Comparative Analysis of Microbiome Metagenomics in Reintroduced Wild Horses and Resident Asiatic Wild Asses in the Gobi Desert Steppe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
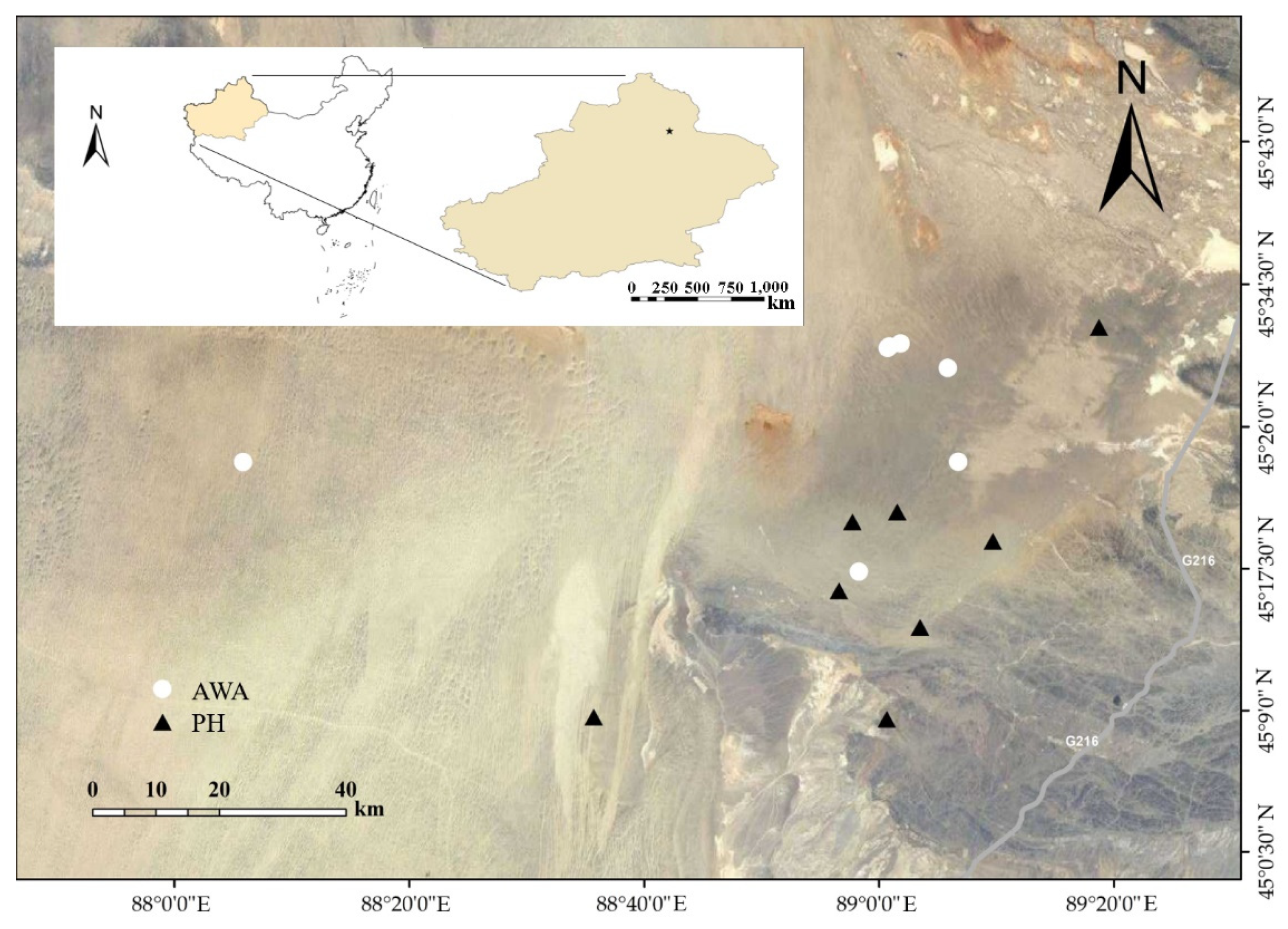
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.3. Bioinformatics
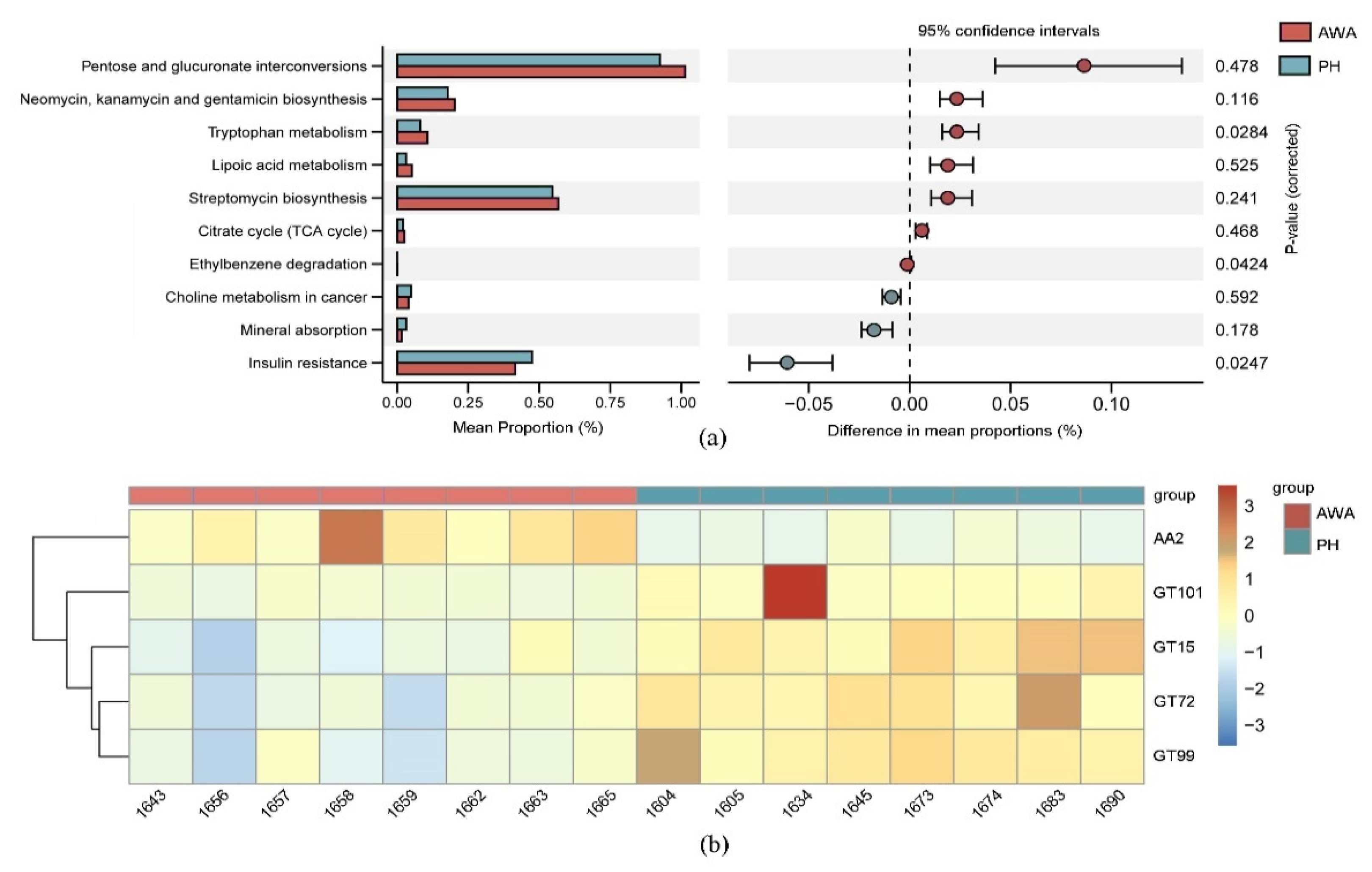
3. Results
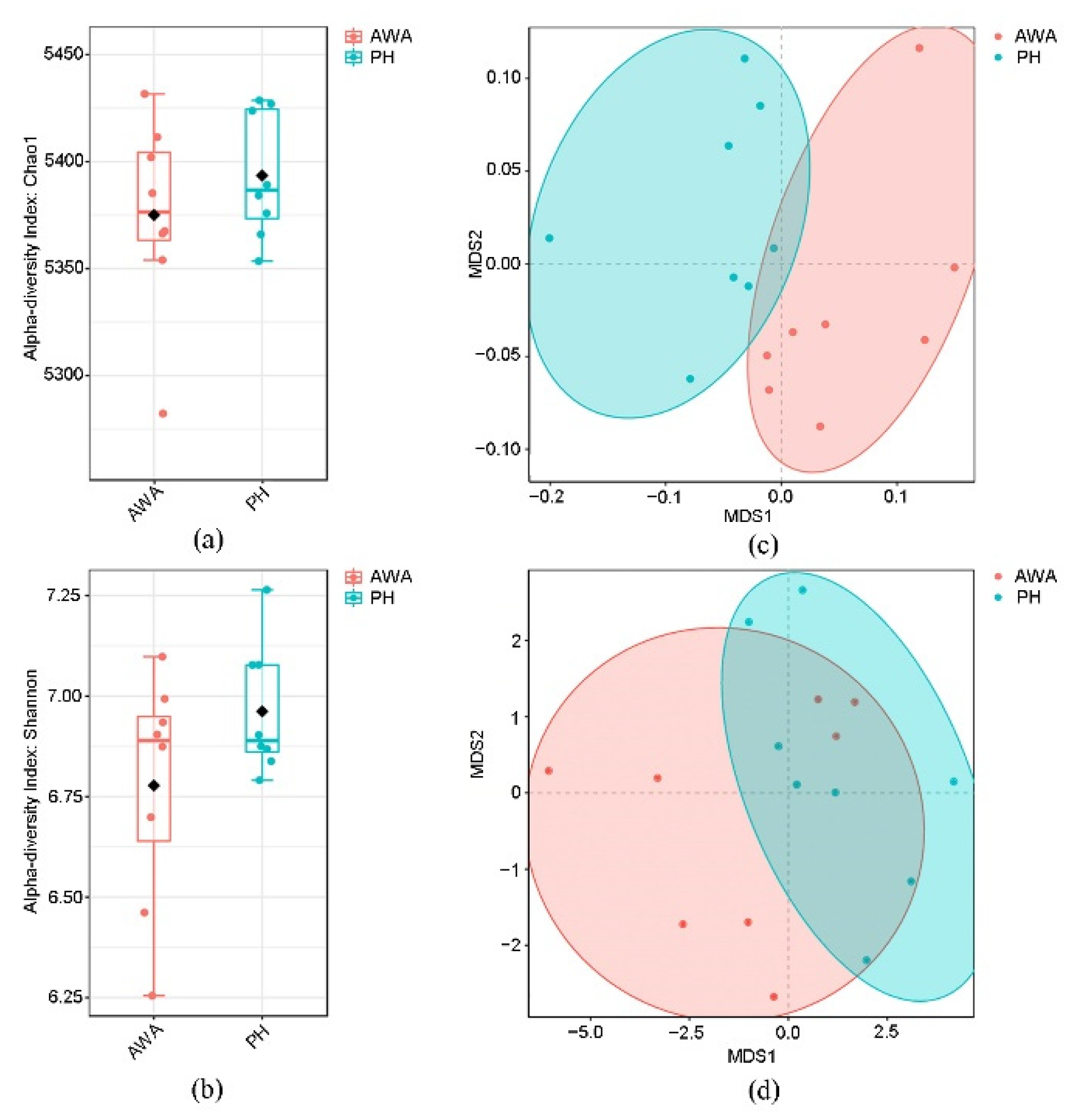
3.1. Sequencing Quality and Microbial Diversity
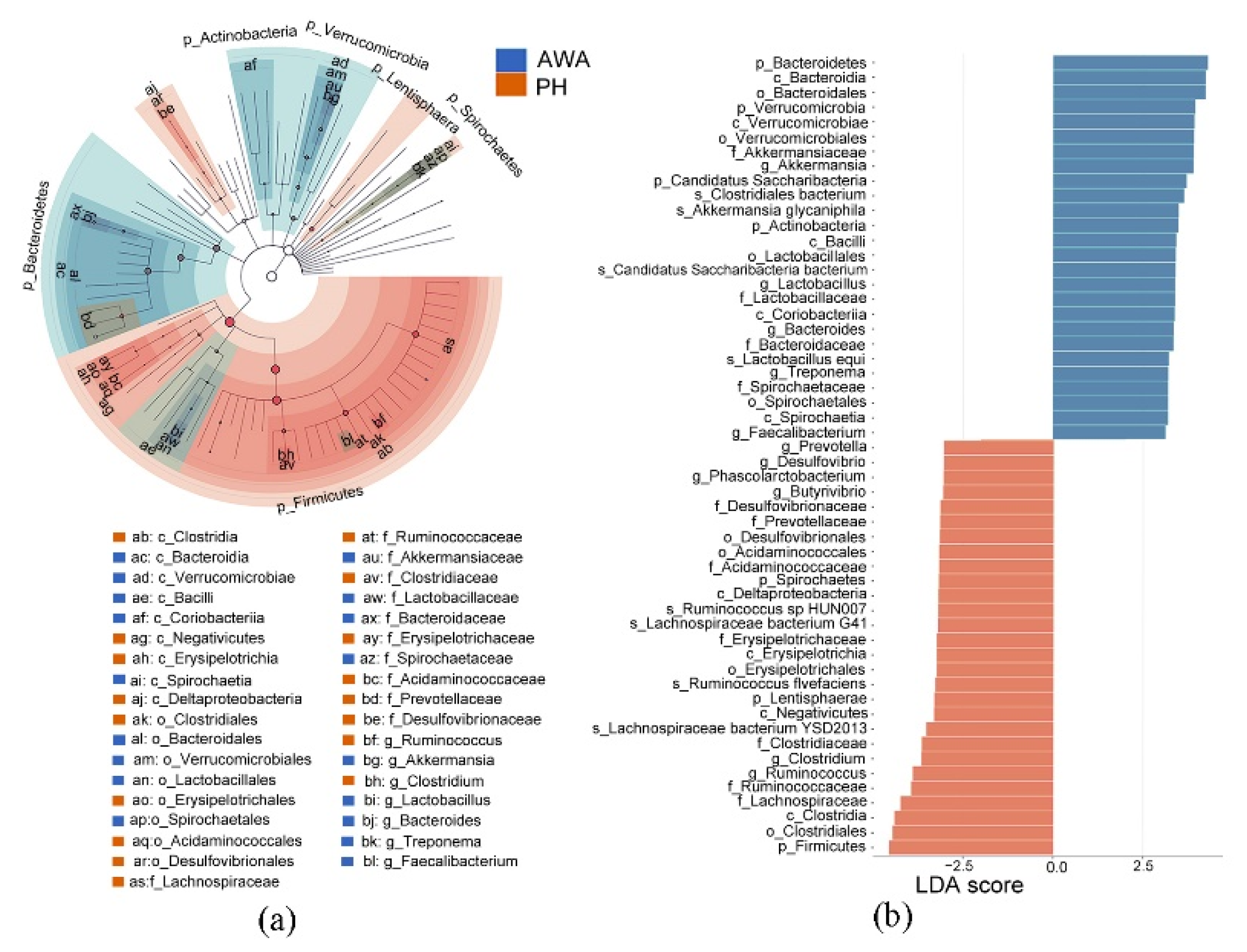
3.2. Differences in Intestinal Microbial Community Structure
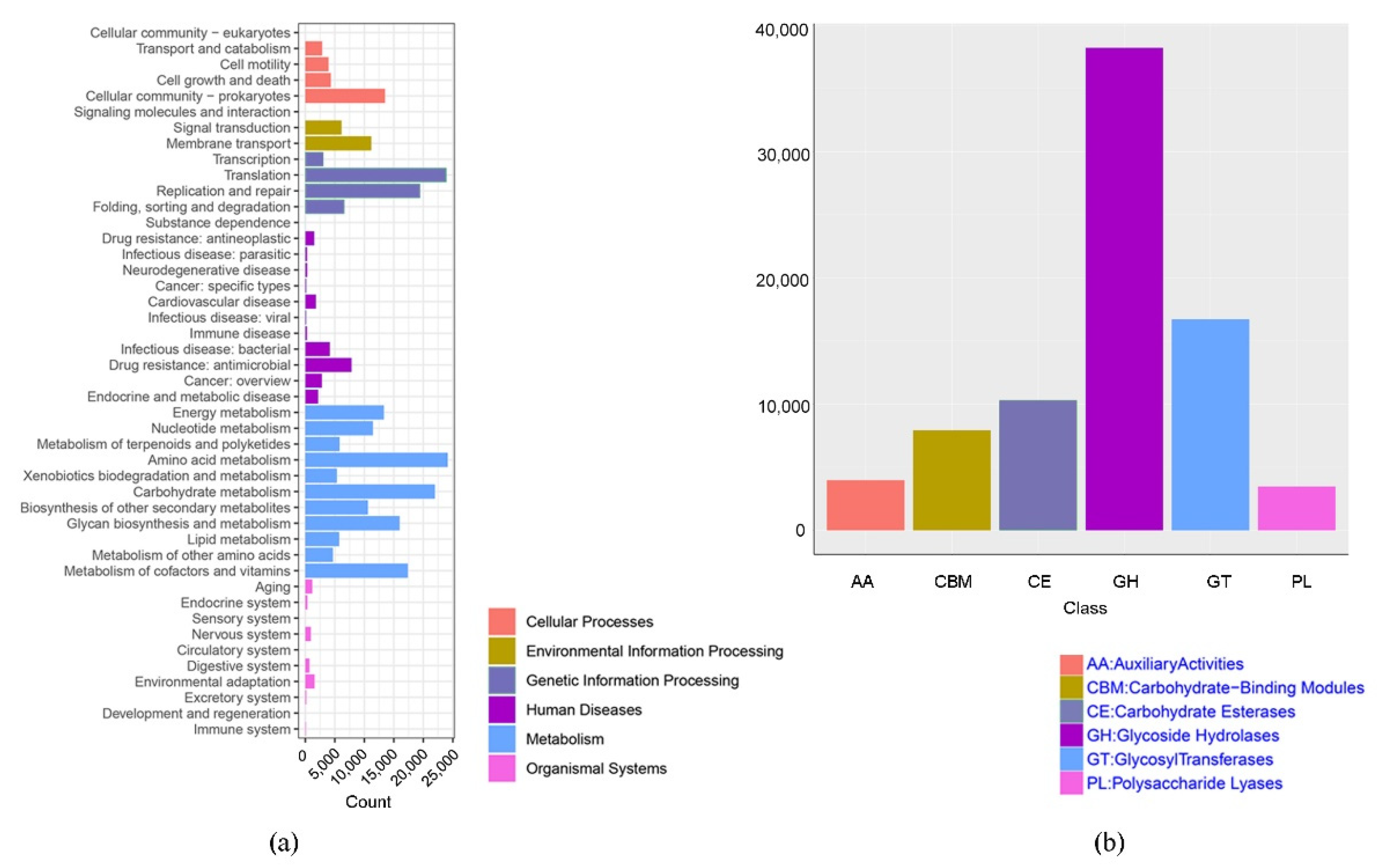
