A Four-Chamber Multimodal Soft Actuator and Its Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
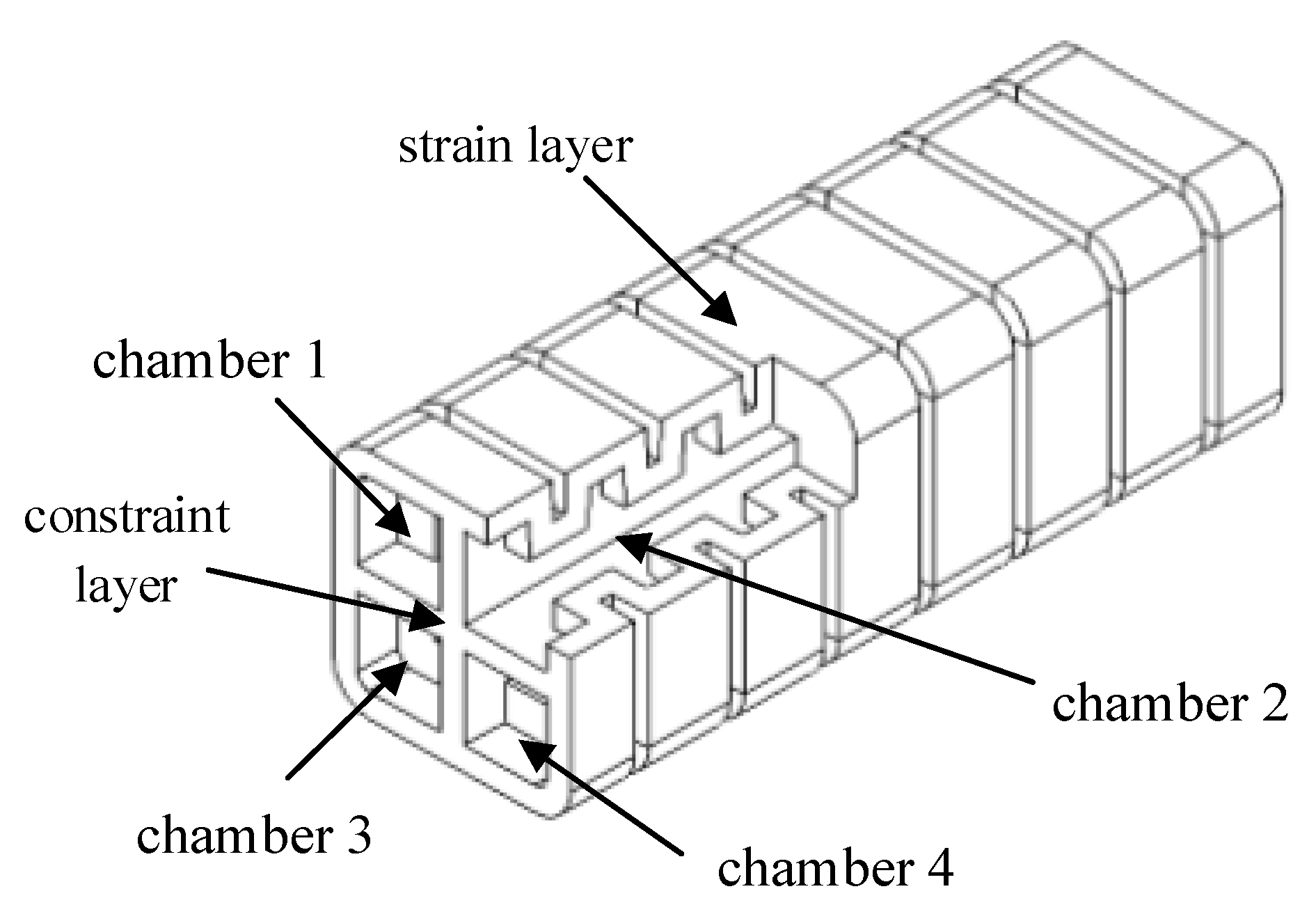
2. Design of Four-Chamber Multimodal Actuator
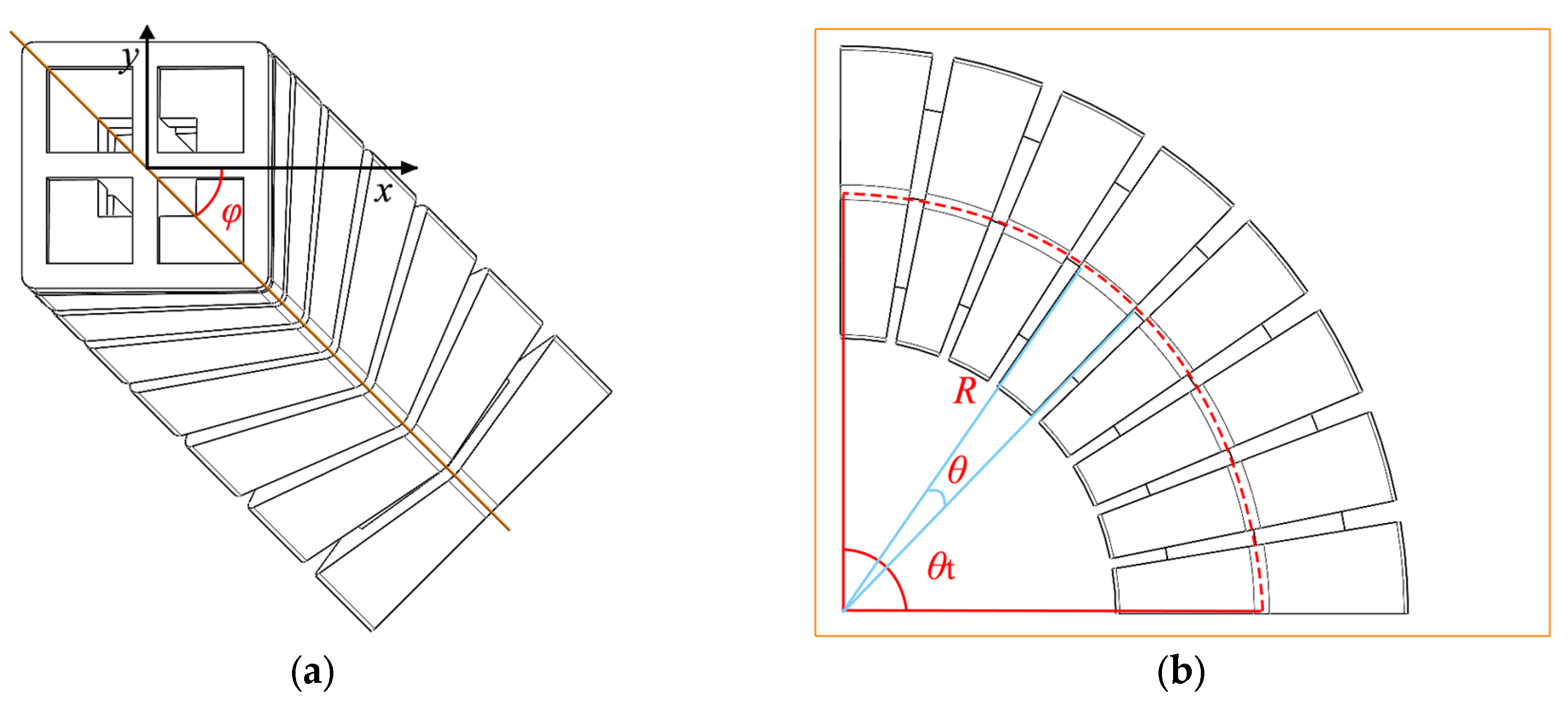
