Can Corrole Dimers Be Good Photosensitizers to Kill Bacteria?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Photosensitizer
2.2. Biological Assays of Corrole PSs against S. aureus
2.2.1. Bacterial Strain and Growth Conditions
2.2.2. Stock Solutions of the Photosensitizers
2.2.3. Light Source Conditions
2.2.4. aPDT Experimental Setup
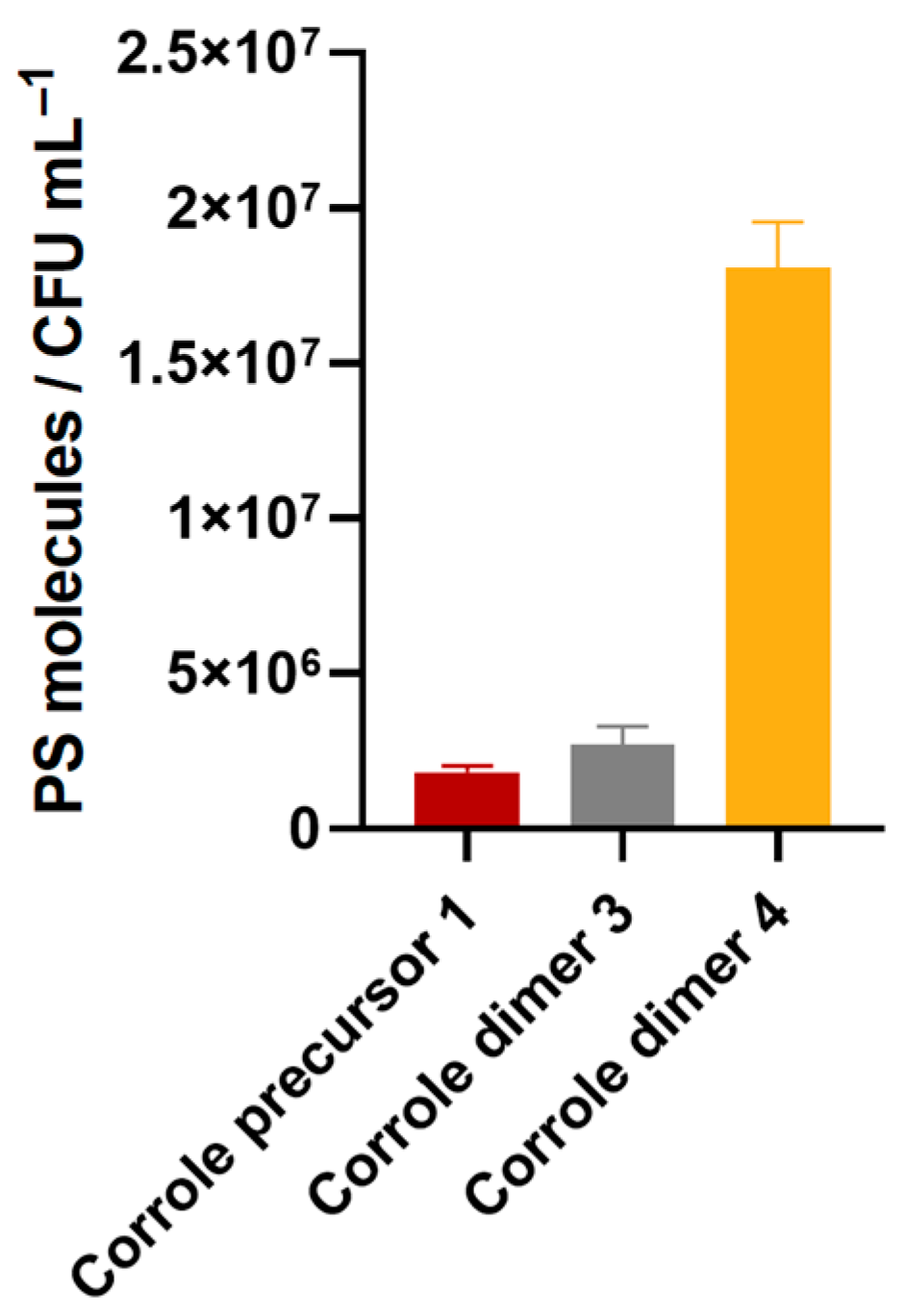
2.2.5. Photosensitizer Binding
2.3. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Corrole Precursor 1 and Dimer 3
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Corrole Oligomers
3.2. Photophysical Properties
3.3. Singlet Oxygen Generation
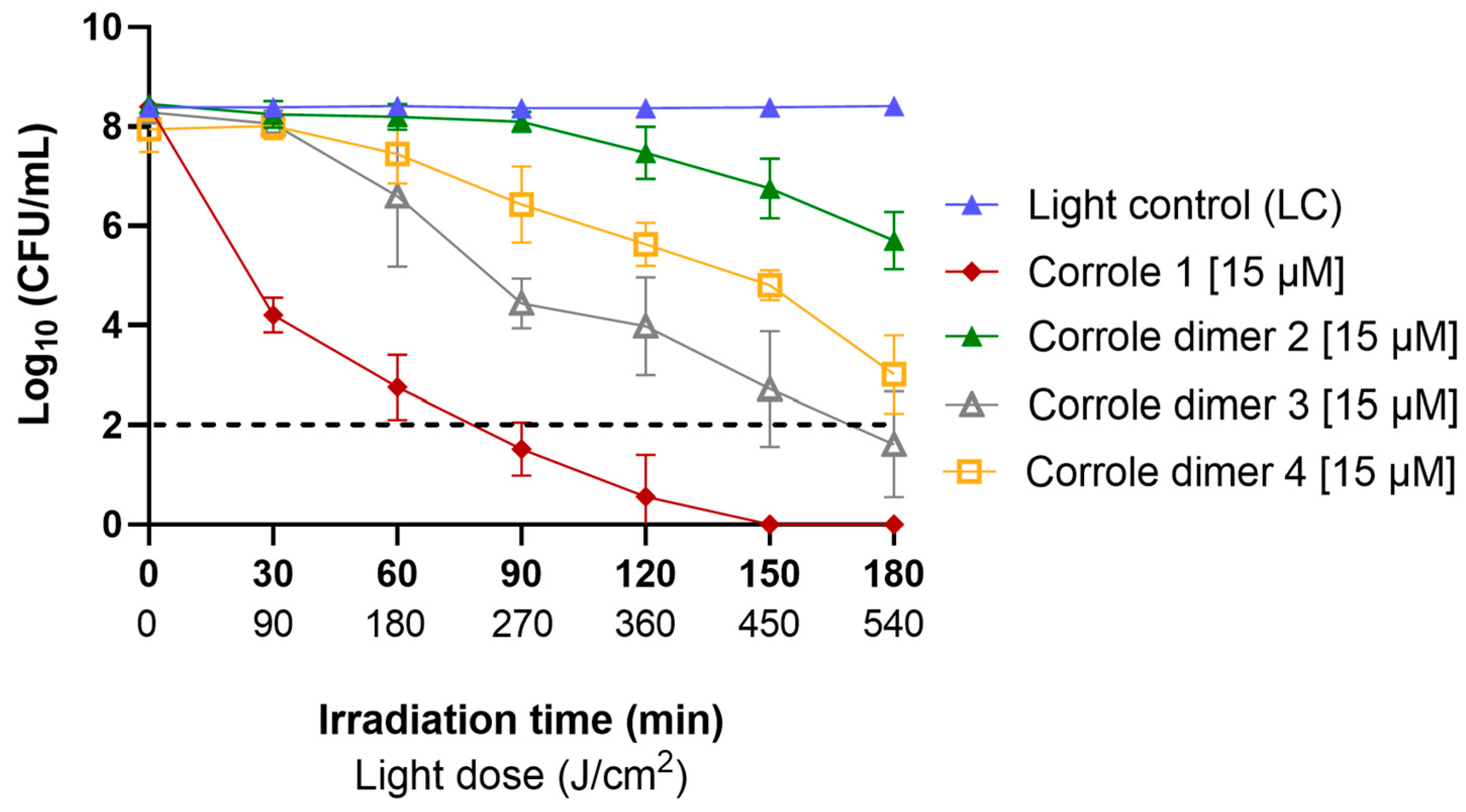
3.4. Biological Assays against Staphylococcus aureus
3.5. PS Cytotoxicity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Natale, C.; Gros, C.P.; Paolesse, R. Corroles at work: A small macrocycle for great applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 1277–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahammed, A.; Gross, Z. Corroles as triplet photosensitizers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 379, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ou, Z.; Kadish, K.M. Electrochemistry of Corroles in Nonaqueous Media. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3377–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolesse, R.; Nardis, S.; Monti, D.; Stefanelli, M.; Di Natale, C. Porphyrinoids for Chemical Sensor Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 2517–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teo, R.D.; Hwang, J.Y.; Termini, J.; Gross, Z.; Gray, H.B. Fighting Cancer with Corroles. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 2711–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soll, M.; Goswami, T.K.; Chen, Q.C.; Saltsman, I.; Teo, R.D.; Shahgholi, M.; Lim, P.; Di Bilio, A.J.; Cohen, S.; Termini, J.; et al. Cell-Penetrating Protein/Corrole Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, B.; Mondal, S.; Kar, S. Corroles. In Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry; Scott, R.A., Storr, T., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2020; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviv, I.; Gross, Z. Corrole-based applications. Chem. Commun. 2007, 20, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, A.R.L.; Tomé, A.C.; Santos, C.I.M.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Moura, N.M.M.; Abu-Orabi, S.T.