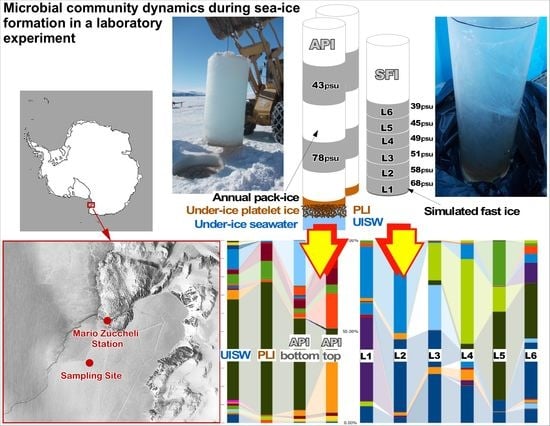
Wintertime Simulations Induce Changes in the Structure, Diversity and Function of Antarctic Sea Ice-Associated Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sampling
2.2. Simulation of Winter Freezing Process and Sea-Ice Brine Formation
2.3. Microbial Community Analysis
2.4. Bioinformatic Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Sequencing Data
2.7. Enrichment Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Physico–Chemical Analysis
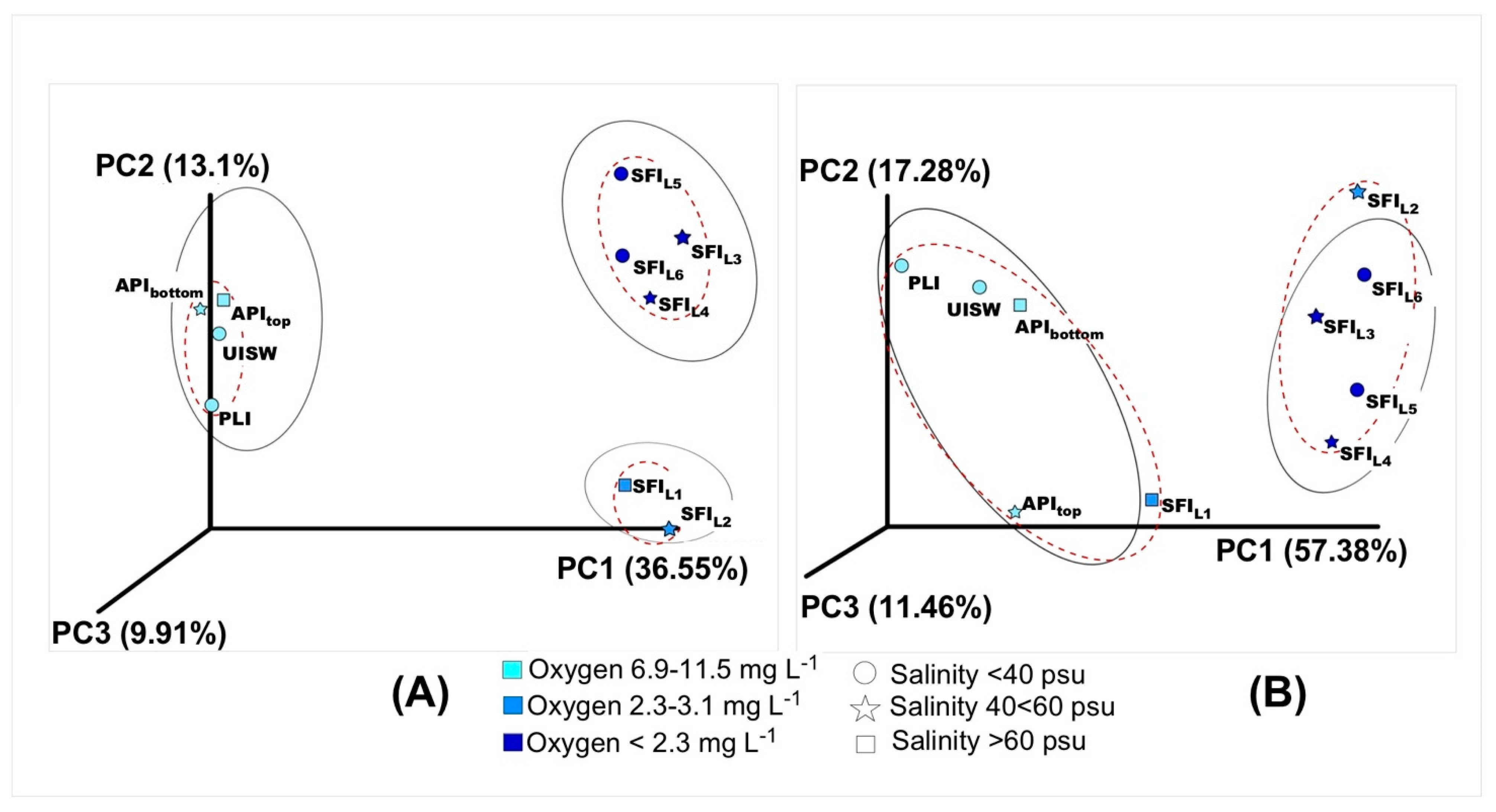
3.2. Alpha and Beta Diversity, Richness Metrics
3.3. Microbial Diversity in Natural Samples
3.4. Microbial Diversity in Simulated Winter Ice
3.5. Anaerobic Enrichments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parkinson, C.L.; Gloersen, P. Global sea ice coverage. In Atlas of Satellite Observations Related to Global Change; Gurney, R.J., Foster, J.L., Parkinson, C.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; pp. 371–383. [Google Scholar]
- Weissenberger, J.; Dieckmann, G.S.; Gradinger, R.; Spindler, M. Sea ice: A cast technique to examine and analyse brine pockets and channel structure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicken, H.; Bock, C.; Wittig, R.; Miller, H.; Poertner, H.-O. Magnetic resonance imaging of sea-ice pore fluids: Methods and thermal evolution of pore microstructure. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2000, 31, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Junge, K.; Eicken, H.; Deming, J.W. Bacterial activity at −2 to −20 °C in arctic wintertime sea ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mock, T.; Thomas, D.N. Recent advances in sea-ice microbiology. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewert, M.; Deming, J.W. Sea ice microorganisms: Environmental constraints and extracellular responses. Biology 2013, 2, 603–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.E.; Rocap, G.; Deming, J.W. Persistence of bacterial and archaeal communities in sea ice through an Arctic winter. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1828–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, B.R.; Mock, T. Polar microalgae: New approaches towards understanding adaptations to an extreme and changing environment. Biology 2014, 3, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R.; Worthen, D.L.; Lizotte, M.P.; Dixon, P.; Dieckmann, G. Primary production in Antarctic sea ice source. Science 1997, 276, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, L.; Carrada, G.; Catalano, G.; Dell’Anno, A.; Fabiano, M.; Lazzara, L.; Mangoni, O.; Pusceddu, A.; Saggiomo, V. Structural and functional properties of sympagic communities in the annual sea ice at Terra Nova Bay (Ross Sea, Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, A.C.; Sullivan, C.W. Sea ice microbial communities (SIMCO). Polar Biol. 1983, 2, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, D.L. Antarctic sea ice biota. Am. Zool. 1991, 31, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnack-Schiel, S.B.; Hagen, W.; Mizdalski, E. Seasonal carbon distribution of copepods in the eastern Weddell Sea, Antarctica. J. Mar. Syst. 1998, 17, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmisano, A.C.; Garrison, D.L. Microorganisms in Antarctic sea ice. In Antarctic Microbiology; Friedmann, E.I., Ed.; Wiley-Liss: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 167–218. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.V.; Bowman, J.P. A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea-ice microbial communities (SIMCO). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001, 35, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krembs, C.; Gradinger, R.; Spindler, M. Implications of brine channel geometry and surface area for the interaction of sympagic organisms in Arctic sea ice. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2000, 243, 55–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karl, D.M. Solar energy capture and transformation in the sea. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2014, 2, 000021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.S. The relationship between sea ice bacterial community structure and biogeochemistry: A synthesis of current knowledge and known unknowns. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2015, 3, 000072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusceddu, A.; Dell’Anno, A.; Vezzulli, L.; Fabiano, M.; Saggiomo, V.; Cozzi, S.; Catalano, G.; Guglielmo, L. Microbial loop malfunctioning in the annual sea ice at Terra Nova Bay (Antarctica). Polar Biol. 2009, 32, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, S.E.; Connelly, T.L.; Bronk, D.A. Nitrogen uptake dynamics in landfast sea ice of the Chukchi Sea. Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.P.; McCammon, S.A.; Brown, M.V.; Nichols, D.S.; McMeekin, T.A. Diversity and association of psychrophilic bacteria in Antarctic sea ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3068–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmeyer, R.; Knittel, K.; Jürgens, J.; Weyland, H.; Amann, R.; Helmke, E. Diversity and structure of bacterial communities in Arctic versus Antarctic pack ice. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6610–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmke, E.; Weyland, H. Bacteria in sea ice and underlying water of the eastern Weddell Sea in midwinter. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 117, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delille, D.; Rosiers, C. Seasonal changes of Antarctic marine bacterioplankton and sea ice bacterial assemblages. Polar Biol. 1996, 16, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmke, E.; Weyland, H. Psychrophilic versus psychrotolerant bacteria occurrence and significance in polar and temperate marine habitats. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2004, 50, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, M.; Kuosa, H.; Kopczynska, E.E.; Oriol, L.; Delille, D. Spatial and seasonal heterogeneity of sea ice microbial communities in the first-year ice of Terre Adelie area (Antarctica). Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 43, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Luhtanen, A.M.; Rintala, J.M.; Delille, B.; Dieckmann, G.; Karkman, A.; Tison, J. An active bacterial community linked to high chl-a concentrations in Antarctic winter-pack ice and evidence for the development of an anaerobic sea-ice bacterial community. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2345–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delille, B.; Vancoppenolle, M.; Geilfus, N.-X.; Tilbrook, B.; Lannuzel, D.; Schoemann, V.; Becquevort, S.; Carnat, G.; Delille, D.; Lancelot, C.; et al. Southern Ocean CO2 sink: The contribution of the sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 6340–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kublanov, I.V.; Perevalova, A.A.; Slobodkina, G.B.; Lebedinsky, A.V.; Bidzhieva, S.K.; Kolganova, T.V.; Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. Biodiversity of thermophilic prokaryotes with hydrolytic activities in hot springs of Uzon Caldera, Kamchatka (Russia). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowd, S.E.; Sun, Y.; Secor, P.R.; Rhoads, D.D.; Wolcott, B.M.; James, G.A.; Wolcott, R.D. Survey of bacterial diversity in chronic wounds using Pyrosequencing, DGGE, and full ribosome shotgun sequencing. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, D.; d’Errico, G.; Fiorentino, F.; Fattorini, D.; Regoli, F.; Angeletti, L.; Bakran-Petricioli, T.; Vetriani, C.; Yücel, M.; Taviani, M.; et al. Diversity and distribution of prokaryotes within a shallow-water pockmark field. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, S.; Foustoukos, D.I.; Giovannelli, D.; Yücel, M.; Vetriani, C. Ecological succession of sulfur-oxidizing Epsilon- and Gammaproteobacteria during colonization of a shallow-water gas vent. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M.; et al. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust. Ecol. 1993, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyksterhouse, S.E.; Gray, J.P.; Herwig, R.P.; Lara, J.C.; Staley, J.T. Cycloclasticus pugetii gen. nov., an aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium from marine sediments. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995, 45, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfennig, N.; Lippert, K.D. Über das Vitamin B12-Bedürfnis phototropher Schwefelbakterien. Arch. Mikrobiol. 1966, 55, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plugge, C.M. Anoxic media design, preparation, and considerations. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 397, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidak, B.L.; Cole, J.R.; Lilburn, T.G.; Parker, C.T.; Saxman, P.R.; Stredwick, J.M.; Garrity, G.M.; Li, B.; Olsen, G.J.; Pramanik, S.; et al. The RDP (Ribosomal Database Project) continues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 173–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R. UniFrac—an online tool for comparing microbial community diversity in a phylogenetic context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; Matero, I.; Bellas, C.; Turpin-Jelfs, T.; Anhaus, P.; Graeve, M.; Fripiat, F.; Tranter, M.; Landy, J.C.; Sanchez-Baracaldo, P.; et al. Monitoring a changing Arctic: Recent advancements in the study of sea ice microbial communities. Ambio 2022, 51, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, J.S.; Rasmussen, S.; Blom, N.; Deming, J.W.; Rysgaard, S.