Modulation of Virulence-Associated Traits in Aspergillus fumigatus by BET Inhibitor JQ1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. A. fumigatus Strain and Culture Conditions
2.2. Antifungal Susceptibility Testing
2.3. JQ1 Activity against Biofilm Formation and Mature Biofilm
2.4. Conidial Surface Hydrophobicity
2.5. Adhesion Assays
2.6. Microscopic Evaluation of Adhesion
2.7. Radial Growth Experiment
2.8. Protein Extraction and Quantification
2.9. Proteomic Profile by Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
2.10. RNA Extraction and cDNA Production
2.11. Quantitative Real Time-PCR (qPCR) Analysis
2.12. Infection of G. mellonella Larvae
2.13. Toxicity of Extracellular Proteins in G. mellonella Larvae and Melanization Assay
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. JQ1 Shows Low Activity against A. fumigatus Planktonic Growth
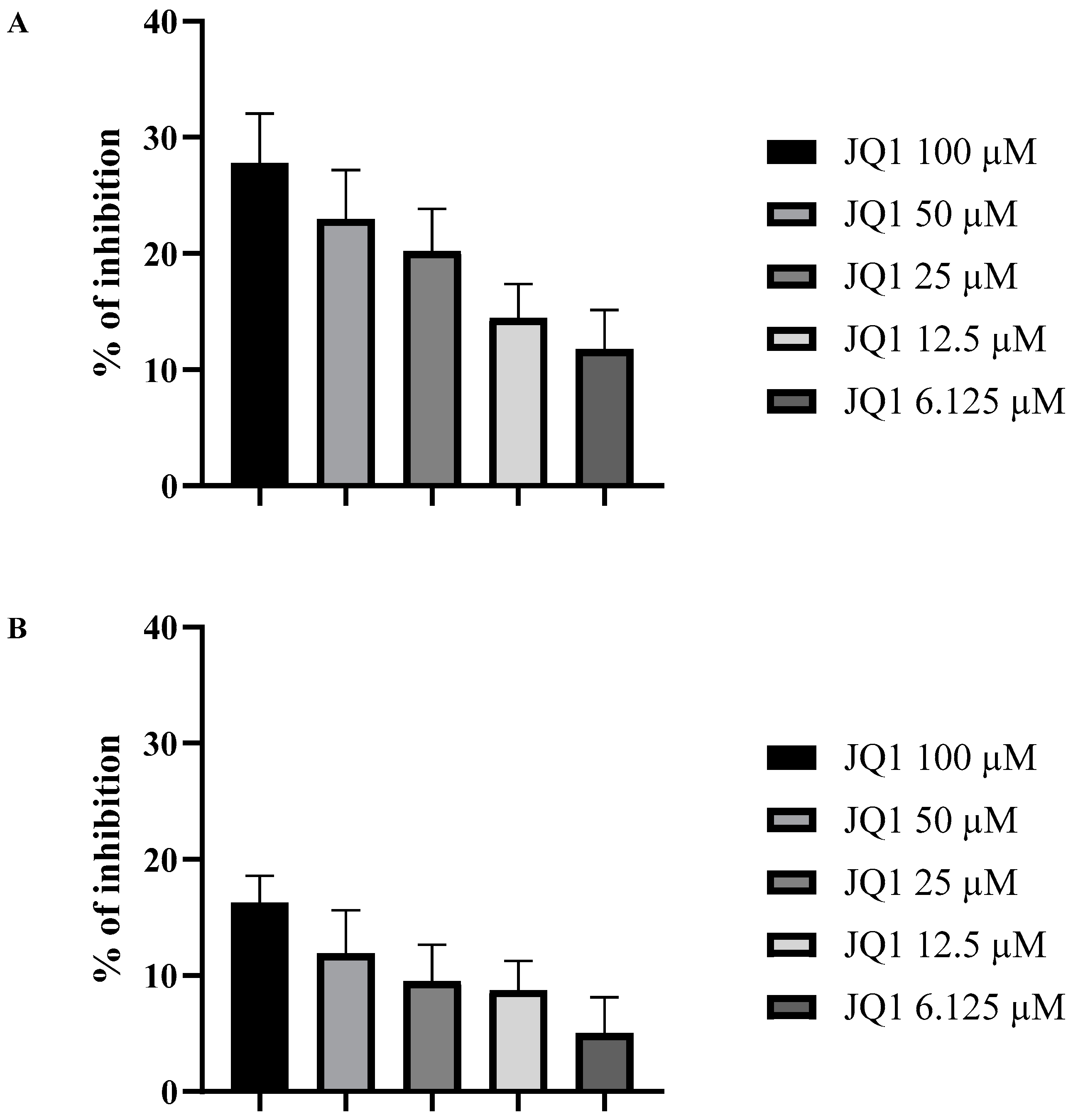
3.2. JQ1 Affects the A. fumigatus Biofilm
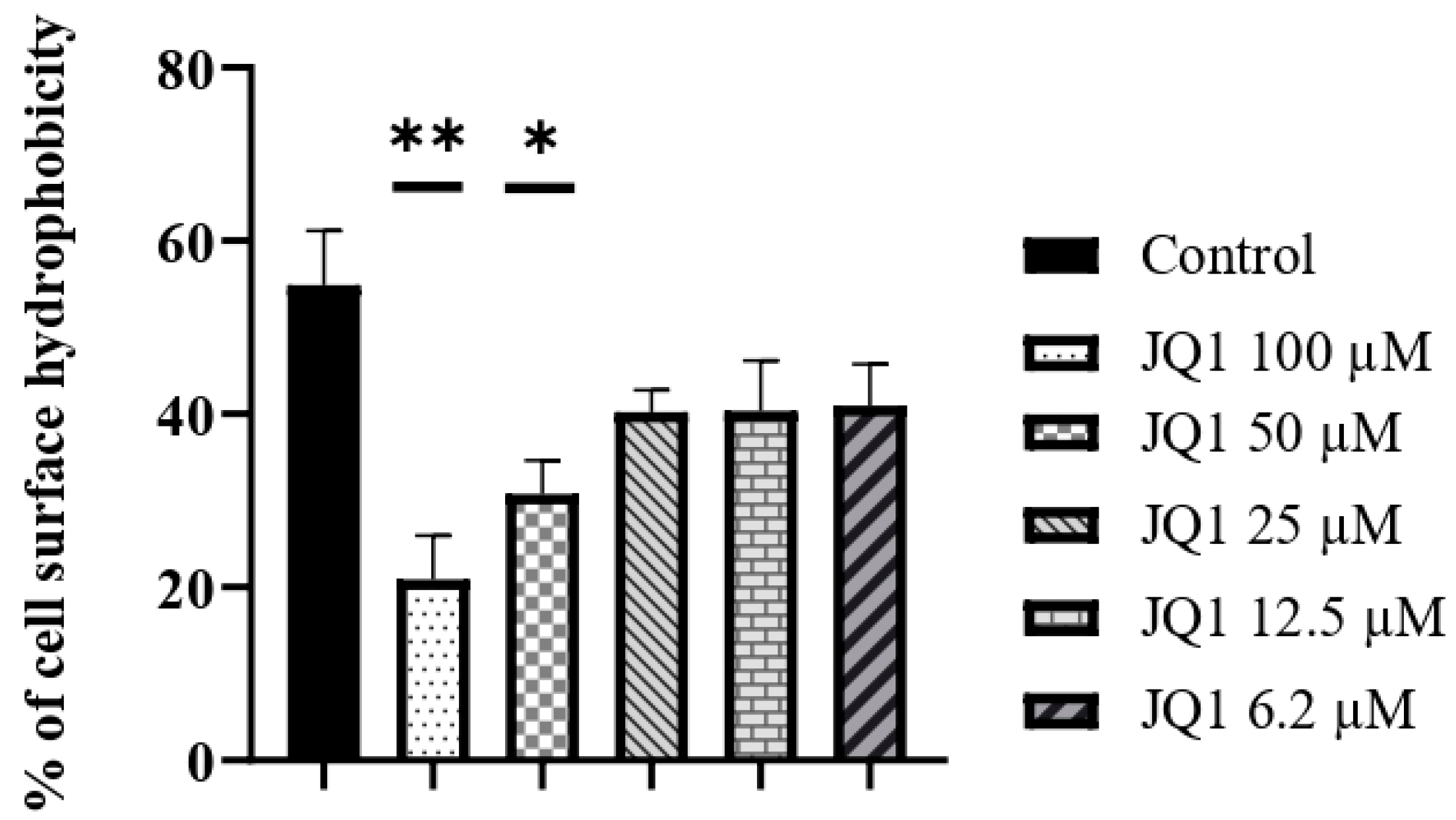
3.3. JQ1 Decreases the Cell Surface Hydrophobicity
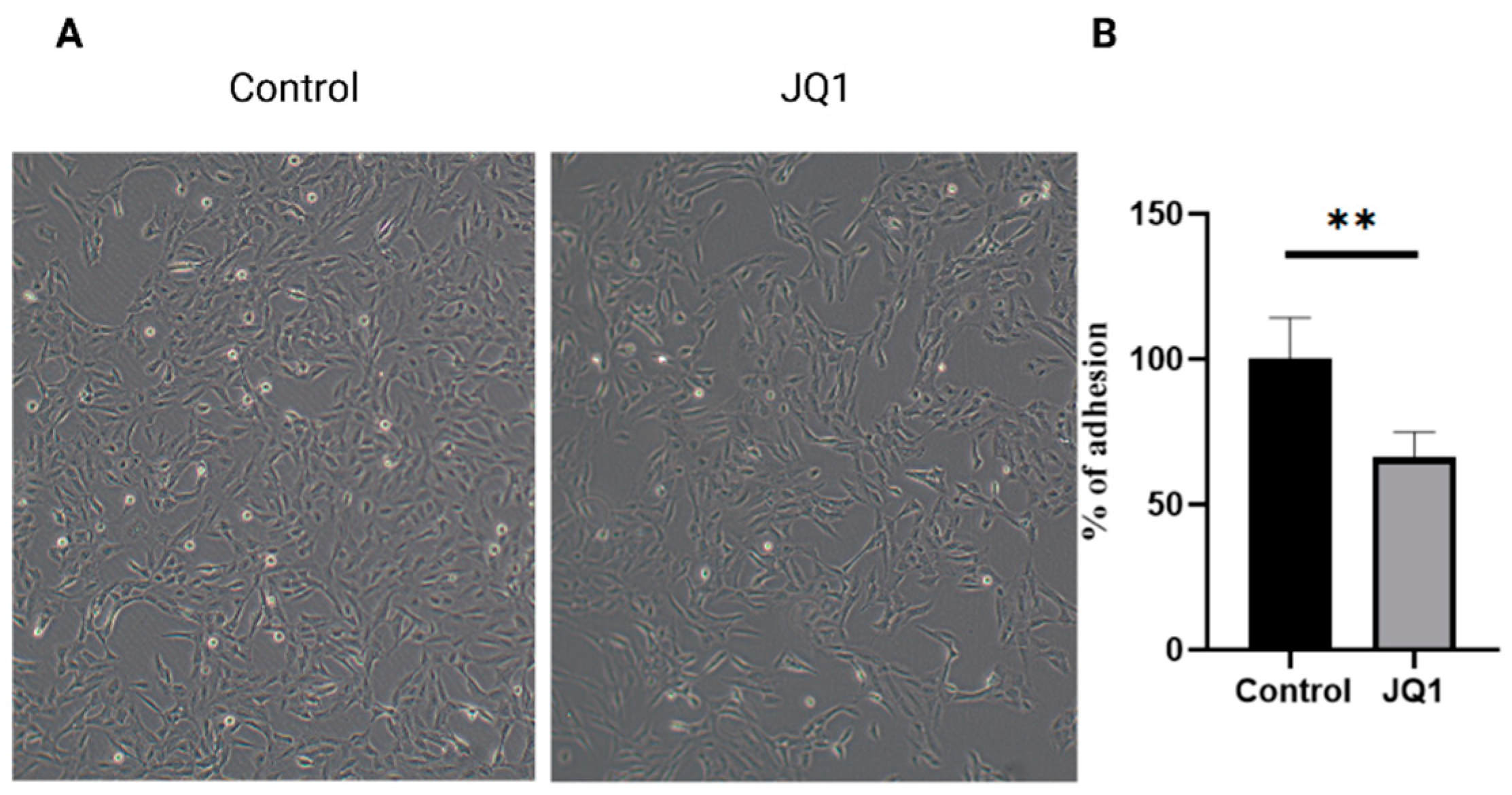
3.4. JQ1 Decreases the Cell Surface Adhesion
3.5. JQ1 Reduces the Radial Growth Rate of A. fumigatus
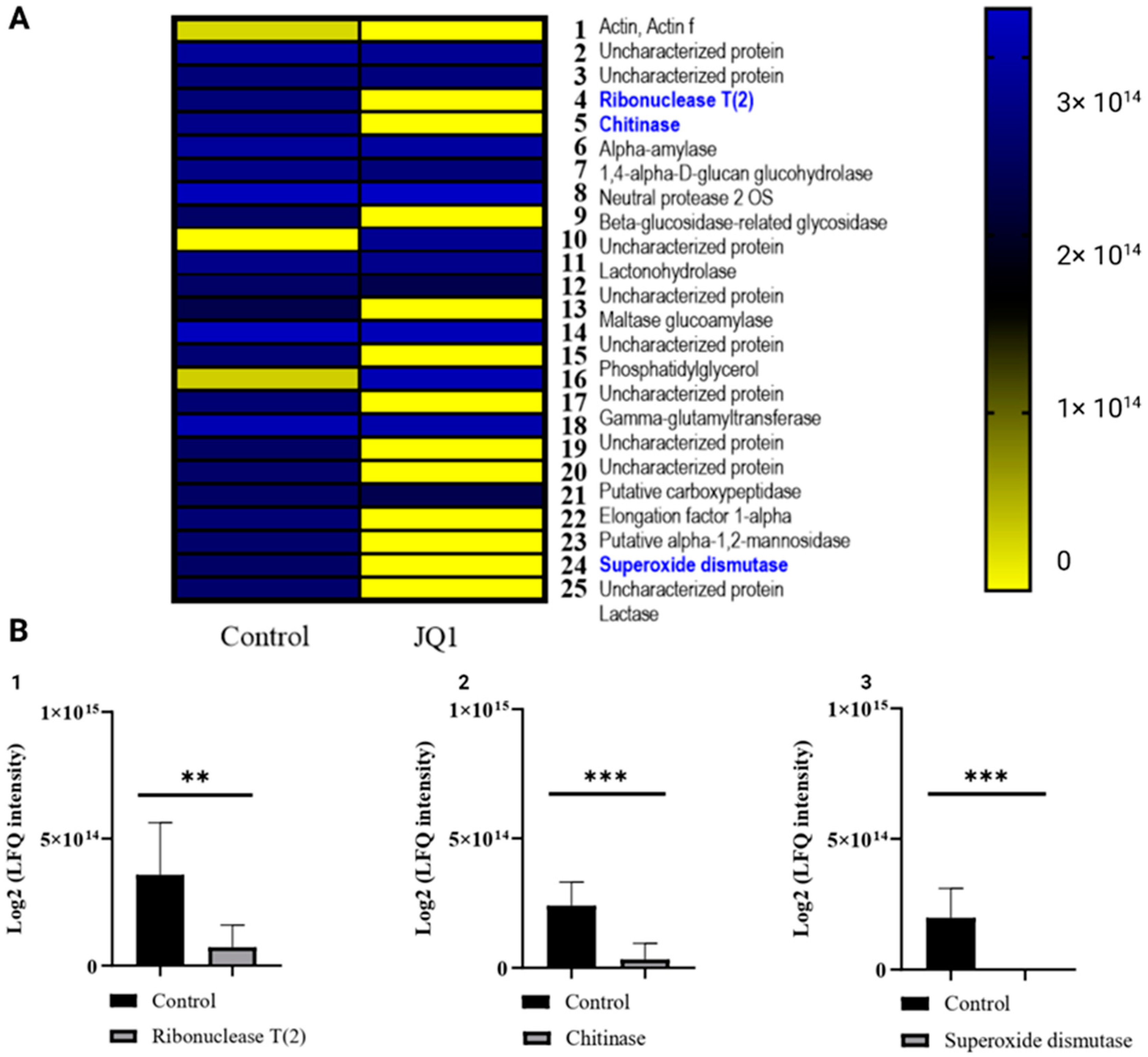
3.6. JQ1 Changes the Concentration of Extracellular Virulence Proteins
3.7. JQ1 Reduces the Protein Related to Melanin Synthesis
3.8. JQ1 Reduces the Gene Expression of Extracellular and Intracellular Virulence Factors
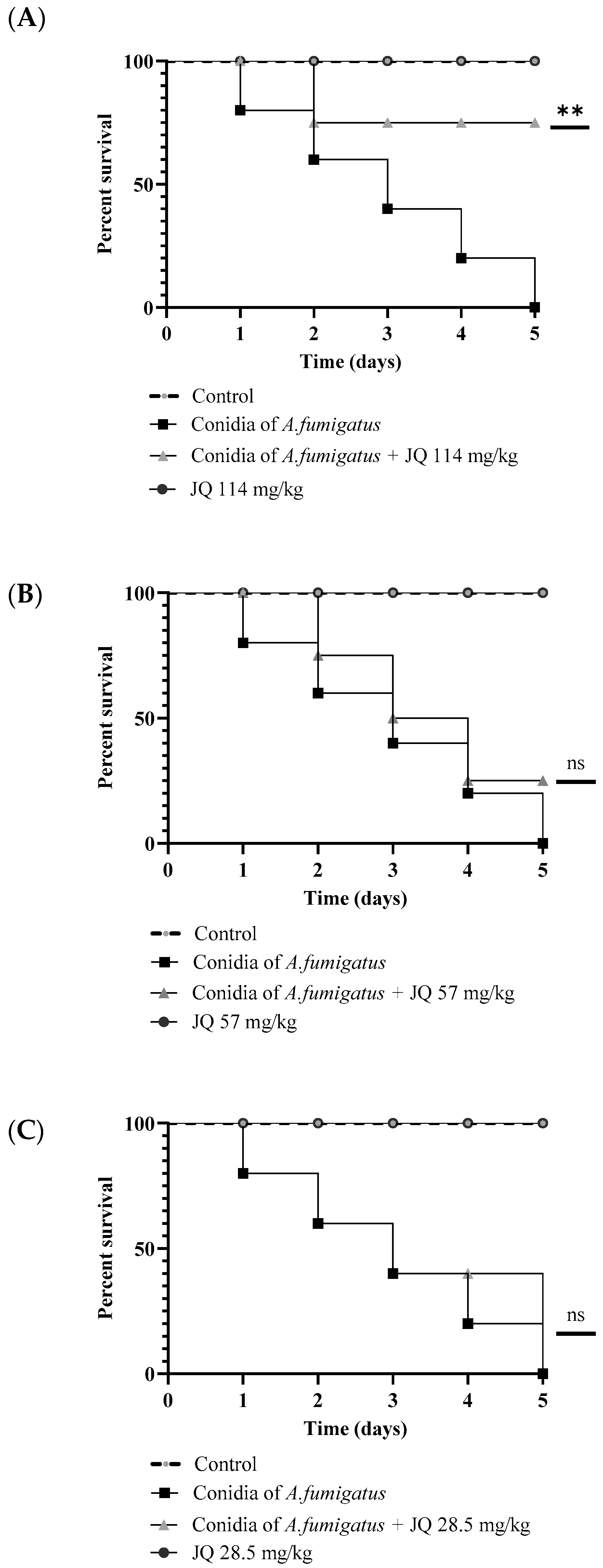
3.9. JQ1 Reduces the Mortality of G. mellonella Larvae Infected with A. fumigatus
3.10. Pretreatment of A. fumigatus with JQ1 Reduces the Mortality in G. mellonella Model
3.11. The Toxicity of Extracellular Protein in G. mellonella Larvae was Reduced after Treatment of A. fumigatus with JQ1
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parente, R.; Doni, A.; Bottazzi, B.; Garlanda, C.; Inforzato, A. The Complement System in Aspergillus fumigatus Infections and Its Crosstalk with Pentraxins. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 2480–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, S.; Cramer, R.A. Regulation of Sterol Biosynthesis in the Human Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus: Opportunities for Therapeutic Development. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanio, A.; Dellière, S.; Fodil, S.; Bretagne, S.; Mégarbane, B. Prevalence of Putative Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e48–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, J.; Abdolrasouli, A.; Dunne, K.; Sewell, T.R.; Zhang, Y.; Ballard, E.; Brackin, A.P.; van Rhijn, N.; Chown, H.; Tsitsopoulou, A.; et al. Population Genomics Confirms Acquisition of Drug-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus Infection by Humans from the Environment. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nywening, A.V.; Rybak, J.M.; Rogers, P.D.; Fortwendel, J.R. Mechanisms of Triazole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 4934–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Lestrade, P.P.A.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Meis, J.F. Azole Resistance Surveillance in Aspergillus fumigatus: Beneficial or Biased? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2079–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinekamp, T.; Thywißen, A.; Macheleidt, J.; Keller, S.; Valiante, V.; Brakhage, A.A. Aspergillus fumigatus Melanins: Interference with the Host Endocytosis Pathway and Impact on Virulence. Front. Microbio. 2013, 3, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihet, M.; Vandeputte, P.; Tronchin, G.; Renier, G.; Saulnier, P.; Georgeault, S.; Mallet, R.; Chabasse, D.; Symoens, F.; Bouchara, J.-P. Melanin Is an Essential Component for the Integrity of the Cell Wall of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoda, S.; Vermani, M.; Joshi, R.K.; Shankar, J.; Vijayaraghavan, P. Anti-Melanogenic Activity of Myristica Fragrans Extract against Aspergillus fumigatus Using Phenotypic Based Screening. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Milagro, F.I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Martinez, J.A. Epigenetic Signatures Underlying Inflammation: An Interplay of Nutrition, Physical Activity, Metabolic Diseases, and Environmental Factors for Personalized Nutrition. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Vakoc, C.R. The Mechanisms behind the Therapeutic Activity of BET Bromodomain Inhibition. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danion, F.; van Rhijn, N.; Dufour, A.C.; Legendre, R.; Sismeiro, O.; Varet, H.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C.; Mouyna, I.; Chamilos, G.; Bromley, M.; et al. Aspergillus fumigatus, One Uninucleate Species with Disparate Offspring. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayou, C.; Govin, J. Functions and Inhibition of BET Bromodomains in Pathogenic Fungi. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022, 34, 100590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Ferreira, A.V.; Jansen, T.; Smithers, N.; Prinjha, R.K.; Furze, R.C.; Netea, M.G. Bromodomain Inhibitor I-BET151 Suppresses Immune Responses during Fungal–Immune Interaction. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, W.; Bruno, V.M.; Phan, Q.T.; Solis, N.V.; Woolford, C.A.; Ehrlich, R.L.; Shetty, A.C.; McCraken, C.; Lin, J.; et al. Determining Aspergillus fumigatus Transcription Factor Expression and Function during Invasion of the Mammalian Lung. PLoS Pathog 2021, 17, e1009235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective Inhibition of BET Bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. M38-A2: Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Filamentous Fungi; Approved Standard—Second Edition; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pierce, C.G.; Uppuluri, P.; Tristan, A.R.; Wormley, F.L.; Mowat, E.; Ramage, G.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. A Simple and Reproducible 96-Well Plate-Based Method for the Formation of Fungal Biofilms and Its Application to Antifungal Susceptibility Testing. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, N.; Marti, L.; Varrot, A.; Guillot, L.; Guitard, J.; Hennequin, C.; Imberty, A.; Corvol, H.; Chignard, M.; Balloy, V. Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Inhibit Aspergillus fumigatus Germination of Extracellular Conidia via FleA Recognition. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Passariello, C.; Rotili, D.; Mai, A.; Garaci, E.; Palamara, A.T. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors May Reduce Pathogenicity and Virulence in Candida albicans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2007, 7, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, E.; Arentshorst, M.; Yilmaz, B.; Swinkels, A.; Reid, I.D.; Visser, J.; Tsang, A.; Ram, A.F.J. Genetic Characterization of Mutations Related to Conidiophore Stalk Length Development in Aspergillus niger Laboratory Strain N402. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 666684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, H.; Neng, J.; Gao, J.