Recent Antimicrobial Responses of Halophilic Microbes in Clinical Pathogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Halophiles: A Potential Source of Antimicrobials
3. Biopotency of Halophiles as Antibacterials for Clinical Drug-Resistant Pathogens
4. Recent Activity Findings from Halophiles—Against Clinically Important Pathogens
4.1. Halophilic Bacillus sp.
4.2. Halophilic Actinomycetes
4.3. Other Halophilic Bacterial Species
4.4. Halophilic Microalgae
5. Novel Antimicrobials and Their Producing Strains from Halophiles
6. Halo-Microbial Derived Products as Antimicrobials
6.1. Pigments
6.2. Biosurfactants
6.3. Exopolysaccharides
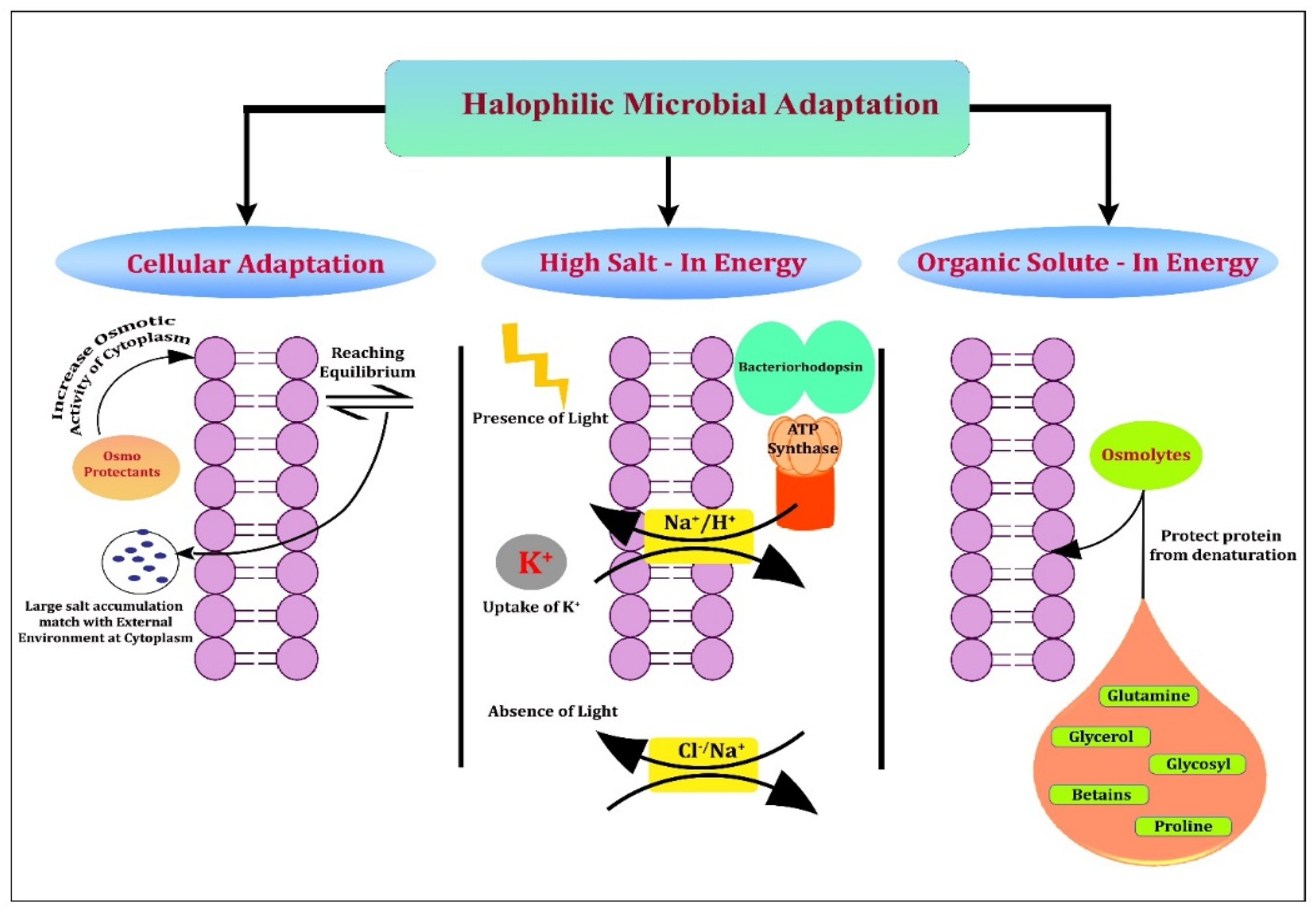
7. Strategies behind Halophiles for Bimolecular Adaptation to Extreme Habitats
8. Applications and Future Perspectives of Halophiles as Pharmaceuticals
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peterson, E.; Kaur, P. Antibiotic resistance mechanisms in bacteria: Relationships between resistance determinants of antibiotic producers, environmental bacteria, and clinical pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report on Surveilance; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/about/where-resistance-spreads.html (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- TATFAR Progress Report 2016–2020; U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021.
