Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
2.2. Species Identification of the Isolates
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Definition of MDR-AB, XDR-AB and PDR-AB Isolates
2.5. DNA Isolation
2.6. PCR-Based Screening for Antimicrobial Resistance Genes (ARGs)
2.7. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS)
2.8. Draft Genome Assembly
2.9. Resistome and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) Analyses
2.10. Phylogenomic Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of the Investigated A. baumannii Isolates
3.2. PCR Screening for ARGs
3.3. Draft Genome Assemblies: Evaluation and Comparison
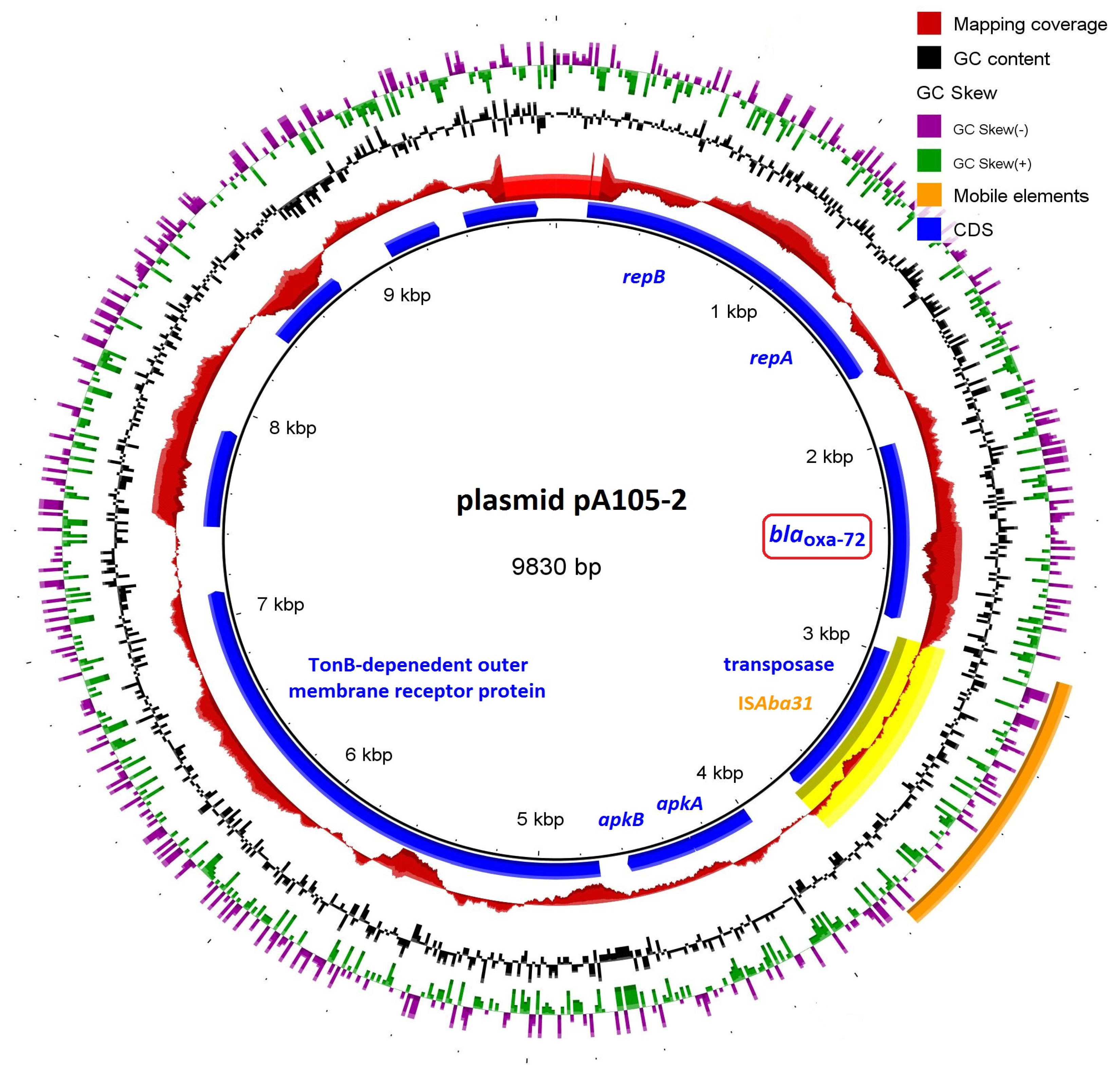
3.4. Resistome Analysis
3.5. MLST Analysis
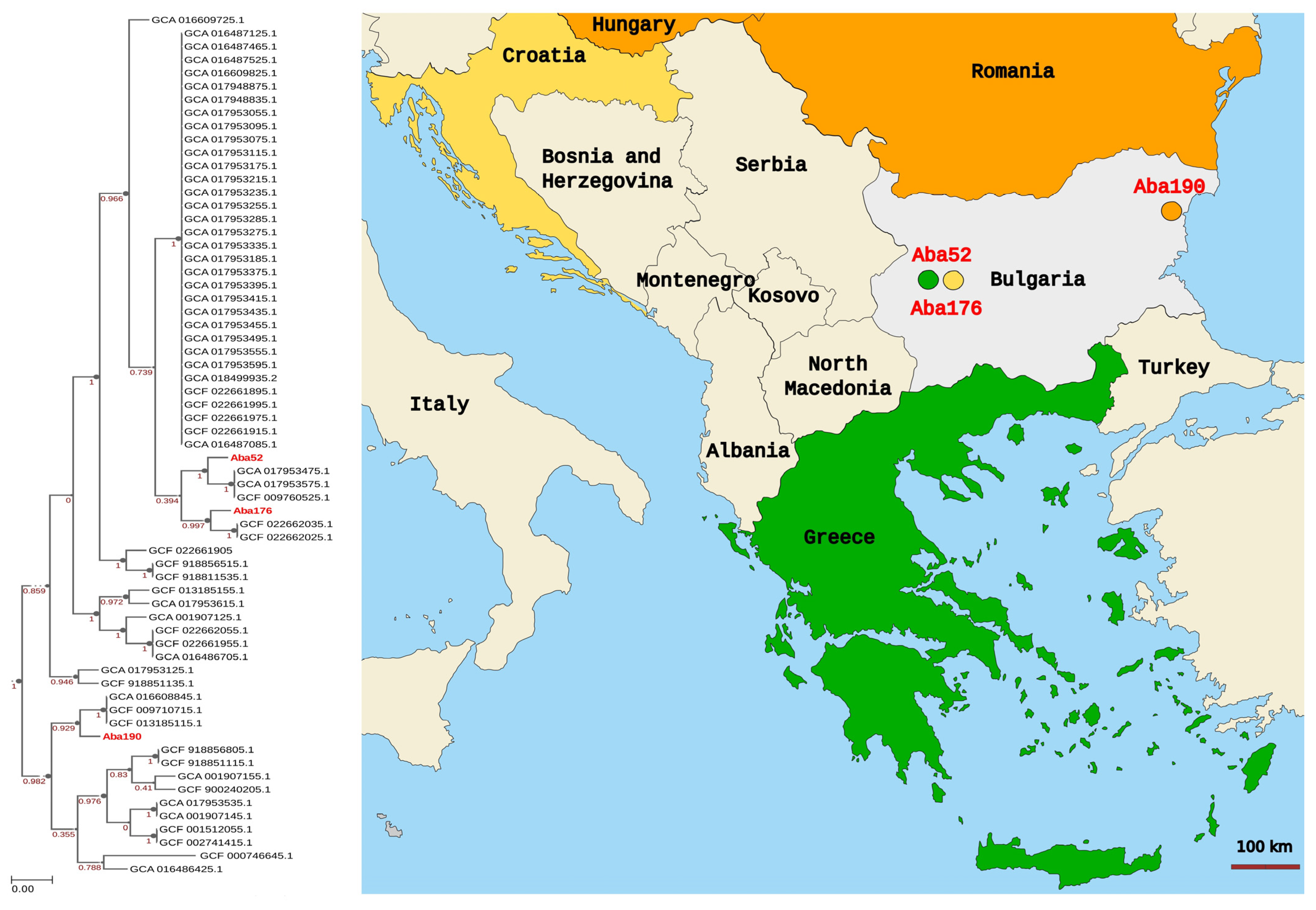
3.6. Phylogenomic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Oliveira, D.M.P.; Forde, B.M.; Kidd, T.J.; Harris, P.N.A.; Schembri, M.A.; Beatson, S.A.; Paterson, D.L.; Walker, M.J. Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00181-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orosz, L.; Lengyel, G.; Ánosi, N.; Lakatos, L.; Burián, K. Changes in Resistance Pattern of ESKAPE Pathogens between 2010 and 2020 in the Clinical Center of University of Szeged, Hungary. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moubareck, C.A.; Halat, D.H. Insights into Acinetobacter baumannii: A Review of Microbiological, Virulence, and Resistance Traits in a Threatening Nosocomial Pathogen. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, J.P.; Zhanel, G.G.; Clark, N.M. Infections Due to Acinetobacter baumannii in the ICU: Treatment Options. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 38, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, X.; Xu, C.F.; Bilya, S.R.; Xu, W. Mechanical Ventilation-Associated Pneumonia Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii in Northeast China Region: Analysis of Genotype and Drug Resistance of Bacteria and Patients’ Clinical Features over 7 Years. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zeng, W.; Xu, Y.; Liao, W.; Xu, W.; Zhou, T.; Cao, J.; Chen, L. Bloodstream Infections Caused by ST2 Acinetobacter baumannii: Risk Factors, Antibiotic Regimens, and Virulence over 6 Years Period in China. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Guerra, G.; Heras-Cañas, V.; Gutiérrez-Soto, M.; del Pilar Aznarte-Padial, M.; Expósito-Ruiz, M.; Navarro-Marí, J.M.; Fernández, J.G. Urinary Tract Infection by Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Evolution of Antimicrobial Resistance and Therapeutic Alternatives. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Hu, Z.; Hu, F. Nosocomial Meningitis Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii: Risk Factors and Their Impact on Patient Outcomes and Treatments. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, C.; Murray, G.L.; Paulsen, I.T.; Peleg, A.Y. Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii: Clinical Characteristics, Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Zhu, H.; Gao, B.; Weng, H.; Ding, Z.; Li, M.; Weng, X.; He, G. Diagnosis of Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii through Next-Generation Sequencing: A Case Report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.T.; Wang, Y.C.; Kuo, S.C.; Shih, F.H.; Chen, T.L.; How, C.K.; Yang, Y.S.; Lee, Y.T. Community-Acquired Bloodstream Infections Caused by Acinetobacter baumannii: A Matched Case–Control Study. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, K.; Chagas, T.P.G.; De-Simone, S.G. Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in Times of COVID-19 Pandemic. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Hua, M.; Liu, X.; Du, C.; Pu, L.; Xiang, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, J. Bacterial and Fungal Co-Infections among COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care Unit. Microbes Infect. 2021, 23, 104806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alenazi, T.A.; Bin Shaman, M.S.; Suliman, D.M.; Alanazi, T.A.; Altawalbeh, S.M.; Alshareef, H.; Lahreche, D.I.; Al-Azzam, S.; Araydah, M.; Karasneh, R.; et al. The Impact of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infection in Critically Ill Patients with or without COVID-19 Infection. Healthcare 2023, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperaki, E.T.; Tzouvelekis, L.S.; Miriagou, V.; Daikos, G.L. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: In Pursuit of an Effective Treatment. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.; Joshi, S.G. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii, and Their Importance in Hospital-Acquired Infections: A Scientific Review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 2715–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacconelli, E.; Carrara, E.; Savoldi, A.; Harbarth, S.; Mendelson, M.; Monnet, D.L.; Pulcini, C.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kluytmans, J.; Carmeli, Y.; et al. Discovery, Research, and Development of New Antibiotics: The WHO Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Tuberculosis. Lancet. Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assimakopoulos, S.F.; Karamouzos, V.; Lefkaditi, A.; Sklavou, C.; Kolonitsiou, F.; Christofidou, M.; Fligou, F.; Gogos, C.; Marangos, M. Triple Combination Therapy with High-Dose Ampicillin/Sulbactam, High-Dose Tigecycline and Colistin in the Treatment of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Caused by Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A Case Series Study. Le Infez. Med. 2019, 27, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanakos, G.; Andrianopoulos, I.; Papathanasiou, A.; Koulenti, D.; Gartzonika, K.; Koulouras, V. Pandrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Treatment: Still a Debatable Topic with No Definite Solutions. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: Mechanisms and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnier, P.D.; Poirel, L.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Worldwide Dissemination of the blaOXA-23 Carbapenemase Gene of Acinetobacter baumannii. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Naas, T.; Nordmann, P. Diversity, Epidemiology, and Genetics of Class D Beta-Lactamases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słoczyńska, A.; Wand, M.E.; Tyski, S.; Laudy, A.E. Analysis of blaCHDL Genes and Insertion Sequences Related to Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains Isolated in Warsaw, Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, M.; Park, K.S.; Bae, I.K.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Biology of Acinetobacter baumannii: Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance Mechanisms, and Prospective Treatment Options. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyanev, T.; Xavier, B.B.; García-Castillo, M.; Lammens, C.; Bravo-Ferrer Acosta, J.