Abstract
Biodegradable ionic polymer metallic composite (IPMC) electroactive polymers (EAPs) were fabricated using poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) with various concentrations of lithium perchlorate. Nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) rods created from a sulfuric acid hydrolysis process were added at various concentrations to increase the EAPs’ elastic modulus and improve their electromechanical properties. The electromechanical actuation was studied. PEONCC composites were created from combining a 35-mg/mL aqueous NCC suspension with an aqueous, PEO solution at varying vol.%. Due to an imparted space charge from the hydrolysis process, composites with an added 1.5 vol.% of NCC suspension exhibited an electromechanical tip displacement, strain, and elastic modulus that was 40.7%, 33.4% and 20.1% higher, respectively, than those for PEO IPMCs without NCC. This performance represented an increase of 300% in the energy density of these samples. However, the electromechanical response decreased when the NCC content was high. NCC without the space charge were also tested to verify the analysis. Additionally, the development of new relationships for modeling and evaluating the time-dependent instantaneous tip angular velocity and acceleration was discussed and applied to these IPMCs.
1. Introduction
Electroactive polymers have gained a lot of attention over the past few decades [1] for their ability to generate large electromechanical actuations without the need for any moving parts or external motors or servos. Thus, characterizing their response and improving on their electromechanical effect has also been a major focus [2]. EAPs are separated into two groups: ionic electroactive polymers (i-EAPs) and electronic electroactive polymers (e-EAPs). Emphasis has concentrated on i-EAPs due to their simple construction and ease of use, [3] with possible applications as artificial muscles, microvalves, biomimetic devices, robotics, etc. [3]. Both types can generate large electromechanical actuations (bending, expanding, etc.), but differ in the manner with which they undergo these actuations. i-EAPs are generally comprised of a polymeric membrane layer doped with an ionic salt and coated with a surface electrode, wherein the diffusion of ions through their matrix results in a directional bending actuation, depending on the applied voltage polarity [1]. e-EAPs function based on the inherent electrostatic properties of the polymer matrix itself, and are generally limited to actuations that are monopolar, irrespective of polarity, due to the electrostrictive effect [1].
The specific target of this study focuses on the creation of biodegradable ionic polymer metallic composites (IPMCs), a subset of i-EAPs, and enhancing their electromechanical properties. IPMCs consist of a polymeric matrix that is infused with an ionic salt; electrodes are then metallically plated or coated on their surface. Electric excitation results in a redistribution of ions within the polymer matrix, which results in an overall bending actuation response [4]. The most commonly studied and commercially available IPMC is based off of Nafion (perfluorinated sulfonic acid) [5]; however, one of its drawbacks is that it is not biodegradable or recyclable [6].
With finding a green alternative, poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) with a nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) filler were chosen as an environmentally friendly IPMC polymer matrix. Poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), a well-known solid polymer electrolyte, [7] is a lesser-known biodegradable IPMC EAP. PEO is a semi-crystalline polymer and its lamella structure is responsible for creating its large degree of crystallinity as spherulites [8]. PEO is biodegradable [9], and has also been approved by the Food and Drug Administration to be used in drug delivery systems [10]. PEO has been widely researched for energy storage applications, such as fuel cells, [11] solar cells, [12] and batteries [13].
In most of the EAP research utilizing PEO, it is typically added to other polymer matrices to enhance the ionic mobility within the composite structure, due to its electrolytic properties [14,15,16]. PEO is a polar polymer arising from the atomic oxygen along the polymer backbone, which enables it to readily dissolve ionic salts into its matrix [17]. This characteristic enables PEO to facilitate the migration of both cations and anions [18]. This ability makes PEO very interesting for IPMC research, and an example of the actuation performance of a PEO-based IPMC is shown in Figure 1a. The tip displacement of over 360° of the actuated film is clearly evident when compared the original sample. The bending mechanism for these actuators is illustrated in Figure 1b, and it shows the ionic migration from an initially random disbursement to them accumulating at their respective electrodes under an applied electric field. The resulting localized volume changes results in the bending response.
