Microbial Ecology of Artisanal Feta and Kefalograviera Cheeses, Part I: Bacterial Community and Its Functional Characteristics with Focus on Lactic Acid Bacteria as Determined by Culture-Dependent Methods and Phenotype Microarrays
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.3. Microbiological Analyses
2.4. Lactic Acid Microbiota Identification
2.4.1. Classical Identification
2.4.2. Molecular Identification
2.4.3. Biolog Microbial Identification with GEN III Microplates
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical and Microbiological Characterization
3.2. Lactic Acid Microbiota Identification
3.2.1. Classical Identification
3.2.2. Molecular Identification
3.2.3. Biolog Microbial Identification with GEN III Microplates
3.3. Lactic Acid Bacteria Microecosystem of Raw Sheep’s Milk, Feta and Kefalograviera
3.4. Biolog Microbial Community Assay with EcoPlates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abou-Donia, S.A. Origin, history and manufacturing process of Egyptian dairy products: An overview. Alex. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 5, 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaiano, D.A.; Hutkins, R.W. Yogurt, cultured fermented milk, and health: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 79, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschopoulou, E.; Moatsou, G. Greek Dairy Products. In Mediterranean Foods Composition and Processing; Cruz, R.M.S., Vieira, M.M.C., Eds.; CRC Press: Ohio, OH, USA, 2016; pp. 267–320. [Google Scholar]
- Manolopoulou, E.; Sarantinopoulos, P.; Zoidou, E.; Aktypis, A.; Moschopoulou, E.; Kandarakis, I.G.; Anifantakis, E.M. Evolution of microbial populations during traditional Feta cheese manufacture and ripening. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 82, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliadis, A.; Psoni, L.; Nikolaou, S.; Arvanitis, L.; Tzanetakis, N.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Changes in microbial populations, kinds of lactic acid bacteria and biochemical characteristics of Greek traditional feta cheese during ripening. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2009, 62, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzora, A.; Nelli, A.; Voidarou, C.; Fthenakis, G.; Rozos, G.; Theodorides, G.; Bonos, E.; Skoufos, I. Microbiota “fingerprint” of Greek Feta cheese through ripening. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozoudi, D.; Torriani, S.; Zdragas, A.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Assessment of microbial diversity of the dominant microbiota in fresh and mature PDO Feta cheese made at three mountainous areas of Greece. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 72, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sossidou, E.; Ligda, C.; Mastranestasis, I.; Tsiokos, D.; Samartzi, F. Sheep and goat farming in Greece: Implications and challenges for the sustainable development of less favoured areas. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 46, 446–449. [Google Scholar]
- Pappa, E.C.; Kondyli, E.; Sotirakoglou, K.; Bosnea, L.; Mataragas, M.; Allouche, L.; Tsiplakou, E.; Pappas, A.C. Farmers profile and characterization of sheep and goat dairy chain in northwestern Greece. Sustainability 2021, 13, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA Standard Methods for the Examination of Dairy Products, 16th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, WA, USA, 1992.
