Towards the Development of Microbial Ecotoxicology Testing Using Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Sediments and Marine Yeast Isolates as a Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Microbiological Culture Media
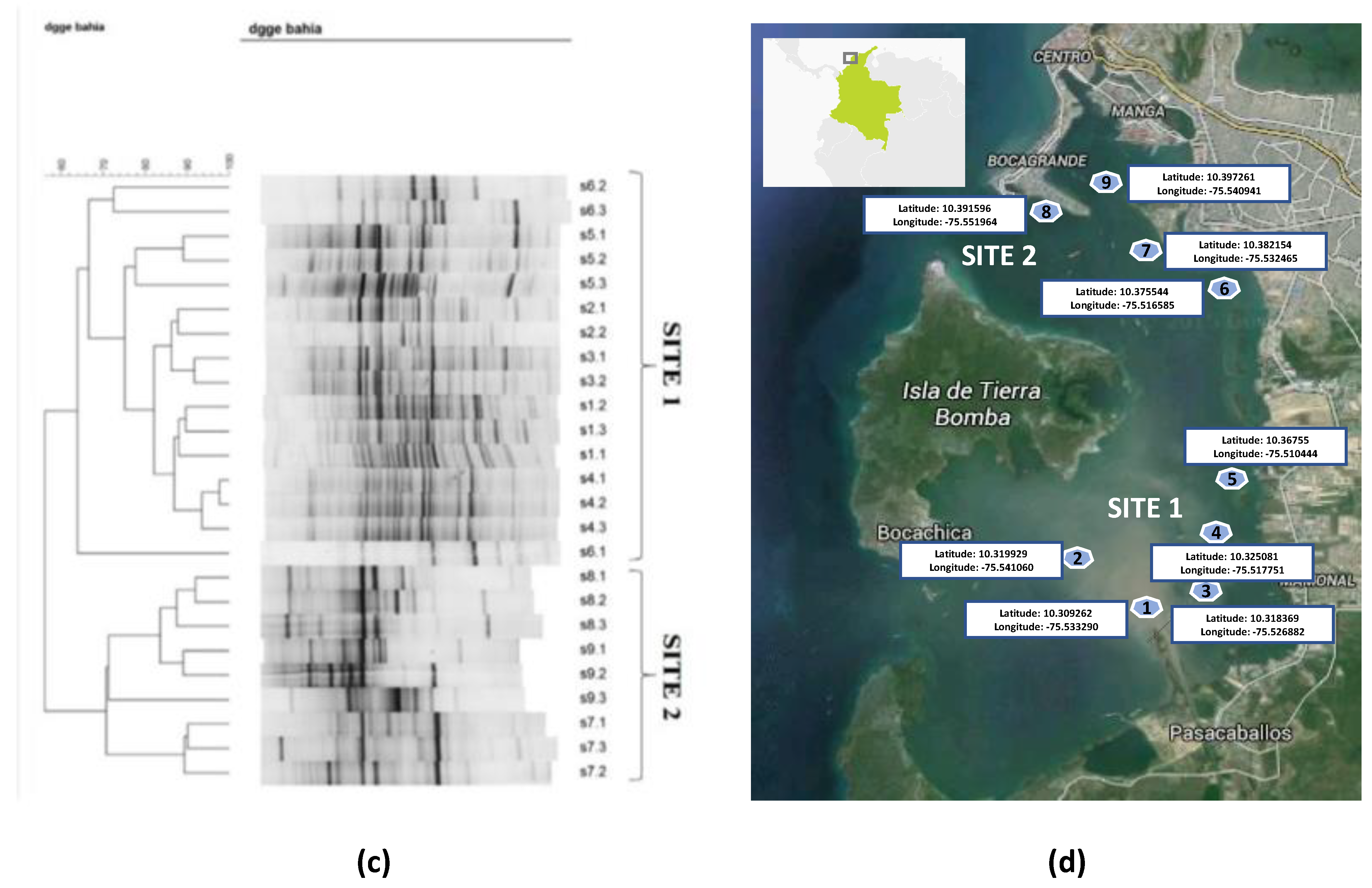
2.3. Sampling and Preparation of Sediments
2.4. Extraction and Quantification of Total DNA in Sediments
2.5. DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) [38,39]
2.6. Isolation and Phenotypic Characterization of Yeasts
2.7. Microbiological Test for Ecotoxicology
3. Results and Discussion
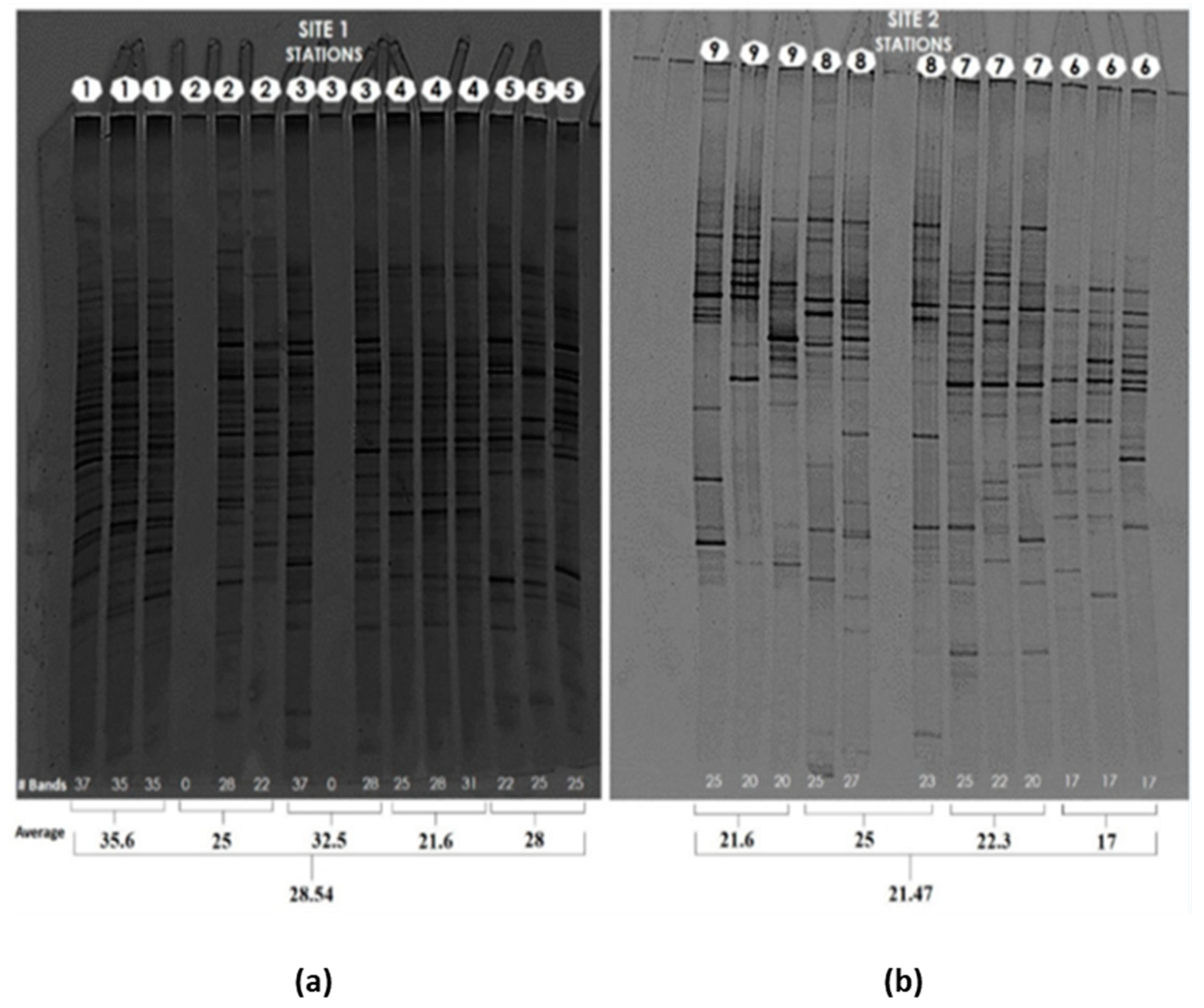
3.1. Yeast/fungal Diversity by Molecular Fingerprinting Profiling by DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) in DNA from Marine Sediments at Cartagena Bay
3.2. Isolation and Biochemical Characterization of Yeasts
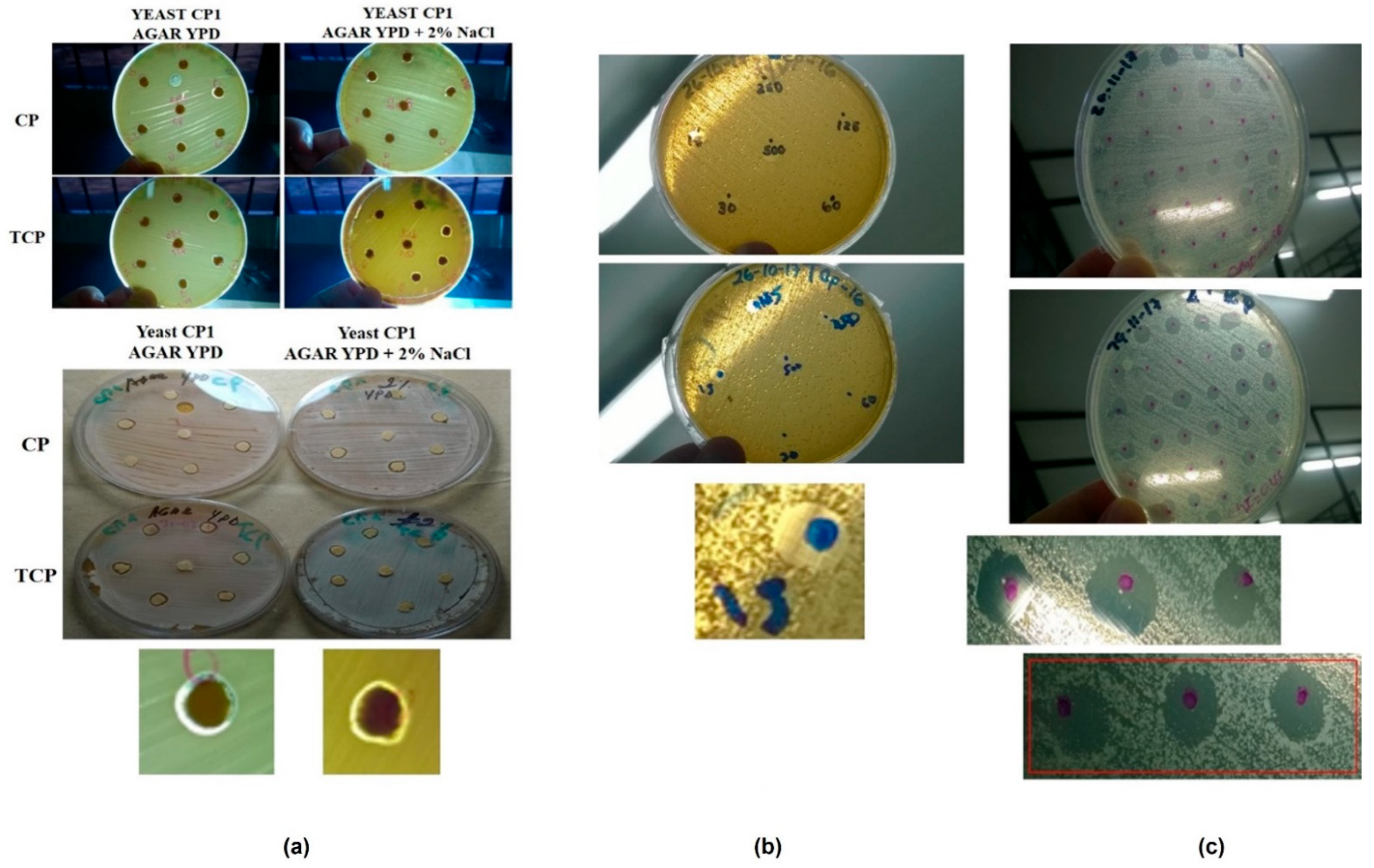
3.3. Agar Surface Tests
3.4. Microbiological Test with Application in Ecotoxicology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Yao, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.; Treb, P.; Zaray, G. Comparative toxicity of Chlorpyrifos and its oxon derivatives to soil microbial activity by combined methods. Chemosphere 2010, 78, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.; Lacasaña, Y. Plaguicidas: Clasificación, uso, toxicología y medición de la exposición. Arch. Prev. Riesgos Labor. 2001, 4, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sogorb, M.; Vilanova, E. Enzymes involved in the detoxification of organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid insecticides through hydrolysis. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 128, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devine, G.J.; Eza, D.; Ogusuku, E.; Furlong, M.J. Uso de insecticidas: Contexto y consecuencias ecológicas. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Pública 2008, 2, 74–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravo, C.; Cagnon, C.; Lauga, B.; Duran, R. Microbial Ecotoxicology; Springer: Gewerbestrasse, Switzerland, 2017; 336p. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiglione, J.; Martin, F.; Pesce, S. Microbial ecotoxicology: An emerging discipline facing contemporary environmental threats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3981–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, M.E.; Gonzalez-Perez, J.A.; Gonzalez-Vila, F.J. Ball AS (2005) Soil health—A new challenge for microbiologists and chemists. Int. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, C.; Pandey, G.; Hartley, C.J.; Jackson, C.J.; Cheesman, M.J.; Taylor, M.C.; Pandey, R.; Khurana, J.L.; Teese, M.; Coppin, C.W.; et al. The enzymatic basis for pesticide bioremediation. Indian J. Microbiol. 2008, 48, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidotti, E.; Rollemberg, M. Algas: Da economia nos ambientes aquáticos à bioremediação e à química analítica. Quim. Nova 2004, 27, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W. Application of Vibrio qinghaiensis sp. Q67 for ecotoxic assessment of environmental waters: A mini review. J. Water Sustain. 