Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Strains
2.3. Preparation of Potato Tuber Extracts
2.4. Obtaining Serum and Isolating Polyclonal Antibodies
2.5. Preparation of Conjugates of Antibodies with Horseradish Peroxidase
2.6. Preparation of Conjugates of Antibodies with Gold Nanoparticles
2.7. Characterization of Sera and Isolated Antibodies by Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay
2.8. Double-Antibody Sandwich Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.9. Preparation of Lateral Flow Test Strips
2.10. Lateral Flow Immunoassay
2.11. Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.12. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
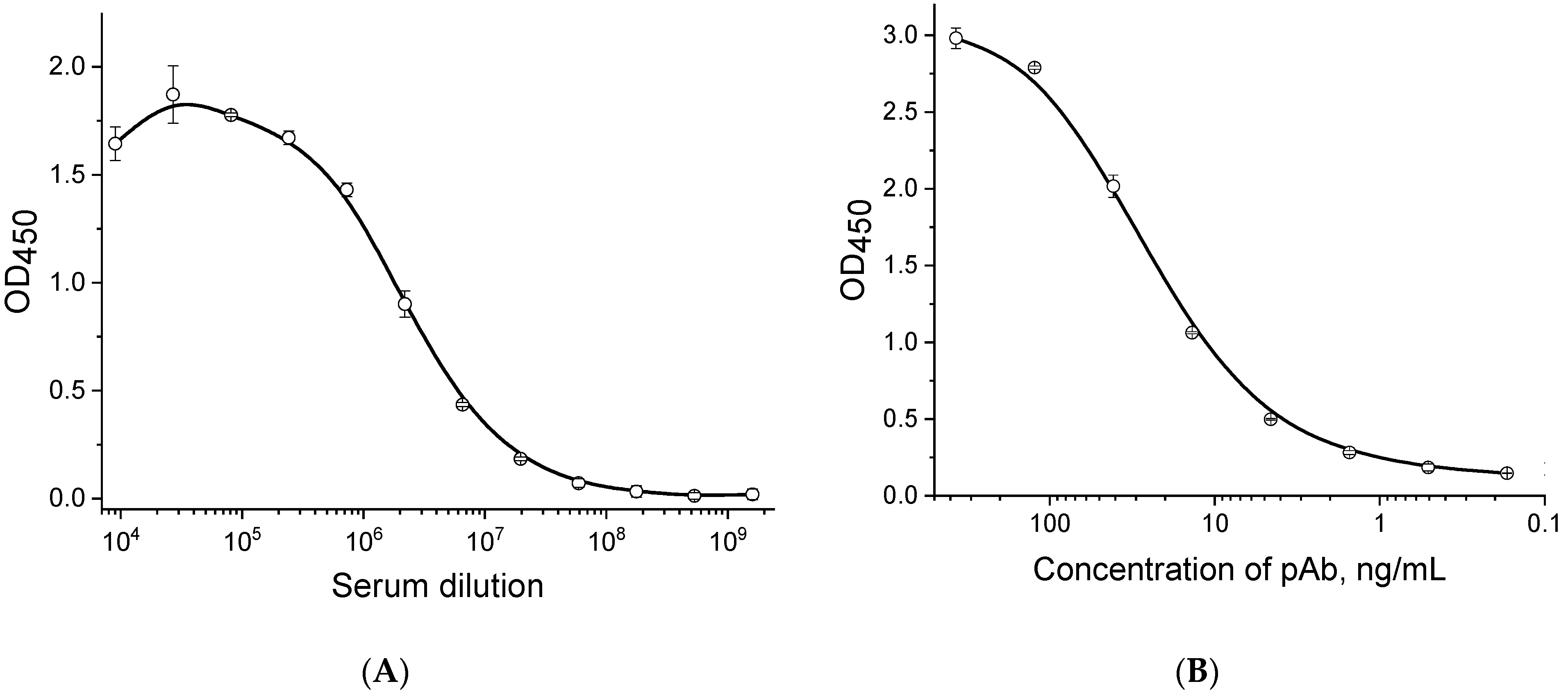
3.1. Characteristics of the Obtained Sera and Isolated IgG
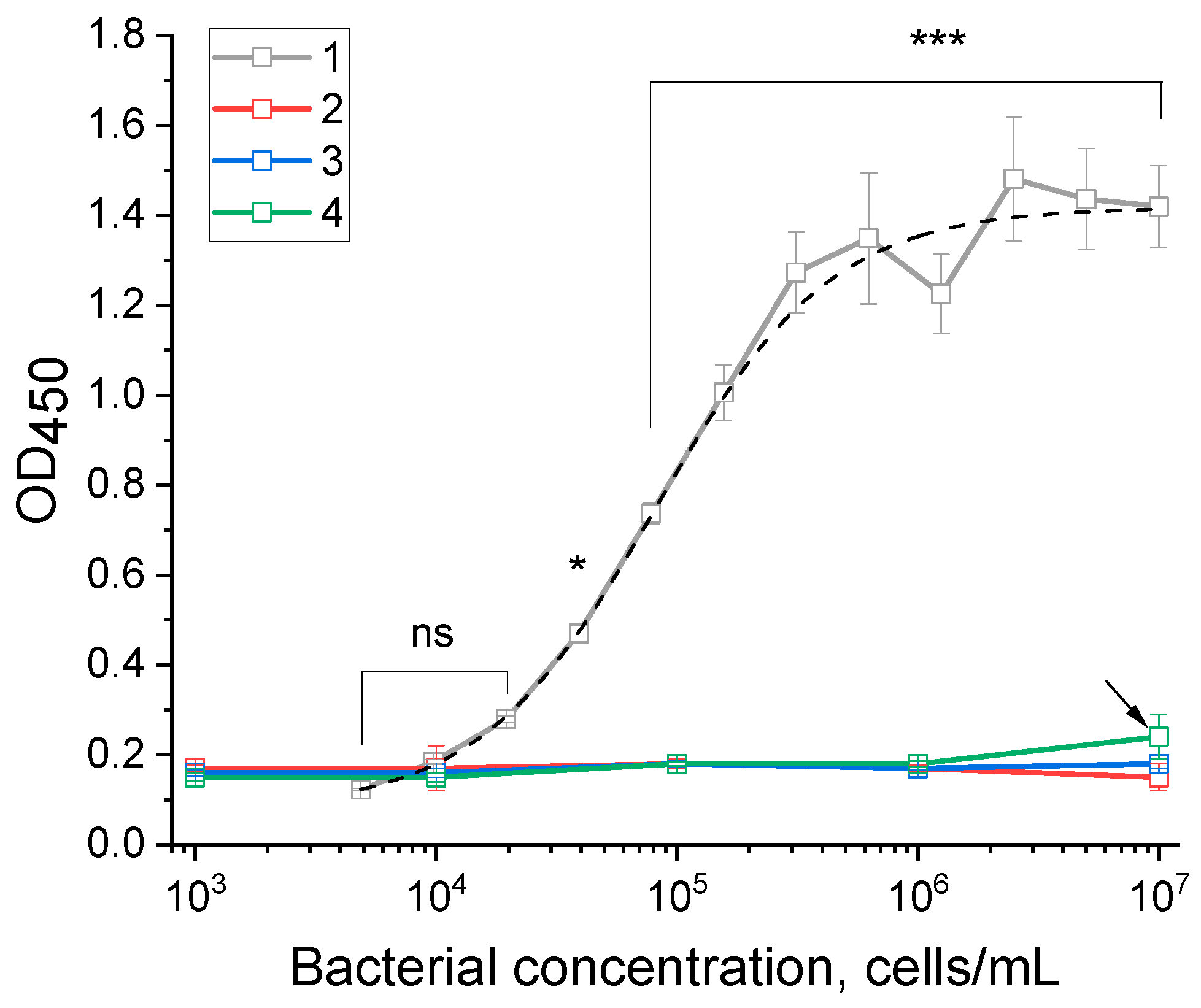
3.2. Development of an ELISA Test System
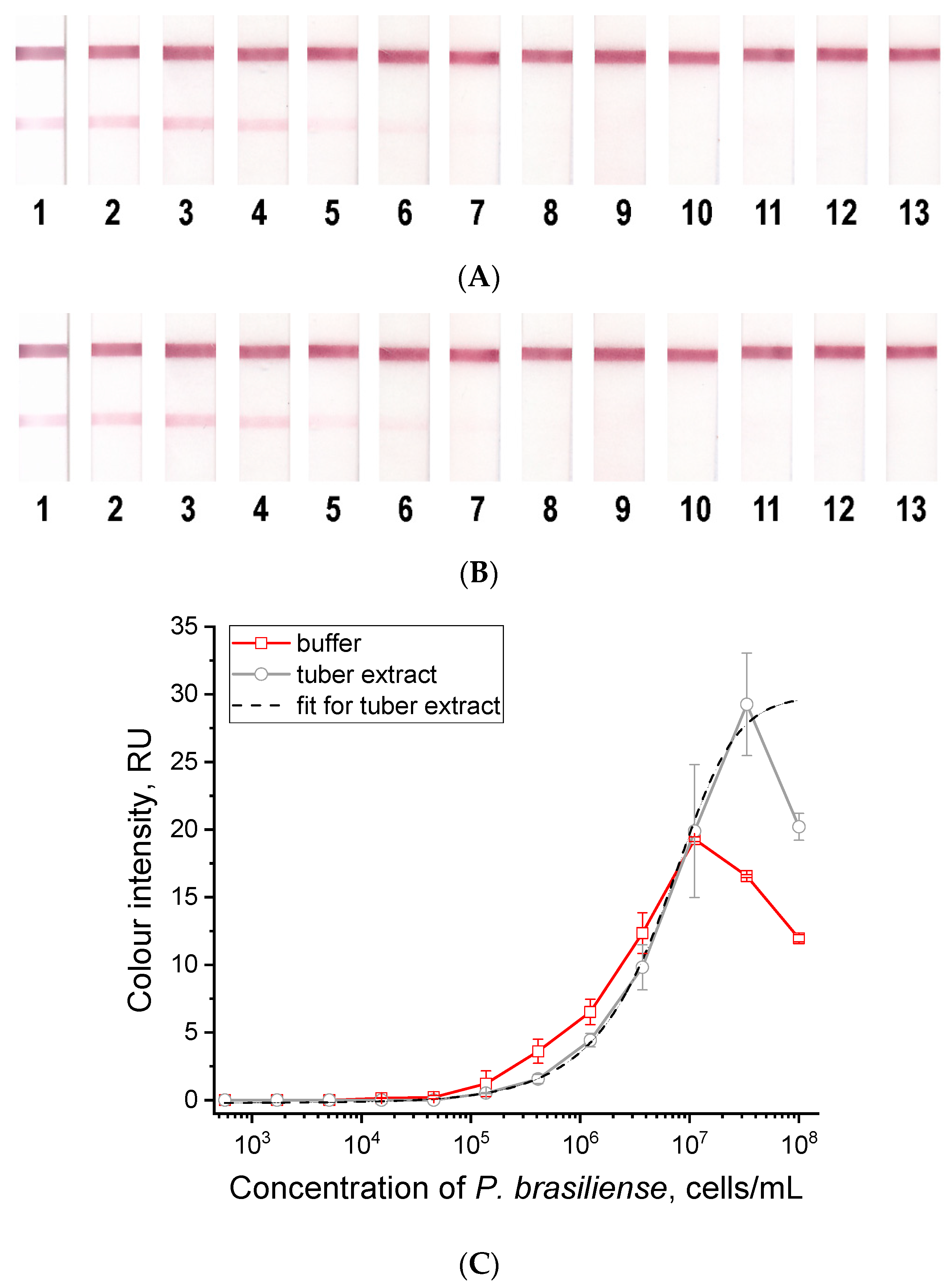
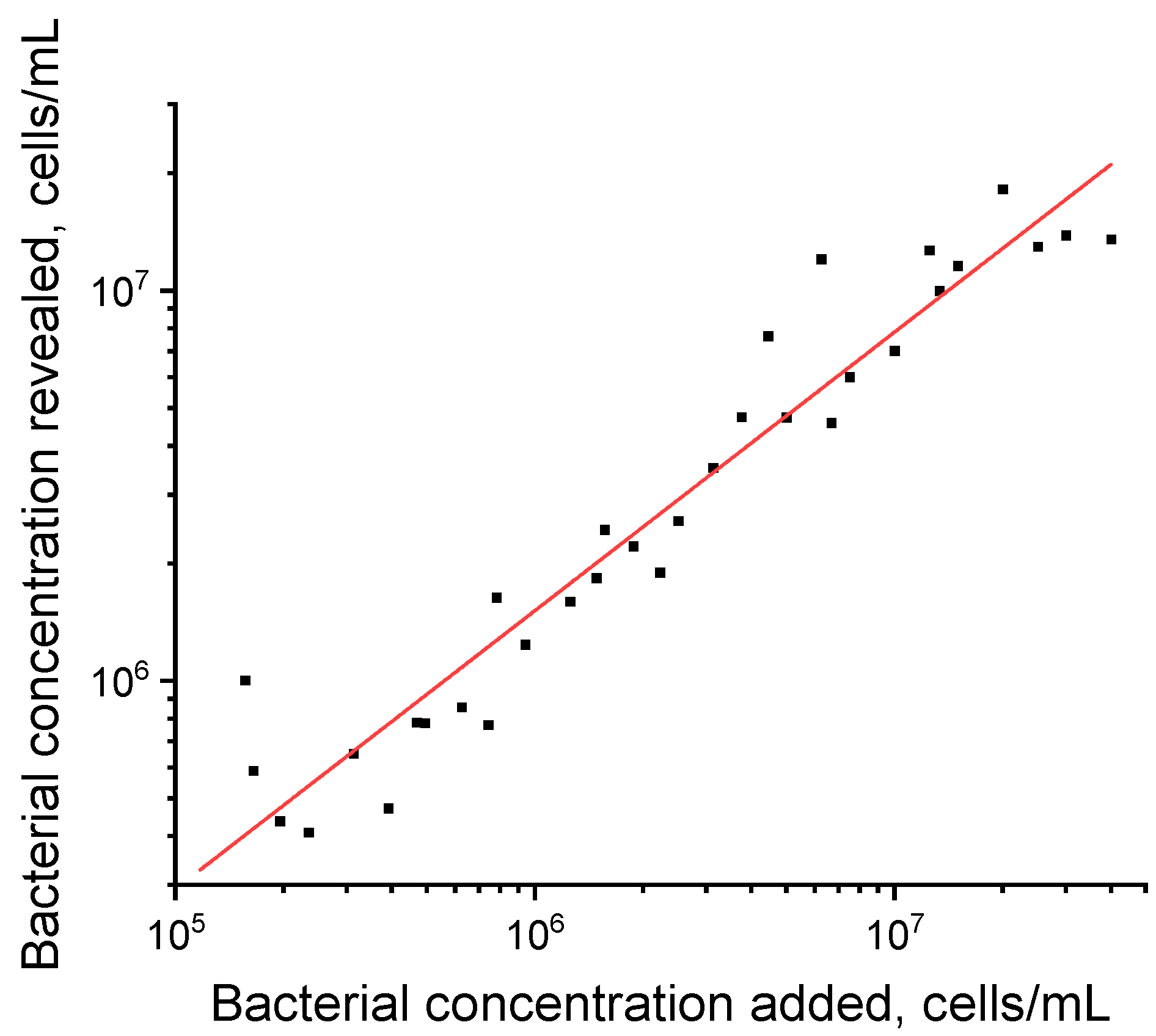
3.3. Development of an LFIA Test System
3.4. Testing Natural Tuber Material with the Developed ELISA and LFIA Test Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Charkowski, A.O. The changing face of bacterial soft-rot diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2018, 56, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat, N.; Condemine, G.; Shevchik, V.E. Bacterial pectate lyases, structural and functional diversity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Utpal, H.; Wu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Feng, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Comparative genomic and transcriptome analyses of two Pectobacterium brasiliense strains revealed distinct virulence determinants and phenotypic features. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1362283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oulghazi, S.; Sarfraz, S.; Zaczek-Moczydłowska, M.A.; Khayi, S.; Ed-Dra, A.; Lekbach, Y.; Campbell, K.; Novungayo Moleleki, L.; O’Hanlon, R.; Faure, D. Pectobacterium brasiliense: Genomics, host range and disease management. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, V.; De Boer, S.H.; Ward, L.J.; de Oliveira, A.M.R. Characterization of atypical Erwinia carotovora strains causing blackleg of potato in Brazil. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portier, P.; Pédron, J.; Taghouti, G.; Fischer-Le Saux, M.; Caullireau, E.; Bertrand, C.; Laurent, A.; Chawki, K.; Oulgazi, S.; Moumni, M.; et al. Elevation of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. odoriferum to species level as Pectobacterium odoriferum sp. nov., proposal of Pectobacterium brasiliense sp. nov. and Pectobacterium actinidiae sp. nov., emended description of Pectobacterium carotovorum and description of Pectobacterium versatile sp. nov., isolated from streams and symptoms on diverse plants. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 3207–3216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Loria, R. A re-evaluation of the taxonomy of phytopathogenic genera Dickeya and Pectobacterium using whole-genome sequencing data. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, L.N.; de Haan, E.G.; Krijger, M.; Kastelein, P.; van der Zouwen, P.S.; van den Bovenkamp, G.W.; Tebaldi, N.D.; van der Wolf, J.M. First report of potato blackleg caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliensis in the Netherlands. New Dis. Rep. 2014, 29, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Dou, J.; Geng, G.M.; Tian, Y.L.; Fan, J.Q.; Li, X.; Hu, B.S. First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense causing blackleg and stem rot on potato in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T. Identification of pathogens and infection routes of potato blackleg disease in Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2022, 88, 421–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronina, M.V.; Kabanova, A.P.; Shneider, M.M.; Korzhenkov, A.A.; Toschakov, S.V.; Miroshnikov, K.K.; Miroshnikov, K.A.; Ignatov, A.N. First report of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense causing blackleg and stem rot disease of potato in Russia. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, V.; Palma, L.; Álvarez, T.D.; Somale, P.S.; Sattler, A.E.; von Baczko, O.H.; Romero, A.M. First report of Pectobacterium brasiliense causing blackleg and soft rot of potato in Argentina. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Wolf, J.M.; Acuña, I.; De Boer, S.H.; Brurberg, M.B.; Cahill, G.; Charkowski, A.O.; Coutinho, T.; Davey, T.; Dees, M.W.; Degefu, Y.; et al. Diseases Caused by Pectobacterium and Dickeya Species around the World. In Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species; Van Gijsegem, F., van der Wolf, J.M., Toth, I.