A Study on Reducing Loss in PCB Motor Stator Using Multi-Via Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
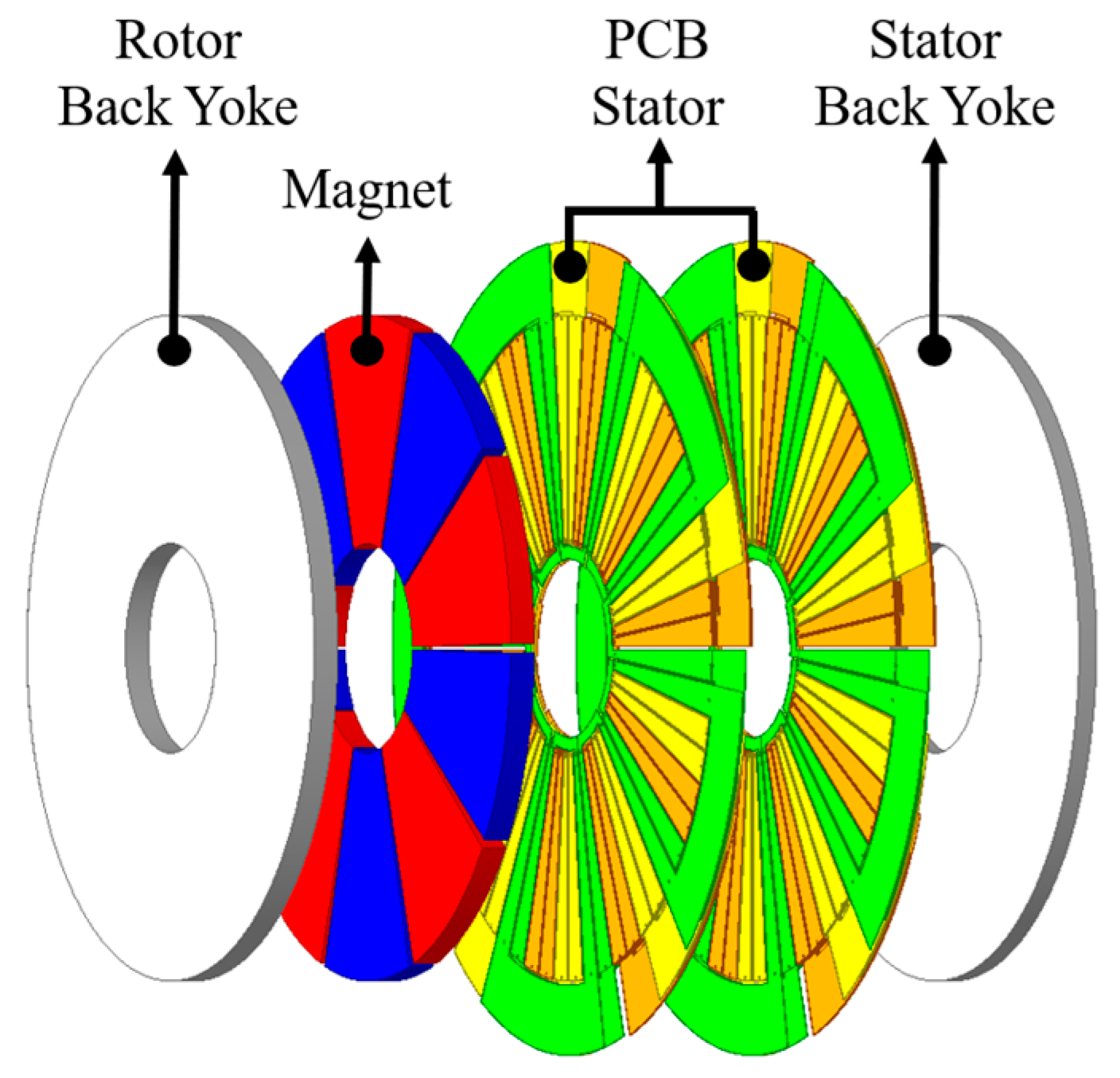
2. Basic Design of PCB Distributed Winding Motor for Actuators
2.1. Distributed Winding PCB Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Motor
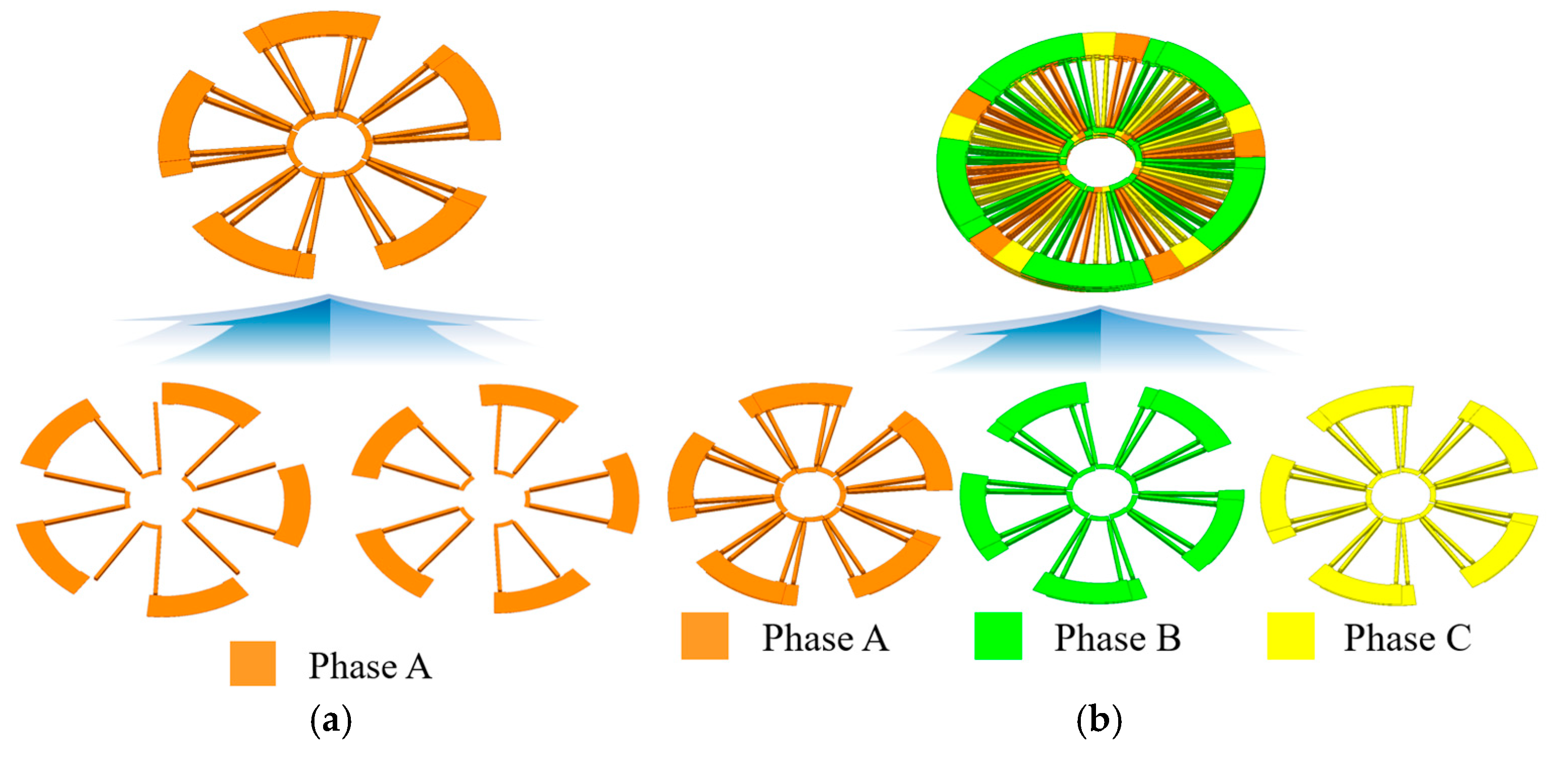
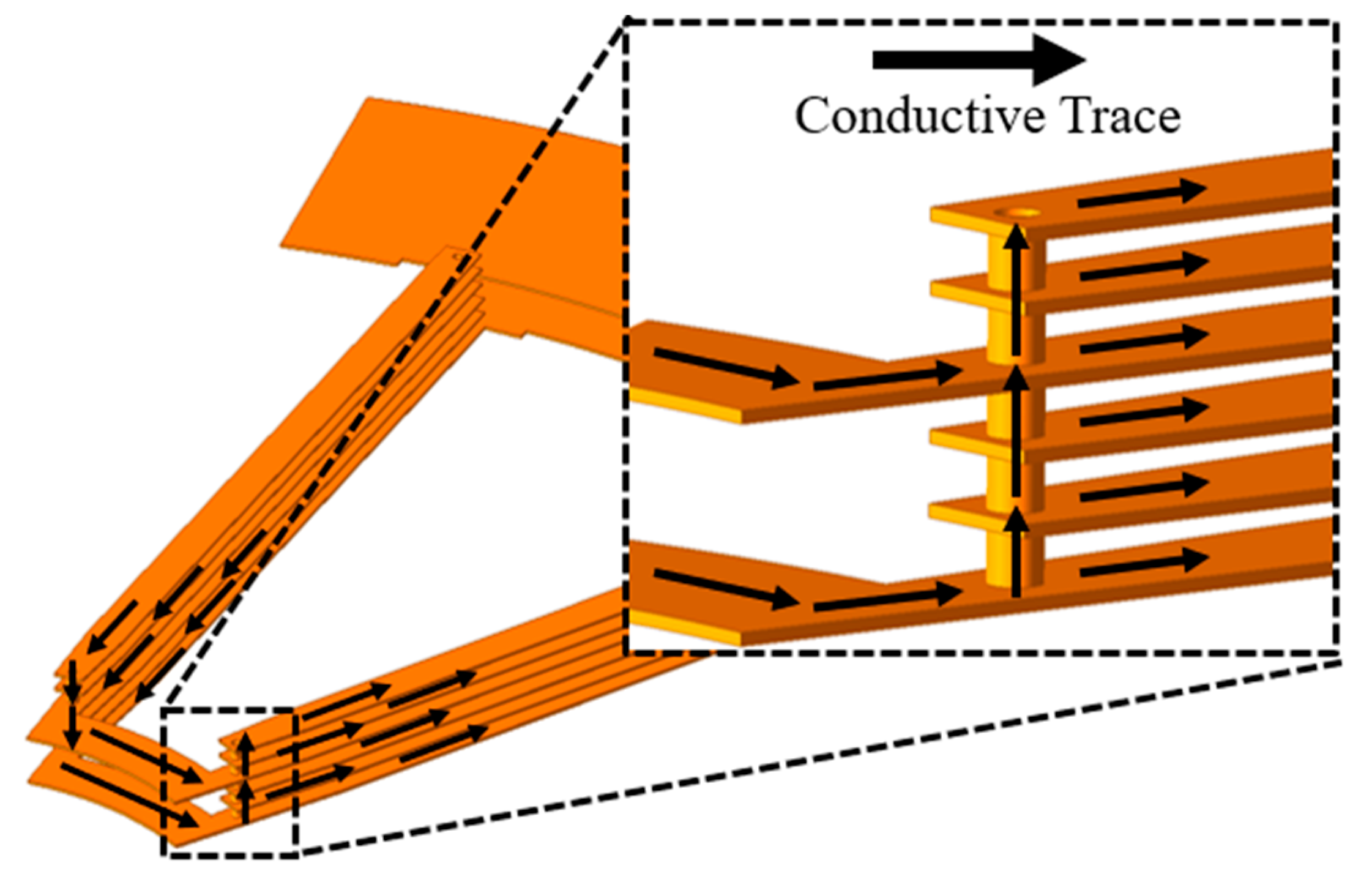
2.2. Trace Configuration of the Distributed Winding PCB Motor
2.3. Distributed Winding End-Turn Structure of the PCB Stator
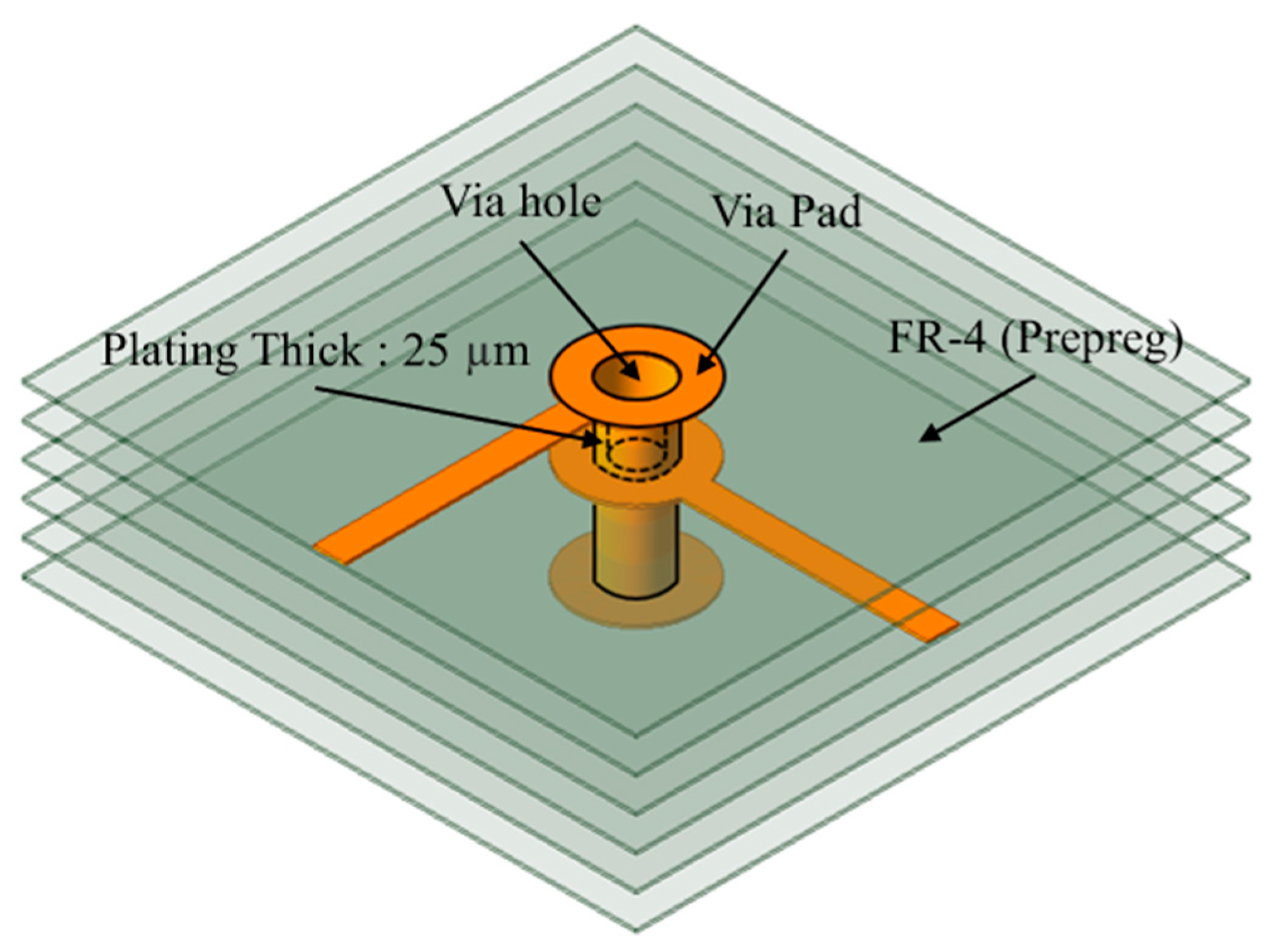
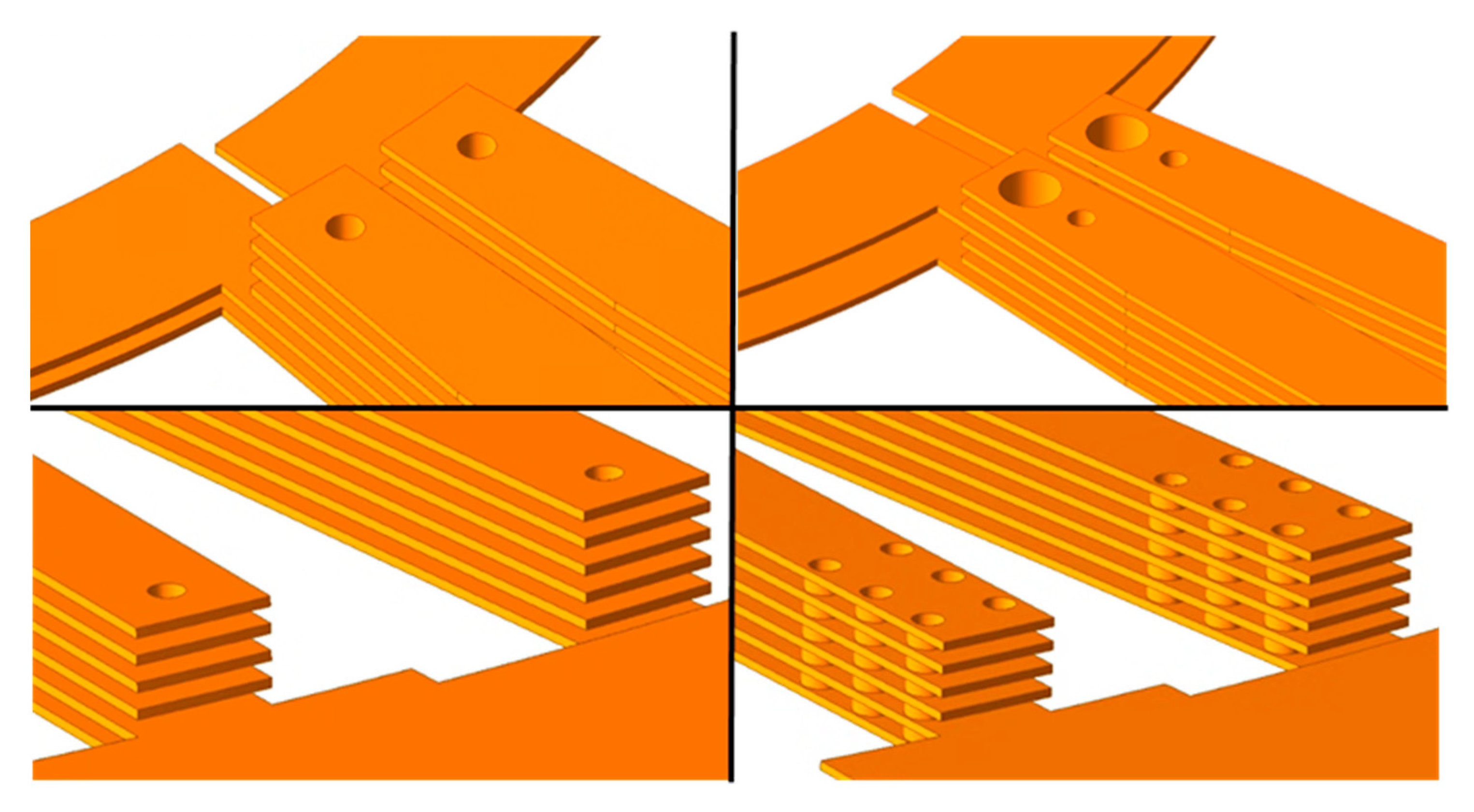
3. Multi-Via Design of the PCB Stator
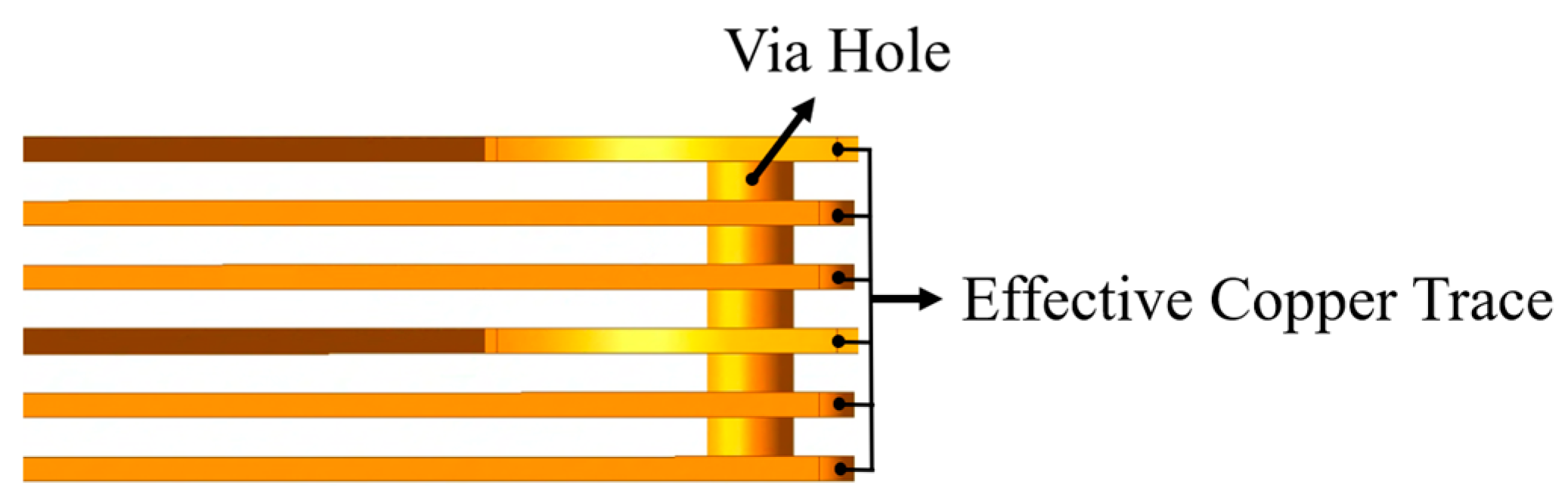
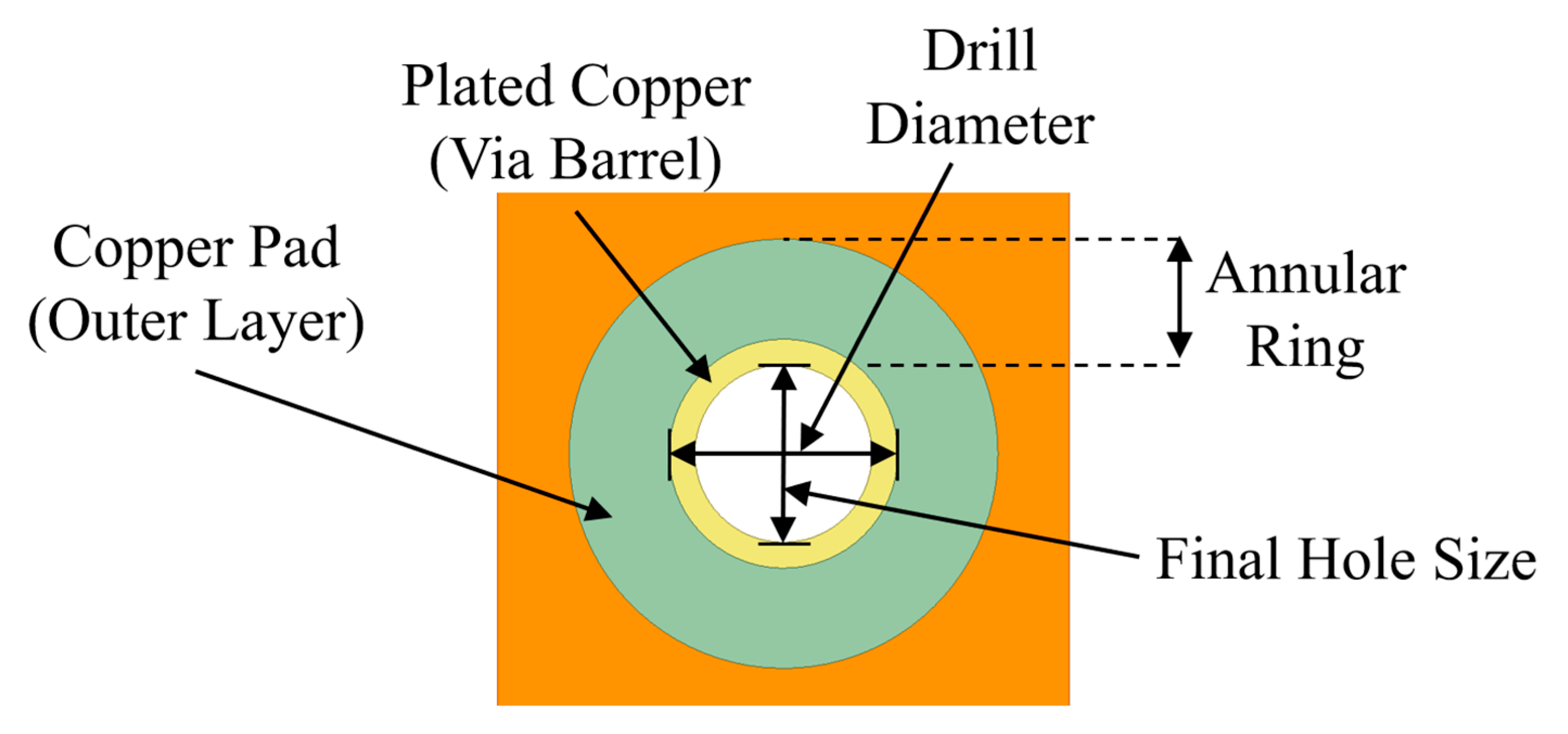
3.1. Limitations of Conventional Single-Via Structures
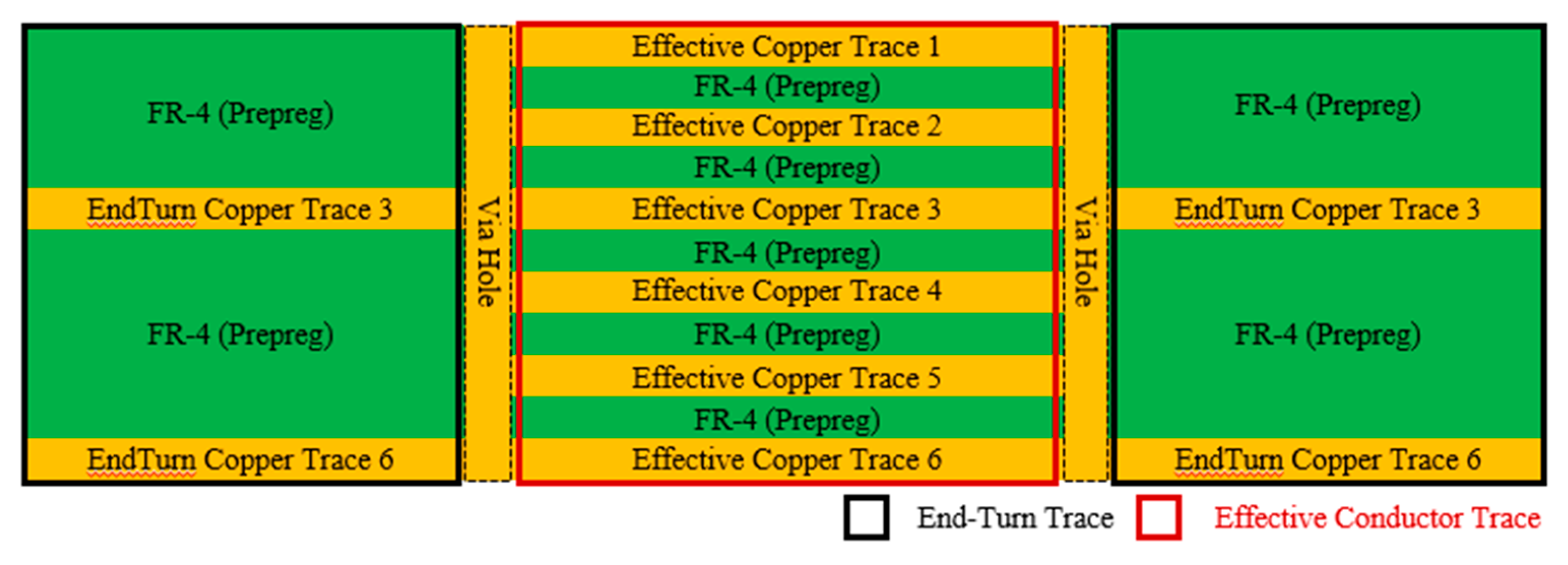
3.2. Multi-Via Structure
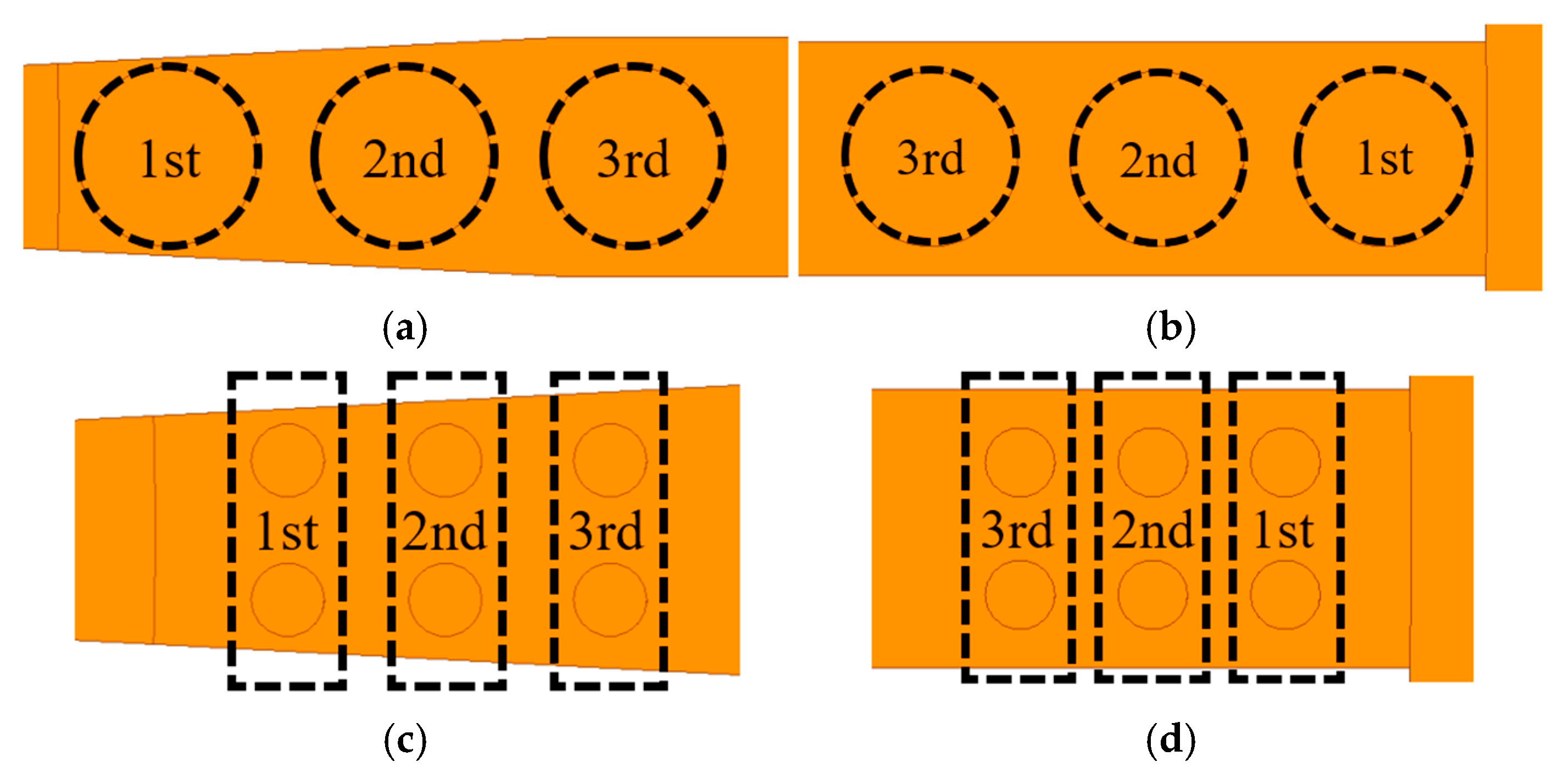
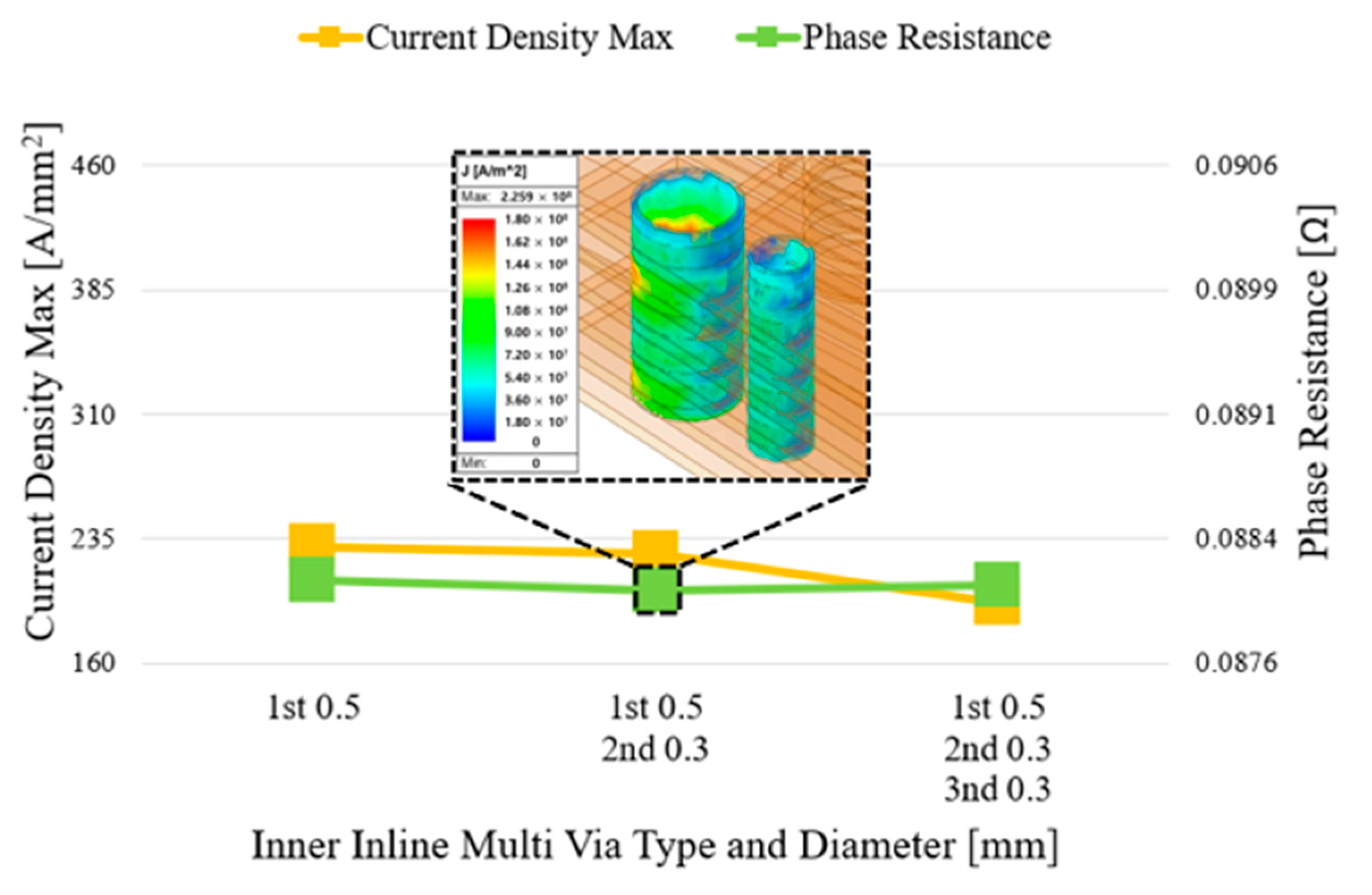
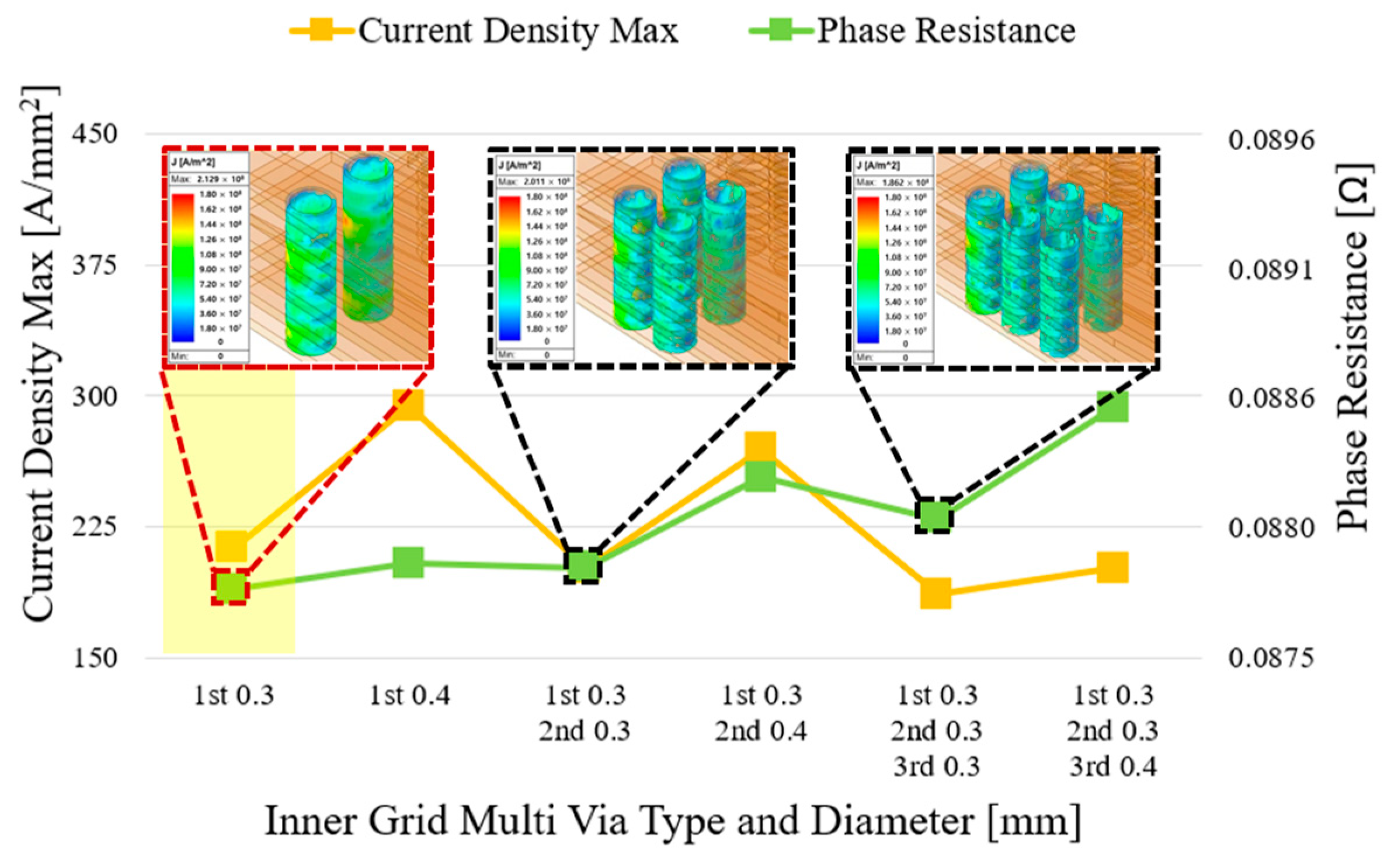
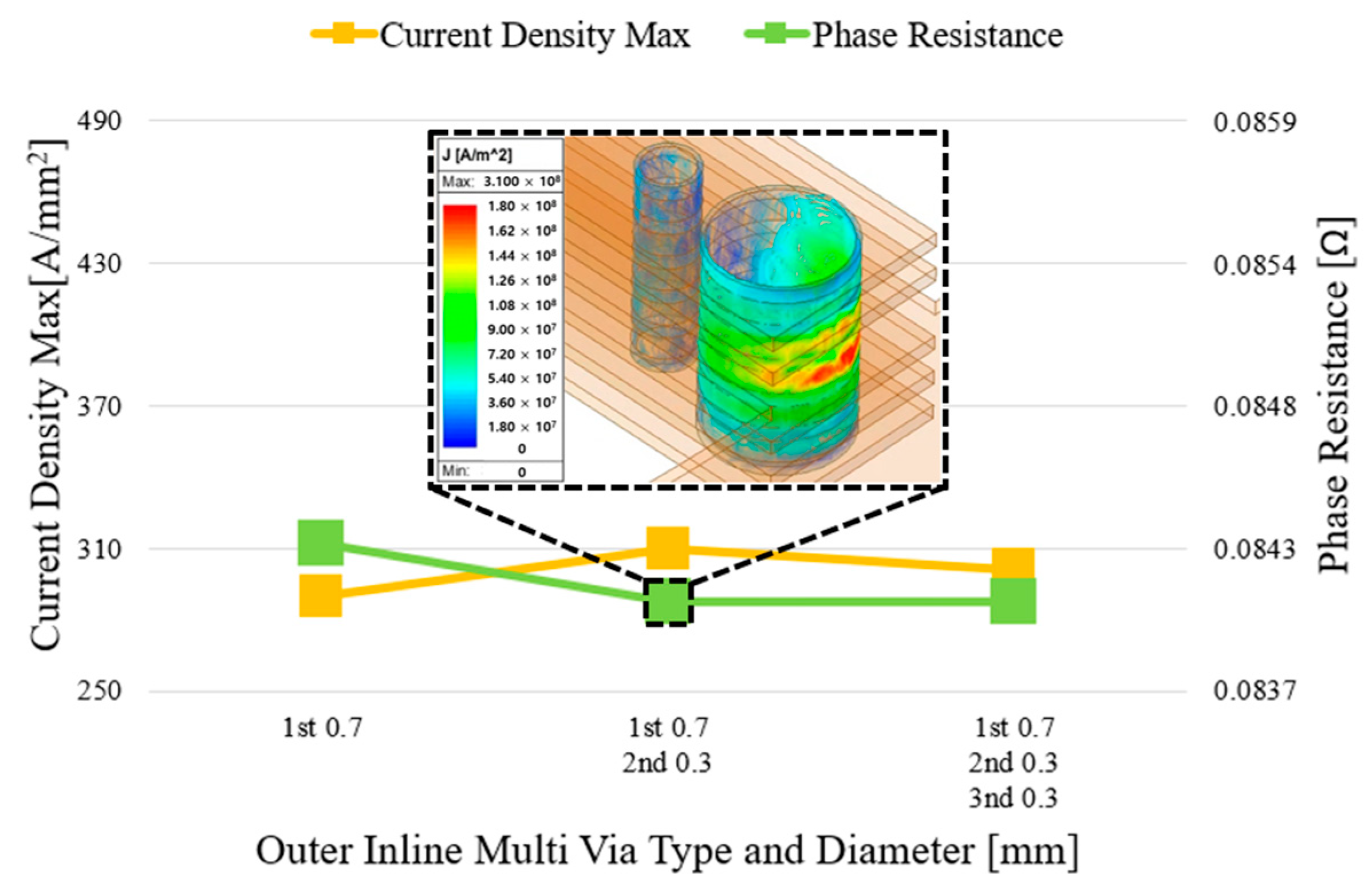