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Cantón, R.; Glupczynski, Y.; Goossens, H. Phenotypic and Molecular Characterizations of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Collected within the EURECA Study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, K.; Kenyon, J.J.; Hamidian, M.; Schultz, M.B.; Pickard, D.J.; Dougan, G.; Hall, R. Five Decades of Genome Evolution in the Globally Distributed, Extensively Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Global Clone 1. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrilli, R.; Pournaras, S.; Giannouli, M.; Tsakris, A. Global Evolution of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clonal Lineages. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2013, 41, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hassan, L.; Elbadawi, H.; Osman, E.; Ali, S.; Elhag, K.; Cantillon, D.; Wille, J.; Seifert, H.; Higgins, P.G. Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii From Khartoum State, Sudan. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 628736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.G.; Dammhayn, C.; Hackel, M.; Seifert, H. Global Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidian, M.; Nigro, S.J. Emergence, Molecular Mechanisms and Global Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.G.; Wisplinghoff, H.; Krut, O.; Seifert, H. A PCR-Based Method to Differentiate between Acinetobacter baumannii and Acinetobacter Genomic Species 13TU. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Gunturu, S.; Harvey, W.T.; Rosselló-Mora, R.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The Microbial Genomes Atlas (MiGA) Webserver: Taxonomic and Gene Diversity Analysis of Archaea and Bacteria at the Whole Genome Level. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W282–W288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 9.0. 2019. Available online: http://www.eucast.org (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 29th ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodford, N.; Ellington, M.J.; Coelho, J.M.; Turton, J.F.; Ward, M.E.; Brown, S.; Amyes, S.G.B.; Livermore, D.M. Multiplex PCR for Genes Encoding Prevalent OXA Carbapenemases in Acinetobacter Spp. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 27, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.G.; Lehmann, M.; Seifert, H. Inclusion of OXA-143 Primers in a Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for Genes Encoding Prevalent OXA Carbapenemases in Acinetobacter Spp. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, P.G.; Pérez-Llarena, F.J.; Zander, E.; Fernández, A.; Bou, G.; Seifert, H. OXA-235, a Novel Class D β-Lactamase Involved in Resistance to Carbapenems in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2121–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, H.; Garny, S.; Elisha, B.G. Is ISABA-1 Customized for Acinetobacter? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 243, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Walsh, T.R.; Cuvillier, V.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Acquired Carbapenemase Genes. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2011, 70, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lixandru, B.E.; Cotar, A.I.; Straut, M.; Usein, C.R.; Cristea, D.; Ciontea, S.; Tatu-Chitoiu, D.; Codita, I.; Rafila, A.; Nica, M.; et al. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in Romania: A Six-Month Survey. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e143214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Arakawa, Y. 16S Ribosomal RNA Methylation: Emerging Resistance Mechanism against Aminoglycosides. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbolla, R.; Catalano, M.; Orman, B.E.; Famiglietti, A.; Vay, C.; Smayevsky, J.; Centrón, D.; Piñeiro, S.A. Class 1 Integrons Increase Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole MICs against Epidemiologically Unrelated Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubenova, Y.; Hubenova, E.; Manasiev, Y.; Peykov, S.; Mitov, M. Draft Genome Sequence of Paenibacillus profundus YoMME, a New Exoelectrogenic Gram-Positive Bacterium. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2022, 11, e0023522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; Van Den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Ech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy Platform for Accessible, Reproducible and Collaborative Biomedical Analyses: 2018 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peykov, S.; Stratev, A.; Kirov, B.; Gergova, R.; Strateva, T. First Detection of a Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella aerogenes Isolate from a Critically Ill Patient with Septic Shock in Bulgaria. Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 2022, 69, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple Prokaryote Genome Comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.H.K.; Bortolaia, V.; Tansirichaiya, S.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Roberts, A.P.; Petersen, T.N. Detection of Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antibiotic Resistance in Salmonella Enterica Using a Newly Developed Web Tool: MobileElementFinder. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diancourt, L.; Passet, V.; Nemec, A.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Brisse, S. The Population Structure of Acinetobacter baumannii: Expanding Multiresistant Clones from an Ancestral Susceptible Genetic Pool. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, A.P.; Cottingham, R.W.; Henry, C.S.; Harris, N.L.; Stevens, R.L.; Maslov, S.; Dehal, P.; Ware, D.; Perez, F.; Canon, S.; et al. KBase: The United States Department of Energy Systems Biology Knowledgebase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, K.M.; Yoo, Y.S.; Yoo, J.S.; Yoo, J.I.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Chung, G.T. Alterations of GyrA, GyrB, and ParC and Activity of Efflux Pump in Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2011, 2, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabic, J.; Novovic, K.; Kekic, D.; Trudic, A.; Opavski, N.; Dimkic, I.; Jovcic, B.; Gajic, I. Comparative Genomics and Molecular Epidemiology of Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strateva, T.; Stoeva, T.; Savov, E.; Marteva-Proevska, Y.; Trifonova, A.; Stratev, A.; Velinov, T.; Mitov, I. Carbapenem-Non-Susceptible Nosocomial Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii with Multidrug Resistance (2014–2016): Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance and Treatment Recommendations. Meditsinski Pregl./Med. Rev. 2017, 53, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Hittle, L.E.; O’Hara, J.A.; Rivera, J.I.; Syed, A.; Shields, R.K.; Pasculle, A.W.; Ernst, R.K.; Doi, Y. Colistin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Beyond Carbapenem Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, J.R.; Smith, N.M.; Bulman, Z.P.; Tao, X.; Thamlikitkul, V.; Shin, B.S.