2012, 2, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Scheerer, S.; Gomez, F.; Lloyd, D. Bioluminescence of Vibrio fischeri in continuous culture: Optimal conditions for stability and intensity of photoemission. J. Microbiol. Methods 2006, 67, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiglione, J.-F.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Stachowski-Haberkorn, S.; Pesce, S.; Vuilleumier, S. The coming of age of microbial ecotoxicology: Report on the first two meetings in France. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 14241–14245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-D.; Wang, Y. Geomicrobial ecotoxicology as a new subject in environmental sciences is proposed. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1823–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margesin, R.; Zimmerbauer, A.; Schinner, F. Monitoring of bioremediation by soil biological activities. Chemosphere 2000, 40, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudur, L.; Shahsavari, E.; Miranda, A.; Morrison, P.; Nugegoda, D.; Ball, A. Evaluating the efficacy of bioremediating a diesel-contaminated soil using ecotoxicological and bacterial community indices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 14809–14819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, M. Healthy Lifestyles. Applications Fields Red or Healthcare Biotechnology/Green or Vegetal Biotechnology. Ann. Behav. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Debbab, A.; Aly, A.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Minireview Bioactive Compounds from Marine Bacteria and Fungi. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alperstein, L.; Gardner, J.; Sundstrom, J.; Sumby, K.; Jiranek, V. Yeast bioprospecting versus synthetic biology—which is better for innovative beverage fermentation? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1939–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Tucke, G.; Yehia, Z.; Du, C. Marine yeast isolation and industrial application. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botstein, D.; Fink, G.R. Yeast: An Experimental Organism for 21st Century Biology. Genetics 2011, 189, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteve, K.; Poupot, C.; Dabert, P.; Mietton, M.; Milistic, V. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based bioassay for assessing pesticide toxicity. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconi, D.; Bernardini, G.; Santucci, A. Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model in ecotoxicological studies: A post-genomics perspective. J. Proteom. 