Uncovering the Resistance Mechanisms in Extended-Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Insights from Gene Expression and Phenotypic Tests
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Strains identified as P. aeruginosa, according to the diagnostic procedures;
- -
- Only the first isolate from each patient;
- -
- Resistance to carbapenems or/and polymyxins (colistin) classes of antibiotics.
2.1. Identification of Study Bacterial Strains
2.2. Phenotypic Detection of Carbapenemase
2.3. Identification of Carbapenemase Genes
2.3.1. DNA Extraction
2.3.2. PCR for Detection of Carbapenemase Genes
2.4. Evaluation of Efflux Pumps
2.4.1. Bacterial RNA Extraction and Purification
2.4.2. Reverse Transcription
2.4.3. Real-Time RT PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
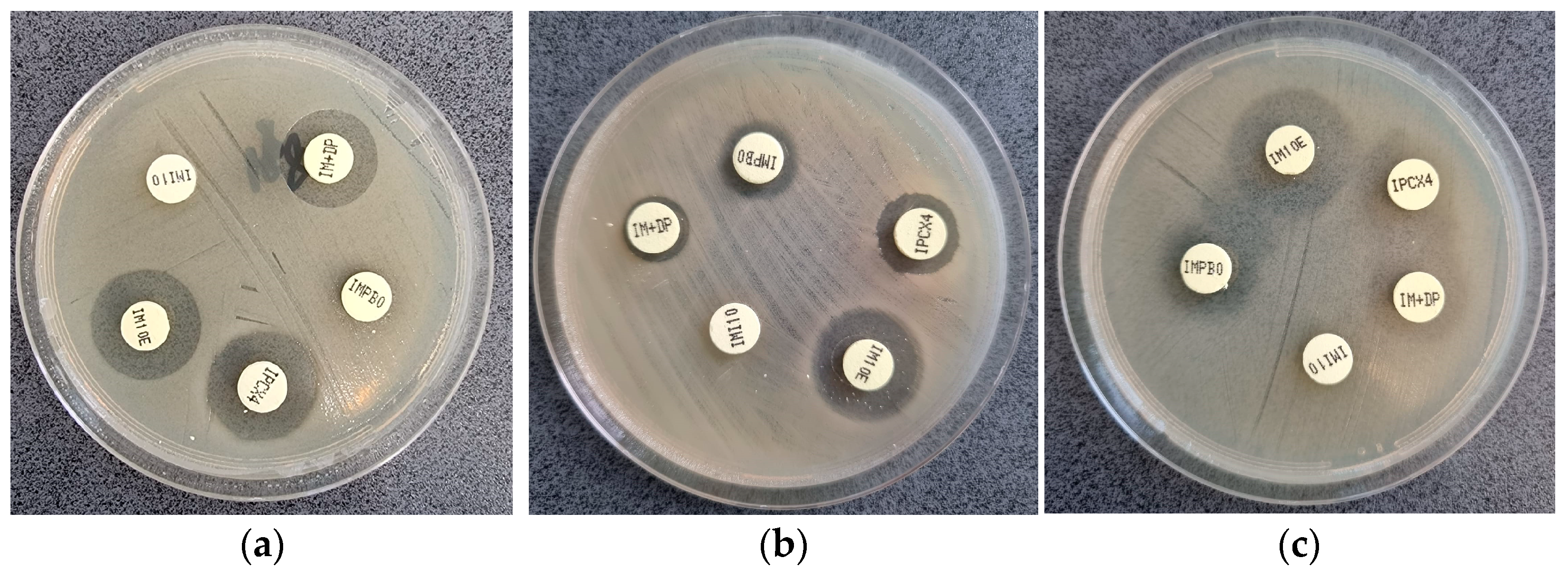
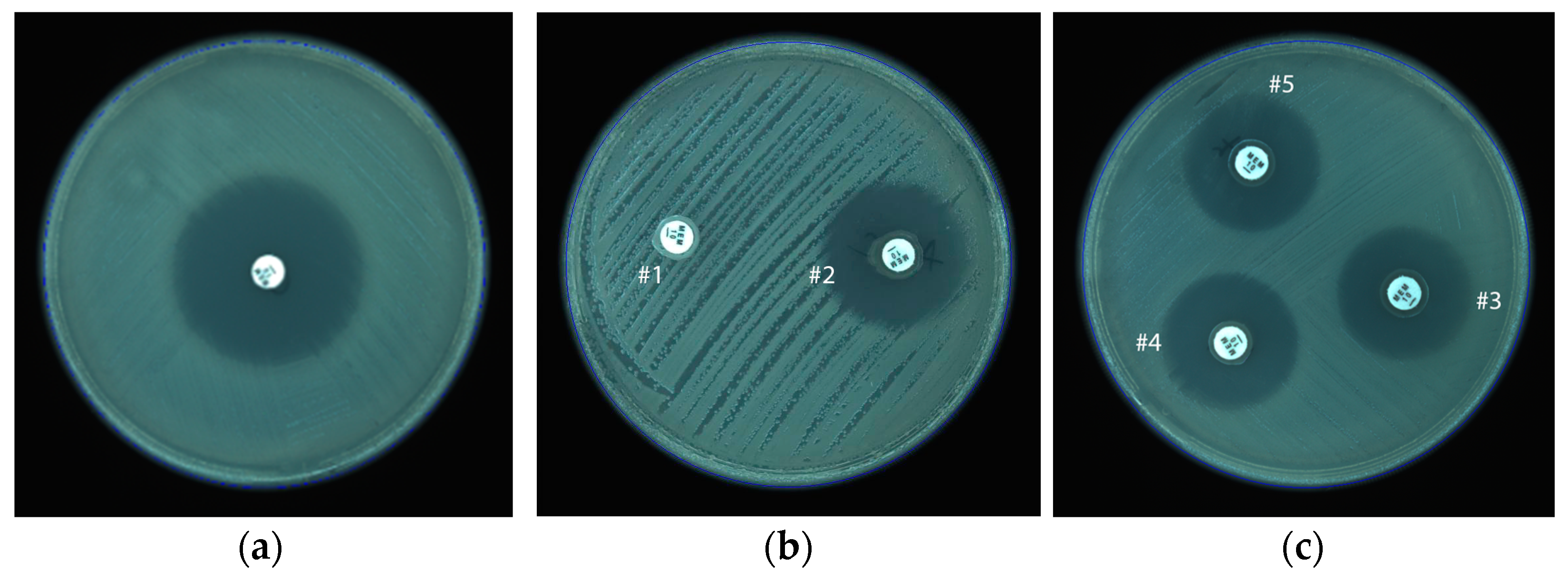
3.1. Modified Hodge Test
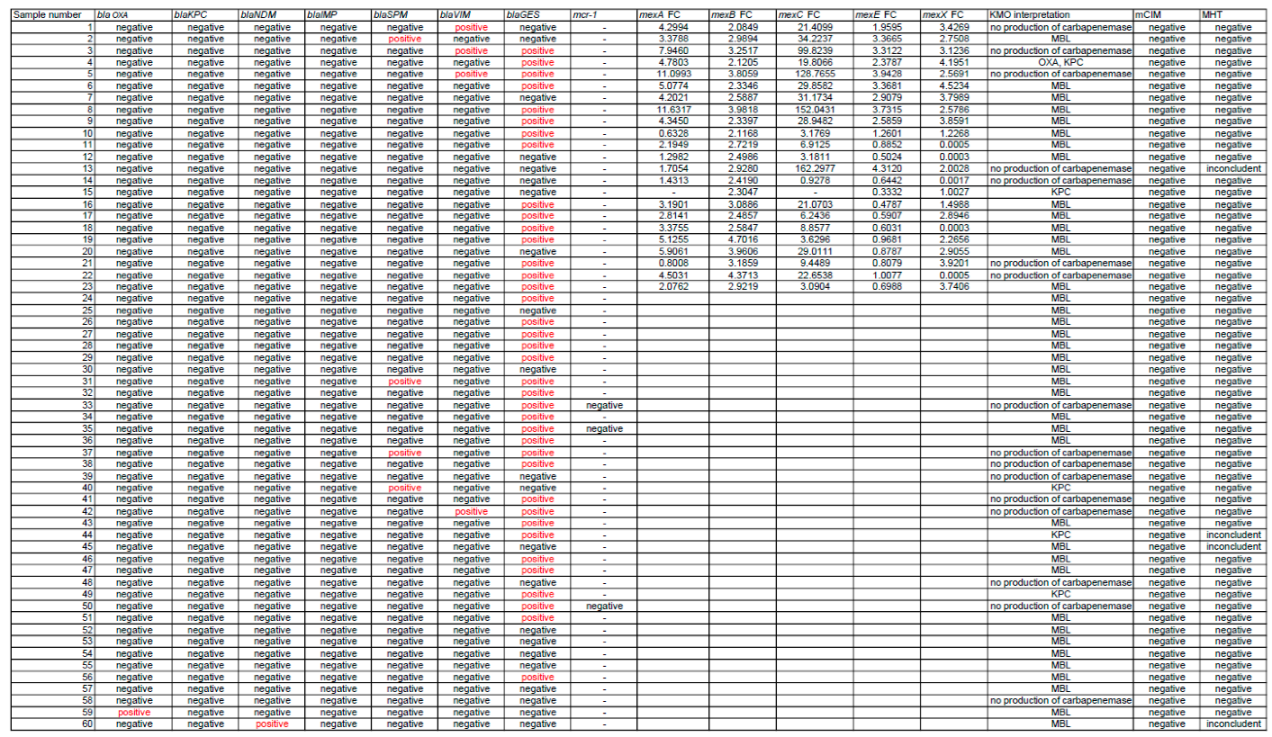
3.2. KPC-MBL-Oxacillinase (KMO) Test
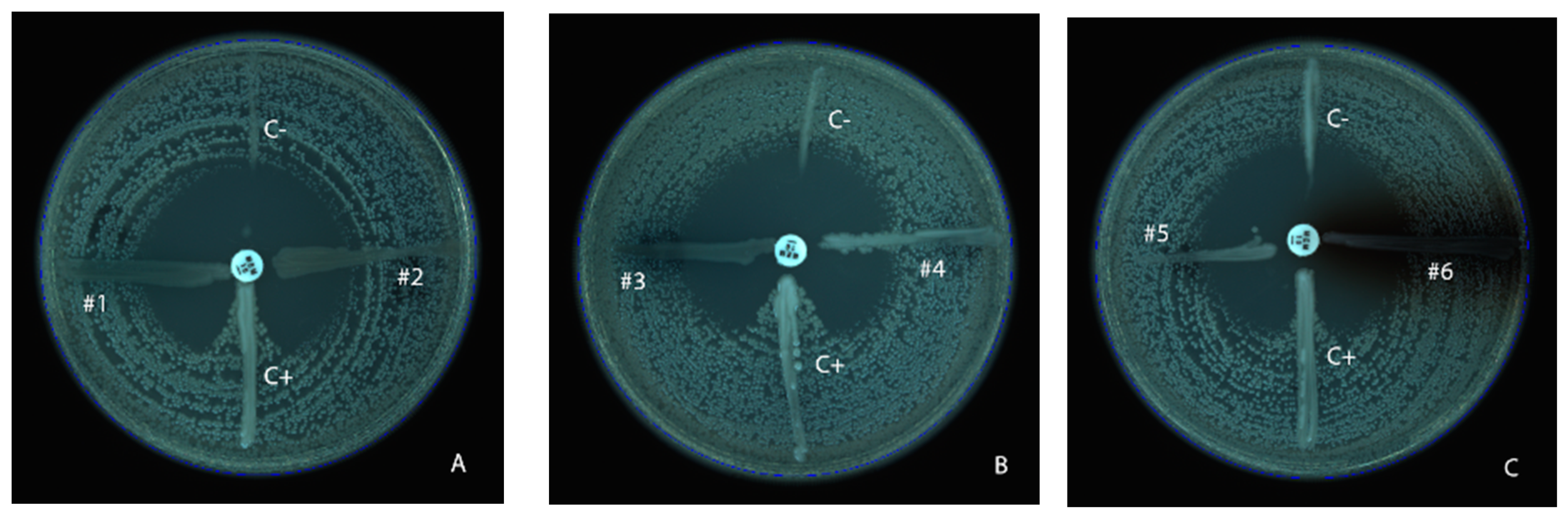
3.3. mCIM Results
3.4. Genetic Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wu, M.; Li, X. Chapter 87—Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In Molecular Medical Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Tang, Y.-W., Sussman, M., Liu, D., Poxton, I., Schwartzman, J.B.T., Eds.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 979–995. ISBN 978-0-12-397169-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Z.; Raudonis, R.; Glick, B.R.; Lin, T.-J.; Cheng, Z. Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Mechanisms and Alternative Therapeutic Strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, V.; Amoah, J.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Tamma, P.D. Antibiotic Therapy for Pseudomonas aeruginosa Bloodstream Infections: How Long Is Long Enough? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 2011–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, M.; Carrara, E.; Retamar, P.; Tängdén, T.; Bitterman, R.; Bonomo, R.A.; de Waele, J.; Daikos, G.L.; Akova, M.; Harbarth, S.; et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) guidelines for the treatment of infections caused by multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacilli (endorsed by European society of intensive care medicine). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 521–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Shi, D.; Ni, Y.; Hua, L.; Li, J. Prevalence and Molecular Characteristics of Polymyxin-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Chinese Tertiary Teaching Hospital. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurilio, C.; Sansone, P.; Barbarisi, M.; Pota, V.; Giaccari, L.G.; Coppolino, F.; Barbarisi, A.; Passavanti, M.B.; Pace, M.C. Mechanisms of Action of Carbapenem Resistance. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, G.T. Continuous Evolution: Perspective on the Epidemiology of Carbapenemase Resistance Among Enterobacterales and Other Gram-Negative Bacteria. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2021, 10, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queenan, A.M.; Bush, K. Carbapenemases: The Versatile beta-Lactamases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saki, M.; Sheikh, A.F.; Seyed-Mohammadi, S.; Dezfuli, A.A.Z.; Shahin, M.; Tabasi, M.; Veisi, H.; Keshavarzi, R.; Khani, P. Occurrence of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from clinical specimens in southwest Iran: A multicentral study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muktan, B.; Shrestha, U.T.; Dhungel, B.; Mishra, B.C.; Shrestha, N.; Adhikari, N.; Banjara, M.R.; Adhikari, B.; Rijal, K.R.; Ghimire, P. Plasmid mediated colistin resistant mcr-1 and co-existence of OXA-48 among Escherichia coli from clinical and poultry isolates: First report from Nepal. Gut Pathog. 2020, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Masoud, S.M.; Mohamed, D.S.; Waly, N.G.; Shafik, E.A.; Mohareb, D.A.; Elkady, A.; Elbadr, M.M.; Hetta, H.F. Prevalence and Some Possible Mechanisms of Colistin Resistance Among Multidrug-Resistant and Extensively Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, H.; Younas, S.; Qamar, M.U.; Junaid, K.; Abdalla, A.E.; Abosalif, K.O.A.; Alameen, A.A.M.; Elamir, M.Y.M.; Ahmad, N.; Hamam, S.S.M.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Extensively Drug-Resistant Mcr Encoded Colistin-Resistant Bacterial Strains Co-Expressing Multifarious β-Lactamases. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.G.; Zhong, L.-L.; Shen, C.; Yang, Y.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.-B. Colistin and its role in the Era of antibiotic resistance: An extended review (2000–2019). Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakashima, R.; Zwama, M.; Hayashi-Nishino, M. Function and Inhibitory Mecha-nisms of Multidrug Efflux Pumps. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 737288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Wu, C.; Gao, H.; Xu, C.; Dai, M.; Huang, L.; Hao, H.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G. Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps at the Frontline of Antimicrobial Resistance: An Overview. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coșeriu, R.L.; Vintilă, C.; Pribac, M.; Mare, A.D.; Ciurea, C.N.; Togănel, R.O.; Cighir, A.; Simion, A.; Man, A. Antibacterial Effect of 16 Essential Oils and Modulation of mex Efflux Pumps Gene Expression on Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Is Cinnamon a Good Fighter? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auda, I.G.; Salman, I.M.A.; Odah, J.G. Efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria in brief. Gene Rep. 2020, 20, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opperman, T.J.; Nguyen, S.T. Recent advances toward a molecular mechanism of efflux pump inhibition. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, E.B.; Devroy, V.K.; Lau, S.Y.; Zgurskaya, H.I. Reconstitution of the Escherichia Coli Macrolide Transporter: The Periplasmic Membrane Fusion Protein MacA Stimulates the ATPase Activity of MacB. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 63, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.B.; Carrara, J.A.; Barroso, C.D.N.; Tuon, F.F.; Faoro, H. Role of Efflux Pumps on Antimicrobial Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderon, J.A.; Corona, F.; Lira, F.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Bernardini, A.; Sanchez, M.B.; Martinez, J.L. Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps: Much More Than Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.C.d.O.; Neto, O.C.d.C.; da Costa, B.S.; Teixeira, C.B.T.; Pontes, L.d.S.; Silveira, M.C.; Rocha-De-Souza, C.M.; Carvalho-Assef, A.P.D. Evaluation of phenotypic detection of carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas spp. from clinical isolates. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, J.; Gatermann, S.G.; Eisfeld, J.; Hans, J.; Pfennigwerth, N. Detection of OXA-181-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Germany. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 312, 151557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhudhairy, M.; Al-Shammari, M. Prevalence of metallo-β-lactamase–producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from diabetic foot infections in Iraq. New Microbes New Infect. 2020, 35, 100661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, M.; Aryal, S.C.; Rai, G.; Rai, K.R.; Pyakurel, S.; Bhandari, B.; Sah, A.K.; Rai, S.K. Prevalence of multidrug-resistance and bla and blaIMP genes among gram-negative clinical isolates in tertiary care hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2021, 13, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-M.; Wang, S.; Chiu, H.-C.; Kao, C.-Y.; Wen, L.-L. Combination of modified carbapenem inactivation method (mCIM) and EDTA-CIM (eCIM) for phenotypic detection of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, M.; Taheri, M.; Arabestani, M.R. Comparison of Different Phenotypic Tests versus PCR in the Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates in Hamadan, Iran. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 5582615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutal, H.; Moguet, C.; Pommiès, L.; Simon, S.; Naas, T.; Volland, H. The Revolution of Lateral Flow Assay in the Field of AMR Detection. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volland, H.; Girlich, D.; Laguide, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Paris, V.; Laroche, M.; Oueslati, S.; Dortet, L.; Simon, S.; Naas, T. Improvement of the Immunochromatographic NG-Test Carba 5 Assay for the Detection of IMP Variants Previously Undetected. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 64, e01940-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahat, S.; Shojapour, M.; Sadeghi, A. Detection of KPC Carbapenemase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Clinical Samples Using Modified Hodge Test and Boronic Acid Phenotypic Methods and Their Comparison With the Polymerase Chain Reaction. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2016, 9, e27249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Zong, H.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, Q.; Kong, D.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Detection of Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing Approach. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, J.-L.; Van Delden, C.; Perron, K.; Köhler, T. Analysis of antibiotic resistance gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by quantitative real-time-PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 254, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjad, A.; Mirza, I.; Abbasi, S.; Farwa, U.; Malik, N.; Zia, F. Modified Hodge test: A simple and effective test for detection of carbapenemase production. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2011, 3, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-Z.; Barré, N.; Poole, K. Influence of the MexA-MexB-OprM multidrug efflux system on expression of the MexC-MexD-OprJ and MexE-MexF-OprN multidrug efflux systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2000, 46, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savli, H.; Karadenizli, A.; Kolayli, F.; Gundes, S.; Ozbek, U.; Vahaboglu, H. Expression stability of six housekeeping genes: A proposal for resistance gene quantification studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, C.M.; Nicolau, D.P.; on behalf of the ERACE-PA Global Study Group. Carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa: An assessment of frequency of isolation from ICU versus non-ICU, phenotypic and genotypic profiles in a multinational population of hospitalized patients. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2022, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Nicolau, D.P.; Gill, C.M. Carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa—An emerging challenge. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 811–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlowsky, J.A.; Bouchillon, S.K.; Kotb, R.E.M.; Mohamed, N.; Stone, G.G.; Sahm, D.F. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas aeruginosa causing infection in Africa and the Middle East: A surveillance study from the ATLAS programme (2018–20). JAC-Antimicrob. Resist. 2022, 4, dlac060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayci, Y.T.; Biyik, I.; Birinci, A. VIM, NDM, IMP, GES, SPM, GIM, SIM Metallobetalactamases in Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from a Turkish University Hospital. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2022, 10, e118712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, D.O.; Nagla, M.M.A. Molecular Detection of Bla OXA-48 Gene Encoding Carbapenem Resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Khartoum State Hospitals, Sudan 2020. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, S.; Goli, H.R. High prevalence of blaVEB, blaGES and blaPER genes in beta-lactam resistant clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. AIMS Microbiol. 2022, 8, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjani, S.; Maamar, E.; Ferjani, A.; Kanzari, L.; Ben Boubaker, I.B. Evaluation of Three Carbapenemase-Phenotypic Detection Methods and Emergence of Diverse VIM and GES Variants among Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates in Tunisia. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hishinuma, T.; Tada, T.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Shimojima, M.; Kirikae, T. Spread of GES-5 carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in Japan due to clonal expansion of ST235. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaballah, A.; Elbaradei, A.; Elsheredy, A.; Kader, O. Emergence of blaVEB and blaGES among VIM-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates in Alexandria, Egypt. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2019, 66, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Jeong, S.H. Mobile Carbapenemase Genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 614058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, L.T.; Hagiu, I.; Popovici, A.; Marinescu, F.; Gheorghe, I.; Curutiu, C.; Ditu, L.M.; Holban, A.-M.; Sesan, T.E.; Lazar, V. Antimicrobial Efficiency of Some Essential Oils in Antibiotic-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates. Plants 2022, 11, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenberger, E.M.; Thaden, J.T. Epidemiology and Mechanisms of Resistance of Extensively Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortet, L.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Rapid Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Pseudomonas spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 50, 3773–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, A.; Huang, T.-D.; Berhin, C.; Hoebeke, M.; Bouchahrouf, W.; Yunus, S.; Bogaerts, P.; Glupczynski, Y. Comparative Evaluation of Four Phenotypic Tests for Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, S.; Lacher, A.; Marschal, M.; Hölzl, F.; Buhl, M.; Autenrieth, I.; Kaase, M.; Willmann, M. Evaluation of phenotypic detection methods for metallo-β-lactamases (MBLs) in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasoo, S.; Cunningham, S.A.; Kohner, P.C.; Simner, P.J.; Mandrekar, J.N.; Lolans, K.; Hayden, M.K.; Patel, R. Comparison of a Novel, Rapid Chromogenic Biochemical Assay, the Carba NP Test, with the Modified Hodge Test for Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Gram-Negative Bacilli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 3097–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Hong, S.G.; Yong, D.