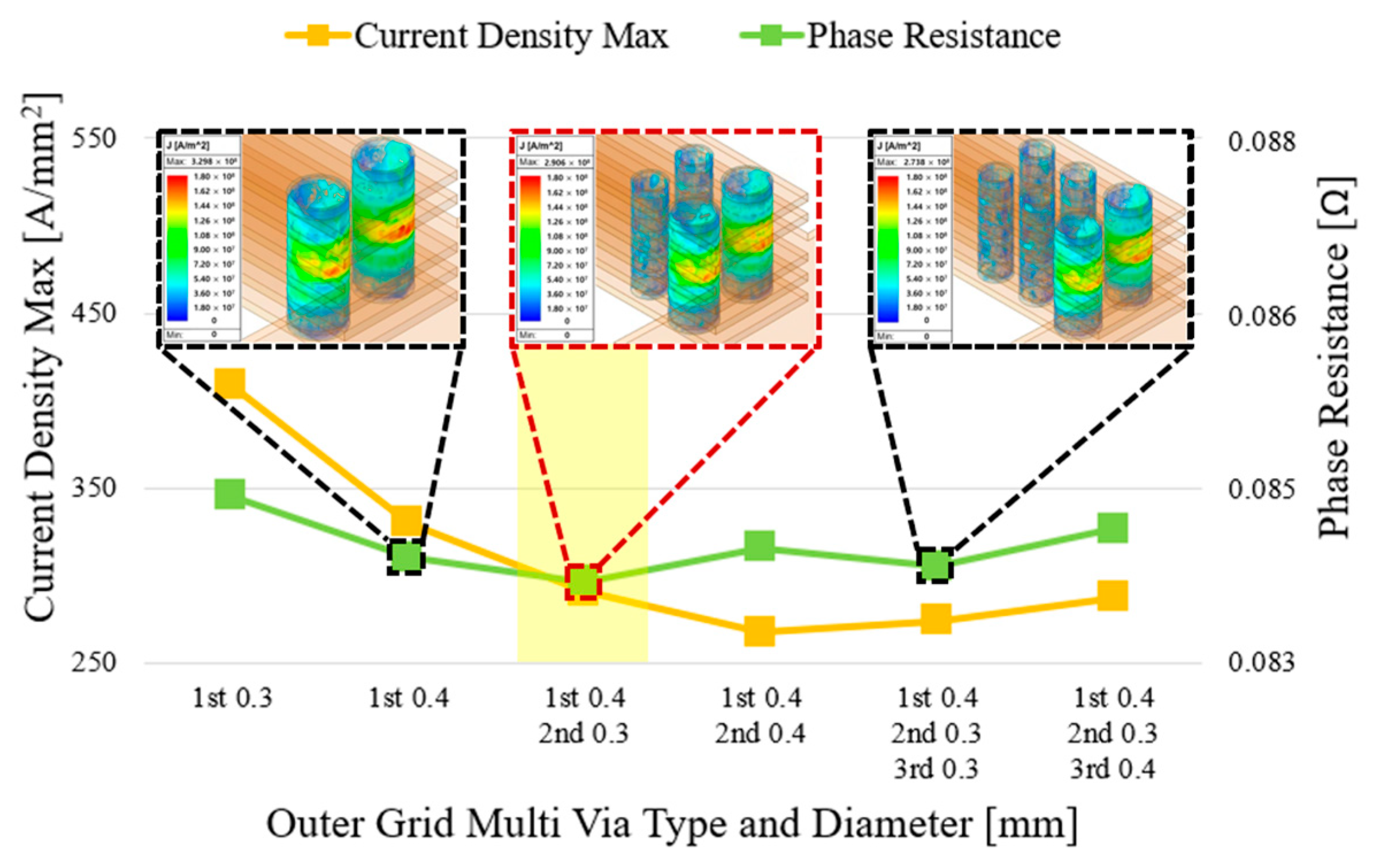
3.3. Inline-Type and Grid-Multi-Via Structures
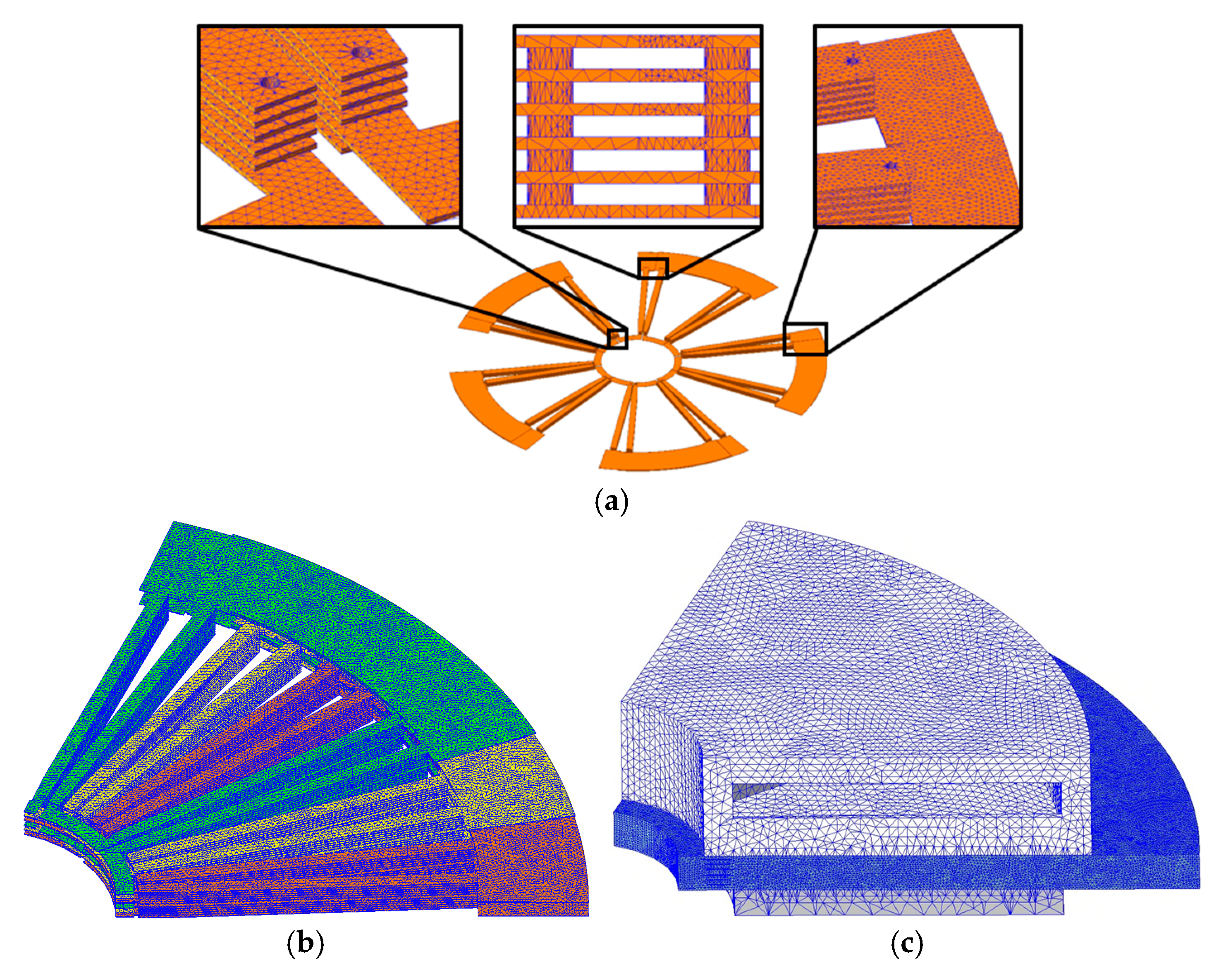
3.4. Simulation Conditions
4. FEM Methodology and Performance Evaluation
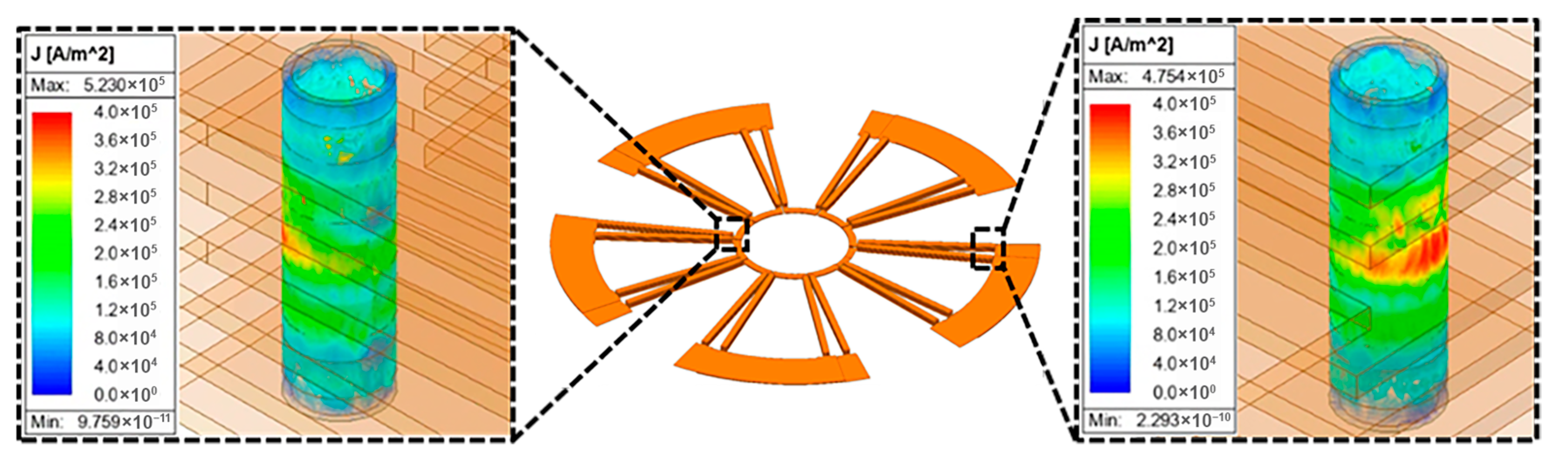
4.1. Analysis Items
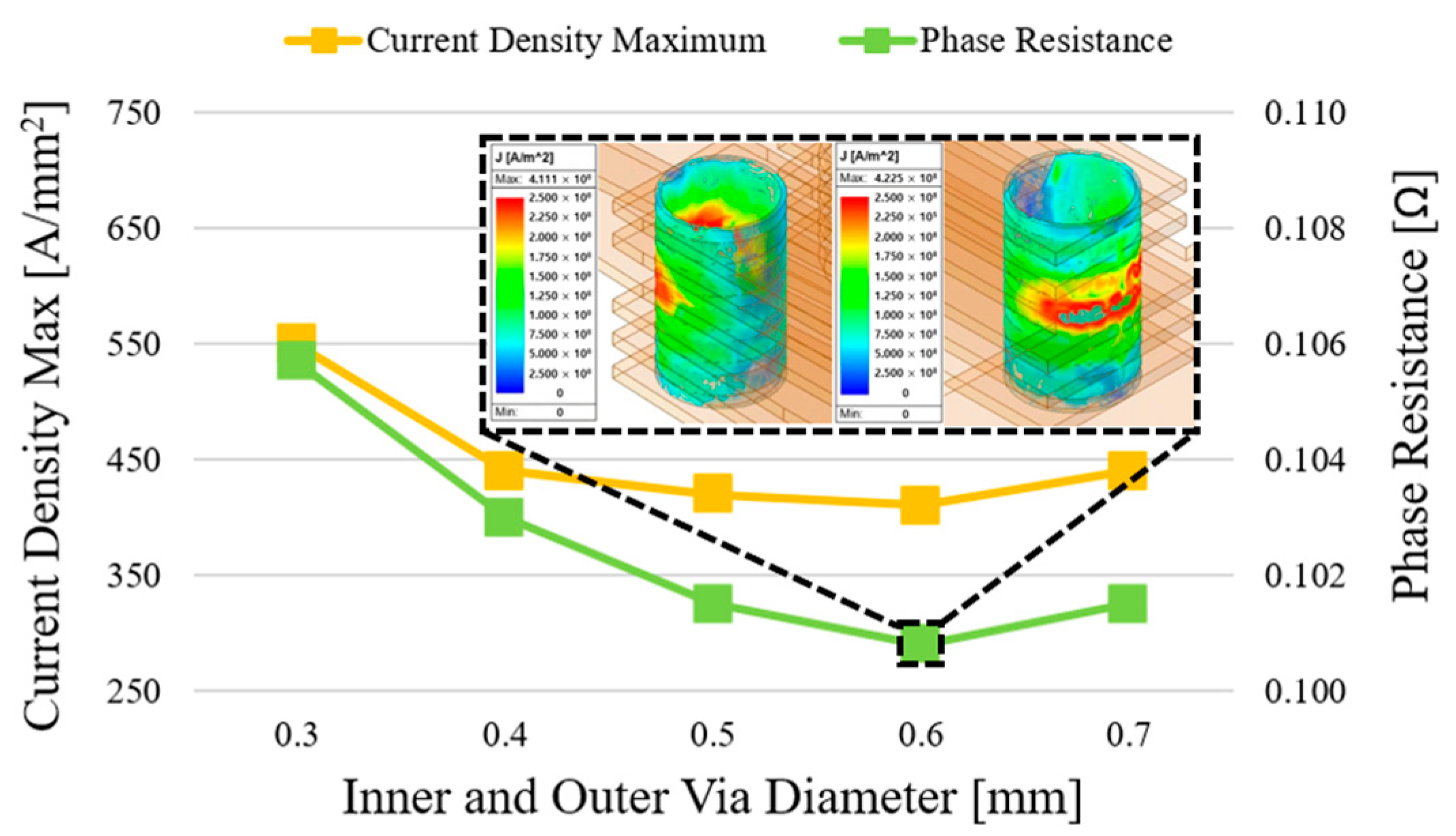
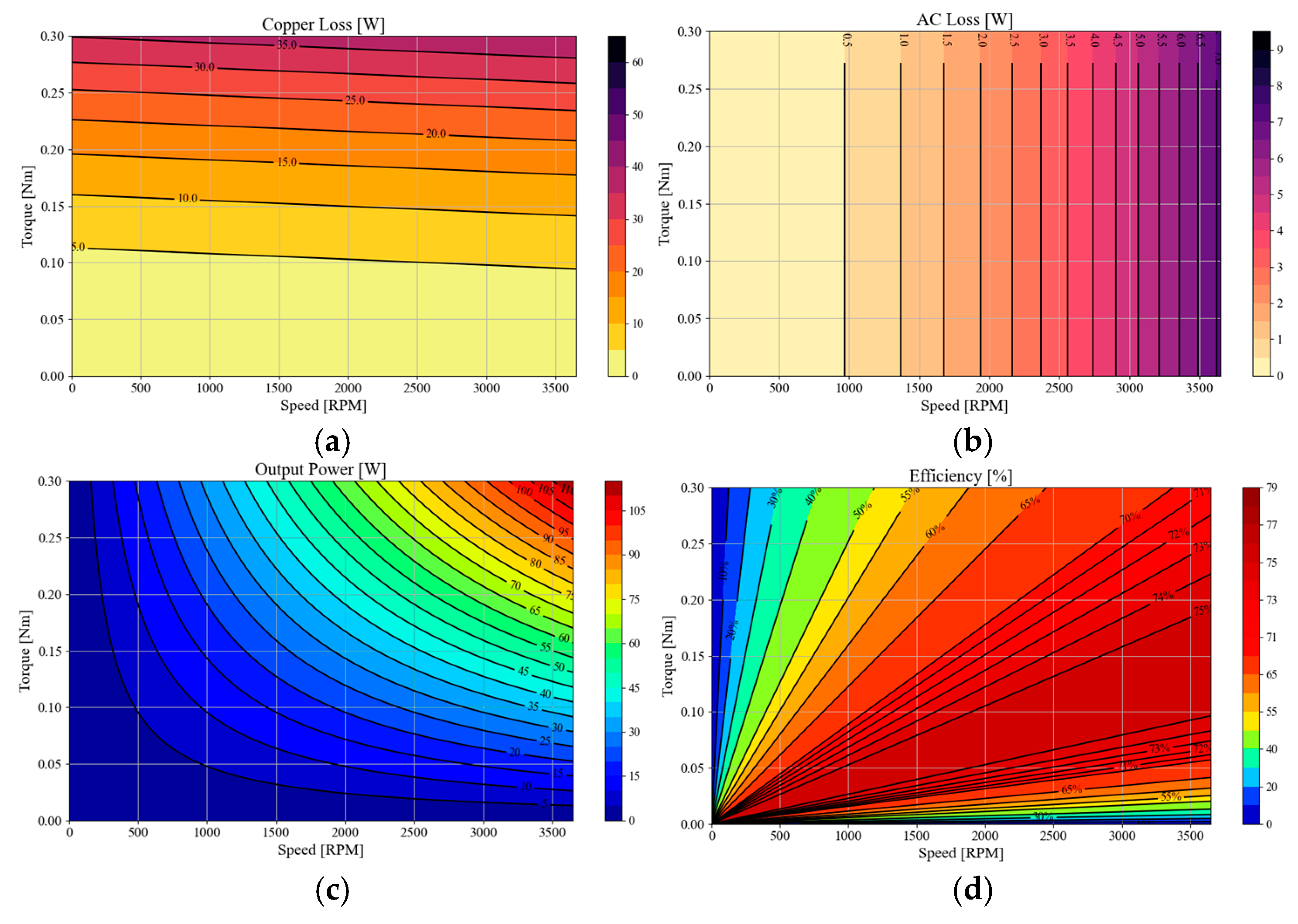
4.2. FEM-Based Performance Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsieh, F.-S. Emerging Research Issues and Directions on MaaS, Sustainability and Shared Mobility in Smart Cities with Multi-Modal Transport Systems. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turoń, K.; Tóth, J. Innovations in Shared Mobility—Review of Scientific Works. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.; Lotwin, M.; Shah, R. A Review of Bio-Inspired Actuators and Their Potential for Adaptive Vehicle Control. Actuators 2025, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Sun, Z.; Xu, H.; Ren, Y.; Tan, C. Design and Analysis of Brake-by-Wire Unit Based on