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. The Influence of NaCl and Glucose Content on Growth and Ochratoxin A Production by Aspergillus ochraceus, Aspergillus carbonarius and Penicillium nordicum. Toxins 2020, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, T.S.; Palanivelu, P. Purification and Characterization of an Extracellular Keratinolytic Protease from a New Isolate of Aspergillus parasiticus. Protein Expr. Purif. 2013, 88, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, M.P.; Marten, M.R. Comparison of Lysis Methods and Preparation Protocols for One- and Two-dimensional Electrophoresis of Aspergillus oryzae Intracellular Proteins. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 2216–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M. (Ed.) The Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) Assay for Protein Quantitation. In The Protein Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Eldarov, C.; Gamisonia, A.; Chagovets, V.; Ibragimova, L.; Yarigina, S.; Smolnikova, V.; Kalinina, E.; Makarova, N.; Zgoda, V.; Sukhikh, G.; et al. LC-MS Analysis Revealed the Significantly Different Metabolic Profiles in Spent Culture Media of Human Embryos with Distinct Morphology, Karyotype and Implantation Outcomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doellinger, J.; Schneider, A.; Hoeller, M.; Lasch, P. Sample Preparation by Easy Extraction and Digestion (SPEED)—A Universal, Rapid, and Detergent-Free Protocol for Proteomics Based on Acid Extraction. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, C.L. Development of LC-MS and Degradation Techniques for the Analysis of Fungal-Derived Chitin. Ph.D. Thesis, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2020; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. The Single-Step Method of RNA Isolation by Acid Guanidinium Thiocyanate–Phenol–Chloroform Extraction: Twenty-Something Years On. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durieux, M.-F.; Melloul, É.; Jemel, S.; Roisin, L.; Dardé, M.-L.; Guillot, J.; Dannaoui, É.; Botterel, F. Galleria mellonella as a Screening Tool to Study Virulence Factors of Aspergillus fumigatus. Virulence 2021, 12, 818–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Ren, B.; Cheng, L. The Regulation of Hyphae Growth in Candida albicans. Virulence 2020, 11, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, G.; Singh, O.; Prattes, J.; Hoenigl, M.; Sheppard, P.W.; Thornton, C.R. Aspergillus fumigatus and Its Allergenic Ribotoxin Asp f I: Old Enemies but New Opportunities for Urine-Based Detection of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis Using Lateral-Flow Technology. J. Fungi 2020, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Clavaud, C.; Lamarre, C.; Aimanianda, V.; Seidl-Seiboth, V.; Mellado, E.; Latgé, J.