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; Bae, I.K. Combined Use of the Modified Hodge Test and Carbapenemase Inhibition Test for Detection of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae and Metallo-β-Lactamase-Producing Pseudomonas spp. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josa, M.D.; Leal, R.; Rojas, J.; Torres, M.I.; Cortés-Muñoz, F.; Esparza, G.; Reyes, L.F. Comparative Evaluation of Phenotypic Synergy Tests versus RESIST-4 O.K.N.V. and NG Test Carba 5 Lateral Flow Immunoassays for the Detection and Differentiation of Carbapenemases in Enterobacterales and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0108021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh Kumar, I.K. To Study The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Pattern of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Detection of Metallo Beta Lactamase Producing Strain with Special Reference to Blandm-1 and Blavim. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 2998–3013. [Google Scholar]
- M100Ed33|Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd Edition. Available online: https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m100/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Giske, C.G. EUCAST Guidelines for Detection of Resistance Mechanisms and Specific Resistances of Clinical and/or Epidemiological Importance. Version 2.0 July 2017. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/resistance_mechanisms (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Gutiérrez, S.; Correa, A.; Hernández-Gómez, C.; De La Cadena, E.; Pallares, C.; Villegas, M.V. Detection of carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Evaluation of the carbapenem inactivation method (CIM). Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 37, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Zwaluw, K.; De Haan, A.; Pluister, G.N.; Bootsma, H.J.; De Neeling, A.J.; Schouls, L.M. The Carbapenem Inactivation Method (CIM), a Simple and Low-Cost Alternative for the Carba NP Test to Assess Phenotypic Carbapenemase Activity in Gram-Negative Rods. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Le, M.H.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, D.L.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Nguyen, T.K.O.; Michalet, S.; Dijoux-Franca, M.-G.; et al. Efflux Pump Inhibitors in Controlling Antibiotic Resistance: Outlook under a Heavy Metal Contamination Context. Molecules 2023, 28, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, E.; Malecki, M.; Tellez-Castillo, C.J.; Pfennigwerth, N.; Marlinghaus, L.; Higgins, P.G.; Mattner, F.; Wendel, A.F. Molecular surveillance of carbapenemase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa at three medical centres in Cologne, Germany. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2019, 8, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, M.G.; Adam, H.J.; Blondeau, J.M.; Walkty, A.J.; Karlowsky, J.A.; Hoban, D.J.; Zhanel, G.G.; Mulvey, M.R.; Baxter, M.R.; Nichol, K.A.; et al. Characterization of carbapenem-resistant and XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Canada: Results of the CANWARD 2007–16 study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, iv32–iv38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialvaei, A.Z.; Rahbar, M.; Hamidi-Farahani, R.; Asgari, A.; Esmailkhani, A.; Dashti, Y.M.; Soleiman-Meigooni, S. Expression of RND efflux pumps mediated antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 153, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, N.; Malathi, J.; Therese, K.L.; Madhavan, H.N. Application of six multiplex PCR’s among 200 clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the detection of 20 drug resistance encoding genes. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Li, S.; Deng, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z. Comparative transcription analysis of resistant mutants against four different antibiotics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 160, 105166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourakbari, B.; Yaslianifard, S.; Yaslianifard, S.; Mahmoudi, S.; Keshavarz-Valian, S.; Mamishi, S. Evaluation of Efflux Pumps Gene Expression in Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates in an Iranian Referral Hospital. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2016, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Gene Type | Primer Sequence (5′ > 3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triplex PCR | blaKPC Forward | ATGTCACTGTATCGCCGTCT | 893 |
| blaKPC Reverse | TTTTCAGAGCCTTACTGCCC | ||
| blaOXA48-like Forward | GCGTGGTTAAGGATGAACAC | 438 | |
| blaOXA48-like Reverse | CATCAAGTTCAACCCAACCG | ||
| blaNDM Forward | GGTTTGGCGATCTGGTTTTC | 621 | |
| blaNDM Reverse | CGGAATGGCTCATCACGATC | ||
| Simplex PCR | blaGES-2 Forward | GTTTTGCAATGTGCTCAACG | 371 |
| blaGES-2 Reverse | TGCCATAGCAATAGGCGTAG | ||
| blaIMP Forward | GGAATAGAGTGGCTTAAYTCTC | 232 | |
| blaIMP Reverse | GGTTTAAYAAAACAACCACC | ||
| blaVIM Forward | GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA | 390 | |
| blaVIM Reverse | CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG | ||
| blaSPM Forward | AAAATCTGGGTACGCAAACG | 271 | |
| blaSPM Reverse | ACATTATCCGCTGGAACAGG | ||
| mcr-1 Forward | CGGTCAGTCCGTTTGTTC | 309 | |
| mcr-1 Reverse | CTTGGTCGGTCTGTAGGG |
| Efflux Pump Gene | Primer Sequence (5′ > 3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| mexA-Forward | ACCTACGAGGCCGACTACCAGA | 252 |
| mexA-Reverse | GTTGGTCACCAGGGCGCCTTC | |
| mexB-Forward | GTGTTCGGCTCGCAGTACTCGA | 244 |
| mexB-Reverse | AACCGTCGGGATTGACCTTGAGC | |
| mexC-Forward | ACGTCGGCGAACTGCAACG | 374 |
| mexC-Reverse | AGCCAGCAGGACTTCGATACCG | |
| mexE-Forward | TCATCCCACTTCTCCTGGCGC | 151 |