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, Q.; Dai, X.; Wei, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, X. A Biomimetic Non-Antibiotic Approach to Eradicate Drug-Resistant Infections. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, G.; Saigal, S.; Elongavan, A. Action and resistance mechanisms of antibiotics: A guide for clinicians. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 33, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavada, S.H.; Thumar, J.T.; Singh, S.P. Secretion of a potent antibiotic by salt-tolerant and alkaliphilic actinomycete Streptomyces sannanensis strain RJT-1. Curr. Sci. 2006, 91, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Chamekh, R.; Deniel, F.; Donot, C.; Jany, J.L.; Nodet, P.; Belabid, L. Isolation, Identification and Enzymatic Activity of Halotolerant and Halophilic Fungi from the Great Sebkha of Oran in Northwestern of Algeria. Mycobiology 2019, 47, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariq, A.; Yasmin, A.; Jamil, M. Production, characterization and antimicrobial activities of bio-pigments by Aquisalibacillus elongatus MB592, Salinicoccus sesuvii MB597, and Halomonas aquamarina MB598 isolated from Khewra Salt Range, Pakistan. Extremophiles 2019, 23, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, T.; Weirathmüller, D.; Herwig, C.; Pflügl, S. Potential applications of halophilic microorganisms for biological treatment of industrial process brines contaminated with aromatics. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Senthilkumar, P.K. An Overview of Saltpan Halophilic Bacterium. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 3, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelam, D.K.; Agrawal, A.; Tomer, A.K.; Bandyopadhayaya, S.; Sharma, A.; Jagannadham, M.V.; Mandal, C.C.; Dadheech, P.K. A Piscibacillus sp. Isolated from a soda lake exhibits anticancer activity against breast cancer mda-mb-231 cells. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlin Jenifer, J.S.C.; Michaelbabu, M.; Eswaramoorthy Thirumalaikumar, C.L.; Jeraldin Nisha, S.R.; Uma, G.; Citarasu, T. Antimicrobial potential of haloalkaliphilic Nocardiopsis sp. AJ1 isolated from solar salterns in India. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesheva, V.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E. Production of enzymes and antimicrobial compounds by halophilic Antarctic Nocardioides sp. grown on different carbon sources. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, P.; Esposito, F.P.; Tedesco, P.; Falco, A.; Tortorella, E.; Tartaglione, L.; Festa, C.; D’Auria, M.V.; Gnavi, G.; Varese, G.C.; et al. Identification of a Sorbicillinoid-Producing Aspergillus Strain with Antimicrobial Activity Against Staphylococcus aureus: A New Polyextremophilic Marine Fungus from Barents Sea. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abirami, G.; Ramprasath, C.; Arthi, M.; Mathivanan, N. Anticandidal activity of halophilic bacterium Vibrio azureus MML1960 isolated from Kelambakkam Saltpan, Tamil Nadu, India. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 13, 8–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.S.; Eom, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y. Anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) substance from the marine bacterium Pseudomonas UJ-6. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.; Alvarez, P.; Jiménez, L.; De la Fuente, M. Improvement of leukocyte functions in young prematurely aging mice after a 5-week ingestion of a diet supplemented with biscuits enriched in antioxidants. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Tafreshi, A.; Shariati, M. Dunaliella biotechnology: Methods and applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 14–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohyanagi, N.; Ishido, M.; Suzuki, F.; Kaneko, K.; Kubota, T.; Miyasaka, N.; Nanki, T. Retinoid ameliorates experimental autoimmune myositis, with modulation of the cell differentiation and antibody production in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Hallsworth, J.E. Microbial weeds in hypersaline habitats: The enigma of the weed-like Haloferax mediterranei. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 359, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, T.; Baserisalehi, M.; Bahador, N. Isolation of Halophilic Bacteria from Maharlu salt Lake—Iran and their evaluation for the production of bioactive compounds. Int. J. Mol. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 1, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yu, Y.H. Biodiversity and screening of halophilic bacteria with hydrolytic and antimicrobial activities from Yuncheng Salt Lake, China. Biologia 2015, 70, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, E.M.; Simoska, O.; Minteer, S.D. The Use of Electroactive Halophilic Bacteria for Improvements and Advancements in Environmental High Saline Biosensing. Biosensors 2021, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballav, S.; Kerkar, S.; Thomas, S.; Augustine, N. Halophilic and halotolerant actinomycetes from a marine saltern of Goa, India producing anti-bacterial metabolites. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.S.M.; Abdelhamid, S.A.; Mohamed, S.S. Secondary metabolites and biodiversity of actinomycetes. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, A.; Ahmad, I.; Bum Kim, S. Isolation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of halophilic bacteria in forshore soils. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, J.; Mohammadipanah, F.; Ventosa, A. Systematic and biotechnological aspects of halophilic and halotolerant actinomycetes. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manteca, A.; Yagüe, P. Streptomyces as a Source of Antimicrobials: Novel Approaches to Activate Cryptic Secondary Metabolite Pathways. In Antimicrobials, Antibiotic Resistance, Antibiofilm Strategies and Activity Methods; InTech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.; Carmeli, S.; Sar, N. Vibrindole a, a metabolite of the marine bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, isolated from the toxic mucus of the boxfish Ostracion cubicus. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donio, M.B.S.; Ronica, S.F.A.; Viji, V.T.; Velmurugan, S.; Jenifer, J.A.; Michaelbabu, M.; Citarasu, T. Isolation and characterization of halophilic Bacillus sp. BS3 able to produce pharmacologically important biosurfactants. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2013, 6, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, S.; Raman, K.; Thanga Viji, V.; Donio, M.B.S.; Adlin Jenifer, J.; Babu, M.M.; Citarasu, T. Screening and characterization of antimicrobial secondary metabolites from Halomonas salifodinae MPM-TC and its in vivo antiviral influence on Indian white shrimp Fenneropenaeus indicus against WSSV challenge. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2013, 25, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najjari, A.; Mejri, H.; Jabbari, M.; Sghaier, H.; Cherif, A.; Ouzari, H.I. Halocins, Bacteriocin-Like Antimicrobials Produced by the Archaeal Domain: Occurrence and Phylogenetic Diversity in Halobacteriales. In Extremophilic Microbes and Metabolites—Diversity, Bioprespecting, and Biotechnological Applications; Intech Open: London, UK; Rijeka, Croatia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanmi, F.; Carré-Mlouka, A.; Vandervennet, M.; Boujelben, I.; Frikha, D.; Ayadi, H.; Peduzzi, J.; Rebuffat, S.; Maalej, S. Antagonistic interactions and production of halocin antimicrobial peptides among extremely halophilic prokaryotes isolated from the solar saltern of Sfax, Tunisia. Extremophiles 2016, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Tiwari, S.K. Activity-guided separation and characterization of new halocin HA3 from fermented broth of Haloferax larsenii HA3. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, S.; Korfanty, G.A.; Liu, J.; Xiang, H. A Halocin Promotes DNA Uptake in Haloferax mediterranei. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, A.; Vandervennet, M.; Goulard, C.; Peduzzi, J.; Isaac, S.; Rebuffat, S.; Carré-Mlouka, A. Halocin C8: An antimicrobial peptide distributed among four halophilic archaeal genera: Natrinema, Haloterrigena, Haloferax, and Halobacterium. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, P.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Ventosa, A. Halophiles and their biomolecules: Recent advances and future applications in biomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGAX: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Siwarungson, N.; Punnapayak, H.; Lotrakul, P.; Prasongsuk, S.; Bankeeree, W.; Rakshit, S.K. Screening of potential biotechnological applications from obligate halophilic fungi, isolated from a man-made solar saltern located in Phetchaburi Province, Thailand. Pakistan J. Bot. 2014, 46, 983–988. [Google Scholar]
- Lauritano, C.; Martín, J.; De La Cruz, M.; Reyes, F.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. First identification of marine diatoms with anti-tuberculosis activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushanth, V.R.; Rajashekhar, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities in the four species of marine microalgae isolated from Arabian Sea of Karnataka Coast. Indian J. Geo-Marine Sci. 2015, 44, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mangamuri, U.K.; Vijayalakshmi, M.; Poda, S.; Manavathi, B.; Chitturi, B.; Yenamandra, V. Isolation and biological evaluation of N-(4-aminocyclooctyl)-3, 5-dinitrobenzamide, a new semisynthetic derivative from the Mangrove-associated actinomycete Pseudonocardia endophytica VUK-10. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Zhu, W. Antimicrobial ergosteroids and pyrrole derivatives from halotolerant Aspergillus flocculosus PT05-1 cultured in a hypersaline medium. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essghaier, B. Antimicrobial Behavior of Intracellular Proteins from Two Moderately Halophilic Bacteria: Strain J31 of Terribacillus halophilus and Strain M3- 23 of Virgibacillus marismortui. J. Plant. Pathol. Microbiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, L. Antimicrobial metabolites from a novel halophilic actinomycete Nocardiopsis terrae YIM 90022. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelev, M.; Tietz, J.I.; Melby, J.O.; Blair, P.M.; Zhu, L.; Livnat, I.; Severinov, K.; Mitchell, D.A. Structure, bioactivity, and resistance mechanism of streptomonomicin, an unusual lasso peptide from an understudied halophilic actinomycete. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, U.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Ng, Y.K.; Shaw, P.N.; Fuerst, J.A.; Hodson, M.P. LC-MS-based metabolomics study of marine bacterial secondary metabolites and antibiotic production in Salinispora arenicola. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, X.; Hao, H.; Li, W.; Lu, C. Nocarbenzoxazoles A-G, Benzoxazoles Produced by Halophilic Nocardiopsis lucentensis DSM 44048. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2123–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzban, A.; Ebrahimipour, G.; Danesh, A. Bioactivity of a novel glycolipid produced by a halophilic Buttiauxella sp. and improving submerged fermentation using a response surface method. Molecules 2016, 21, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasri, M.R.; Baserisalehi, M.; Kurdtabar, M. solation and Identification of Halophilic Actinomyces with Antimicrobial Activity and Partial Characterization of their Bioactive Compounds. Electron. J. Biol. 2017, 13, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Frikha Dammak, D.; Zarai, Z.; Najah, S.; Abdennabi, R.; Belbahri, L.; Rateb, M.E.; Mejdoub, H.; Maalej, S. Antagonistic properties of some halophilic thermoactinomycetes isolated from superficial sediments of a solar saltern and production of cyclic antimicrobial peptides by the novel isolate Paludifilum halophilum. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1205258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde-Martinez, N.; Acosta-González, A.; Díaz, L.E.; Tello, E. Use of a mixed culture strategy to isolate halophilic bacteria with antibacterial and cytotoxic activity from the Manaure solar saltern in Colombia. BMC Microbio. 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj Rabia-Boukhalfa, Y.; Eveno, Y.; Karama, S.; Selama, O.; Lauga, B.; Duran, R.; Hacène, H.; Eparvier, V. Isolation, purification and chemical characterization of a new angucyclinone compound produced by a new halotolerant Nocardiopsis sp. HR-4 strain. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, A.; Nasir, K.; Fatima, N.; Jamil, N. Characterization of Halophilic Isolates Producing Bioactive Metabolites Against Pathogens. LGU J. Life Science 2019, 3, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, A. Halophilic microbial communities and their environments. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, F.; Forján, E.; Vázquez, M.; Toimil, A.; Montero, Z.; Ruiz-Domínguez, M.d.C.; Garbayo, I.; Castaño, M.; Vílchez, C.; Vega, J.M. Antimicrobial activity of the acidophilic eukaryotic microalga Coccomyxa onubensis. Phycol. Res. 2017, 65, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Negative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and overcoming approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, H.M.H.N.; Wood, D.L.A.; Vanwonterghem, I.; Hugenholtz, P.; Cheung, B.P.K.; Samaranayake, L.P. Fluconazole resistance in Candida albicans is induced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, P.; Moopantakath, J.; Imchen, M.; Kumavath, R.; SenthilKumar, P.K. Identification of Multi-Potent Protein Subtilisin A from halophilic bacterium Bacillus firmus VE2. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 157, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, T.; Kerkar, S. Bacteria from Salt Pans: A Potential Resource of Antibacterial Metabolites. Recent Res. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Cardozo, V.F.; Oliveira, A.G.; Nishio, E.K.; Perugini, M.R.E.; Andrade, C.G.T.J.; Silveira, W.D.; Durán, N.; Andrade, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Nakazato, G. Antibacterial activity of extracellular compounds produced by a Pseudomonas strain against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strains. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2013, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Q.; Zeng, J.W.; Jiang, C.H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.Z.; Wen, W.H.; Li, J.H.; Wang, F.; Ting, W.J.; Sun, Z.Y.; et al. Isolation and determination of four potential antimicrobial components from Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracts. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Henciya, S.; Vengateshwaran, T.D.; Gokul, M.S.; Dahms, H.U.; James, R.A. Antibacterial Activity of Halophilic Bacteria Against Drug-Resistant Microbes Associated with Diabetic Foot Infections. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 3711–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, L.; Suar, M.; Pattnaik, A.K.; Raina, V. Streptomyces chilikensis sp. nov. a halophilic streptomycete isolated from brackish water sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, A.; Santhi, S.; Solomon, R.D.J. In Vitro Antimicrobial potential and growth characteristics of Nocardiopsis sp. JAJ16 isolated from crystallizer pond. Int. J. Cur. Res. 2010, 3, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, K.A.; Mitchell, S.S.; Tsueng, G.; Rheingold, A.; White, D.J.; Grodberg, J.; Lam, K.S.; Potts, B.C. Lynamicins A-E, chlorinated bisindole pyrrole antibiotics from a novel marine actinomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.C.; Prieto-Davo, A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. ChemInform Abstract: The Marinopyrroles, Antibiotics of an Unprecedented Structure Class from a Marine Streptomyces sp. ChemInform 2008, 39, 4–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaibani, M.M.; Mohamadzin, N.; Jalil, J.; Sidik, N.M.; Ahmad, S.J.; Kamal, N.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Isolation, purification, and characterization of five active diketopiperazine derivatives from endophytic Streptomyces SUK 25 with antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarvey, N.A.; Keller, J.M.; Bernan, V.; Dworkin, M.; Sherman, D.H. Isolation and characterization of novel marine-derived actinomycete taxa rich in bioactive metabolites. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 7520–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, R.; Meklat, A.; Bouras, N.; Zitouni, A.; Mathieu, F.; Spröer, C.; Klenk, H.P.; Sabaou, N. Diversity and antagonistic properties of culturable halophilic actinobacteria in soils of two arid regions of septentrional Sahara: M’zab and Zibans. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 2241–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohel, S.D.; Sharma, A.K.; Dangar, K.G.; Thakrar, F.; Singh, S.P. Antimicrobial and biocatalytic potential of haloalkaliphilic actinobacteria. In Halophiles; Maheshwari, D.K., Saraf, M., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 6, pp. 