Understanding Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates—How Far Have We Come?
Abstract
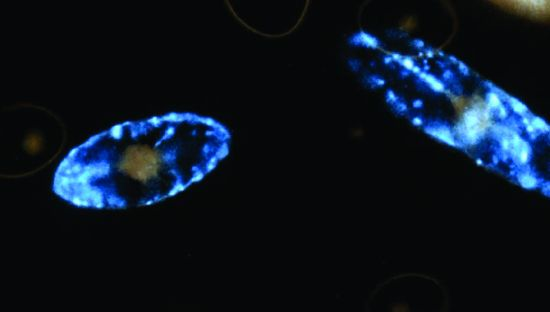
:1. Introduction
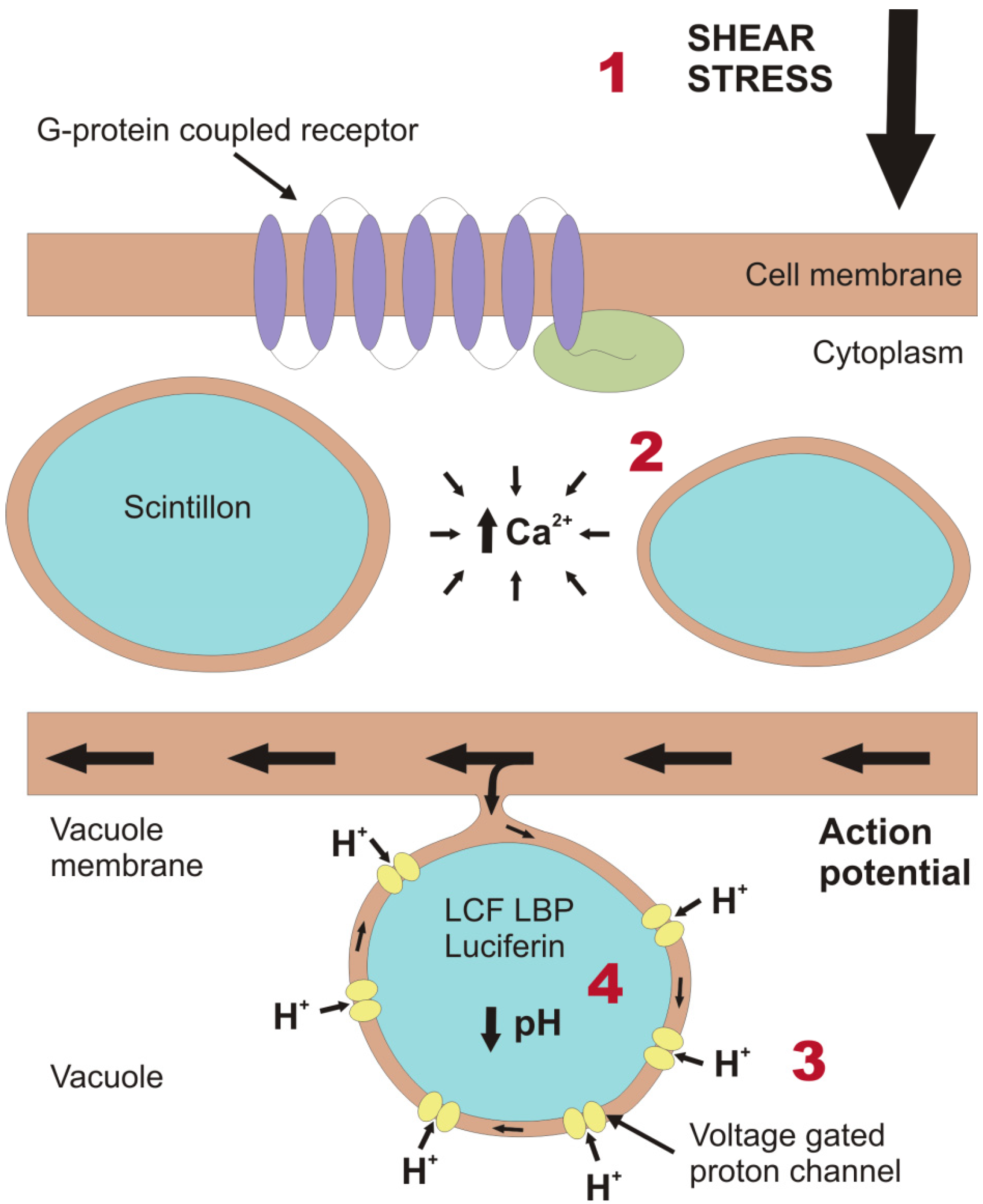
2. Light Production in the Cell
3. Molecular Composition and Evolution of the Bioluminescence System
3.1. Luciferases and Luciferin Binding Proteins
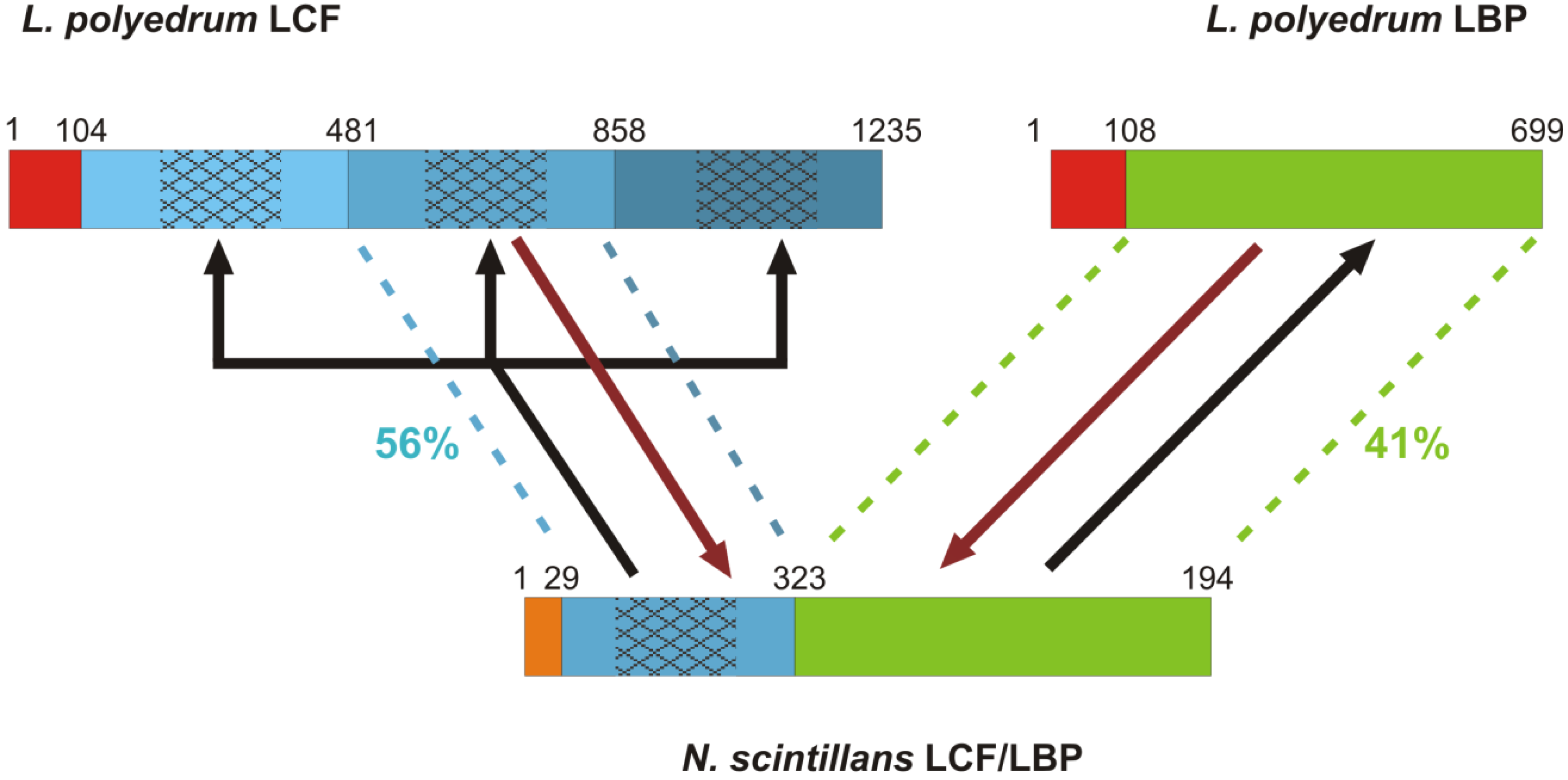
3.1.1. Luciferase Genes of Photosynthetic Species
3.1.2. Luciferin Binding Protein Genes of Photosynthetic Species
3.1.3. Insights from the Bioluminescence Gene of Noctiluca scintillans
3.2. The Elusive Luciferin
4. Diversity of Bioluminescent Species
| Order | Genus | No. of reported | Total no. of |
|---|---|---|---|
| Family | BL species | species in genus | |
| Gonyaulacales | |||
| Ceratiaceae | (Neo)ceratium | 4 | 77 |
| Goniodomaceae | Alexandrium | 7 | 31 |
| Pyrodinium | 1 | 1 | |
| Cladopixidaceae? | Peridiniella | 1 | 3 |
| Ceratocoryaceae | Ceratocorys | 1 | 11 |
| Gonyaulaceae | Gonyaulax | 11 | 72 |
| Lingulodinium | 1 | 2 | |
| Pyrocystaceae | Pyrocystis | 4 | 16 |
| Pyrophacaceae | Fragilidium | 4 | 5 |
| Pyrophacus | 1 | 4 | |
| Gymnodiniales | |||
| Gymnodiniaceae | Polykrikos | 2 | 5 |
| Noctilucales | |||
| Noctilucaceae | Noctiluca | 1 | 1 |
| Peridiniales | |||
| Proroperidiniaceae | Protoperidinium | 31 | 295 |
5. Factors Affecting the Intensity of Bioluminescence Emissions
5.1. Diurnal Rhythms of Bioluminescence
5.2. Species-Specific Bioluminescence Signatures
5.3. Physiological State
6. The Function of Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates

7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haddock, S.H.D.; Moline, M.A.; Case, J.F. Bioluminescence in the sea. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 443–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widder, E.A. Bioluminescence in the ocean: Origins of biological, chemical, and ecological diversity. Science 2010, 328, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.; Hastings, J.W. Bioluminescence. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1998, 14, 197–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.W. Chemistry and control of luminescence in marine organisms. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1983, 33, 818–828. [Google Scholar]
- Widder, E.A. Marine bioluminescence. Biosci. Explain. 2001, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Poupin, J.; Cussatlegras, A.S.; Geistdoerfer, P. Plancton Marin Bioluminescen; Rapport Scientifique du LOEN: Brest, France, 1999; p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Valiadi, M.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.D.; Amorim, A. Distribution and genetic diversity of the luciferase gene within marine dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, P.B. The relation between dinoflagellates and the bioluminescence of sea water. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1971, 51, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, E.N. A History of Luminescence from the Earliest Times Until 1900: From the Earliest Times Until 1900; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1957; p. 692. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, R.V. The Occurence and Distribution of Surface Bioluminescence in the Oceans during 1966 through 1977; Naval Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, F. A quantitative review of the lifestyle, habitat and trophic diversity of dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata, Alveolata). Syst. Biodivers. 2012, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSa, R.; Hastings, J.W. The characterization of scintillons. Bioluminescent particles from the marine dinoflagellate, Gonyaulax polyedra. J. Gen. Physiol. 1968, 51, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto, H.; Wu, C.; Kinumi, T.; Ohmiya, Y. Biological rhythmicity in expressed proteins of the marine dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum demonstrated by chronological proteomics. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Inoue, S.; Flint, A.; Hastings, J.W. Compartmentalization of algal bioluminescence—autofluorescence of bioluminescent particles in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax as studied with image-intensified video microscopy and flow cytometry. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 1435–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaust, R.; Urbig, T.; Li, L.M.; Taylor, W.; Hastings, J.W. The circadian rhythm of bioluminescence in Pyrocystis is not due to differences in the amount of luciferase: A comparative study of three bioluminescent marine dinoflagellates. J. Phycol. 1998, 34, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitter, R.E.; Njus, D.; Sulzman, F.M.; Gooch, V.D.; Hastings, J.W. Dinoflagellate bioluminescence—Comparative study of in vitro components. J. Cell. Physiol. 1976, 87, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.T.; Sweeney, B.M.; Hastings, J.W. The ultrastructural localization of luciferase in three bioluminescent dinoflagellates, two species of Pyrocystis, and Noctiluca, using anti-luciferase and immunogold labelling. J. Cell Sci. 1987, 87, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, L.; Morse, D.; Hastings, J.W. The circadian bioluminescence rhythm of Gonyaulax is related to daily variations in the number of light-emitting organelles. J. Cell Sci. 1990, 95, 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, K.S.; Fritz, L. Cell ultrastructural changes correlate with circadian rhythms in Pyrocystis lunula (Pyrrophyta). J. Phycol. 2000, 36, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, E.M.; Latz, M.I. Shear-stress dependence of dinoflagellate bioluminescence. Biol. Bull. 2007, 212, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, M.I.; Bovard, M.; VanDelinder, V.; Segre, E.; Rohr, J.; Groisman, A. Bioluminescent response of individual dinoflagellate cells to hydrodynamic stress measured with millisecond resolution in a microfluidic device. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.K.; Latz, M.I.; Sobolewski, P.; Frangos, J.A. Evidence for the role of G-proteins in flow stimulation of dinoflagellate bioluminescence. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R2020–R2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.C.; Raghu, P. Visual transduction in Drosophila. Nature 2001, 413, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dassow, P.; Latz, M.I. The role of Ca2+ in stimulated bioluminescence of the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum. J. Exp. Biol. 2002, 205, 2971–2986. [Google Scholar]