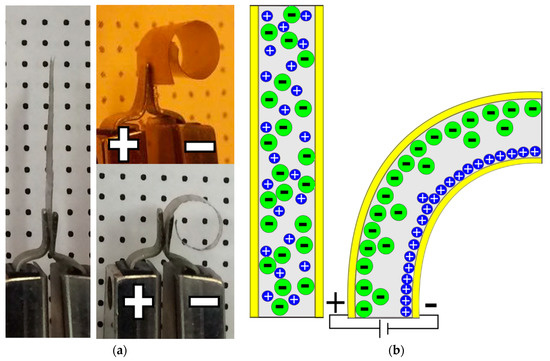
Figure 1.
(a) Ionic polymer metallic composite (IPMC) sample before and after electric excitation; (b) representation of IPMC bending actuation mechanism where the initial randomly oriented ions (Li+ and ClO4−) in the poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) matrix are attracted towards and traverse to their respective electrodes when an external voltage is applied.
IPMCs were created using poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO), dissolved in a water-based solution with a lithium perchlorate (LP) salt. To counter the softening of the PEO matrix from the addition of the LP, nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC), a biomass derivative, was added as a filler material at varying concentrations. Cellulose fiber is comprised of repeating glucose molecules that form in alternating crystalline and amorphous regions [19]. NCC, a derivative of cellulose, is a green material that is renewable, biodegradable, and inexpensive to obtain [20]. This biomaterial has exceptional material properties, with an estimated elastic modulus of 110–220 GPa for an individual NCC chain [21].
NCC–PEO EAP composites were fabricated with varying concentrations of NCC created through a sulfuric acid (H2SO4) hydrolysis process. It was found that their elastic modulus increased with the increasing vol.% NCC suspension. Furthermore, it was found that not only did the incorporation of NCC increase the actuator’s stiffness: their electromechanical actuation performance also improved. The research demonstrated that maximum performance occurred with composites containing 1.5 vol.% NCC. These actuators generated an electromechanical strain, tip displacement, and elastic modulus that were 33.4%, 40.7%, and 20.1% larger, respectively, than those recorded for the non-NCC actuators. These results make NCC a possible additive for improving EAP properties.
The increased actuation response was believed to be due to the sulfate space charge that was imparted on the cellulose chain during the hydrolysis process, and that this space charge became mobile under electric excitation and contributed to the ionic migration. To test this hypothesis, NCC was also generated through a hydrochloric acid (HCl) hydrolysis process wherein no space charge was imparted on the cellulose chain. It was found that the actuation performance greatly diminished when using the HCl-based NCC compared to NCC made from the H2SO4 hydrolysis process.
This paper will directly compare the performance of PEO–NCC composites, and will illustrate how these composites are viable green IPMC actuators.
2. Materials and Methods
The NCC was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich and began as microcrystalline cellulose (Avicel PH-101). The Avicel PH 101 underwent sulfuric acid hydrolysis, which was reported elsewhere, ref. [22] to remove the amorphous regions of the cellulose fibers. The procedure had a twofold result where the acid eliminated the amorphous regions, leaving the nanocrystalline rods, while also imparting a negative surface charge on the NCC, where some of the hydroxyl groups along the NCC backbone are replaced with sulfate () ions. This charge made the NCC rods more stable and better dispersed in the final aqueous suspension [23]. The resulting crystalline rods were cylindrical in shape and ranged between 100–400 nm in length and 20–50 nm in diameter. An example of their size and structure is shown in Figure 2a. The final NCC suspension concentration was roughly 35 mg/mL with a calculated 0.8 wt.% sulfur content (roughly a 2.0 wt.% concentration). It will be shown that this surface charge enhances the IPMC actuation response. PEO IPMCs were also made with an NCC generated from a hydrochloric acid (HCl) hydrolysis process for comparison. HCl hydrolysis does not impart a surface charge on the resulting NCC chains, and the samples were used to confirm the benefits of the added sulfate space charge. It is widely known that the moiety of the sulfate groups attached at the NCC surface during sulfuric acid hydrolysis is rather labile, and can readily be removed when submitted to mild alkali conditions; ref. [24] thus, their incorporation into the PEO matrix is likely responsible for the added performance.
