Retrospective Analysis of Leishmaniasis in Sicily (Italy) from 2013 to 2021: One-Health Impact and Future Control Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Clinical Samples
2.3. Diagnosis
2.4. Entomological Survey
2.5. Ethical Statement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
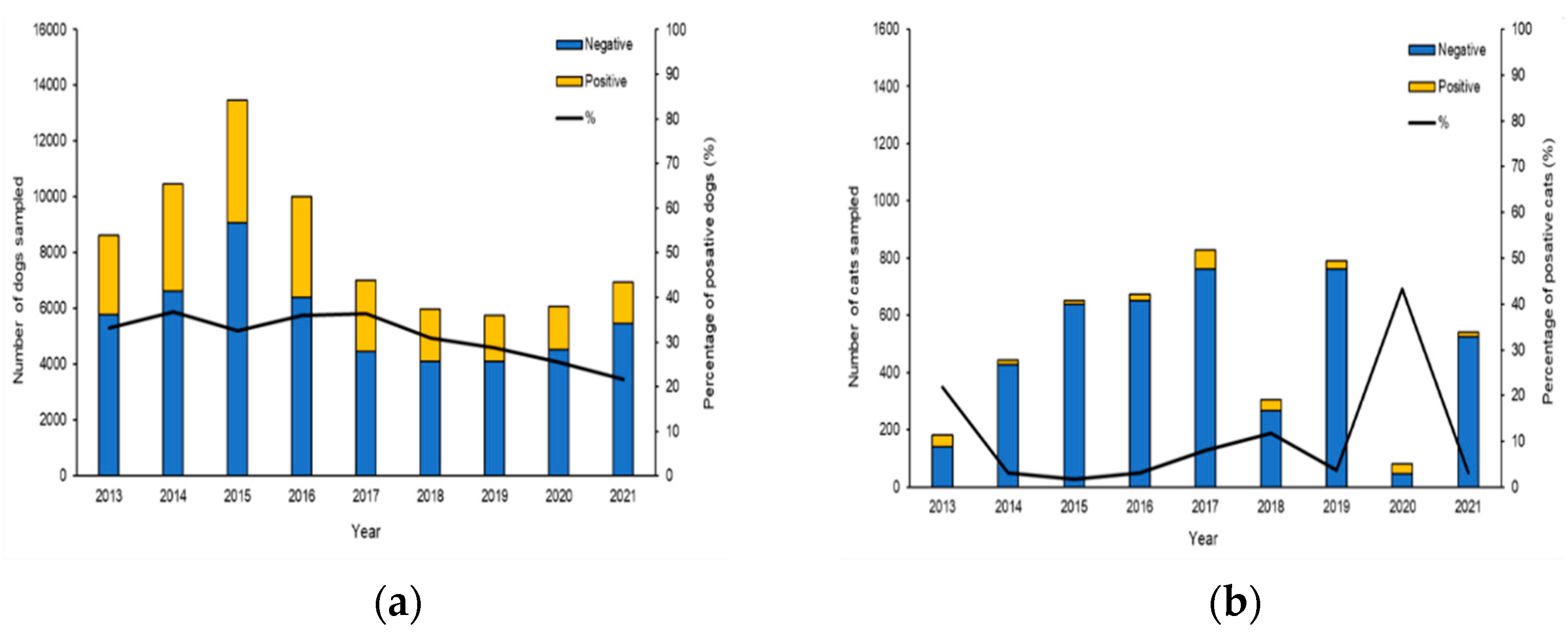
3.1. Canine and Feline Data
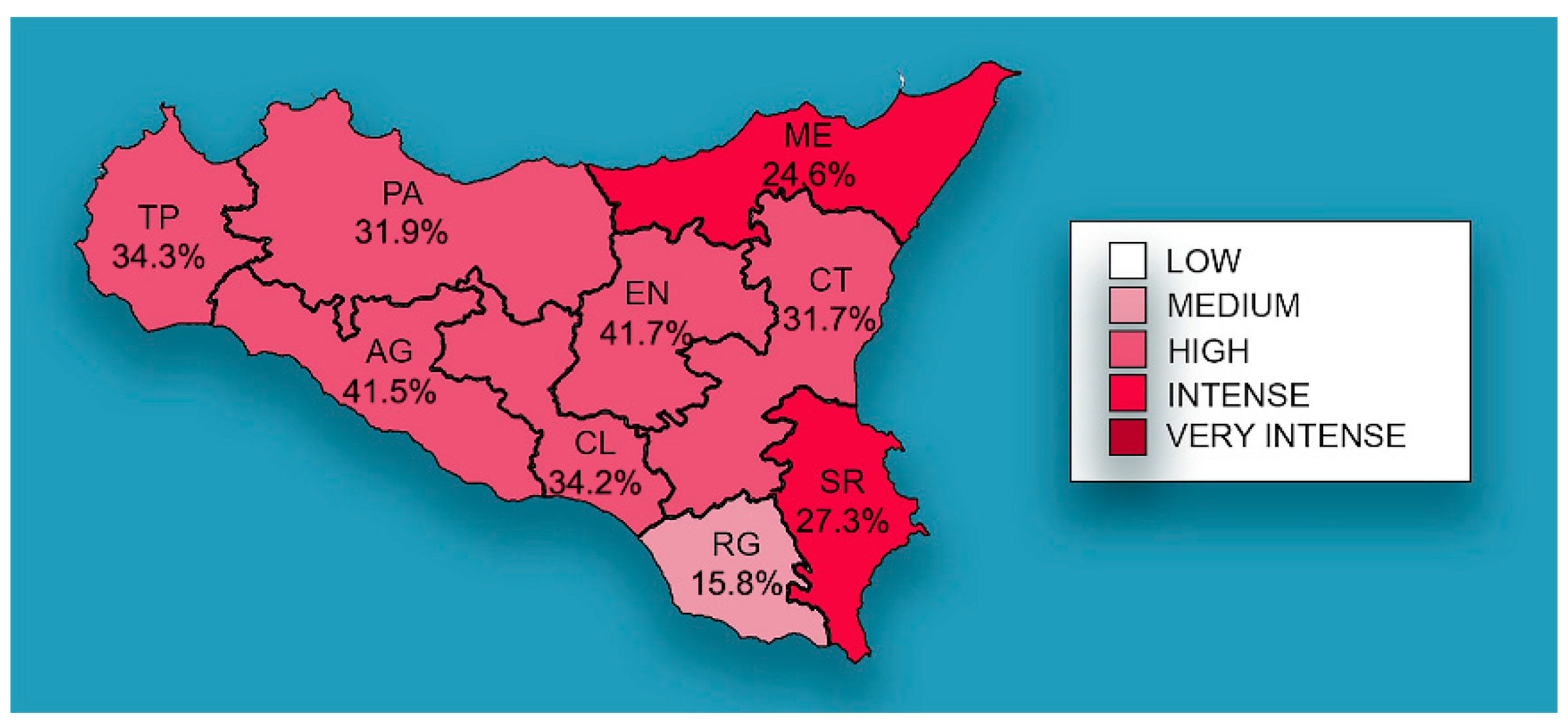
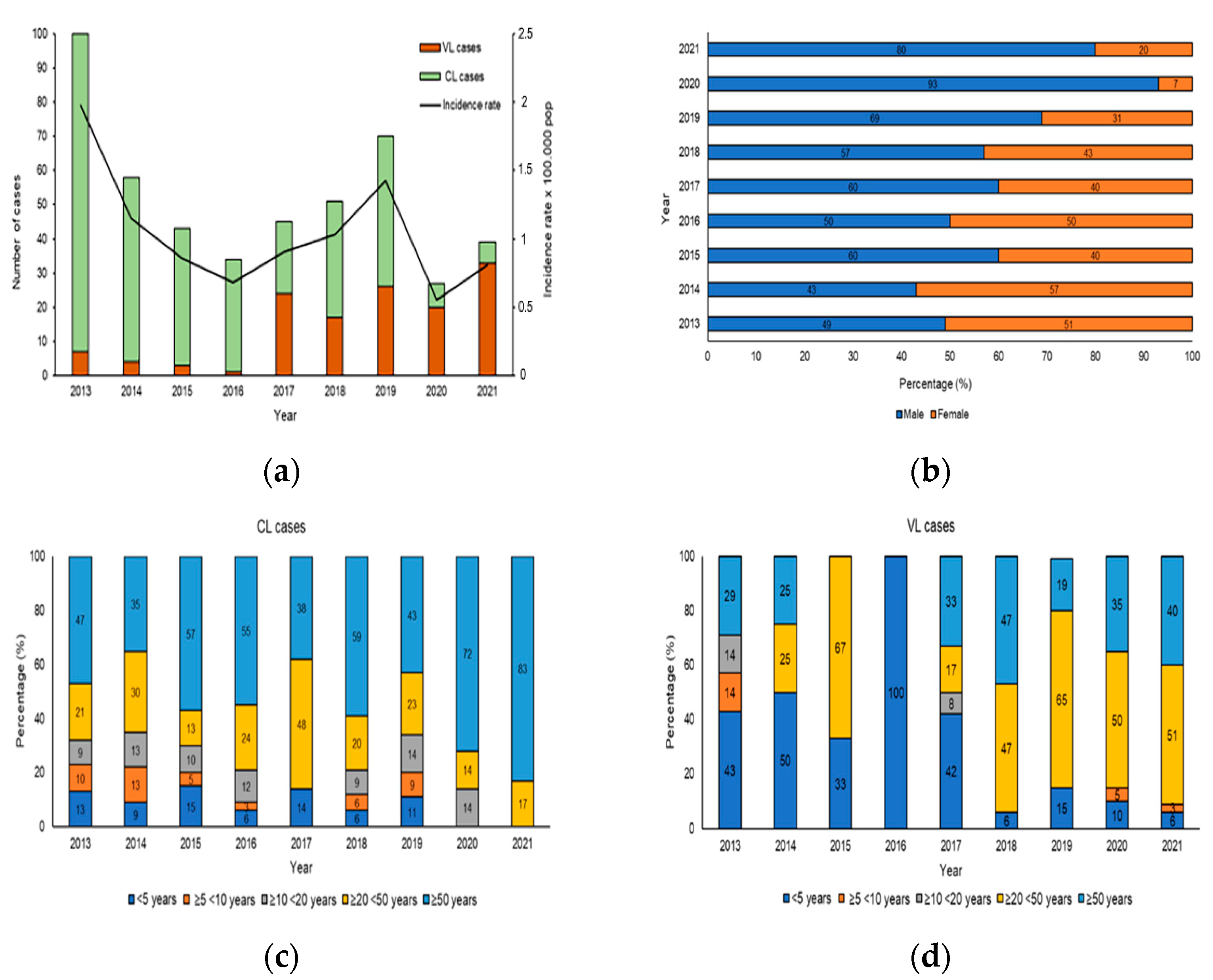
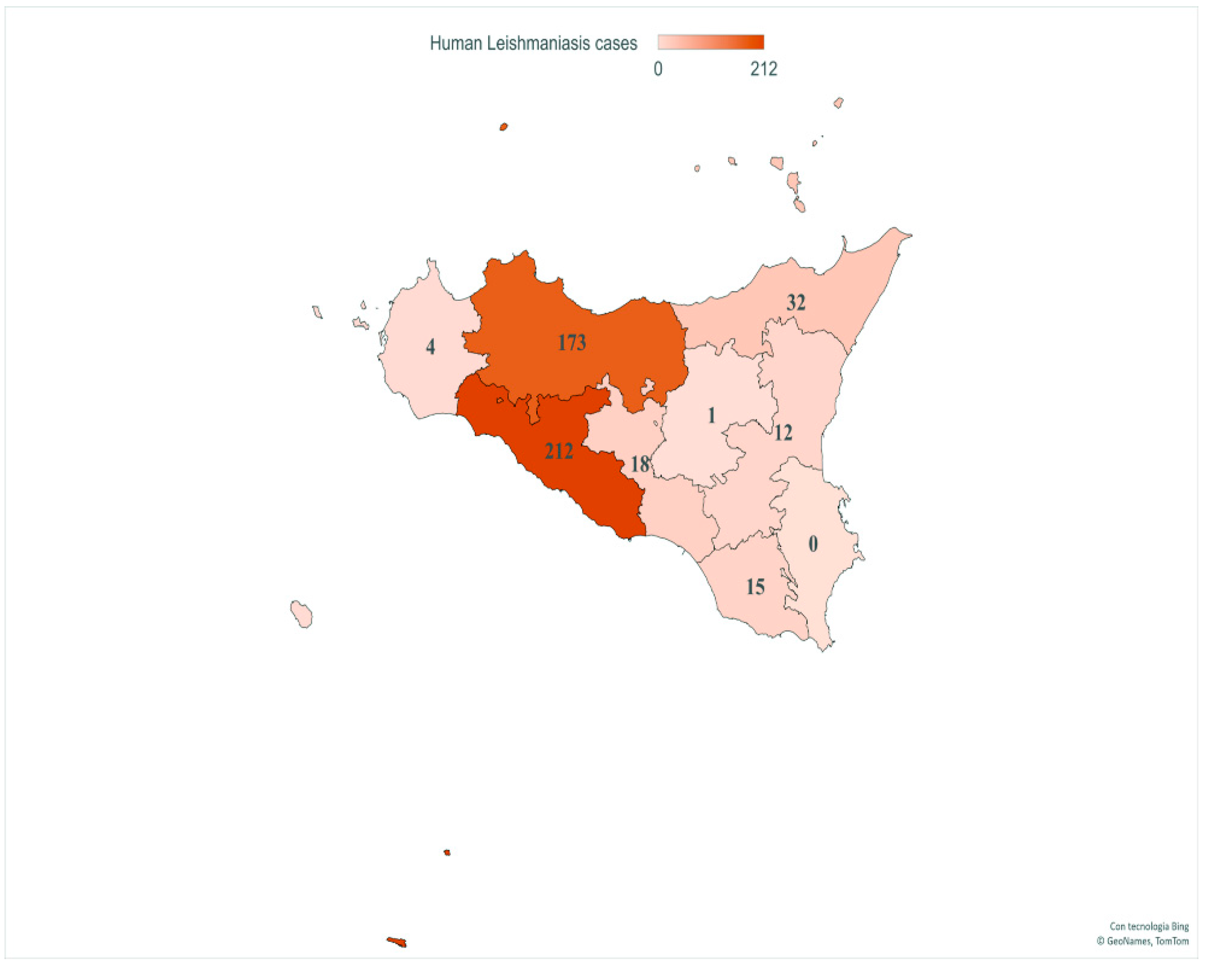
3.2. Human Data
3.3. Sandfly Data
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alemayehu, B.; Alemayehu, M. Leishmaniasis: A Review on Parasite, Vector and Reservoir Host. Health Sci. J. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedla, D.G.; Bariagabr, F.H.; Abreha, H.H. Incidence and Trends of Leishmaniasis and Its Risk Factors in Humera, Western Tigray. J. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 2018, 8463097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leta, S.; Dao, T.H.T.; Mesele, F.; Alemayehu, G. Visceral Leishmaniasis in Ethiopia: An Evolving Disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ready, P.D. Leishmaniasis emergence in Europe. Eurosurveillance 2010, 15, 19505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, R.C. Review of “Mathematical Models for Neglected Tropical Diseases: Essential Tools for Control and Elimination, Part B” Edited by Maria-Gloria Basáñez and Roy M. Anderson. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oryan, A.; Alidadi, S.; Akbari, M. Risk Factors Associated with Leishmaniasis. Trop. Med. Surg. 2014, 2, e118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, P.D. Leishmaniasis Emergence and Climate Change. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2008, 27, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Brandão-Filho, S.P. Visceral Leishmaniasis in Brazil: Revisiting Paradigms of Epidemiology and Control. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2006, 48, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desjeux, P. Leishmaniasis: Current situation and new perspectives. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 27, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, W.; Tekie, H.; Balkew, M.; Gebre-Michael, T.; Warburg, A.; Hailu, A. Population dynamics and habitat preferences of Phlebotomus orientalis in extra-domestic habitats of Kafta Humera lowlands—Kala azar endemic areas in Northwest Ethiopia. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Murray, H.W.; Berman, J.D.; Davies, C.R.; Saravia, N.G. Advances in leishmaniasis. Lancet 2005, 366, 1561–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvar, J.; Yactayo, S.; Bern, C. Leishmaniasis and poverty. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvar, J.; Vélez, I.D.; Bern, C.; Herrero, M.; Desjeux, P.; Cano, J.; Jannin, J.; den Boer, M.; WHO. Leishmaniasis Control Team Leishmaniasis Worldwide and Global Estimates of Its Incidence. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, R.; Sandoval, C.M.; Rodriguez-Morales, A.J.; Franco-Paredes, C. Impact of climate variability in the occurrence of leishmaniasis in northeastern Colombia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, C.; Alwassouf, S.; Cristóvão, J.M.; Ayhan, N.; Pereira, A.; Charrel, R.N.; Campino, L. Serological association between Leishmania infantum and sand fly fever Sicilian (but not Toscana) virus in sheltered dogs from southern Portugal. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennisi, M.G. Leishmaniosis of companion animals in Europe: An update. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 208, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvar, J.; Cañavate, C.; Molina, R.; Moreno, J.; Nieto, J. Canine Leishmaniasis. In Advances in Parasitology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; Volume 57, pp. 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Iatta, R.; Furlanello, T.; Colella, V.; Tarallo, V.D.; Latrofa, M.S.; Brianti, E.; Trerotoli, P.; Decaro, N.; Lorusso, E.; Schunack, B.; et al. A nationwide survey of Leishmania infantum infection in cats and associated risk factors in Italy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatta, R.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Latrofa, M.S.; Cascio, A.; Brianti, E.; Pombi, M.; Gabrielli, S.; Otranto, D. Leishmania tarentolae and Leishmania infantum in humans, dogs and cats in the Pelagie archipelago, southern Italy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L.K.; Kochmann, J.; Klimpel, S.; Cunze, S. Modeling the climatic suitability of leishmaniasis vector species in Europe. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroli, M.; Feliciangeli, M.D.; Bichaud, L.; Charrel, R.N.; Gradoni, L. Phlebotomine sandflies and the spreading of leishmaniases and other diseases of public health concern. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2013, 27, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signorini, M.; Cassini, R.; Drigo, M.; DI Regalbono, A.F.; Pietrobelli, M.; Montarsi, F.; Stensgaard, A.-S. Ecological niche model of Phlebotomus perniciosus, the main vector of canine leishmaniasis in north-eastern Italy. Geospat. Health 2014, 9, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, B. Sampling methods for phlebotomine sandflies. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2000, 14, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlock, J.M.; Hansford, K.M.; Van Bortel, W.; Zeller, H.; Alten, B. A summary of the evidence for the change in European distribution of phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera: Psychodidae) of public health importance. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alten, B.; Maia, C.; Afonso, M.O.; Campino, L.; Jiménez, M.; González, E.; Molina, R.; Bañuls, A.L.; Prudhomme, J.; Vergnes, B.; et al. Seasonal Dynamics of Phlebotomine Sand Fly Species Proven Vectors of Mediterranean Leishmaniasis Caused by Leishmania infantum. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradoni, L.; Gramiccia, M.; Scalone, A. Visceral Leishmaniasis Treatment, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1617–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moirano, G.; Zanet, S.; Giorgi, E.; Battisti, E.; Falzoi, S.; Acquaotta, F.; Fratianni, S.; Richiardi, L.; Ferroglio, E.; Maule, M. Integrating environmental, entomological, animal, and human data to model the Leishmania infantum transmission risk in a newly endemic area in Northern Italy. One Health 2020, 10, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, T. One Health Approach Prospect for Integrated Control and Elimination of Visceral Leishmaniasis in Ethiopia: A Narrative Review Article. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2016, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vilas, V.J.D.R.; Maia-Elkhoury, A.N.S.; Yadon, Z.E.; Cosivi, O.; Sanchez-Vazquez, M.J. Visceral leishmaniasis: A One Health approach. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Caputo, V.; Fiorella, S.; Sammarco, I.; Lupo, T.; Migliazzo, A.; Vitale, F.; Reale, S. Genetic tools discriminate strains of Leishmania infantum isolated from humans and dogs in Sicily, Italy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orndorff, G.R.; Cooper, B.A.; Smith, W.; Ryan, J.R. Canine Visceral Leishmaniasis in Sicily. Mil. Med. 2000, 165, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Verso, M.G.; Vitale, F.; Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Migliazzo, A.; Bongiorno, M.R.; Santi, F.; Pistone, G.; Amodio, E.; Picciotto, D. Suspected Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in a Sample of Westerns Sicily Residents: What Correlation with Occupation? Med. Lav. 2017, 108, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, F.; Bruno, F.; Migliazzo, A.; Galante, A.; Vullo, A.; Graziano, R.; D’Avola, S.; Caputo, V.; Castelli, G. Cross-Sectional Survey of Canine Leishmaniasis in Pantelleria Island in Sicily. Vet. Ital. 2020, 56, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Office of Epizootics. Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals, 8th ed.; Chapter 3.1.11 Leishmaniosis; OIE: Paris, France, 2021; ISBN 978-92-95115-59-0. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, G.; Bruno, F.; Reale, S.; Catanzaro, S.; Valenza, V.; Vitale, F. Molecular Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis: Quantification of Parasite Load by a Real-Time PCR Assay with High Sensitivity. Pathogens 2021, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romi, R.; Khoury, C.; Bigliocchi, F.; Maroli, M. Fact Sheet on Mites and Insects of Medical Importance. Schede Guida Su Acari e Insetti Di Interesse Sanitario; Istituto Superiore Di Sanità: Rome, Italy, 1994.
