Abstract
Carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria are a public health threat that requires urgent action. The fact that these pathogens commonly also harbor resistance mechanisms for several other antimicrobial classes further reduces patient treatment options. The present study aimed to provide information regarding the multidrug resistance genetic background of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria in Central Greece. Strains from a tertiary care hospital, collected during routine practice, were characterized using a DNA microarray-based assay. Various different resistance determinants for carbapenems, other beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, quinolones, trimethoprim, sulfonamides and macrolides were detected among isolates of the same sequence type. Eighteen different multidrug resistance genomic profiles were identified among the twenty-four K. pneumoniae ST258, seven different profiles among the eight K. pneumoniae ST11, four profiles among the six A. baumannii ST409 and two among the three K. oxytoca. This report describes the multidrug resistance genomic background of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria from a tertiary care hospital in Central Greece, providing evidence of their continuous genetic evolution.
1. Introduction
The dissemination of carbapenem-resistant (CR) Gram-negative bacteria, including Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, has dramatically increased over the last years [1]. Infections caused by these microorganisms are linked with prolonged time of hospitalization leading to increased healthcare costs as well as with elevated mortality rates [2]. Detailed knowledge of the characteristics of these pathogens is essential for the development of novel antibiotics and potential new therapeutic targets [3].
Two main resistance mechanisms against carbapenems in enterobacteria are known: ampC overexpression accompanied by a porin loss [4,5] and transmissible genes encoding carbapenemases [6]. The corresponding genes and alleles are usually located on plasmids as well as other mobile genetic elements (MGEs) [7]. Plasmids with carbapenemase genes often additionally harbor toxin–antitoxin systems which prevent plasmid loss even in the absence of selective pressure caused by antibiotics [8]. Furthermore, the capacity of these bacteria to survive in the nosocomial environment helps them to acquire genetic elements from other bacteria, which include novel antibiotic-resistance determinants or pathogenicity genes [9].
Recent reports showed an increasing prevalence of CR Gram-negative bacteria and their rapid worldwide spread. The four most prevalent carbapenemase genes are blaKPC, blaNDM, blaOXA-48 and blaVIM [6]. Infections caused by CR Gram-negative bacteria are usually difficult to treat [10]. Treatment options are limited since carbapenemase genes are often co-localized on mobile genetic elements together with additional resistance genes conferring resistance to aminoglycosides and/or fluoroquinolones. Therefore, only a few antibiotics remain effective, such as colistin, fosfomycin and tigecycline, as well as, in some cases, the monobactam aztreonam, which is not hydrolyzed by metallo-beta-lactamases (e.g., VIM and NDM) [11].
As early as 2009 the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommended an active screening as a prerequisite for specific quarantine arrangements that might help to prevent the dissemination of carbapenem-resistant pathogens [12,13]. Several other governmental institutions and agencies such as the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) and the US Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) also shared this view [14,15,16,17].
In Greece, the rate of CR Gram-negative bacteria is among the highest worldwide [18,19,20,21]. Given that the detection of different resistance genes and MGEs is costly and time-consuming, no data from our country are available regarding the characterization of the whole genetic background of these pathogens. The purpose of the present study was the detection of a plethora of resistance genes in a representative collection of CR Gram-negative bacteria, using the microarray-based CarbDetect AS-2 Kit (Abbott, Jena, Germany).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of the CR Gram-Negative Isolates
The study was conducted in the University Hospital of Larissa (UHL), a tertiary care 600-bed hospital in the Thessaly region (Central Greece) which serves a population of approximately 1,000,000 inhabitants. Based on the UHL surveillance protocol, all CR bacteria are routinely tested for carbapenemase-encoding genes, are subjected to multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) and are stored at −80° for epidemiological purposes. Identification and susceptibility testing of all CR strains are performed using the automated system BD Phoenix™ M50. The detection of carbapenemase-encoding genes (blaKPC, blaNDM, blaVIM, blaOXA-like) and MLST typing are performed as previously described [22].
A total of 44 CR Gram-negative isolates (6 Acinetobacter baumannii, 3 Pseudomonas aeruginosa and 35 Klebsiella spp.) were selected from the collection of routine isolates as described above. The inclusion of the bacteria into the study was based on the type of carbapenemase they produced, their sequence type, and their antibiotic susceptibility profiles, so as to include as many different profiles for each sequence type as possible. All strains were isolated from clinical samples between January 2019 and April 2020.