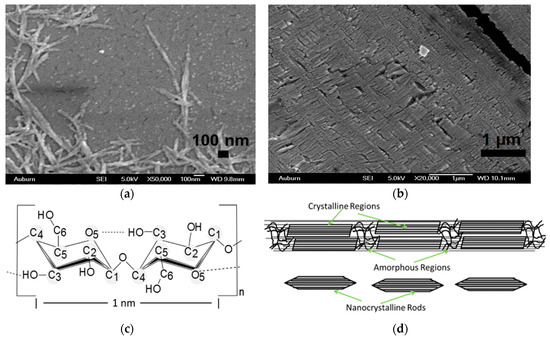
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrograph of: (a) individual H2SO4-based nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) rods and, (b) PEO electroactive polymers (EAPs) with 5.0 wt.% LP and 7.5 vol.% NCC; (c) cellulose molecule; (d) representation of whole cellulose fiber and resulting nanocrystalline rods after sulfuric acid hydrolysis.
The effect of the NCC addition can be seen in Figure 2b, where 7.5 vol.% NCC was added to the PEO–salt matrix. The patterned surface shows that there is clear interplay between the NCC rods and the polymer matrix. The NCC rods themselves are chains of cellulose molecules bundled together in specific crystalline structures and held together via the hydrogen bonding of their hydroxyl groups to the oxygen atoms in the adjoining cellulose molecules [25]. In the NCC–PEO EAP composites, the same hydroxyl groups on the outer surface of the NCC rods undergo hydrogen bonding with the oxygen atoms along the PEO chain [15], generating the structures that are seen in the figure.
The NCC molecule is shown in Figure 2c. There are three hydroxyl groups surrounding a five-carbon, one-oxygen member ring. A small fraction of these hydroxyl groups are replaced by sulfate groups during the hydrolysis process. The general structure of a cellulose fiber is shown in Figure 2d, where there is a clear delineation between the crystalline and amorphous regions. During the acid hydrolysis process, the amorphous regions are eliminated at a faster rate compared to the crystalline regions. The strong hydrogen bonding between the cellulose molecules in the crystalline region makes them more resistant to enzymatic hydrolysis [26], and it is this lowered rate of elimination for the crystalline regions that is responsible for the creation of the NCC rods. The combination of the stiffness of the NCC chains and the contribution of the sulfate ions to the actuation are responsible for the enhanced actuation performance.
The PEO and LP were also obtained from Sigma Aldrich, with the PEO having a viscosity-average molecular weight of 100,000. PEO solutions were comprised of 0.3 g of total mass (PEO and 5.0 wt.% LP) being dissolved into 12.5 mL of deionized water. EAP composites were fabricated by adding set amounts of the NCC suspension to the total solution at: 0.0 vol.%., 0.5 vol.%., 1.0 vol.%., 1.5 vol.%., 2.5 vol.%., 5.0 vol.%., and 7.5 vol.%. The solutions were magnetically stirred for 12 h, and then placed in an ultrasonic bath for 90 min to better disperse the NCC in the solution and remove any PEO clusters that had formed during the stirring process [27]. IPMCs were fabricated by casting 5 mL of solution onto glass slides and heated them at 65 °C for 90 min. The films were immediately placed into an ice bath for five min and cooled rapidly. Approximately 20-nm layers of gold were sputtered onto each side of the films using a Pelco SC-6 sputter coater to act as electrodes. Finally, the films were cut into 19.1 × 6.35 mm rectangles with an average thickness of the films, across all the samples, measured at 54.5 ± 5.0 µm using a Mitutoyo 543-252 Absolute Digimatic Indicator.
3. Results
3.1. Elastic Modulus Evaluation
The elastic modulus of the samples was determined using a TA Instruments RSA3 Dynamic Mechanical Analysis device, with the results averaged across five samples. Films were clamped at 0.20-Nm torque and loaded under a constant axial extension of 0.05 mm/s until fracture. The elastic modulus was calculated from the slope of the resulting stress–strain curve. Figure 3 shows the resulting elastic moduli. For the PEO IPMCs without NCC, there is a linear decrease (−6.0 MPa per wt.% LP) in the elastic modulus with an increasing salt concentration that shows how increased salt content softens the PEO matrix due to a reduced crystallinity [28]. PEO–NCCs were created with 5.0 wt.% LP, and at that salt concentration, there was a linear increase in the elastic modulus, with increasing NCC content, of 30 MPa per vol.% NCC. This result clearly illustrates the strong interaction between the PEO matrix and the NCC filler. It is of note that at 1.5 vol.% NCC concentration, it was determined that the elastic modulus was found to be 133 MPa, which is a 20% increase in stiffness compared to non-NCC IPMCs. Elastic modulus determination was also conducted on dried films of pure NCC, where 10 mL of a 100% NCC suspension was dried at room temperature, and samples of equal dimensions to the IPMCs were cut. Thicknesses for the pure NCC films averaged 69.7 ± 1.5 µm. Although not a direct method for calculating the elastic modulus of a single NCC chain, the bulk elastic modulus for NCC was found to be 7.70 ± 2.2 GPa, which is an order of magnitude higher than the PEO IPMCs, and therefore directly responsible for the increase in the sample stiffness.