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Tarallo, V.D.; Otranto, D. Morphological keys for the identification of Italian phlebotomine sand flies (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogan, W.J.; Gladen, B. Estimating Prevalence from the Results of a Screening Test. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1978, 107, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, G. Brucellosis Seropositivity in Animals and Humans in Ethiopia: A Meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0005006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroli, M.; Pampiglione, S.; Tosti, A. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in Western Sicily (Italy) and Preliminary Survey of Phlebotomine Sandflies (Diptera: Psychodidae). Parassitologia 1988, 30, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Lisi, O.; D’Urso, V.; Vaccalluzzo, V.; Bongiorno, G.; Khoury, C.; Severini, F.; Di Muccio, T.; Gramiccia, M.; Gradoni, L.; Maroli, M. Persistence of phlebotomine Leishmania vectors in urban sites of Catania (Sicily, Italy). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palatnik-De-Sousa, C.B.; Day, M.J. One Health: The global challenge of epidemic and endemic leishmaniasis. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, M.J. One health: The importance of companion animal vector-borne diseases. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, J.-C.; Campino, L.; Cañavate, C.; Dedet, J.-P.; Gradoni, L.; Soteriadou, K.; Mazeris, A.; Ozbel, Y.; Boelaert, M. Spread of Vector-Borne Diseases and Neglect of Leishmaniasis, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 14, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzillo, V.F.; Gizzarelli, M.; Vitale, F.; Montagnaro, S.; Torina, A.; Sotera, S.; Oliva, G. Serological and entomological survey of canine leishmaniasis in Lampedusa island, Italy. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otranto, D.; Napoli, E.; Latrofa, M.S.; Annoscia, G.; Tarallo, V.D.; Greco, G.; Lorusso, E.; Gulotta, L.; Falsone, L.; Basano, F.S.; et al. Feline and canine leishmaniosis and other vector-borne diseases in the Aeolian Islands: Pathogen and vector circulation in a confined environment. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 236, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asfaram, S.; Fakhar, M.; Teshnizi, S.H. Is the cat an important reservoir host for visceral leishmaniasis? A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 25, e20190012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Maia, C. Leishmania infection in cats and feline leishmaniosis: An updated review with a proposal of a diagnosis algorithm and prevention guidelines. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector-Borne Dis. 2021, 1, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramo, F.; Albanese, F.; Gattuso, S.; Randone, A.; Fileccia, I.; Dedola, C.; Ibba, F.; Ottaiano, P.; Brianti, E. Skin Lesions in Feline Leishmaniosis: A Systematic Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramiccia, M.; Scalone, A.; Di Muccio, T.; Orsini, S.; Fiorentino, E.; Gradoni, L. The Burden of Visceral Leishmaniasis in Italy from 1982 to 2012: A Retrospective Analysis of the Multi-Annual Epidemic That Occurred from 1989 to 2009. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Silveira, F.; Abad-Franch, F. Sex Bias in Infectious Disease Epidemiology: Patterns and Processes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloots, K.; Burza, S.; Malaviya, P.; Hasker, E.; Kansal, S.; Mollett, G.; Chakravarty, J.; Roy, N.; Lal, B.K.; Rijal, S.; et al. Male predominance in reported Visceral Leishmaniasis cases: Nature or nurture? A comparison of population-based with health facility-reported data. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0007995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.; Mercuriali, L.; Figuerola, J.; Montalvo, T.; Bueno-Marí, R.; Millet, J.-P.; Simón, P.; Masdeu, E.; Rius, C. Trends in the Epidemiology of Leishmaniasis in the City of Barcelona (1996–2019). Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 653999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrador, Z.; Gherasim, A.; Jimenez, B.C.; Granados, M.; Martín, J.V.S.; Aparicio, P. Epidemiological Changes in Leishmaniasis in Spain According to Hospitalization-Based Records, 1997–2011: Raising Awareness towards Leishmaniasis in Non-HIV Patients. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez Rodríguez, B.; Isidoro Fernández, B.; Santos Sanz, S.; Sierra Moros, M.J.; Molina Moreno, R.; Astray Mochales, J.; Amela Heras, C. Situación Epidemiológica y de Los Factores de Riesgo de Transmisión de Leishmania Infantum En España. Rev. Esp. Salud Pública 2012, 86, 555–564. [Google Scholar]