2.2. Molecular Characterization
A molecular characterization of the selected strains was performed using the CarbDetect AS-2 Kit (Abbott, Jena, Germany), according to the manufacturer′s instructions, as previously described [23]. The kit detects a total of 134 genes including 111 genes and alleles associated with resistance to carbapenems, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, trimethoprim, sulfonamides and macrolides, as well as 10 genes encoding multidrug efflux pumps and toxin–antitoxin systems (Table 1). The Result Collector 2.0 (Abbott, Jena, Germany) was used to automatically summarize the results obtained from the microarray analysis.

Table 1.
Genes and alleles detected by the CarbDetect AS-2 Kit, per category of genes.
3. Results
The group of 44 carbapenem-resistant strains that were selected for analysis consisted of 32 K. pneumoniae, six A. baumannii, three Klebsiella oxytoca and three P. aeruginosa.
Thirty-three of the selected isolates harbored one carbapenemase gene and eleven isolates harbored two. Among K. pneumoniae strains blaKPC was the most commonly identified carbapenemase gene, found in 24 out of the 32 isolates. blaNDM was detected in eight isolates, while blaVIM was only detected in five and in all cases co-existed with blaKPC. All A. baumannii strains harbored a blaOXA-23-like gene, whereas all the K. oxytoca and all the P. aeruginosa harbored blaVIM. Variant blaVIM-2 was specifically identified in a single P. aeruginosa isolate.
Genes responsible for ESBL and broad-spectrum beta-lactamases’ production were detected in 40 out of the 44 carbapenem-resistant strains. The gene blaSHV was identified in 28 K. pneumoniae isolates and in two K. oxytoca, blaCTX-M-1/15 in 21 K. pneumoniae, blaTEM in 13 K. pneumoniae and in four A. baumannii, blaVEB in four K. pneumoniae, blaOXA-1 in 16 K. pneumoniae and in two P. aeruginosa, blaOXA-9 in two K. pneumoniae and blaOXA-6 in one K. pneumoniae. AmpC genes were detected in four isolates; two K. pneumoniae harbored blaACT and two K. oxytoca harbored blaMOX-CMY9.
Aminoglycoside resistance genes were present in 41 out of the 44 carbapenem-resistant strains. Among K. pneumoniae, the combination of genes aac(3′)-Ia, aac(6′)-Ib, aadA1, and aphA was detected in six isolates, the combination aac(6′)-Ib, strA, and strB in four, the aac(6′)-Ib, aadA1, and aadA2 in three, the aac(6′)-Ib, aadA2, and aphA in three, the aac(6′)-Ib and aadA2 in three, the aadA1, aadB, ant2, aphA, strA, and strB in two, the aadA1, aadB, ant2, rmtB, strA, and strB in two, the aac(6′)-Ib, aadA2, aphA, strA, and strB in one and the aadA1, aphA, strA, and strB in one. Four K. pneumoniae only possessed aac(6′)-Ib and one only aphA. Additionally, five out of the six A. baumannii isolates harbored aminoglycoside resistance genes. Four co-harbored the aphA, armA, strA, and strB and one the aac(3′)-Ia, aadA1, armA, strA, and strB. Regarding the three K. oxytoca, the aac(6′)-Ib, aac(6′)-IIc, aadA2, aphA, strA, and strB genes were detected in two strains and the aac(6′)-Ib, aac(6′)-IIc, aphA, and strB genes in one isolate. Concerning the P. aeruginosa isolates, one harbored the combination aac(6′)-Ib, aadA1, strA, and strB, while one only harbored the aac(6′)-Ib and one the aac(6′)-Iic. Overall, aac(6′)-Ib was the most common gene, found in 29 out of the 44 CR strains.
Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance (PMQR) genes were identified in seven strains. In particular, gene qnrS was detected in four K. pneumoniae and in the three K. oxytoca.