2015, 137, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vighi, M.; Villa, S. Ecotoxicology: The Challenges for the 21 st Century. Toxics 2013, 1, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bempelou, E.; Vontas, J.; Liapis, K.; Ziogas, V. Herbicidal eff ects of Satureja hortensis L. and Melissa offi cinalis L. essential oils on germination and root length of Lollium rigidum L. and Phalaris brachystachys L. grass weeds. Hell. Plant. Prot. J. 2013, 6, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, N.; Wever, B.; De Fuchs, H.W.; Gaca, M.; Krul, C.; Roggen, E.L. Toxicology in Vitro Toxicology in the 21st century—Working our way towards a visionary reality. Toxicol. Vitr. J. 2011, 25, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wever, B.; Fuchs, H.; Gaca, M.; Krul, C.; Mikulowski, S.; Poth, A.; Roggen, E.; Vilà, M. Implementation challenges for designing Integrated In Vitro Testing Strategies (ITS) aiming at reducing and replacing animal experimentation. Toxicol. Vitr. J. 2012, 26, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, A.; Saidi, N.; Boudabous, A. Resistance of environmental bacteria to heavy metal. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 64, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshwardhan, K.; Nandkar, P. Evaluation of algal bioassay for pesticide toxicity by agar well diffusion method. Int. J. of Life Sciences. 2016, A6, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Hayyan, M.; Ali, M.; Al, M.A.; Hayyan, A.; Alnashef, I.M.; Mirghani, M. Assessment of cytotoxicity and toxicity for phosphonium-based deep eutectic solvents. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Välimaa, A.; Kivistö, A.; Virta, M.; Karp, M. Real-time Monitoring of Non-specific Toxicity Using a Saccharomyces cerevisiae Reporter System. Sensors 2008, 8, 6433–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.C.; Peña, A. Estrategias de adaptación de microorganismos halófilos y Debaryomyces hansenii (Levadura halófila). Rev. Lat. Microbiol. 2002, 44, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Rohban, R.; Amoozegar, A.; Ventosa, A. Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolyses from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzini, P.; Martini, A. Extracellular enzymatic activity profiles in yeast and yeast-like strains isolated from tropical environments. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.; Menom, T.; Sundararajan, T.; Nalini, S.; Thirunarayan, M.; Rajasekaram, S.; Venkatadesikalu, M. Esterase activity of Candida species isolated from immunocomprimed hosts. Rev. Iberoam Micol. 2006, 23, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Imfeld, G.; Vuilleumier, S. Measuring the effects of pesticides on bacterial communities in soil: A critical review. Eur. J. Soil Biology 2012, 49, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilham, D.; Lehner, R. Techniques to measure lipase and esterase activity in vitro. Methods 2005, 36, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.; Sultan, S.; Kertesz, M.A. Bacterial community analysis in Chlorpyrifos enrichment cultures via DGGE and use of bacterial consortium for CP biodegradation Bacterial community analysis in Chlorpyrifos enrichment cultures via DGGE and use of bacterial consortium for CP biodegradation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 30, 2755–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, H.; Cury, J.; Carmo, F.; Rosado, A.; Peixoto, R. 18S rDNA Sequences from Microeukaryotes Reveal Oil Indicators in Mangrove Sediment. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tedersoo, L.; Anslan, S.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Riit, T.; Liiv, I.; Kõljalg, U.; Kisand, V.; Nilsson, H.; Hildebrand, F.; et al. Shotgun metagenomes and multiple primer pair- in metabarcoding analyses of fungi. MycoKeys 2015, 43, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, A.; Kheiralla, Z.; Hamed, E.; Youssry, A.; El Aty, A. Screening of some marine-derived fungal isolates for lignin degrading enzymes ( LDEs ) production. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2010, 1, 591–599. [Google Scholar]
- Kossuga, M.; Romminger, S.; Xavier, C.; Milanetto, M.; Valle, M.; Pimenta, E.; Morais, R.P.; De Carvalho, E.; Mizuno, C.M.; Coradello, L.F.C. Evaluating methods for the isolation of marine-derived fungal strains and production of bioactive secondary metabolites. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2011, 22, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matei, F.; Brinduse, E.; Getuta, N.; Tudorache, A.; Razvan, T. Yeast biodiversity evolution over decades in Dealu Mare-Valea Calugareasca vineyard. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 16, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, R.; Rubio, L. Lyophilisation improves the extraction of PCR-quality community DNA from pig faecal samples. J. Sci Food Agric. 2009, 89, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Z.; Huang, H.; Cao, X.; Song, Z.; Shao, M. Degradation of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by a microbial consortium in dryland soil with anaerobic incubation. Biodegradation 2019, 30, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarenga, N.; Birolli, W.G.; Helena, M.; Seleghim, R. Biodegradation of the Organophosphate Pesticide Profenofos by Marine Fungi. In Applied Bioremediation—Active and Passive Approaches Diation; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2013; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Deshmukh, R.; Khardenavis, A.; Purohit, H. Diverse Metabolic Capacities of Fungi for Bioremediation. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fell, J. Collection and Identification of Marine Yeasts. Methods Microbiol. 2001, 30, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Kutty, S.; Philip, R. Marine yeasts—A review. Yeast 2008, 25, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moubasher, A.; Abdel, M.; Soliman, Z. Diversity of yeasts and filamentous fungi in mud from hypersaline and freshwater bodies in Egypt. Czech. Mycol. 2018, 70, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, C.; Maury, M.; Pagnocca, F.; Araujo, F.; Mendonra, L.; Hagler, A. Ascomycetous yeasts southeast from tropical intertidal dark mud of southeast Brazilian estuaries. J. App. Gen. Microbiol. 1997, 43, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kutty, S.; Philip, R.; Damodaran, R. Marine yeasts in the slope sediments of Arabian sea and bay of Bengal. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 3, 311–327. [Google Scholar]
