Extremophilic Microorganisms for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain Culture Conditions
2.2. Selection of Strains Producing Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
2.3. AgNP Production, Isolation, and Purification
2.4. Selection of Strains Producing Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs)
2.5. SeNP Synthesis, Isolation, and Purification
2.6. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.6.1. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
2.6.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.6.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.6.5. Zeta Potential
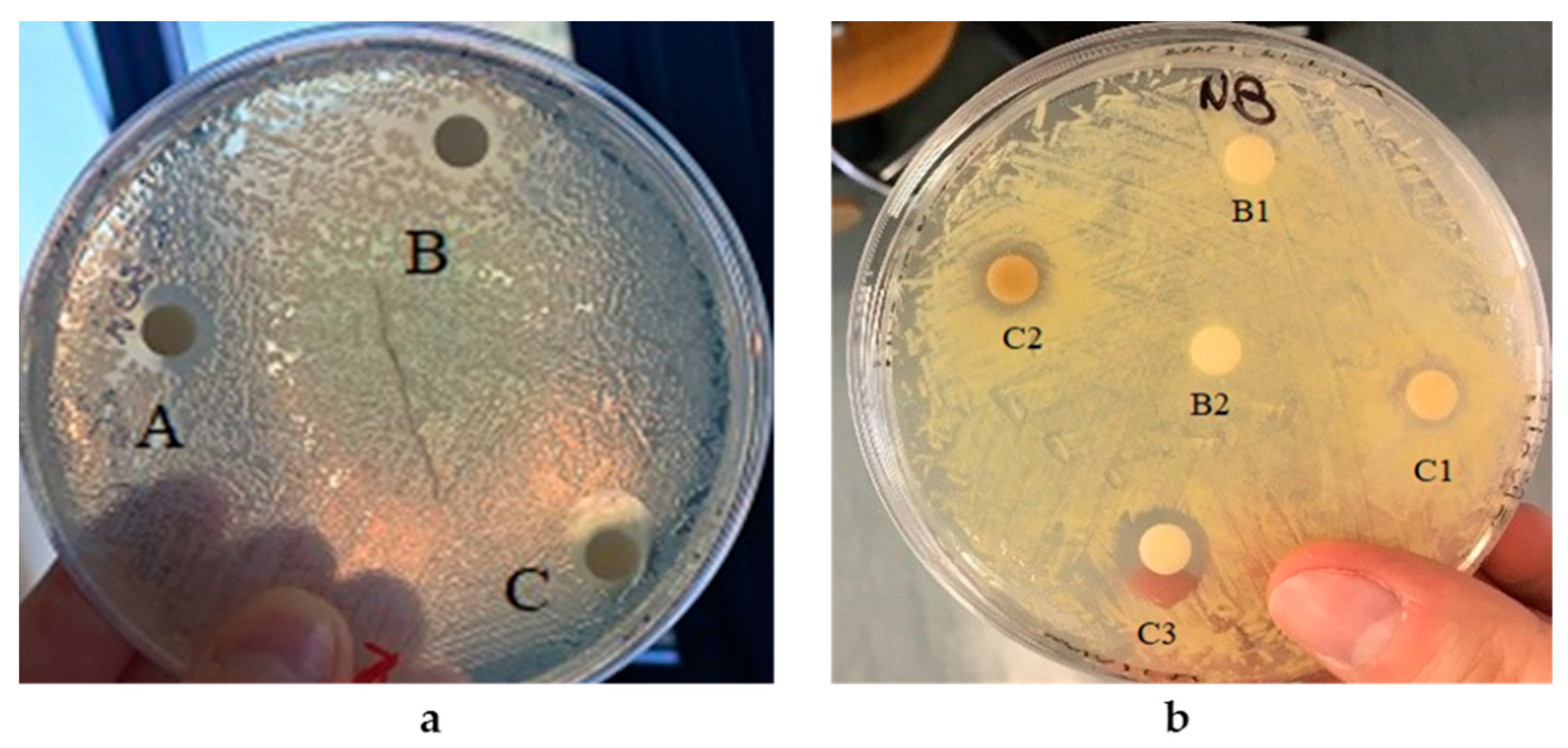
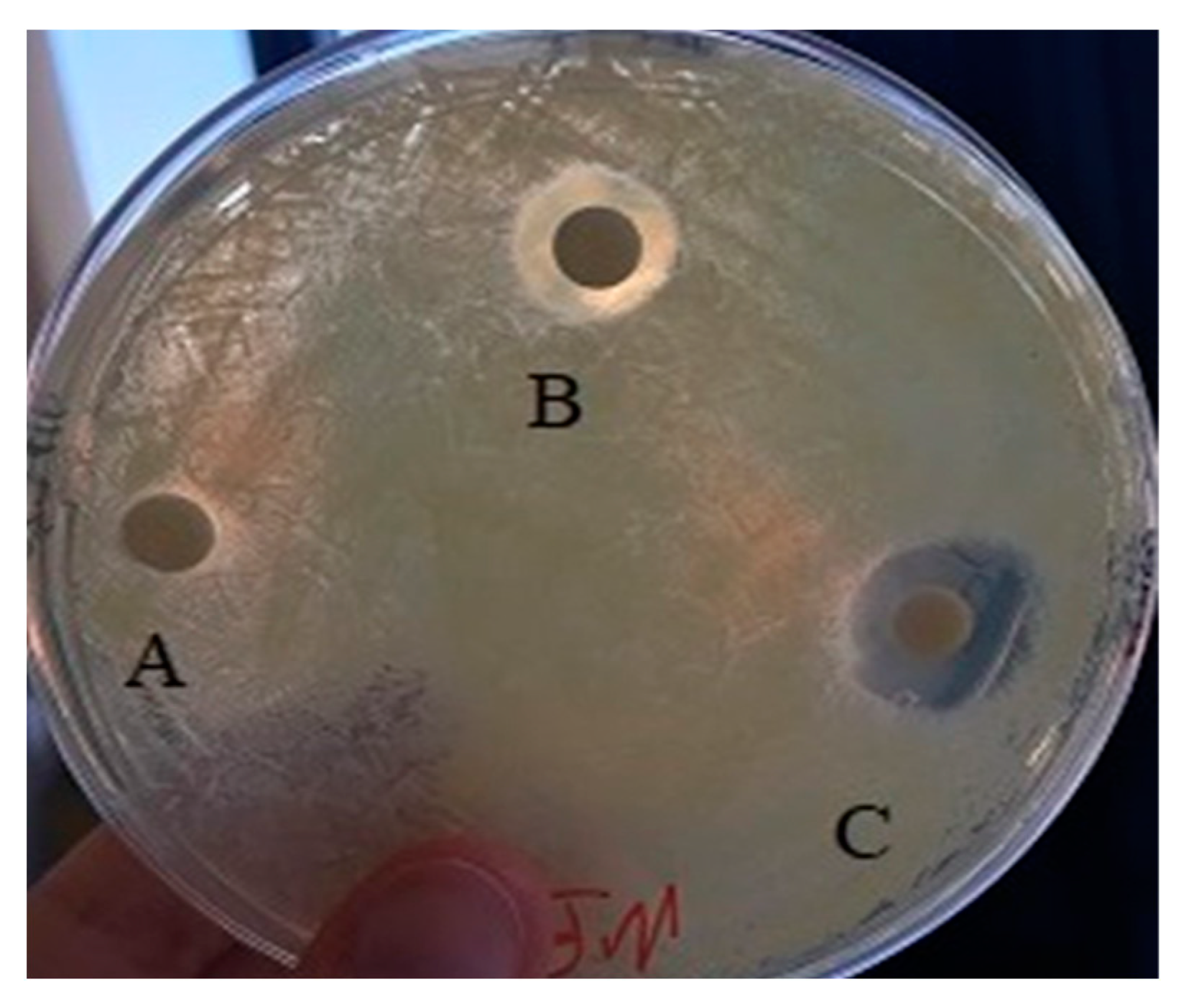
2.6.6. Nanoparticle Antibacterial Activity Assay
3. Results
3.1. Selection of NP Producer Strains
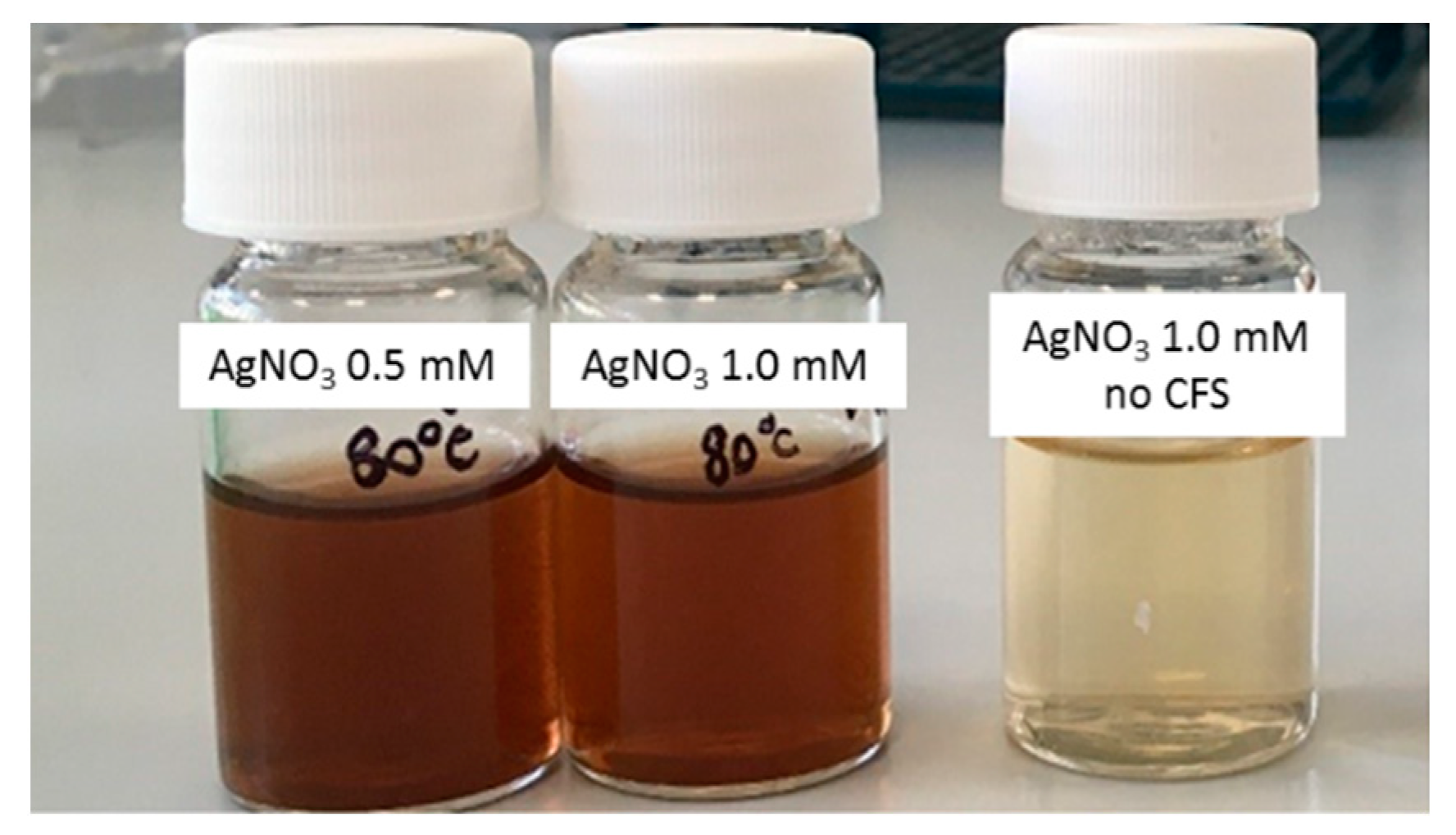
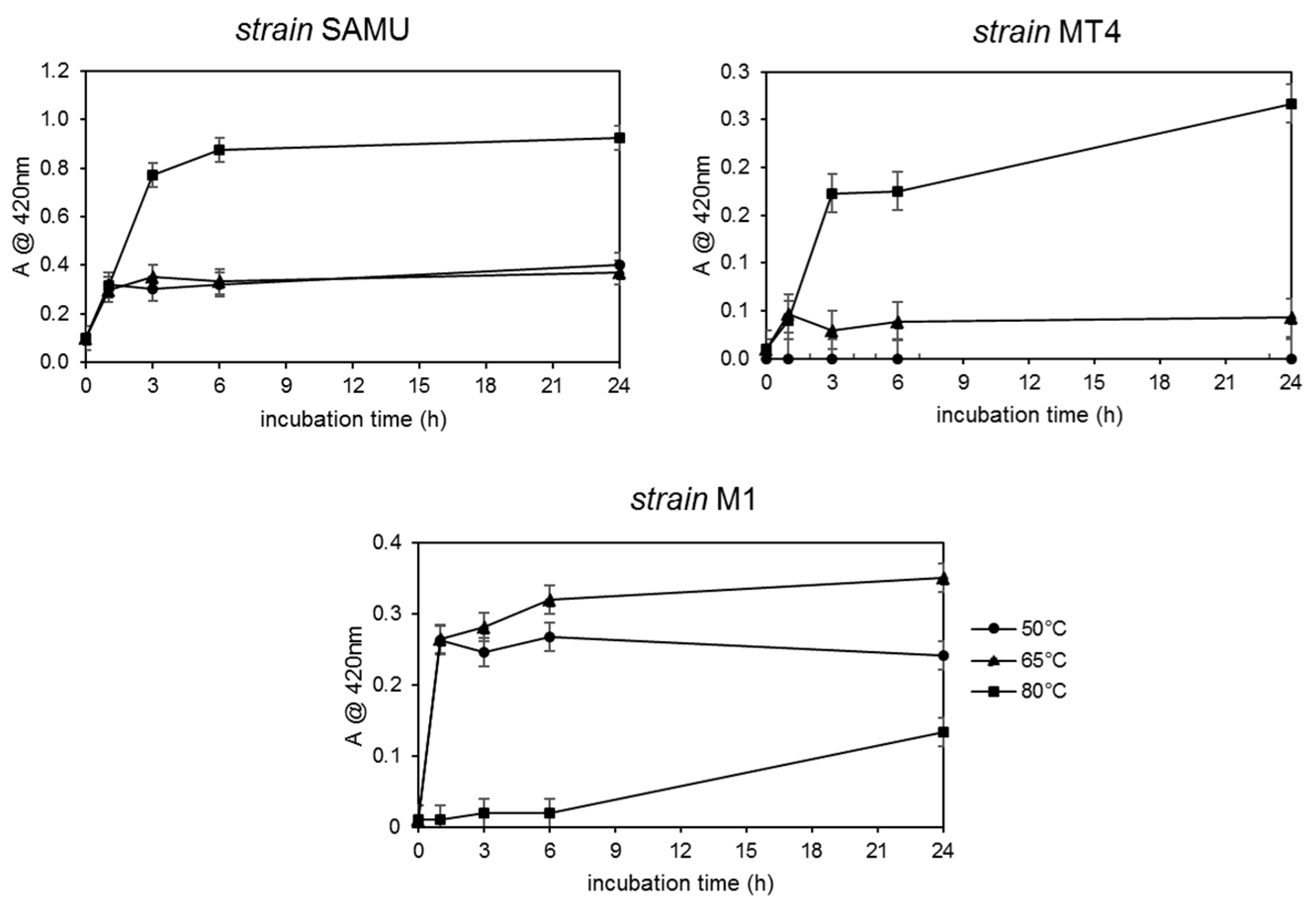
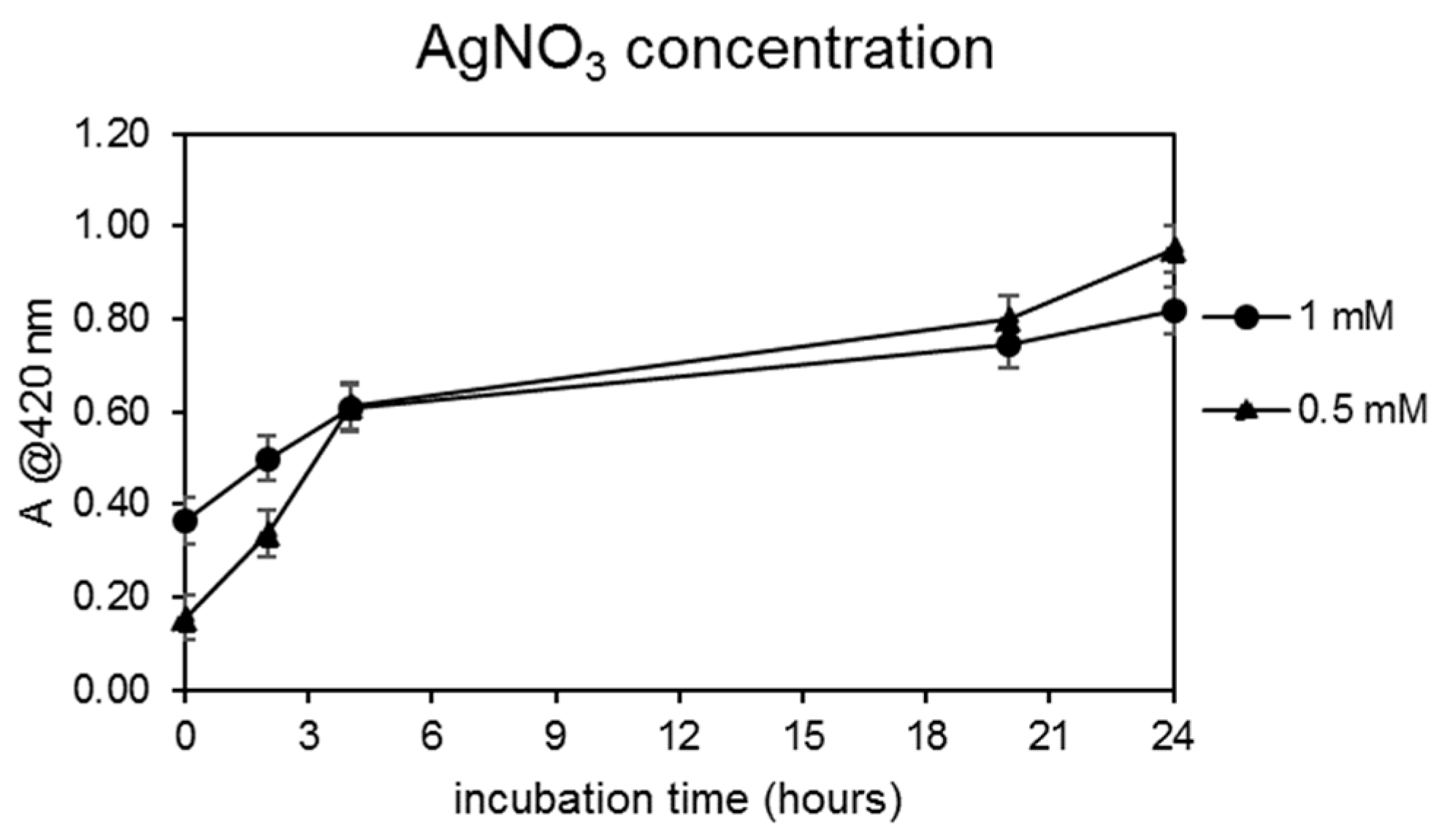
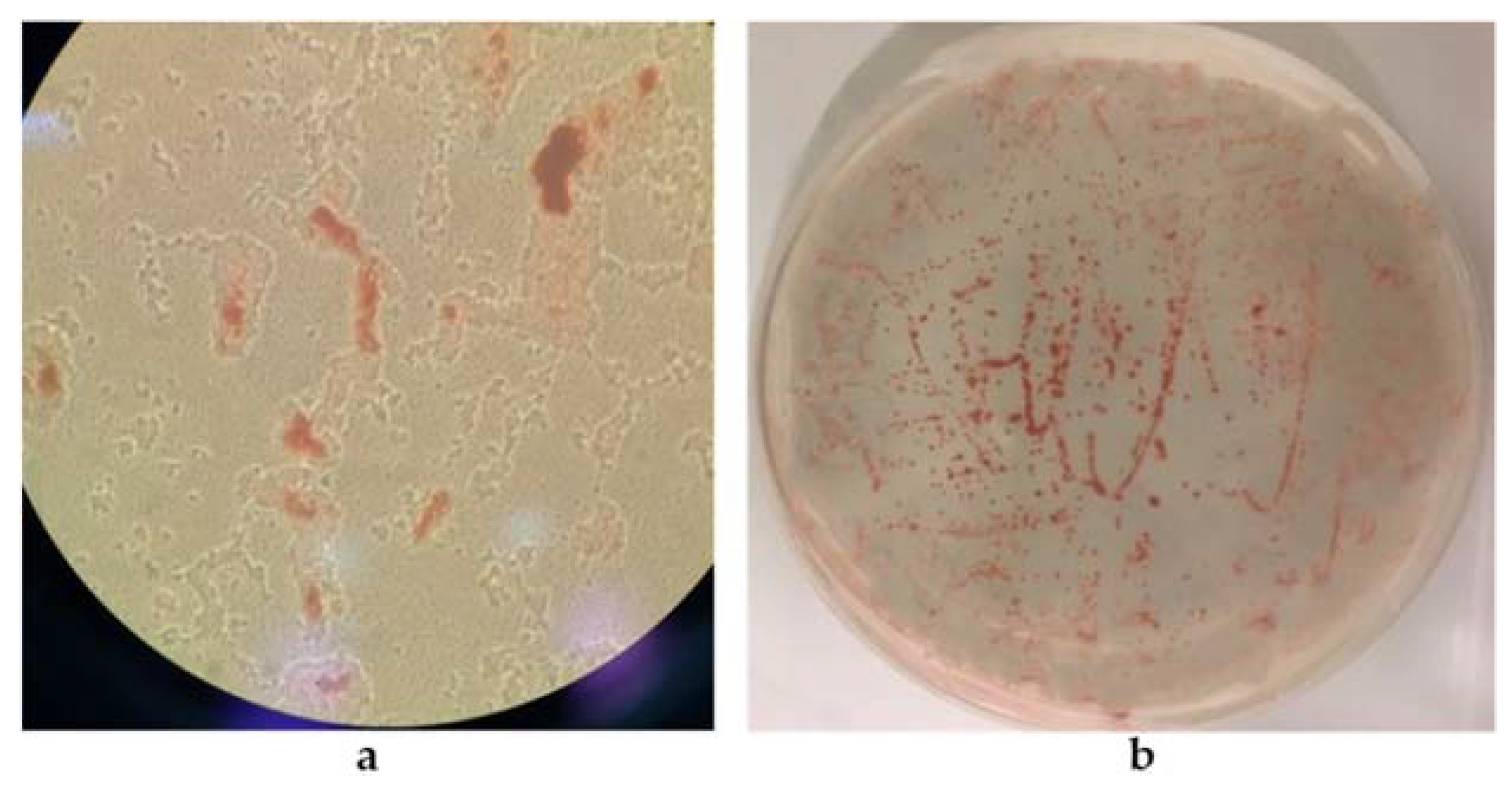
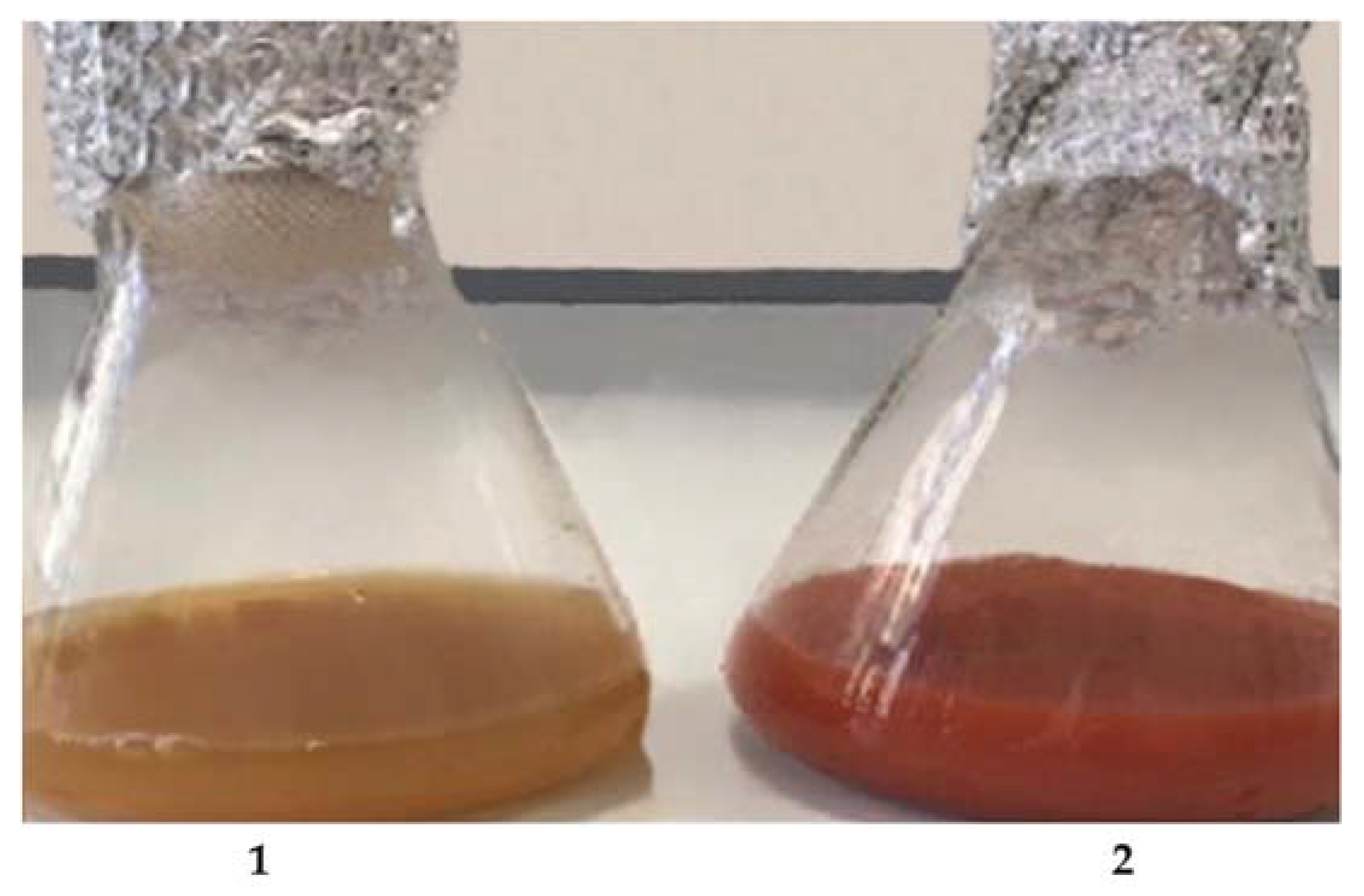
3.1.1. Selection of AgNP Producer Strains and Biosynthesis Optimization
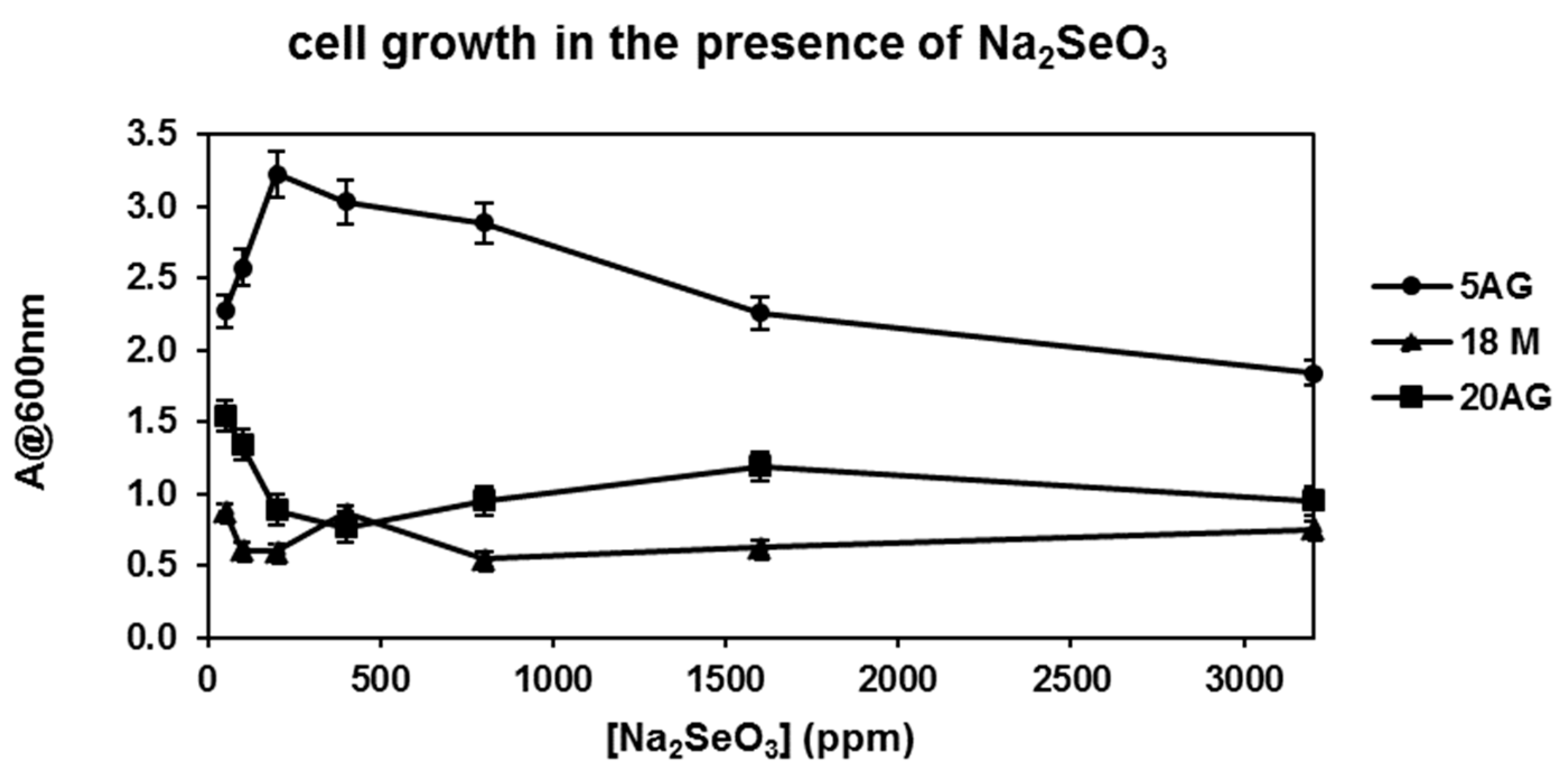
3.1.2. Selection of SeNP Producer Strains and Biosynthesis Optimization
3.2. AgNPs’ and SeNPs’ Physicochemical Characterization
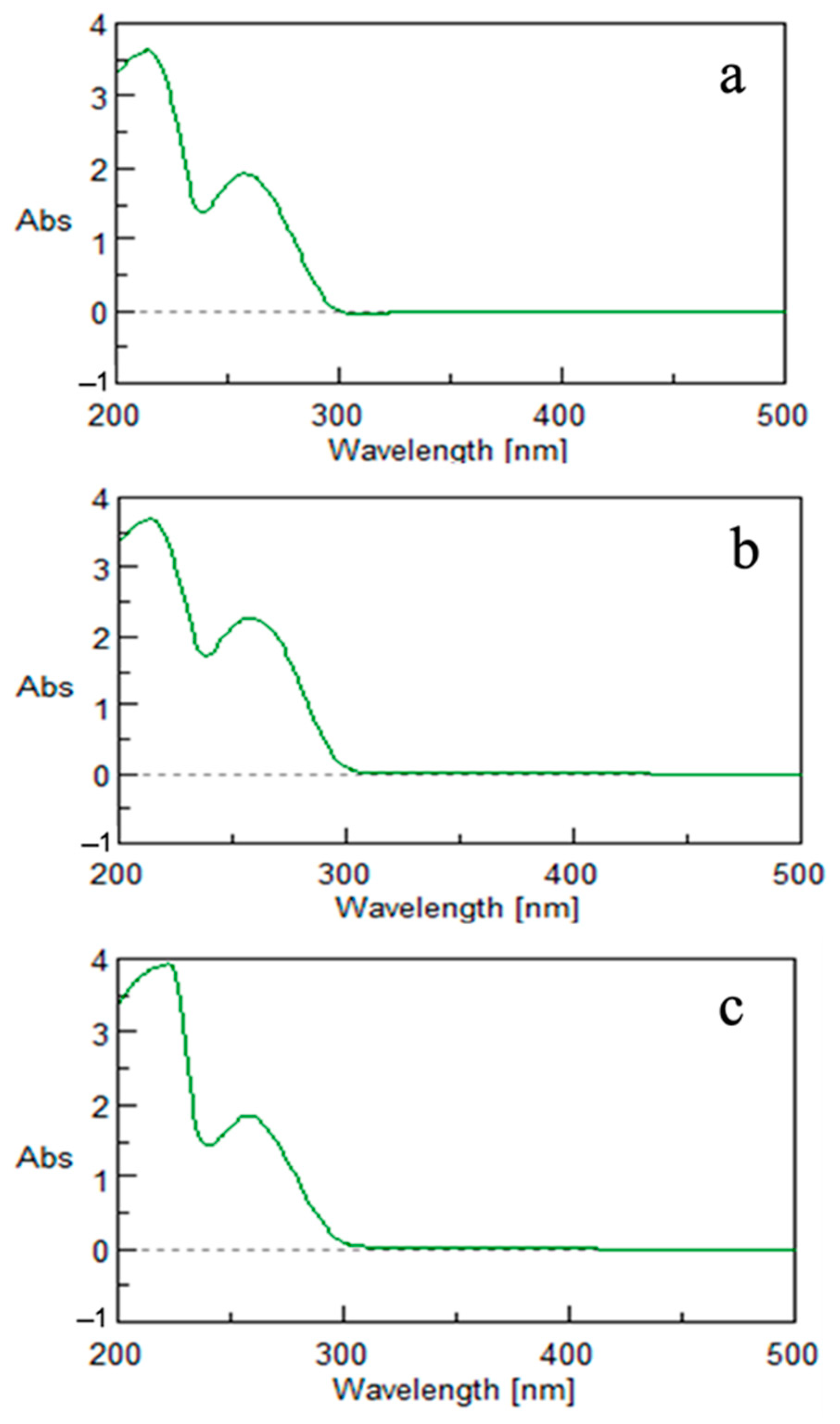
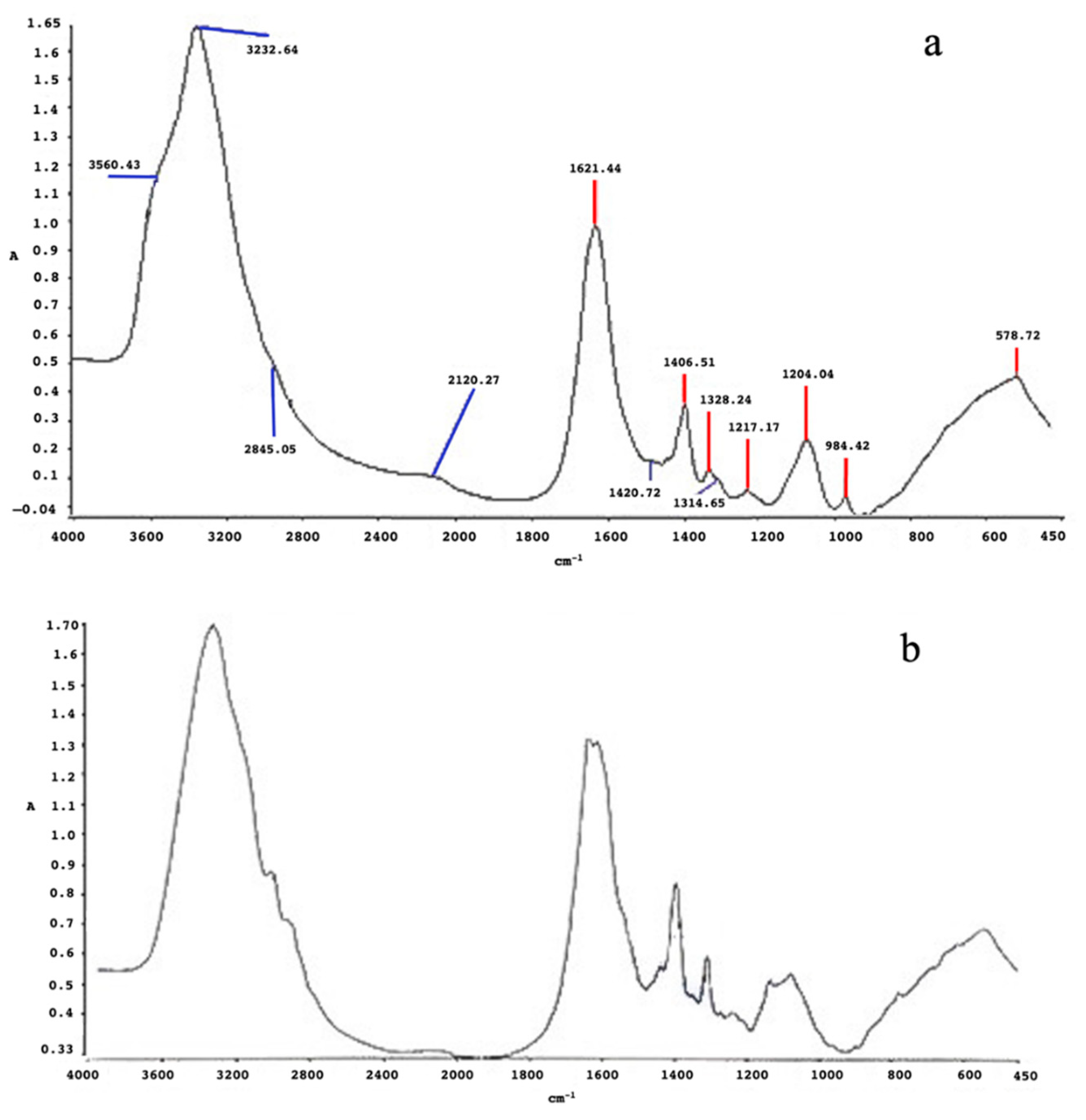
3.2.1. Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
3.2.2. Selenium Nanoparticles (SeNPs)
3.3. Antibacterial Properties of AgNPs and SeNPs
