Hospital Context Determinants of Variability in Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevalence: Multi-Level Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
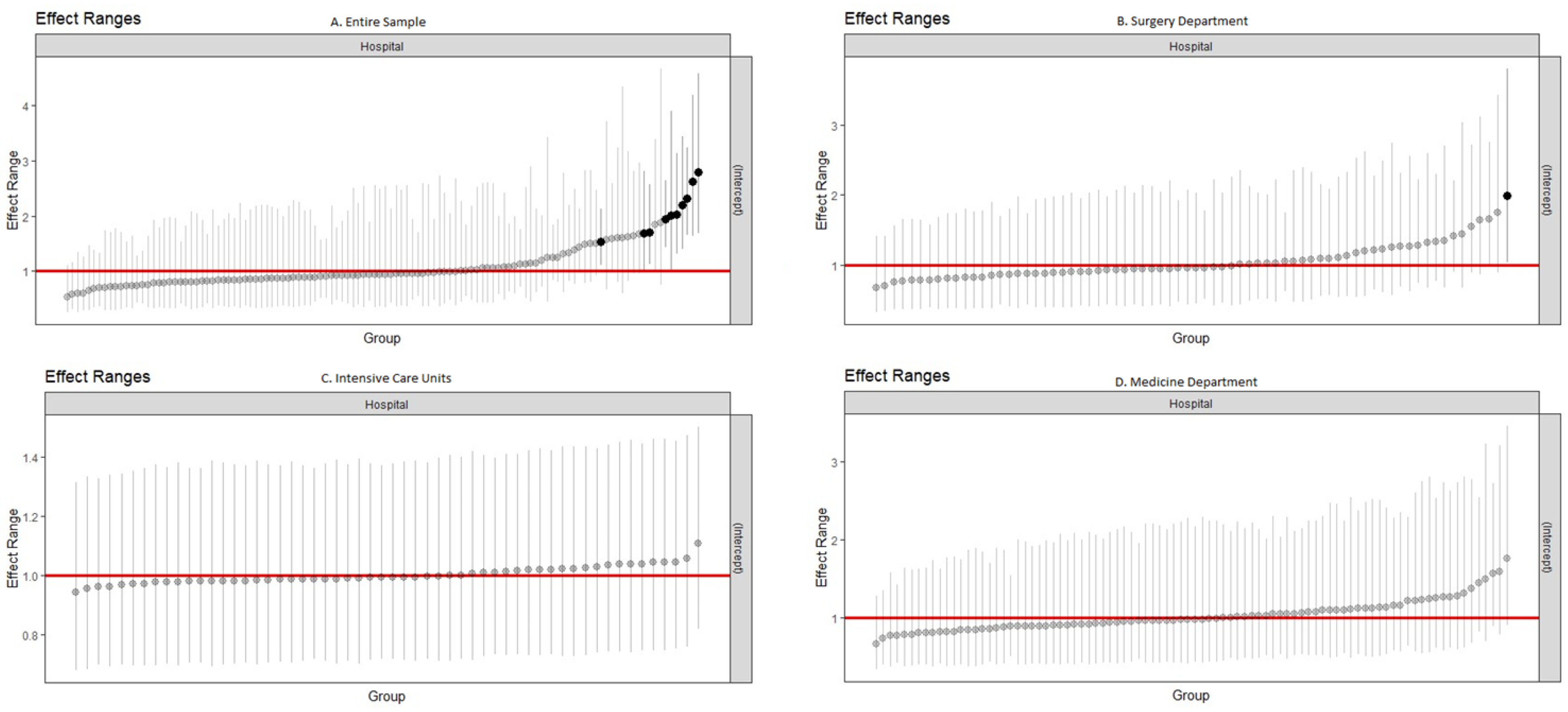
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umscheid, C.A.; Mitchell, M.D.; Doshi, J.A.; Agarwal, R.; Williams, K.; Brennan, P.J. Estimating the proportion of healthcare-associated infections that are reasonably preventable and the related mortality and costs. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassini, A.; Plachouras, D.; Eckmanns, T.; Abu Sin, M.; Blank, H.P.; Ducomble, T.; Haller, S.; Harder, T.; Klingeberg, A.; Sixtensson, M.; et al. Burden of Six Healthcare-Associated Infections on European Population Health: Estimating Incidence-Based Disability-Adjusted Life Years through a Population Prevalence-Based Modelling Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ministério da Saúde. Despacho n.º 2902/2013, de 22 de Fevereiro. Available online: https://diariodarepublica.pt/dr/detalhe/despacho/2902-2013-1937340 (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of Surgical Site Infections and Prevention Indicators in European Hospitals—HAI-Net SSI Protocol, Version 2.2; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Direção-Geral da Saúde, Stop Infeção Hospitalar 2.0. Available online: https://www.dgs.pt/em-destaque/stop-infecao-hospitalar-20.aspx (accessed on 11 September 2024).