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Azides and porphyrinoids: Synthetic approaches and applications. Part 1—Azides, Porphyrins and Corroles. Molecules 2020, 25, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, C.I.M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.; Gonçalves, G.; Pinto, S.N.; Melle-Franco, M.; Marques, P.A.A.P.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Herranz, M.Á.; Martin, N.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; et al. Novel hybrids based on graphene quantum dots covalently linked to glycol corroles for multiphoton bioimaging. Carbon 2020, 166, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, M.E.; De Simone, B.C.; Liuzzi, S.; Marino, T.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. Iodine substituted phosphorus corrole complexes as possible photosensitizers in photodynamic therapy: Insights from theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2020, 41, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomassen, I.K.; McCormick-McPherson, L.J.; Borisov, S.M.; Ghosh, A. Iridium Corroles Exhibit Weak Near-Infrared Phosphorescence but Efficiently Sensitize Singlet Oxygen Formation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, J.F.B.; Zamarrón, A.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, A.C.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Röder, B.; Juarranz, Á.; Sanz-Rodríguez, F. Photodynamic effects induced by meso-tris(pentafluorophenyl)corrole and its cyclodextrin conjugates on cytoskeletal components of HeLa cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.I.M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, L.; Gonçalves, G.; Dias, C.J.; Monteiro, F.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Vieira, S.I.; Helguero, L.A.; Herranz, M.A.; Martin, N.; et al. Enhanced Photodynamic Therapy Effects of Graphene Quantum Dots Conjugated with Aminoporphyrins. ACS Appl. Nano Mater 2021, 2021, 13079–13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardote, T.A.F.; Barata, J.F.B.; Amador, C.; Alves, E.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Cunha, Â.; Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F. Evaluation of meso-substituted cationic corroles as potential antibacterial agents. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2018, 90, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preuß, A.; Saltsman, I.; Mahammed, A.; Pfitzner, M.; Goldberg, I.; Gross, Z.; Röder, B. Photodynamic inactivation of mold fungi spores by newly developed charged corroles. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2014, 133, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashef, N.