MPrESS: An R-Package for Accurately Predicting Power for Comparisons of 16S rRNA Microbiome Taxa Distributions including Simulation by Dirichlet Mixture Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Implementation
2.1. MPrESS: Microbiome Power Estimates Using Sampling and Simulation
2.2. Microbiome Datasets Analyzed
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Analysis
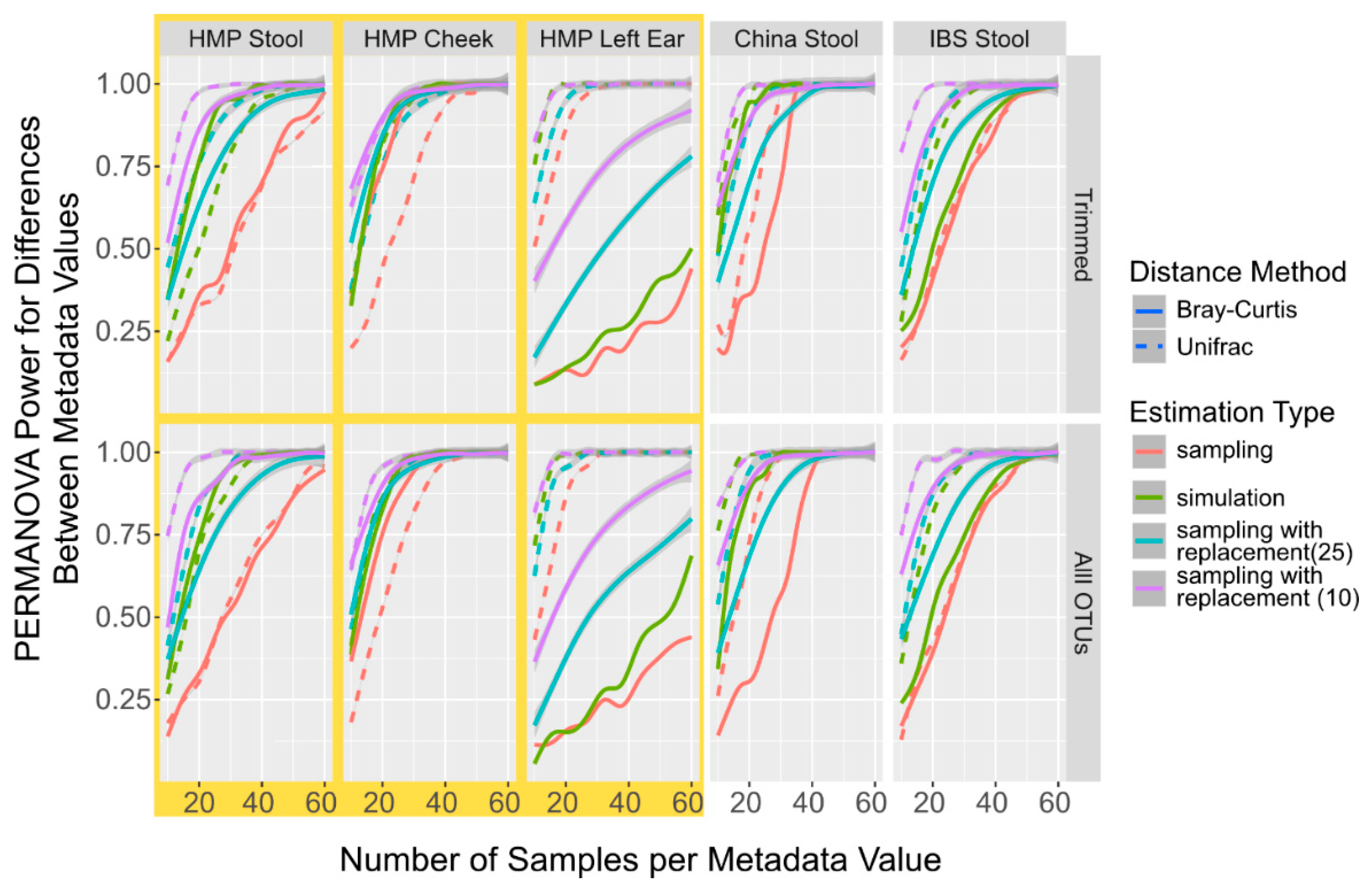
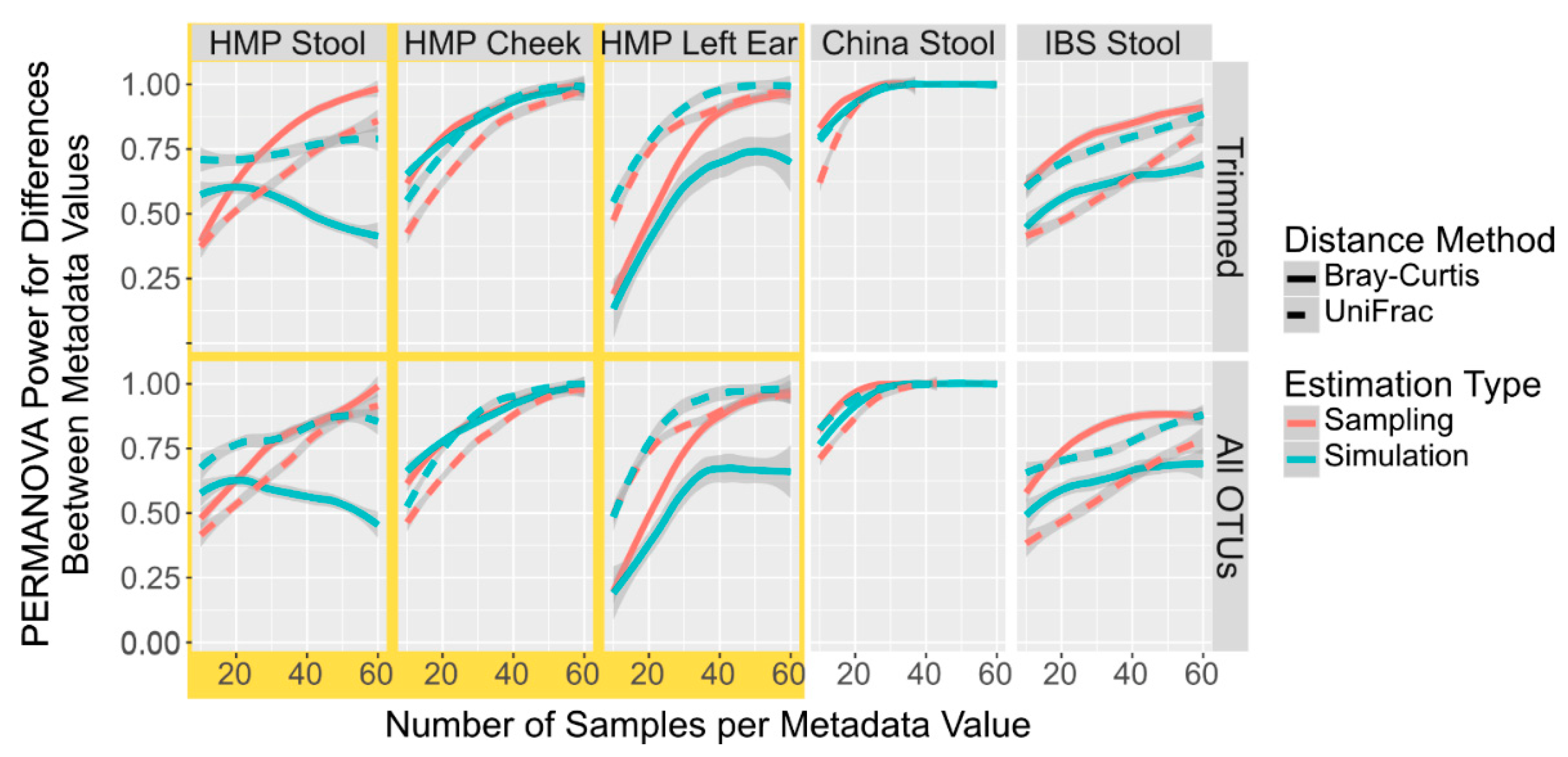
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison of Body Sites and OTU Tables in the Simulation versus Sampling
3.2. Simulation of OTU Tables Underestimates the Number of Samples to Reach the Power Calculation
3.3. Sampling versus Simulating after Identifying Discriminating Taxa with DESeq2
3.4. Using Simulation to Extend Small Sample Data
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Availability and Requirements
Consent for Publication
Abbreviations
References
- Watanabe, H.; Nakamura, I.; Mizutani, S.; Kurokawa, Y.; Mori, H.; Kurokawa, K.; Yamada, T. Minor taxa in human skin microbiome contribute to the personal identification. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmedes, S.E.; Woerner, A.E.; Novroski, N.M.; Wendt, F.R.; King, J.L.; Stephens, K.M.; Budowle, B. Targeted sequencing of clade-specific markers from skin microbiomes for forensic human identification. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2018, 32, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkac, L.; Clarke, T.H.; Singh, H.; Greco, C.; Gomez, A.; Torralba, M.G.; Frank, B.; Nelson, K.E. Spatial and Environmental Variation of the Human Hair Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.Z.; He, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lin, Q.; Nie, Y.; Li, M.; Zhi, F.; Liu, S.; et al. Gut Microbiota Offers Universal Biomarkers across Ethnicity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Diagnosis and Infliximab Response Prediction. Msystems 2018, 3, e00188-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton-Marcell, J.T.; Lopez, J.V.; Gilbert, J.A. The human microbiome: An emerging tool in forensics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, J.L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Bouslimani, A.; Dorrestein, P.; Carter, D.O.; Knight, R. Microbiome Tools for Forensic Science. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.H.; Gomez, A.; Singh, H.; Nelson, K.E.; Brinkac, L.M. Integrating the microbiome as a resource in the forensics toolkit. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2017, 30, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Peters, B.A.; Dominianni, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pei, Z.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Purdue, M.P.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; et al. Cigarette smoking and the oral microbiome in a large study of American adults. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2435–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, X.C.; Tickle, T.; Sokol, H.; Gevers, D.; Devaney, K.L.; Ward, D.V.; Reyes, J.A.; Shah, S.A.; Leleiko, N.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.A.; Dominianni, C.; Shapiro, J.A.; Church, T.R.; Wu, J.; Miller, G.; Yuen, E.; Freiman, H.; Lustbader, I.; Salik, J.; et al. The gut microbiota in conventional and serrated precursors of colorectal cancer. Microbiome 2016, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rensburg, J.J.; Lin, H.; Gao, X.; Toh, E.; Fortney, K.R.; Ellinger, S.; Zwickl, B.; Janowicz, D.M.; Katz, B.P.; Nelson, D.E.; et al. The Human Skin Microbiome Associates with the Outcome of and Is Influenced by Bacterial Infection. mBio 2015, 6, e01315-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.; Brinkac, L.; Greco, C.; Alleyne, A.T.; Carrasco, P.; Inostroza, C.; Tau, T.; Wisitrasameewong, W.; Torralba, M.G.; Nelson, K.; et al. Sampling from Four Geographically Divergent Young Female Populations Demonstrates Forensic Geolocation Potential in Microbiomes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A New Phylogenetic Method for Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Sun, J. Hypothesis testing and statistical analysis of microbiome. Genes Dis. 2017, 4, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Hofstaedter, C.E.; Zhao, C.; Mattei, L.; Tanes, C.; Clarke, E.; Lauder, A.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Chehoud, C.; Kelsen, J.; et al. Optimizing methods and dodging pitfalls in microbiome research. Microbiome 2017, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.J.; Gross, R.; Bittinger, K.; Sherrill-Mix, S.; Lewis, J.D.; Collman, R.G.; Bushman, F.D.; Li, H. Power and sample-size estimation for microbiome studies using pairwise distances and PERMANOVA. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiello, F.; Verbist, B.; Faust, K.; Raes, J.; Shannon, W.D.; Bijnens, L.; Thas, O. A web application for sample size and power calculation in case-control microbiome studies. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2038–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, P.S.; Brooks, J.P.; Deych, E.; Boone, E.L.; Edwards, D.J.; Wang, Q.; Sodergren, E.; Weinstock, G.; Shannon, W.D. Hypothesis Testing and Power Calculations for Taxonomic-Based Human Microbiome Data. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Bravo, H.C.; Tom, J.; Paulson, J.N. MicrobiomeDASim: Simulating Longitudinal Differential Abundance for Microbiome Data. F1000Res 2020, 8, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L. Powmic: An R Package for Power Assessment in Microbiome Case–Control Studies. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 3563–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eastwood, A.; Bourdon, P.C.; Snowden, K.R.; Gore, C.J. Detraining Decreases Hbmass of Triathletes. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2012, 33, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, H. A Dirichlet-tree multinomial regression model for associating dietary nutrients with gut microorganisms. Biometrics 2017, 73, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Chen, J.; Fung, W.K.; Li, H. A Logistic Normal Multinomial Regression Model for Microbiome Compositional Data Analysis. Biometrics 2013, 69, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bartow-McKenney, C.; Meisel, J.S.; Grice, E.A. HmmUFOtu: An HMM and phylogenetic placement based ultra-fast taxonomic assignment and OTU picking tool for microbiome amplicon sequencing studies. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Revell, L.J. phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2—Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; Chinwalla, A.T.; Creasy, H.H.; Earl, A.M.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Fulton, R.S.; et al. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 2012, 486, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailman, M.D.; Feolo, M.; Jin, Y.; Kimura, M.; Tryka, K.; Bagoutdinov, R.; Hao, L.; Kiang, A.; Paschall, J.; Phan, L.; et al. The NCBI dbGaP database of genotypes and phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xue, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Cao, H.; et