- Mouajou, V.; Adams, K.; DeLisle, G.; Quach, C. Hand hygiene compliance in the prevention of hospital-acquired infections: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2022, 119, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop-Vicas, A.E.; Abad, C.; Baubie, K.; Osman, F.; Heise, C.; Safdar, N. Colorectal bundles for surgical site infection prevention: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Reviejo, R.; Tejada, S.; Jansson, M.; Ruiz-Spinelli, A.; Ramirez-Estrada, S.; Ege, D.; Vieceli, T.; Maertens, B.; Blot, S.; Rello, J. Prevention of ventilator-associated pneumonia through care bundles: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Intensive Med. 2023, 3, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, U.; Okolie, O.J.; Ismail, S.U.; Adukwu, E. Effectiveness of infection prevention and control interventions in health care facilities in Africa: A systematic review. Am. J. Infect. Control 2024, 52, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Schmid, M.N.; Parneix, P.; Lebowitz, D.; de Kraker, M.; Sauser, J.; Zingg, W.; Pittet, D. Impact of environmental hygiene interventions on healthcare-associated infections and patient colonization: A systematic review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malheiro, R.; Peleteiro, B.; Correia, S. Beyond the operating room: Do hospital characteristics have an impact on surgical site infections after colorectal surgery? A systematic review. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.; Shamliyan, T.; Mueller, C.; Duval, S.; Wilt, T. The Association of Registered Nurse Staffing Levels and Patient Outcomes. Med. Care 2007, 45, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Yun, I.; Jang, S.Y.; Park, E.C.; Jang, S.I. Association between nurse staffing level in intensive care settings and hospital-acquired pneumonia among surgery patients: Result from the Korea National Health Insurance cohort. Epidemiol. Infect. 2024, 152, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donabedian, A. Evaluating the quality of medical care. 1966. Milbank Q. 2005, 84, 691–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals—Protocol Version 6.1; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, W.R.; Jackson, G.G. Gram-negative bacteremia. I. Etiology and ecology. Arch. Intern. Med. 1962, 110, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Global Guidelines for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zingg, W.; Metsini, A.; Balmelli, C.; Neofytos, D.; Behnke, M.; Gardiol, C.; Widmer, A.; Pittet, D.; Swissnoso, N. National point prevalence survey on healthcare-associated infections in acute care hospitals, Switzerland, 2017. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.; Monette, G. Generalized Collinearity Diagnostics. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1992, 87, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenert, M.C.; Miller, R.A.; Vorobeychik, Y.; Walsh, C.G. A method for analyzing inpatient care variability through physicians’ orders. J. Biomed. Inform. 