Preliminary SAR of Novel Pleuromutilin–Polyamine Conjugates
Abstract
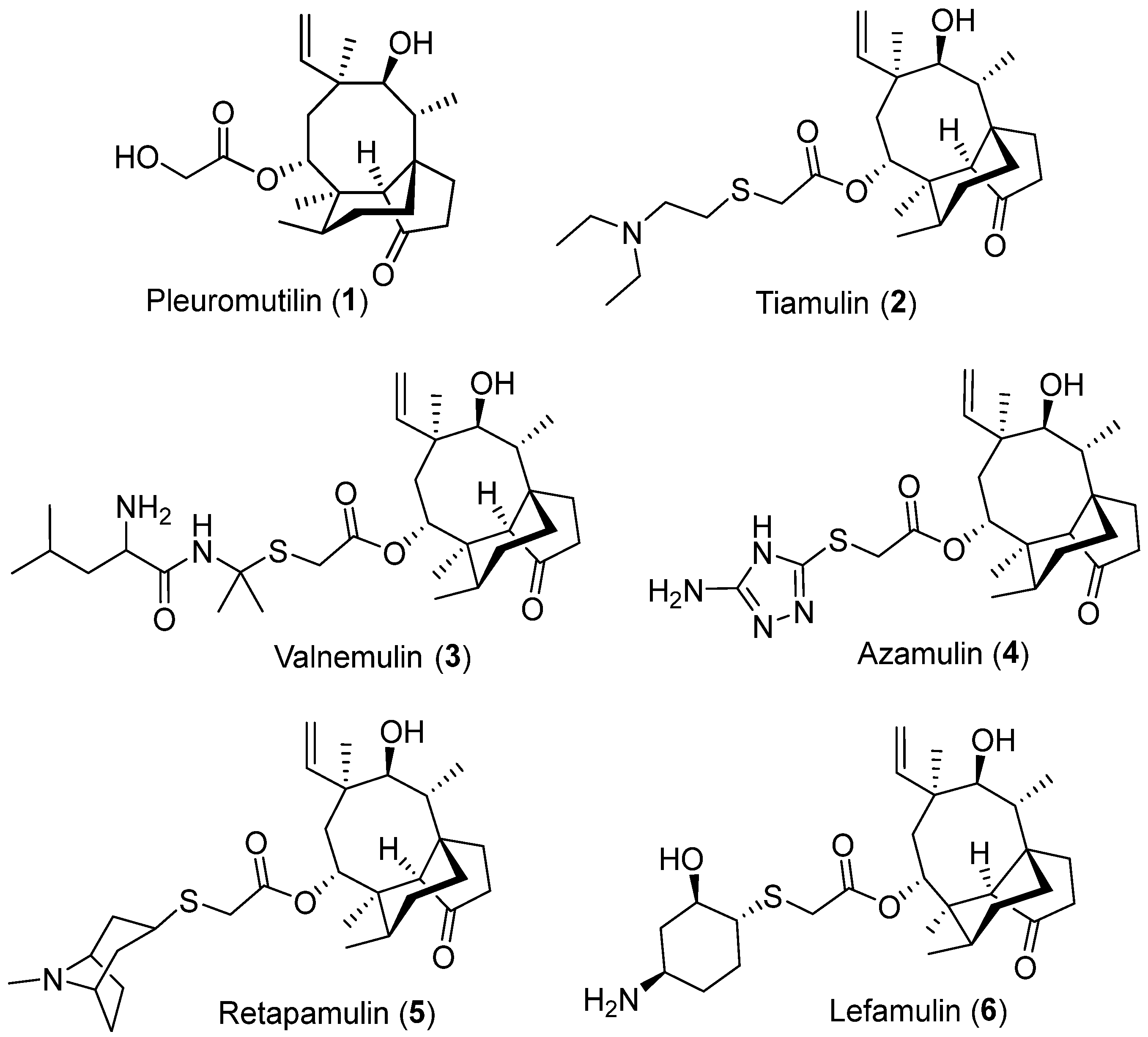
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Synthesis General Methods
2.2. Synthesis of Compounds
2.2.1. Pleuromutilin 22-O-Tosylate (8)
2.2.2. Tiamulin (2)
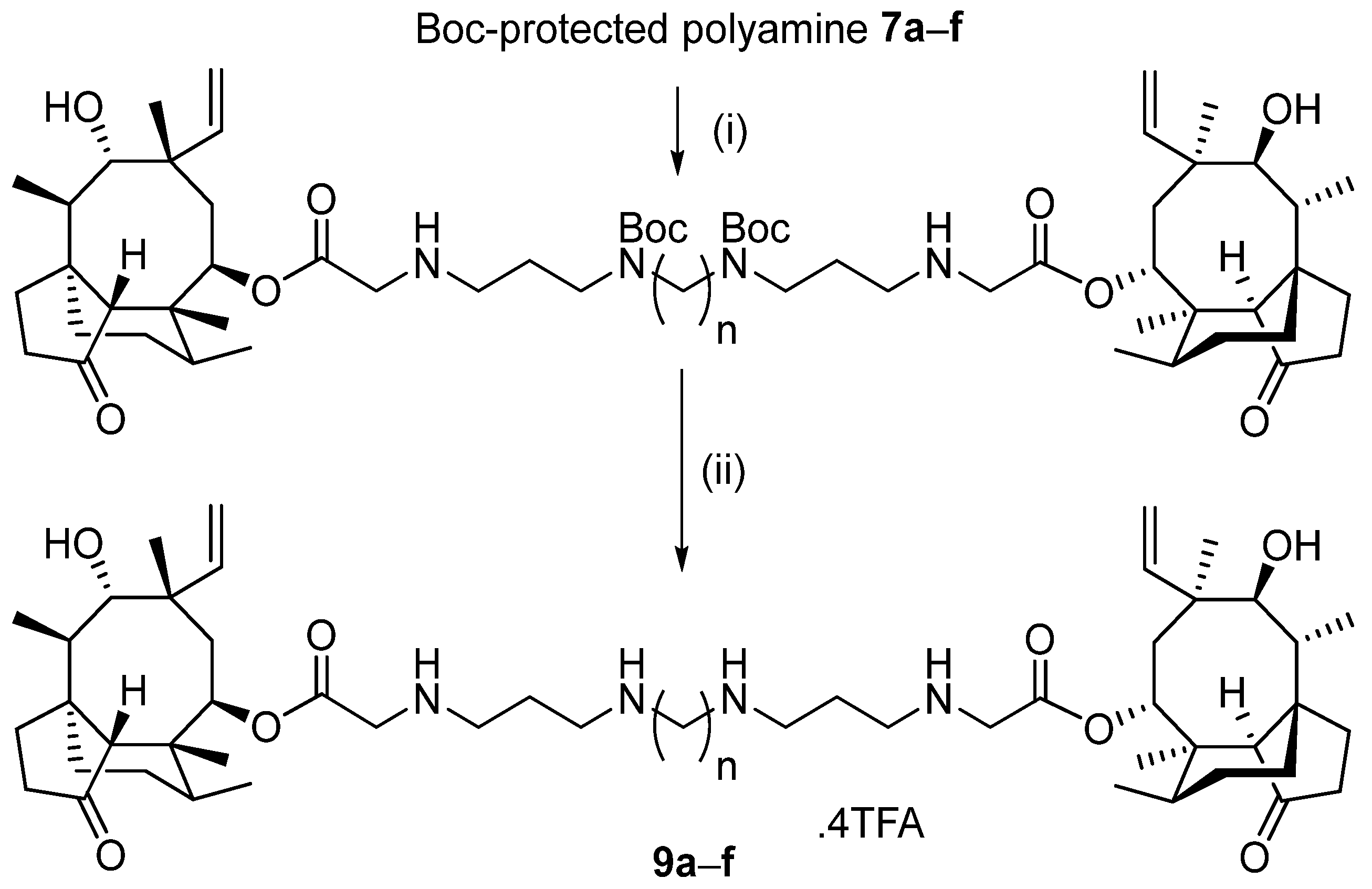
2.2.3. N1,N1′-(Butane-1,4-diyl)bis(N3-(2-(((3aR,4R,5R,7S,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-8-hydroxy-4,7,9,12-tetramethyl-3-oxo-7-vinyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta [8]annulen-5-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)propane-1,3-diaminium) 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9a)
2.2.4. N1,N1′-(Hexane-1,6-diyl)bis(N3-(2-(((3aR,4R,5R,7S,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-8-hydroxy-4,7,9,12-tetramethyl-3-oxo-7-vinyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta [8]annulen-5-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)propane-1,3-diaminium) 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9b)
2.2.5. N1,N1′-(Heptane-1,7-diyl)bis(N3-(2-(((3aR,4R,5R,7S,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-8-hydroxy-4,7,9,12-tetramethyl-3-oxo-7-vinyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta [8]annulen-5-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)propane-1,3-diaminium) 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9c)