-P. Functional Analysis of the Fungal/Plant Class Chitinase Family in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2011, 48, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdom, M.D.; Hay, R.J.; Hamilton, A.J. The Cu,Zn Superoxide Dismutases of Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus nidulans, and Aspergillus terreus: Purification and Biochemical Comparison with the Aspergillus fumigatus Cu,Zn Superoxide Dismutase. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 3326–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Zeng, M.; Sang, H. Exploring the Molecular Mechanism of Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. De Mycol. Médicale 2020, 30, 100915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauwerky, K.; Borelli, C.; Korting, H.C. Targeting Virulence: A New Paradigm for Antifungals. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello, L.; Gómez-Herreros, E.; Fernández-Pereira, J.; Maicas, S.; Martínez-Esparza, M.C.; de Groot, P.W.J.; Valentín, E. Deletion of GLX3 in Candida albicans Affects Temperature Tolerance, Biofilm Formation and Virulence. FEMS Yeast Res. 2019, 19, foy124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R.; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Executive Summary: Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rubio, R.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Mellado, E. Triazole Resistance in Aspergillus Species: An Emerging Problem. Drugs 2017, 77, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyotome, T. Resistance in the Environmental Pathogenic Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Med. Mycol. J. 2019, 60, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, T.F.; Horta, M.A.C.; Colabardini, A.C.; Fernandes, C.M.; Silva, L.P.; Bastos, R.W.; de Fonseca, M.V.L.; Wang, F.; Martins, C.; Rodrigues, M.L.; et al. Screening of Chemical Libraries for New Antifungal Drugs against Aspergillus fumigatus Reveals Sphingolipids Are Involved in the Mechanism of Action of Miltefosine. mBio 2021, 