- Fogel, M.; Hastings, J.W. Bioluminescence—Mechanism and mode of control of scintillon activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.E.; Morgan, D.; Musset, B.; Cherny, V.V.; Place, A.R.; Hastings, J.W.; DeCoursey, T.E. Voltage-gated proton channel in a dinoflagellate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18162–18167. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, L.W.; Liu, L.; Cegielski, M.; Hastings, J.W. Crystal structure of a pH-regulated luciferase catalyzing the bioluminescent oxidation of an open tetrapyrrole. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O. Bioluminescence: Chemical Principles and Methods; World Scientific: Singapore, Singapore, 2006; p. 470. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, T.; Hastings, J. Bioluminescence: Living Lights, Lights for Living; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; p. 185. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.Y.; Wilson, T.; Hastings, J.W. Molecular evolution of dinoflagellate luciferases, enzymes with three catalytic domains in a single polypeptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16555–16560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hastings, J.W. The structure and organization of the luciferase gene in the photosynthetic dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polyedra. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 36, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Hastings, J.W. Two different domains of the luciferase gene in the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans occur as two separate genes in photosynthetic species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hong, R.; Hastings, J.W. Three functional luciferase domains in a single polypeptide chain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8954–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, Y.; Hastings, J. Cloning, sequencing and expression of dinoflagellate luciferase DNA from a marine alga. Gonyaulax polyedra. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Struct. Expr. 1994, 1219, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki-Ogoh, C.; Wu, C.; Ohmiya, Y. C-terminal region of the active domain enhances enzymatic activity in dinoflagellate luciferase. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2008, 7, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, L.; Hong, R.; Robertson, D.; Hastings, J.W. N-terminal intramolecularly conserved histidines of three domains in Gonylaulax luciferase are responsible for loss of activity in the alkaline region. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, O.K.; Liu, L.; Robertson, D.L.; Hastings, J.W. Members of a dinoflagellate luciferase gene family differ in synonymous substitution rates. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 15862–15868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Hastings, J.W. Novel and rapidly diverging intergenic sequences between tandem repeats of the luciferase genes in seven dinoflagellate species. J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, E.; Sullivan, J.M.; Batchelder, H.P.; van Keuren, J.; Vaillancourt, R.D.; Bidigare, R.R. Bioluminescent organisms and bioluminescence measurements in the North Atlantic Ocean near latitude 59.5 N, longitude 21 W. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1995, 100, 6527–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogel, M.; Hastings, J.W. A substrate-binding protein in the Gonyaulax bioluminescence reaction. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1971, 142, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdner, D.L.; Anderson, D.M. Global transcriptional profiling of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense using Massively Parallel Signature Sequencing. BMC Genomics 2006, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, P.; Fuentes, D.; Valdés, J.; Shmaryahu, A.; Zúñiga, A.; Holmes, D.; Valenzuela, P.D.T. Preparation and analysis of an expressed sequence tag library from the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, J.D.; Scheetz, T.E.; Yoon, H.S.; Soares, M.B.; Bonaldo, M.F.; Casavant, T.L.; Bhattacharya, D. Insights into a dinoflagellate genome through expressed sequence tag analysis. BMC Genomics 2005, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeckisch, N.; Yang, I.; Wohlrab, S.; Glöckner, G.; Kroymann, J.; Vogel, H.; Cembella, A.; John, U. Comparative genomic and transcriptomic characterization of the toxigenic marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium ostenfeldii. PLoS One 2011, 6, e28012. [Google Scholar]
- Machabée, S.; Wall, L.; Morse, D. Expression and genomic organization of a dinoflagellate gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Mittag, M.; Sczekan, S.; Morse, D.; Hastings, J.W. Molecular cloning and genomic organization of a gene for luciferin-binding protein from the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polyedra. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8842–8850. [Google Scholar]
- Morse, D.; Pappenheimer, A.M.; Hastings, J.W. Role of a luciferin-binding protein in the circadian bioluminescent reaction of Gonyaulax polyedra. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 11822–11826. [Google Scholar]
- Toulza, E.; Shin, M.-S.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Laabir, M.; Collos, Y.; Claverie, J.-M.; Grzebyk, D. Gene expression in proliferating cells of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4521–4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanikawa, N.; Akimoto, H.; Ogoh, K.; Chun, W.; Ohmiya, Y. Expressed sequence tag analysis of the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum during dark phase. Photochem. Photobiol. 