Genes associated with trimethoprim resistance were detected in 23 K. pneumoniae and in the three K. oxytoca. Fifteen K. pneumoniae harbored dfrA14, 10 dfrA12 and four dfrA1. DfrA14 and dfrA12 co-existed in six isolates. All the K. oxytoca harbored dfrA19. Regarding sulfonamide resistance genes, these were detected in 27 K. pneumoniae, two A. baumannii, the three K. oxytoca and in two P. aeruginosa. Sul1 was identified in 16 K. pneumoniae, one A. baumannii, the three K. oxytoca and in two P. aeruginosa. Sul2 was detected in 21 K. pneumoniae, one A. baumannii and two K. oxytoca, while sul3 was present in three K. pneumoniae.
Macrolide resistance genes were identified in 16 strains. Ten K. pneumoniae harbored mph alone (n = 3) or in combination with mrx (n = 7). Additionally, all six A. baumannii isolates harbored mph.
Genes associated with MGEs were detected in a total of 36 out of the 44 carbapenem-resistant isolates. intl1 was detected in 29 K. pneumoniae, one A. baumannii, the three K. oxytoca and the three P. aeruginosa. Twenty of the intl1 positive K. pneumoniae additionally harbored tnpISEcp1.
Finally, the oqxA and oqxB genes, encoding oqxAB efflux pump, were present in 26 K. pneumoniae, while the splA and splT genes, encoding the SplTA toxin–antitoxin system, were present in all the six A. baumannii isolates.
Overall, 18 distinct genomic profiles were identified among the 24 K. pneumoniae ST258, seven distinct profiles among the eight K. pneumoniae ST11, four profiles among the six A. baumannii ST409 and two among the three untyped K. oxytoca.
The genomic characteristics of the carbapenem-resistant isolates are presented in Table 2 and in Figure 1. The antibiotic susceptibility profiles of the isolates were in concordance with the genotypes.

Table 2.
Genomic characterization of the carbapenem-resistant isolates.
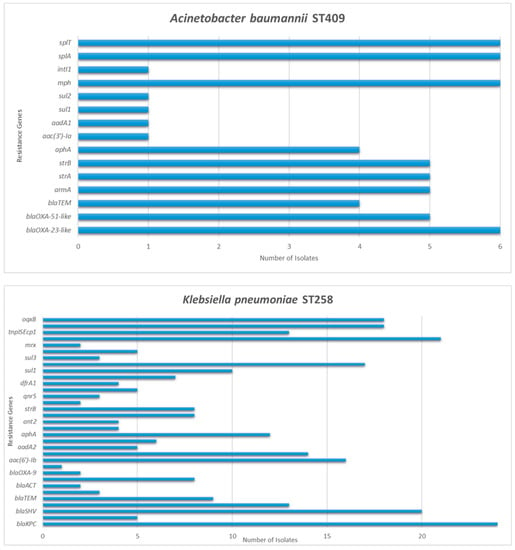
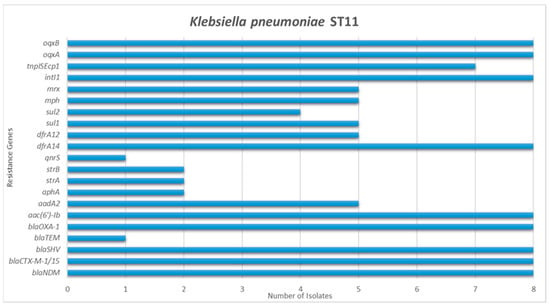
Figure 1.
Detection frequency of each resistance gene among Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates.
4. Discussion
In recent years, multidrug resistance has evolved to one of the greatest challenges in the health sector, affecting not only hospital settings but also the community, animals and the environment [24,25]. Carbapenem-resistant pathogens represent a threat highly potent to cause outbreaks, while it is anticipated that new unique β-lactamases with unusual properties will be identified in the near future given the widespread presence of β-lactamases genes and the unceasing pressure from the use of β-lactam antibiotics [26,27,28]. The present study aimed to unveil the molecular multidrug resistance determinants of CR Gram-negative bacteria isolated from the University Hospital of Larissa, a hospital that serves the population of Central Greece. A microarray-based assay was selected as the typing tool, as an alternative to whole genome sequencing, since it is a technique suitable for screening research, excellent in specificity and sensitivity [29].