2.2.6. N1,N1′-(Octane-1,8-diyl)bis(N3-(2-(((3aR,4R,5R,7S,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-8-hydroxy-4,7,9,12-tetramethyl-3-oxo-7-vinyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta [8]annulen-5-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)propane-1,3-diaminium) 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9d)
2.2.7. N1,N1′-(Decane-1,10-diyl)bis(N3-(2-(((3aR,4R,5R,7S,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-8-hydroxy-4,7,9,12-tetramethyl-3-oxo-7-vinyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta [8]annulen-5-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)propane-1,3-diaminium) 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9e)
2.2.8. N1,N1′-(Dodecane-1,12-diyl)bis(N3-(2-(((3aR,4R,5R,7S,8S,9R,9aS,12R)-8-hydroxy-4,7,9,12-tetramethyl-3-oxo-7-vinyldecahydro-4,9a-propanocyclopenta [8]annulen-5-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)propane-1,3-diaminium) 2,2,2-trifluoroacetate (9f)
2.3. Antimicrobial Assays
2.4. Determination of the MICs of Antibiotics in the Presence of Synergizing Compounds
2.5. Nitrocefin Assay
2.6. Cytotoxicity Assays
2.7. Hemolytic Assays
2.8. Real-Time Growth Curves
2.9. ATP Efflux Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Tiamulin (2)
3.2. Synthesis of Pleuromutilin–Polyamine Conjugates
3.3. Antimicrobial Activities
3.4. Cytotoxic and Hemolytic Activities
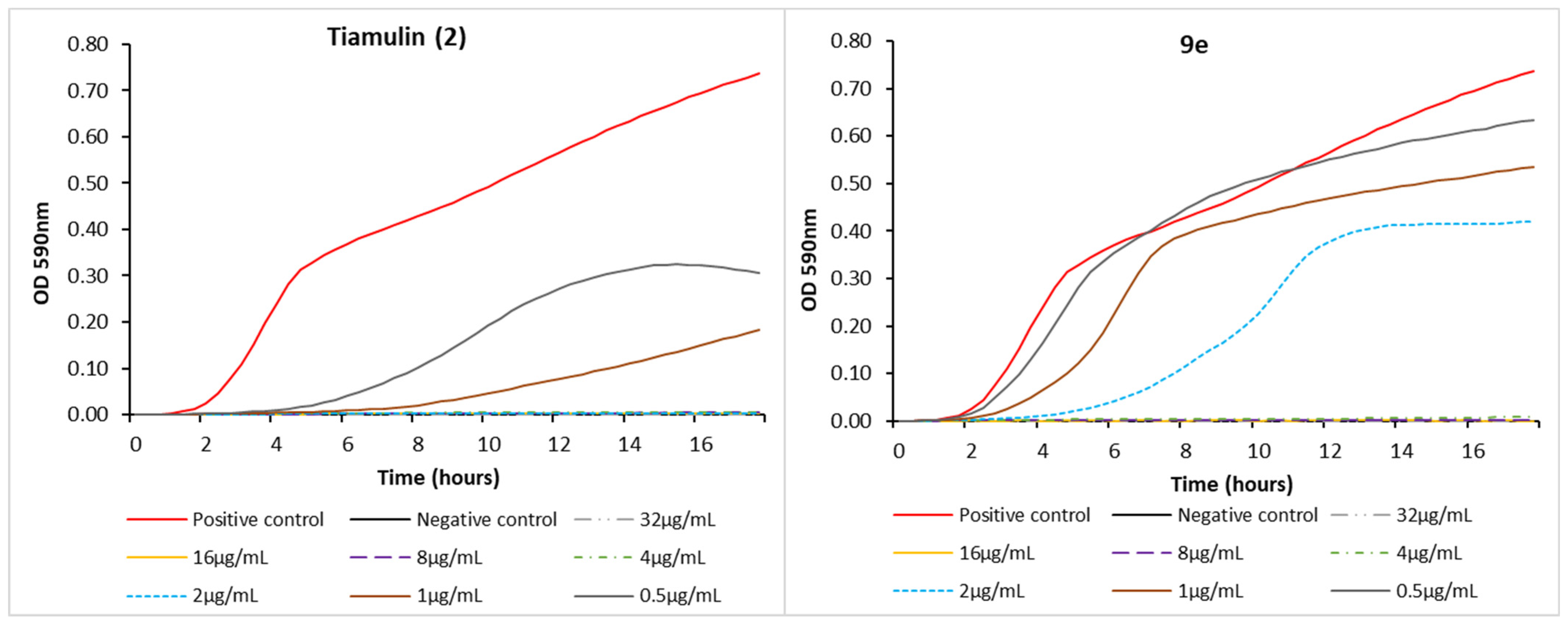
3.5. Real-Time Growth Inhibition Assay
3.6. Antibiotic Enhancement Activities
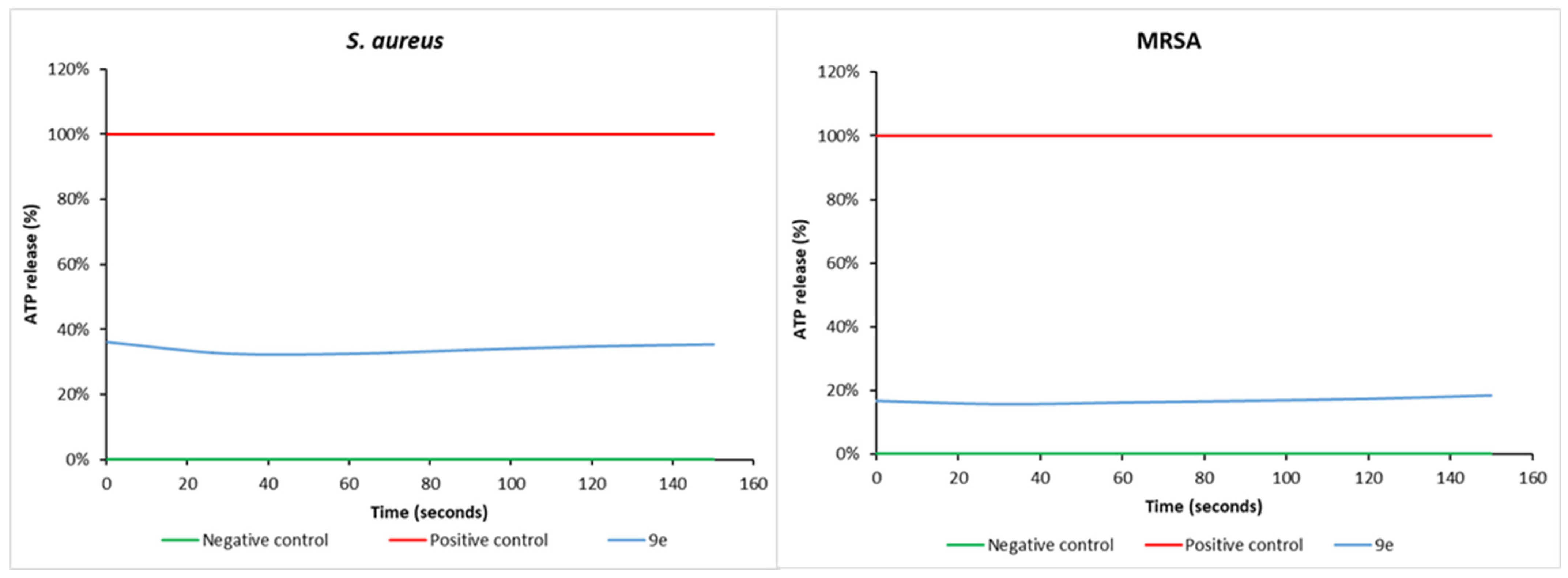
