Assessment of Diagnostic Specificity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests and Their Application for Monitoring of Seroconversion and Stability of Antiviral Antibody Response in Healthcare Workers in Moscow
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
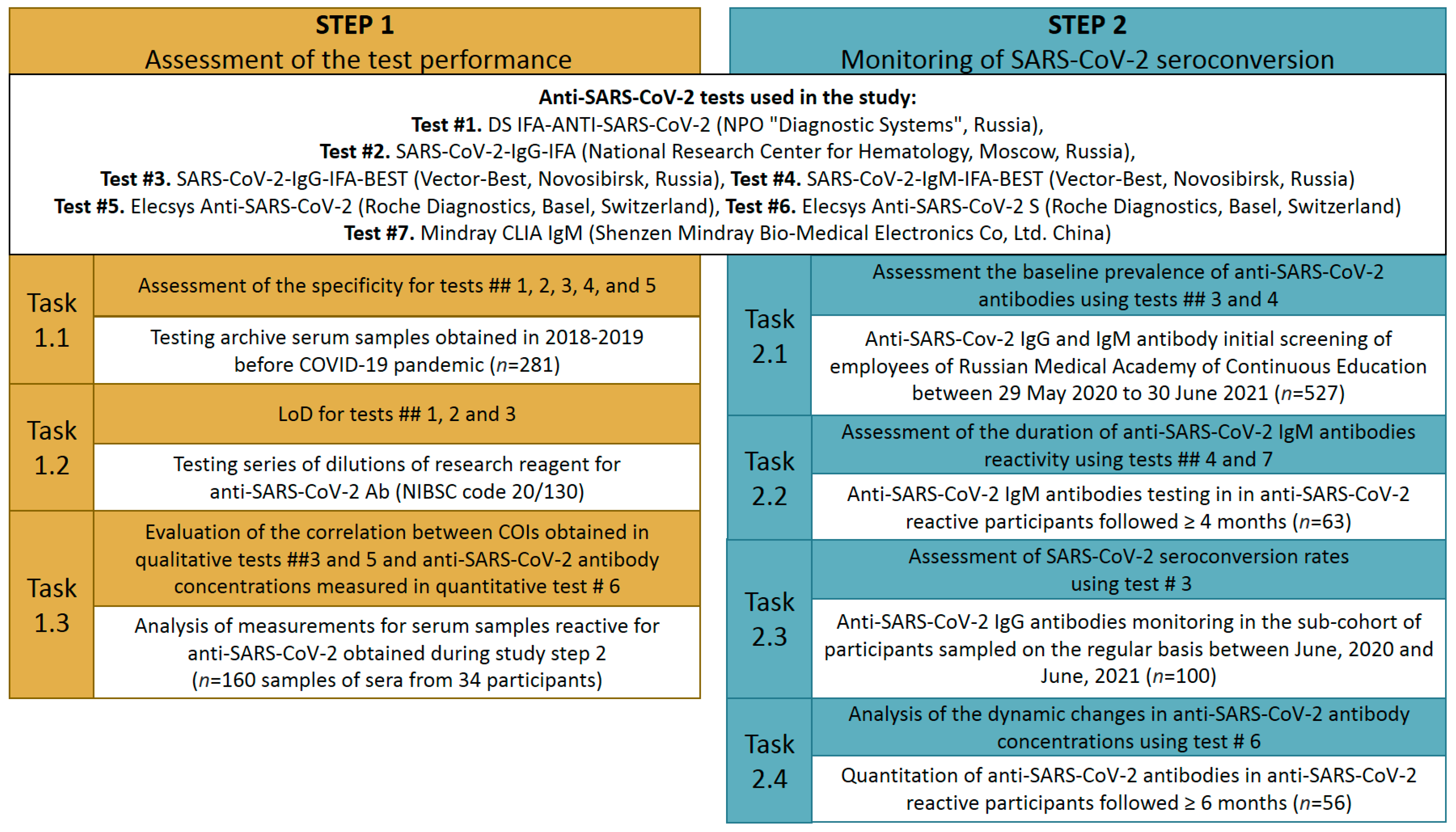
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Participants and Study Samples
2.3. Tests Used to Assess Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies
2.4. Assessment of the Specificity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Tests