- Vakaleris, D.G.; Price, W.V. A rapid spectrophotometric method for measuring cheese ripening. J. Dairy Sci. 1959, 42, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramithiotis, S.; Hondrodimou, O.L.; Drosinos, E.H. Development of the microbial community during spontaneous cauliflower fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjilouka, A.; Mantzourani, K.-S.; Katsarou, A.; Cavaiuolo, M.; Ferrante, A.; Paramithiotis, S.; Mataragas, M.; Drosinos, E.H. Estimation of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7 prevalence and levels in naturally contaminated rocket and cucumber samples by deterministic and stochastic approaches. J. Food Prot. 2015, 78, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, W.P.; Hertel, C. Genus I. Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, 212AL. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; De Vos, P., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 3 The Firmicutes, pp. 465–510. [Google Scholar]
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Ludwig, W.; Dicks, L.M.T. Genus III. Pediococcus Claussen 1903, 68AL. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; De Vos, P., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 3 The Firmicutes, pp. 513–532. [Google Scholar]
- Svec, P.; Devriese, L.A. Genus I. Enterococcus (ex Thiercelin and Jouhaud 1903) Schleifer and Kilpper-Balz 1984, 32VP. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; De Vos, P., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 3 The Firmicutes, pp. 594–606. [Google Scholar]
- Holzapfel, W.H.; Bjorkroth, J.A.; Dicks, L.M.T. Genus I. Leuconostoc van Tieghem 1878, 198AL emend. mut. char. (Hucker and Pederson 1930), 66AL. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; De Vos, P., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 3 The Firmicutes, pp. 624–634. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkroth, J.; Dicks, L.M.T.; Holzapfel, W.H. Genus III. Weissella Collins, Samelis, Metaxopoulos and Wallbanks 1994, 370VP. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; De Vos, P., Garrity, G.M., Jones, D., Krieg, N.R., Ludwig, W., Rainey, F.A., Schleifer, K.-H., Whitman, W.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 3 The Firmicutes, pp. 643–654. [Google Scholar]
- Doulgeraki, A.I.; Paramithiotis, S.; Kagkli, D.M.; Nychas, G.-J.E. Lactic acid bacteria population dynamics during minced beef storage under aerobic or modified atmosphere packaging conditions. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjilouka, A.; Andritsos, N.D.; Paramithiotis, S.; Mataragas, M.; Drosinos, E.H. Listeria monocytogenes serotype prevalence and biodiversity in diverse food products. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torriani, S.; Felis, G.E.; Dellaglio, F. Differentiation of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. pentosus and L. paraplantarum by recA gene sequence analysis and multiplex PCR assay with recA gene-derived primers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3450–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, A.; Wolcott, M.; Daefler, S.; Rozak, D.A. Biolog phenotype microarrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 881, 331–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Pasquale, I.; Calasso, M.; Mancini, L.; Ercolini, D.; La Storia, A.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Casual relationship between microbial ecology dynamics and proteolysis during manufacture and ripening of Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) cheese Canestrato Pugliese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4085–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, S.; Tian, S.; Du, Q.; Liu, S. A statistics and analyses system of microbial Community Level Physiological Profiles (CLPP) based on Excel. Mol. Soil Biol. 2019, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Du, H.; Gao, Y.; Qiu, W. Analysis on metabolic functions of stored rice microbial communities by BIOLOG ECO microplates. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Garland, J.L.; Mills, A.L. Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community level sole-carbon-source utilization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1991, 57, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.H.; Haynes, R.J. Catabolic diversity of soil microbial communities under sugarcane and other land uses estimated by Biolog and substrate-induced respiration methods. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 29, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiari, M.C.; Voutsinas, L.P.; Alichanidis, E.; Roussis, I.G. Manufacture of Kefalograviera cheese with less sodium by partial replacement of NaCl with KCl. Food Chem. 1998, 61, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiari, M.C.; Alichanidis, E.; Voutsinas, L.P.; Roussis, I.G. Proteolysis in reduced sodium Kefalograviera cheese made by partial replacement of NaCl with KCl. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiari, M.C.; Voutsinas, L.P.; Alichanidis, E.; Roussis, I.G. Lipolysis in reduced sodium Kefalograviera cheese made by partial replacement of NaCl with KCl. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondyli, E.; Pappa, E.C.; Svarnas, C. Ripening changes of the chemical composition, proteolysis, volatile fraction and organoleptic characteristics of a white-brined goat milk cheese. Small Rum. Res. 2016, 145, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, R.; Katz, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Oliver, G. Characterization of the lactic acid bacteria in ewe’s milk and cheese from northwest Argentina. J. Food Prot. 2001, 64, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Disouza, J.; Pawar, S. Shelf life stability of encapsulated lactic acid bacteria isolated from sheep milk thrived in different milk as natural media. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 170, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, A.R.; Perea, J.M.; Palop, M.L.; Garzón, A.; Arias, R. Influence of environmental and productive factors on the biodiversity of lactic acid bacteria population from sheep milk. Animals 2020, 10, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Kilcawley, K.; O’Sullivan, O.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. Microbial succession and flavor production in the fermented dairy beverage kefir. mSystems 2016, 1, e00052-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H. Unraveling microbial community diversity and succession of Chinese Sichuan sausages during spontaneous fermentation by high-throughput sequencing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 3254–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, M.; Deutsch, S.-M.; Falentin, H.; Pawtowski, A.; Poirier, E.; Visenti, G.; Le Meur, C.; Maillard, M.-B.; Thierry, A.; Mounier, J.; et al. Deciphering microbial community dynamics and biochemical changes during nyons black olive natural fermentations. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanetakis, N.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Biochemical activities of Pediococcus pentosaceus isolates of dairy origin. J. Dairy Sci. 1989, 72, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, R.; Comi, G.; Cocolin, L. Ecology of lactic acid bacteria in Italian fermented sausages: Isolation, identification and molecular characterization. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 29, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, M.; Tabla, R.; Moriche, J.; Roa, I.; Gonzalez, J.; Rebollo, J.E.; Caceres, P. Ibores goat’s milk cheese: Microbiological and physicochemical changes throughout ripening. Le Lait 2002, 82, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roh, S.W.; Kim, K.H.; Nam, Y.D.; Chang, H.W.; Park, E.J.; Bae, J.W. Investigation of archaeal and bacterial diversity in fermented seafood using barcoded pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Nishio, S.; Tsurii, J.; Kawamoto, T.; Sonomoto, K.; Nakayama, J. Monitoring of the microbiota profile in nukadoko, a naturally fermented rice bran bed for pickling vegetables. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 118, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuka, M.M.; Wallisch, S.; Engel, M.; Welzl, G.; Havranek, J.; Schloter, M. Dynamics of bacterial communities during the ripening process of different Croatian cheese types derived from raw ewe’s milk cheeses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80734. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, S.H.; Wu, R.J.; Watanabe, K.; Tsai, Y.C. Diversity of lactic acid bacteria in suan-tsai and fu-tsai, traditional fermented mustard products of Taiwan. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostinek, M.; Specht, I.; Edward, V.A.; Pinto, C.; Egounlety, M.; Sossa, C.; Mbugua, S.; Dortu, C.; Thonart, P.; Taljaard, L.; et al. Characterisation and biochemical properties of predominant lactic acid bacteria from fermenting cassava for selection as starter cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 114, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.-T.T.; Chen, Y.-S.; Yanagida, F. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from Yan-dong-gua (fermented wax gourd), a traditional fermented food in Taiwan. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2009, 108, 484–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Wu, H.-C.; Wang, C.-M.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Jhong, Y.-J.; Yanagida, F. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from pobuzihi (fermented cummingcordia), a traditional fermented food in Taiwan. Folia Microbiol. 2013, 58, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-S.S.; Wu, H.C.; Yu, C.R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Yanagida, F. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from xi-gua-mian (fermented watermelon), a traditional fermented food in Taiwan. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2016, 28, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Yanagida, F.; Hsu, J.S. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from dochi (fermented black beans), a traditional fermented food in Taiwan. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathara, J.M.; Schillinger, U.; Kutima, P.M.; Mbugua, S.K.; Holzapfel, W.H. Isolation, identification and characterisation of the dominant microorganisms of kule naoto: The Maasai traditional fermented milk in Kenya. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasi, E.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Tzanetakis, N. Microbiological study of Manura, a hard cheese made from raw ovine milk in the Greek island Sifnos. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2003, 56, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampe, F.; Ben Omar, N.; Moizan, C.; Wacher, C.; Guyot, J.P. Polyphasic study of the spatial distribution of microorganisms in Mexican pozol, a fermented maize dough, demonstrates the need for cultivation-independent methods to investigate traditional fermentations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 5464–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, V.; Quero, G.M.; Cho, G.-S.; Kabisch, J.; Meske, D.; Neve, H.; Bockelmann, W.; Franz, C.M.A.P. The genus Weissella: Taxonomy, ecology and biotechnological potential. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.C.; Boyette, M.; Goforth, C.; Sperry, K.-V.; Greene, S.R. Comparison of the Biolog OmniLog Identification System and 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing for accuracy in identification of atypical bacteria of clinical origin. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 79, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
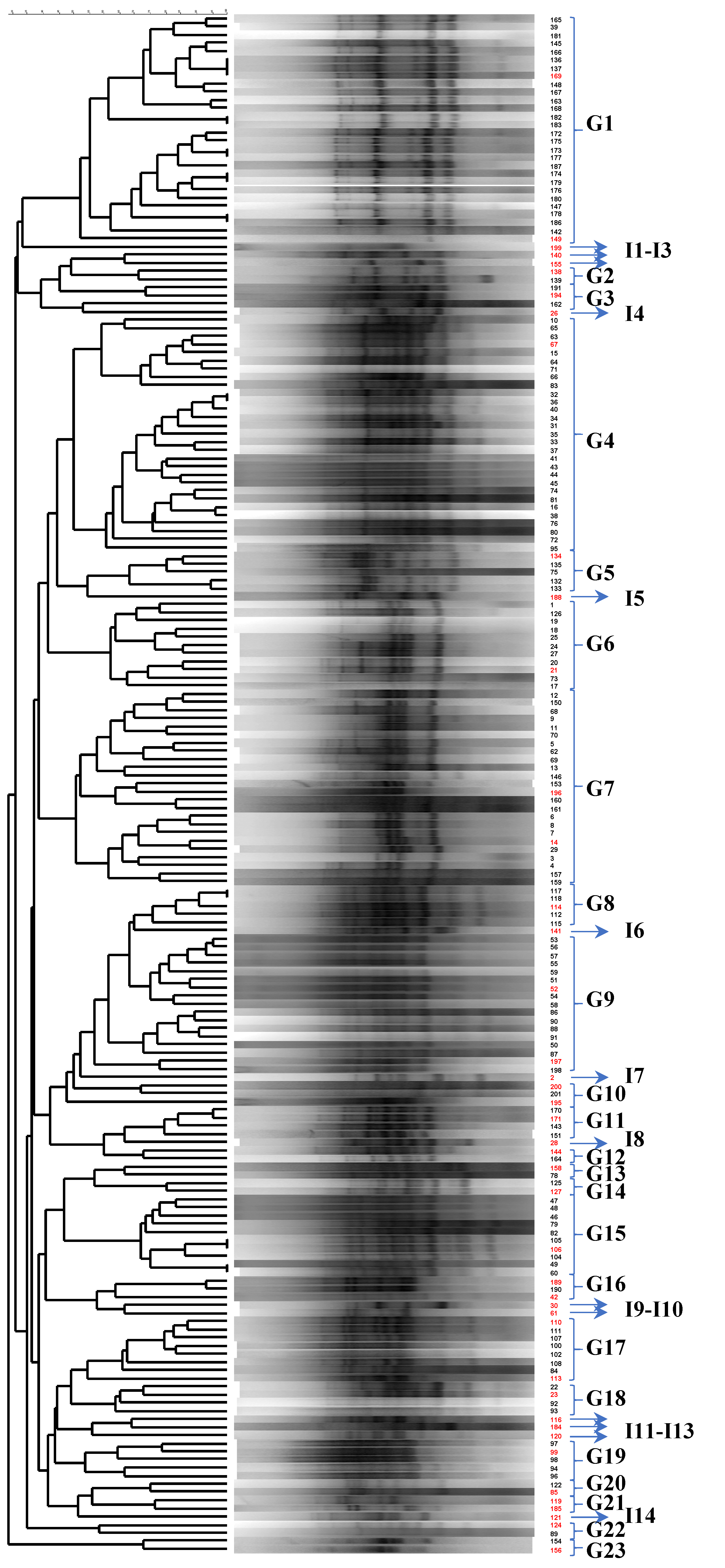

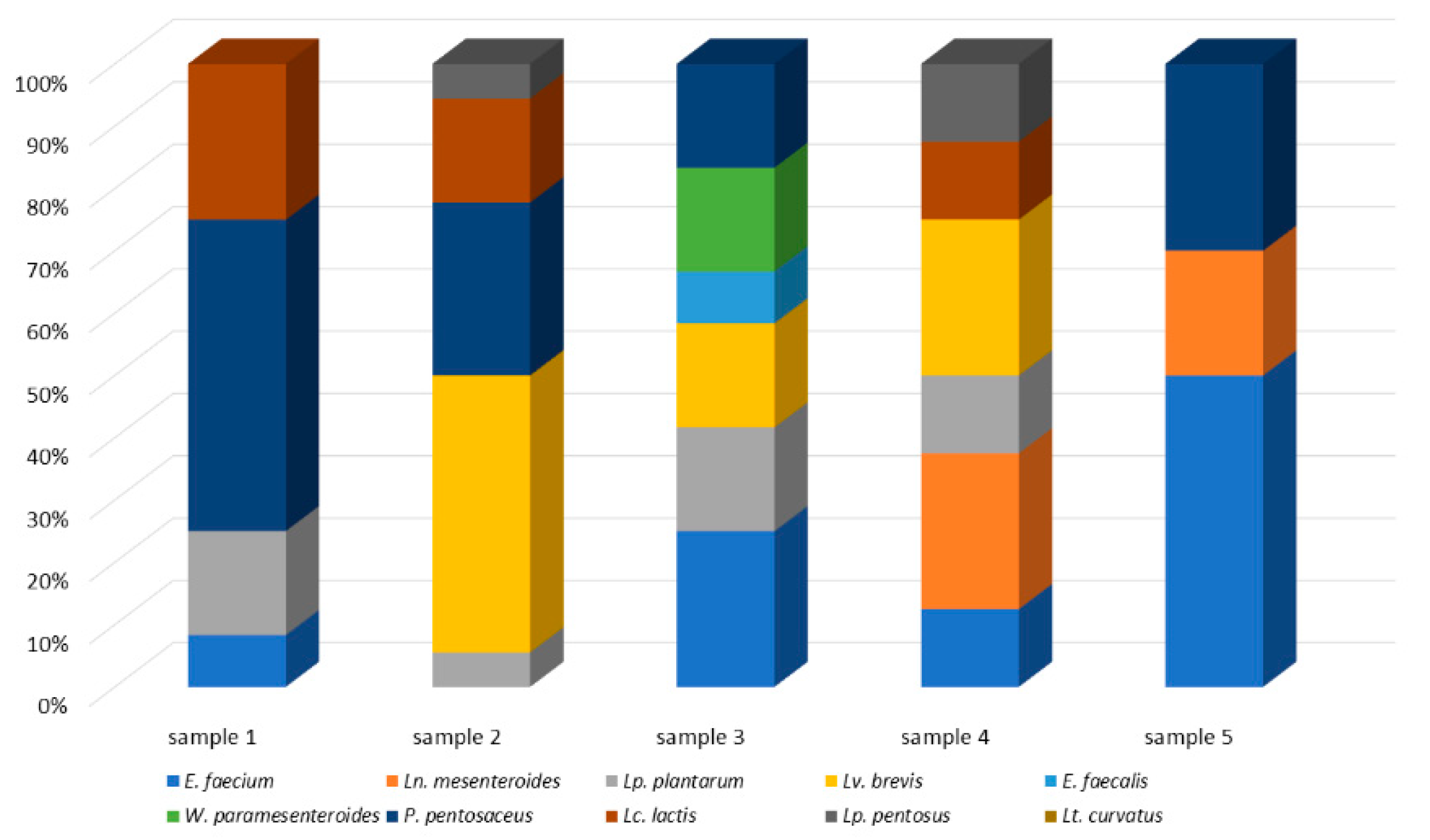