3.3. Convergence in Functional Potential of Microbial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belkaid, Y.; Hand, T.W. Role of the Microbiota in Immunity and inflammation. Cell 2014, 157, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tu, C.; Luo, J.; Lu, M.; Zhang, S.; Xu, L. Metabolic and immunological effects of gut microbiota in leaf beetles at the local and systemic levels. Integr. Zool. 2021, 16, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, T.; Shi, M.; Zhang, B.; Hu, X.; Xu, S.; Ding, J.; Liu, S.; Hu, D.; Rubenstein, D. Characterization of intestinal microbiota and fecal cortisol, T3, and IgA in forest musk deer (Moschus berezovskii) from birth to weaning. Integr. Zool. 2021, 16, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Mind-altering microorganisms: The impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2012, 13, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; Zilber-Rosenberg, I. The hologenome concept of evolution after 10 years. Microbiome 2018, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, G.D.D. Extended genomes: Symbiosis and evolution. Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20170001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, L.P.; Bruijning, M.; Forsberg, S.K.G.; Ayroles, J.F. The microbiome extends host evolutionary potential. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greyson-Gaito, C.J.; Bartley, T.J.; Cottenie, K.; Jarvis, W.M.C.; Newman, A.E.M.; Stothart, M.R. Into the wild: Microbiome transplant studies need broader ecological reality. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20192834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Lu, M. Gut commensal bacteria in biological invasions. Integr. Zool. 2019, 14, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Yang, W.; Blank, D. Reintroduction of Przewalski’s horse (Equus ferus przewalskii) in Xinjiang, China: The status and experience. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 177, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zong, H. Reintroduction of the przewalski’s horse in China: Status quo and outlook. Nat. Conserv. Res. 2019, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Shao, C.L.; Ge, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, W.X.; Yang, W.K. Suitable summer habitat of the khulan in the Mt.Kalamaili Ungulate Nature Reserve and estimation of its population. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 2993–3004. [Google Scholar]
- IUCN. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org (accessed on 23 May 2022).