2.5. Determination of the Limit of Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Tests
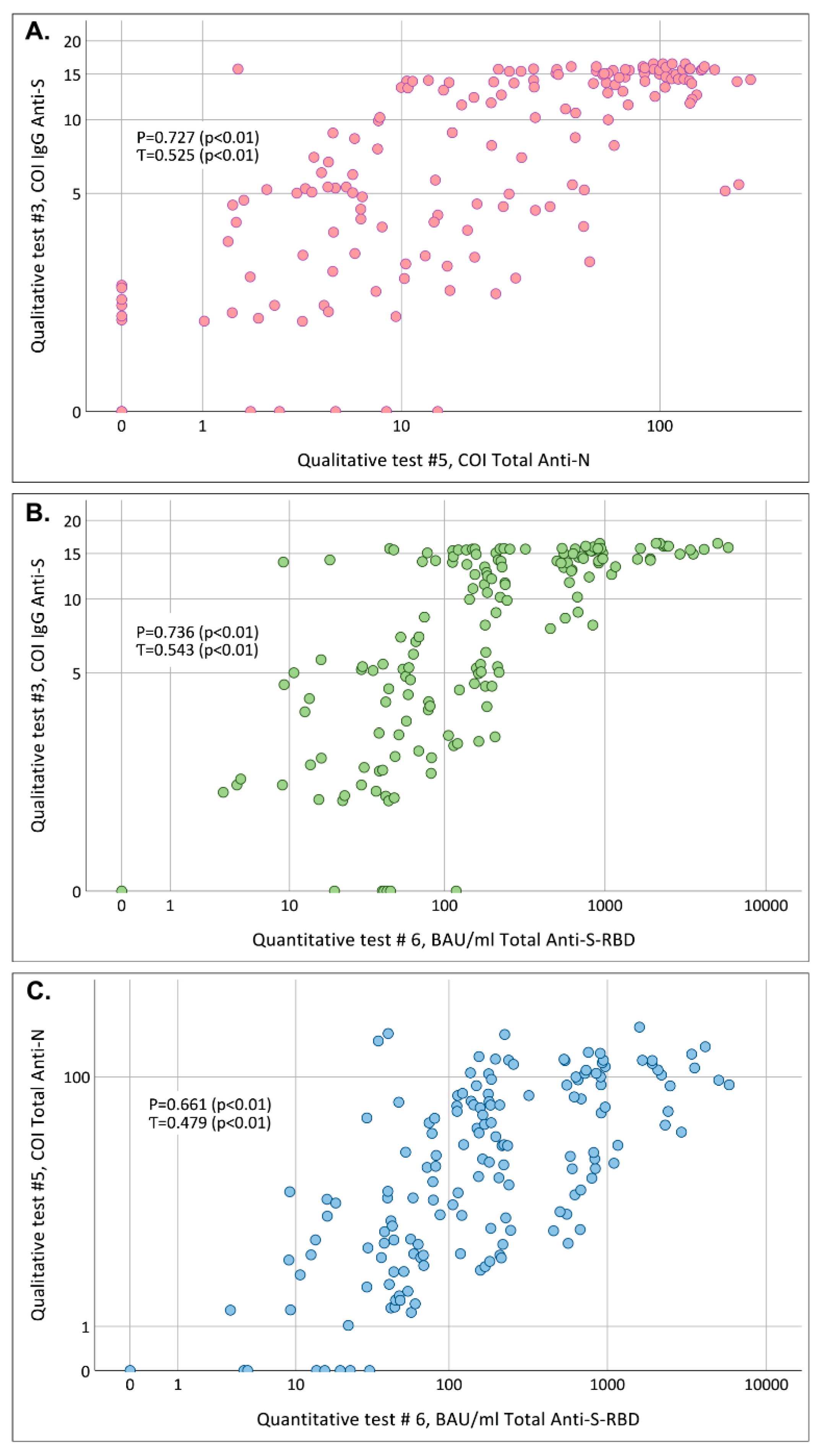
2.6. Evaluation of Correlation between Cut-Off Indexes Obtained in Qualitative and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Concentrations Obtained in Quantitative Test
2.7. Monitoring of the Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Cohort of Healthcare Workers
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Performance of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Tests