2019, 91, 103111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.; Roman, E.; Lambert, J.; Moke, L.; Scheys, L.; Kesteloot, K.; Roodhooft, F.; Cardoen, B. Variability drivers of treatment costs in hospitals: A systematic review. Health Policy 2022, 126, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.; Robertson, C.; Kennedy, S.; Kavanagh, K.; Haahr, L.; Manoukian, S.; Mason, H.; Dancer, S.; Cook, B.; Reilly, J. Personalized infection prevention and control: Identifying patients at risk of healthcare-associated infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 114, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, L. Risk factors of central catheter bloodstream infections in intensive care units: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Acelas, A.L.; de Abreu Almeida, M.; Engelman, B.; Canon-Montanez, W. Risk factors for health care-associated infection in hospitalized adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, e149–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian. STOP Infeção Hospitalar! Um Desafio Gulbenkian; Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian: Lisbon, Portugal, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- von Lengerke, T.; Lutze, B.; Graf, K.; Krauth, C.; Lange, K.; Schwadtke, L.; Stahmeyer, J.; Chaberny, I.F. Psychosocial determinants of self-reported hand hygiene behaviour: A survey comparing physicians and nurses in intensive care units. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 91, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicentini, C.; Bussolino, R.; Gastaldo, C.; Castagnotto, M.; D’Ancona, F.P.; Zotti, C.M.; Working group “Unita Prevenzione Rischio Infettivo, Regione Piemonte. Level of implementation of multimodal strategies for infection prevention and control interventions and prevalence of healthcare-associated infections in Northern Italy. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2024, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, R.; Traverson, L.; Chabrol, F.; Gautier, L.; de Araujo Oliveira, S.R.; David, P.M.; Lucet, J.C.; Zinszer, K.; Ridde, V. Communication and Information Strategies Implemented by Four Hospitals in Brazil, Canada, and France to Deal with COVID-19 Healthcare-Associated Infections. Health Syst. Reform. 2023, 9, 2223812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, B.G.; Hall, L.; White, N.; Barnett, A.G.; Halton, K.; Paterson, D.L.; Riley, T.V.; Gardner, A.; Page, K.; Farrington, A.; et al. An environmental cleaning bundle and health-care-associated infections in hospitals (REACH): A multicentre, randomised trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Park, J.E.; Hwang, S.; Kwon, K.T. Crucial role of temporary airborne infection isolation rooms in an intensive care unit: Containing the COVID-19 outbreak in South Korea. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Abraham, R.; Keller, N.; Szold, O.; Vardi, A.; Weinberg, M.; Barzilay, Z.; Paret, G. Do isolation rooms reduce the rate of nosocomial infections in the pediatric intensive care unit? J. Crit. Care 2002, 17, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A.; Eisenring, M.C.; Troillet, N.; Kuster, S.P.; Widmer, A.; Zwahlen, M.; Marschall, J. Surveillance quality correlates with surgical site infection rates in knee and hip arthroplasty and colorectal surgeries: A call to action to adjust reporting of SSI rates. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troillet, N.; Aghayev, E.; Eisenring, M.C.; Widmer, A.F.; Swissnoso. First Results of the Swiss National Surgical Site Infection Surveillance Program: Who Seeks Shall Find. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2017, 38, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaiopanos, K.; Krystallaki, D.; Mellou, K.; Kotoulas, P.; Kavakioti, C.A.; Vorre, S.; Vertsioti, G.; Gkova, M.; Maragkos, A.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; et al. Healthcare-associated infections and antimicrobial use in acute care hospitals in Greece, 2022; results of the third point prevalence survey. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2024, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbadoro, P.; Dolcini, J.; Fortunato, C.; Mengarelli Detto Rinaldini, D.; Martini, E.; Gioia, M.G.; Mengoni, D.; D’Errico, M.M.; Marche’s, I.C.A.N.W.C.G. Point prevalence survey of antibiotic use and healthcare-associated infections in acute care hospitals: A comprehensive report from the Marche Region of Italy. J. Hosp. Infect. 2023, 141, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Hospital Variables | All Hospitals | ICU Department | Surgical Department | Medical Department |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. hospitals | 119 | 56 | 72 | 90 |
| No. patients | 18,261 | 736 | 3160 | 8081 |
| No. patients with HAI (prevalence) | 638 (3.5) | 58 (7.9) | 187 (5.9) | 138 (1.7) |
| Age (median [IQR]) | 71 (56–82) | 67 (55–76) | 68 (56–78) | 76 (64–85) |
| Male sex | 9182 (50.3) | 455 (61.2) | 1653 (52.3) | 4184 (51.8) |
| McCabe score | ||||
| Ultimately fatal | 4068 (22.3) | 148 (19.9) | 524 (16.6) | 2437 (30.1) |
| Rapidly fatal | 1033 (5.7) | 72 (9.7) | 67 (2.1) | 648 (8.0) |
| Non-fatal | 12,943 (70.9) | 500 (67.2) | 2531 (80.1) | 4931 (61.0) |
| Unknown | 204 (1.1) | 16 (2.2) | 38 (1.2) | 65 (0.8) |
| Device use | ||||
| CVC | 1529 (8.4) | 461 (62.0) | 285 (9.0) | 506 (6.3) |
| Urinary catheter | 4250 (23.3) | 585 (78.6) | 726 (23.0) | 1906 (23.6) |
| Intubation | 461 (2.5) | 277 (37.2) | 50 (1.6) | 84 (1.0) |
| Has any device | 5045 (27.6) | 608 (81.7) | 912 (29.2) | 2309 (28.6) |
| Hospital bed size | ||||
| 0–250 | 6109 (28.0) | 130 (17.5) | 703 (22.2) | 2273 (28.1) |
| 251–500 | 6264 (34.3) | 290 (39.0) | 1116 (35.3) | 2537 (31.4) |
| >500 | 6888 (37.7) | 316 (52.5) | 1341 (42.4) | 3271 (40.5) |
| Hospital type | ||||
| Primary | 1366 (7.5) | 34 (4.6) | 127 (4.0) | 727 (9.0) |
| Secondary | 7248 (39.7) | 233 (31.3) | 930 (29.4) | 3585 (44.4) |
| Specialized | 840 (4.6) | 19 (2.6) | 208 (6.6) | 195 (2.4) |
| Tertiary | 8807 (48.2) | 450 (60.5) | 1895 (60.0) | 3574 (44.2) |
| Hospital location | ||||
| Norte | 6146 (33.7) | 311 (41.8) | 1221 (38.6) | 2319 (828.7) |
| Centro | 3488 (19.1) | 88 (11.8) | 633 (20.0) | 1461(18.1) |
| Lisbon | 6083 (33.3) | 261 (35.1) | 877 (27.8) | 3056 (37.8) |
| Other | 2544 (13.9) | 76 (10.2) | 429 (13.6) | 1245 (15.4) |
| No. hospital isolation rooms | 5 (1–10) | 8 (2–14) | 6 (1–8) | 5 (1–8) |
| Clinical tests on weekend | ||||