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T. Microbial community structure of Arctic multiyear sea ice and surface seawater by 454 sequencing of the 16S RNA gene. ISME J. 2012, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, K.R.; Thomas, D.N. Large scale importance of sea ice biology in the Southern Ocean. Antarct. Sci. 2004, 16, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartokallio, H.; Tuomainen, J.; Kuosa, H.; Kuparinen, J.; Martikainen, P.; Servomaa, K. Succession of sea-ice bacterial communities in the Baltic Sea fast ice. Polar Biol. 2008, 31, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, J.W. Sea ice bacteria and viruses. In Sea Ice, 2nd ed.; Thomas, D.N., Dieckmann, G.S., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 247–282. [Google Scholar]
- Hatam, I.; Charchuk, R.; Lange, B.; Beckers, J.; Haas, C.; Lanoil, B. Distinct bacterial assemblages reside at different depths in Arctic multiyear sea ice. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatam, I.; Lange, B.; Beckers, J.; Haas, C.; Lanoil, B. Bacterial communities from Arctic seasonal sea ice are more compositionally variable than those from multi-year sea ice. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2543–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Lyra, C.; Rintala, J.M.; Jurgens, K.; Ikonen, V.; Kaartokallio, H. Ice formation and growth shape bacterial community structure in Baltic Sea drift ice. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucciarelli, S.; Devaraj, R.R.; Mancini, A.; Ballarini, P.; Castelli, M.; Schrallhammer, M.; Petroni, G.; Miceli, C. Microbial consortium associated with the Antarctic marine ciliate Euplotes focardii: An investigation from genomic sequences. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 484–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rzeszutek, E.; van der Voort, M.; Wu, C.-H.; Thoen, E.; Skaar, I.; Bulone, V.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; de Bruijn, I. Diversity of aquatic Pseudomonas species and their activity against the fish pathogenic oomycete Saprolegnia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, S.A.; Carey, C.L.; Reuszer, H.W. Marine bacteria and their role in the cycle of life in the sea. I. Decomposition of marine plant and animal residues by bacteria. Biol. Bull. 1933, 65, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, S.A.; Butler, M.R. Relation of bacteria to diatoms in sea water. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 1937, 22, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J. Interactions between bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1982, 13, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.A.; Parker, M.S.; Armbrust, E.V. Interactions between diatoms and bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.E.; Adams, C.M.; Homolka, K.K.; Neibauer, J.A.; Mayer, L.M.; Keil, R.G. Degradation of diatom protein in seawater: A peptide-level view. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 757245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eronen-Rasimus, E.; Kaartokallio, H.; Lyra, C.; Autio, R.; Kuosa, H.; Dieckmann, G.; Thomas, D.N. Bacterial community dynamics and activity in relation to dissolved organic matter availability during sea-ice formation in a mesocosm experiment. MicrobiologyOpen 2014, 3, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, O.U.; Han, J.; Woyke, T.; Jansson, J.K. Single-cell genomics reveals features of a Colwellia species that was dominant during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Giuliano, L.; Gentile, G.; Crisafi, E.; Chernikova, T.N.; Abraham, W.-R.; Lünsdorf, H.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Oleispira antarctica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic coastal sea water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003, 53, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Obligate oil-degrading marine bacteria. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Bargiela, R.; Golyshin, P.N. Calm and Frenzy: Marine obligate hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria sustain ocean wellness. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 73, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; McCarthy, E.D.; Hoeven, W.V.; Calvin, M.; Bradley, W.H. Organic geochemical studies II. A preliminary report on the distribution of aliphatic hydrocarbons in algae, in bacteria, and in recent lake sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 59, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Calvin, M. Hydrocarbon distribution of algae and bacteria, and microbiological activity in sediments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1969, 64, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.E.M.; Brandini, F.P.; Staubes, R. The influence of light and temperature on carbon-specific DMS release by cultures of Phaeocystis antarctica and three antarctic diatoms. Mar. Chem. 1994, 45, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur, M.; Gosselin, M.; Michaud, S. A new source of dimethylsulfide (DMS) for the arctic atmosphere: Ice diatoms. Mar. Biol. 1994, 121, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levasseur, M.; Scarratt, M.G.; Michaud, S.; Merzouk, A.; Wong, C.S.; Arychuk, M.; Richardson, W.; Rivkin, R.B.; Hale, M.; Wong, E.; et al. DMSP and DMS dynamics during a mesoscale iron fertilization experiment in the Northeast Pacific—Part I: Temporal and vertical distributions. Deep-Sea Res. Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2006, 53, 2353–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curson, A.; Sullivan, M.; Todd, J.; Johnston, A.W.B. DddY, a periplasmic dimethylsulfoniopropionate lyase found in taxonomically diverse species of Proteobacteria. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.F.; Kiene, R.P. Microbial metabolism of dimethyl sulfide. In Biogenic Sulfur in the Environment; Saltzman, E.S., Cooper, W.J., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 202–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.; Loy, A.; Nickel, M.; Arnosti, C.; Baranyi, C.; Brüchert, V.; Ferdelman, T.; Finster, K.; Christensen, F.M.; Rosa de Rezende, J.; et al. A constant flux of diverse thermophilic bacteria into the cold Arctic seabed. Science 2009, 325, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmers, J.; Voget, S.; Dietrich, S.; Gollnow, K.; Smits, M.; Meyer, K.; Brinkhoff, T.; Simon, M.; Daniel, R. Poles apart: Arctic and Antarctic Octadecabacter strains share high genome plasticity and a new type of xanthorhodopsin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rysgaard, S.; Glud, R.N.; Sejr, M.K.; Blicher, M.E.; Stahl, H.J. Denitrification activity and oxygen dynamics in Arctic sea ice. Polar Biol. 2008, 31, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, E.; Carpenter, S.D.; Sørensen, H.L.; Collins, R.E.; Blum, J.D. Bacterial use of choline to tolerate salinity shifts in sea-ice brines. Elem. Sci. Anth. 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanueva, A.; Tuffin, M.; Cary, C.; Cowan, D.A. Molecular adaptations to psychrophily: The impact of ‘omic’ technologies. Trends Microbiol. 2010, 18, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiene, R.P. Uptake of choline and its conversion to glycine betaine by bacteria in estuarine waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaartokallio, H. Food web components, and physical and chemical properties of Baltic Sea ice. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 273, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuosa, H.; Kaartokallio, H. Experimental evidence on nutrient and substrate limitation of Baltic Sea sea-ice algae and bacteria. Hydrobiologia 2006, 554, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, A.; Michel, C.; Gosselin, M. Grazing of large-sized bacteria by sea-ice heterotrophic protists on the Mackenzie shelf during the winter-spring transition. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2007, 50, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.E.; Carpenter, S.D.; Deming, J.W. Spatial heterogeneity and temporal dynamics of particles, bacteria, and pEPS in Arctic winter sea ice. J. Mar. Sys. 2008, 74, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piiparinen, J.; Kuosa, H. Impact of UVA radiation on algae and bacteria in Baltic Sea ice. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2011, 63, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Collins, R.E. Microbial evolution under extreme conditions. In Microbial Evolution Under Extreme Conditions; Bakermans, C., Ed.; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Göttingen, Germany, 2015; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
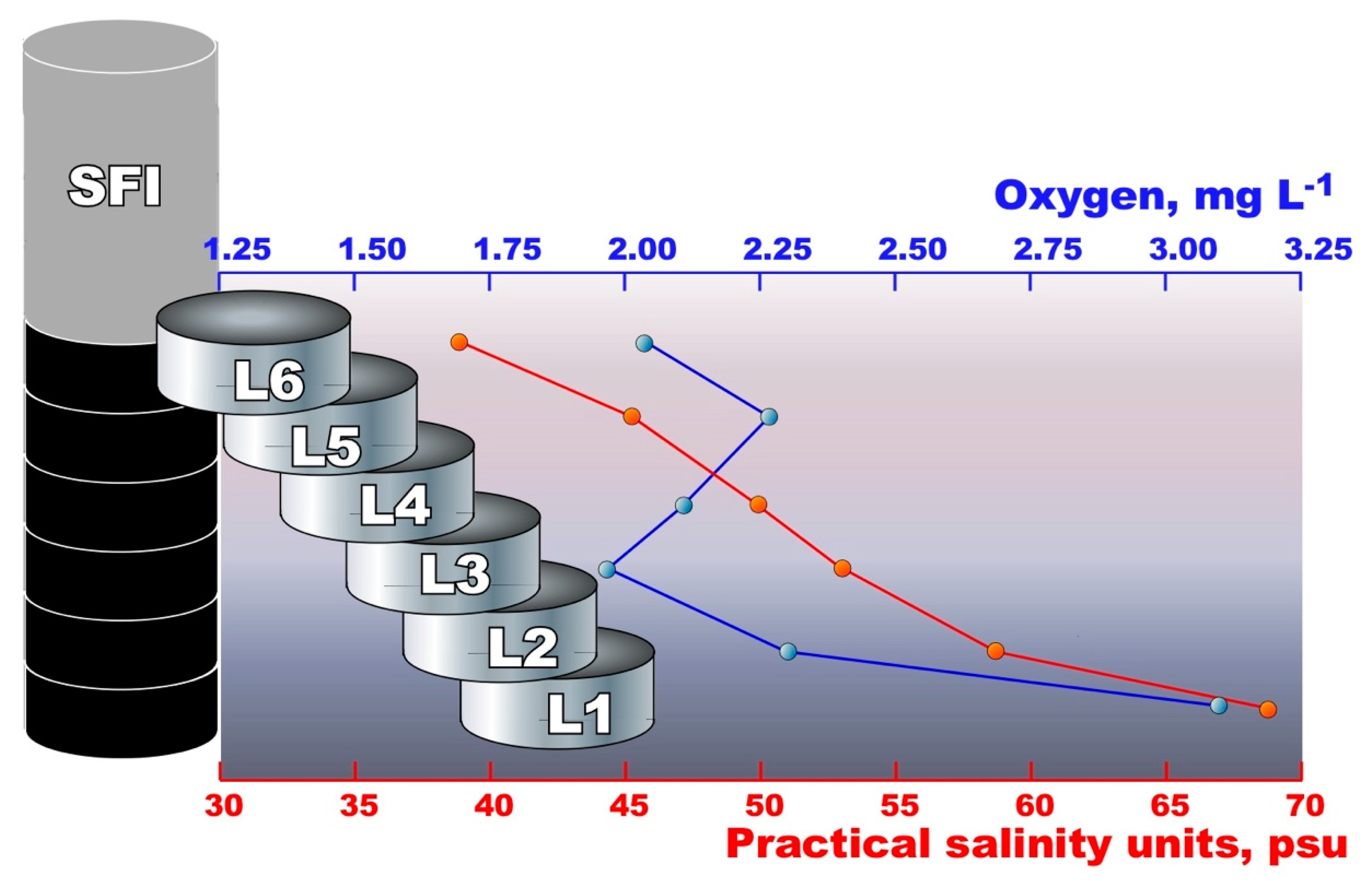