2004, 80, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, J.C.; Hastings, J.W. The biological clock in Gonyaulax controls luciferase activity by regulating turnover. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 10509–10518. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, Y.; Endoh, H. Phylogenetic analyses of the dinoflagellate Noctiluca scintillans based on beta-tubulin and Hsp90 genes. Eur. J. Protistol. 2008, 44, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppenrath, M.; Leander, B.S. Dinoflagellate phylogeny as inferred from heat shock protein 90 and ribosomal gene sequences. PLoS One 2010, 5, e13220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, F.; Moreira, D.; Lopez-Garcia, P. Molecular phylogeny of noctilucoid dinoflagellates (Noctilucales, Dinophyceae). Protist 2010, 161, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R.J.S.; Murray, S.A.; Stüken, A.; Rhodes, L.; Jakobsen, K.S. When naked became armored: An eight-gene phylogeny reveals monophyletic origin of theca in dinoflagellates. PLoS One 2012, 7, e50004. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Kishi, Y.; Shimomura, O.; Morse, D.; Hastings, J.W. Structure of dinoflagellate luciferin and its enzymic and nonenzymic air-oxidation products. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 7607–7611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Akimoto, H.; Ohmiya, Y. Tracer studies on dinoflagellate luciferin with [15N]-glycine and [15N]-l-glutamic acid in the dinoflagellate Pyrocystis lunula. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalov, G.; Kishi, Y. Chlorophyll catabolism leading to the skeleton of dinoflagellate and krill luciferins: Hypothesis and model studies. Angew. Chem. 2001, 40, 3892–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.P.; Seliger, H.H. The mechanical triggering of bioluminescence in marine dinoflagellates: Chemical basis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1972, 80, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Horiguchi, T. Culture of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Protoperidinium crassipes (Dinophyceae) with noncellular food items. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 1090–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, O. The roles of the two highly unstable components F and P involved in the bioluminescence of euphausiid shrimps. J. Biolumin. Chemilumin. 1995, 10, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinko, C.L.J.; Allen, J.T.; Poulton, A.J.; Painter, S.C.; Martin, A.P. Diurnal variations of dinoflagellate bioluminescence within the open-ocean north-east Atlantic. J. Plankton Res. 2013, 35, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinko, C.L.J.; Painter, S.C.; Martin, A.P.; Allen, J.T. A review of the measurement and modelling of dinoflagellate bioluminescence. Prog. Oceanogr. 2013, 109, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase World-Wide Electronic Publication; National University of Ireland: Galway, Ireland, 2013. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 28 April 2013).