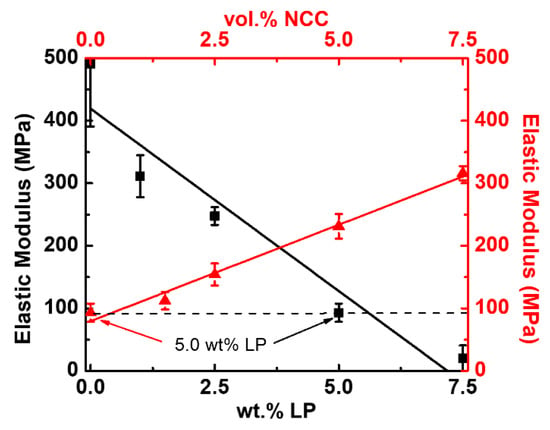
Figure 3.
Elastic modulus trending for increasing lithium perchlorate (LP) (black curve with squares, elastic modulus vs. content of LP for PEO–LP) and NCC vol.% (red curve with triangles, elastic modulus vs. content of NCC for PEO with 5.0 wt.% LP) concentrations.
The elastic modulus and elastic energy densities for all of the tested IPMCs are listed in Table 1. The elastic modulus for the HCl-based NCC also increased with increasing NCC content. However, there is not the corresponding actuation boost, as seen with the sulfuric acid-based NCC. The energy densities are calculated with the fitted maximum strain for the bending actuation performance. A free-standing film for the hydrochloric acid-based NCC was not obtainable, so its value is not included in this table. For an actuator, its performance can be characterized by its volumetric energy density (W), which is defined as:
where is the sample’s elastic modulus, and is the maximum sample strain [29].

Table 1.
Elastic modulus and energy density data for various IPMC composites.
3.2. Electromechanical Actuation Analysis
EAP samples were tested under an applied 4 V DC for 2.5 min under ambient conditions. Three separate samples from each NCC concentration were tested twice, with their electromechanical actuation results being averaged. The bending actuation for the studied PEO–EAP composites was conducted by recording the progression of the tip of the film during the experiments, and then calculating and analyzing the corresponding tip displacement angle. Films were modeled as segments of constant arc length on a contracting circle with respect to time. Newton’s method was used to calculate the tip displacement angle from the arc length and the distance from the base to tip of the sample. It is experimentally found that the time-dependent actuation response of the films can be characterized in three phases: initially slow, followed by steady actuation, and finally a saturated response. It was found that this time-dependence behavior could be expressed as:
where, is the tip displacement angle, and B is a time constant [30].
Figure 4a,b shows the fitted time-dependent tip-displacement angle behavior for various PEO-based IPMCs with increasing LP, and for composites with sulfuric acid-based NCC content in linear time and s−1. With increasing LP concentrations, the actuation performance increases. Maximum electromechanical actuation occurred for the 1.5 vol.% NCC composites, where there was an increase in both tip displacement angle and strain of 43.7% and 33.4%, respectively, compared to the non-NCC PEO-based IPMCs at 5.0 wt.% LP. It is of note that with increasing NCC content over 2.5 vol.%, that there is a sharp decrease in the electromechanical response of the actuators; the 7.5 vol.% NCC samples reached only ~30° actuation, with a roughly 0.1% maximum strain. These results indicate that with increasing NCC content, the ionic mobility is reduced in the matrix, which decreases the mechanical actuation. Therefore, finding the right balance of NCC for a given polymer matrix is key for using NCC as a filler material. The inserts in Figure 4a relate what the observed actuator performance was and the corresponding tip displacement angle calculations.
