Genomic Investigation and Comparative Analysis of European High-Risk Clone of Acinetobacter baumannii ST2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.3. Genome Sequence Analysis
2.4. Analysis of A. baumannii Strains from Pathogenwatch
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
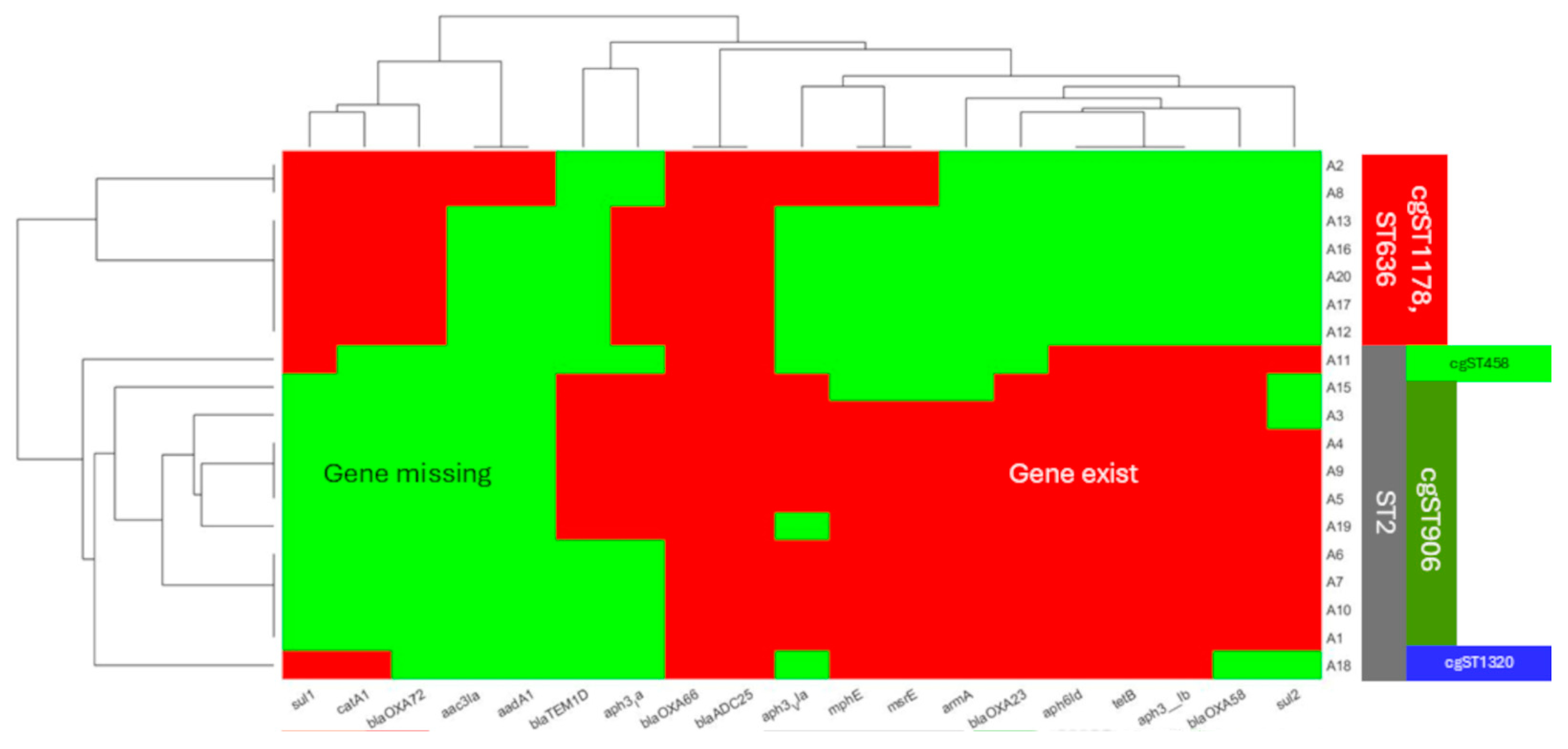
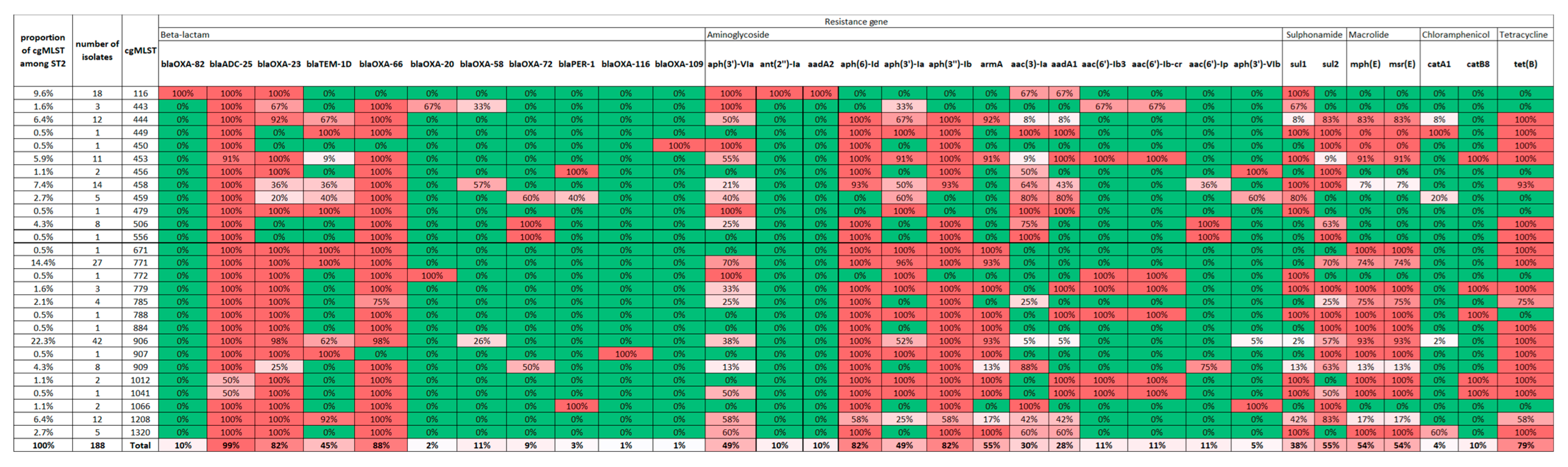
3.1. WGS Analysis, Antibiotic Resistance Profile of the 19 A. baumannii
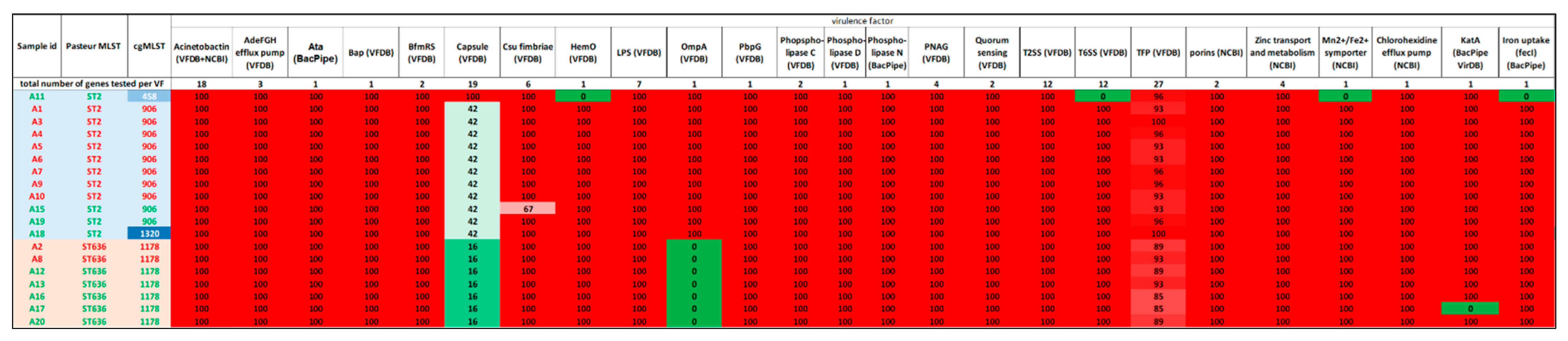
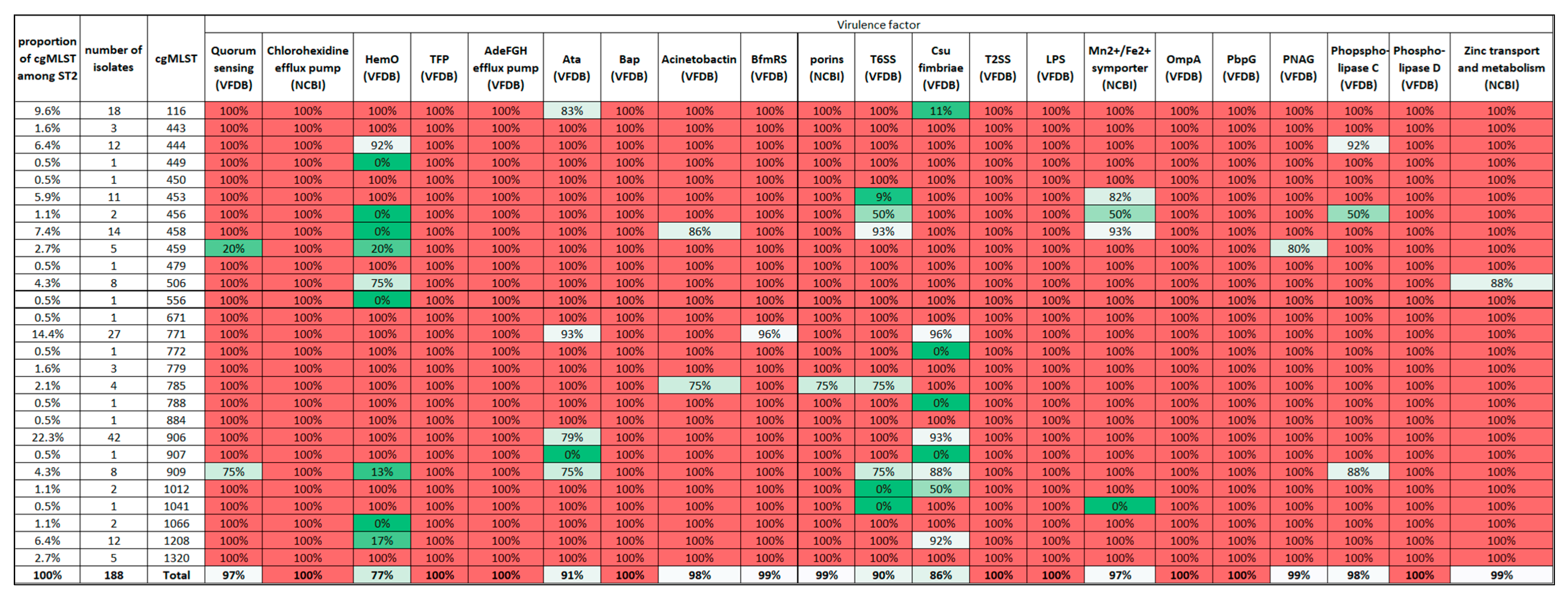
3.2. Virulence Profile of the Isolates
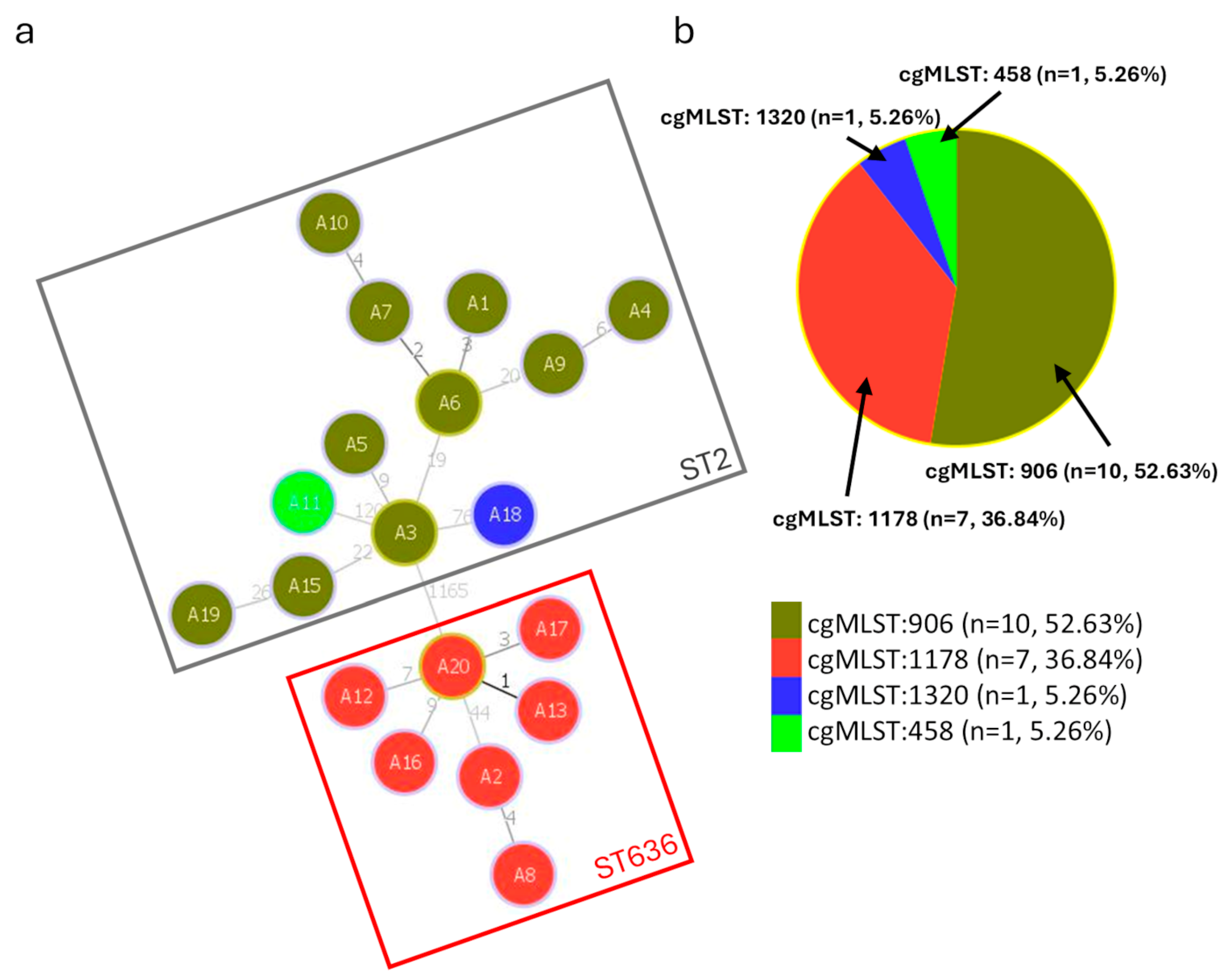
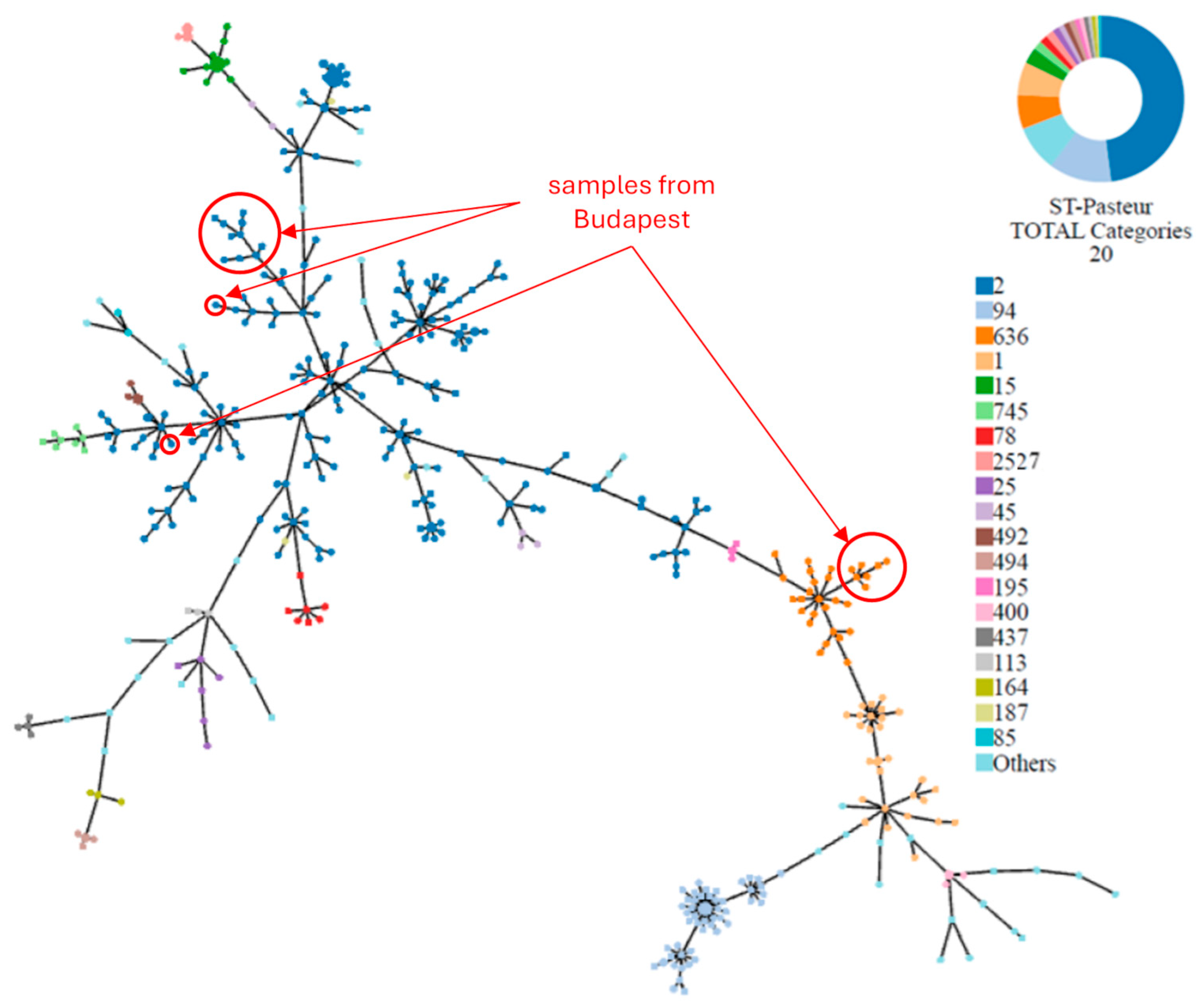
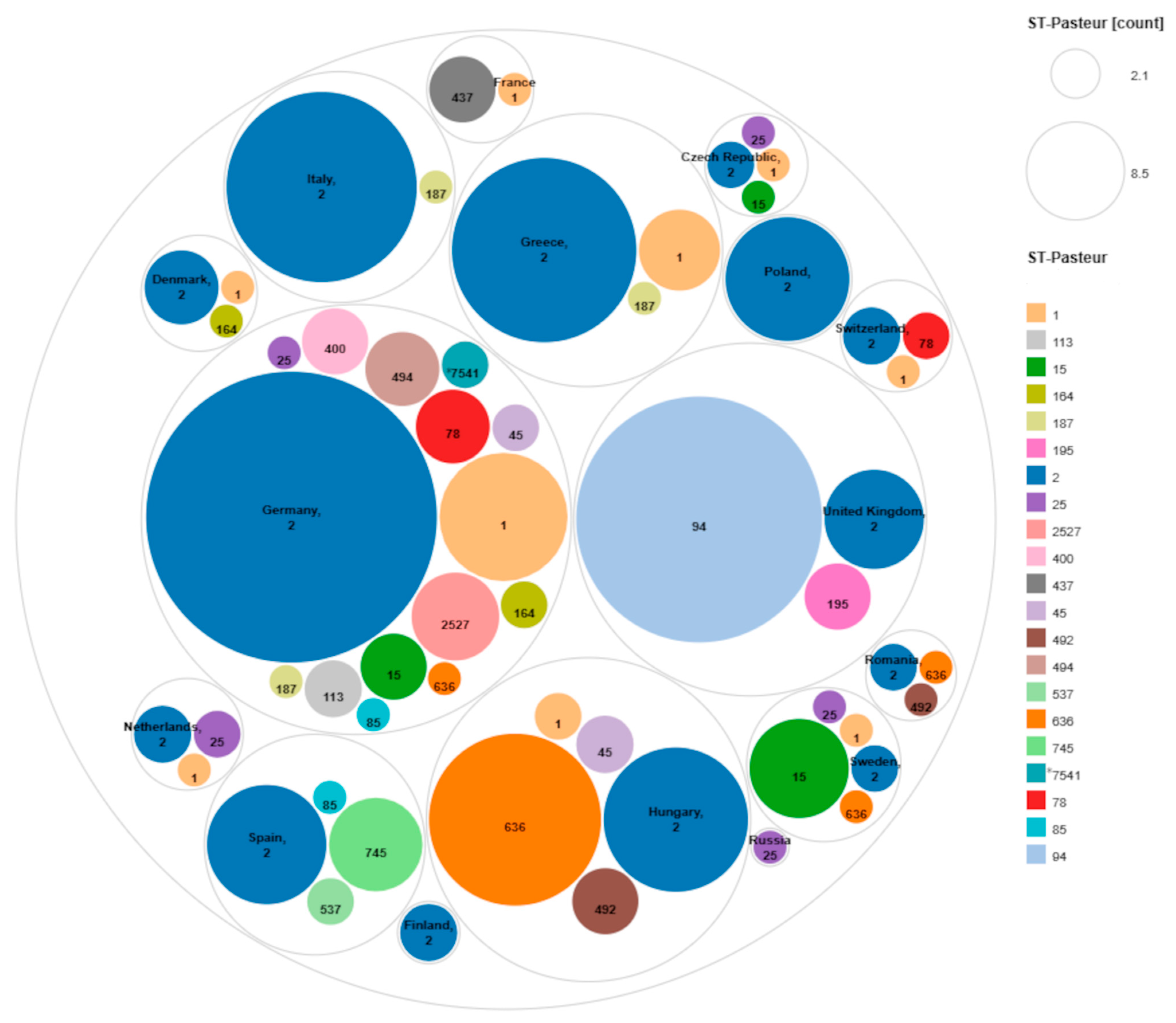
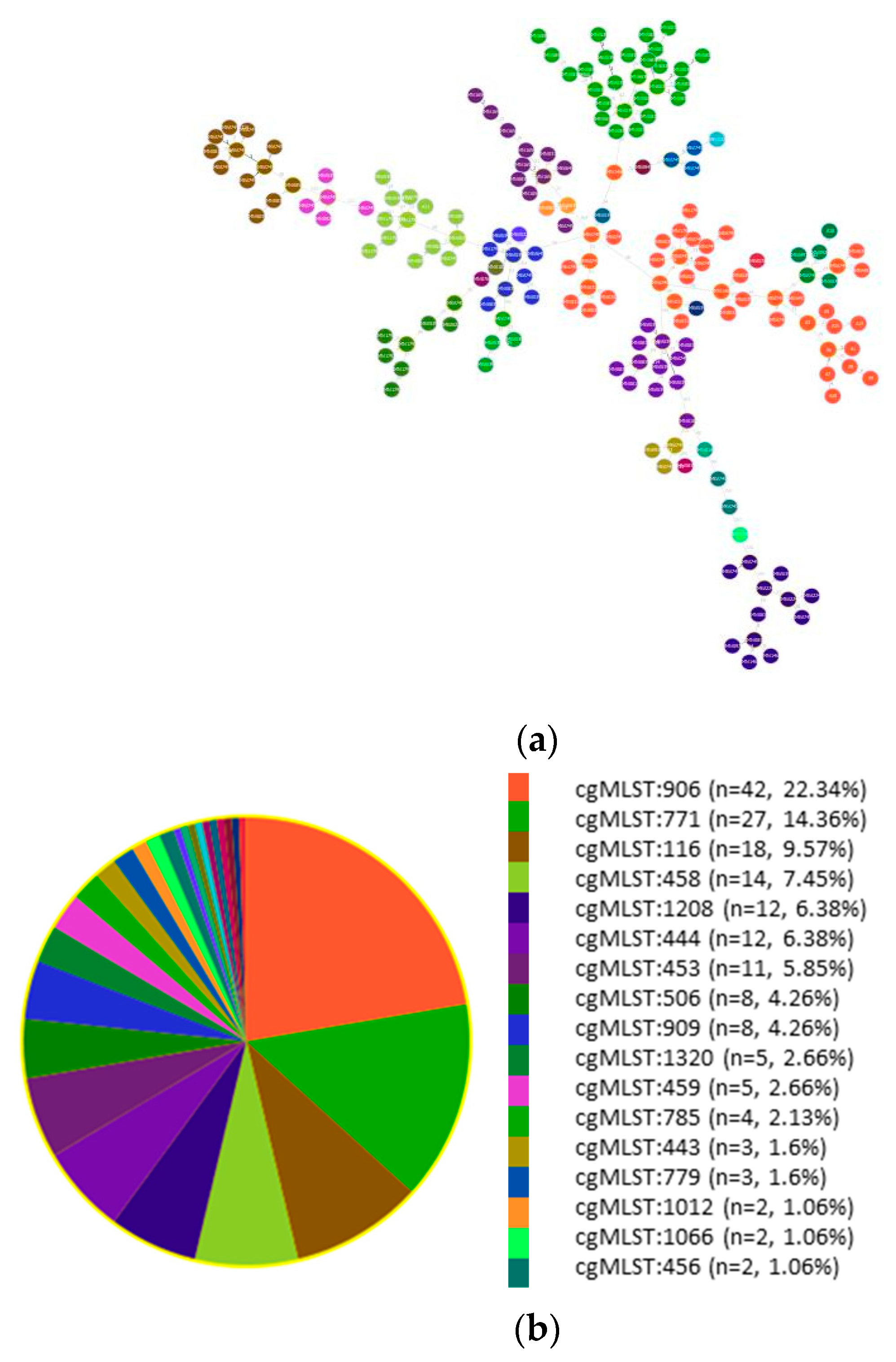
3.3. cgMLST Allelic Profiles and Phylogenetic Relationships
3.4. Study of ST2 Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frenk, S.; Temkin, E.; Lurie-Weinberger, M.N.; Keren-Paz, A.; Rov, R.; Rakovitsky, N.; Wullfhart, L.; Nutman, A.; Daikos, G.L.; Skiada, A.; et al. Large-scale WGS of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates reveals patterns of dissemination of ST clades associated with antibiotic resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahl, J.W.; Johnson, J.K.; Harris, A.D.; Phillippy, A.M.; Hsiao, W.W.; Thom, K.A.; Rasko, D.A. Genomic comparison of multi-drug resistant invasive and colonizing Acinetobacter baumannii isolated from diverse human body sites reveals genomic plasticity. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024: Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Harding, C.M.; Hennon, S.W.; Feldman, M.F. Uncovering the mechanisms of Acinetobacter baumannii virulence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.; Joshi, S.G. Carbapenem resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii, and their importance in hospital-acquired infections: A scientific review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2715–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Wei, Y.; Jian, C.; Liu, J.; Zeng, Z. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A challenge in the intensive care unit. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1045206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidian, M.; Nigro, S.J. Emergence, molecular mechanisms and global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control and World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe. Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance in Europe 2023–2021 Data; ECDC and WHO Regional Office for Europe: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net) Annual Epidemiological Report 2022; 9289056681; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Point Prevalence Survey of Healthcare-Associated Infections and Antimicrobial Use in European Acute Care Hospitals; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, P.; Paluchowska, P. Acinetobacter baumannii: Biology and drug resistance—Role of carbapenemases. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2016, 54, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyanev, T.; Xavier, B.B.; Garcia-Castillo, M.; Lammens, C.; Bravo-Ferrer Acosta, J.; Rodriguez-Bano, J.; Canton, R.; Glupczynski, Y.; Goossens, H.; Group, E.W.B. Phenotypic and molecular characterizations of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates collected within the EURECA study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Li, F.P.; Awan, F.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zeng, Z.L.; Lv, W.B. Molecular Epidemiology and Clone Transmission of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in ICU Rooms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 633817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Shu, J.; Chen, C.-L.; Chiu, C.-H. A glimpse into evolution and dissemination of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates in East Asia: A comparative genomics study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balázs, B.; Tóth, Z.; Nagy, F.; Kovács, R.; Tóth, H.; Nagy, J.B.; Tóth, Á.; Szarka, K.; Majoros, L.; Kardos, G. The Role of Uniform Meropenem Usage in Acinetobacter baumannii Clone Replacement. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balázs, B.; Tóth, Z.; Nagy, J.B.; Majoros, L.; Tóth, Á.; Kardos, G. Faecal Carriage of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Comparison to Clinical Isolates from the Same Period (2017–2019). Pathogens 2022, 11, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghe, I.; Barbu, I.C.; Surleac, M.; Sârbu, I.; Popa, L.I.; Paraschiv, S.; Feng, Y.; Lazăr, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Oţelea, D.; et al. Subtypes, resistance and virulence platforms in extended-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Romanian isolates. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheorghe-Barbu, I.; Barbu, I.C.; Popa, L.I.; Pîrcălăbioru, G.G.; Popa, M.; Măruțescu, L.; Niță-Lazar, M.; Banciu, A.; Stoica, C.; Gheorghe, Ș.; et al. Temporo-spatial variations in resistance determinants and clonality of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from Romanian hospitals and wastewaters. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajic, I.; Jovicevic, M.; Milic, M.; Kekic, D.; Opavski, N.; Zrnic, Z.; Dacic, S.; Pavlovic, L.; Mijac, V. Clinical and molecular characteristics of OXA-72-producing Acinetobacter baumannii ST636 outbreak at a neonatal intensive care unit in Serbia. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 112, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafaj, S.; Kostyanev, T.; Xavier, B.B.; Fluit, A.C.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Lammens, C.; Osmalli, D.; Raka, L.; Goossens, H.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; et al. Clonal transmission of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii harbouring blaOXA-24-like and blaOXA-23-like genes in a tertiary hospital in Albania. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 23, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschek, E.; Brown, D.; Kahlmeter, G. Development of the EUCAST disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility testing method and its implementation in routine microbiology laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O255–O266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, B.B.; Mysara, M.; Bolzan, M.; Ribeiro-Goncalves, B.; Alako, B.T.F.; Harrison, P.; Lammens, C.; Kumar-Singh, S.; Goossens, H.; Carrico, J.A.; et al. BacPipe: A Rapid, User-Friendly Whole-Genome Sequencing Pipeline for Clinical Diagnostic Bacteriology. iScience 2020, 23, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.; Bray, J.; Maiden, M. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Nemec, A.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Brisse, S. The Population Structure of Acinetobacter baumannii: Expanding Multiresistant Clones from an Ancestral Susceptible Genetic Pool. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, C.; Reuter, S.; Wille, J.; Xanthopoulou, K.; Stefanik, D.; Grundmann, H.; Higgins, P.G.; Seifert, H. A global view on carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. mBio 2023, 14, e02260-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Total-Genome-Sequenced Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Rapid and precise alignment of raw reads against redundant databases with KMA. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, D.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Jin, Q. VFDB 2016: Hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis—10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D694–D697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehbanipour, R.; Ghalavand, Z. Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, virulence factors, novel therapeutic options and mechanisms of resistance to antimicrobial agents with emphasis on tigecycline. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2022, 47, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub Moubareck, C.; Hammoudi Halat, D. Insights into Acinetobacter baumannii: A Review of Microbiological, Virulence, and Resistance Traits in a Threatening Nosocomial Pathogen. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, A.P.; Bugalho, M.; Ramirez, M.; Carriço, J.A. Global optimal eBURST analysis of multilocus typing data using a graphic matroid approach. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, E.J.; Li, B.C.; Aanensen, D.M.; Hanage, W.P.; Spratt, B.G. eBURST: Inferring Patterns of Evolutionary Descent among Clusters of Related Bacterial Genotypes from Multilocus Sequence Typing Data. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.; Park, K.S.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.-J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Biology of Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms, and Prospective Treatment Options. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, B.; Shahzad, S.; Huang, W.; Wilks, A. Heme uptake and utilization by hypervirulent Acinetobacter baumannii LAC-4 is dependent on a canonical heme oxygenase (abHemO). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 672, 108066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, M.S.; Bonomo, R.A.; Tolmasky, M.E. Carbapenemases: Transforming Acinetobacter baumannii into a Yet More Dangerous Menace. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelenkov, A.; Akimkin, V.; Mikhaylova, Y. International Clones of High Risk of Acinetobacter Baumannii—Definitions, History, Properties and Perspectives. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strateva, T.V.; Sirakov, I.; Stoeva, T.J.; Stratev, A.; Peykov, S. Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrović, K.; Škrobo, T.; Selec, K.; Jelić, M.; Čivljak, R.; Peršec, J.; Sakan, S.; Bušić, N.; Mihelčić, A.; Hleb, S.; et al. Healthcare-Associated Bloodstream Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in COVID-19 Intensive Care Unit: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukovic, B.; Gajic, I.; Dimkic, I.; Kekic, D.; Zornic, S.; Pozder, T.; Radisavljevic, S.; Opavski, N.; Kojic, M.; Ranin, L. The first nationwide multicenter study of Acinetobacter baumannii recovered in Serbia: Emergence of OXA-72, OXA-23 and NDM-1-producing isolates. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, A.; Del Campo, R.; Escandón-Vargas, K.; Perenguez, M.; Rodríguez-Baños, M.; Hernández-Gómez, C.; Pallares, C.; Perez, F.; Arias, C.A.; Cantón, R.; et al. Distinct Genetic Diversity of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from Colombian Hospitals. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Linde, J.