| Both days | 10,140 (55.5) | 463 (62.2) | 314 (9.9) | 4390 (54.3) |
| One day only | 2329 (12.8) | 48 (6.5) | 1851 (58.6) | 1394 (17.2) |
| Screening tests on weekend | ||||
| Both days | 10,567 (57.9) | 470 (63.2) | 492 (15.6) | 4610 (57.0) |
| One day only | 3079 (16.9) | 77 (10.3) | 1927 (61.0) | 1604 (19.9) |
| IPC doctors-to-acute beds ratio (median [IQR]) | 0.1 (0.0–0.2) | 0.1 (0.0–0.3) | 0.1 (0.0–0.3) | 0.1 (0.0–0.2) |
| IPC nurses-to-acute beds ratio (median [IQR]) | 0.5 (0.4–0.7) | 0.5 (0.4–0.7) | 0.5 (0.4–0.8) | 0.5 (0.4–0.7) |
| AMS consultants-to-acute beds ratio (median [IQR]) | 0.1 (0.0–0.1) | 0.1 (0.0–0.1) | 0.1 (0.0–0.1) | 0.0 (0.0–0.1) |
| CEO-approved IPC plan | 14,890 (81.5) | 630 (84.7) | 2572 (81.4) | 6560 (81.2) |
| CEO-approved IPC report | 15,669 (85.8) | 670 (90.1) | 2781 (88.0) | 6855 (84.8) |
| Universal masking | ||||
| Care | 7833 (42.9) | 1471 (46.6) | 3169 (39.2) | |
| Always | 412 (2.3) | 81 (2.6) | 126 (1.6) | |
| Participation in surveillance networks | ||||
| Surgical site infection | 8597 (47.1) | - | 1604 (50.8) | - |
| HAI in intensive care units | 9171 (50.2) | 418 (56.2) | - | - |
| Clostridium difficile | 3715 (20.3) | 123 (16.5) | 495 (15.7) | 1804 (22.3) |
| Antimicrobial resistance | 10,900 (59.7) | 453 (60.9) | 1991 (63.0) | 4839 (59.9) |
| Antimicrobial consumption | 11,070 (60.6) | 478 (64.2) | 2070 (65.5) | 4987 (61.7) |
| Multimodal strategy use | ||||
| System change | ||||
| Element not included | 104 (0.6) | 4 (0.5) | 0 (0.0) | 41 (0.5) |
| L1 | 3891 (21.3) | 143 (19.4) | 584 (18.5) | 1906 (23.6) |
| L2 | 9786 (53.6) | 445 (60.5) | 1931 (61.1) | 4010 (49.6) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| Education and training | ||||
| L1 | 2185 (12.0) | 57 (7.7) | 310 (9.8) | 867 (10.7) |
| L2 | 11,596 (63.5) | 535 (72.7) | 2205 (69.8) | 5090 (63.0) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| Monitoring and feedback | ||||
| Element not included | 40 (0.2) | 5 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.02) |
| L1 | 3194 (17.5) | 175 (23.8) | 557 (17.6) | 1426 (17.6) |
| L2 | 10,547 (57.8) | 412 (55.9) | 1958 (61.9) | 4529 (56.0) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| Communications and reminders | ||||
| L1 | 8267 (45.3) | 365 (49.6) | 1554 (49.2) | 3504 (43.4) |
| L2 | 5514 (30.2) | 227 (30.8) | 961 (30.4) | 2453 (30.4) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| Safety climate and culture change | ||||
| Element not included | 2702 (14.8) | 80 (10.9) | 413 (13.1) | 1336 (16.5) |
| L1 | 5322 (29.1) | 222 (30.2) | 899 (28.4) | 2442 (30.2) |
| L2 | 5685 (31.1) | 290 (39.4) | 1203 (38.1) | 2125 (26.3) |
| Unknown | 4552 (24.9) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2178 (26.6) |
| Is a multidisciplinary team used to implement IPC multimodal strategies | ||||
| Yes | 12,620 (69.1) | 535 (72.7) | 2265 (71.8) | 5350 (66.2) |
| No | 1161 (6.4) | 57 (7.7) | 250 (7.9) | 607 (7.5) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| Link to developing multimodal strategy with colleagues | ||||
| Yes | 11,210 (61.4) | 496 (67.4) | 1981 (62.7) | 4723 (58.4) |
| No | 2571 (14.1) | 96 (13.0) | 534 (16.9) | 1234 (15.3) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| Bundles or checklists | ||||