al. A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozuelo, M.; Panda, S.; Santiago, A.; Mendez, S.; Accarino, A.; Santos, J.; Guarner, F.; Azpiroz, F.; Manichanh, C. Reduction of butyrate- and methane-producing microorganisms in patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tap, J.; Derrien, M.; Törnblom, H.; Brazeilles, R.; Cools-Portier, S.; Doré, J.; Störsrud, S.; Le Nevé, B.; Öhman, L.; Simrén, M. Identification of an Intestinal Microbiota Signature Associated With Severity of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 111–123.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, I.M.; Ringel-Kulka, T.; Siddle, J.P.; Ringel, Y. Alterations in composition and diversity of the intestinal microbiota in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2012, 24, 521-e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; Souza, M.D.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of Phylogenetics and Evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Paul, S.; Dutta, C. Geography, Ethnicity or Subsistence-Specific Variations in Human Microbiome Composition and Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clarke, T.H.; Greco, C.; Brinkac, L.; Nelson, K.E.; Singh, H. MPrESS: An R-Package for Accurately Predicting Power for Comparisons of 16S rRNA Microbiome Taxa Distributions including Simulation by Dirichlet Mixture Modeling. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051166
Clarke TH, Greco C, Brinkac L, Nelson KE, Singh H. MPrESS: An R-Package for Accurately Predicting Power for Comparisons of 16S rRNA Microbiome Taxa Distributions including Simulation by Dirichlet Mixture Modeling. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(5):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051166
Chicago/Turabian StyleClarke, Thomas H., Chris Greco, Lauren Brinkac, Karen E. Nelson, and Harinder Singh. 2023. "MPrESS: An R-Package for Accurately Predicting Power for Comparisons of 16S rRNA Microbiome Taxa Distributions including Simulation by Dirichlet Mixture Modeling" Microorganisms 11, no. 5: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051166
APA StyleClarke, T. H., Greco, C., Brinkac, L., Nelson, K. E., & Singh, H. (2023). MPrESS: An R-Package for Accurately Predicting Power for Comparisons of 16S rRNA Microbiome Taxa Distributions including Simulation by Dirichlet Mixture Modeling. Microorganisms, 11(5), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11051166