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 215–261. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, I.K.; Barny, M.; Brurberg, M.B.; Condemine, G.; Czajkowski, R.; Elphinstone, J.G.; Helias, V.; Johnson, S.B.; Moleleki, L.N.; Pirhonen, M.; et al. Pectobacterium and Dickeya: Environment to Disease Development. In Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species; Van Gijsegem, F., van der Wolf, J.M., Toth, I.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 39–84. [Google Scholar]
- Dupuis, B.; Nkuriyingoma, P.; Van Gijsegem, F. Economic Impact of Pectobacterium and Dickeya Species on Potato Crops: A Review and Case Study. In Plant Diseases Caused by Dickeya and Pectobacterium Species; Van Gijsegem, F., van der Wolf, J.M., Toth, I.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 263–282. [Google Scholar]
- Mansotra, R.; Vakhlu, J. Comprehensive account of present techniques for in-field plant disease diagnosis. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 5309–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khater, M.; de la Escosura-Muniz, A.; Merkoci, A. Biosensors for plant pathogen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, A.; Donovan, N.; Mantri, N. Review: The future of plant pathogen diagnostics in a nursery production system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 145, 111631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranwal, V.K.; Un Nabi, S.; Yadav, M.K. Plant Virus Diagnostics: Traditional to Recent and Emerging Advances. In Emerging Trends in Plant Pathology; Singh, K.P., Jahagirdar, S., Sarma, B.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 97–111. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Safenkova, I.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. The potential use of isothermal amplification assays for in-field diagnostics of plant pathogens. Plants 2021, 10, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Lee, T.A.J.; van Gent-Pelzer, M.P.E.; Jonkheer, E.M.; Brankovics, B.; Houwers, I.M.; van der Wolf, J.M.; Bonants, P.J.M.; van Duivenbode, I.; Vreeburg, R.A.M.; Nas, M.; et