Direct Drive Pump–Valve Cooperative. Actuators 2023, 12, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Qian, L.; Ge, W.; Wang, L. Research on the Anti-Disturbance Control Method of Brake-by-Wire Unit for Electric Vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2019, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, P.; Luo, G.; Chen, Y. A Review of Axial-Flux Permanent-Magnet Motors: Topological Structures, Design, Optimization and Control Techniques. Machines 2022, 10, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-K.; Zou, X.-P.; Guo, Q.-C.; Zhu, L.-K. Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Cogging Torque Calculation Method Based on Harmonic Screening. Energies 2025, 18, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Pei, L.; Rafiei, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B. Structural Optimization and Electromagnetic Performance Research of Axial Magnetic Field Tidal Current Generators. Energies 2025, 18, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X. The Design of a Permanent Magnet In-Wheel Motor with Dual-Stator and Dual-Field-Excitation Used in Electric Vehicles. Energies 2018, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, T.; Cui, X.; Zhao, X. Design and Analysis of Coreless Axial Flux Permanent Magnet Machine with Novel Composite Structure Coils. Energies 2022, 15, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, H.; Li, X. Winding Design and Analysis for a Disc-Type Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor with a PCB Stator. Energies 2018, 11, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.-H.; Han, H.-S.; Hong, M.-K.; Jung, D.-H.; Kim, W.-H. Design for Loss Reduction in a Compact AFPM Electric Water Pump with a PCB Motor. Energies 2025, 18, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasteh, E.; Assadian, F. A Comparative Analysis of Brake-by-Wire Smart Actuators Using Optimization Strategies. Energies 2022, 15, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musumeci, S.; Barba, V. Gallium