The majority of K. pneumoniae strains in our study expressed carbapenem resistance due to carriage of blaKPC. Carbapenemases of the KPC family have the most extensive global distribution of all carbapenemases that are associated with Enterobacteriaceae and are highly prevalent in Mediterranean countries, especially Italy and Greece [30]. Despite the fact that Greece used to be the epicenter of VIM-producing Enterobacteriaceae [31], these did not predominate, underlining the fast evolution in the molecular epidemiology of carbapenemases, as has previously been illustrated by Galani et al. [32]. Coexistence of OXA-23-like and TEM was the primary resistance profile in the A. baumannii isolates, as has previously been described in China [33]. The oxacillinase blaOXA-23-like is also amongst the most dominant resistance genes that have been reported in A. baumannii from Germany [34]. All the P. aeruginosa harbored blaVIM, which was expected considering the pre-existing data from the region [20].
Genes associated with aminoglycoside resistance were detected in 41 strains. Aminoglycosides are usually part of the empirical treatment of serious nosocomial infections in most Greek tertiary hospitals and constitute one of the few remaining options in the battle against CR pathogens. That could explain and drive the wide dissemination of the respective resistance genes. The aac(6′)-Ib was the most common gene detected in this study. Former studies have also stated its frequent co-occurrence with carbapenemases genes in Switzerland [35], Spain [36], and India [37], as well as Greece [38].
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistance genes sul and dfrA were detected in 24 strains. DfrA14 was the most common trimethoprim resistance gene, which is in agreement with a recent study from South Africa [39]. Concerning sulfonamide resistance genes, sul2 predominated, which is in contrast with former findings from Brazil [40]. Sul2 variant has, however, also been detected in high rates among carbapenemase-producing K. pneumoniae strains isolated from intensive care unit patients in Turkey [41].
Concerning quinolone resistance genes, the plasmid-encoded gene qnrS was detected in seven strains; six harbored qnrS and possessed blaVIM alone (n = 3) or in combination with blaKPC (n = 3), while the remaining one possessed blaNDM. The presence of genes oqxA and oqxB might also have contributed to the fluoroquinolone resistance profile of 26 K. pneumoniae. The plasmidic efflux pump OqxAB confers resistance to multiple agents, including fluoroquinolones as well as biocides, and has been shown to play a role in the selection of fluoroquinolone resistance in different K. pneumoniae clones [42,43].
One of the main drivers for the recorded rapid dispersion of multidrug resistance is the presence of MGEs [44]. In our study, intl1 was the only integrase gene detected among the CR strains, while the intl2 and intl3 genes were not present in any isolate. These findings are in concordance with earlier reports about KPC-2 positive K. pneumoniae from a pediatric hospital in China [45]. In Southern Brazil, though, class 2 integrons were more frequently detected than class 1 among OXA-23 A. baumannii [46]. Class I integrons are known to harbor various antimicrobial resistance gene cassettes encoding β-lactamases, dfr and sul variants, qacEΔ1 (quaternary ammonium compound disinfectant), as well as aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes [47]. This probably explains the genotypic profile of the intl1 positive strains that we examined, which presented different combinations of resistance determinants for at least three classes of antimicrobials. Furthermore, we detected the ISEcp1 element, known to be implicated in the mobilization of AMR genes such as blaCTX-M and blaKPC [48,49]. The resistance determinants identified in isolates that were tested positive for tnpISEcp1 are subsequently considered more likely to be disseminated horizontally via ISEcp1-mediated transposition among the same or different bacterial species.
Finally, genes splA and splT, encoding the plasmid borne SplTA toxin–antitoxin system, were identified in all the CR A. baumannii isolates of our study. The SplTA is widely spread in the A. baumannii plasmidome, including carbapenem-resistant clinical isolates, and can act as a plasmid stabilization and maintenance mechanism even in the absence of antimicrobial selective pressure. It is also involved in the successful transmission of plasmids carrying carbapenemase genes, favoring even further their dissemination [50].