al. An efficient triplex TaqMan quantitative PCR to detect a blackleg-causing lineage of Pectobacterium brasiliense in potato based on a pangenome analysis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzhinji, N.; Dube, J.P.; de Haan, E.G.; Woodhall, J.W.; van der Waals, J.E. Development of a TaqMan PCR assay for specific detection and quantification of Pectobacterium brasiliense in potato tubers and soil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2020, 158, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, R.; Yang, R.; Wei, X.; Xie, H.; Shi, Y.; Xie, X.; Chai, A.; Fan, T.; Li, B.; et al. Rapid detection and quantification of viable cells of Pectobacterium brasiliense using propidium monoazide combined with real-time PCR. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joko, T.; Alan, S.; Muhammad Saifur, R. A novel subspecies-specific primer targeting the gyrase B gene for the detection of Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. brasiliense. Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers. 2019, 20, 3042–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safenkova, I.V.; Zaitsev, I.A.; Varitsev, Y.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. lateral flow immunoassay for rapid diagnosis of potato blackleg caused by Pectobacterium atrosepticum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2015, 12, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safenkova, I.V.; Zaitsev, I.A.; Varitsev, Y.A.; Byzova, N.A.; Drenova, N.V.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Development of a lateral flow immunoassay for rapid diagnosis of potato blackleg caused by Dickeya species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukianova, A.A.; Evseev, P.V.; Stakheev, A.A.; Kotova, I.B.; Zavriev, S.K.; Ignatov, A.N.; Miroshnikov, K.A. Development of qPCR detection assay for potato pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum based on a unique target sequence. Plants 2021, 10, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, G.T. Chapter 20—Antibody Modification and Conjugation. In Bioconjugate Techniques, 3rd ed.; Hermanson, G.T., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 867–920. [Google Scholar]
