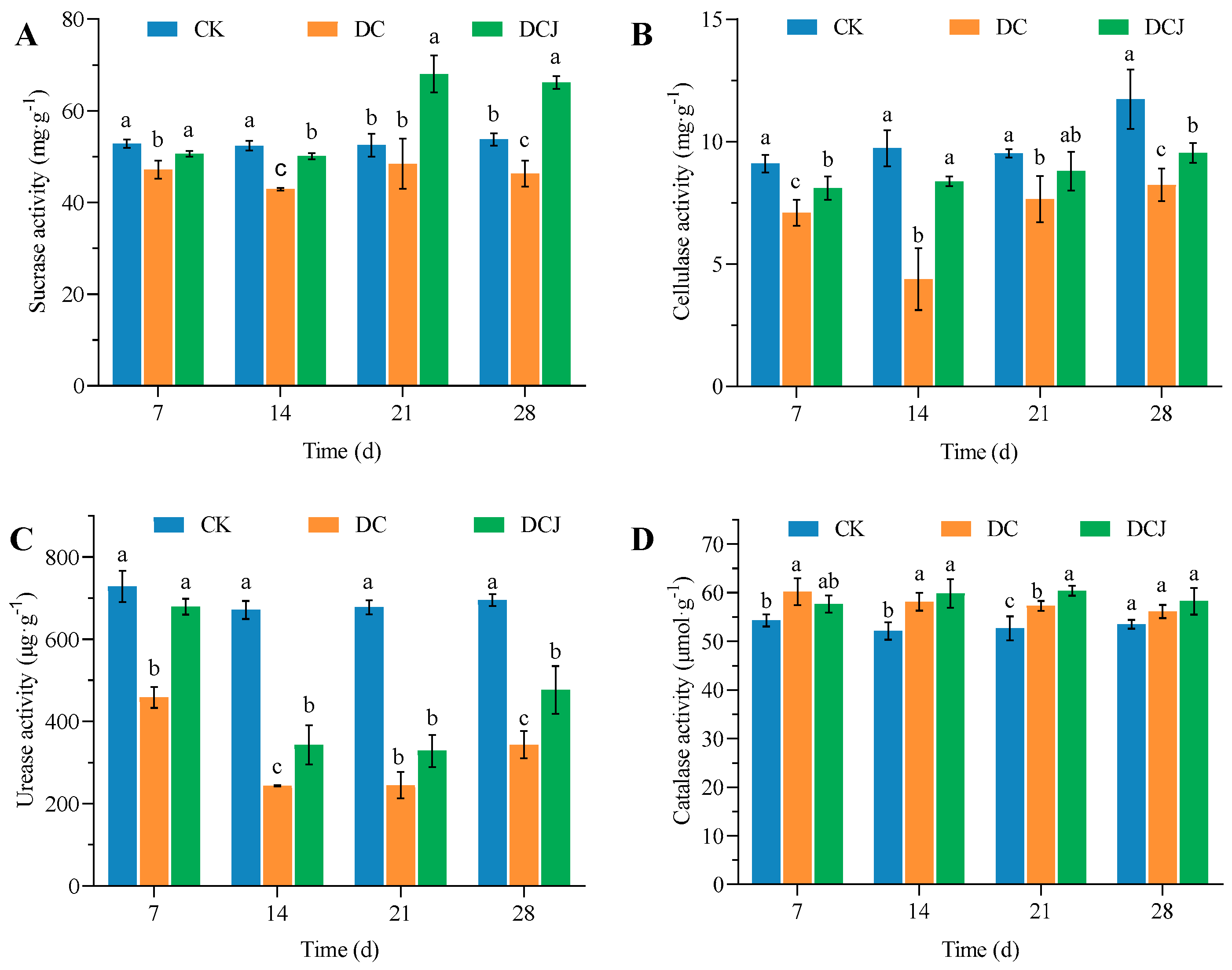
3.6. The Impact of Butachlor on Soil Enzymes
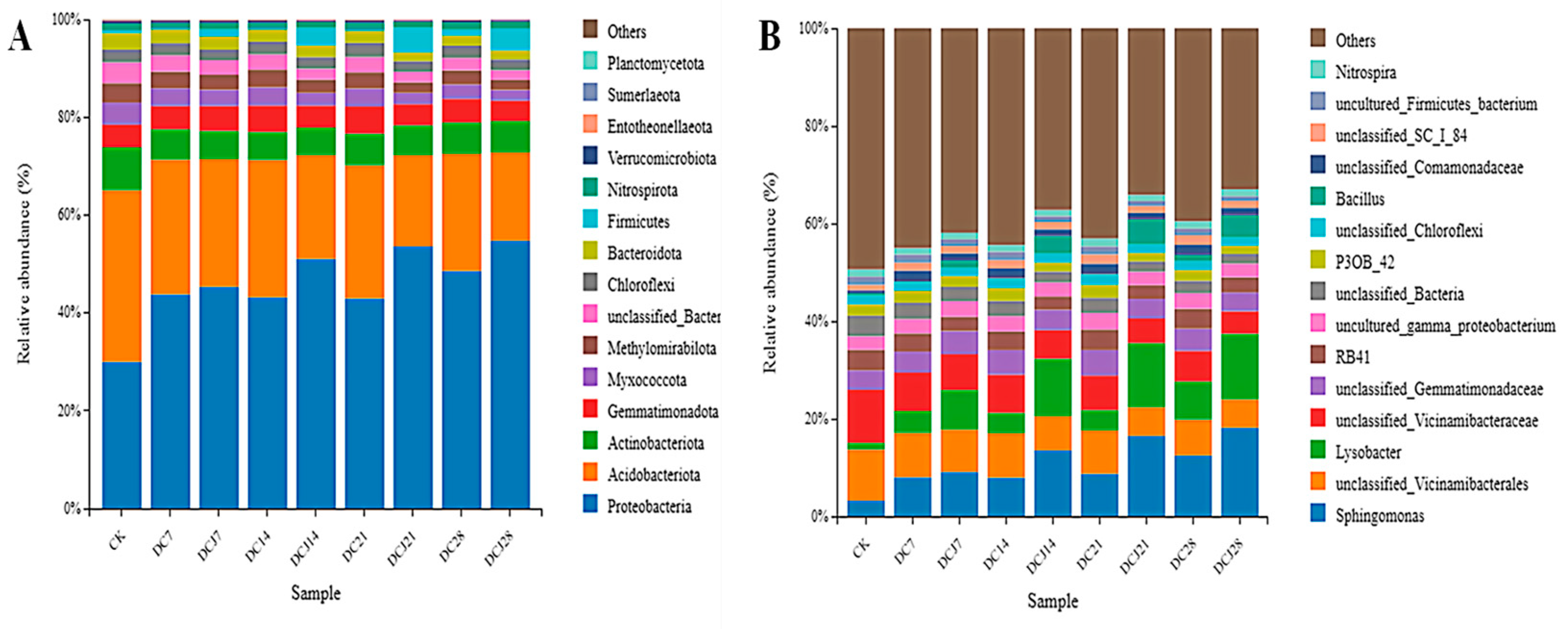
3.7. Impact on Soil Microbial Community
4. Comment
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dwivedi, S.; Saquib, Q.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A.; Musarrat, J. Butachlor induced dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential, oxidative DNA damage and necrosis in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Toxicology 2022, 302, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Koskinen, W.C.; Graff, C.D.; Anderson, J.L.; Mulla, D.J.; Nater, E.A.; Alonso, D.G. Acetochlor Persistence in Surface and Subsurface Soil Samples. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1747–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.P.; Jaiswal, D.K.; Sagar, R. Pesticide relevance and their microbial degradation: A-state-of-art. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2014, 13, 429–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolodar, N.R.; Katimi, S.; Bouteh, E.; Balist, J.; Prosser, R. Human health and ecological risk assessment of pesticides from rice production in the Babol Roud River in Northern Iran. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 144729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, V.; Solhi, H.M.E.; Mehri, F.; Atamaleki, A.; Moridi, F.M.; Mahmudiono, T.; Fakhri, Y. Concentration and non-dietary human health risk assessment of pesticide residues in soil of farms in Golestan province, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2024, 34, 968–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zou, W.; Cui, G.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L. Ecological risk assessment of current-use pesticides in an aquatic system of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Shutes, B.; Niu, T. Effect of butachlor on Microcystis aeruginosa: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 449, 131042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Karbalaei, S.; Zad Bagher, F.; Amin, I.; Simpson, S.L.; Courtenay, S.C. Alterations in juvenile diploid and triploid African catfish skin gelatin yield and amino acid composition: Effects of chlorpyrifos and butachlor exposures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabi, M.; Mahmoodian, F. Comparative toxicity of fresh and expired butachlor to earthworms Eisenia fetida in natural soil: Biomarker responses. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Yi, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, B.; Mehmood, K.; Hussain, R.; et al. Exposure to the herbicide butachlor activates hepatic stress signals and disturbs lipid metabolism in mice. Chemosphere 2021, 283, 131226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Liu, F.; Si, W.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Z.; Li, L.; Kiani, F.A.; Jiang, X. Pesticide butachlor exposure perturbs gut microbial homeostasis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhou, S.; Wang, M.; Zhu, G. Effects of butachlor on reproduction and hormone levels in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yi, J.; Yang, B.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, B.; Shang, P.; Mehmood, K.; et al. The potential risks of herbicide butachlor to immunotoxicity via induction of autophagy and apoptosis in the spleen. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, G.; Yokofuji, H.; Terayama, M.; Yoshinao, D.; Fujino, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Endo, S. Course of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and pulmonary oxygenation in acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by oral ingestion of large doses of oxadiazon·butachlor emulsion: A case report. Acute Med. Sur. 2020, 7, e552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.J.; Choi, S.C.; Gil, H.W.; Ohyang, J.; Lee, E.Y.; Song, H.Y.; Hong, S.Y. Acute oral poisoning due to chloracetanilide herbicides. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2022, 27, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Goyal, D. Biodegradation of Butachlor by Bacillus altitudinis and Identification of Metabolites. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raut, A.K.; Kulshrestha, G. Biotransformation of butachlor by soil fungi. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2008, 61, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Cao, L.; Lu, P.; Ni, H.; Li, Y.X.; Yan, X.; Hong, X.; Li, S.P. Biodegradation of butachlor by Rhodococcus sp. strain B1 and purification of its hydrolase (ChlH) responsible for N-dealkylation of chloroacetamide herbicides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12238–12244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jin, L.; Shi, H.; Chu, Z. Characterization of a novel butachlor biodegradation pathway and cloning of the debutoxylase (Dbo) gene responsible for debutoxylation of butachlor in Bacillus sp. hys-1. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Dong, W.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Shen, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, Z. Degradation of acetochlor by a bacterial consortium of Rhodococcus sp. T3-1, Delftia sp. T3-6 and Sphingobium sp. MEA3-1. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 59, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, R.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; He, J.; Li, S.; Jiang, J. Degradation of the chloroacetamide herbicide butachlor by Catellibacterium caeni sp. nov. DCA-1(T). Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2022, 73, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Jena, H.M. Degradation kinetics and mechanistic study on herbicide bioremediation using hyper butachlor-tolerant Pseudomonas putida G3. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 125, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Nandabalan, Y.K. Prospecting Ammoniphilus sp. JF isolated from agricultural fields for butachlor degradation. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Bao, Y.X.; Xu, J.Y.; Qiu, J.G.; He, J. Isolation, identification and degradation characteristics of an anaerobic butachlor-degrading bacterium BAD-20. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2021, 64, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, J.W.; Liang, B.; Wang, C.H.; Cai, S.; Ni, Y.Y.; He, J.; Li, S.P. Biodegradation of chloroacetamide herbicides by Paracoccus sp. FLY-8 in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4614–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, C.H.; Deng, S.K.; Wu, Y.D.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Jiang, J.D.; Yan, X.; He, J.; Li, S.P. Novel three-component Rieske non-heme iron oxygenase system catalyzing the N-dealkylation of chloroacetanilide herbicides in Sphingomonads DC-6 and DC-2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 5078–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, T.; Sha, G.