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buijs, Y.; Bech, P.K.; Vazquez-Albacete, D.; Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L.; Zhang, S. Da Marine Proteobacteria as a source of natural products: Advances in molecular tools and strategies. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 1333–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, J.A.; Dávila-Céspedes, A.; Kehraus, S.; Crüsemann, M.; Köse, M.; Müller, C.E.; König, G.M. Cyclopropane-containing fatty acids from the marine bacterium Labrenzia sp. 011 with antimicrobial and GPR84 activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyasifar, B.; Jafari, S.; Hallaj-Nezhadi, S.; Chapeland-Leclerc, F.; Ruprich-Robert, G.; Dilmaghani, A. Isolation and identification of antibiotic-producing halophilic bacteria from Dagh Biarjmand and Haj aligholi salt deserts, Iran. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 25, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawale, A.; Kadam, T.A.; Karale, M.A. Antimicrobial activity of Secondary metabolites from Halophilic Bacillus pumilus sp. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2014, 3, 506–512. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, V.A.; Patil, R.B.; Pawar, P.V. Comparative study of antimicrobial potentials of phospholipid compounds produced by halophilic and alkaliphiles Bacillus subtilis isolated from alkaline meteorite crater Lonar lake, India. Int. J. Life Sci. 2017, 5, 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Thacharodi, A.; Reghu, A.P.; Priyadharshini, R.; Kathikeyan, G.; Thacharodi, D. Bioprospecting of Halotolerant Bacillus subtilis: A Study depicting its Potential Antimicrobial Activity against Clinically Important Pathogens. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karabli, N. Antimicrobial Activity of Bacillus persicus 24-DSM Isolated from Dead Sea Mud. Open Microbiol. J. 2018, 11, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maher, O. Isolation and characterization of extremely halotolerant Bacillus species from Dead Sea black mud and determination of their antimicrobial and hydrolytic activities. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 11, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, I.; Sapre, S.; Tiwari, S. Diversity of halophilic bacteria and actinobactreia from India and their biotechnological applications. Indian J. Geomarine Sci. 2017, 8, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, S.; Jayashree, M.; Shivani, R.; Anwesha, S.; Bhaskara Rao, K.V. Characterisation and identification of antibacterial compounds from marine actinobacteria: In vitro and in silico analysis. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Jadeja, V.J. Characterization and partial purification of an antibacterial agent from halophilic actinomycetes Kocuria sp. Strain RSK4. BioImpacts 2018, 8, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepalaxmi, R.K.; Gayathri, C. Screening of bioactive compound, antimicrobial activity producing halophilic isolates from the saltpans of Thoothukudi district. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 12, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tatar, D. Isolation, phylogenetic analysis and antimicrobial activity of halophilic actinomycetes from different saline environments located near Çorum province. Biologia 2012, 76, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Divya, R.; Narendrakumar, G.; Abirami, S.; Dhiva, S.; Prakash, P.; Jane Cypriyana, P.J.; Padmanaban, S. Bioprospecting studies of Halophilic bacteria—Streptomyces sp. MA05 nad Halobactreium sp MA06. Lett. Appl. Nanobiosci. 2020, 9, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenifer, J.; Selva Donio, M.; Michaelbabu, M.; Vincent, S.G.P.; Citarasu, T. Haloalkaliphilic Streptomyces spp. AJ8 isolated fom solar saltworks and its pharmacological potential. AMB Expr. 2015, 5, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menasria, T.; Monteoliva-Sánchez, M.; Benammar, L.; Benhadj, M.; Ayachi, A.; Hacène, H.; Gonzalez-Paredes, A.; Aguilera, M. Culturable halophilic bacteria inhabiting Algerian saline ecosystems: A source of promising features and potentialities. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyadzhieva, I.; Tomova, I.; Radchenkova, N.; Kambourova, M.; Poli, A.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E. Diversity of Heterotrophic Halophilic Bacteria Isolated from Coastal Solar Salterns, Bulgaria and Their Ability to Synthesize Bioactive Molecules with Biotechnological Impact. Microbiol. Russian Fed. 2018, 87, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrico, A.; Trupo, M.; Magarelli, R. Effectiveness of Dunaliella salina Extracts against Bacillus subtilis and Bacterial Plant Pathogens. Pathogens 2020, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnakumar, S.; Dooslin, V.; Bai, M.; Rajan, R.A. Evaluation of bioactive metabolites from halophilic microalgae Dunaliella Salina by GC—MS analysis. Int J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 96–303. [Google Scholar]
- Corona, E.; Fernandez-Acero, J.; Bartual, A. Screening study for antibacterial activity from marine and freshwater microalgae. Int. J. Pharm. Bio Sci. 2017, 8, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, S.; Mobasher, M.A.; Najafipour, S.; Ghasemi, Y.; Mohkam, M.; Ebrahime, M.A.; Mobasher, N. Antibacterial potential of Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella salina extracts against Streptococcus mutans. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2018, 13, e13226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Kaur, M.; Jangra, M.; Mishra, S.; Nandanwar, H.; Pinnaka, A.K. Antimicrobial properties of the novel bacterial isolate Paenibacilllus sp. SMB1 from a halo-alkaline lake in India. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalehno, A.D.; Ghavidel-Aliabadi, M.; Shahmohamadi, Z.; Mehrshad, M.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Danesh, A. Isolation and Discovery of New Antimicrobial-agent Producer Strains Using Antibacterial Screening of Halophilic Gram-positive Endospore-forming Bacteria Isolated from Saline Lakes of Iran. Arak. Med. Univ. J. 2018, 20, 10–23. [Google Scholar]