| Yes | 11,596 (63.5) | 587 (79.8) | 2477 (78.4) | 5762 (71.3) |
| No | 2185 (12.0) | 5 (0.68) | 38 (1.2) | 195 (2.4) |
| Unknown | 4480 (24.5) | 144 (19.6) | 645 (20.4) | 2124 (26.3) |
| All Hospitals | ICU | Surgery | Medicine | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariate | Multivariable | Univariate | Multivariable | Univariate | Multivariable | Univariate | Multivariable | |||||||||
| Patient Variable | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value | β | p-Value |
| Age | 0.01 | <0.001 | 0.01 | <0.001 | −0.01 | 0.573 | - | - | 0.00 | 0.393 | −6.32 | <0.001 | 0.04 | <0.001 | 0.04 | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 0.20 | 0.013 | 0.12 | 0.204 | 0.45 | 0.146 | 0.39 | 0.225 | 0.45 | 0.004 | 0.31 | 0.07900 | −0.19 | 0.274 | - | - |
| McCabe score | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-fatal | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ||||||||
| Rapidly fatal | 0.25 | 0.138 | −0.24 | 0.227 | −0.04 | 0.940 | - | - | 0.94 | 0.0180 | 0.64 | 0.1600 | −0.12 | 0.73 | −0.30 | 0.445 |
| Ultimately fatal | 0.45 | <0.001 | 0.15 | 0.163 | 0.30 | 0.381 | - | - | 0.91 | <0.001 | 0.76 | <0.001 | 0.31 | 0.09 | −0.12 | 0.618 |
| Device no. | 0.92 | <0.001 | 0.91 | <0.001 | 1.06 | <0.001 | 0.11 | <0.001 | 0.28 | 0.025 | 0.06 | 0.6970 | 1.14 | <0.001 | 1.49 | <0.001 |
| Hospital variable | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value |
| Hospital bed size | ||||||||||||||||
| 0–250 | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | |||||||||
| 250–500 | 0.52 | 0.001 | 0.02 | 0.936 | −0.46 | 0.259 | - | - | 0.38 | 0.150 | −0.44 | 0.301 | 0.09 | 0.711 | - | - |
| >500 | 0.67 | <0.001 | 0.45 | 0.257 | 0.09 | 0.810 | - | - | 0.68 | 0.013 | −0.73 | 0.342 | −0.09 | 0.704 | - | - |
| Hospital type | ||||||||||||||||
| Primary | ref | Ref | Ref | ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | |||||||||
| Secondary | 0.20 | 0.416 | −0.12 | 0.666 | 0.29 | 0.706 | - | - | −0.25 | 0.571 | −0.19 | 0.823 | −0.09 | 0.794 | - | - |
| Specialized | 0.49 | 0.156 | −0.89 | 0.076 | −0.11 | 0.928 | - | - | 0.84 | 0.080 | 2.17 | 0.029 | 0.31 | 0.599 | - | - |
| Tertiary | 0.32 | 0.202 | −0.02 | 0.949 | 0.28 | 0.708 | - | - | 0.11 | 0.795 | 0.84 | 0.309 | −0.23 | 0.494 | - | - |
| Hospital location | ||||||||||||||||
| Lisbon | Ref | - | - | Ref | ref | Ref | Ref | ref | ||||||||
| Centro | 0.02 | 0.918 | - | - | 0.82 | 0.060 | 0.03 | 0.963 | −0.13 | 0.667 | - | - | 0.09 | 0.765 | 0.29 | 0.534 |
| Norte | 0.13 | 0.481 | - | - | 0.39 | 0.263 | −0.42 | 0.517 | 0.07 | 0.763 | - | - | −0.08 | 0.766 | −0.65 | 0.156 |
| Other | 0.044 | 0.846 | - | - | 0.730 | 0.115 | −0.40 | 0.526 | −0.09 | 0.779 | - | - | 0.38 | 0.196 | 0.06 | 0.913 |
| No. hospital isolation rooms | ||||||||||||||||
| 1st quartile | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | |||||||||
| 2nd quartile | 0.48 | 0.006 | 0.07 | 0.745 | 0.31 | 0.433 | −0.23 | 0.684 | 0.64 | 0.014 | −0.65 | 0.188 | 0.19 | 0.49 | - | - |
| 3rd quartile | 0.43 | 0.044 | −0.30 | 0.244 | 0.50 | 0.193 | 0.04 | 0.936 | 0.65 | 0.029 | −0.36 | 0.531 | −0.27 | 0.393 | - | - |