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ren, K.; Yang, C. Soil enzyme activities of typical plant communities after vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ren, L.; Zhang, J.; Awasthi, M.K.; Yan, B.; Zhang, L.; Wan, F.; Luo, L.; Huang, H.; Zhao, K. Activities of functional enzymes involved in C, N, and P conversion and their stoichiometry during agricultural waste composting with biochar and biogas residue amendments. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 345, 126489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Huang, C.; Luo, Y.; Long, J.; Yao, H. Microbial activities and functional diversity of community in soils polluted with Pb-Zn-Ac mine tailings. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2004, 41, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, B.; Zhu, L. Effects of two herbicides on soil microbes and enzyme activities in a paddy field. Bulletion Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 35, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, W.; Han, L.; Qin, L. Soil bacterial communities with an indicative function response to nutrients in wetlands of Northeastern China that have undergone natural restoration. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.X.; Sun, G.D.; Liu, Z.P. Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil mesocosms by microbial·plant bioaugmentation: Performance and mechanism. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Weng, L.; Li, Y. Efficient Removal of Butachlor and Change in Microbial Community Structure in Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Dong, W.; Li, J.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Zuo, R. Shifts in microbial community structure and function in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soils at petrochemical landfill sites revealed by metagenomics. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Ye, Y.F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Wu, W.X.; Yufeng, D. Effects of butachlor on microbial populations and enzyme activities in paddy soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2001, 36, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; An, Y.Q.; An, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Bai, J. Acinetobacter calcoaceticus CSY-P13 mitigates stress of ferulic and p-hydroxybenzoic acids in cucumber by affecting antioxidantenzyme activity and soil bacterial community. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Fu, Q.; Xiao, C.; Ding, M.; Liang, D.; Li, H.; Liu, R. Impact of Paenarthrobacter ureafaciens ZF1 on the soil enzyme activity and microbial community during the bioremediation of atrazine-contaminated soils. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchanska, H.; Sajdak, M.; Szczypka, K.; Swientek, A.; Tworek, M.; Kurek, M. Atrazine, triketone herbicides, and their degradation products in sediment, soil and surface water samples in Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Yi, M.; Yi, H.; Guo, E.; Zhang, A. Shift of millet rhizosphere bacterial community during the maturation of parent soil revealed by 16s rDNA high-throughput sequencing. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Takagi, K.; Fujii, K.; Iwasaki, A. Transformation of methylthio-s-triazines via sulfur oxidation by strain jun7, a bacillus cereus species—Sciencedirect. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 2952–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, L.; Li, G.; An, T.; Wong, P. Biodegradation kinetics and mechanism of 2,4,6-tribromophenol by Bacillus sp. GZT: A phenomenon of xenobiotic methylation during debromination. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahmy, M.A.; Salem, S.H.; Qattan, S.Y.; Abourehab, M.A.; Ashkan, M.F.; Al-Quwaie, D.A.; Abd El-Fattah, H.I.; Akl, B.A. Biodegradation of chlorantraniliprole and flubendiamide by some bacterial strains isolated from different polluted sources. Processes 2022, 10, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Wójcik, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Biodegradation of the organophosphorus insecticide diazinon by Serratia sp. and Pseudomonas sp. and their use in bioremediation of contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.X.; Ni, H.; He, J.; Yan, X.; Gu, J.-G.; Li, S.-P. Sphingomonas chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov.; a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from activated sludge. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, F.; Bai, S.; Yang, J.; Qi, S. Pseudomonas sp.zxy-1, a newly isolated and highly efficient atrazine-degrading bacterium, and optimization of biodegradation using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. 2017, 54, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, X.Y. Isolation of Acetochlor-degrading bacterium Rhodococcus sp. AC-1 and its degradability. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2016, 30, 0662–0669. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Song, W.; Chen, M.; Yuan, M. Abiotic degradation and influencing factors of acetochlor, butachlor and metolachlor in different waters under natural conditions. Environ. Chem. 2021, 33, 2136–2143. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Soil enzymes as indicators of saline soil fertility under various soil amendments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 274–279. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey, K.A.; Gaw, S.K.; Northcott, G.L.; Lauren, D.R.; Hackenburg, S. The effects of copper on microbial activity and the degradation of atrazine and indoxacarb in a New Zealand soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Akram, N.A.; Sürücü, A.; Ashraf, M. Alleviating effect of nitric oxide on oxidative stress and antioxidant defence system in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants exposed to cadmium and lead toxicity applied separately or in combination. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 255, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wen, B.; Xu, H. Effects of butachlor on the reed growth and soil enzymatic activity in the wetland. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2015, 17, 674–679. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, M.; Yu, Y.-L.; Fang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Chu, X.; Bo, F. Effect of butachlor on soil microbial populations and enzyme activities. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2005, 7, 383–386. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, N.W.; Jing, B.; Ge, F.; Liu, X.H. The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Ding, H.; Shen, G. Effect of cadmium alone and in combination with butachlor on soil enzymes. Environ. Geochem. Health 2007, 29, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborowska, M.; Wyszkowska, J.; Kucharski, J. Soil enzyme response to bisphenol F contamination in the soil bioaugmented using bacterial and mould fungal consortium. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Yu, L. Effects of Cd or·and Pb on soil enzyme activities and microbial community structure. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Meng, Z. Application of a simazine degrading bacterium, Arthrobacter ureafaciens XMJ-Z01 for bioremediation of simazine pollution. Water Environ. J. 2020, 4, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozdrój, J.; Trevors, J.T.; van Elsas, J.D. Influence of introduced potential biocontrol agents on maize seedling growth and bacterial community structure in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Qian, J.; Zhou, J.; Wei, Q. Crop Microbiome: Breakthrough Technology for Agriculture. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Braganca, I.; Mucha, A.P.; Tomasino, M.P.; Santos, F.; Lemos, P.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Domingues, V.F. Deltamethrin impact in a cabbage planted soil: Degradation and effect on microbial community structure. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujakic, I.; Piwosz, K.; Koblizek, M. Phylum Gemmatimonadota and Its Role in the Environment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.N.; Ni, Y.X.; Cao, Z.Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Tuwang, M.C.; Yang, H.; Chen, M.X.; Mou, R.X. Chemistry-specific responses due to rice-microbe interactions in the rhizosphere to counteract mefenacet stress. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 179, 104970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, A. Remediation of Cd-As-Ni co-contaminated soil by extracellular polymeric substances from Bacillus subtilis: Dynamic improvements of soil properties and ecotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Luo, C.; Li, Y.; Qin, L.; Yan, D. Impact of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens beneficial bacterial agents on soil-borne diseases, growth, and economics of continuous cropping of flue-cured tobacco. Crop Prot. 2024, 177, 106556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Ding, M.Y.; Fu, Q.; Liu, R.M. Isolation and characterization of a high-efficiency atrazine-degrading strain paenarthrobacter ureafaciens zf1. J. Northeast. Agric. Univ. Engl. Ed. 2022, 29, 39–49. [Google Scholar]

| Detection Metrics | Detection Results | Detection Metrics | Detection Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | + | Citrate salt | - |
| Non-Xylose | - | VP Response | + |
| Non-maltose | + | Nitrate reduction | + |
| Amylum | + | Gelatin liquefaction | + |
| Urea | - | Lysine decarboxylaselysine decarBoxylase | - |
| Hydrogen sulFide | - | Ornithine decarboxylase | - |
| Hesperidin | + | Arginine dihydrolase | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, Y.; Fu, Q.; Xiong, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, Q.; He, F.; Li, H.; Liu, R. The Degradation Characteristics and Soil Remediation Capabilities of the Butachlor-Degrading Strain DC-1. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122568
Cheng Y, Fu Q, Xiong G, Huang Y, Li X, Yu Q, He F, Li H, Liu R. The Degradation Characteristics and Soil Remediation Capabilities of the Butachlor-Degrading Strain DC-1. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122568
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Yue, Qian Fu, Guixin Xiong, Yaning Huang, Xu Li, Qingyue Yu, Fuxia He, Haitao Li, and Rongmei Liu. 2024. "The Degradation Characteristics and Soil Remediation Capabilities of the Butachlor-Degrading Strain DC-1" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122568
APA StyleCheng, Y., Fu, Q., Xiong, G., Huang, Y., Li, X., Yu, Q., He, F., Li, H., & Liu, R. (2024). The Degradation Characteristics and Soil Remediation Capabilities of the Butachlor-Degrading Strain DC-1. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122568