- Jape, A.; Sapre, V.; Harsulkar, A. Marine Yeasts from Coastal Waters of Kokan (India), as a Promising Source of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Asian J. Multidiscip. Stud. 2016, 4, 122–126. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L.; Ramirez, M.; Osorio, E. Yeast diversity associated to sediments and water from two Colombian artificial lakes. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sansone, C.; Rita Massardo, D.; Pontieri, P.; Maddaluno, L.; De Stefano, M.; Maurizio Tredici, S.; Talà, A.; Alifano, P.; Del Giudice, L. Isolation of a psychrotolerant Debaryomyces hansenii strain from fermented tea plant (Camellia sinensis) leaves. J. Plant. Interact. 2007, 2, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M. Importancia de la identificación de levaduras. Rev. Soc. Venez. De Microbiol. 2005, 25, 103–117. [Google Scholar]
- García, P.; García, L.; Ruiz, J.; Saldarreaga, A. Asimilación de carbohidratos por cepas de Rhodotorula glutinis de origen clínico y ambiental. Rev. Iberoam Micol. 2004, 21, 90–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, L.; Malfeito, M.; Quintieri, L.; Silva, A.; Baruzzi, F. Growth and metabolite production of a grape sour rot yeast-bacterium consortium on di ff erent carbon sources. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 296, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, M.; Sohail, M. Citrus limetta peels: A promising substrate for the production of multienzyme preparation from a yeast consortium. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2019, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suastes, J.; Hernández, R.; Mena, V.; Valdez, R. Efficient production of fatty acid methyl esters by a wastewater-isolated microalgae-yeast co-culture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28490–28499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, G.; Sidabutar, F.; Felina, H.; Wira, D.; Lobo, R. The utilization of fruit and vegetable wastes for bioethanol production with the inoculation of indigenous yeasts consortium. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 25, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zuccaro, G.; Steyer, J.; Lis, R. The algal trophic mode affects the interaction and oil production of a synergistic microalga-yeast consortium. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 273, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, R.; Panciera, A.; Macedo, G.; Mazutti, M.; Maugeri, F.; Rodrigues, M. Improvement of lipase production from Geotrichum sp in shaken flasks. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2012, 18, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Saxena, R.; Gupta, R.; Davidson, S. Lipase Production by Aspergillus and Penicillium species. Folia Microbiol. 1998, 43, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Cortes, C.; Luis, M.; Gonzalez, J. Hongos y Levaduras: Fábricas de Lipasas. Interciencia 2019, 44, 378–385. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarenga, N.; Birolli, W.; Nitschke, M.; Rezende, M.; Seleghim, M.; Porto, A. Biodegradation of Chlorpyrifos by Whole Cells of Marine-Derived Fungi Aspergillus sydowii and Trichoderma sp. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2015, 7, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messias, J.; Zucoloto, B.; Marta, V.; Lima, G. Microbial lipases: Production, properties and biotechnological applications. Semin. Ciências Exatas Tecnológicas 2011, 32, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.; Loke, P.; Wei, C.; Al, E. Novel Lipase Purification Methods—A Review of the latest developments a review. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, R.; Vázquez, G.; Carlos, M.; Penagos, C.; Alberto, L.; Carlos, M. Bioinformatic characterization of the extracellular lipases from Kluyveromyces marxianus. Yeast 2020, 37, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aamri, L.; Scordino, F.; Barresi, C.; Romeo, O.; Criseo, G.; Hafidi, M. Esterase profiling and molecular identification of yeasts isolated from different environmental samples from Morocco. J. Biol. Res. 2019, 92, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demera, L.; Barahona, P.; Carvajal, E. Production, Extraction and Characterization of Lipases from the Antarctic Yeast Guehomyces pullulans. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 15, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahay, S.; Chouhan, D. Study on the potential of cold-active lipases from psychrotrophic fungi for detergent formulation. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butinar, L.; Santos, S.; Spencer, I.; Oren, A. Yeast diversity in hypersaline habitats. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bass, D.; Howe, A.; Brown, N.; Barton, H.; Demidova, M.; Michelle, H.; Li, L.; Sanders, H.; Watkinson, S.C.; Willcock, S. Yeast forms dominate fungal diversity in the deep oceans in the deep oceans. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 274, 3069–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, N.; Rafiq, M.; Hayat, M.; Nadeem, S. Potential of psychrotrophic fungi isolated from Siachen glacier, Pakistan, to produce antimicrobial metabolites. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2017, 15, 1157–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, N.; Rafiq, M.; Hayat, M.; Ali, A.; Hasan, F. Psychrophilic and psychrotrophic fungi: A comprehensive review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 147–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, N.; Zenouche, A.; Gunde, N.; Caseregola, S. Increased diversity in the genus Debaryomyces from Arctic glacier samples. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2014, 107, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, L.; Prieto, J.; Gil, J.; Baeza, M.; Randezl, F. The Antarctic yeast Candida sake: Understanding cold metabolism impact on wine. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 245, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, P.; Palma, V.; Fernandes, R.; Soares, A.; Barbosa, I. Acute toxicity of atrazine, endosulfan sulphate and Chlorpyrifos to Vibrio fischeri, Thamnocephalus platyurus and Daphnia magna, relative to their concentrations in surface waters from the Alentejo region of Portugal. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somasundaram, L.; Coats, J.; Racke, K.; Stahr, H. Application of the microtox system to assess the toxicity of pesticides and their hydrolysis metabolites. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1990, 44, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, S.; Abdel-Hamid, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Mahmoud, N.; Moselhy, W. Toxicity of Some Pesticides, Heavy Metals and Their Mixtures to Vibrio fischeri Bacteria and Daphnia magna: Comparative Study. J. Biol. Life Sci. 2015, 6, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, N.; Siddiqui, P.; Khalid, H. Toxicity of Chlorpyrifos on some marine cyanobacteria species. Pak. J. Bot. 2012, 44, 1131–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Asselborn, V.; Fernández, C.; Zalocar, Y.; Parodi, E.R. Effects of Chlorpyrifos on the growth and ultrastructure of green algae, Ankistrodesmus gracilis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverri, G.; Jaramillo, B.; Sabater, C.; Castillo, M.A. Acute toxicity of Chlorpyrifos and its metabolite 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol alone and in combination using a battery of bioassays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 32770–32778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, L.; Marin, D. Methodologies for evaluating the In vitro antibacterial activity of natural compounds of plant origin. Sci. Tech. 2009, 15, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, Z.; Aslam, M.; Ahmad, S.; Iftikhar, Y.; Yasin, M.; Nawaz, A.; Saleem, A. Determination of Minumum Inhibitory Concentrations of Fungicides Against Fungus Fusarium Mangiferae. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 3525–3532. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Luo, K.; Alex, D.; Hu, X.; Li, Á.; Cao, Á. In Vitro Susceptibility of Berberine Combined with Antifungal Agents Against the Yeast Form of Talaromyces marneffei. Mycopathologia 2019, 184, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trioui, L.; Bouchra, D.; Faouzi, E.; Mohammed, B. Study of chromium uptake by three yeasts: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida tropicalis, and Yarrowia lipolytica. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2019, 13, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Yeast | API 20 C |
|---|---|
| G35 | Cryptococcus laurentis |
| G43 | Candida spherica |
| YPD1 | Candida famata |
| LAC4 | Rhodotorula glutinis |
| LAC6 | Rhodotorula minuta |
| LAC7 | Rhodotorula sp. |
| CP1 | Candida sp. |
| CP2 | Candida krusei/inconspicua |
| CP4 | Candida famate |
| CP8 | Candida krusei/inconspicua |
| Yeast Code | Yeast | Total Diameter (Average in mm) | SCALE (mm) Negative = 0; Low = 0.1–5; Medium = 5.1–10; High = 10.1–15 |