3.7. Membrane Perturbation Activities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging Strategies to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, VMBF-0016-5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, J.G.; Gilbert, D.N.; Spellberg, B. Seven Ways to Preserve the Miracle of Antibiotics. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddock, L.J. The Crisis of No New Antibiotics—What Is the Way Forward? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.D. Solving the Antibiotic Crisis. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, F.; Hervey, A.; Robbins, W.J. Antibiotic Substances from Basidiomycetes: VIII. Pleurotus Multilus (Fr.) Sacc. and Pleurotus Passeckerianus Pilat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1951, 37, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-Z.; Liu, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-X. Pleuromutilin and Its Derivatives-The Lead Compounds for Novel Antibiotics. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, P.S.; Singh, A. METABOLIC PATHWAYS|Production of Secondary Metabolites—Fungi. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 570–578. ISBN 978-0-12-384733-1. [Google Scholar]
- Novak, R. Are Pleuromutilin Antibiotics Finally Fit for Human Use? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1241, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolk, L.; Pøhlsgaard, J.; Jepsen, A.S.; Hansen, L.H.; Nielsen, H.; Steffansen, S.I.; Sparving, L.; Nielsen, A.B.; Vester, B.; Nielsen, P. A Click Chemistry Approach to Pleuromutilin Conjugates with Nucleosides or Acyclic Nucleoside Derivatives and Their Binding to the Bacterial Ribosome. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4957–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevrioukova, I.F. Structural Insights into the Interaction of Cytochrome P450 3A4 with Suicide Substrates: Mibefradil, Azamulin and 6′,7′-Dihydroxybergamottin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.N.; Fritsche, T.R.; Sader, H.S.; Ross, J.E. Activity of Retapamulin (SB-275833), a Novel Pleuromutilin, against Selected Resistant Gram-Positive Cocci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2583–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- File, T.M.; Alexander, E.; Goldberg, L.; Das, A.F.; Sandrock, C.; Paukner, S.; Moran, G.J. Lefamulin Efficacy and Safety in a Pooled Phase 3 Clinical Trial Population with Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia and Common Clinical Comorbidities. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, R.R.; File, T.M. Lefamulin: A Novel Semisynthetic Pleuromutilin Antibiotic for Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paukner, S.; Riedl, R. Pleuromutilins: Potent Drugs for Resistant Bugs—Mode of Action and Resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a027110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paukner, S.; Sader, H.S.; Ivezic-Schoenfeld, Z.; Jones, R.N. Antimicrobial Activity of the Pleuromutilin Antibiotic BC-3781 against Bacterial Pathogens Isolated in the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program in 2010. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4489–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veve, M.P.; Wagner, J.L. Lefamulin: Review of a Promising Novel Pleuromutilin Antibiotic. Pharmacotherapy 2018, 38, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, H. Multidrug Efflux Pumps of Gram-Negative Bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5853–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, D.; Ruzin, A.; McAleese, F.; Murphy, E.; Bradford, P.A. MarA-Mediated Overexpression of the AcrAB Efflux Pump Results in Decreased Susceptibility to Tigecycline in Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadelis, M.M.; Li, S.A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Blanchet, M.; Douafer, H.; Brunel, J.M.; Copp, B.R. Spermine Derivatives of Indole-3-Carboxylic Acid, Indole-3-Acetic Acid and Indole-3-Acrylic Acid as Gram-Negative Antibiotic Adjuvants. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, A.N.; Kaiser, M.; Copp, B.R. Synthesis and Antimalarial Evaluation of Artesunate-Polyamine and Trioxolane-Polyamine Conjugates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenke, B.; Gilbert, I.H. Nitrile Reduction in the Presence of Boc-Protected Amino Groups by Catalytic Hydrogenation over Palladium-Activated Raney-Nickel. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 2480–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klenke, B.; Stewart, M.; Barrett, M.P.; Brun, R.; Gilbert, I.H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of S-Triazine Substituted Polyamines as Potential New Anti-Trypanosomal Drugs. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 44, 3440–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemieux, M.R.; Siricilla, S.; Mitachi, K.; Eslamimehr, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Pressly, J.D.; Kong, Y.; Park, F.; Franzblau, S.G.; et al. An Antimycobacterial Pleuromutilin Analogue Effective against Dormant Bacilli. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4787–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cadelis, M.M.; Rouvier, F.; Troia, T.; Edmeades, L.R.; Fraser, K.; Gill, E.S.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Brunel, J.M.; Copp, B.R. α,ω-Diacyl-Substituted Analogues of Natural and Unnatural Polyamines: Identification of Potent Bactericides That Selectively Target Bacterial Membranes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaskovich, M.A.T.; Zuegg, J.; Elliott, A.G.; Cooper, M.A. Helping Chemists Discover New Antibiotics. ACS Infect. Dis. 2015, 1, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troudi, A.; Bolla, J.M.; Klibi, N.; Brunel, J.M. An Original and Efficient Antibiotic Adjuvant Strategy to Enhance the Activity of Macrolide Antibiotics against Gram-Negative Resistant Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Huang, Y.-Z.; Luo, J.; Jin, Z.; Liu, Y.-H.; Tang, Y.-Z. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of Novel Pleuromutilin Derivatives Bearing an Aminothiophenol Moiety. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 92, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, S.; Farha, M.; Ellis, M.J.; Sameer, Z.; Côté, J.-P.; Cotroneo, N.; Lister, T.; Rubio, A.; Brown, E.D. Potentiation of Antibiotics against Gram-Negative Bacteria by Polymyxin B Analogue SPR741 from Unique Perturbation of the Outer Membrane. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 6, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
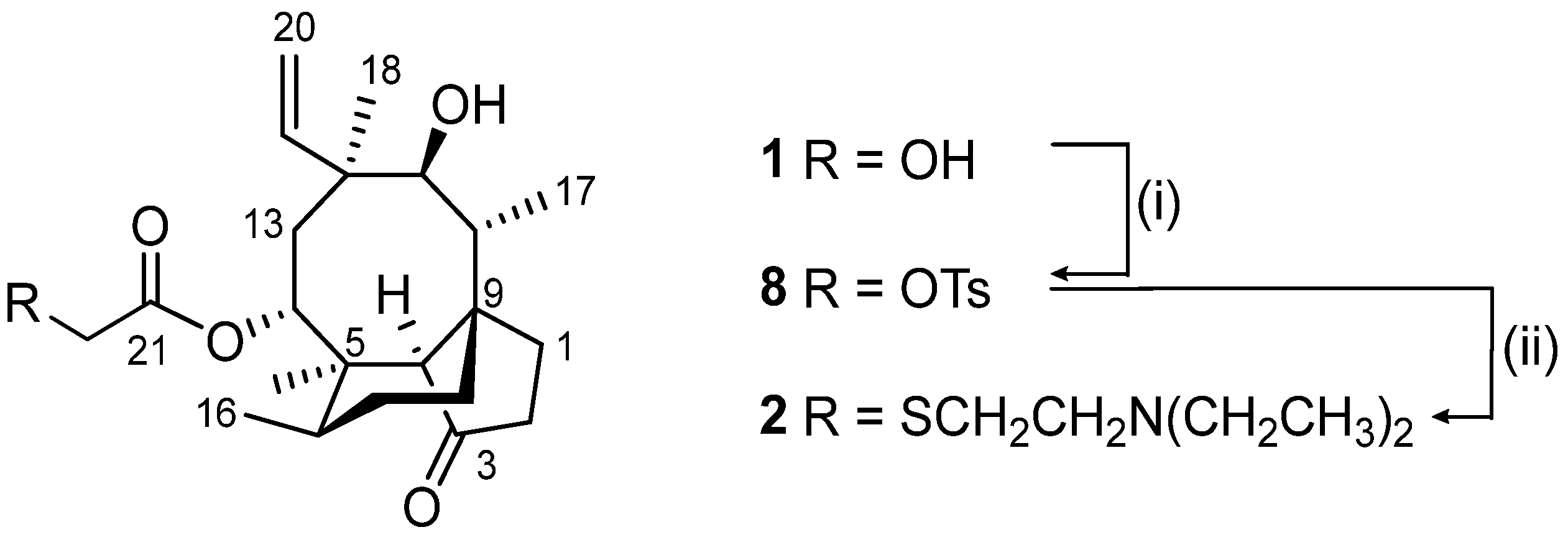
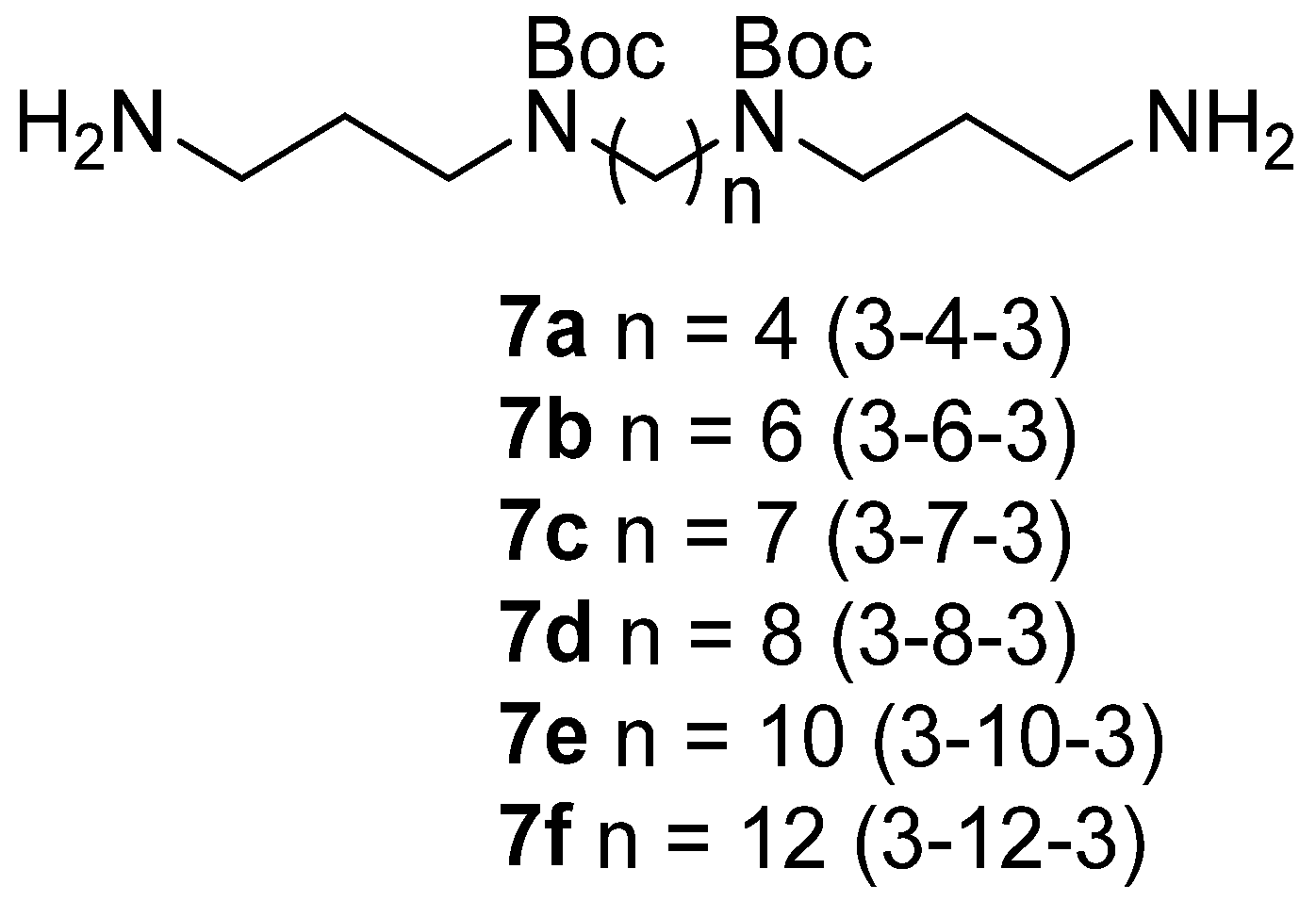

| Compound | S.a. a | MRSA b | E.c. c | P.a. d | K.p. e | A.b. f | C.a. g | C.n. h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.125 | n.t. i | 400 | 800 | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. | n.t. |
| 2 | 3.125 | ≤0.51 | 200 | 800 | >64.8 | >64.8 | >64.8 | >64.8 |
| 9a | 18.1 | 23.2 | 18.1 | 72.5 | >23.2 | >23.2 | >23.2 | 0.72 |
| 9b | 17.8 | ≤0.18 | 8.88 | 142 | >22.7 | >22.7 | >22.7 | ≤0.18 |
| 9c | 17.6 | ≤0.18 | 35.2 | >141 | >22.5 | >22.5 | >22.5 | ≤0.18 |
| 9d | 34.8 | 5.57 | 70 | >139 | >22.3 | >22.3 | >22.3 | ≤0.17 |
| 9e | 4.27 | ≤0.17 | 4.27 | >88 | >21.9 | >21.9 | 10.9 | ≤0.17 |
| 9f | 2.10 | ≤0.17 | 4.19 | 33.5 | 21.5 | 2.7 | 21.5 | ≤0.17 |
| Compound | Cytotoxicity a | Hemolysis b |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | >64.8 | >64.8 |
| 9a | >23.2 | >23.2 |
| 9b | >22.7 | >22.7 |
| 9c | >22.5 | >22.5 |
| 9d | >22.3 | >22.3 |