| Samples | Fat (%) | Moisture (%) | pH | NaCl (%) | Lactose (%) | Protein (%) | Fat Hydrolysis | Protein Hydrolysis | MRS Counts (log CFU/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feta | |||||||||
| Early ripening | 25.5 | 51.3 | 5.07 | 2.53 | 0 | 15.85 | 3.9 | 0.764 | 7.02 |
| Late ripening | 26 | 49.3 | 4.25 | 3.4 | 0 | 16.24 | 2 | 0.702 | 6.60 |
| Kefalograviera | |||||||||
| Early ripening | 30.5 | 36.1 | 5.14 | 3.05 | 0.3 | 26.28 | 2.5 | 0.58 | 6.02 |
| Late ripening | 30 | 36.7 | 5.12 | 2.91 | 0.31 | 26.10 | 4.1 | 0.589 | 6.77 |
| Cheese Samples | Richness—S | Shannon-Wiener—H | Shannon Evenness—E | Simpson—D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feta-ER | 2.500 ± 0.236 a | 1.154 ± 0.104 a | 1.349 ± 0.319 a | 0.601 ± 0.012 a |
| Feta-LR | 8.667 ± 0.472 b | 2.307 ± 0.040 b | 1.069 ± 0.008 a | 0.880 ± 0.006 a |
| Kefalograviera-ER | 14.167 ± 0.235 c | 2.650 ± 0.003 b,c | 1.002 ± 0.006 a | 0.922 ± 0.001 a |
| Kefalograviera-LR | 7.167 ± 1.179 d | 1.821 ± 0.173 d | 0.932 ± 0.003 a | 0.810 ± 0.039 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsigkrimani, M.; Bakogianni, M.; Paramithiotis, S.; Bosnea, L.; Pappa, E.; Drosinos, E.H.; Skandamis, P.N.; Mataragas, M. Microbial Ecology of Artisanal Feta and Kefalograviera Cheeses, Part I: Bacterial Community and Its Functional Characteristics with Focus on Lactic Acid Bacteria as Determined by Culture-Dependent Methods and Phenotype Microarrays. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010161
Tsigkrimani M, Bakogianni M, Paramithiotis S, Bosnea L, Pappa E, Drosinos EH, Skandamis PN, Mataragas M. Microbial Ecology of Artisanal Feta and Kefalograviera Cheeses, Part I: Bacterial Community and Its Functional Characteristics with Focus on Lactic Acid Bacteria as Determined by Culture-Dependent Methods and Phenotype Microarrays. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(1):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010161
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsigkrimani, Markella, Magdalini Bakogianni, Spiros Paramithiotis, Loulouda Bosnea, Eleni Pappa, Eleftherios H. Drosinos, Panagiotis N. Skandamis, and Marios Mataragas. 2022. "Microbial Ecology of Artisanal Feta and Kefalograviera Cheeses, Part I: Bacterial Community and Its Functional Characteristics with Focus on Lactic Acid Bacteria as Determined by Culture-Dependent Methods and Phenotype Microarrays" Microorganisms 10, no. 1: 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010161
APA StyleTsigkrimani, M., Bakogianni, M., Paramithiotis, S., Bosnea, L., Pappa, E., Drosinos, E. H., Skandamis, P. N., & Mataragas, M. (2022). Microbial Ecology of Artisanal Feta and Kefalograviera Cheeses, Part I: Bacterial Community and Its Functional Characteristics with Focus on Lactic Acid Bacteria as Determined by Culture-Dependent Methods and Phenotype Microarrays. Microorganisms, 10(1), 161. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10010161