| mexE-Reverse | CGTCCCACTCGTTCAGCGG | |
| mexX-Forward | CCAGCAGGAATAGGGCGACCA | 82 |
| mexX-Reverse | AATCGAGGGACACCCATGCACATC | |
| rpoD-Forward | GCGGATGATGTCTTCCACCTGTTCC | 132 |
| rpoD-Reverse | GCGCAACAGCAATCTCGTCTGAAAGA |
| Statistic | Value | 95% Confidence Indices (CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 6.00% | 1.25% to 16.55% |
| Specificity | 94.44% | 72.71% to 99.86% |
| Positive Predictive Value | 75.00% | 19.41% to 99.37% |
| Negative Predictive Value | 26.56% | 16.30% to 39.09% |
| Accuracy | 29.41% | 18.98% to 41.71% |
| Statistic | Value | 95% Confidence Indices (CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 7.89% | 1.66% to 21.38% |
| Specificity | 90.91% | 70.84% to 98.88% |
| Positive Predictive Value | 60.00% | 14.66% to 94.73% |
| Negative Predictive Value | 36.36% | 23.81% to 50.44% |
| Accuracy | 38.33% | 26.07% to 51.79% |
| mexA | mexB | mexC | mexE | mexX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average ΔCt (±SD) | 5.62 (±1.24) | −0.14 (±0.43) | 7.71 (1.96) | 1.26 (±1.17) | 4.5 (±5.29) |
| Minimal ΔCt | 3.62 | −1.14 | 23.11 | −0.42 | 1.04 |
| Maximal ΔCt | 7.42 | 0.02 | 11.86 | 3.72 | 15.18 |
| Average FC (±SD) | 4.17 (±2.93) | 2.94 (±0.75) | 37.57 (±49.65) | 1.8 (±1.33) | 2.27 (±1.52) |
| Minimal FC | 0.63 | 2.08 | 0.92 | 0.33 | 0.0003 |
| Maximal FC | 11.63 | 4.70 | 162.29 | 4.312 | 4.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coșeriu, R.L.; Mare, A.D.; Toma, F.; Vintilă, C.; Ciurea, C.N.; Togănel, R.O.; Cighir, A.; Simion, A.; Man, A. Uncovering the Resistance Mechanisms in Extended-Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Insights from Gene Expression and Phenotypic Tests. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092211
Coșeriu RL, Mare AD, Toma F, Vintilă C, Ciurea CN, Togănel RO, Cighir A, Simion A, Man A. Uncovering the Resistance Mechanisms in Extended-Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Insights from Gene Expression and Phenotypic Tests. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(9):2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092211
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoșeriu, Răzvan Lucian, Anca Delia Mare, Felicia Toma, Camelia Vintilă, Cristina Nicoleta Ciurea, Radu Ovidiu Togănel, Anca Cighir, Anastasia Simion, and Adrian Man. 2023. "Uncovering the Resistance Mechanisms in Extended-Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Insights from Gene Expression and Phenotypic Tests" Microorganisms 11, no. 9: 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092211
APA StyleCoșeriu, R. L., Mare, A. D., Toma, F., Vintilă, C., Ciurea, C. N., Togănel, R. O., Cighir, A., Simion, A., & Man, A. (2023). Uncovering the Resistance Mechanisms in Extended-Drug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates: Insights from Gene Expression and Phenotypic Tests. Microorganisms, 11(9), 2211. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11092211