In conclusion, according to our findings, strains that belonged to the same MLST clone had different molecular resistance patterns, indicating a potential continuous genetic evolution of antimicrobial resistance. The ability of bacteria to evolve their AMR characteristics might continue to undermine health care, economic development, and life expectancy if infection control measures are not implemented.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.T., Z.A., S.D.B., S.M., V.S., C.B., G.N.D., R.E. and E.P.; methodology, K.T., Z.A., S.B.-V., Z.F., S.D.B., S.M., N.K.G., K.Z., M.S., V.S., C.B., G.N.D. and E.P.; software, E.M. and S.D.B.; validation, K.T., Z.A., S.B.-V., Z.F., S.D.B., S.M., C.B., R.E. and E.P.; formal analysis, K.T., Z.A., E.M., S.B.-V., Z.F., S.D.B., S.M. and R.E.; investigation, K.T., Z.A., E.M., S.B.-V., Z.F., S.D.B. and E.P.; resources, N.K.G., K.Z., A.S., I.T., G.N.D., R.E. and E.P.; data curation, K.T., Z.A. and S.D.B.; writing—original draft preparation, K.T. and Z.A.; writing—review and editing, K.T., Z.A., S.D.B., S.M., N.K.G., K.Z., M.S., V.S., C.B., G.N.D., R.E. and E.P.; supervision, S.D.B., S.M., V.S., C.B., G.N.D., R.E. and E.P.; project administration, S.D.B., S.M., N.K.G., A.S., V.S., C.B., G.N.D., R.E. and E.P.; funding acquisition, S.D.B., S.M., N.K.G., A.S., M.S., V.S., C.B., G.N.D., R.E. and E.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was carried out under the project “Novel technologies for surveillance and characterization of Extended-spectrum β-lactamase and Carbapenemase producing Enterobacteriaceae, in humans and animals (CARBATECH)”, of the Bilateral S&T Cooperation Program Greece–Germany 2017. The European Union and the General Secretariat for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Development and Investments co-funded the Greek side (T2DGE-0944). The Federal Ministry of Education and Research funded the German side (01EI1701). This support is gratefully acknowledged.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All humans included in this study gave their informed consent before participation. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Scientific Board of the General University Hospital of Larissa (37000/02-08-2018). All samples were obtained by noninvasive rectal swabs that were collected during routine practice.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated during this study are presented within the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Van Duin, D.; Paterson, D.L. Multidrug Resistant Bacteria in the Community: Trends and Lessons Learned. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H.; Török, M.E. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, F.; Villegas, M.V. The Role of Surveillance Systems in Confronting the Global Crisis of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 28, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumith, M.; Ellington, M.J.; Livermore, D.M.; Woodford, N. Molecular Mechanisms Disrupting Porin Expression in Ertapenem-Resistant Klebsiella and Enterobacter Spp. Clinical Isolates from the UK. J. AntiMicrob. Chemother. 2009, 63, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.; Pascual, A.; Hernández-Allés, S.; Alvarez-Díaz, D.; Suárez, A.I.; Tran, J.; Benedí, V.J.; Jacoby, G.A. Roles of β-Lactamases and Porins in Activities of Carbapenems and Cephalosporins against Klebsiella Pneumoniae. AntiMicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duin, D.; Doi, Y. The Global Epidemiology of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. Virulence 2016, 8, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diene, S.M.; Rolain, J.-M. Carbapenemase Genes and Genetic Platforms in Gram-Negative Bacilli: Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter Species. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnif, B.; Vimont, S.; Boyd, A.; Bourit, E.; Picard, B.; Branger, C.; Denamur, E.; Arlet, G. Molecular Characterization of Addiction Systems of Plasmids Encoding Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases in Escherichia Coli. J. AntiMicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Ruiz-Garbajosa, P. Co-Resistance: An Opportunity for the Bacteria and Resistance Genes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2011, 11, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrill, H.J.; Pogue, J.M.; Kaye, K.S.; LaPlante, K.L. Treatment Options for Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Infections. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandon, J.L.; Nicolau, D.P. Human Simulated Studies of Aztreonam and Aztreonam-Avibactam To Evaluate Activity against Challenging Gram-Negative Organisms, Including Metallo-β-Lactamase Producers. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Guidance for Control of Infections with Carbapenem-Resistant or Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Acute Care Facilities. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2009, 58, 256–260.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Vital Signs: Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 165–170.