3.2. Correlation of COIs Obtained in Qualitative #3 (SARS-CoV-2-IgG-IFA-BEST) and #5 (Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2) Tests and Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Concentrations in Quantitative # 6 (Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S) Test
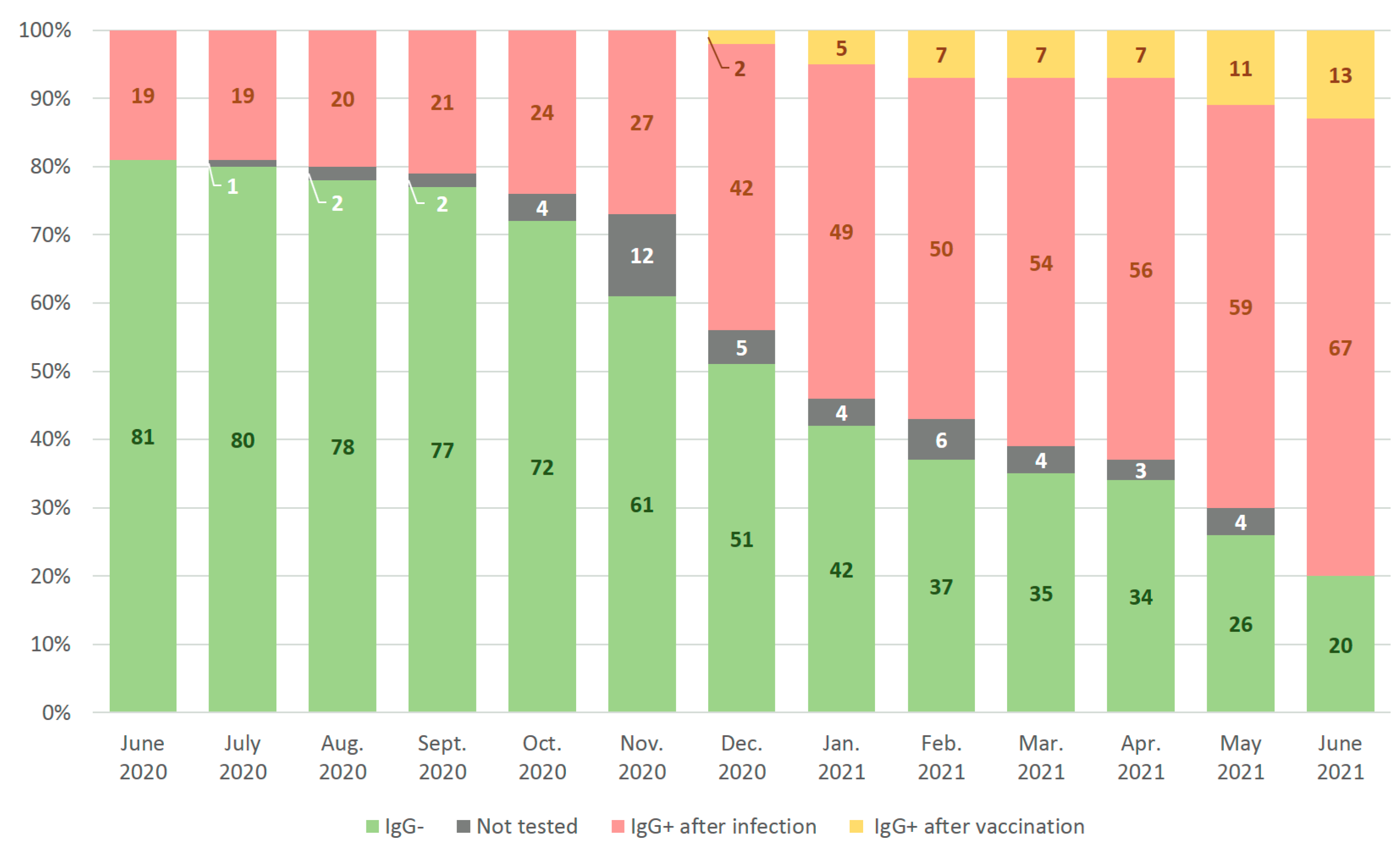
3.3. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Prevalence Rates at Initial Screening Conducted at Different Stages of COVID-19 Pandemic
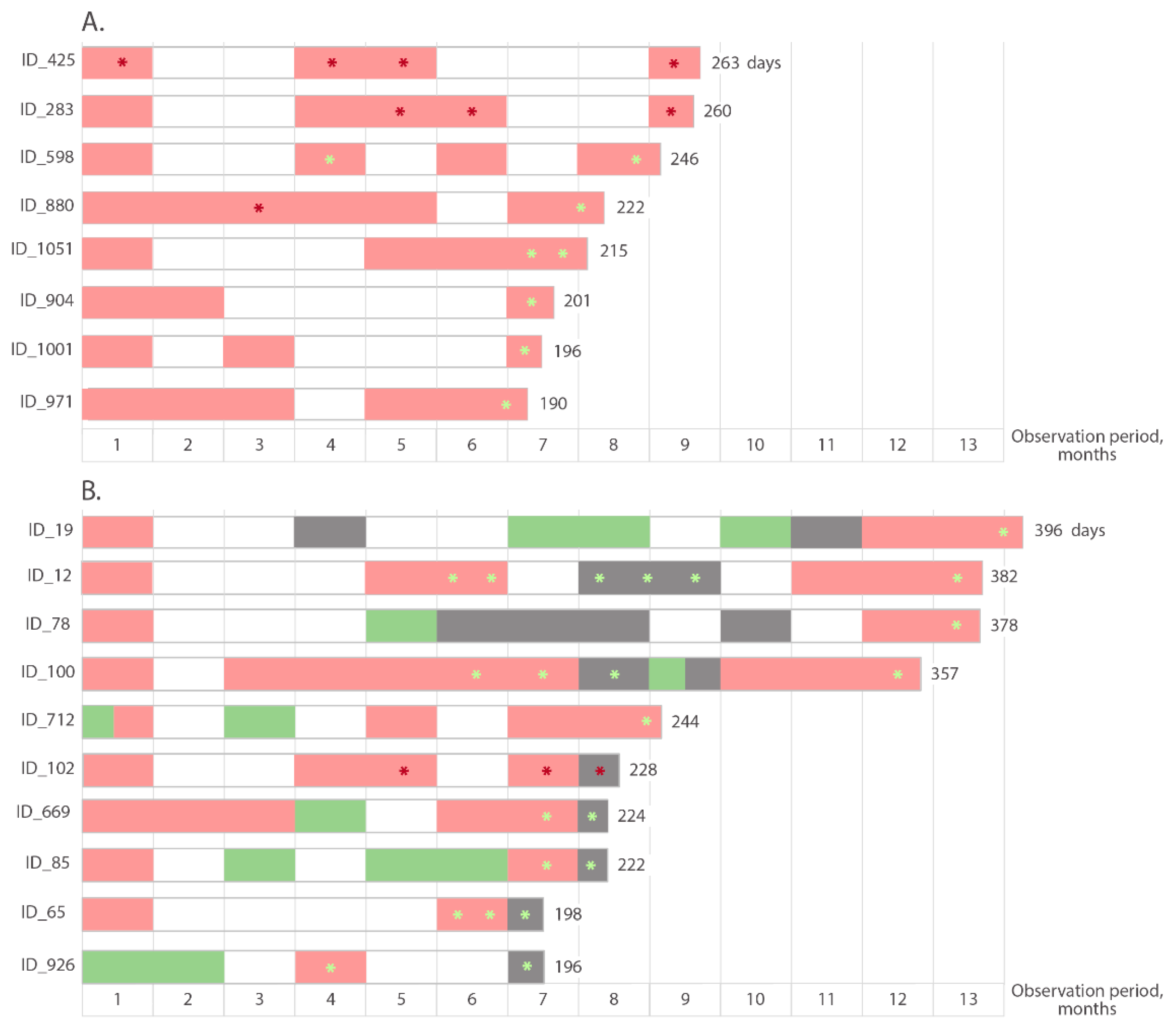
3.4. Duration of Reactivity for IgM Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2
3.5. Monthly Rates of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Cohort of Healthcare Professionals
3.6. Changes in Anti-S Antibody Concentrations during the Follow-Up for More Than 6 Months
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Coronavirus: Statistics. Available online: https://yandex.ru/covid19/stat/index (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Interim Guidelines for Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19. Version 14 (27 December 2021). Available online: https://static-0.minzdrav.gov.ru/system/attachments/attaches/000/059/041/original/%D0%92%D0%9C%D0%A0_COVID-19_V14_27-12-2021.pdf (accessed on 2 February 2022).