- Van Dierendonck, M.C.; Wallis De Vries, M.F. Ungulate reintroductions: Experiences with the takhi or Przewalski horse (Equus ferus przewalskii) in Mongolia. Conserv. Biol. 1996, 10, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahloul, K.; Pereladova, O.B.; Soldatova, N.; Fisenko, G.; Sidorenko, E.; Sempéré, A.J. Social organization and dispersion of introduced kulans (Equus hemionus kulan) and Przewalski horses (Equus przewalski) in the Bukhara Reserve, Uzbekistan. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 47, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chu, H.; Lan, W.; Shi, K.; Tao, Y.; Shao, C. Trophic Niche Width and Overlap of Equus przewalskii, E. hemionus and Gazella subgutturosa in Autumn. Arid Zone Res. 2011, 47, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Burnik Šturm, M.; Ganbaatar, O.; Voigt, C.C.; Kaczensky, P. Sequential stable isotope analysis reveals differences in dietary history of three sympatric equid species in the Mongolian Gobi. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczensky, P.; Ganbaatar, O.; Von Wehrden, H.; Walzer, C. Resource selection by sympatric wild equids in the Mongolian Gobi. J. Appl. Ecol. 2008, 45, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xia, C.; Yang, W.; Blank, D.A.; Qiao, J.; Liu, W. Seasonal diet of Khulan (Equidae) in Northern Xinjiang, China. Ital. J. Zool. 2012, 79, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.; Hastie, P.; Murray, J.A. Factors Influencing Equine Gut Microbiota: Current Knowledge. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 88, 102943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poinar, H.N.; Schwarz, C.; Qi, J.; Shapiro, B.; MacPhee, R.D.E.; Buigues, B.; Tikhonov, A.; Huson, D.M.; Tomsho, L.P.; Auch, A.; et al. Metagenomics to paleogenomics: Large-scale sequencing of mammoth DNA. Science 2006, 311, 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.L.; Xu, S.Y.; Ren, Z.G.; Tao, L.; Jiang, J.W.; Zheng, S.S. Application of metagenomics in the human gut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, C.S.; Grueber, C.E. Functional Diversity within Gut Microbiomes: Implications for Conserving Biodiversity. Conservation 2021, 1, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Yang, J.; Qi, Y.; Li, B.; Li, K.; Mok, K.M. Metagenomic Analysis of Fecal Archaea, Bacteria, Eukaryota, and Virus in Przewalski’s Horses Following Anthelmintic Treatment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Srivathsan, A.; Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Hu, D.; Zhang, D. Gut Microbiomes of Endangered Przewalski’s Horse Populations in Short- and Long-Term Captivity: Implication for Species Reintroduction Based on the Soft-Release Strategy. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Tang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wei, L.U.; Wang, B.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, X.; Defu, H.U.; Junqing, L.I.; Zhang, D. Metagenomics reveals contrasting energy utilization efficiencies of captive and wild camels (Camelus ferus). Integr. Zool. 2021, 17, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.M.; Leung, C.M.; Ting, H.F.; Sadakane, K.; Yamashita, H.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT v1.0: A fast and scalable metagenome assembler driven by advanced methodologies and community practices. Methods 2016, 102, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huson, D.H.; Mitra, S.; Ruscheweyh, H.J.; Weber, N.; Schuster, S.C. Integrative analysis of environmental sequences using MEGAN4. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 1552–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantarel, B.I.; Coutinho, P.M.; Rancurel, C.; Bernard, T.; Lombard, V.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): An expert resource for Glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, J.N.; Pop, M.; Bravo, H.C. Metastats: An improved statistical method for analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, P17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, D.; Wang, L.; Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, W.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. Convergent Evolution of Rumen Microbiomes in High-Altitude Mammals. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manor, O.; Dai, C.L.; Kornilov, S.A.; Smith, B.; Price, N.D.; Lovejoy, J.C.; Gibbons, S.M.; Magis, A.T. Health and disease markers correlate with gut microbiome composition across thousands of people. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerbi, H.; Rejeb, A.; Erdoǧan, S.; Pérez, W. Anatomical and morphometric study of gastrointestinal tract of donkey (Equus africanus asinus). J. Morphol. Sci. 2014, 31, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Godon, J.J.; Arulazhagan, P.; Steyer, J.P.; Hamelin, J. Vertebrate bacterial gut diversity: Size also matters. BMC Ecol. 2016, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoelzer, F.; Burger, A.L.; Dierkes, P.W. Unraveling differences in fecal microbiota stability in mammals: From high variable carnivores and consistently stable herbivores. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A. Diversity is the question, not the answer. ISME J. 2016, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.E.; Shetty, S.A.; van den Berg, P.; Burden, F.; van Doorn, D.A.; Pellikaan, W.F.; Dijkstra, J.; Smidt, H. Multi-kingdom characterization of the core equine fecal microbiota based on multiple equine (sub)species. Anim. Microbiome 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, A.H.; Peeters, M.; Ndjango, J.B.; Li, Y.; Hahn, B.H.; Ochman, H. Sympatric chimpanzees and gorillas harbor convergent gut microbial communities. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Orlando, L. Genomics and the Evolutionary History of Equids. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 9, 81–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransom-Jones, E.; Jones, D.L.; McCarthy, A.J.; McDonald, J.E. The Fibrobacteres: An Important Phylum of Cellulose-Degrading Bacteria. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulund, F.; Pereira, M.B.; Jonsson, V.; Kristiansson, E. Computational and Statistical Considerations in the Analysis of Metagenomic Data. Metagenomics Perspect. Methods Appl. 2018, 63, 81–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fan, H.; Ding, X.; Hong, Z.; Nei, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G.; Guo, H. Analysis of the gut microbiota by high-throughput sequencing of the v5-v6 regions of the 16s rRNA gene in donkey. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 68, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Han, X.; Xu, S.; Zhao, L.; Hu, L.; Xu, T.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Comparative study of gut microbiota in Tibetan wild asses (Equus kiang) and domestic donkeys (Equus asinus) on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Aalvink, S.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia glycaniphila sp. nov., an anaerobic mucin-degrading bacterium isolated from reticulated python faeces. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 4614–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Y. Function of Akkermansia muciniphila in Obesity: Interactions with Lipid Metabolism, Immune Response and Gut Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blikslager, A.; Gonzalez, L. Equine Intestinal Mucosal Pathobiology. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2018, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.G.; Burden, F.A. Practical donkey and mule nutrition. In Equine Applied and Clinical Nutrition: Health, Welfare and Performance; Geor, R., Coenen, M., Harris, P., Eds.; Sauders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakeer, S.; Varma, M.; Sharma, J.; Mattoo, F.; Gupta, D.; Singh, J.; Kumar, M.; Gaur, N.A. Metagenomic analysis of the fecal microbiome of an adult elephant reveals the diversity of CAZymes related to lignocellulosic biomass degradation. Symbiosis 2020, 81, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, L.; Gao, Y.; Yan, L.; Jia, H.; Chu, H.; Ma, X.; He, L.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Hu, D.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Microbiome Metagenomics in Reintroduced Wild Horses and Resident Asiatic Wild Asses in the Gobi Desert Steppe. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061166
Tang L, Gao Y, Yan L, Jia H, Chu H, Ma X, He L, Wang X, Li K, Hu D, et al. Comparative Analysis of Microbiome Metagenomics in Reintroduced Wild Horses and Resident Asiatic Wild Asses in the Gobi Desert Steppe. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(6):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061166
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Liping, Yunyun Gao, Liping Yan, Huiping Jia, Hongjun Chu, Xinping Ma, Lun He, Xiaoting Wang, Kai Li, Defu Hu, and et al. 2022. "Comparative Analysis of Microbiome Metagenomics in Reintroduced Wild Horses and Resident Asiatic Wild Asses in the Gobi Desert Steppe" Microorganisms 10, no. 6: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061166
APA StyleTang, L., Gao, Y., Yan, L., Jia, H., Chu, H., Ma, X., He, L., Wang, X., Li, K., Hu, D., & Zhang, D. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Microbiome Metagenomics in Reintroduced Wild Horses and Resident Asiatic Wild Asses in the Gobi Desert Steppe. Microorganisms, 10(6), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10061166