- Frens, G. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gold suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byzova, N.A.; Safenkova, I.V.; Chirkov, S.N.; Zherdev, A.V.; Blintsov, A.N.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Atabekov, I.G. Development of immunochromatographic test systems for express detection of plant viruses. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2009, 45, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razo, S.C.; Safenkova, I.V.; Drenova, N.V.; Kharchenko, A.A.; Tsymbal, Y.S.; Varitsev, Y.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Pakina, E.N.; Dzantiev, B.B. New lateral flow immunoassay for on-site detection of Erwinia amylovora and its application on various organs of infected plants. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 114, 101637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venbrux, M.; Crauwels, S.; Rediers, H. Current and emerging trends in techniques for plant pathogen detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1120968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from extinction spectra. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 6620–6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, M.; Proll, G.; Builes-Münden, E.; Dietzel, A.; Wagner, S.; Gauglitz, G. Tools to compare antibody gold nanoparticle conjugates for a small molecule immunoassay. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Bacterium | Strain | ELISA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD450 | Assay Result | |||
| 1 | Pectobacterium brasiliense | F126 | 1.23 | + |
| 2 | Pectobacterium atrosepticum | DSM 18077 | 0.11 | - |
| 3 | Pectobacterium atrosepticum | VNIIF 5128 | 0.07 | - |
| 4 | Pectobacterium atrosepticum | VNIIKR 0143 | 0.10 | - |
| 5 | Pectobacterium wasabie | DSM 18074 | 0.07 | - |
| 6 | Pectobacterium betavasculorum | DSM 18076 | 0.10 | - |
| 7 | Pectobacterium carotovorum | VNIIF 3391 | 0.09 | - |
| 8 | Pectobacterium carotovorum | VNIIF 3398 | 0.17 | - |
| 9 | Pectobacteriumodoriferum | DSM 22566 | 0.07 | - |
| 10 | Pectobacterium carotovorum | VNIIF C966 | 0.08 | - |
| 11 | Pectobacterium carotovorum | DSM 30168 | 0.07 | - |
| 12 | Clavibacter sepedonicus | VNIIKR 0435 | 0.11 | - |
| 13 | Clavibacter sepedonicus | VNIIKR 0668 | 0.07 | - |
| 14 | Clavibacter michiganensis | VNIIKR 0496 | 0.06 | - |