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J.; Bulitta, J.B.; Tsuji, B.T. High-Dose Ampicillin-Sulbactam Combinations Combat Polymyxin-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a Hollow-Fiber Infection Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01268-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcone, M.; Tiseo, G.; Nicastro, M.; Leonildi, A.; Vecchione, A.; Casella, C.; Forfori, F.; Malacarne, P.; Guarracino, F.; Barnini, S.; et al. Cefiderocol as Rescue Therapy for Acinetobacter baumannii and Other Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Infections in Intensive Care Unit Patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 2021–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Taglietti, F.; Schiavone, F.; Petrosillo, N. Durlobactam in the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifert, H.; Müller, C.; Stefanik, D.; Higgins, P.G.; Miller, A.; Kresken, M. In Vitro Activity of Sulbactam/Durlobactam against Global Isolates of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2616–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, S.M.; Shapiro, A.B.; Moussa, S.H.; Johnstone, M.; McLaughlin, R.E.; De Jonge, B.L.M.; Millera, A.A. Frequency and Mechanism of Spontaneous Resistance to Sulbactam Combined with the Novel β-Lactamase Inhibitor ETX2514 in Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01576-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusradze, I.; Karumidze, N.; Rigvava, S.; Dvalidze, T.; Katsitadze, M.; Amiranashvili, I.; Goderdzishvili, M. Characterization and Testing the Efficiency of Acinetobacter baumannii Phage VB-GEC_Ab-M-G7 as an Antibacterial Agent. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Ryu, C.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, J.H.; Yong, D.; Lee, K. In Vivo Application of Bacteriophage as a Potential Therapeutic Agent To Control OXA-66-Like Carbapenemase-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Belonging to Sequence Type 357. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4200–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thummeepak, R.; Kitti, T.; Kunthalert, D.; Sitthisak, S. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Acinetobacter baumannii Bacteriophage ØABP-01 Endolysin (LysABP-01) in Combination with Colistin. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelenboom-Boskamp, A.; Haaijman, J.; Bos, M.; Saris, K.; Poot, E.; Voss, A.; Stobberingh, E.; Gorissen-Douven, E.; Molenaar, P.; Hoentjen, R.; et al. Dutch Guideline for Preventing Nosocomial Transmission of Highly-Resistant Micro-Organisms (HRMO) in Long-Term Care Facilities (LTCFs). Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strateva, T.; Sirakov, I.; Stoeva, T.; Stratev, A.; Dimov, S.; Savov, E.; Mitov, I. Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: Current Status of the Problem in Four Bulgarian University Hospitals (2014–2016). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratev, A.; Tanova, R.; Dimov, S.; Mitov, I.; Strateva, T. Clonal Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates among Bulgarian Critically Ill Patients Undergoing Renal Replacement Therapy (2016–2018). Infect. Dis. 2020, 52, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Li, T.; Fu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lan, P.; Zhao, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; et al. OXA-23 Is a Prevalent Mechanism Contributing to Sulbactam Resistance in