- Hastings, J.W. The Gonyaulax clock at 50: Translational control of circadian expression. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 2007, 72, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, D.; Milos, P.M.; Roux, E.; Hastings, J.W. Circadian regulation of bioluminescence in Gonyaulax involves translational control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittag, M.; Li, L.; Hastings, J.W. The mRNA level of the circadian regulated Gonyaulax luciferase remains constant over the cycle. Chronobiol. Int. 1998, 1998, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittag, M.; Lee, D.H.; Hastings, J.W. Circadian expression of the luciferin-binding protein correlates with the binding of a protein to the 3′ untranslated region of its mRNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5257–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, M.; Morse, D. Reassessing the role of a 3′-UTR-binding translational inhibitor in regulation of circadian bioluminescence rhythm in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.H.; Roeber, J.F.; Hastings, J.W. Circadian changes in enzyme concentration account for rhythm of enzyme activity in Gonyaulax. Science 1984, 223, 1428–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Esaias, W.E.; Curl, H.C.; Seliger, H.H. Action spectrum for a low intensity, rapid photoinhibition of mechanically stimulable bioluminescence in the marine dinoflagellates Gonyaulax catenella, G. acatenella, and G. tamarensis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1973, 82, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.P.; Biggley, W.H.; Seliger, H.H. Action spectrum for the photoinhibition of bioluminescence in the marine dinoflagellate Dissodinium lunula. Photochem. Photobiol. 1981, 33, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.P.; Seliger, H.H. The chemical mimicking of the mechanical stimulation, photoinhibition, and recovery from photoinhibition of bioluminescence in the marine dinoflagellate, Gonyaulax polyedra. J. Cell. Physiol. 1982, 111, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; Swift, E.; Buskey, E.J. Photoinhibition of mechanically stimulable bioluminescence in the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Protoperidinium depressum (Pyrrophyta). J. Phycol. 1996, 32, 974–982. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, J.M.; Swift, E. Photoinhibition of mechanically stimulable bioluminescence in the autotrophic dinoflagellate Ceratium fusus (Pyrrophyta). J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, B.M.; Haxo, F.T.; Hastings, J.W. Action spectra for two effects of light on luminescence in Gonyaulax polyedra. J. Gen. Physiol. 1959, 43, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskey, E.J.; Strom, S.; Coulter, C. Biolumiscence of heterotrophic dinoflagellates from Texas coastal waters. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1992, 159, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, J.A.; DeVries, A.L. Bioluminescence in McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1976, 21, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.P.; Biggley, W.H.; Seliger, H.H. Photoinhibition of stimulable bioluminescence in marine dinoflagellates. Photochem. Photobiol. 1981, 33, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapota, D.; Young, D.K.; Bernstein, S.A.; Geiger, M.L.; Huddell, H.D.; Case, J.F. Diel bioluminescence in heterotrophic and photosynthetic marine dinoflagellates in an Arctic fjord. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1992, 72, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelder, H.P.; Swift, E.; Keuren, J.R. Diel patterns of planktonic bioluminescence in the northern Sargasso Sea. Mar. Biol. 1992, 113, 329–339. [Google Scholar]
- Biggley, W.H.; Swift, E.; Buchanan, R.J.; Seliger, H.H. Stimulable and spontaneous bioluminescence in the marine dinoflagellates Pyrodinium bahamense, Gonyaulax polyedra and Pyrocystis lunula. J. Gen. Physiol. 1969, 54, 96–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnow, R.; Dunlap, J.; Taylor, W.; Hastings, J.W.; Vetterling, W.; Gooch, V. Circadian spontaneous bioluminescent glow and flashing of Gonyaulax polyedra. J. Comp. Physiol. B 1980, 138, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colepicolo, P.; Roenneberg, T.; Morse, D.; Taylor, W.R.; Hastings, J.W. Circadian regulation of bioluminescence in the dinoflagellate Pyrocystis lunula. J. Phycol. 1993, 29, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Latz, M.I.; Lee, A.O. Spontaneous and stimulated bioluminescence of the dinoflagellate Ceratocorys horrida (Peridiniales). J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 120–132. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, R. Excitation and luminescence in Noctiluca miliaris. In Bio-luminescence in Progress; Johnson, F.H., Haneda, Y., Eds.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA; pp. 269–300.