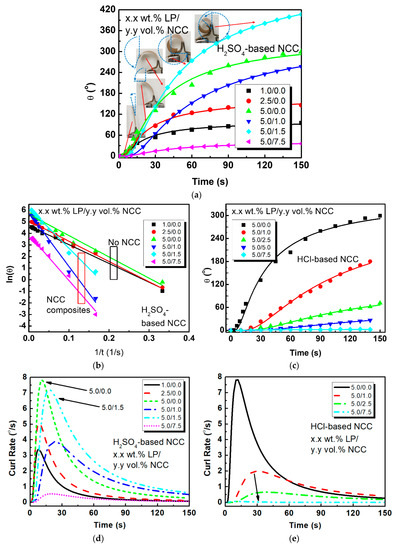
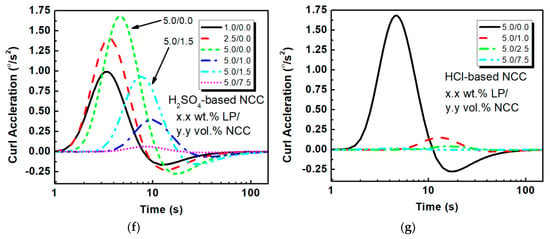
Figure 4.
(a) Nonlinear and (b) linear fitting for PEO–NCC IPMCs utilizing sulfuric acid-based NCC; (c) nonlinear fitting for PEO–NCC IPMCs utilizing hydrochloric acid hydrolysis-based NCC; (d,f) velocity and acceleration modeling for H2SO4–NCC composites; (e,g) velocity and acceleration modeling for HCl–NCC composites.
Additionally, an examination of Figure 4a and the linear representation of the IPMC actuation, Figure 4b, clearly show differences in the initial sample response and their rate of actuation. PEO samples with NCC began their bending more slowly, but then more quickly reached their saturation response when compared to the non-NCC samples.
Samples with 5.0 wt.% LP had 30% lower stiffness than the 1.0 wt.% LP samples, but with an increased displacement of 250%. For the 5.0 wt.% LP samples, the addition of 1.5 vol.% NCC yielded both a 20% increase in elastic modulus and a 33% increase in the displacement. Additionally, when considering energy density, the addition of 1.5 vol.% NCC yielded a near 300% increase in energy density from 4.3 kJ/m3 to 12.1 kJ/m3 for PEO with no NCC to the 1.5 vol.% NCC, respectively. This is a dramatic increase in the material response and properties, and is due to the combination of NCC stiffness and the additional sulfate space charge, which contributes to the available mobile ions for generating the actuation response. Conversely, it is clear from Figure 4c that even with only 1.0 vol.% added HCl-based NCC suspension, there is a dramatic decrease in actuation response. This again confirms that the added space charge directly effects the actuation response.
The applicability of Equation (2) is clear when analyzing Figure 4a–c. The closed-form solution that it offers with respect to tip displacement can be logically extended into new relationships for a more in-depth analysis of not just the films portrayed in this study, but also IPMCs in general. This extension is showcased in Equations (3) and (4), below.
where can be thought of as the instantaneous curl rate (ICR) and as the instantaneous curl acceleration (ICA). Through introducing these relationships, it is possible to quantify actuation parameters that would otherwise be difficult to obtain experimentally.
Using the fitting parameters shown in Table 2 generated from fitting Figure 4a–c, Figure 4d–g can be generated. Figure 4d shows the ICR for PEO films with and without H2SO4-based NCC. Interestingly, it can be seen that the non-NCC samples reached an 8.3% higher ICR at 3.4 °/s compared to the NCC samples at 7.2 °/s. This is likely due to the slower propagation of ions through the PEO matrix when NCC is present. However, the continued inspection of Figure 4d shows that even though the ICR is lower and that the rate drops off with respect to time for both types of ICMPs, for the NCC composites, the ICR is delivers a higher rate after roughly 20 s, and maintains the higher rate for the duration of the experiment. This was in agreement with the experimental observations. It is also interesting to note that the peak velocities for all of the films occur within the first 30 s of excitation, and could be due to the contribution of ions starting near the electrode interface versus those that have to travel the length of the film thickness. Conversely, the HCl-based composites, which are illustrated in Figure 4e, showed a 74.3% drop in performance, when even 1.0 vol.% suspension is added.

Table 2.
Experimental fitting parameters for PEO IPMCs with varying concentrations of LP/NCC.
A similar analysis can be concluded when evaluating the ICA between the EAPs, as shown in Figure 4f,g. Virtually all of the films obtain their peak accelerations within the first 10 s, with the 5.0 wt.% LP PEO samples without NCC, and the 5.0 wt.% LP/1.5 vol.% NCC–PEO samples reaching their peaks of 1.7 °/s2 and 0.94 °/s2 in 4.5 s and 7.0 s, respectively. For the best HCl-based NCC composites, they only reached 0.15 °/s2, which again shows the added contribution of the space charge with the H2SO4 samples.