|---|---|---|---|
| G35 | Cryptococcus laurentis | 10.3 | High |
| CP2 | Candida krusei/inconspicua | 9 | Medium |
| YPD1 | Candida famata | 5.3 | Medium |
| LAC4 | Rhodotorula glutinis | 10.6 | High |
| C | Saccharomyces cereviciae | 10.6 | High |
| CP8 | Candida krusei/inconspicua | 8 | Medium |
| CP1 | Candida sp. | 8.3 | Medium |
| LAC7 | Rhodotorula sp. | 10 | Medium |
| G43 | Candida spherica | 10 | Medium |
| CP4 | Candida famata | 12 | High |
| LAC6 | Rhodotorula minuta | 10 | Medium |
| Extreme Yeast | Growth 4 °C | Growth 45 °C | Growth 2% NaCl | Growth 4% NaCl | Growth 10% NaCl | Growth 25% NaCl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control 51669 Saccharomyces cerevisiae | X | |||||
| 43 Candida spherica | X | X | X | |||
| YPD1 Candida famata | X | X | X | |||
| LAC6 Rhodotorula minuta | X | X | X | |||
| CP1 Candida sp. | X | X | ||||
| CP2 Candida krusei/incospicua | X | X | ||||
| CP8 Candida krusei/incospicua | X | X |
| 7.5 ppm | 3.7 ppm | 1.8 ppm | 0.9 ppm | 0.45 ppm | 0.23 ppm | 0.12 ppm | 0.06 ppm | 0.03 ppm | 0.015 ppm | C- | CMI ppm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP1 | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 1.8 |
| TCP1 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.45 |
| CP2 | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.9 |
| TCP2 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.45 |
| CP3 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.45 |
| TCP3 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.45 |
| CP4 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.45 |
| TCP4 | - | - | - | - | - | + | + | + | + | + | + | 0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Echeverri-Jaramillo, G.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.; Junca, H.; Consuegra-Mayor, C. Towards the Development of Microbial Ecotoxicology Testing Using Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Sediments and Marine Yeast Isolates as a Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102019
Echeverri-Jaramillo G, Jaramillo-Colorado B, Junca H, Consuegra-Mayor C. Towards the Development of Microbial Ecotoxicology Testing Using Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Sediments and Marine Yeast Isolates as a Model. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102019
Chicago/Turabian StyleEcheverri-Jaramillo, Gustavo, Beatriz Jaramillo-Colorado, Howard Junca, and Claudia Consuegra-Mayor. 2022. "Towards the Development of Microbial Ecotoxicology Testing Using Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Sediments and Marine Yeast Isolates as a Model" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102019
APA StyleEcheverri-Jaramillo, G., Jaramillo-Colorado, B., Junca, H., & Consuegra-Mayor, C. (2022). Towards the Development of Microbial Ecotoxicology Testing Using Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Sediments and Marine Yeast Isolates as a Model. Microorganisms, 10(10), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10102019