- Health Center for Devices and Radiological In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/in-vitro-diagnostics-euas (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- CDC Healthcare Workers. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/testing-overview.html (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Falzone, L.; Gattuso, G.; Tsatsakis, A.; Spandidos, D.A.; Libra, M. Current and Innovative Methods for the Diagnosis of COVID-19 Infection (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Qin, R.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Wen, W.; Li, J. Clinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgA Antibody for the Diagnosis of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 104, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zeng, W.; He, H.; Zhao, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, P.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, X.; Jin, T. Serum IgA, IgM, and IgG Responses in COVID-19. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid-Abdi, M.; Krifors, A.; Sälléber, A.; Eriksson, J.; Månsson, E. Low Rate of COVID-19 Seroconversion in Health-Care Workers at a Department of Infectious Diseases in Sweden during the Later Phase of the First Wave; a Prospective Longitudinal Seroepidemiological Study. Infect. Dis. 2021, 53, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Diagnostic Testing for SARS-CoV-2: Interim Guidance, 11 September 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Wong, B.H.; Tsoi, H.; Fung, A.M.; Kao, R.Y.; Chan, K.; Peiris, J.M.; Yuen, K. Differential Sensitivities of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Coronavirus Spike Polypeptide Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) and SARS Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein ELISA for Serodiagnosis of SARS Coronavirus Pneumonia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3054–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, X.; Qiu, L.; Pan, Y.; Wen, K.; Hao, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Hua, X.; Cheng, V.C.C.; et al. Sensitive and Specific Monoclonal Antibody-Based Capture Enzyme Immunoassay for Detection of Nucleocapsid Antigen in Sera from Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 2629–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okba, N.M.A.; Müller, M.A.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Corman, V.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Bruin, E.; Chandler, F.D.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2−Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.A.; Mok, C.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Lv, H.; Ko, R.L.; Wu, N.C.; Yuan, M.; Leung, W.S.; Chan, J.M.; Chik, T.S.; et al. Serological Assays for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), March 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallano, A.; Ascione, A.; Flego, M. Antibody Response against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Implications for Diagnosis, Treatment and Vaccine Development. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, B.T.; Bryan, A.; Fink, S.L.; Goecker, E.A.; Roychoudhury, P.; Huang, M.-L.; Zhu, H.; Chaudhary, A.; Madarampalli, B.; Lu, J.Y.C.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Levels Measured by the AdviseDx SARS-CoV-2 Assay Are Concordant with Previously Available Serologic Assays but Are Not Fully Predictive of Sterilizing Immunity. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0098921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creech, C.B.; Walker, S.C.; Samuels, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. JAMA 2021, 325, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Huth, S.; Lillevang, S.T.; Røge, B.T.; Madsen, J.S.; Mogensen, C.B.; Coia, J.E.; Möller, S.; Justesen, U.S.; Johansen, I.S. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence among 7950 Healthcare Workers in the Region of Southern Denmark. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 112, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.J.; Wilmore, S.M.S.; McCann, N.S.; Donnelly, O.; Lai, R.W.L.; Kinsella, M.J.; Rochford, H.L.; Patel, T.; Kelsey, M.C.; Andrews, J.A. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Healthcare Workers at a London NHS Trust. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2021, 42, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houlihan, C.F.; Vora, N.; Byrne, T.; Lewer, D.; Kelly, G.; Heaney, J.; Gandhi, S.; Spyer, M.J.; Beale, R.; Cherepanov, P.; et al. Pandemic Peak SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Seroconversion Rates in London Frontline Health-Care Workers. Lancet 2020, 396, e6–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation Dated May 22, 2020 No. 15 on Approval of the Sanitary and Epidemiological Rules SP 3.1.3597-20 “Prevention of a New Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19)”. Available online: http://www.garant.ru/products/ipo/prime/doc/74077903/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-NCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, C.L.; Kanji, J.N.; Johal, K.; Bailey, A.; Plitt, S.S.; MacDonald, C.; Kunst, A.; Buss, E.; Burnes, L.E.; Fonseca, K.; et al. Evaluation of Six Commercial Mid- to High-Volume Antibody and Six Point-of-Care Lateral Flow Assays for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01361-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, J.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Kalish, H.; Shunmugavel, A.; Mehalko, J.; Denson, J.-P.; Snead, K.R.; Drew, M.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; et al. Serologic Cross-Reactivity of SARS-CoV-2 with Endemic and Seasonal Betacoronaviruses. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 41, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woudenberg, T.; Pelleau, S.; Anna, F.; Attia, M.; Donnadieu, F.; Gravet, A.; Lohmann, C.; Seraphin, H.; Guiheneuf, R.; Delamare, C.; et al. Humoral Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and Seasonal Coronaviruses in Children and Adults in North-Eastern France. EBioMedicine 2021, 70, 103495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letter of the Federal Service for Supervision in the Sphere of Healthcare Dated July 5, 2021. Available online: http://ivo.garant.ru/#/document/401481102/paragraph/1:0 (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- WHO/BS.2020.2403 Establishment of the WHO International Standard and Reference Panel for Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody. WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/WHO-BS-2020.2403 (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Premkumar, L.; Segovia-Chumbez, B.; Jadi, R.; Martinez, D.R.; Raut, R.; Markmann, A.; Cornaby, C.; Bartelt, L.; Weiss, S.; Park, Y.; et al. The Receptor Binding Domain of the Viral Spike Protein Is an Immunodominant and Highly Specific Target of Antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 Patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabc8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pei, D.; Jiang, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhai, J.; Du, Z.; Li, B.; et al. Antigenicity Analysis of Different Regions of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Nucleocapsid Protein. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Jeremiah, S.S.; Miyakawa, K.; Saji, R.; Nishii, M.; Takeuchi, I.; Ryo, A. Whole Nucleocapsid Protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 May Cause False-Positive Results in Serological Assays. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, 1291–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, F.; Buonfrate, D.; Moro, L.; Rodari, P.; Piubelli, C.; Caldrer, S.; Riccetti, S.; Sinigaglia, A.; Barzon, L. Antibody Response to the BNT162b2 MRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Subjects with Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapovalov, K.; Stepanov, A.; Burdinskaya, J. Three-month results of vaccination of monostationary health workers with the drug «Gam-Covid-Vac». Immunologiya 2021, 42, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasztelewicz, B.; Janiszewska, K.; Burzyńska, J.; Szydłowska, E.; Migdał, M.; Dzierżanowska-Fangrat, K. Prevalence of IgG Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 among Healthcare Workers in a Tertiary Pediatric Hospital in Poland. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkurt, G.; Murt, A.; Aydin, Z.; Tatli, O.; Agaoglu, N.B.; Irvem, A.; Aydin, M.; Karaali, R.; Gunes, M.; Yesilyurt, B.; et al. Seroprevalence of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) among Health Care Workers from Three Pandemic Hospitals of Turkey. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barallat, J.; Fernández-Rivas, G.; Quirant-Sánchez, B.; González, V.; Doladé, M.; Martinez Caceres, E.; Piña, M.; Aguilar, J.; Estrada, O.; Blanco, I. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Specific Antibodies among Healthcare Workers in the Northern Metropolitan Area of Barcelona, Spain, after the First Pandemic Wave. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanis, P.; Vraka, I.; Fragkou, D.; Bilali, A.; Kaitelidou, D. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies and Associated Factors in Healthcare Workers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 108, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-C.; Wang, J.-H.; Hsueh, P.