| 4th quartile | 0.37 | 0.060 | −0.62 | 0.011 | −0.31 | 0.502 | −0.06 | 0.913 | 0.39 | 0.152 | −0.8 | 0.131 | −0.14 | 0.637 | - | - |
| Clinical tests on weekends | ||||||||||||||||
| One day only | −0.31 | 0.247 | 0.09 | 0.852 | −0.68 | 0.380 | - | - | −0.45 | 0.246 | - | - | −0.25 | 0.455 | 0.27 | 0.808 |
| Both days | −0.33 | 0.055 | 0.93 | 0.762 | 0.07 | 0.843 | - | - | −0.23 | 0.316 | - | - | −0.32 | 0.172 | 0.87 | 0.530 |
| Screening tests on weekends | ||||||||||||||||
| One day only | −0.13 | 0.603 | −0.78 | 0.026 | −0.44 | 0.475 | - | - | −0.29 | 0.410 | - | - | −0.55 | 0.104 | −0.56 | 0.468 |
| Both days | −0.30 | 0.104 | −0.93 | 0.220 | 0.09 | 0.800 | - | - | −0.21 | 0.420 | - | - | 0.42 | 0.089 | −1.55 | 0.243 |
| IPC doctors-to-acute beds ratio | ||||||||||||||||
| 1st quartile | Ref | Ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ||||||||
| 2nd quartile | −0.24 | 0.188 | 0.27 | 0.185 | −0.93 | 0.033 | −0.24 | 0.672 | 0.11 | 0.686 | 1.31 | 0.006 | −0.57 | 0.0531 | 0.12 | 0.797 |
| 3rd quartile | 0.08 | 0.673 | −0.03 | 0.909 | −0.59 | 0.132 | −0.03 | 0.958 | 0.41 | 0.147 | 0.99 | 0.048 | −0.14 | 0.6146 | 1.06 | 0.063 |
| 4th quartile | 0.29 | 0.145 | 0.50 | 0.031 | −0.06 | 0.862 | 0.75 | 0.293 | 0.33 | 0.256 | 0.80 | 0.089 | −0.14 | 0.6206 | 0.99 | 0.121 |
| IPC nurses-to-acute beds ratio | ||||||||||||||||
| 1st quartile | Ref | Ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | |||||||||
| 2nd quartile | 0.27 | 0.118 | 0.62 | 0.028 | 0.27 | 0.531 | 0.33 | 0.557 | 0.48 | 0.071 | 2.44 | <0.001 | −0.13 | 0.666 | 0.09 | 0.848 |
| 3rd quartile | 0.69 | <0.001 | 0.70 | 0.007 | 0.53 | 0.189 | 0.68 | 0.255 | 0.52 | 0.052 | 2.20 | 0.004 | 0.42 | 0.104 | 0.55 | 0.167 |
| 4th quartile | 0.42 | 0.044 | 0.25 | 0.936 | 0.15 | 0.743 | 0.00 | 1.000 | 0.66 | 0.025 | 2.09 | 0.005 | −0.32 | 0.298 | −0.95 | 0.037 |
| AMS consultants-to-acute beds ratio | ||||||||||||||||
| 1st quartile | Ref | - | - | ref | ref | ref | ref | ref | ||||||||
| 2nd quartile | −0.04 | 0.841 | - | - | −0.29 | 0.456 | - | - | −0.22 | 0.424 | - | - | 0.02 | 0.941 | 0.28 | 0.451 |
| 3rd quartile | 0.11 | 0.616 | - | - | −0.47 | 0.247 | - | - | 0.31 | 0.234 | - | - | −0.46 | 0.129 | −0.17 | 0.736 |
| 4th quartile | 0.23 | 0.269 | - | - | −0.13 | 0.724 | - | - | 0.28 | 0.302 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.978 | −0.30 | 0.572 |
| CEO-approved IPC plan | 0.01 | 0.967 | - | - | 0.01 | 0.979 | - | - | 0.26 | 0.324 | - | - | −0.50 | 0.0294 | −0.70 | 0.206 |
| CEO-approved IPC report | 0.18 | 0.39 | - | - | 0.59 | 0.337 | - | - | 0.22 | 0.472 | - | - | −0.242 | 0.382 | - | - |
| Participation in surveillance network | ||||||||||||||||
| SSI | 0.15 | 0.418 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.12 | 0.636 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ICU | 0.15 | 0.377 | - | - | 0.32 | 0.332 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| CDI | 0.09 | 0.642 | - | - | −0.45 | 0.318 | - | - | 0.30 | 0.221 | - | - | 0.29 | 0.287 | - | - |
| AMR | 0.34 | 0.055 | 0.21 | 0.538 | −0.35 | 0.314 | - | - | 0.87 | 0.003 | 0.84 | 0.237 | 0.48 | 0.102 | −0.04 | 0.957 |
| AMC | 0.34 | 0.039 | 0.49 | 0.242 | −0.46 | 0.185 | −0.89 | 0.126 | 0.62 | 0.011 | 0.29 | 0.701 | 0.59 | 0.0354 | 1.10 | 0.15 |