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Advances in antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation at the nanoscale. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 853–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation: A bright new technique to kill resistant microbes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 33, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braz, M.; Salvador, D.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Mesquita, M.Q.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Almeida, A. Photodynamic inactivation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus on skin using a porphyrinic formulation. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, M.; Maisch, T.; Nonell, S.; Plaetzer, K.; Almeida, A.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Photoantimicrobials—Are we afraid of the light? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e49–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahamse, H.; Hamblin, M.R. New photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klausen, M.; Ucuncu, M.; Bradley, M. Design of Photosensitizing Agents for Targeted Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.; Ueta, K.; Tanaka, T.; Osuka, A. Singly, Doubly, and Triply Linked Corrole Oligomers: Synthesis, Structures, and Linking Position Dependent Properties. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Liang, J.X. Screening metal-dicorrole-based dyes with excellent photoelectronic properties for dye-sensitized solar cells by density functional calculations. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2020, 24, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiroto, S.; Furukawa, K.; Shinokubo, H.; Osuka, A. Synthesis and biradicaloid character of doubly linked corrole dimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 12380–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, J.F.B.; Silva, A.M.G.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Tomé, A.C.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. β,β′-Corrole dimers. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 8171–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, S.; Kosa, M.; Mizrahi, A.; Fridman, N.; Saphier, M.; Stanger, A.; Gross, Z. The planar cyclooctatetraene bridge in bis-metallic macrocycles: Isolating or conjugating? Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronner, S.; Monteil, H.; Prévost, G. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus: Complexity and applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 28, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Bae, J.S.; Otto, M. Pathogenicity and virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2021, 12, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomeu, M.; Rocha, S.; Cunha, Â.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Almeida, A. Effect of photodynamic therapy on the virulence factors of Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. The Evolving Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gryko, D.T.; Koszarna, B. Refined methods for the synthesis of meso-substituted A3- and trans-A2B-corroles. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendix, J.; Dmochowski, I.J.; Gray, H.B.; Mahammed, A.; Simkhovich, L.; Gross, Z. Structural, electrochemical, and photophysical properties of gallium(III) 5,10,15-tris(pentafluorophenyl)corrole. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 4048–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, S.; Ahmed, S.; Wang, F.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chai, X.; Wu, Y.; Cai, J.; Cheng, G. Antimicrobial activity and resistance: Influencing factors. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Qiu, Y.; Shi, H.; Yin, H. The importance of lag time extension in determining bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Analyst 2016, 141, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eng, R.H.K.; Padberg, F.T.; Smith, S.M.; Tan, E.N.; Cherubin, C.E. Bactericidal effects of antibiotics on slowly growing and nongrowing bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 1824–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Mehring, A.; Erdmann, N.; Walther, J.; Stiefelmaier, J.; Strieth, D.; Ulber, R. A simple and low-cost resazurin assay for vitality assessment across species. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 333, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orłowski, R.; Tasior, M.; Staszewska-Krajewska, O.; Dobrzycki, Ł.; Schilf, W.; Ventura, B.; Cyrański, M.K.; Gryko, D.T. Hydrogen Bonds Involving Cavity NH Protons Drives Supramolecular Oligomerization of Amido-Corroles. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 10195–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, J.F.B.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Tomé, A.C.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. How light affects 5,10,15-tris(pentafluorophenyl)corrole. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujesh, S.; Basumatary, B.; Kumar, A.; Sankar, J. Pyrene appended free-base, phosphorus(V) and gallium(III) corroles and their β,β′-linked corrole dimers: Synthesis, photophysical and electrochemical properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2021, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, F.; Liang, Z.H.; Liu, C.F.