-R. Population-Based Seroprevalence Surveys of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody: An up-to-Date Review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, Y.; Cole, M.; Duffy, E.; de la Cena, K.; Schechter-Perkins, E.M.; Bouton, T.C.; Werler, M.M.; Pierre, C.; Ragan, E.J.; Weber, S.E.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 IgG Antibodies and Risk Factors in Health Care Workers at an Academic Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, R.; Dana, T.; Buckley, D.I.; Selph, S.; Fu, R.; Totten, A.M. Epidemiology of and Risk Factors for Coronavirus Infection in Health Care Workers: A Living Rapid Review. Ann. Intern. Med. 2020, 173, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poustchi, H.; Darvishian, M.; Mohammadi, Z.; Shayanrad, A.; Delavari, A.; Bahadorimonfared, A.; Eslami, S.; Javanmard, S.H.; Shakiba, E.; Somi, M.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Seroprevalence in the General Population and High-Risk Occupational Groups across 18 Cities in Iran: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireles, P.; Amaro, J.; Pinto da Costa, J.; Lopes, M.M.; Varandas, T.; Norton, P.; Guimarães, J.T.; Severo, M.; Barros, H. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies among Workers of the Public Higher Education Institutions of Porto, Portugal: A Cross-Sectional Study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2021, 78, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollán, M.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Oteo, J.; Hernán, M.A.; Pérez-Olmeda, M.; Sanmartín, J.L.; Fernández-García, A.; Cruz, I.; Fernández de Larrea, N.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in Spain (ENE-COVID): A Nationwide, Population-Based Seroepidemiological Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altawalah, H. Antibody Responses to Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection or after COVID-19 Vaccination. Vaccines 2021, 9, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epaulard, O.; Buisson, M.; Nemoz, B.; Maréchal, M.L.; Terzi, N.; Payen, J.-F.; Froidure, M.; Blanc, M.; Mounayar, A.-L.; Quénard, F.; et al. Persistence at One Year of Neutralizing Antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Influence of Initial Severity and Steroid Use. J. Infect. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haveri, A.; Ekström, N.; Solastie, A.; Virta, C.; Österlund, P.; Isosaari, E.; Nohynek, H.; Palmu, A.A.; Melin, M. Persistence of Neutralizing Antibodies a Year after SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Humans. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 3202–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhu, B.; Guo, X.; Xu, K.; Song, C.; Fu, J.; Yu, H.; Kong, X.; Peng, J.; et al. Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Specific and Neutralizing Antibodies over Seven Months after Symptom Onset in COVID-19 Patients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0059021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallais, F.; Gantner, P.; Bruel, T.; Velay, A.; Planas, D.; Wendling, M.-J.; Bayer, S.; Solis, M.; Laugel, E.; Reix, N.; et al. Evolution of Antibody Responses up to 13 Months after SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Risk of Reinfection. EBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capetti, A.F.; Borgonovo, F.; Mileto, D.; Gagliardi, G.; Mariani, C.; Lupo, A.; Dedivitiis, G.; Meraviglia, P.; Pellicciotta, M.; Armiento, L.; et al. One-Year Durability of Anti-Spike IgG to SARS-CoV-2: Preliminary Data from the Anticrown Prospective Observational Study One Year Durability of COVID-19 Anti-Spike IgG. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 237–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiá, M.; Fernández-González, M.; Telenti, G.; Agulló, V.; García, J.A.; Padilla, S.; García-Abellán, J.; Galiana, A.; Gonzalo-Jiménez, N.; Gutiérrez, F. Durable Antibody Response One Year after Hospitalization for COVID-19: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 123, 102703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellam, P.; Barclay, W. The Dynamics of Humoral Immune Responses Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the Potential for Reinfection. J. Gen. Virol. 2020, 101, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRee, A.-L.; Gilkey, M.B.; Dempsey, A.F. HPV Vaccine Hesitancy: Findings from a Statewide Survey of Health Care Providers. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2014, 28, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamisy-Farah, R.; Adawi, M.; Jeries-Ghantous, H.; Bornstein, J.; Farah, R.