Diverse Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 63, e01676-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Onofrio, V.; Conzemius, R.; Varda-Brkić, D.; Bogdan, M.; Grisold, A.; Gyssens, I.C.; Bedenić, B.; Barišić, I. Epidemiology of Colistin-Resistant, Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter baumannii in Croatia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 81, 104263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Pelegrin, A.C.; Perrot, N.; Mirande, C.; Blanc, B.; Legakis, N.; Goossens, H.; Rossolini, G.M.; van Belkum, A. Abundance of Colistin-Resistant, OXA-23- and ArmA-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii Belonging to International Clone 2 in Greece. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/antimicrobial-resistance-eueea-ears-net-annual-epidemiological-report-2020 (accessed on 14 February 2023).
- Lin, M.F.; Lan, C.Y. Antimicrobial Resistance in Acinetobacter baumannii: From Bench to Bedside. World J. Clin. Cases 2014, 2, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, T.; Higgins, P.G.; Bojkova, K.; Seifert, H. Clonal Spread of Carbapenem-Resistant OXA-23-Positive Acinetobacter baumannii in a Bulgarian University Hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, T.; Higgins, P.G.; Savov, E.; Markovska, R.; Mitov, I.; Seifert, H. Nosocomial Spread of OXA-23 and OXA-58 β-Lactamase-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii in a Bulgarian Hospital. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strateva, T.; Markova, B.; Marteva-Proevska, Y.; Ivanova, D.; Mitov, I. Widespread Dissemination of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Producing OXA-23 Carbapenemase and ArmA 16S Ribosomal RNA Methylase in a Bulgarian University Hospital. Brazilian J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeva, T.; Higgins, P.; Bojkova, K.; Seifert, H. Molecular Epidemiology of Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates from Two Bulgarian Hospitals. Scr. Sci. Med. 2014, 46, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeifer, Y.; Trifonova, A.; Pietsch, M.; Brunner, M.; Todorova, I.; Gergova, I.; Wilharm, G.; Werner, G.; Savov, E. Clonal Transmission of Gram-Negative Bacteria with Carbapenemases NDM-1, VIM-1, and OXA-23/72 in a Bulgarian Hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Poirel, L.; Licker, M.; Nordmann, P. Genetic Diversity of Carbapenem-Hydrolysing β-Lactamases in Acinetobacter baumannii from Romanian Hospitals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeka, A.N.; Poirel, L.; Sipahi, O.R.; Bonnin, R.A.; Arda, B.; Özinel, M.; Ulusoy, S.; Bor, C.; Nordmann, P. GES-Type and OXA-23 Carbapenemase-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii in Turkey. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 1145–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcek, A.; Nesporova, K.; Whiteway, C.; De Pooter, T.; De Coster, W.; Strazisar, M.; Van der Henst, C. Genomic Analysis of a Strain Collection Containing Multidrug-, Extensively Drug-, Pandrug-, and Carbapenem-Resistant Modern Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e00892-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, B.; Velinov, T.; Ivanov, I.; Dobreva, E.; Kantardjiev, T. First Detection of OXA-24 Carbapenemase-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates in Bulgaria. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dortet, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Bernabeu, S.; Escaut, L.; Vittecoq, D.; Girlich, D.; Imanci, D.; Fortineau, N.; Naas, T. First Occurrence of OXA-72-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii in Serbia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5724–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, B.S.; Amyes, S.G.B. Role of ISAba1 and ISAba125 in Governing the Expression of Bla ADC in Clinically Relevant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Resistant to Cephalosporins. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Luan, G.; Wang, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Deng, S.; Ling, B.; Jia, X. Coexistence of BlaOXA-23 with ArmA in Quinolone-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from a Chinese University Hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 84, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, J.K.; Kim, M.J.; Pham, J.; Tapsall, J.; White, P.A. Antibiotic Resistance Determinants in Nosocomial Strains of Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Azimi, H. Dissemination of Classes 1, 2, and 3 Integrons in Acinetobacter baumannii Strains Recovered from Intensive Care Units Using Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2017, 10, 13100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenk, S.; Temkin, E.; Lurie-Weinberger, M.N.; Keren-Paz, A.; Rov, R.; Rakovitsky, N.; Wullfhart, L.; Nutman, A.; Daikos, G.L.; Skiada, A.; et al. Large-Scale WGS of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates Reveals Patterns of Dissemination of ST Clades Associated with Antibiotic Resistance. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 77, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherubini, S.; Perilli, M.; Segatore, B.; Fazii, P.; Parruti, G.; Frattari, A.; Amicosante, G.; Piccirilli, A. Whole-Genome Sequencing of ST2 A. baumannii Causing Bloodstream Infections in COVID-19 Patients. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajic, I.; Jovicevic, M.; Milic, M.; Kekic, D.; Opavski, N.; Zrnic, Z.; Dacic, S.; Pavlovic, L.; Mijac, V. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics of OXA-72-Producing Acinetobacter baumannii ST636 Outbreak at a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Serbia. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 112, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukovic, B.; Gajic, I.; Dimkic, I.; Kekic, D.; Zornic, S.; Pozder, T.; Radisavljevic, S.; Opavski, N.; Kojic, M.; Ranin, L. The First Nationwide Multicenter Study of Acinetobacter baumannii Recovered in Serbia: Emergence of OXA-72, OXA-23 and NDM-1-Producing Isolates. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer Pairs | Target | Sequence (5′–3′) a | Product Size (bp) | Ta (°C) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXA23LF b OXA23LR b | OXA-23-like CHDLs | GATCGGATTGGAGAACCAGA ATTTCTGACCGCATTTCCAT | 501 | 58.3 | [37] |
| OXA24LF b OXA24LR b | OXA-40/24-like CHDLs | GGTTAGTTGGCCCCCTTAAA AGTTGAGCGAAAAGGGGATT | 246 | 58.3 | [37] |
| OXA51LF b OXA51LR b | OXA-51-like CHDLs | TAATGCTTTGATCGGCCTTG TGGATTGCACTTCATCTTGG | 353 | 58.3 | [37] |
| OXA58LF b OXA58LR b | OXA-58-like CHDLs | AAGTATTGGGGCTTGTGCTG CCCCTCTGCGCTCTACATAC | 599 | 58.3 | [37] |
| OXA143F OXA143R | OXA-143-like CHDLs | TGGCACTTTCAGCAGTTCCT TAATCTTGAGGGGGCCAACC | 146 | 60 | [38] |
| OXA235F OXA235R | OXA-235-like CHDLs | TTGTTGCCTTTACTTAGTTGC CAAAATTTTAAGACGGATCG | 768 | 56 | [39] |
| ISAba1F ISAba1R | ISAba1 | CACGAATGCAGAAGTTG CGACGAATACTATGACAC | 549 | 50 | [40] |