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.Q.; Peng, S.H.; Wang, X.; Ying, X.; et al. Investigation of excited-state photophysical properties of water-soluble gallium corrole. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 12350–12357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.; Gamelas, S.R.D.; Vieira, C.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Almeida, A.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Lourenço, L.M.O. Pyrazole-pyridinium porphyrins and chlorins as powerful photosensitizers for photoinactivation of planktonic and biofilm forms of E. coli. Dye Pigment. 2021, 193, 109557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeRosa, M. Photosensitized singlet oxygen and its applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 233–234, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Tomé, A.C.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Cunha, Â.; Almeida, A. Involvement of type I and type II mechanisms on the photoinactivation of non-enveloped DNA and RNA bacteriophages. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 120, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Mesquita, M.Q.; Moura, N.M.M.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Almeida, A. An Insight into the Potentiation Effect of Potassium Iodide on aPDT Efficacy. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batalha, P.N.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Forezi, L.S.M.; Costa, L.; De Souza, M.C.B.V.; Boechat, F.D.C.S.; Ferreira, V.F.; Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; et al. Synthesis of new porphyrin/4-quinolone conjugates and evaluation of their efficiency in the photoinactivation of Staphylococcus aureus. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71228–71239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, C.; Gomes, M.C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cunha, Â.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Tomé, A.C.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F. Photodynamic inactivation of Escherichia coli with cationic meso-tetraarylporphyrins—The charge number and charge distribution effects. Catal. Today 2016, 266, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, E.; Costa, L.; Carvalho, C.M.B.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Tomé, A.C.