Nitride Power Devices in Power Electronics Applications: State of Art and Perspectives. Energies 2023, 16, 3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Fu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Ai, C. A Comprehensive Investigation of Winding Eddy and Circulating Current Losses of Stator Iron Coreless PMBLDC Motors. Energies 2023, 16, 5523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Dieterich, D.; Urschel, S. Comparison of Eddy Current Loss Calculation Techniques for Axial Flux Motors with Printed Circuit Board Windings. Energies 2025, 18, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.; Nikam, S.P.; Pal, S.; Wankhede, A.K.; Fernandes, B.G. Multiphysics analysis of printed circuit board winding for high-speed axial flux permanent magnet motor. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2019, 13, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulaee, Y.; Lewis, D.; Heins, G.; Patterson, D.; Ionel, D.M. Winding Losses in Coreless Axial Flux PM Machines with Wave and Spiral PCB Stator Topologies. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Detroit, MI, USA, 9–13 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmouditabar, F.; Baker, N. A Review on the Effect of Electrical Steel Manufacturing Processes on the Performance of Electric Machines. Energies 2023, 16, 7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chulaee, Y.; Lewis, D.; Mohammadi, A.; Heins, G.; Patterson, D.; Ionel, D.M. Circulating and Eddy Current Losses in Coreless Axial Flux PM Machine Stators with PCB Windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 4010–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaibu, I.; Wei, E.H.T.; Kannan, R.; Samaila, Y.A. The Utilization of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) in Axial Flux Machines: A Systematic Review. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Magnet | - | N45UH |
| Rotor | - | S45C |
| Stator | - | 35PN230 |
| Number of phases | - | 3 |