- Riera, C.; Napp, S.; Manzanares, S. Epidemiología de la leishmaniasis humana en la ciudad de Barcelona (1997–2014). Rev. Enf. Emerg. 2016, 15, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Abbate, J.M.; Maia, C.; Pereira, A.; Arfuso, F.; Gaglio, G.; Rizzo, M.; Caracappa, G.; Marino, G.; Pollmeier, M.; Giannetto, S.; et al. Identification of trypanosomatids and blood feeding preferences of phlebotomine sand fly species common in Sicily, Southern Italy. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaglio, G.; Brianti, E.; Napoli, E.; Falsone, L.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Tarallo, V.D.; Otranto, D.; Giannetto, S. Effect of night time-intervals, height of traps and lunar phases on sand fly collection in a highly endemic area for canine leishmaniasis. Acta Trop. 2014, 133, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volf, P.; Benkova, I.; Myskova, J.; Sadlova, J.; Campino, L.; Ravel, C. Increased transmission potential of Leishmania major/Leishmania infantum hybrids. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, W.; Stevens, J. Genetic Exchange in the Trypanosomatidae. In Advances in Parasitology; Baker, J.R., Muller, R., Rollinson, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999; Volume 43, pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Chalghaf, B.; Chemkhi, J.; Mayala, B.; Harrabi, M.; Benie, G.B.; Michael, E.; Ben Salah, A. Ecological niche modeling predicting the potential distribution of Leishmania vectors in the Mediterranean basin: Impact of climate change. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Specimens of Phlebotomus Species Collected in 2013 | |||||
| Provinces | P. pernicious | P. perfiliewi | S. minuta | P. papatasi | Total |
| Agrigento | 1593 | 683 | 703 | 0 | 2979 |
| Catania | 312 | 36 | 683 | 0 | 1031 |
| Palermo | 648 | 1572 | 315 | 0 | 2535 |
| Trapani | 43 | 24 | 43 | 0 | 110 |
| Caltanissetta | 664 | 8497 | 205 | 0 | 9366 |
| Siracusa | 47 | 3 | 53 | 0 | 103 |
| Enna | 325 | 3706 | 798 | 0 | 4829 |