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Cunha, Â.; Almeida, A. Charge effect on the photoinactivation of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria by cationic meso-substituted porphyrins. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Preuß, A.; Zeugner, L.; Hackbarth, S.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Roeder, B. Photoinactivation of Escherichia coli (SURE2) without intracellular uptake of the photosensitizer. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesslich, S.; Kamen, A.A. Vero cell upstream bioprocess development for the production of viral vectors and vaccines. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 44, 107608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
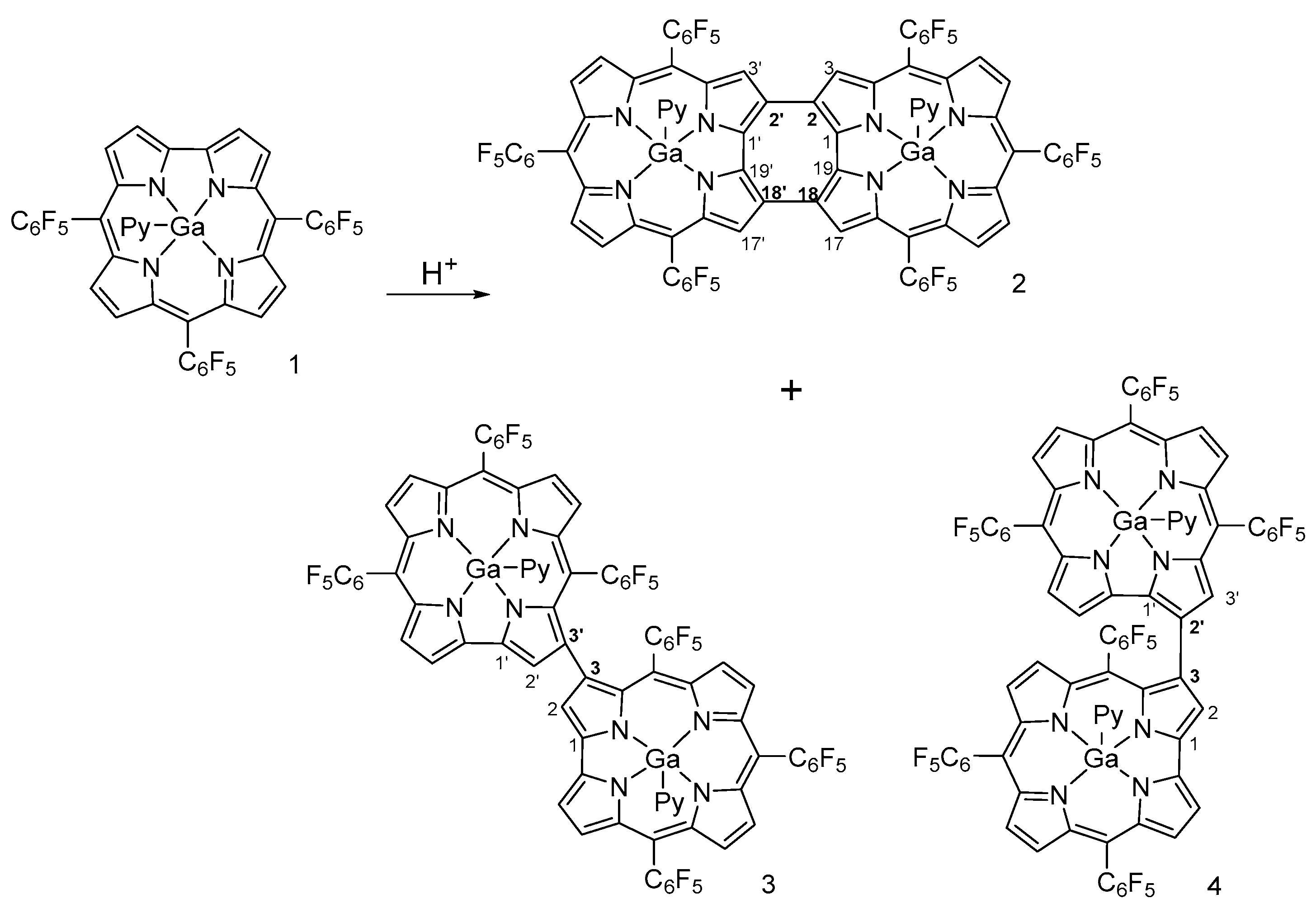



| Experimental Conditions | Yield /% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Acids | Temp. (°C) | Time | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | AcOH/TFA/5% H2SO4 (4:2:1) | 100 | 2 h | - | 15 | 5 | 14 |
| 2 | AcOH/TFA/5% H2SO4 (4:2:1) | 100 | 30 min | 19 | 10 (12) a | ≤1 | 8 (10) a |
| 3 | AcOH/TFA/5% H2SO4 (4:2:1) | 40 | 2 h | 99 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 |
| 4 | AcOH | 100 | 2 h | 61 | ≤1 | 10 (26) a | 3 (8) a |
| 5 | AcOH/TFA (5:2) b | 100 | 1 h | 37 | ≤1 | 5 (8) a | 11 (17) a |
| 6 | AcOH/5% H2SO4 (6:1) | 100 | 2 h | 56 | 12 (27) a | 10 (23) a | 15 (34) a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lacerda, P.S.S.; Bartolomeu, M.; Gomes, A.T.P.C.; Duarte, A.S.; Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Barata, J.F.B. Can Corrole Dimers Be Good Photosensitizers to Kill Bacteria? Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061167
Lacerda PSS, Bartolomeu M, Gomes ATPC, Duarte AS, Almeida A, Faustino MAF, Neves MGPMS, Barata JFB. Can Corrole Dimers Be Good Photosensitizers to Kill Bacteria? Microorganisms. 2022; 10(6):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061167
Chicago/Turabian StyleLacerda, Paula S. S., Maria Bartolomeu, Ana T. P. C. Gomes, Ana S. Duarte, Adelaide Almeida, Maria A. F. Faustino, Maria G. P. M. S. Neves, and Joana F. B. Barata. 2022. "Can Corrole Dimers Be Good Photosensitizers to Kill Bacteria?" Microorganisms 10, no. 6: 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061167
APA StyleLacerda, P. S. S., Bartolomeu, M., Gomes, A. T. P. C., Duarte, A. S., Almeida, A., Faustino, M. A. F., Neves, M. G. P. M. S., & Barata, J. F. B. (2022). Can Corrole Dimers Be Good Photosensitizers to Kill Bacteria? Microorganisms, 10(6), 1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061167










