Whole-Genome Sequencing Revealed the Fusion Plasmids Capable of Transmission and Acquisition of Both Antimicrobial Resistance and Hypervirulence Determinants in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Susceptibility Testing and DNA Isolation
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.3. Genome Assembly, Data Processing and Annotation
3. Results
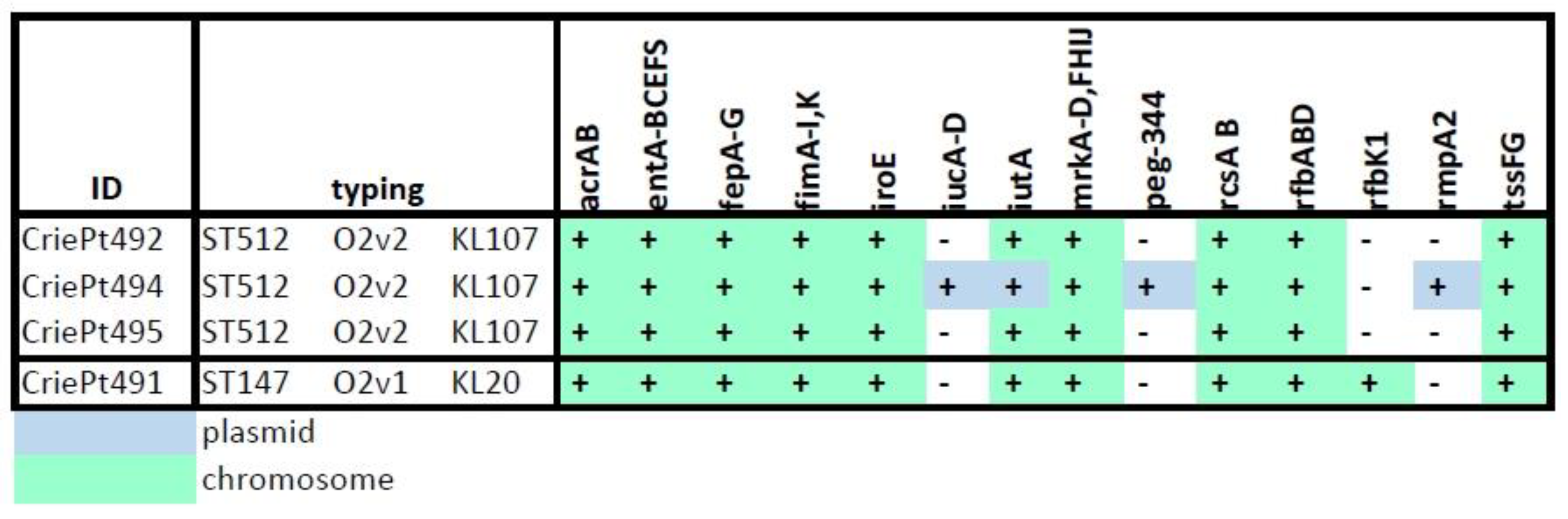
3.1. Isolate Typing and Resistance Profiles
3.2. Isolate Typing and Resistance Profiles
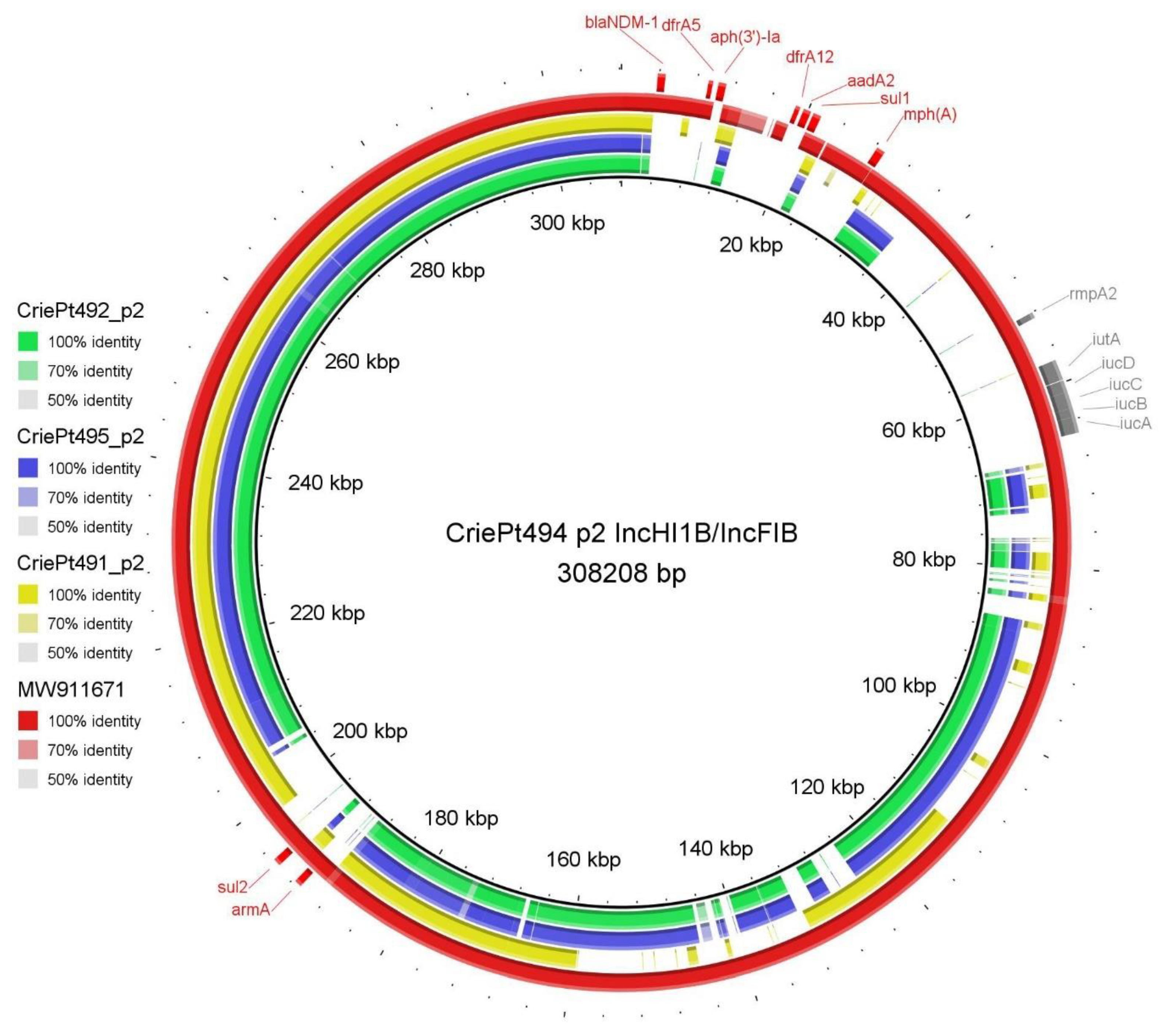
3.3. Plasmid Typing, Classification, Annotation and Comparison
3.3.1. Plasmids of CriePt492, 494 and 495
3.3.2. Plasmids of CriePt491
3.4. CRISPR-Cas Systems and Anti-CRISPR Genes
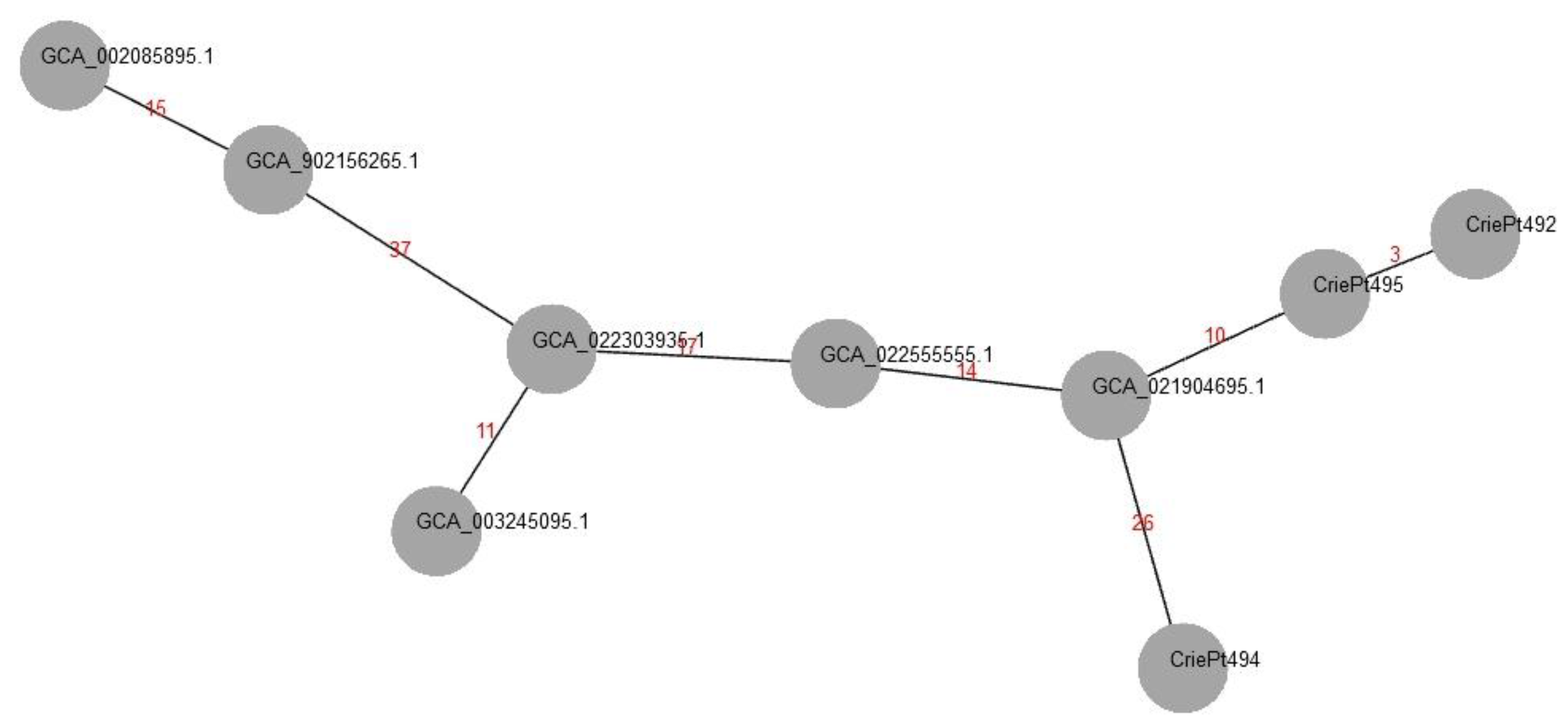
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magill, S.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Bamberg, W.; Beldavs, Z.G.; Dumyati, G.; Kainer, M.A.; Lynfield, R.; Maloney, M.; McAllister-Hollod, L.; Nadle, J.; et al. Multistate point-prevalence survey of health care-associated infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrie, C.L.; Mirceta, M.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Lam, M.M.C.; Gomi, R.; Abbott, I.J.; Thomson, N.R.; Strugnell, R.A.; Pratt, N.F.; et al. Genomic dissection of Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in hospital patients reveals insights into an opportunistic pathogen. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Holt, K.E. Population genomics of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Chen, F.; Yu, R. Analysis of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae and classic Klebsiella pneumoniae infections in a Chinese hospital. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 132, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcari, G.; Carattoli, A. Global spread and evolutionary convergence of multidrug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae high-risk clones. Pathog. Glob. Health 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial Resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Hypervirulence-Associated Determinants, and Resistance Mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae—Clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; La Hoz, R.M.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of Biomarkers for Differentiation of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from Classical K. pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Kong, X.; Hao, J.; Liu, J. Epidemiological Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Multidrug-Resistant Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 581543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Nguyen, T.N.T.; Lam, M.M.C.; Judd, L.M.; van Vinh Chau, N.; Dance, D.A.B.; Ip, M.; Karkey, A.; Ling, C.L.; Miliya, T.; et al. Genomic surveillance for hypervirulence and multi-drug resistance in invasive Klebsiella pneumoniae from South and Southeast Asia. Genome. Med. 2020, 12, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Criscuolo, A.; Ailloud, F.; Passet, V.; Jones, L.; Delannoy-Vieillard, A.S.; Garin, B.; Le Hello, S.; Arlet, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; et al. Genomic definition of hypervirulent and multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Siu, L.K.; Ma, L.; Yeh, K.M.; Fung, C.P.; Lin, J.C.; Chang, F.Y. Community-acquired liver abscess caused by serotype K1 Klebsiella pneumoniae with CTX-M-15-type extended-spectrum beta-lactamase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 804–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejas, D.; Fernandez Canigia, L.; Rincon Cruz, G.; Elena, A.X.; Maldonado, I.; Gutkind, G.O.; Radice, M.A. First isolate of KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumonaie sequence type 23 from the Americas. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3483–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surgers, L.; Boyd, A.; Girard, P.M.; Arlet, G.; Decre, D. ESBL-Producing Strain of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae K2, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1687–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Lin, D.; Chan, E.W.; Gu, D.; Chen, G.X.; Chen, S. Emergence of Carbapenem-Resistant Serotype K1 Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaidullina, E.; Shelenkov, A.; Yanushevich, Y.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Shagin, D.; Alexandrova, I.; Ershova, O.; Akimkin, V.; Kozlov, R.; Edelstein, M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Genomic Characterization of OXA-48- and CTX-M-15-Co-Producing Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST23 Recovered from Nosocomial Outbreak. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaertynov, K.S.; Anokhin, V.A.; Davidyuk, Y.N.; Nicolaeva, I.V.; Khalioullina, S.V.; Semyenova, D.R.; Alatyrev, E.Y.; Skvortsova, N.N.; Abrahamyan, L.G. Case of Meningitis in a Neonate Caused by an Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase-Producing Strain of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Dong, N.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, D.; Huang, M.; Wang, L.; Chan, E.W.; Shu, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; et al. A fatal outbreak of ST11 carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in a Chinese hospital: A molecular epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennequin, C.; Robin, F. Correlation between antimicrobial resistance and virulence in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Froumine, R.; Tokolyi, A.; Gorrie, C.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Duchene, S.; Jenney, A.; Holt, K.E. Distinct evolutionary dynamics of horizontal gene transfer in drug resistant and virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a key trafficker of drug resistance genes from environmental to clinically important bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, S.; Bosio, M.; Gross, C.; Bezdan, D.; Gutierrez, J.; Oberhettinger, P.; Liese, J.; Vogel, W.; Dorfel, D.; Berger, L.; et al. Tracking of Antibiotic Resistance Transfer and Rapid Plasmid Evolution in a Hospital Setting by Nanopore Sequencing. mSphere 2020, 5, e00525-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelenkov, A.; Petrova, L.; Mironova, A.; Zamyatin, M.; Akimkin, V.; Mikhaylova, Y. Long-Read Whole Genome Sequencing Elucidates the Mechanisms of Amikacin Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Obtained from COVID-19 Patients. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmenkov, A.Y.; Trushin, I.V.; Vinogradova, A.G.; Avramenko, A.A.; Sukhorukova, M.V.