- Farida, B.; Abdelghani, Z.; Florence, M.; Ahmed, L.; Nasserdine, S. Taxonomy and antimicrobial activities of two novel halophilic Saccharomonospora strains isolated in Algerian Sahara soils. Ann. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrance, A.; Balakrishnan, M.; Gunasekaran, R.; Srinivasan, R.; Valsalan, V.N.; Gopal, D.; Ramalingam, K. Unexplored deep sea habitats in active volcanic Barren Island, Andaman and Nicobar Islands are sources of novel halophilic Eubacteria. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.Z.; Pu, X.; Luo, G.; Zhao, L.X.; Xu, L.H.; Li, W.J.; Luo, Y. Isolation and characterization of new p-terphenyls with antifungal, antibacterial, and antioxidant activities from the halophilic actinomycete Nocardiopsis gilva YIM 90087. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikita, P.; Mitesh, D.; Shahnawaz, J.; Rasheedunnisa, B. Antibacterial Activity of Marine Bacterial Pigments Obtained from Arabian Sea Water Samples. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Srilekha, V.; Krishna, G.; Seshasrinivas, V.; Alha Singara Charya, M. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activities of marine Brevibacterium sp. Res. Pharm Sci. 2017, 12, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srilekha, V.; Krishna, G.; Sesha Srinivas, V.; Singara, M.A. Antimicrobial Evaluation of Bioactive Pigment from Salinicoccus sp. isolated from Nellore sea coast. Int J. Biotech. Biochem. 2017, 13, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Rasha, A.M.; Sikaily, A.E.; Nermeen, A.E.; Hanan, A.G.; Soraya, A.S. Antimicrobial activity of textile fabrics dyed with prodigiosin pigment extracted from marine Serratia rubidaea RAM_Alex bacteria. Egypt J. Aquat. Res. 2021, 47, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Yang, N.; Huang, L.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, M.M.; Fan, H.; Bao, X. Pyocyanin Inhibits Chlamydia infection by Disabling infectivity of the Elementary Body and Disrupting Intracellular Growth. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02260-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, G.S.; Jackson, S.A.; Priyadharsini, S.; Dobson, A.D.; Selvin, J. Synthesis of Nm-PHB (nanomelanin-polyhydroxy butyrate) nanocomposite film and its protective effect against biofilm-forming multi drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danevcic, T.; Boric Vezjak, M.; Tabor, M.; Zorec, M.; Stopar, D. Prodigiosin induces autolysins in actively grown Bacillus subtilis cells. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ye, X.; Anjum, K.; Lian, X.Y.; Zhang, Z. New streptophenazines from marine Streptomyces sp. 182SMLY. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, D.S.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, J.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Xu, C.D. Medermycin-type naphthoquinones fromthe marine-derived Streptomyces sp. XMA39. J. Natural Products. 2018, 81, 2120–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, P.; Venil, C.K.; Veera, R.; Arumugam, D.A.; Laurent, D. Marine Bacteria Is the Cell Factory to Produce Bioactive Pigments: A Prospective Pigment Source in the Ocean. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 589655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocberber Kilic, N.; Kubra, D.; Gonul, D. Bioactive compounds produced by Dunaliella species, Antimicrobial effects and optimization of the efficiency. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat Sci. 2019, 19, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, C.; Vinithkumar, N.V.; Kirubagaran, R.; Venil, C.K.; Dufosse, L. Multifaceted Applications of Microbial Pigments: Current Knowledge, Challenges and Future Directions for Public Health Implications. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvionita, M.; Hertadi, R. Bioconversio of Glycerol to Biosurfactant by Halophilic bacteria Halomonas elongata BK-AG18.Indones. J. Chem. 2019, 19, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, T.; Murugan, M. Antibacterial effect of Surface active agent produced by Pseudomonas sp. isolated from Saltpan. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2018, 10, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kayanadath, S.; Nathan, V.K.; Ammini, P. Anti-Biofilm Activity of Biosurfactant Derived from Halomonas sp., a Lipolytic Marine Bacterium from the Bay of Bengal. Microbiology 2019, 88, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes Camargo, S.; Acuna Avila, P.E.; Arrieta Baez, D.; Montanez Barragan, B.; Morato, A.I.; Sanz Martin, J.L.; Barragan Huerta, B.E. Biosurfactant Production by Bacillus tequilensis ZSB10: Structural Characterization, Physicochemical, and Antifungal Properties. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2021, 24, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaiya, M.; Anchana Devi, C.; Leela, K. A Study on Biosurfactant Production from Marine Bacteria. Int J. Sci and Res. 2017, 7, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Sayeda, A.; Sahar, S.; Manal, S. Medical application of exopolymers produced by marine bacteria. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, A.; Lagana, P.; Visalli, G.; Maugeri, T.L.; Gugliandolo, C. In vitro antibiofilm activity of an exopolysaccharide from the marine thermophilic Bacillus licheniformis T14. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahar, S.M.; Shaimaa, K.A.; Manal, S.S.; Hala, M.R. Characterization and applications of exopolysaccharide produced by marine Bacillus altitudinis MSH2014 from Ras Mohamed, Sinai, Egypt. Egypt J. Basic App. Sci. 2018, 5, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AA Abdrabo, M.; AH Ibrahim, H.; Hassan, S.W.; M Abdul-Raouf, U. Antimicrobial and anti-tumor activities of exopolysaccharides produced by the biofilm of marine Halomonas saccharevitans AB2 isolated from Suez Gulf, Egypt. Egypt J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2018, 22, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aullybux, A.A.; Puchooa, D.; Bahorun, T.; Jeewon, R. Phylogenetics and antibacterial properties of exopolysaccharides from marine bacteria isolated from Mauritius seawater. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunde-Cimerman, N.; Plemenitas, A.; Oren, A. Strategies of adaptation of microorganisms of the three domains of life to high salt concentrations. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 353–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventosa, A.; de la Haba, R.R.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; Papke, R.T. Microbial diversity of hypersaline environments: A metagenomic approach. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DasSarma, S.; DasSarma, P. Halophiles and their enzymes: Negativity put to good use. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2015, 25, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edbeib, M.F.; Wahab, R.A.; Huyop, F. Halophiles: Biology, adaptation, and their role in decontamination of hypersaline environments. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plemenitas, A.; Lenassi, M.; Konte, T.; Kejžar, A.; Zajc, J.; Gostinčar, C.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Adaptation to high salt concentrations in halotolerant/halophilic fungi: A molecular perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, T.; Roger, A.J.; Simpson, A.G.B. Adaptations to high salt in a halophilic protist: Differential expression and gene acquisitions through duplications and gene transfers. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Gurunathan, J. Differential Production of Pigments by Halophilic Bacteria Under the Effect of Salt and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Activity. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 190, 391–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remonsellez, F.; Castro-Severyn, J.; Pardo-Esté, C.; Aguilar, P.; Fortt, J.; Salinas, C.; Barahona, S.; León, J.; Fuentes, B.; Areche, C.; et al. Characterization and salt response in recurrent halotolerant Exiguobacterium sp. SH31 isolated from sediments of salar de huasco, Chilean altiplano. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cycil, L.M.; DasSarma, S.; Pecher, W.; McDonald, R.; AbdulSalam, M.; Hasan, F. Metagenomic Insights into the Diversity of Halophilic Microorganisms Indigenous to the Karak Salt Mine, Pakistan. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waditee-Sirisattha, R.; Kageyama, H.; Takabe, T. Halophilic microorganism resources and their applications in industrial and environmental biotechnology. AIMS Microbiol. 2016, 2, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrio, J.L.; Demain, A.L. Microbial enzymes: Tools for biotechnological processes. Biomolecules 2014, 4, 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuan, N.H.; An, T.T.; Shrestha, A.; Canh, N.X.; Sohng, J.K.; Dhakal, D. Recent Advances in Exploration and Biotechnological Production of Bioactive Compounds in Three Cyanaliobacterial Genera: Nostoc, Lyngbya, and Microcystis. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkia, I.; Al-Haj, L.; Abdul Hamid, A.; Zakaria, M.; Saari, N.; Zadjali, F. Indigenous marine diatoms as novel sources of bioactive peptides with antihypertensive and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1514–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.; Abdullah, M.A. Anticancer Compounds Derived from Marine Diatoms. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citarasu, T.; Thirumalaikumar, E.; Abinaya, P.; Babu, M.M.; Uma, G. Biosurfactants from halophilic origin and their potential applications. In Green Sustainable Process for Chemical and Environmental Engineering and Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molchanova, N.; Nielsen, J.E.; Sørensen, K.B.; Prabhala, B.K.; Hansen, P.R.; Lund, R.; Barron, A.E.; Jenssen, H. Halogenation as a tool to tune antimicrobial activity of peptoids. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias Flaviana, R.F.; Novais, J.S.; Devillart, S.; da Silva, W.A.; Fereirra, M.O.; Loureiro, R.d.S.; Campos, V.R.; Fereirra, V.F.; de Souza, M.C.B.V.; Castro, H.C.; et al. Synthesis and antimicrobial evaluation of amino sugar-based naphthoquinones and isoquinoline-5,8-diones and their halogenated compounds. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Cardenas, C.; Rojas, L.Y.; Fiorentino, S.; Cala, M.P.; Diaz, J.I.; Ramos, F.A.; Armengaud, J.; Restrepo, S.; Baena, S. Bioactive potential of extracts of Labrenzia aggregate strain USBA 371, a halophilic bacterium isolated from a terrestrial source. Molecules 2020, 25, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seck, E.; Diop, A.; Armstrong, A.; Delerce, J.; Fournier, P.-E.; Raoult, D.; Khelaifia, S. Microbial culturomics to isolate halophilic bacteria from table salt: Genome sequence and description of the moderately halophilic bacterium Bacillus salis sp. nov. New Microbes New Infect. 2018, 23, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothe, C.I.; Bolotin, A.; Kraïem, B.; Dridi, B.; Team, F.M.; Renault, P. Unraveling the world of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria in cheese by combining cultural, genomic and metagenomic approaches. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 350, 109312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