| 9e | >21.9 | >21.9 |
| 9f | 8.3 | 13.2 |
| Compound | Dox/P.a. a | Erythro/E.c. b |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | >405 (2) | >405 (0.5) |
| 9a | 18.1 (4) | 9.06 (2) |
| 9b | 35.5 (4) | 8.88 (1) |
| 9c | 141 (1) | 17.6 (2) |
| 9d | 139 (1) | 34.8 (2) |
| 9e | 34.2 (2) | 8.54 (0.5) |
| 9f | 8.38 (4) | 8.38 (0.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sue, K.; Cadelis, M.M.; Hainsworth, K.; Rouvier, F.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L.; Brunel, J.M.; Copp, B.R. Preliminary SAR of Novel Pleuromutilin–Polyamine Conjugates. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112791
Sue K, Cadelis MM, Hainsworth K, Rouvier F, Bourguet-Kondracki M-L, Brunel JM, Copp BR. Preliminary SAR of Novel Pleuromutilin–Polyamine Conjugates. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(11):2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112791
Chicago/Turabian StyleSue, Kenneth, Melissa M. Cadelis, Kerrin Hainsworth, Florent Rouvier, Marie-Lise Bourguet-Kondracki, Jean Michel Brunel, and Brent R. Copp. 2023. "Preliminary SAR of Novel Pleuromutilin–Polyamine Conjugates" Microorganisms 11, no. 11: 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112791
APA StyleSue, K., Cadelis, M. M., Hainsworth, K., Rouvier, F., Bourguet-Kondracki, M.-L., Brunel, J. M., & Copp, B. R. (2023). Preliminary SAR of Novel Pleuromutilin–Polyamine Conjugates. Microorganisms, 11(11), 2791. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11112791