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Dekhnich, A.V.; Edelstein, M.V.; Kozlov, R.S. AMRmap: An Interactive Web Platform for Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Data in Russia. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 620002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillippy, A.M.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving bacterial genome assemblies from short and long sequencing reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, M.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Pevzner, P.A. Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Holt, K.E. Polypolish: Short-read polishing of long-read bacterial genome assemblies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelenkov, A.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Yanushevich, Y.; Samoilov, A.; Petrova, L.; Fomina, V.; Gusarov, V.; Zamyatin, M.; Shagin, D.; Akimkin, V. Molecular Typing, Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Profiling and Analysis of Whole-Genome Sequence of Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelenkov, A.; Petrova, L.; Zamyatin, M.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Akimkin, V. Diversity of International High-Risk Clones of Acinetobacter baumannii Revealed in a Russian Multidisciplinary Medical Center during 2017–2019. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J.; Bessonov, K.; Schonfeld, J.; Nash, J.H.E. Universal whole-sequence-based plasmid typing and its utility to prediction of host range and epidemiological surveillance. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Neron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Gagnon, J.N.; Brouns, S.J.; Fineran, P.C.; Brown, C.M. CRISPRTarget: Bioinformatic prediction and analysis of crRNA targets. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Gorrie, C.; Jenney, A.; Follador, R.; Thomson, N.R.; Holt, K.E. Identification of Klebsiella capsule synthesis loci from whole genome data. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.M.C.; Wick, R.R.; Watts, S.C.; Cerdeira, L.T.; Wyres, K.L.; Holt, K.E. A genomic surveillance framework and genotyping tool for Klebsiella pneumoniae and its related species complex. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijao, P.; Yao, H.T.; Fornika, D.; Gardy, J.; Hsiao, W.; Chauve, C.; Chindelevitch, L. MentaLiST—A fast MLST caller for large MLST schemes. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurch, A.C.; Arredondo-Alonso, S.; Willems, R.J.L.; Goering, R.V. Whole genome sequencing options for bacterial strain typing and epidemiologic analysis based on single nucleotide polymorphism versus gene-by-gene-based approaches. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftie-Eaton, W.; Rawlings, D.E. Diversity, biology and evolution of IncQ-family plasmids. Plasmid 2012, 67, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smillie, C.; Garcillan-Barcia, M.P.; Francia, M.V.; Rocha, E.P.; de la Cruz, F. Mobility of plasmids. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, E.; Schwabe, M.; Schulig, L.; Hubner, N.O.; Bohnert, J.A.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Heiden, S.E.; Muller, J.U.; Adnan, F.; Becker, K.; et al. Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Counteracts Fitness and Virulence Costs That Accompanied Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance Acquisition. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0014822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochan, T.J.; Nozick, S.H.; Medernach, R.L.; Cheung, B.H.; Gatesy, S.W.M.; Lebrun-Corbin, M.; Mitra, S.D.; Khalatyan, N.; Krapp, F.; Qi, C.; et al. Genomic surveillance for multidrug-resistant or hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae among United States bloodstream isolates. BMC. Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starkova, P.; Lazareva, I.; Avdeeva, A.; Sulian, O.; Likholetova, D.; Ageevets, V.; Lebedeva, M.; Gostev, V.; Sopova, J.; Sidorenko, S. Emergence of Hybrid Resistance and Virulence Plasmids Harboring New Delhi Metallo-beta-Lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae in Russia. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, J. An outbreak of extensively drug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae in an intensive care unit of a teaching hospital in Southwest China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 979219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudabadi, S.; Goudarzi, H.; Goudarzi, M.; Ardebili, A.; Faghihloo, E.; Sharahi, J.Y.; Hashemi, A. Detection of extensively drug-resistant and hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST15, ST147, ST377 and ST442 in Iran. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2021, 69, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, P.; Xiao, N.; Ji, F.; Russo, T.A.; Guo, J. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae is emerging as an increasingly prevalent K. pneumoniae pathotype responsible for nosocomial and healthcare-associated infections in Beijing, China. Virulence 2020, 11, 1215–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolourchi, N.; Naz, A.; Sohrabi, M.; Badmasti, F. Comparative in silico characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae hypervirulent plasmids and their antimicrobial resistance genes. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2022, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, W.; Xiang, T.X.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wei, D.D.; Fan, L.; Huang, S.; Liao, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Horizontal gene transfer via OMVs co-carrying virulence and antimicrobial-resistant genes is a novel way for the dissemination of carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 945972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.H.; Moore, L.S.; Sundsfjord, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Regmi, S.; Karkey, A.; Guerin, P.J.; Piddock, L.J. Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance. Lancet 2016, 387, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, P.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Yu, Y. A global perspective on the convergence of hypervirulence and carbapenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.; Zhang, R.; Chen, S. Klebsiella species: Taxonomy, hypervirulence and multidrug resistance. eBioMedicine 2022, 79, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Du, P.; Yang, P.; Lu, M.; Shen, N. Fusion plasmid enhanced the endemic extensively drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clone ST147 harbored bla(OXA-48) to acquire the hypervirulence and cause fatal infection. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2023, 22, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, C.; Vasudevan, K.; Jacob, J.J.; Baker, S.; Isaac, B.J.; Neeravi, A.R.; Sethuvel, D.P.M.; George, B.; Veeraraghavan, B. Hybrid Plasmids Encoding Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence Traits Among Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae ST2096 in India. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 875116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozad Duzgun, A. From Turkey: First Report of KPC-3- and CTX-M-27-Producing Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 Clone Carrying OmpK36 and Ompk37 Porin Mutations. Microb. Drug. Resist. 2021, 27, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngbede, E.O.; Adekanmbi, F.; Poudel, A.; Kalalah, A.; Kelly, P.; Yang, Y.; Adamu, A.M.; Daniel, S.T.; Adikwu, A.A.; Akwuobu, C.A.; et al. Concurrent Resistance to Carbapenem and Colistin Among Enterobacteriaceae Recovered from Human and Animal Sources in Nigeria is Associated with Multiple Genetic Mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 740348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, N.; Akeda, Y.; Sugawara, Y.; Takeuchi, D.; Motooka, D.; Yamamoto, N.; Laolerd, W.; Santanirand, P.; Hamada, S. Genomic Characterization of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae with Chromosomally Carried bla(NDM-1). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01520-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ji, F.; Chang, H.; Qin, J.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Jia, Z.; et al. Multiple-Replicon Resistance Plasmids of Klebsiella Mediate Extensive Dissemination of Antimicrobial Genes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 754931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasanidou, D.; Geros, A.S.; Mohanraju, P.; Nieuwenweg, A.C.; Nobrega, F.L.; Staals, R.H.J. Keeping crispr in check: Diverse mechanisms of phage-encoded anti-crisprs. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2019, 366, fnz098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Lv, L.; Wang, X.; Xiu, Z.; Chen, G. Comparative analysis of CRISPR-Cas systems in Klebsiella genomes. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, Y.; Fu, P.; Tian, D.; Yu, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, G.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. The type I-E CRISPR-Cas system influences the acquisition of bla(KPC)-IncF plasmid in Klebsiella pneumonia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackow, N.A.; Shen, J.; Adnan, M.; Khan, A.S.; Fries, B.C.; Diago-Navarro, E. CRISPR-Cas influences the acquisition of antibiotic resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, D.; Guo, Q.; Wang, M. Coexistence of blaKPC-IncFII plasmids and type I-E* CRISPR-Cas systems in ST15 Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1125531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Iredell, J.R. CRISPR-Cas System in Antibiotic Resistance Plasmids in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Tian, D.; Ai, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Yu, F.; Chen, L.; et al. Exploiting a conjugative endogenous CRISPR-Cas3 system to tackle multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. eBioMedicine 2023, 88, 104445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Ge, H.; Qiao, J.; Li, Y. Global prevalence, characteristics, and future prospects of IncX3 plasmids: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 979558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viehweger, A.; Blumenscheit, C.; Lippmann, N.; Wyres, K.L.; Brandt, C.; Hans, J.B.; Holzer, M.; Irber, L.; Gatermann, S.; Lubbert, C.; et al. Context-aware genomic surveillance reveals hidden transmission of a carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodcroft, E.B.; De Maio, N.; Lanfear, R.; MacCannell, D.R.; Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Stamatakis, A.; Goldman, N.; Dessimoz, C. Want to track pandemic variants faster? Fix the bioinformatics bottleneck. Nature 2021, 591, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampatakis, T.; Tsergouli, K.; Behzadi, P. Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Virulence Factors, Molecular Epidemiology and Latest Updates in Treatment Options. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelenkov, A.A.; Slavokhotova, A.A.; Odintsova, T.I. Cysmotif Searcher Pipeline for Antimicrobial Peptide Identification in Plant Transcriptomes. Biochemistry 2018, 83, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, C.M.; da Silva, A.P.; Junior, N.G.O.; Martinez, O.F.; Franco, O.L. Peptides as a therapeutic strategy against Klebsiella pneumoniae. Trends. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 43, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodnichev, R.B.; Volozhantsev, N.V.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Bodoev, I.N.; Kornienko, M.A.; Kuptsov, N.S.; Popova, A.V.; Makarenko, G.I.; Manolov, A.I.; Slukin, P.V.; et al. Novel Klebsiella pneumoniae K23-Specific Bacteriophages from Different Families: Similarity of Depolymerases and Their Therapeutic Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 669618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho, F.R.T.; Telles, J.P.; Tuon, F.F.B.; Rabello Filho, R.; Caruso, P.; Correa, T.D. Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs: A Review of Strategies to Avoid Polymyxins and Carbapenems Misuse in Low Middle-Income Countries. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Isolate Id | Patient Age (Years) | Patient Gender | Isolation Date | Department | Locus | Diagnosis (Main) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CriePt491 | 75 | female | 12 December 2021 | ICU 1 | BAL 2 | Thrombosis of the superior mesenteric artery with necrosis of the colon |
| CriePt492 | 82 | female | 12 December 2021 | ICU | BAL | Acute thrombosis of the femoral artery |
| CriePt494 | 64 | male | 8 December 2021 | pulmonology | sputum | Interstitial pneumonitis |
| CriePt495 | 58 | male | 9 December 2021 | ICU | BAL | Intracerebral parenchymal hemorrhage in the suprasellar region of the brain |
| Sample Id/Plasmids | num | Col(pHAD28) | ColRNAI | IncFIA | IncFIB | IncHI1B | IncR | IncX3 | Unkn1 1 | Unkn2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CriePt491 | 5 | + | - | - | + | + | + | - | - | + |
| CriePt492 | 6 | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| CriePt494 | 7 | + | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| CriePt495 | 6 | + | + | - | + | + | - | + | + | - |