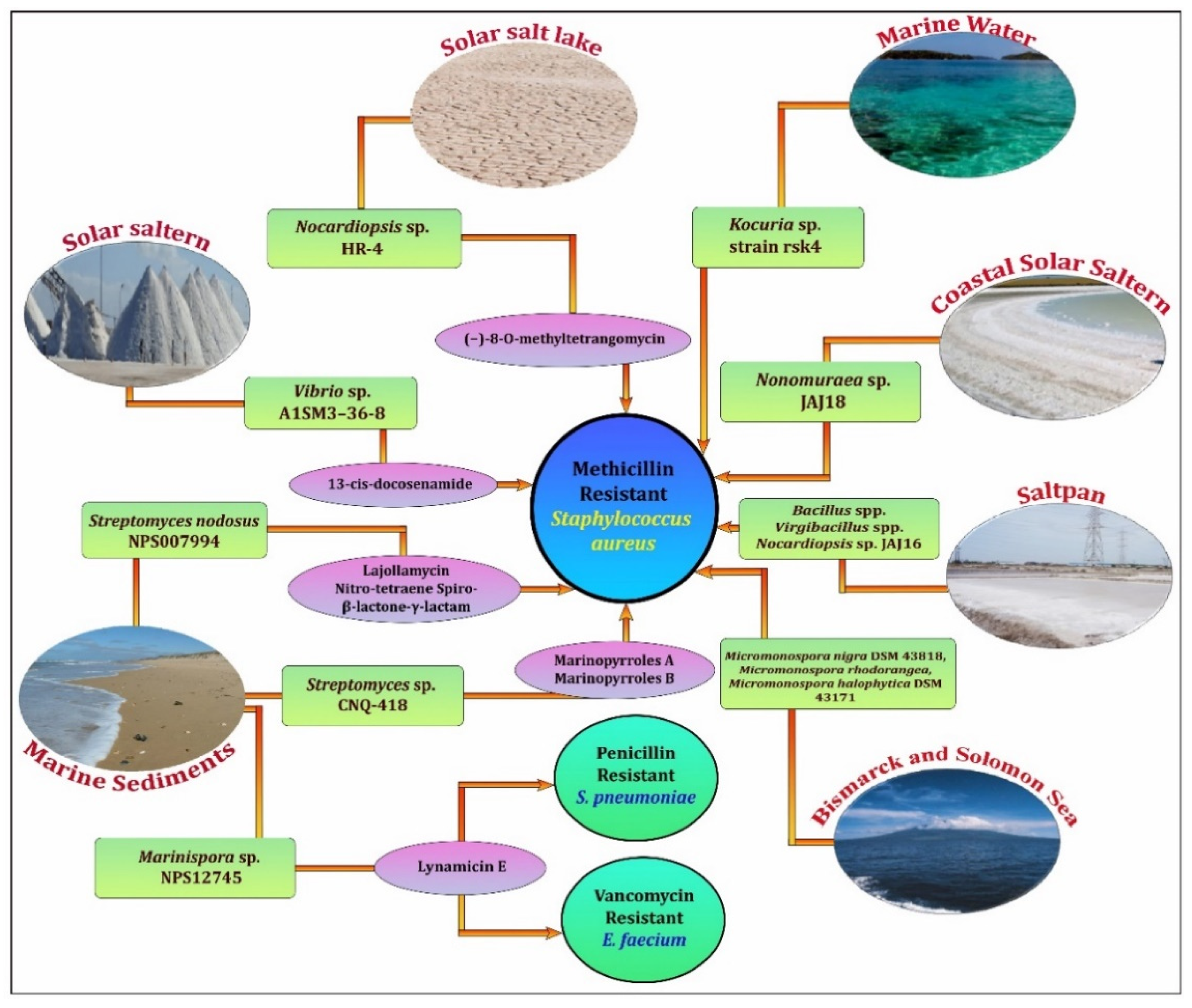
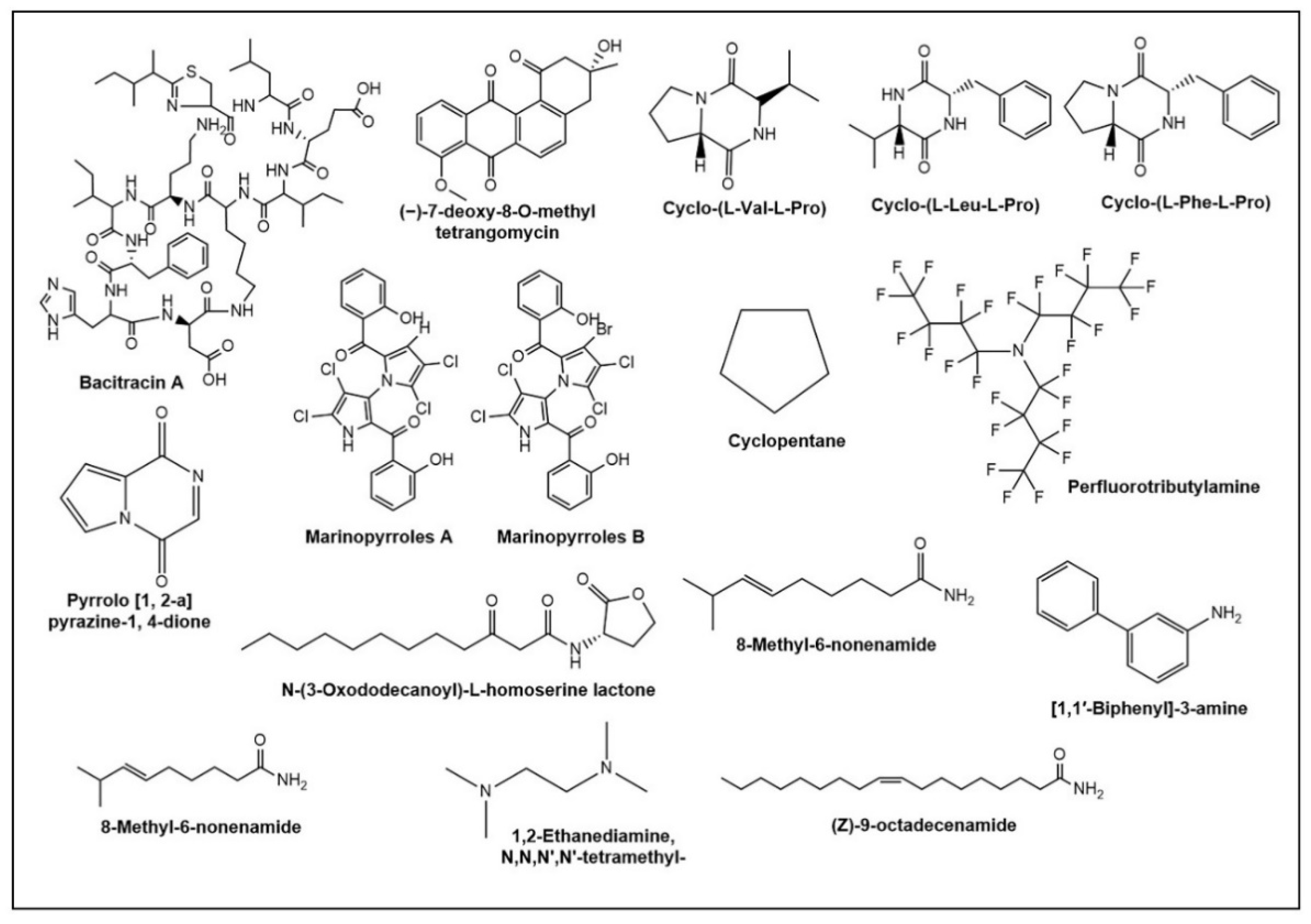
| S.No | Organism | Isolation Source | Compound | Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bacillus sp. | Condenser water, solar salt works in Thamaraikulam, Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, India | 13-Docosenamide, 9-Octadecenamide, Cylohex-1,4,5-triol-3-one-1-carbo | Antibacterial and Antifungal | [31] |
| 2. | Halomonassalifodinae | Solar salt condenser, Thamaraikulam solar astern, Kanyakumari district, Tamil Nadu, India | Perfluorotributylamine, Pyridine, 4-(phenylmethyl), Nonadecane | Antibacterial | [32] |
| 3. | Pseudonocardiaendophytica | Sediments of mangrove Nizampatnam, Bay of Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, India | 3-((1H-indol-6-yl) methyl) hexahydropyrrolo [1,2-a] pyrazine-1,4-dione | Antibacterial | [43] |
| 4. | Piscibacillus sp. | Sambhar Lake in India | Crude extract | Antibacterial and anticancer | [12] |
| 5. | Nocardiopsis sp. | Saline soil of Kovalam solar salterns India | Pyrrolo (1,2-A (pyrazine-1,4-dione, hexahydro-3-(2-methylpropyl)-) | Antibacterial | [13] |
| 6. | Nocardioides sp. | Antarctic Casey Station, Wilkes Land, | Glycolipids and/or lipopeptides | Enzymatic and antimicrobial activities | [14] |
| 7. | Aspergillus flocculosus | Putian saltern of Fujian, China | 6-(1H-pyrrol-2-yl) hexa-1,3,5-trienyl-4-methoxy-2H-pyran-2-one | Antibacterial | [44] |
| 8. | Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis | Halophilic MaharluSalt Lake—Iran | glycoprotein | Antifungal, Antibacterial | [22] |
| 9. | Virgibacillusmarismortu, Terribacillushalophilus | Halophilic Tunisian Sebkha | Glucanase, thermotolerant chitinases | Antimicrobial activity, Antifungal enzymes | [45] |
| 10. | Nocardiopsis terrae | Saline soil, Qaidam Basin, north-west China | Quinoloid alkaloid 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide, Indole-3-carboxylic acid | Antibacterial and anticancer | [46] |
| 11. | Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus gracilis | Solar saltern, Phetchaburi, Thailand | Crude extracellular compounds | Antibacterial and antioxidant | [40] |
| 12. | Halomonas sp. | Halophilic bacteria Yuncheng Salt Lake, China | Amylase, protease, lipase, cellulase, pectinase and DNAase | Antimicrobial activity, hydrolytic activities. | [23] |
| 13. | Streptomonosporaalba | Soil sample, Xinjiang Province, China | Streptomonomicin | Antibacterial | [47] |
| 14. | Salinisporaarenicola | Great Barrier Reef (GBR) sponges, Queensland, Australia | Rifamycin B, S and W | Antifungal | [48] |
| 15. | Nocardiopsis lucentensis | Salt marsh soil, Alicante, Spain | Nocarbenzoxazole G | Antibacterial and anticancer | [49] |
| 16. | Buttiauxella sp. | Halophilic, marine bacteria mangrove forest, Qeshm Island, south of Iran | Glycolipid biosurfactant | Antimicrobial activity | [50] |
| 17. | Actinomyces sp. | Halophilic AranBidgolandMaharlu Lakes in center and south of Iran | Chloroacetate, ethylcholoroacetate and 4-chloro-3hydroxybutyronitrite groups | Antimicrobial activities | [51] |
| 18. | Paludifilumhalophilum | Sfax solar saltern, Tunisia | Gramicidin S, Cyclo(l -4-OH-Pro- l -Leu), Cyclo(l -Leu- l -Pro) | Antibacterial | [52] |
| 19. | Vibrio sp. | Brine and sediments from Manaure solar saltern. La Guajira, Colombia | 13-cis-docosenamide | Antibacterial | [53] |
| 20. | Nocardiopsis sp. | Salt lake soil, Algerian Sahara. Algeria | Compound 1:(−)-8-O-methyltetrangomycin | Anticancer | [54] |
| 21. | A. protuberus | Arctic sub-sea sediments from the Barents Sea | Bisvertinolone | Antifungal | [15] |
| 22. | Bacillus sp. | Halophilic | carotenoids, polyhydroxy alkanoates, ectoine, bioplastics and enzyme | Antibacterial Activity | [55] |
| 23. | Halomonas elongate, Halobacilluskarajiensis, Alkalibacillus almallahensis | Halophilic extreme saline soil samples of Khewra Salt Mines, Pakistan | Peptide furanomycin, biosurfactants | Radical scavenging activity, antioxidant potential, antimicrobial activity | [9] |
| 24. | Halomonaselongata | Halophilic | Ectoine | Antimicrobial activity | [56] |
| 25. | Coccomyxaonubensis | Tinto river, Spain | Palmitic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid | Antibacterial and Antifungal | [57] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santhaseelan, H.; Dinakaran, V.T.; Dahms, H.-U.; Ahamed, J.M.; Murugaiah, S.G.; Krishnan, M.; Hwang, J.-S.; Rathinam, A.J. Recent Antimicrobial Responses of Halophilic Microbes in Clinical Pathogens. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020417
Santhaseelan H, Dinakaran VT, Dahms H-U, Ahamed JM, Murugaiah SG, Krishnan M, Hwang J-S, Rathinam AJ. Recent Antimicrobial Responses of Halophilic Microbes in Clinical Pathogens. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(2):417. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020417
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanthaseelan, Henciya, Vengateshwaran Thasu Dinakaran, Hans-Uwe Dahms, Johnthini Munir Ahamed, Santhosh Gokul Murugaiah, Muthukumar Krishnan, Jiang-Shiou Hwang, and Arthur James Rathinam. 2022. "Recent Antimicrobial Responses of Halophilic Microbes in Clinical Pathogens" Microorganisms 10, no. 2: 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020417
APA StyleSanthaseelan, H., Dinakaran, V. T., Dahms, H.-U., Ahamed, J. M., Murugaiah, S. G., Krishnan, M., Hwang, J.-S., & Rathinam, A. J. (2022). Recent Antimicrobial Responses of Halophilic Microbes in Clinical Pathogens. Microorganisms, 10(2), 417. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020417