| 15 | Dickeya solani | DSM 28711 | 0.09 | - |
| 16 | Dickeya dadantii subsp. dadantii | DSM18020 | 0.07 | - |
| 17 | Dickeya paradisiaca | DSM 18069 | 0.09 | - |
| 18 | Dickeya fangzhongdai | DSM 101947 | 0.08 | - |
| 19 | Dickeya dadantii subsp. dieffenbachiae | DSM 18012 | 0.07 | - |
| 20 | Dickeya dianthicola | CFBP 3705 | 0.11 | - |
| 21 | Dickeya zeae | DSM 18068 | 0.07 | - |
| 22 | Dickeya dianthicola | VNIIKR 0144 | 0.09 | - |
| 23 | Ralstonia solanacearum, race 3, bv.2 | NCPPB 2316 | 0.07 | - |
| 24 | Pseudomonas fluorescence | VNIIKR 0213 | 0.08 | - |
| - | Tuber extract from healthy potato | 0.09 | - | |
| + | Tuber extract from healthy potato with added P. brasiliense | 1.65 | + | |
| Sample No | Potato Variety | ELISA | LFIA | Real-Time PCR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OD450 | Assay Result | Color Intensity of Test Zone | Assay Result | Ct | Assay Result | ||
| 1 | Lady Claire | 0.45 | + | 0.00 | - | 38 | + |
| 2 | VR 808 | 0.34 | + | 0.00 | - | 28 | + |
| 3 | Opal | 0.22 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 4 | Papageno | 0.11 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 5 | Lady Claire | 0.24 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 6 | Austin | 0.47 | + | 2.79 | + | no | - |
| 7 | Riviera | 0.22 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 8 | Lady Claire | 0.17 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 9 | Red Scarlet | 0.09 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 10 | Vineta | 0.15 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 11 | Asterix | 0.07 | - | 0.00 | - | 38 | + |
| 12 | Gala | 0.07 | - | 0.00 | - | 38 | + |
| 13 | Prime | 0.06 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 14 | Unknown | 0.06 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 15 | Unknown | 0.69 | + | 9.09 | + | 30 | + |
| 16 | Unknown | 0.08 | - | 0.00 | - | 38 | + |
| 17 | Sudarynya | 0.07 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 18 | Sudarynya | 0.09 | - | 0.00 | - | 32 | + |
| 19 | Sudarynya | 0.08 | - | 0.00 | - | 35 | + |
| 20 | Sudarynya | 1.12 | + | 20.25 | + | 31 | + |
| 21 | Sudarynya | 0.07 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 22 | Belaroza | 0.06 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 23 | Belaroza | 0.06 | - | 0.00 | - | 36 | + |