| ID | Size, bp | GC Content | Replicon Type (s) | Relaxase Type | mpf_Type | Predicted Mobility | AMR/Virulence (VIR) Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CriePt491 | |||||||
| p2 | 179,707 | 0.448 | IncHI1B/IncFIB | - | MPF_F | non-mobilizable | - |
| p3 | 109,649 | 0.493 | IncFIB | - | - | non-mobilizable | - |
| p4 | 53,009 | 0.534 | - | - | - | non-mobilizable | - |
| p5 | 46,984 | 0.534 | IncR | - | - | mobilizable | AMR |
| p6 | 4915 | 0.431 | Col(pHAD28) | - | - | non-mobilizable | - |
| CriePt492 | |||||||
| p2 | 250,630 | 0.461 | IncHI1B/IncFIB | MOBH | MPF_F | conjugative | - |
| p3 | 184,725 | 0.533 | IncFIB | MOBF | - | mobilizable | AMR |
| p4 | 53,292 | 0.496 | IncX3 | MOBP | MPF_T | conjugative | AMR |
| p5 | 10,689 | 0.475 | Col(pHAD28) | - | - | non-mobilizable | AMR |
| p6 | 9730 | 0.532 | ColRNAI | MOBC | - | mobilizable | - |
| p7 | 2963 | 0.650 | - | MOBV | - | mobilizable | - |
| CriePt494 | |||||||
| p2 | 308,208 | 0.472 | IncHI1B/IncFIB | MOBH | MPF_F | conjugative | AMR, VIR |
| p3 | 93,808 | 0.521 | IncFIB | - | - | non-mobilizable | - |
| p4 | 89,753 | 0.510 | IncFIA | MOBF | MPF_F | conjugative | AMR |
| p5 | 53,292 | 0.496 | IncX3 | MOBP | MPF_T | conjugative | AMR |
| p6 | 10,689 | 0.475 | Col(pHAD28) | - | - | non-mobilizable | AMR |
| p7 | 9737 | 0.532 | ColRNAI | MOBC | - | mobilizable | - |
| p8 | 2963 | 0.650 | - | MOBV | - | mobilizable | - |
| CriePt495 | |||||||
| p2 | 251,830 | 0.461 | IncHI1B/IncFIB | MOBH | MPF_F | conjugative | - |
| p3 | 190,476 | 0.533 | IncFIB | MOBF | - | mobilizable | AMR |
| p4 | 53,292 | 0.496 | IncX3 | MOBP | MPF_T | conjugative | AMR |
| p5 | 10,689 | 0.475 | Col(pHAD28) | - | - | non-mobilizable | AMR |
| p6 | 9730 | 0.532 | ColRNAI | MOBC | - | mobilizable | - |
| p7 | 2963 | 0.650 | - | MOBV | - | mobilizable | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shelenkov, A.; Mikhaylova, Y.; Voskanyan, S.; Egorova, A.; Akimkin, V. Whole-Genome Sequencing Revealed the Fusion Plasmids Capable of Transmission and Acquisition of Both Antimicrobial Resistance and Hypervirulence Determinants in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051314
Shelenkov A, Mikhaylova Y, Voskanyan S, Egorova A, Akimkin V. Whole-Genome Sequencing Revealed the Fusion Plasmids Capable of Transmission and Acquisition of Both Antimicrobial Resistance and Hypervirulence Determinants in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(5):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051314
Chicago/Turabian StyleShelenkov, Andrey, Yulia Mikhaylova, Shushanik Voskanyan, Anna Egorova, and Vasiliy Akimkin. 2023. "Whole-Genome Sequencing Revealed the Fusion Plasmids Capable of Transmission and Acquisition of Both Antimicrobial Resistance and Hypervirulence Determinants in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates" Microorganisms 11, no. 5: 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051314
APA StyleShelenkov, A., Mikhaylova, Y., Voskanyan, S., Egorova, A., & Akimkin, V. (2023). Whole-Genome Sequencing Revealed the Fusion Plasmids Capable of Transmission and Acquisition of Both Antimicrobial Resistance and Hypervirulence Determinants in Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates. Microorganisms, 11(5), 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051314