| Universal masking | ||||||||||||||||
| Care | 0.39 | 0.010 | 0.44 | 0.007 | 0.25 | 0.430 | - | - | 0.32 | 0.173 | 0.19 | 0.627 | 0.67 | 0.726 | - | - |
| Always | 0.73 | 0.039 | 1.34 | 0.012 | 0.38 | 0.728 | - | - | 0.80 | 0.119 | 1.03 | 0.401 | 0.78 | 0.248 | - | - |
| Multimodal strategies | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value | β | p-value |
| System change | ||||||||||||||||
| L2 vs. L1 | 0.02 | 0.941 | - | - | 0.09 | 0.813 | - | - | 0.19 | 0.537 | - | - | −0.31 | 0.201 | - | - |
| Education and training | ||||||||||||||||
| L2 vs. L1 | −0.15 | 0.508 | - | - | 0.50 | 0.412 | - | - | −0.10 | 0.769 | - | - | −0.48 | 0.089 | 0.08 | 0.885 |
| Monitoring and feedback | ||||||||||||||||
| L2 vs. L1 | −0.06 | 0.795 | - | - | −0.18 | 0.578 | - | - | −0.31 | 0.295 | - | - | −0.30 | 0.255 | - | - |
| Communication | ||||||||||||||||
| L2 vs. L1 | −0.37 | 0.048 | −0.46 | 0.006 | −0.34 | 0.293 | - | - | −0.03 | 0.912 | - | - | −0.24 | 0.33 | - | - |
| Safety culture change | ||||||||||||||||
| L1 | −0.35 | 0.154 | 0.52 | 0.065 | −0.43 | 0.375 | - | - | −0.31 | 0.385 | −0.87 | 0.175 | −0.61 | 0.0211 | −0.06 | 0.922 |
| L2 | −0.28 | 0.255 | 0.59 | 0.091 | 0.11 | 0.807 | - | - | −0.60 | 0.096 | −1.59 | 0.019 | −0.64 | 0.0223 | −0.01 | 0.987 |
| Multidisciplinary team | −0.38 | 0.337 | - | - | −0.10 | 0.847 | - | - | −0.32 | 0.492 | - | - | −0.61 | 0.0879 | −0.43 | 0.561 |
| Link to developing strategies with colleagues | −0.52 | 0.025 | −0.42 | 0.151 | 0.17 | 0.749 | - | - | −0.57 | 0.052 | 0.89 | 0.168 | −0.24 | 0.397 | - | - |
| Bundles or checklists | 0.33 | 0.530 | - | - | 0.24 | 0.526 | - | - | 0.81 | 0.464 | - | - | 0.24 | 0.731 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malheiro, R.; Gomes, A.A.; Fernandes, C.; Fareleira, A.; Lebre, A.; Pascoalinho, D.; Gonçalves-Pereira, J.; Paiva, J.-A.; Sá-Machado, R. Hospital Context Determinants of Variability in Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevalence: Multi-Level Analysis. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122522
Malheiro R, Gomes AA, Fernandes C, Fareleira A, Lebre A, Pascoalinho D, Gonçalves-Pereira J, Paiva J-A, Sá-Machado R. Hospital Context Determinants of Variability in Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevalence: Multi-Level Analysis. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122522
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalheiro, Rui, André Amaral Gomes, Carlos Fernandes, Ana Fareleira, Ana Lebre, Dulce Pascoalinho, João Gonçalves-Pereira, José-Artur Paiva, and Rita Sá-Machado. 2024. "Hospital Context Determinants of Variability in Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevalence: Multi-Level Analysis" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122522
APA StyleMalheiro, R., Gomes, A. A., Fernandes, C., Fareleira, A., Lebre, A., Pascoalinho, D., Gonçalves-Pereira, J., Paiva, J.-A., & Sá-Machado, R. (2024). Hospital Context Determinants of Variability in Healthcare-Associated Infection Prevalence: Multi-Level Analysis. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2522. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122522