- Richards, M.; Cruickshank, M.; Cheng, A.; Gandossi, S.; Quoyle, C.; Stuart, R.; Sutton, B.; Turnidge, J.; Bennett, N.; Buising, K.; et al. Recommendations for the Control of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE): A Guide for Acute Care Health Facilities. Infect. Dis. Health 2017, 22, 159–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Control and Prevention Toolkit. Available online: http://www.ahrq.gov/hai/patient-safety-resources/cre-toolkit/index.html (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- World Health Organization Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae, Acinetobacter Baumannii and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Health Care Facilities; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-155017-8.
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Burns, K.; Rodríguez Baño, J.; Borg, M.; Daikos, G.; Dumpis, U.; Lucet, J.C.; Moro, M.L.; Tacconelli, E.; Simonsen, G.S.; et al. Infection Prevention and Control Measures and Tools for the Prevention of Entry of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae into Healthcare Settings: Guidance from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. AntiMicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2017, 6, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolund, A.; Lagerqvist, N.; Byfors, S.; Struelens, M.J.; Monnet, D.L.; Albiger, B.; Kohlenberg, A.; European Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Surveillance Network (EURGen-Net) Capacity Survey Group. Worsening Epidemiological Situation of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Europe, Assessment by National Experts from 37 Countries, July 2018. Eurosurveillance 2019, 24, 1900123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suay-García, B.; Pérez-Gracia, M.T. Present and Future of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) Infections. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampatakis, T.; Antachopoulos, C.; Tsakris, A.; Roilides, E. Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in an Endemic Area: Comparison with Global Data. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karampatakis, T.; Antachopoulos, C.; Tsakris, A.; Roilides, E. Molecular Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii in Greece: An Extended Review (2000–2015). Future Microbiol. 2017, 12, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagiannitsis, C.C.; Malli, E.; Florou, Z.; Sarrou, S.; Hrabak, J.; Mantzarlis, K.; Zakynthinos, E.; Petinaki, E. Emergence of Sequence Type 11 Klebsiella Pneumoniae Coproducing NDM-1 and VIM-1 Metallo-β-Lactamases in a Greek Hospital. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 87, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, S.D.; Jamil, B.; Syed, M.A.; Abbasi, S.A.; Weiß, D.; Slickers, P.; Monecke, S.; Engelmann, I.; Ehricht, R. Prevalence of Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms at the Kidney Center of Rawalpindi (Pakistan) and Evaluation of an Advanced Molecular Microarray-Based Carbapenemase Assay. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 1225–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duin, D.; Paterson, D.L. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Community: An Update. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 34, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.-Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.-K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia Coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, R. Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae—Second Update; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019; p. 17.
- Dhillon, R.H.-P.; Clark, J. ESBLs: A Clear and Present Danger? Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 625170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K. Past and Present Perspectives on β-Lactamases. AntiMicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01076-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael Dunne, W.; Pouseele, H.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; van Belkum, A. Epidemiology of Transmissible Diseases: Array Hybridization and next Generation Sequencing as Universal Nucleic Acid-Mediated Typing Tools. Infect Genet Evol 2018, 63, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albiger, B.; Glasner, C.; Struelens, M.J.; Grundmann, H.; Monnet, D.L.; The European Survey of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae (EuSCAPE) working group. Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Europe: Assessment by National Experts from 38 Countries, May 2015. Eurosurveillance 2015, 20, 30062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.R.; Toleman, M.A.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Metallo-β-Lactamases: The Quiet before the Storm? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 18, 306–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galani, I.; Karaiskos, I.; Karantani, I.; Papoutsaki, V.; Maraki, S.; Papaioannou, V.; Kazila, P.; Tsorlini, H.; Charalampaki, N.; Toutouza, M.; et al. Epidemiology and Resistance Phenotypes of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Greece, 2014 to 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 1700775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lei, J.; Xu, J.; Han, S. BlaOXA-23-like and BlaTEM Rather than BlaOXA-51-like Contributed to a High Level of Carbapenem Resistance in Acinetobacter Baumannii Strains from a Teaching Hospital in Xi’an, China. Medicine 2017, 96, e8965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Brandt, C.; Sprague, L.D.; Neubauer, H.; Pletz, M.W. Spatio-Temporal Distribution of Acinetobacter Baumannii in Germany—A Comprehensive Systematic Review of Studies on Resistance Development in Humans (2000–2018). Microorganisms 2020, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodendoerfer, E.; Marchesi, M.; Imkamp, F.; Courvalin, P.; Böttger, E.C.; Mancini, S. Co-Occurrence of Aminoglycoside and β-Lactam Resistance Mechanisms in Aminoglycoside- Non-Susceptible Escherichia Coli Isolated in the Zurich Area, Switzerland. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Martínez, M.; Ruiz del Castillo, B.; Lecea-Cuello, M.J.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Pascual, Á.; Martínez-Martínez, L. Prevalence of Aminoglycoside-Modifying Enzymes in Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae Producing Extended Spectrum β-Lactamases Collected in Two Multicenter Studies in Spain. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinu, P.; Bareja, R.; Nair, A.B.; Mishra, V.; Hussain, S.; Venugopala, K.N.; Sreeharsha, N.; Attimarad, M.; Rasool, S.T. Monitoring of Non-β-Lactam Antibiotic Resistance-Associated Genes in ESBL Producing Enterobacterales Isolates. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galani, I.; Nafplioti, K.; Adamou, P.; Karaiskos, I.; Giamarellou, H.; Souli, M.; Maraki, S.; Mauromanolaki, V.E.; Papaioannou, V.; Tsiplakou, S.; et al. Nationwide Epidemiology of Carbapenem Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates from Greek Hospitals, with Regards to Plazomicin and Aminoglycoside Resistance. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madni, O.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Rout, J.; Essack, S.Y. Genomic Investigation of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumonia Colonization in an Intensive Care Unit in South Africa. Genes 2021, 12, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raro, O.H.F.; da Silva, R.M.C.; Filho, E.M.R.; Sukiennik, T.C.T.; Stadnik, C.; Dias, C.A.G.; Oteo Iglesias, J.; Pérez-Vázquez, M. Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae From Transplanted Patients in Brazil: Phylogeny, Resistome, Virulome and Mobile Genetic Elements Harboring BlaKPC–2 or BlaNDM–1. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unlu, O.; Demirci, M. Detection of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains Harboring Carbapenemase, Beta-Lactamase and Quinolone Resistance Genes in Intensive Care Unit Patients. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2020, 15, Doc31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, F.; Rudin, S.D.; Marshall, S.H.; Coakley, P.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Rather, P.N.; Hujer, A.M.; Toltzis, P.; van Duin, D.; et al. OqxAB, a Quinolone and Olaquindox Efflux Pump, Is Widely Distributed among Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae Isolates of Human Origin. AntiMicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4602–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, O.; Kocsis, B.; Szabo, N.; Kristof, K.; Szabo, D. Contribution of OqxAB Efflux Pump in Selection of Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 2018, 4271638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, C.; Hall, J.P.; Harrison, E.; Wood, A.J.; Brockhurst, M.A. Gene Mobility Promotes the Spread of Resistance in Bacterial Populations. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1930–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Wan, L.-G.; Jiang, W.-Y.; Li, F.-Q.; Yang, J.-H. Molecular Characterization of the Bla KPC-2 Gene in Clinical Isolates of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from the Pediatric Wards of a Chinese Hospital. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.; Nunes, L.S.; Niada, M.; Barth, A.L.; Martins, A.F. Comparative Analysis of Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Sequence Types in Southern Brazil: From the First Outbreak (2007–2008) to the Endemic Period (2013–2014). Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akrami, F.; Rajabnia, M.; Pournajaf, A. Resistance Integrons; A Mini Review. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 10, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-H.; Hu, Z.-Q. Epidemiology and Genetics of CTX-M Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 39, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, T.; Vázquez, G.J.; Aquino, E.E.; Martínez, I.; Robledo, I.E. ISEcp1-Mediated Transposition of BlaKPC into the Chromosome of a Clinical Isolate of Acinetobacter Baumannii from Puerto Rico. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japoni-Nejad, A.; Mood, E.H.; Ehsani, P.; Sardari, S.; Heravi, F.S.; Bouzari, S.; Shahrokhi, N. Identification and Characterization of the Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in the Carbapenem-Resistant Acinetobacter Baumannii. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 158, 105052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).