- Widder, E.; Case, J. Two flash forms in the bioluminescent dinoflagellate Pyrocystis fusiformis. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1981, 143, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Gooch, V.D.; Loeblich, A.R.; Hastings, J.W. Comparative study of luminescent and non-luminescent strains of Gonyaulax excavata (Pyrrhophyta). J. Phycol. 1978, 14, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussatlegras, A.S.; Le Gal, P. Variability in the bioluminesence response of the dinoflagellate Pyrocystis lunula. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 343, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskey, E.J.; Swift, E. An encounter model to predict natural planktonic bioluminescence. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1990, 35, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.M. Ultrastructure of Noctiluca miliaris (Pyrrophyta) with green flagellate symbionts. J. Phycol. 1978, 14, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, R.; Reynolds, G. The subcellular origin of bioluminescence in Noctiluca miliaris. J. Gen. Physiol. 1967, 50, 1429–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, M.I.; Case, J.F.; Gran, R.L. Excitation of bioluminescence by laminar fluid shear associated with simple Couette flow. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1994, 39, 1424–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Dassow, P.; Bearon, R.N.; Latz, M.I. Bioluminescent response of the dinoflagellate Lingulodinium polyedrum to developing flow: Tuning of sensitivity and the role of desensitization in controlling a defensive behaviour of a planktonic cell. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.M. The loss of the circadian rhythm in photosynthesis in an old strain of Gonyaulax polyedra. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, I. Bioluminescent Organelle Changes in Four Species of Dinoflagellates Using Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. MRes Dissertation, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, E.; Biggley, W.H.; Seliger, H.H. Species of oceanic dinoflagellates in genera Dissodinium and Pyrocystis—Interclonal and interspecific comparisons of color and photon yield of bioluminescence. J. Phycol. 1973, 9, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Buskey, E.J.; Coulter, C.J.; Brown, S.L. Feeding, growth and bioluminescence of the heterotrophic dinoflagellate Protoperidinium huberi. Mar. Biol. 1994, 121, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, B.M. Variations of the Bioluminescence per Cell in Dinoflagellates. In Bioluminescence Current Perspectives; Nealson, K.H., Ed.; Burgess Publishing: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1981; pp. 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Latz, M.I.; Jeong, H.J. Effect of red tide dinoflagellate diet and cannibalism on the bioluminescence of the heterotrophic dinoflagellates Protoperidinium spp. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 132, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.M.; Swift, E. Photoenhancement of bioluminescence capacity in natural and laboratory populations of the autotrophic dinoflagellate Ceratium fusus (Ehrenb.) Dujardin. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1995, 100, 6565–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaias, W.E.; Curl, H.C. Effect of dinoflagellate bioluminescence on copepod ingestion rates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1972, 17, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.H. Effects of dinoflagellate bioluminescence on the ingestion rates of herbivorous zooplankton. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1979, 36, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskey, E.; Mills, L.; Swift, E. The effects of dinoflagellate bioluminescence on the swimming behavior of a marine copepod. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskey, E.J.; Mann, C.G.; Swift, E. Photophobic responses of calanoid copepods: Possible adaptive value. J. Plankton Res. 1987, 9, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buskey, E.J.; Swift, E. Behavioral responses of oceanic zooplankton to simulated bioluminescence. Biol. Bull. 1985, 168, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkenroad, M.D. A possible function of bioluminescence. J. Mar. Res. 1943, 5, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams, M.V.; Townsend, L.D. Bioluminescence in dinoflgellates: A test of the burgular alarm hypothesis. Ecology 1993, 74, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesinger, A.F.; Case, J.F. Dinoflagellate luminescence increases susceptibility of zooplankton to teleost predation. Mar. Biol. 1992, 112, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, E.; Lessard, E.J.; Biggley, W.H. Organisms associated with stimulated epipelagic bioluminescence in the Sargasso Sea and the Gulf Stream. J. Plankton Res. 1985, 7, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, M.I.; Frank, T.M.; Case, J.F. Spectral composition of bioluminescence of epipelagic organisms from the Sargasso Sea. Mar. Biol. 1988, 98, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilson, D.J.; Latz, M.I.; Case, J.F. Temporal variability in the vertical structure of bioluminescence in the North Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1995, 100, 6591–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.; Robbins, I.; Moline, M.A.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, M.D. Oligonucleotide primers for the detection of bioluminescent dinoflagellates reveal novel luciferase sequences and information on the molecular evolution of this gene. J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Valiadi, M.; Iglesias-Rodriguez, D. Understanding Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates—How Far Have We Come? Microorganisms 2013, 1, 3-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms1010003
Valiadi M, Iglesias-Rodriguez D. Understanding Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates—How Far Have We Come? Microorganisms. 2013; 1(1):3-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms1010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleValiadi, Martha, and Debora Iglesias-Rodriguez. 2013. "Understanding Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates—How Far Have We Come?" Microorganisms 1, no. 1: 3-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms1010003
APA StyleValiadi, M., & Iglesias-Rodriguez, D. (2013). Understanding Bioluminescence in Dinoflagellates—How Far Have We Come? Microorganisms, 1(1), 3-25. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms1010003