12, e01458-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, W.W.; Zejnullahu, K.; Bradner, J.E.; Varmus, H. Sensitivity of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines to Targeted Inhibition of BET Epigenetic Signaling Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19408–19413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puissant, A.; Frumm, S.M.; Alexe, G.; Bassil, C.F.; Qi, J.; Chanthery, Y.H.; Nekritz, E.A.; Zeid, R.; Gustafson, W.C.; Greninger, P.; et al. Targeting MYCN in Neuroblastoma by BET Bromodomain Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhayay, P.; Bergthold, G.; Nguyen, B.; Schubert, S.; Gholamin, S.; Tang, Y.; Bolin, S.; Schumacher, S.E.; Zeid, R.; Masoud, S.; et al. BET Bromodomain Inhibition of MYC -Amplified Medulloblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spriano, F.; Stathis, A.; Bertoni, F. Targeting BET Bromodomain Proteins in Cancer: The Example of Lymphomas. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 215, 107631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, M.-K.; Hu, K.-D.; Sun, K.-K.; Li, Y.-H.; Hu, L.-Y.; Chen, X.-Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Tang, J.; et al. Deletion of Cu/Zn Superoxide Dismutase Gene SodC Reduces Aspergillus niger Virulence on Chinese White Pear. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2017, 142, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Huber, P.W.; Wool, I.G. The Ribonuclease Activity of the Cytotoxin Alpha-Sarcin. The Characteristics of the Enzymatic Activity of Alpha-Sarcin with Ribosomes and Ribonucleic Acids as Substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, T.; Arora, N.; Sarma, P.U. Ribonuclease Activity Dependent Cytotoxicity of Asp Fl, a Major Allergen of A. fumigatus. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1997, 175, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, R.; Williams, C.; Lappin, D.F.; Millington, O.; Martins, M.; Ramage, G. Extracellular DNA Release Acts as an Antifungal Resistance Mechanism in Mature Aspergillus fumigatus Biofilms. Eukaryot. Cell 2013, 12, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, B.; Boukhallouk, F.; Lotz, J.; Langfelder, K.; Wanner, G.; Brakhage, A.A. Interaction of Human Phagocytes with Pigmentless Aspergillus Conidia. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3736–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugareva, V.; Härtl, A.; Brock, M.; Hübner, K.; Rohde, M.; Heinekamp, T.; Brakhage, A.A. Characterisation of the Laccase-Encoding Gene Abr2 of the Dihydroxynaphthalene-like Melanin Gene Cluster of Aspergillus fumigatus. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 186, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamilos, G.; Carvalho, A. Aspergillus fumigatus DHN-Melanin. In The Fungal Cell Wall; Latgé, J.-P., Ed.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 425, pp. 17–28. ISBN 978-3-030-49927-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dague, E.; Alsteens, D.; Latgé, J.-P.; Dufrêne, Y.F. High-Resolution Cell Surface Dynamics of Germinating Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.F.Q.; Casadevall, A. Fungal Immunity and Pathogenesis in Mammals versus the Invertebrate Model Organism Galleria mellonella. Pathog. Dis. 2021, 79, ftab013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.-Y.; Loh, J.M.S.; Proft, T. Galleria mellonella Infection Models for the Study of Bacterial Diseases and for Antimicrobial Drug Testing. Virulence 2016, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, S.; Edwards, J.; Brown, J.; Dixon, R. Galleria mellonella Infection Model Identifies Both High and Low Lethality of Clostridium Perfringens Toxigenic Strains and Their Response to Antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojda, I. Immunity of the Greater Wax Moth Galleria mellonella: Galleria mellonella Immunity. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Nadir, S.; Lihua, G.; Xu, J.; Holmes, K.A.; Dewen, Q. Identification and Characterization of an Insect Toxin Protein, Bb70p, from the Entomopathogenic Fungus, Beauveria Bassiana, Using Galleria mellonella as a Model System. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 133, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, V.; Giorni, P.; Cirlini, M.; Ludovici, M.; Visentin, I.; Cardinale, F.; Fabbri, A.A.; Fanelli, C.; Reverberi, M.; Battilani, P.; et al. LDS1-Produced Oxylipins Are Negative Regulators of Growth, Conidiation and Fumonisin Synthesis in the Fungal Maize Pathogen Fusarium Verticillioides. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannenstiel, B.T.; Keller, N.P. On Top of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters: How Epigenetic Machinery Influences Secondary Metabolism in Fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