| Sample | Salinity, psu | Oxygen, mg L−1 | pH | Temperature, °C | Redox, mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Pack Ice, Platelet Ice and Seawater | |||||
| APItop | 43 | 6.93 | 7.5 | −7.1 | ND |
| APIbottom | 78 | 7.36 | 7.8 | −4.3 | ND |
| PLI | 35 | 11.52 | 8.3 | −1.8 | ND |
| UISW | 34 | 8.80 | 8.1 | −1.8 | ND |
| Simulated Fast Ice | |||||
| SFIL6 | 39 | 2.04 | 8.0 | −2.0 | +108.0 |
| SFIL5 | 45 | 2.26 | 8.0 | −2.0 | +101.4 |
| SFIL4 | 49 | 2.10 | 7.6 | −2.0 | +103.2 |
| SFIL3 | 53 | 1.96 | 7.7 | −2.0 | +91.3 |
| SFIL2 | 58 | 2.33 | 7.5 | −2.0 | +91.8 |
| SFIL1 | 68 | 3.10 | 7.3 | −2.0 | +86.3 |
| Sample | Chimera Check | ASV | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon | Simpson | Dominance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | |||||||
| Annual Pack Ice, Platelet Ice and Seawater | ||||||||
| APItop | 25,950 | 24,602 | 692 | 1376.11 | 1302.66 | 5.411 | 0.914 | 0.086 |
| APIbottom | 24,889 | 22,407 | 768 | 1470.22 | 1305.66 | 4.793 | 0.814 | 0.186 |
| PLI | 27,614 | 26,913 | 541 | 959.96 | 925.17 | 5.252 | 0.930 | 0.070 |
| UISW | 25,127 | 23,583 | 1057 | 1943.7 | 1745.59 | 6.593 | 0.956 | 0.044 |
| Simulated Fast Ice | ||||||||
| SFIL6 | 24,132 | 23,307 | 461 | 726.08 | 687.78 | 4.716 | 0.885 | 0.115 |
| SFIL5 | 29,267 | 28,377 | 227 | 403.08 | 389.03 | 3.353 | 0.832 | 0.168 |
| SFIL4 | 16,334 | 14,335 | 350 | 550.38 | 554.19 | 3.833 | 0.788 | 0.212 |
| SFIL3 | 10,472 | 10,298 | 174 | 258.43 | 260.89 | 3.034 | 0.762 | 0.238 |
| SFIL2 | 19,822 | 11,586 | 310 | 421.15 | 388.76 | 3.384 | 0.743 | 0.257 |
| SFIL1 | 25,205 | 18,856 | 445 | 768.55 | 749.55 | 4.236 | 0.808 | 0.192 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cono, V.L.; Smedile, F.; Crisafi, F.; Marturano, L.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Spada, G.L.; Bản, N.K.; Yakimov, M.M. Wintertime Simulations Induce Changes in the Structure, Diversity and Function of Antarctic Sea Ice-Associated Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030623
Cono VL, Smedile F, Crisafi F, Marturano L, Toshchakov SV, Spada GL, Bản NK, Yakimov MM. Wintertime Simulations Induce Changes in the Structure, Diversity and Function of Antarctic Sea Ice-Associated Microbial Communities. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(3):623. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030623
Chicago/Turabian StyleCono, Violetta La, Francesco Smedile, Francesca Crisafi, Laura Marturano, Stepan V. Toshchakov, Gina La Spada, Ninh Khắc Bản, and Michail M. Yakimov. 2022. "Wintertime Simulations Induce Changes in the Structure, Diversity and Function of Antarctic Sea Ice-Associated Microbial Communities" Microorganisms 10, no. 3: 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030623
APA StyleCono, V. L., Smedile, F., Crisafi, F., Marturano, L., Toshchakov, S. V., Spada, G. L., Bản, N. K., & Yakimov, M. M. (2022). Wintertime Simulations Induce Changes in the Structure, Diversity and Function of Antarctic Sea Ice-Associated Microbial Communities. Microorganisms, 10(3), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10030623