Table 2 displays a sampling of the fitting results for the PEO-based composites with NCC, as well as the peak accelerations for each film. For the sulfuric acid hydrolysis-based NCC composite IPMCs, the addition of small concentrations of NCC can increase actuator performance, but too much NCC will degrade the performance due to increases in film stiffness.
Figure 5 displays the energy density versus the applied electric field for various types of both ionic and electronic EAPs. Using the biologic muscle as a reference, the PEO-based films that were discussed in this study have comparable performance, but require a larger driving voltage. Further investigation into the effects of NCC on the PEO matrix may make it possible to tailor this family of EAPs to behave more closely in line with that of biologic muscle.
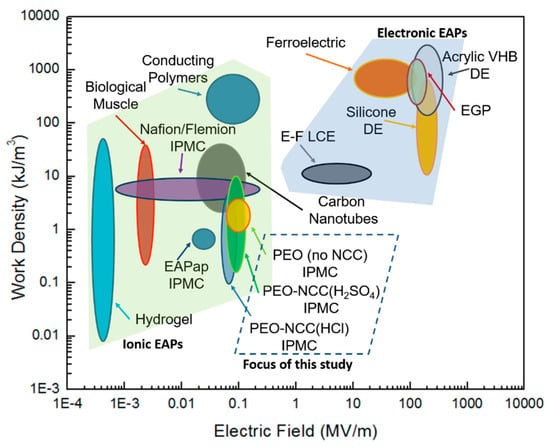
Figure 5.
Electromechanical performance comparison for ionic and electronic EAPs (i-EAP and e-EAP data generated, in part, from data posted in Madden, et al. [4]).
4. Conclusions
Biodegradable PEO-based IPMC EAPs were created with varying concentrations of H2SO4 and HCl-based NCC composites. When comparing the response of these two types of IPMCs, it was proven that the space charge imparted on the NCC, due to the sulfuric acid hydrolysis process that was used in its creation, greatly benefited the actuation response of the composites when comparing their behavior to the HCl-based NCC without the space charge. Performance was also better when compared to the non-NCC PEO-based EAPs, with increases in the tip displacement, strain, and elastic modulus of 40.7%, 33.4%, and 20.1%, respectively. This indicated that NCC is a viable filler material that can improve the actuation performance, although too much NCC can overly stiffen the films and negatively impact performance.
It was also shown that the previously published actuation model could be extended to develop relationships for evaluating the instantaneous angular velocity and acceleration of IPMCs. This new methodology enables a more comprehensive study of these types of actuators that would otherwise be difficult to obtain experimentally. The new relationships also offer a new approach to studying the time-dependent rotational kinematics of IPMC actuators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.B., L.Z., M.T., Z.C.; data curation, P.B., L.Z.; formal analysis, P.B., L.Z., M.T., Z.C.; funding acquisition, P.B., M.T., Z.C.; investigation, P.B., L.Z., Z.C.; methodology, P.B., L.Z., M.T., Z.C.; project administration, P.B., M.T., Z.C.; resources, P.B., Z.C.; software, P.B., Z.C.; supervision, P.B., M.T., Z.C.; validation, P.B., Z.C.; visualization, P.B., Z.C.; writing—original draft preparation, P.B.; writing—review and editing, P.B., L.Z., Z.C.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation through the Auburn University IGERT on Integrated Biorefining (Award #1069004). Partial funding was also contributed through USDA-NIFA under grants #2014-60722-21694 and #2016-67022-25071 (G00009848).
Acknowledgments
Patrick Bass gratefully acknowledges Maria Auad for providing access to her Dynamic Mechanical Analysis machine for use with elastic modulus testing.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bar-Cohen, Y.; Cardoso, V.; Ribeiro, C.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Electroactive polymers as actuators. In Advanced Piezoelectric Materials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 319–352. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, Q. Field-activated electroactive polymers. MRS Bull. 2008, 33, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinpoor, M. Ionic polymer-conductor composites as biomimetic sensors, robotic actuators and artificial muscles—A review. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, J.D.; Vandesteeg, N.A.; Anquetil, P.A.; Madden, P.G.; Takshi, A.; Pytel, R.Z.; Lafontaine, S.R.; Wieringa, P.A.; Hunter, I.W. Artificial muscle technology: Physical principles and naval prospects. Ocean. Eng. IEEE J. 2004, 29, 706–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramzadeh, Y.; Shahinpoor, M. A review of ionic polymeric soft actuators and sensors. Soft Robot. 2014, 1, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe Handling and Use of Perfluorosulfonic Acid Products; DuPont: Wilmington, DE, USA, 2009.