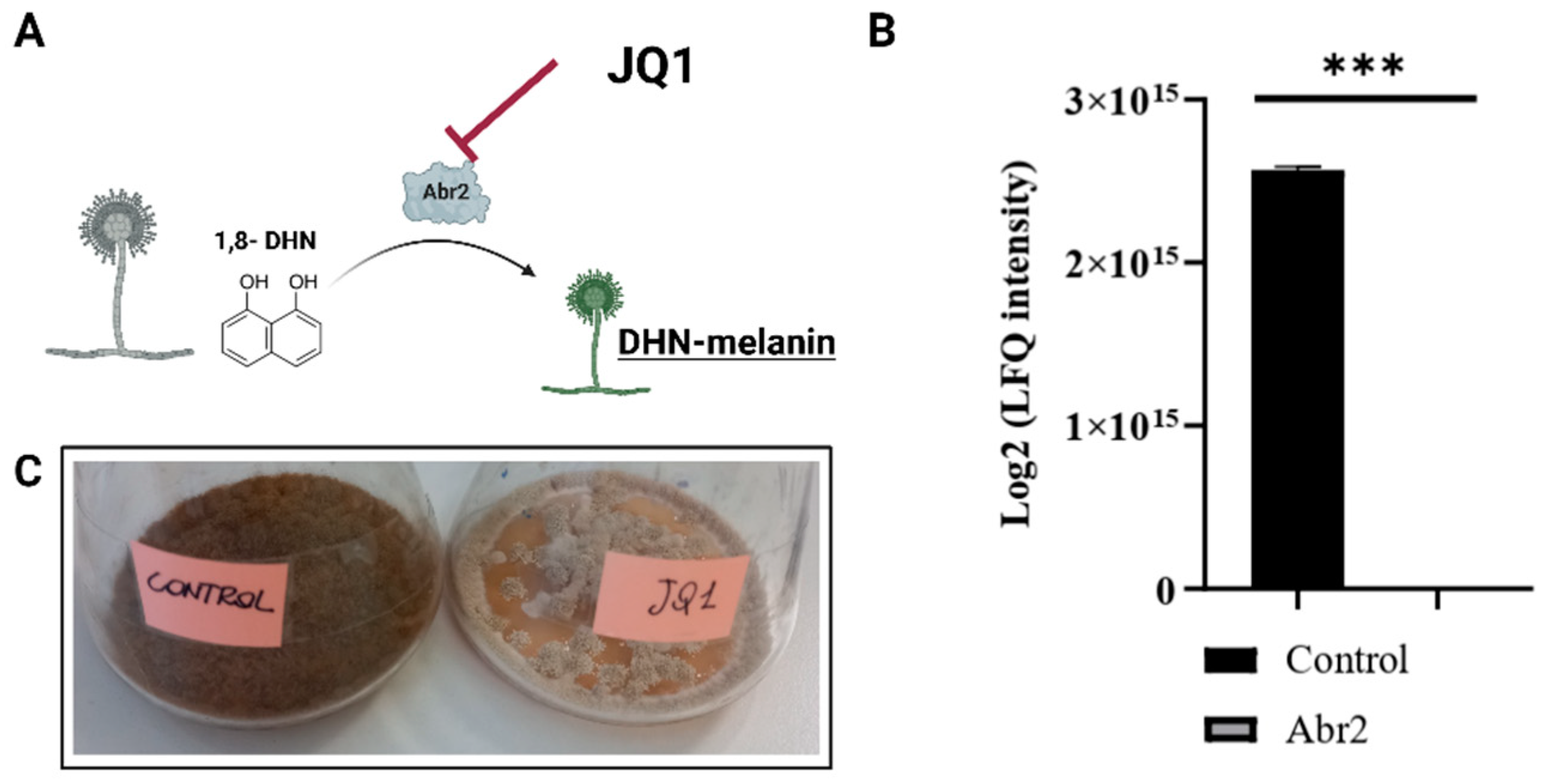
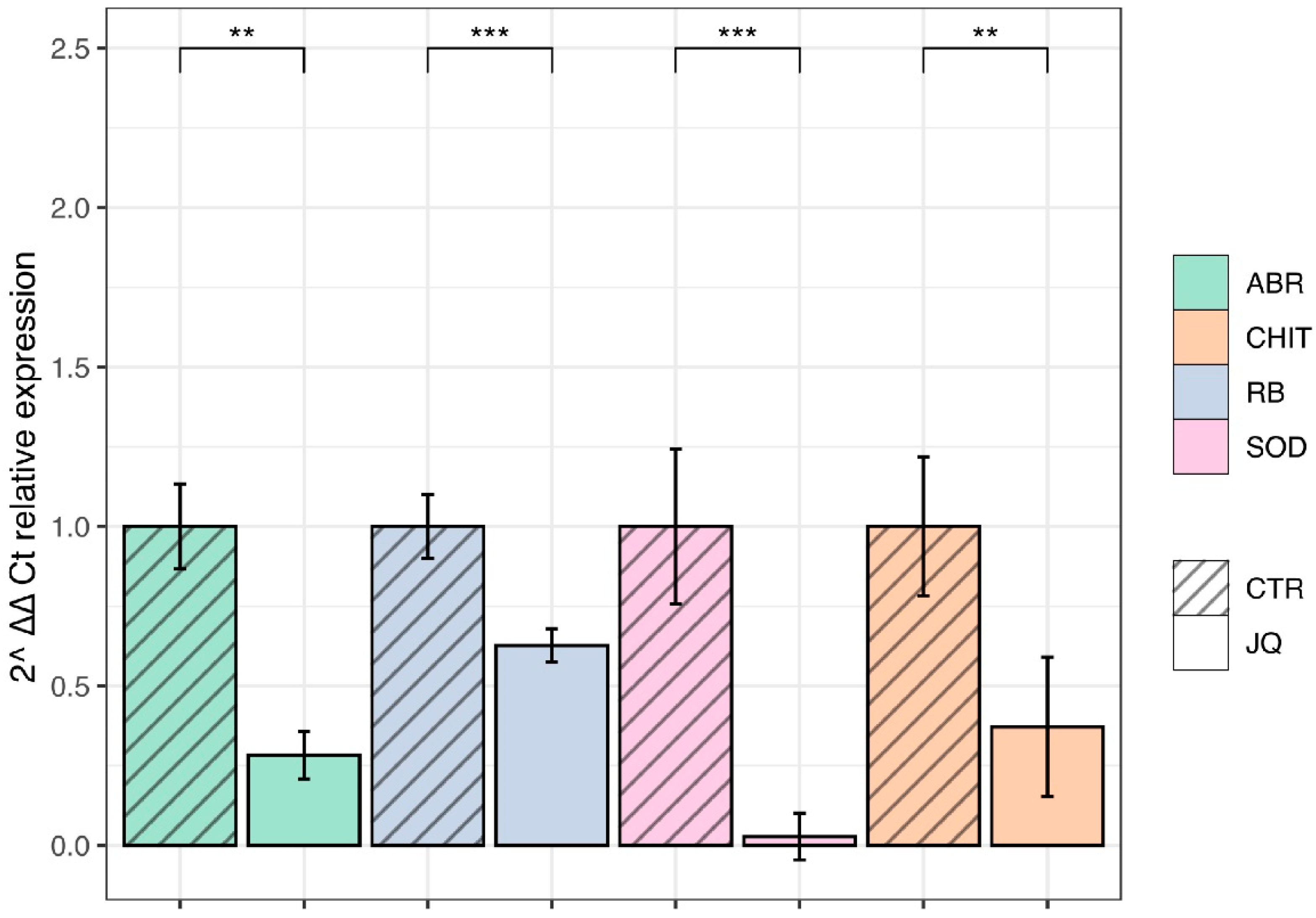



| Gene Name | Primer | Nucleotide Sequence | GenBank |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFUA_1G06390 (Elongation factor-1) | EF1-F | 5′-AGGTCATCGTCCTCAACCAC-3′ | XM_745295.2 |
| EF1-R | 5′-ACCGGACTTGATGAACTTGG-3′ | ||
| AFUA_2G17530 (Conidial pigment biosynthesis oxidase ABR2) | ABR-F | 5′-CAATCAAAGAGGCCAAGGAG-3′ | KAH1289617.1 |
| ABR-R | 5′-TATGGCAGTGCAACAGGAAC-3′ | ||
| AFUA_1G11640 (Superoxide dismutase putative) | SOD-F | 5′-TCTCCCACATAGACAGAACACG-3′ | KAF4252661.1 |
| SOD-R | 5′-ATGCTAGGGCTTCATTGTCG-3′ | ||
| AFUA_1G16600 (Ribonuclease T2 putative) | RB-F | 5′-GCTGCTGTCCTACATGCAAA-3′ | KAH2174949.1 |
| RB-R | 5′-GGCCCTTGAAAAGATCAACA-3′ | ||
| AFUA_3G11280 (Chitinase class V chitinase, putative) | CHIT-F | 5′-TTTACGGCTGCATCAAACAG-3′ | KAH2766398.1 |
| CHIT-R | 5′-GAGCCTCAACTTCGTTCTGG-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orekhova, A.; De Angelis, M.; Cacciotti, A.; Reverberi, M.; Rotili, D.; Giorgi, A.; Protto, V.; Bonincontro, G.; Fiorentino, F.; Zgoda, V.; et al. Modulation of Virulence-Associated Traits in Aspergillus fumigatus by BET Inhibitor JQ1. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112292
Orekhova A, De Angelis M, Cacciotti A, Reverberi M, Rotili D, Giorgi A, Protto V, Bonincontro G, Fiorentino F, Zgoda V, et al. Modulation of Virulence-Associated Traits in Aspergillus fumigatus by BET Inhibitor JQ1. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(11):2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112292
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrekhova, Anastasia, Marta De Angelis, Andrea Cacciotti, Massimo Reverberi, Dante Rotili, Alessandra Giorgi, Virginia Protto, Graziana Bonincontro, Francesco Fiorentino, Victor Zgoda, and et al. 2022. "Modulation of Virulence-Associated Traits in Aspergillus fumigatus by BET Inhibitor JQ1" Microorganisms 10, no. 11: 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112292
APA StyleOrekhova, A., De Angelis, M., Cacciotti, A., Reverberi, M., Rotili, D., Giorgi, A., Protto, V., Bonincontro, G., Fiorentino, F., Zgoda, V., Mai, A., Palamara, A. T., & Simonetti, G. (2022). Modulation of Virulence-Associated Traits in Aspergillus fumigatus by BET Inhibitor JQ1. Microorganisms, 10(11), 2292. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10112292









