Rapeseed Domestication Affects the Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbiota
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Cultivation and Soil Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis on 16S rRNA Gene Profiling
2.4. Core Microbial Analysis
2.5. Rhizosphere Microbiota Functional Prediction and Co-Occurrence Network Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rhizosphere Microbiota Diversity of B. oleracea, B. rapa, and B. napus
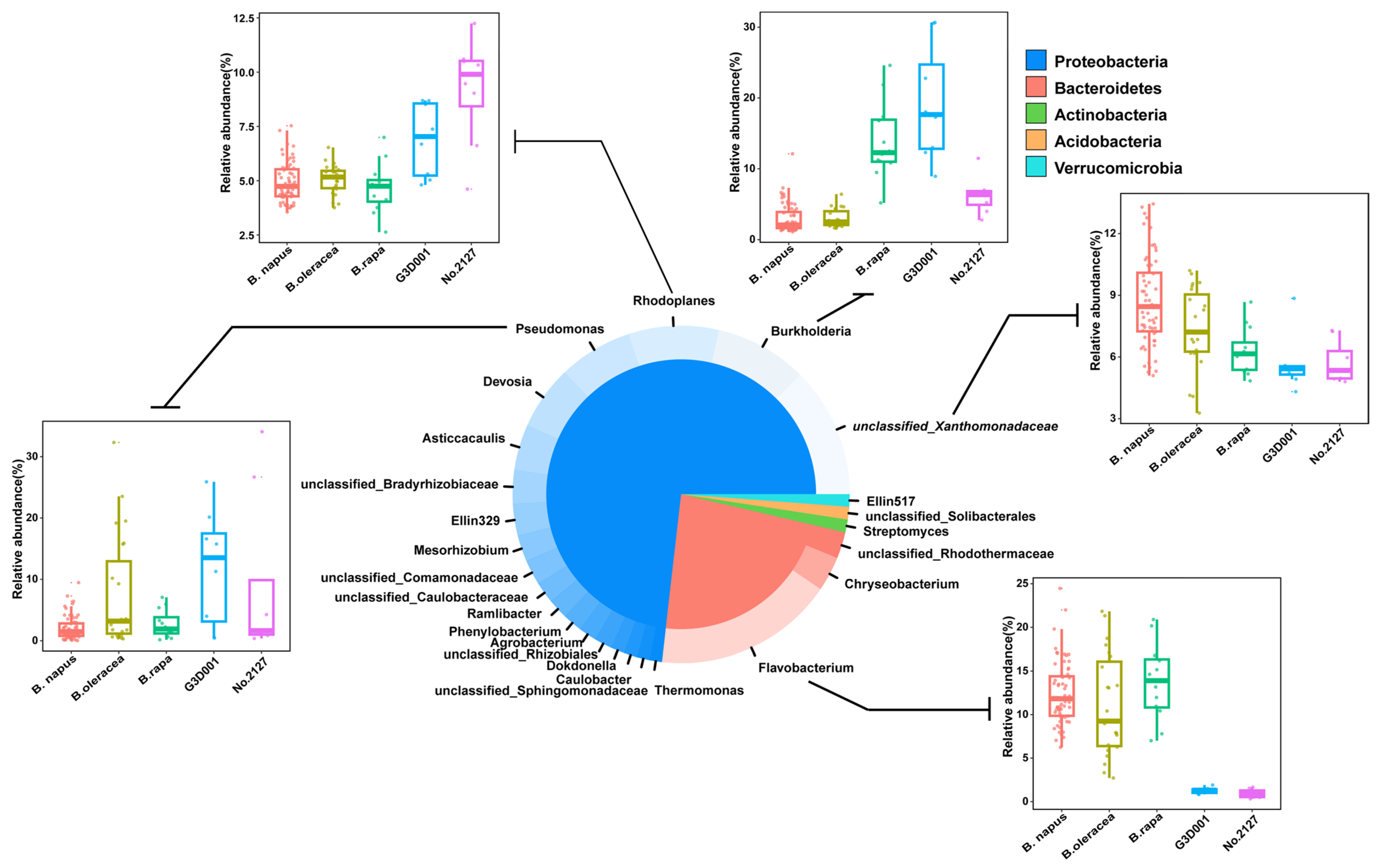
3.2. Taxonomic Structure of the Rhizosphere Microbiota of B. oleracea, B. rapa, and B. napus
3.3. Rhizosphere Core Microbiota Communities of B. napus, B. oleracea, and B. rapa
3.4. Synthetic B. napus Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities Have Higher Nitrogen Metabolism Capacity
3.5. Co-Occurrence Analysis of B. napus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bulgarelli, D.; Schlaeppi, K.; Spaepen, S.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and Functions of the Bacterial Microbiota of Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2013, 64, 807–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Leach, J.E.; Tringe, S.G.; Sa, T.M.; Singh, B.K. Plant-microbiome interactions: From community assembly to plant health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillo, G.; Teixeira, P.J.P.L.; Paredes, S.H.; Law, T.F.; de Lorenzo, L.; Feltcher, M.E.; Finkel, O.M.; Breakfield, N.W.; Mieczkowski, P.; Jones, C.D.; et al. Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity. Nature 2017, 543, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Muller, D.B.; Srinivas, G.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Potthoff, E.; Rott, M.; Dombrowski, N.; Munch, P.C.; Spaepen, S.; Remus-Emsermann, M.; et al. Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Rott, M.; Schlaeppi, K.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Ahmadinejad, N.; Assenza, F.; Rauf, P.; Huettel, B.; Reinhardt, R.; Schmelzer, E.; et al. Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 2012, 488, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenhausen, N.; Horton, M.W.; Bergelson, J. Bacterial Communities Associated with the Leaves and the Roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, M.W.; Bodenhausen, N.; Beilsmith, K.; Meng, D.Z.; Muegge, B.D.; Subramanian, S.; Vetter, M.M.; Vilhjalmsson, B.J.; Nordborg, M.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Genome-wide association study of Arabidopsis thaliana leaf microbial community. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaeppi, K.; Dombrowski, N.; Oter, R.G.; van Themaat, E.V.L.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Quantitative divergence of the bacterial root microbiota in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarelli, D.; Garrido-Oter, R.; Munch, P.C.; Weiman, A.; Droge, J.; Pan, Y.; McHardy, A.C.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Structure and Function of the Bacterial Root Microbiota in Wild and Domesticated Barley. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiffer, J.A.; Spor, A.; Koren, O.; Jin, Z.; Tringe, S.G.; Dangl, J.L.; Buckler, E.S.; Ley, R.E. Diversity and heritability of the maize rhizosphere microbiome under field conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6548–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.A.; Jin, Z.; Youngblut, N.; Wallace, J.G.; Sutter, J.; Zhang, W.; Gonzalez-Pena, A.; Peiffer, J.; Koren, O.; Shi, Q.J.; et al. Large-scale replicated field study of maize rhizosphere identifies heritable microbes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7368–7373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, J.; Johnson, C.; Santos-Medellin, C.; Lurie, E.; Podishetty, N.K.; Bhatnagar, S.; Eisen, J.A.; Sundaresan, V. Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E911–E920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knief, C.; Delmotte, N.; Chaffron, S.; Stark, M.; Innerebner, G.; Wassmann, R.; von Mering, C.; Vorholt, J.A. Metaproteogenomic analysis of microbial communities in the phyllosphere and rhizosphere of rice. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, L.W.; Kuramae, E.E.; Navarrete, A.A.; van Veen, J.A.; Tsai, S.M. Taxonomical and functional microbial community selection in soybean rhizosphere. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, S.; Mohammadi, S.A.; Salekdeh, G.H. Changes in root microbiome during wheat evolution. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, D.B.; Vogel, C.; Bai, Y.; Vorholt, J.A. The Plant Microbiota: Systems-Level Insights and Perspectives. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome (vol 348, 1260782, 2014). Science 2014, 345, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wei, L.J.; Li, X.L.; Wang, Y.T.; Wu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.Y.; Xiao, Z.C.; Jian, H.J.; et al. Whole-genome resequencing reveals Brassica napus origin and genetic loci involved in its improvement. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.D.; Zhang, W.S.; Zhang, Y.K.; Chang, S.H.; Chen, L.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.D.; Shen, J.X.; Meng, J.L.; Zou, J. Reconstituting the genome of a young allopolyploid crop, Brassica napus, with its related species. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bus, A.; Korber, N.; Snowdon, R.J.; Stich, B. Patterns of molecular variation in a species-wide germplasm set of Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, F.; Chen, B.Y.; Xu, K.; Yan, G.X.; Qiao, J.W.; Li, J.; Gao, G.Z.; Bancroft, I.; Meng, J.L.; et al. Genome-wide investigation of genetic changes during modern breeding of Brassica napus. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.W.; Qian, W.; Snowdon, R.J. Sub-genomic selection patterns as a signature of breeding in the allopolyploid Brassica napus genome. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Jaramillo, J.E.; de Hollander, M.; Ramirez, C.A.; Mendes, R.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Carrion, V.J. Deciphering rhizosphere microbiome assembly of wild and modern common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in native and agricultural soils from Colombia. Microbiome 2019, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.K.; Jeon, J.; Harris, W.A.; Lee, Y.H. Domestication of Oryza species eco-evolutionarily shapes bacterial and fungal communities in rice seed. Microbiome 2020, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullaeva, Y.; Ambika Manirajan, B.; Honermeier, B.; Schnell, S.; Cardinale, M. Domestication affects the composition, diversity, and co-occurrence of the cereal seed microbiota. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 31, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Jaramillo, J.E.; Mendes, R.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Impact of plant domestication on rhizosphere microbiome assembly and functions. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 90, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Jaramillo, J.E.; Carrion, V.J.; de Hollander, M.; Raaijmakers, J.M. The wild side of plant microbiomes. Microbiome 2018, 6, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Jaramillo, J.E.; Carrion, V.J.; Bosse, M.; Ferrao, L.F.V.; de Hollander, M.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Ramirez, C.A.; Mendes, R.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Linking rhizosphere microbiome composition of wild and domesticated Phaseolus vulgaris to genotypic and root phenotypic traits. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2244–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.M.; Guan, Z.L.; Hu, J.L.; Guo, C.C.; Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.X.; Wang, B.; Lu, S.P.; Zhou, R.; et al. Eight high-quality genomes reveal pan-genome architecture and ecotype differentiation of Brassica napus. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.Z.; Liang, Z.; Yan, T.; Xu, Y.; Xuan, L.J.; Tang, J.; Zhou, G.; Lohwasser, U.; Hua, S.J.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. Whole-Genome Resequencing of a Worldwide Collection of Rapeseed Accessions Reveals the Genetic Basis of Ecotype Divergence. Mol. Plant 2019, 12, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, I.; Mason, A.S.; Banga, S.; Bharti, S.; Kaur, B.; Gurung, A.M.; Salisbury, P.A.; Batley, J.; Banga, S.S. Cytogenetic and Molecular Characterization of B-Genome Introgression Lines of Brassica napus L. G3-Genes Genom. Genet. 2017, 7, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.M.; Fan, G.Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, Y.M.; Guan, M.; Tong, C.B.; Li, J.N.; Du, D.Z.; Qi, C.K.; Jiang, L.C.; et al. The high-quality genome of Brassica napus cultivar ‘ZS11’ reveals the introgression history in semi-winter morphotype. Plant J. 2017, 92, 452–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Y.; Heneen, W.K.; Jonsson, R. Resynthesis of Brassica napus L. through Interspecific Hybridization between Brassica alboglabra Bailey and B. campestris L. with Special Emphasis on Seed Color. Plant Breed. 1988, 101, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.J.; Kong, H.G.; Choi, K.; Kwon, S.K.; Song, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, P.A.; Choi, S.Y.; Seo, M.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Rhizosphere microbiome structure alters to enable wilt resistance in tomato (vol 36, pg 1100, 2018). Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.F.; Trivedi, P.; Riera, N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Fan, G.Y.; Tang, J.L.; Coletta, H.D.; et al. The structure and function of the global citrus rhizosphere microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahe, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. Peerj 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechin, A.; Boyarskikh, U.; Kel, A.; Filipenko, M. cutPrimers: A New Tool for Accurate Cutting of Primers from Reads of Targeted Next Generation Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2017, 24, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2 (vol 37, pg 852, 2019). Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Price, M.N.; Goodrich, J.; Nawrocki, E.P.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Probst, A.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Hugenholtz, P. An improved Greengenes taxonomy with explicit ranks for ecological and evolutionary analyses of bacteria and archaea. ISME J. 2012, 6, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation Evaluation and Phylogenetic Diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and qualitative beta diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2019. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. Stat. 2011, 174, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.; Widder, S. Deciphering microbial interactions and detecting keystone species with co-occurrence networks. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Alm, E.J. Inferring Correlation Networks from Genomic Survey Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, Z.D.; Muller, C.L.; Miraldi, E.R.; Littman, D.R.; Blaser, M.J.; Bonneau, R.A. Sparse and Compositionally Robust Inference of Microbial Ecological Networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media 2009, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 8, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar]
- De Mendiburu, F. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research; R Package Version 1.3-3. 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=agricolae (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Zhang, H.Y.; Shi, Y.C.; Dong, Y.X.; Lapen, D.R.; Liu, J.H.; Chen, W. Subsoiling and conversion to conservation tillage enriched nitrogen cycling bacterial communities in sandy soils under long-term maize monoculture. Soil Till Res. 2022, 215, 105197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, M.; Grube, M.; Erlacher, A.; Quehenberger, J.; Berg, G. Bacterial networks and co-occurrence relationships in the lettuce root microbiota. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, G.; Saxena, S.; Kumar, K.; Verma, A.; Sahu, P.K.; Pandey, A.; White, J.F.; Verma, S.K. Endophytic Burkholderia: Multifunctional roles in plant growth promotion and stress tolerance. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 265, 127201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannaa, M.; Park, I.; Seo, Y.S. Genomic Features and Insights into the Taxonomy, Virulence, and Benevolence of Plant-Associated Burkholderia Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.F.; Kvitko, B.; He, S.Y. Pseudomonas syringae: What it takes to be a pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado-Blanco, J.; Alos, E.; Rey, M.D.; Prieto, P. Pseudomonas fluorescens PICF7 displays an endophytic lifestyle in cultivated cereals and enhances yield in barley. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, G.; Kumar, K.; Verma, A.; Verma, S.K. Seed inhabiting bacterial endophytes of maize promote seedling establishment and provide protection against fungal disease. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 255, 126926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Flory, E.; Koyro, H.W.; Abideen, Z.; Schikora, A.; Suarez, C.; Schnell, S.; Cardinale, M. Consistent associations with beneficial bacteria in the seed endosphere of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 41, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.H.; Qian, W.; Zou, J.; Meng, J.L. Genetic dissection of intersubgenomic heterosis in Brassica napus carrying genomic components of B. rapa. Euphytica 2012, 184, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girke, A.; Schierholt, A.; Becker, H.C. Extending the rapeseed gene pool with resynthesized Brassica napus II: Heterosis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 124, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurgobin, B.; Golicz, A.A.; Bayer, P.E.; Chan, C.K.K.; Tirnaz, S.; Dolatabadian, A.; Schiessl, S.V.; Samans, B.; Montenegro, J.D.; Parkin, I.A.P.; et al. Homoeologous exchange is a major cause of gene presence/absence variation in the amphidiploid Brassica napus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malagoli, P.; Laine, P.; Rossato, L.; Ourry, A. Dynamics of nitrogen uptake and mobilization in field-grown winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus) from stem extension to harvest. II. An N-15-labelling-based simulation model of N partitioning between vegetative and reproductive tissues. Ann. Bot. 2005, 95, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Kindred, D.R. Analysing nitrogen responses of cereals to prioritize routes to the improvement of nitrogen use efficiency. J. Exp Bot 2009, 60, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathke, G.W.; Behrens, T.; Diepenbrock, W. Integrated nitrogen management strategies to improve seed yield, oil content and nitrogen efficiency of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.): A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 117, 80–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Ding, G.D.; Li, L.; Cai, H.M.; Ye, X.S.; Zou, J.; Xu, F.S. Identification and characterization of improved nitrogen efficiency in interspecific hybridized new-type Brassica napus. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, N.; Hu, B.; Jin, T.; Xu, H.R.; Qin, Y.; Yan, P.X.; Zhang, X.N.; Guo, X.X.; et al. NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malique, F.; Ke, P.; Boettcher, J.; Dannenmann, M.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Plant and soil effects on denitrification potential in agricultural soils. Plant Soil 2019, 439, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.S.; Liu, F.; Xu, S.J.; Wu, S.H.; Zhuang, G.Q.; Deng, Y.; Wu, J.S.; Zhuang, X.L. Myriophyllum aquaticum Constructed Wetland Effectively Removes Nitrogen in Swine Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Chang, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Ge, X.; Cheng, J.; Xie, J.; Lin, Y.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, D.; et al. Rapeseed Domestication Affects the Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbiota. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030724
Zhang Z, Chang L, Liu X, Wang J, Ge X, Cheng J, Xie J, Lin Y, Fu Y, Jiang D, et al. Rapeseed Domestication Affects the Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbiota. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(3):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030724
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhen, Lu Chang, Xiuxiu Liu, Jing Wang, Xianhong Ge, Jiasen Cheng, Jiatao Xie, Yang Lin, Yanping Fu, Daohong Jiang, and et al. 2023. "Rapeseed Domestication Affects the Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbiota" Microorganisms 11, no. 3: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030724
APA StyleZhang, Z., Chang, L., Liu, X., Wang, J., Ge, X., Cheng, J., Xie, J., Lin, Y., Fu, Y., Jiang, D., & Chen, T. (2023). Rapeseed Domestication Affects the Diversity of Rhizosphere Microbiota. Microorganisms, 11(3), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030724