| Magnet thickness | mm | 2.7 |
| Rotor backyoke thickness | mm | 2.7 |
| Stator backyoke thickness | mm | 2 |
| Outer diameter | mm | 65.4 |
| Inner diameter | mm | 20.6 |
| Axial length | mm | 10.1 |
| Parameter | Unit | Conventional Model |
|---|---|---|
| Back EMF | Vrms | 3.23 |
| Rated Speed | Rpm | 3650 |
| Load Torque | Nm | 0.3 |
| Current | Arms | 12.37 |
| Current density | A/mm2 | 29.46 |
| Copper Loss | W | 48.52 |
| AC Loss | W | 5.2 |
| Output Power | W | 114.67 |
| Efficiency | % | 68.10 |
| Parameter | Unit | Conventional Model | Improvement Through FEM Approach Model | Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Back EMF | Vrms | 3.2 | 3.23 | - |
| Load Torque | Nm | 0.3 | 0.3 | - |
| Current | Arms | 12.57 | 12.57 | - |
| Current density | A/mm2 | 42.19 | 33.45 | 20.7% |
| Phase Resistance | Ohm | 0.106 | 0.083 | 21.7% |
| Copper Loss | W | 50.08 | 39.70 | 20.7% |
| AC Loss | W | 7.11 | 7.11 | - |
| Output Power | W | 114.67 | 114.67 | - |
| Efficiency | % | 66.72 | 71.01 | 6.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, S.-B.; Choi, D.-H.; Han, H.-S.; Song, Y.-H.; Kim, W.-H. A Study on Reducing Loss in PCB Motor Stator Using Multi-Via Structure. Actuators 2025, 14, 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090424
Jeon S-B, Choi D-H, Han H-S, Song Y-H, Kim W-H. A Study on Reducing Loss in PCB Motor Stator Using Multi-Via Structure. Actuators. 2025; 14(9):424. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090424
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Su-Bin, Do-Hyeon Choi, Hyung-Sub Han, Yun-Ha Song, and Won-Ho Kim. 2025. "A Study on Reducing Loss in PCB Motor Stator Using Multi-Via Structure" Actuators 14, no. 9: 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090424
APA StyleJeon, S.-B., Choi, D.-H., Han, H.-S., Song, Y.-H., & Kim, W.-H. (2025). A Study on Reducing Loss in PCB Motor Stator Using Multi-Via Structure. Actuators, 14(9), 424. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14090424