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, T.N.M.; Sprague, L.D.; Pletz, M.W.; Neubauer, H. WGS-Based Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in Vietnam and Molecular Characterization of Antimicrobial Determinants and MLST in Southeast Asia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Minimap and miniasm: Fast mapping and de novo assembly for noisy long sequences. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hummel, D.; Juhasz, J.; Kamotsay, K.; Kristof, K.; Xavier, B.B.; Koster, S.D.; Szabo, D.; Kocsis, B. Genomic Investigation and Comparative Analysis of European High-Risk Clone of Acinetobacter baumannii ST2. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122474
Hummel D, Juhasz J, Kamotsay K, Kristof K, Xavier BB, Koster SD, Szabo D, Kocsis B. Genomic Investigation and Comparative Analysis of European High-Risk Clone of Acinetobacter baumannii ST2. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122474
Chicago/Turabian StyleHummel, David, Janos Juhasz, Katalin Kamotsay, Katalin Kristof, Basil Britto Xavier, Sien De Koster, Dora Szabo, and Bela Kocsis. 2024. "Genomic Investigation and Comparative Analysis of European High-Risk Clone of Acinetobacter baumannii ST2" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122474
APA StyleHummel, D., Juhasz, J., Kamotsay, K., Kristof, K., Xavier, B. B., Koster, S. D., Szabo, D., & Kocsis, B. (2024). Genomic Investigation and Comparative Analysis of European High-Risk Clone of Acinetobacter baumannii ST2. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2474. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122474







