Performance Enhancement of Seismically Protected Buildings Using Viscoelastic Tuned Inerter Damper
Abstract
1. Introduction
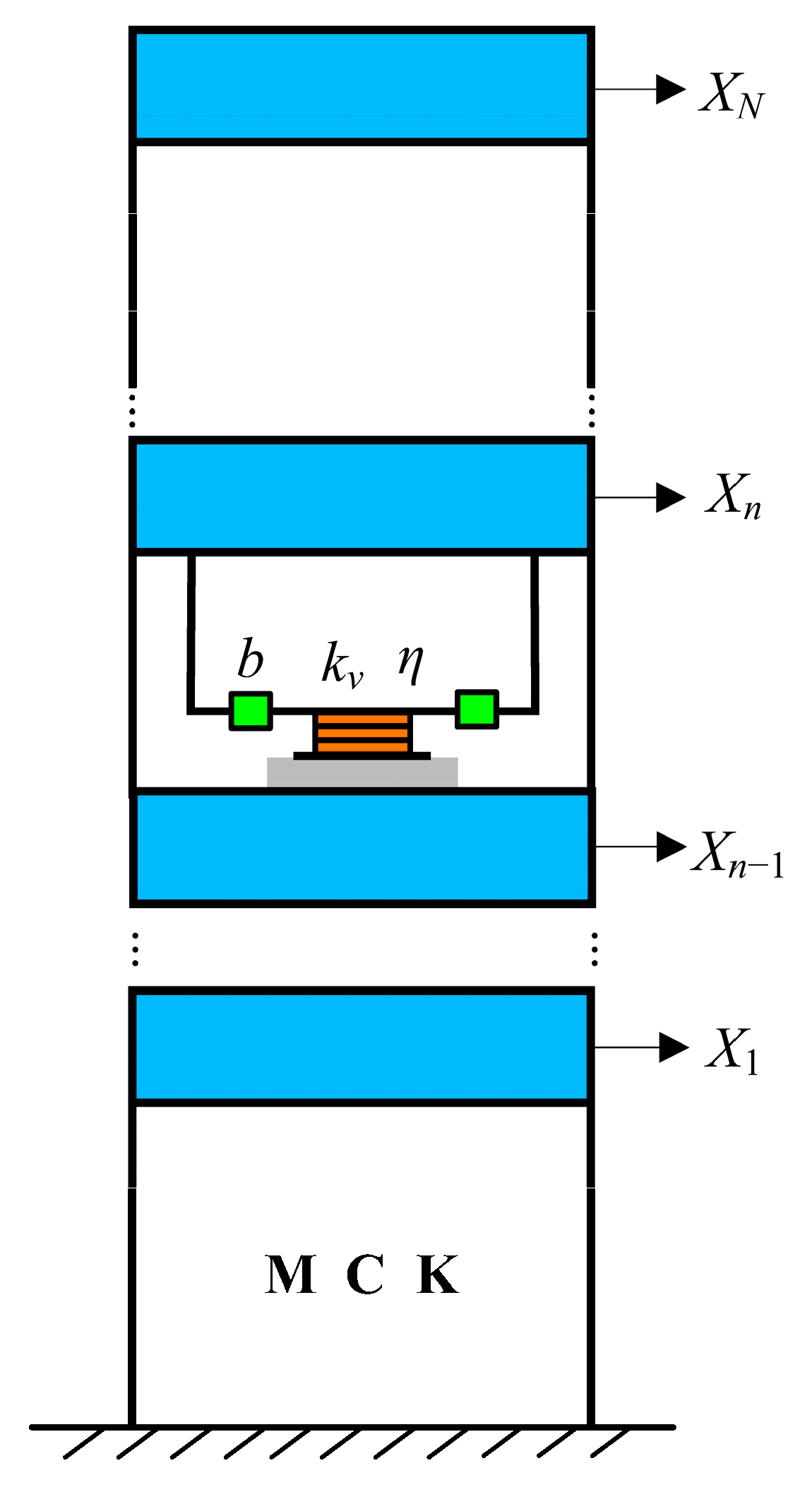
2. Problem Formulation
3. Optimal Design of VE TID
3.1. The Single-DOF Structure
3.2. The Multiple-DOF Structure
4. Validation of Optimal Solution
5. Numerical Examples
5.1. The Viscoelastically Damped Building with the VE TID
5.2. The Base-Isolated Building with the VE TID
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rana, R.; Soong, T.T. Parametric study and simplified design of tuned mass dampers. Eng. Struct. 1998, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konar, T.; Ghosh, A.D. Tuned mass damper inerter for seismic control of multi-story buildings: Ten years since inception. Structure 2024, 63, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, W. Experimental study on adaptive-passive tuned mass damper with variable stiffness for vertical human-induced vibration control. Eng. Struct. 2023, 280, 115714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sedaghati, R.; Esmailzadeh, E. Vibration suppression of structures using tuned mass damper technology: A state-of-the-art review. J. Vib. Control 2022, 28, 812–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xu, Z.D.; Gai, P.P. Parameter determination of the tuned mass damper mitigating the vortex-induced vibration in bridges. Eng. Struct. 2022, 221, 111084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, M.; Sensoy, S.; Uygar, E. Vibration control of midrise buildings by semi-active tuned mass damper including multi-layered soil-pile-structure-interaction. Structures 2022, 43, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xu, Z.D.; Dyke, S.J. Robust control of vortex-induced vibration in flexible bridges using an active tuned mass damper. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2022, 29, e2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Bi, K.; Hao, H. Inerter-based structural vibration control: A state-of-the-art review. Eng. Struct. 2021, 243, 112655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikago, K.; Saito, K.; Inoue, N. Seismic control of single-degree-of-freedom structure using tuned viscous mass damper. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2012, 41, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, I.F.; Neild, S.A.; Wagg, D.J. Vibration suppression of cables using tuned inerter dampers. Eng. Struct. 2016, 122, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bi, K.; Hao, H. Development of a novel tuned negative stiffness inerter damper for seismic induced structural vibration control. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 70, 106341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, L.; Giaralis, A. Optimal design of a novel tuned mass-damper–inerter (TMDI) passive vibration control configuration for stochastically support-excited structural systems. Probabilistic Eng. Mech. 2014, 38, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerouni, S.; Elias, S.; Abdeddaim, M.; Rupakhety, R. Optimal design and performance assessment of multiple tuned mass damper inerters to mitigate seismic pounding of adjacent buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 103994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, P. A novel tuned mass damper inerter: Optimal design, effectiveness comparison, and robustness investigation. Structures 2023, 55, 1262–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Hua, X. Design and evaluation of tuned inerter-based dampers for the seismic control of MDOF structures. J. Struct. Eng. 2017, 143, 04016207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhao, Z.; Pan, C.; Ikago, K.; Xue, S. Damping enhancement principle of inerter system. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2020, 27, e2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, N.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, C.; Xia, Y.; Bian, J. Concise analytical solutions to negative-stiffness inerter-based DVAs for seismic and wind hazards considering multi-target responses. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 53, 3820–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Gai, P.P.; Xu, Z.D.; Huang, X.H. Inerter location effect on the generalized tuned mass damper inerter control. Structures 2023, 58, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deastra, P.; Wagg, D.; Sims, N.; Akbar, M. Tuned inerter dampers with linear hysteretic damping. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 49, 1216–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.; Xu, Z.D.; Wang, F.; Gai, P.P.; Gomez, D.; Dyke, S.J. Development and validation of a nonlinear model to describe the tension–compression behavior of rubber-like base isolators. J. Eng. Mech. 2023, 149, 04022104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, P.P.; Xu, Z.D.; Guo, Y.Q.; Dai, J. Gradient chain structure model for characterizing frequency dependence of viscoelastic materials. J. Eng. Mech. 2020, 146, 04020094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikago, K.; Sugimura, Y.; Saito, K.; Inoue, N. Modal response characteristics of a multiple-degree-of-freedom structure incorporated with tuned viscous mass dampers. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2012, 11, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tan, P.; Hao, L.; Xu, K.; Xiang, Y. Optimal design of tuned viscous mass damper for acceleration response control of civil structures under seismic excitations. Eng. Struct. 2022, 252, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Impollonia, N.; Ricciardi, G. Soil-dependent optimum design of a new passive vibration control system combining seismic base isolation with tuned inerter damper. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 105, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, L.; Giaralis, A. The tuned mass-damper-inerter for harmonic vibrations suppression, attached mass reduction, and energy harvesting. Smart Struct. Syst. 2017, 19, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, J.L.; Sun, F.F.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Du, X.L. Closed-form optimal solution of two-degree-of-freedom system with Inerter based on equal modal damping with potential application in non-structural elevator for seismic control. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 53, 4785–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xu, Z.D.; Gai, P.P.; Li, H.W. Effect of frequency dependence of large mass ratio viscoelastic tuned mass damper on seismic performance of structures. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 130, 105998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudinger, F. Tuned mass damper with fractional derivative damping. Eng. Struct. 2006, 28, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batou, A.; Adhikari, S. Optimal parameters of viscoelastic tuned-mass dampers. J. Sound. Vib. 2019, 445, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtori, Y.; Christenson, R.E.; Spencer, B.F., Jr.; Dyke, S.J. Benchmark control problems for seismically excited nonlinear buildings. J. Eng. Mech. 2004, 130, 366–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Variable | Minimum | Maximum | Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.1 | |
| 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Story | Mass (ton) | Stiffness (kN/m) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 700 | 279,960 |
| 2 | 682 | 383,550 |
| 3 | 680 | 383,020 |
| 4 | 676 | 328,260 |
| 5 | 670 | 306,160 |
| VE TID | VE Damper Installation | VE Damper Contribution | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1–5 floors | 8.69% | / | / | |
| A2 | 1–5 floors | 13.2% | / | / | |
| B1 | 2–5 floors | 5.32% | 1000 tons | 7.98% | |
| B2 | 2–5 floors | 5.32% | 2000 tons | 15.97% | |
| B3 | 2–5 floors | 6.94% | 1000 tons | 9.64% | |
| B4 | 2–5 floors | 6.94% | 2000 tons | 19.28% | |
| C1 | 1–5 floors | 8.69% | 1000 tons | 6.15% | |
| C2 | 1–5 floors | 8.69% | 2000 tons | 12.31% | |
| C3 | 1–5 floors | 13.2% | 1000 tons | 6.15% | |
| C4 | 1–5 floors | 13.2% | 2000 tons | 12.31% |
| VE TID | D1 | D2 | D3 | E1 | E2 | F1 | F2 | G1 | G2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.35% | 13.6% | 26.5% | 7.35% | 7.35% | 13.6% | 13.6% | 26.5% | 26.5% | |
| / | / | / | 1000 tons | 2000 tons | 1000 tons | 2000 tons | 1000 tons | 2000 tons | |
| / | / | / | 14.7% | 29.4% | 14.7% | 29.4% | 14.7% | 29.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gai, P.-P.; Dai, J.; Yang, Y.; Bi, Q.-S.; Guan, Q.-S.; Zhang, G.-Y. Performance Enhancement of Seismically Protected Buildings Using Viscoelastic Tuned Inerter Damper. Actuators 2025, 14, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14080360
Gai P-P, Dai J, Yang Y, Bi Q-S, Guan Q-S, Zhang G-Y. Performance Enhancement of Seismically Protected Buildings Using Viscoelastic Tuned Inerter Damper. Actuators. 2025; 14(8):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14080360
Chicago/Turabian StyleGai, Pan-Pan, Jun Dai, Yang Yang, Qin-Sheng Bi, Qing-Song Guan, and Gui-Yu Zhang. 2025. "Performance Enhancement of Seismically Protected Buildings Using Viscoelastic Tuned Inerter Damper" Actuators 14, no. 8: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14080360
APA StyleGai, P.-P., Dai, J., Yang, Y., Bi, Q.-S., Guan, Q.-S., & Zhang, G.-Y. (2025). Performance Enhancement of Seismically Protected Buildings Using Viscoelastic Tuned Inerter Damper. Actuators, 14(8), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14080360