| IMP-F c IMP-R c | IMP-type MBLs | GGAATAGAGTGGCTTAAYTCTC GGTTTAAYAAAACAACCACC | 232 | 58.5 | [41] |
| VIM-F c VIM-R c | VIM-type MBLs | GATGGTGTTTGGTCGCATA CGAATGCGCAGCACCAG | 390 | 58.5 | [41] |
| NDM-F c NDM-R c | NDM-type MBLs | GGTTTGGCGATCTGGTTTTC CGGAATGGCTCATCACGATC | 621 | 58.5 | [41] |
| KPC-F KPC-R | KPC-type class A carbapenemases | CTGTCTTGTCTCTCATGGCC CCTCGCTGTRCTTGTCATCC | 796 | 60 | [42] |
| ArmA-F ArmA-R | ArmA 16S rRNA methylase | ATTCTGCCTATCCTAATTGG ACCTATACTTTATCGTCGTC | 315 | 56 | [43] |
| Sul1-F Sul1-R | Dihydropteroate synthase type I | ACGGTGTTCGGCATTCT TTTGAAGGTTCGACAGC | 581 | 53 | [44] |
| Isolate No. | Origin | Hospital | Year | Antimicrobial Agent: MIC [mg/l] (Interpretation) | PCR-Detected ARGs | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMP | MEM | AMK | GEN | TOB | LVX | TGC | SXT | COL | |||||
| Aba52 | Blood | SIR-S | 2018 | >32 (R) | >32 (R) | >256 (R) | >256 (R) | >256 (R) | 24 (R) | 2 (R) | >256 (R) | 1 (S) | blaOXA-51-like, blaOXA-23-like, armA, sul1 |
| Aba176 | TBA | SIR-S | 2019 | 16 (R) | >32 (R) | >256 (R) | >256 (R) | >256 (R) | 16 (R) | 1.5 (R) | >256 (R) | 1 (S) | blaOXA-51-like, blaOXA-23-like, armA, sul1 |
| Aba190 | TBA | SM-V | 2019 | >32 (R) | >32 (R) | 48 (R) | 8 (R) | 6 (R) | 8 (R) | 1.5 (R) | 128 (R) | 1 (S) | blaOXA-51-like, blaOXA-23-like, blaOXA-24/40-like, sul1 |
| Isolate | Genome Size (Mbp) | GC% | N50 (bp) | No. of Contigs | ST | Alleles | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cnp60 | fusA | gltA | pyrG | recA | rplB | rpoB | ||||||
| Aba52 | 3.96 | 38.9 | 122,028 | 109 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Aba176 | 3.97 | 38.9 | 83,512 | 131 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Aba190 | 4.14 | 38.9 | 92,248 | 182 | 636 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| ARGs/MGEs | Aba52 | Aba176 | Aba190 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGEs | ISAba24, ISAba125, ISVsa3, IS6100 | ISAba24, ISAba125, ISVsa3, IS6100 | Tn6018, ISAba31, IS17 |
| β-Lactam Resistance | blaADC-25, blaOXA-23, blaOXA-66 | blaADC-25, blaOXA-23, blaOXA-66 | blaADC-25, blaOXA-23, blaOXA-66, blaOXA-72 |
| Aminoglycoside Resistance | armA, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, aac(3)-Ia, ant(3″)-IIa, aadA1 | armA, aph(3′)-VIa, aph(3″)-Ib, aph(6)-Id, aac(3)-Ia, ant(3″)-IIa, aadA1 | aph(3′)-Ia, aph(3′)-VIa, aac(3)-Ia, ant(3″)-IIa, aadA1 |
| Macrolide Resistance | mph(E), msr(E) | mph(E), msr(E) | mph(E), msr(E) |
| Others | sul1, tet(B), catA1 | sul1, tet(B), catA1 | sul1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strateva, T.V.; Sirakov, I.; Stoeva, T.J.; Stratev, A.; Peykov, S. Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040875
Strateva TV, Sirakov I, Stoeva TJ, Stratev A, Peykov S. Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(4):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040875
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrateva, Tanya V., Ivo Sirakov, Temenuga J. Stoeva, Alexander Stratev, and Slavil Peykov. 2023. "Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients" Microorganisms 11, no. 4: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040875
APA StyleStrateva, T. V., Sirakov, I., Stoeva, T. J., Stratev, A., & Peykov, S. (2023). Phenotypic and Molecular Characteristics of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Isolates from Bulgarian Intensive Care Unit Patients. Microorganisms, 11(4), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11040875