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kshtriya, V.; Koshti, B.; Gour, N. Green synthesized nanoparticles: Classification, synthesis, characterization, and applications. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2021, 94, 173–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Gade, A.; Yadav, A. Biogenic Nanoparticles: An Introduction to What They Are, How They Are Synthesized and Their Applications. In Metal Nanoparticles in Microbiology; Rai, M., Duran, N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri Narayanan, K.B.; Sakthivel, N. Biological synthesis of metal nanoparticles by microbes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 156, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrulolum, H.; Nooraei, S.; Javanshir, N.; Tarrahimofrad, H.; Mirbagheri, V.S.; Easton, A.J.; Ahmadian, G. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using microorganisms and their application in the agrifood sector. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkoti, N.I.; Taranath, T.C. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using microbes—A review. Colloid Surf. B 2014, 121, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fariq, A.; Khan, T.; Yasmin, A. Microbial synthesis of nanoparticles and their potential applications in biomedicine. J. Appl. Biomed. 2017, 15, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, V.L.; Thomas, R.; Varghese, R.T.; Soniya, E.V.; Mathew, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Extracellular synthesis of silver nanoparticles by the Bacillus strain CS 11 isolated from industrialized area. 3 Biotech 2014, 4, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnia, M.; Makhdoumi, A.; Mashreghi, M.; Eshghi, H. Exploring the potentials of halophilic prokaryotes from a solar saltern for synthesizing nanoparticles: The case of silver and selenium. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, N.; Ušjak, D.; Milenković, M.T.; Zheng, K.; Liverani, L.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Stevanović, M.M. Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Selenium Nanoparticles with Different Surface Chemistry and Structure. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, L.; Mancinelli, R. Life in extreme environments. Nature 2001, 409, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuta, E.V.; Hoover, R.B.; Tang, J. Microbial Extremophiles at the limits of Life. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 33, 183–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, I.; Lama, L.; Moriello, V.S.; Poli, A.; Gambacorta, A.; Nicolaus, B. Isolation of a new thermohalophilic Thermus thermophilus strain from hot spring, able to grow on a renewable source of polysaccharide. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, M.; Gambacorta, A.; Bu’Lock, J.D. Extremely Thermophilic Acidophilic Bacteria Convergent with Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1975, 86, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyu, H.; Lebre, P.; Blom, J.; Cowan, D.; De Maayer, P. Phylogenomic re-assessment of the thermophilic genus Geobacillus. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 39, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaus, B.; Lama, L.; Esposito, E.; Manca, M.C.; di Prisco, G.; Gambacorta, A. “Bacillus thermoantarcticus’’ sp. nov., from Mount Melbourne, Antarctica: A novel thermophilic species. Polar Biol. 1996, 16, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coorevits, A.; Dinsdale, A.E.; Halket, G.; Lebbe, L.; De Vos, P.; Van Landschoot, A.; Logan, N.A. Taxonomic revision of the genus Geobacillus: Emendation of Geobacillus, G. stearothermophilus, G. jurassicus, G. toebii, G. thermodenitrificans and G. thermoglucosidans (nom. corrig., formerly ‘thermoglucosidasius’); transfer of Bacillus thermantarcticus to the genus as G. thermantarcticus comb. nov.; proposal of Caldibacillus debilis gen. nov., comb nov.; transfer of G. tepidamans to Anoxybacillus as A. tepidamans comb. nov.; and proposal of Anoxybacillus caldiproteolyticus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1470–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, I.; Giordano, A.; Lama, L.; Nicolaus, B.; Gambacorta, G. Halomonas campaniensis sp. nov., a haloalkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a mineral pool of Campania Region, Italy. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 28, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, I.; Gambacorta, A.; Lama, L.; Nicolaus, B.; Giordano, A. Salinivibrio costicola subsp. alcaliphilus subsp. nov., a haloalkaliphilic aerobe from Campania Region (Italy). Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 28, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, I.; Lama, L.; Nicolaus, B.; Poli, A.; Gambacorta, A.; Giordano, A. Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi subsp. Incaldanensis subsp. nov., an alkalitolerant halophile isolated from an algal mat collected from a sulfurous spring in Campania (Italy), and emended description of Oceanobacillus oncorhynchi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryshchepa, O.; Pomastowski, P.; Buszewski, B. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, investigation techniques, and properties. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomakin, A.; Teplow, D.B.; Benedek, G.B. Quasielastic light scattering for protein assembly studies. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 299, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchini, A.; Heenan, R.K.; Paduano, L.; Vitiello, G. Functionalized SPIONs: The surfactant nature modulates the self-assembly and cluster formation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 18441–18449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallucci, N.; Vitiello, G.; Di Girolamo, R.; Imbimbo, P.; Monti, D.M.; Tarallo, O.; Vergar, A.; Krauss, I.R.; Paduano, L. Towards the Development of Antioxidant Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: Controlling the Properties by Tuning Synthesis Conditions. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallucci, N.; Hmoudah, M.; Martinez, E.; El-Qanni, A.; Di Serio, M.; Paduano, L.; Vitiello, G.; Russo, V. Photodegradation of ibuprofen using CeO2 nanostructured materials: Reaction kinetics, modelling, and thermodynamics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Dai, C.; Wang, P.; Fan, S.; Yu, B.; Qu, Y. Antibacterial properties and mechanism of selenium nanoparticles synthesized by Providencia sp. DCX. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dixit, C.K. Methods for characterization of nanoparticles. Adv. Nanomed. Deliv. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalu, S.; Antoniac, I.V.; Fritea, L.; Mates, I.M.; Milea, C.; Laslo, V.; Vicas, S.; Mohan, A. Surface modifications of the titanium mesh for cranioplasty using selenium nanoparticles coating. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shubharani, R.; Mahesh, M.; Murthy, V.N.Y. Biosynthesis and Characterization, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Selenium Nanoparticles from Ethanol Extract of Bee Propolis. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgarini, A.; Lampis, S.; Turner, R.J.; Vallini, G. Biomolecular composition of capping layer and stability of biogenic selenium nanoparticles synthesized by five bacterial species. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinteros, M.A.; Bonilla, J.O.; Alborés, S.V.; Villegas, L.B.; Páez, P.L. Biogenic nanoparticles: Synthesis, stability and biocompatibility mediated by proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacenza, E.; Presentato, A.; Ferrante, F.; Cavallaro, G.; Alduina, R.; Martino, D.F.C. Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles: A Fine Characterization to Unveil Their Thermodynamic Stability. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, D.; Mittal, A.; Malik, D.K. Antimicrobial activity of PVP coated silver nanoparticles synthesized by Lysinibacillus varians. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Singh, H.; Wang, C.; Hwang, K.H.; Farh Mel, A.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis, characterization, and antimicrobial applications of silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 2567–2577. [Google Scholar]
- Vaigankar, D.C.; Mujawar, S.Y.; Mohanty, A.K.; Dubey, S.K. Biogenesis of selenium nanospheres using Halomonas venusta strain GUSDM4 exhibiting potent environmental applications. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| NPs’ Stability | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|
| Rapid aggregation | From 0 to ±5 |
| Weak stability | From ±10 to ±30 |
| Moderate stability | From ±30 to ±40 |
| Good stability | From ±40 to ±60 |
| Excellent stability | ≥±61 |
| Strain | AgNPs (mg) | Inhibition Halos (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.04 | 0.7 | |
| E. coli | 0.08 | 1.1 |
| 0.16 | 1.3 | |
| 0.04 | 0.7 | |
| K. rhizophila | 0.08 | 1.0 |
| 0.16 | 1.2 |
| Inhibition Halos (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | NPs (mg) | Medium A | Medium B | Medium C |
| K. rhizophila | 10.0 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| 20.0 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 1.0 | |
| 40.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 1.5 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romano, I.; Vitiello, G.; Gallucci, N.; Di Girolamo, R.; Cattaneo, A.; Poli, A.; Di Donato, P. Extremophilic Microorganisms for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanoparticles. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101885
Romano I, Vitiello G, Gallucci N, Di Girolamo R, Cattaneo A, Poli A, Di Donato P. Extremophilic Microorganisms for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanoparticles. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101885
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomano, Ida, Giuseppe Vitiello, Noemi Gallucci, Rocco Di Girolamo, Andrea Cattaneo, Annarita Poli, and Paola Di Donato. 2022. "Extremophilic Microorganisms for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanoparticles" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101885
APA StyleRomano, I., Vitiello, G., Gallucci, N., Di Girolamo, R., Cattaneo, A., Poli, A., & Di Donato, P. (2022). Extremophilic Microorganisms for the Green Synthesis of Antibacterial Nanoparticles. Microorganisms, 10(10), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101885