| Ragusa | 8 | 2 | 158 | 0 | 168 |
| Total (%) | 3640 (17.2) | 14,523 (68.7) | 2958 (14) | 0 | 21,121 |
| Specimens of Phlebotomus Species Collected in 2021 | |||||
| Provinces | P. pernicious | P. perfiliewi | S. minuta | P. papatasi | Total |
| Agrigento | 1384 | 1505 | 30 | 90 | 3009 |
| Catania | 1205 | 39 | 66 | 0 | 1310 |
| Palermo | 1039 | 861 | 633 | 0 | 2533 |
| Trapani | 86 | 17 | 17 | 0 | 120 |
| Caltanissetta | 1987 | 7379 | 94 | 0 | 9460 |
| Siracusa | 142 | 23 | 41 | 0 | 206 |
| Enna | 1281 | 3548 | 99 | 0 | 4928 |
| Ragusa | 85 | 17 | 48 | 0 | 150 |
| Total (%) | 7209 (33.2) | 13,389 (61.7) | 1028 (4.7) | 90 (0.4) | 21,716 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruno, F.; Vitale, F.; La Russa, F.; Reale, S.; Späth, G.F.; Oliveri, E.; Gargano, V.; Valenza, V.; Facciponte, F.; Giardina, S.; et al. Retrospective Analysis of Leishmaniasis in Sicily (Italy) from 2013 to 2021: One-Health Impact and Future Control Strategies. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091704
Bruno F, Vitale F, La Russa F, Reale S, Späth GF, Oliveri E, Gargano V, Valenza V, Facciponte F, Giardina S, et al. Retrospective Analysis of Leishmaniasis in Sicily (Italy) from 2013 to 2021: One-Health Impact and Future Control Strategies. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(9):1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091704
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruno, Federica, Fabrizio Vitale, Francesco La Russa, Stefano Reale, Gerald F. Späth, Eugenia Oliveri, Valeria Gargano, Viviana Valenza, Flavia Facciponte, Susanna Giardina, and et al. 2022. "Retrospective Analysis of Leishmaniasis in Sicily (Italy) from 2013 to 2021: One-Health Impact and Future Control Strategies" Microorganisms 10, no. 9: 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091704
APA StyleBruno, F., Vitale, F., La Russa, F., Reale, S., Späth, G. F., Oliveri, E., Gargano, V., Valenza, V., Facciponte, F., Giardina, S., Marino, G., Galante, A., & Castelli, G. (2022). Retrospective Analysis of Leishmaniasis in Sicily (Italy) from 2013 to 2021: One-Health Impact and Future Control Strategies. Microorganisms, 10(9), 1704. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10091704