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Odeh, M. Knowledge of Human Papillomavirus (HPV), Attitudes and Practices Towards Anti-HPV Vaccination Among Israeli Pediatricians, Gynecologists, and Internal Medicine Doctors: Development and Validation of an Ad Hoc Questionnaire. Vaccines 2019, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyuregyan, K.K.; Kichatova, V.S.; Isaeva, O.V.; Potemkin, I.A.; Malinnikova, E.Y.; Lopatukhina, M.A.; Karlsen, A.A.; Asadi Mobarhan, F.A.; Mullin, E.V.; Slukinova, O.S.; et al. Coverage with Timely Administered Vaccination against Hepatitis B Virus and Its Influence on the Prevalence of HBV Infection in the Regions of Different Endemicity. Vaccines 2021, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Test No. | Test System (Manufacturer) | Type of Test | Antibody Isotype | Target Protein | Positive Result | Grey Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | DS IFA-ANTI-SARS-CoV-2 (NPO “Diagnostic Systems”, Russia) | Qualitative, ELISA | IgG + IgM | N and S | COI > Cut-off +20% | Yes (COI between Cut-off −20% to Cut-off +20%) |
| 2 | SARS-CoV-2-IgG-IFA (National Research Center for Hematology, Moscow, Russia) | Qualitative, ELISA | IgG | S-RBD | COI ≥ 1.1 | Yes (COI from 0.9 to 1.1) |
| 3 | SARS-CoV-2-IgG-IFA-BEST (Vector-Best, Novosibirsk, Russia) | Qualitative, ELISA | IgG | S | COI ≥ 1.1 | Yes (COI from 0.8 to 1.1) |
| 4 | SARS-CoV-2-IgM-IFA-BEST (Vector-Best, Novosibirsk, Russia) | Qualitative, ELISA | IgM | N and S-RBD | COI ≥ 1.1 | Yes (COI from 0.8 to 1.1) |
| 5 | Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) | Qualitative, CLIA | Total Abs | N | COI ≥ 1.0 | No |
| 6 | Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) | Quantitative, CLIA | Total Abs | S-RBD | U/mL > 0.8 | No |
| 7 | Mindray CLIA IgM (Shenzen Mindray Bio-Medical Electronics Co, Ltd. China) | Qualitative, CLIA | IgM | N and S | COI ≥ 1 | No |
| Test No. | Test System (Manufacturer) | N Reactive Samples/ N Tested | Specificity of Test | Mean COI in Reactive Samples | N Samples in Grey Zone/ N Total | LoD, BAU/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DS IFA-ANTI-SARS-CoV-2 (NPO “Diagnostic Systems”, Russia) | version 1 | 6/194 | 96.9% (93.3–98.7%) | 1.73 | 5/194 | n.d.* |
| version 2 | 7/194 | 96.4% (92.6–98.4%) | 1.66 | 3/194 | n.d. | ||
| version 4/5 | 2/281 | 99.3% (97.3–99.9%) | 2.79 | 3/281 | 0.1 | ||
| 2 | SARS-CoV-2-IgG-IFA (National Research Center for Hematology, Moscow, Russia) | 3/281 | 98.9% (96.8–99.8%) | 2.61 | 3/281 | 0.4 | |
| 3 | SARS-CoV-2-IgG-IFA-BEST (Vector-Best, Novosibirsk, Russia) | 4/281 | 98.5% (96.3–99.6%) | 1.80 | 2/281 | 0.5 | |
| 4 | SARS-CoV-2-IgM-IFA-BEST (Vector-Best, Novosibirsk, Russia) | 3/279 | 98,9% (97.3–99.9) | 2.11 | 1/279 | n.d. | |
| 5 | Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2 (Roche Diagnostics, Basal, Switzerland) | 0/281 | 100% (98.4–100%) | - | 0/281 | n.d. | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kichatova, V.S.; Asadi Mobarkhan, F.A.; Potemkin, I.A.; Zlobin, S.P.; Perfilieva, O.M.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Ivanov, A.V.; Solonin, S.A.; Godkov, M.A.; Belikova, M.G.; et al. Assessment of Diagnostic Specificity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests and Their Application for Monitoring of Seroconversion and Stability of Antiviral Antibody Response in Healthcare Workers in Moscow. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020429
Kichatova VS, Asadi Mobarkhan FA, Potemkin IA, Zlobin SP, Perfilieva OM, Valuev-Elliston VT, Ivanov AV, Solonin SA, Godkov MA, Belikova MG, et al. Assessment of Diagnostic Specificity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests and Their Application for Monitoring of Seroconversion and Stability of Antiviral Antibody Response in Healthcare Workers in Moscow. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020429
Chicago/Turabian StyleKichatova, Vera S., Fedor A. Asadi Mobarkhan, Ilya A. Potemkin, Sergey P. Zlobin, Oksana M. Perfilieva, Vladimir T. Valuev-Elliston, Alexander V. Ivanov, Sergey A. Solonin, Mikhail A. Godkov, Maria G. Belikova, and et al. 2022. "Assessment of Diagnostic Specificity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests and Their Application for Monitoring of Seroconversion and Stability of Antiviral Antibody Response in Healthcare Workers in Moscow" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020429
APA StyleKichatova, V. S., Asadi Mobarkhan, F. A., Potemkin, I. A., Zlobin, S. P., Perfilieva, O. M., Valuev-Elliston, V. T., Ivanov, A. V., Solonin, S. A., Godkov, M. A., Belikova, M. G., Mikhailov, M. I., & Kyuregyan, K. K. (2022). Assessment of Diagnostic Specificity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Tests and Their Application for Monitoring of Seroconversion and Stability of Antiviral Antibody Response in Healthcare Workers in Moscow. Microorganisms, 10(2), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020429