- Fergus, J.W. Ceramic and polymeric solid electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4554–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.P.; Woo, E.M. Effects of entrapment on spherulite morphology and growth kinetics in poly(ethylene oxide)/epoxy networks. Polymer 2001, 42, 6493–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, A.M.; Gilding, D.K. Biodegradable polymers for use in surgery—Poly(ethylene oxide)/poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PEO/PET) copolymers: 2. In vitro degradation. Polymer 1981, 22, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles based drug delivery systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.C.; Xu, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Xing, L.; Scott, K. A poly(ethylene oxide)/graphene oxide electrolyte membrane for low temperature polymer fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8377–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, J.E.; Goncalves, A.D.; Formiga, A.L.B.; De Paoli, M.A.; Li, X.; Durrant, J.R.; Norueira, A.F. A polymer gel electrolyge composed of a poly(ethylene oxide) copolymer and the influence of its composition on the dynamics and performance of dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Schomer, M.; Peng, H.; Page, K.A.; Wilms, D.; Frey, H.; Soles, C.L.; Yoon, D.Y. Correlations between ion conductivity and polymer dynamics in hyperbranched poly(ethylene oxide) electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2685–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinpoor, M.; Kim, K.J. Solid-state soft actuator exhibiting large electromechanical effect. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 3445–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Kim, J.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.M. Effect of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(ethylene glycol) addition on actuation behavior of cellulose electroactive paper. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009b, 114, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesse, C.; Khaldi, A.; Wang, Q.; Cattan, E.; Teyssié, D.; Chevrot, C.; Vidal, F. Polyethylene oxide-polytetrahydrofurane-PEDOT conducting interpenetrating polymer networks for high speed actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.; Vincent, C. Structure of an amorphous polymer electrolyte, poly(ethylene oxide) 3: LiCF3SO3. Chem. Commun. 1997, 2, 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hayamizu, K.; Akiba, E.; Bando, T.; Aihara, Y.; Price, W.S. NMR studies on poly(ethylene oxide)-based polymer electrolytes with different cross-linking doped with LiN (SO2CF3) 2. Restricted diffusion of the polymer and lithium ion and time-dependent diffusion of the anion. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’SULLIVAN, A.C. Cellulose: The structure slowly unravels. Cellulose 1997, 4, 173–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, S.; Kai, W.; Isogai, A.; Iwata, T. Elastic modulus of single cellulos microfibrils from tunicate measured by atomic force microscopy. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2571–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elazzouzi-Hafraoui, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Putaux, J.L.; Heux, L.; Dubreuil, F.; Rochas, C. The shape and size distribution of crystalline nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis of native cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Rojas, O.J.; Lucia, L.A.; Sain, M. Cellulosic nanocomposites: A review. Bioresources 2008, 55, 929–980. [Google Scholar]
- Habibi, Y.; Chanzy, H.; Vignon, M.R. TEMPO-mediated surface oxidation of cellulose whiskers. Cellulose 2006, 13, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, M.A.S.A.; Alloin, F.; Dufresne, A. Review of recent research into cellulosic whiskers, their properties and their application in nanocomposite field. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, Y.; Langan, P.; Chanzy, H. Crystal structure and hydrogen-bonding system in cellulose Iβ from synchrotron X-ray and neutron fiber diffraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9074–9082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammouda, B.; Ho, D.L.; Kline, S. Insight into clustering in poly(ethylene oxide). Marcomolecules 2004, 37, 6932–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Huo, H.; Jiang, S. Effects of lithium perchlorate on poly(ethylene oxide) spherulite morphology and spherulite growth kinetics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragavan, V. Materials Science and Engineering—A first Course; Prentice Hall of India: New Delhi, India, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, P.S.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.Y. Time-dependence of the electromechanical bending actuation observed in ionic-electroactive polymers. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2017, 7, 1720002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).