| 24 | Belaroza | 0.06 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 25 | Belaroza | 0.05 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 26 | Belaroza | 0.11 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 27 | Lady Claire | 1.03 | + | 12.53 | + | 31 | + |
| 28 | VR 808 | 1.14 | + | 19.05 | + | 32 | + |
| 29 | Austin | 1.10 | + | 23.15 | + | 33 | + |
| 30 | Lady Claire | 1.16 | + | 22.23 | + | 33 | + |
| 31 | Prado | 1.12 | + | 18.53 | + | 32 | + |
| 32 | VR 808 | 0.62 | + | 19.01 | + | 24 | + |
| 33 | Austin | 0.74 | + | 11.47 | + | 34 | + |
| 34 | Papageno | 0.61 | + | 0.53 | + | 36 | + |
| 35 | Lady Claire | 0.50 | + | 0.00 | - | no | - |
| 36 | Fontane | 0.70 | + | 2.54 | + | 36 | + |
| 37 | Opal | 1.00 | + | 16.22 | + | 31 | + |
| 38 | Lady Claire | 0.91 | + | 20.56 | + | 33 | + |
| 39 | Opal | 1.13 | + | 20.99 | + | 33 | + |
| 40 | Gala | 0.39 | + | 1.40 | + | no | - |
| 41 | Prime | 0.71 | + | 19.33 | + | 24 | + |
| 42 | Carmen | 0.80 | + | 17.52 | + | 23 | + |
| 43 | Unknown | 0.10 | - | 0.00 | - | no | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Safenkova, I.V.; Galushka, P.A.; Varitsev, Y.A.; Kamionskaya, M.V.; Drenova, N.V.; Vasilyeva, A.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Uskov, A.I.; Dzantiev, B.B. Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122436
Safenkova IV, Galushka PA, Varitsev YA, Kamionskaya MV, Drenova NV, Vasilyeva AA, Zherdev AV, Uskov AI, Dzantiev BB. Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122436
Chicago/Turabian StyleSafenkova, Irina V., Pavel A. Galushka, Yuri A. Varitsev, Maria V. Kamionskaya, Natalia V. Drenova, Anna A. Vasilyeva, Anatoly V. Zherdev, Alexander I. Uskov, and Boris B. Dzantiev. 2024. "Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122436
APA StyleSafenkova, I. V., Galushka, P. A., Varitsev, Y. A., Kamionskaya, M. V., Drenova, N. V., Vasilyeva, A. A., Zherdev, A. V., Uskov, A. I., & Dzantiev, B. B. (2024). Highly Targeted Detection of Priority Phytopathogen Pectobacterium brasiliense: From Obtaining Polyclonal Antibodies to Development and Approbation of Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay and Lateral Flow Immunoassay. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122436