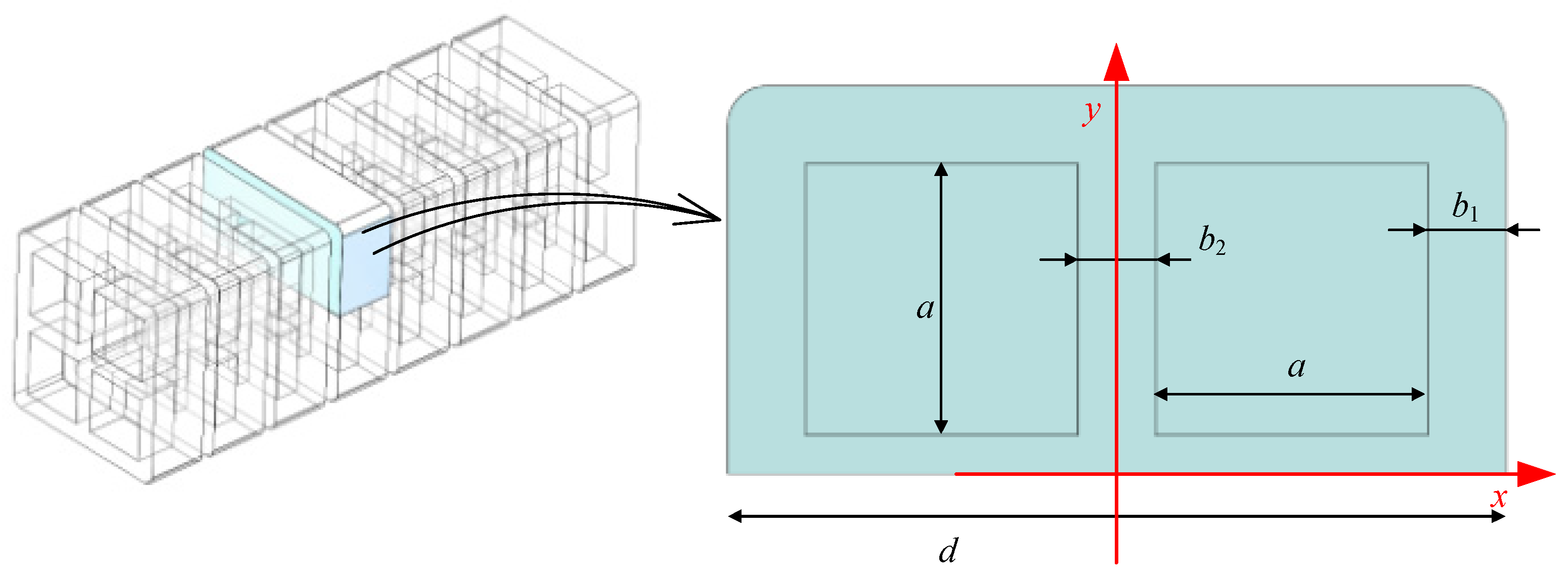
2.1. Structure
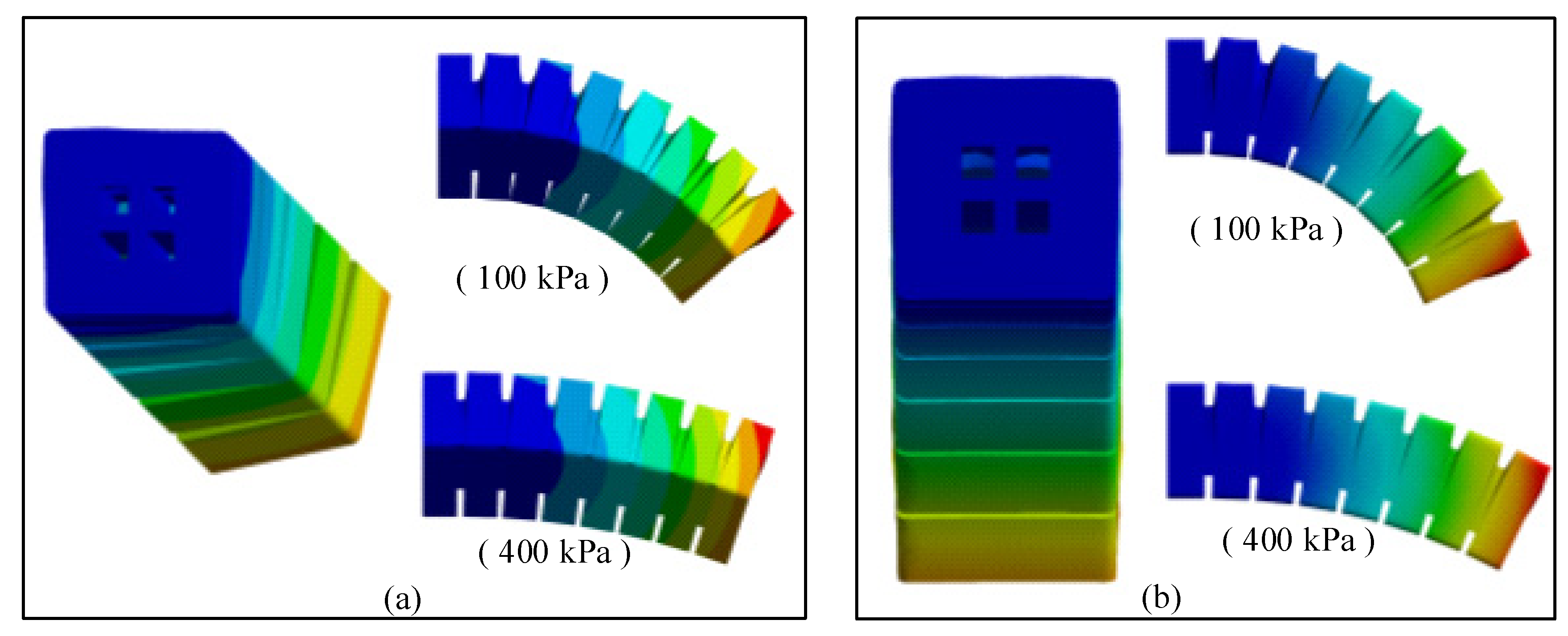
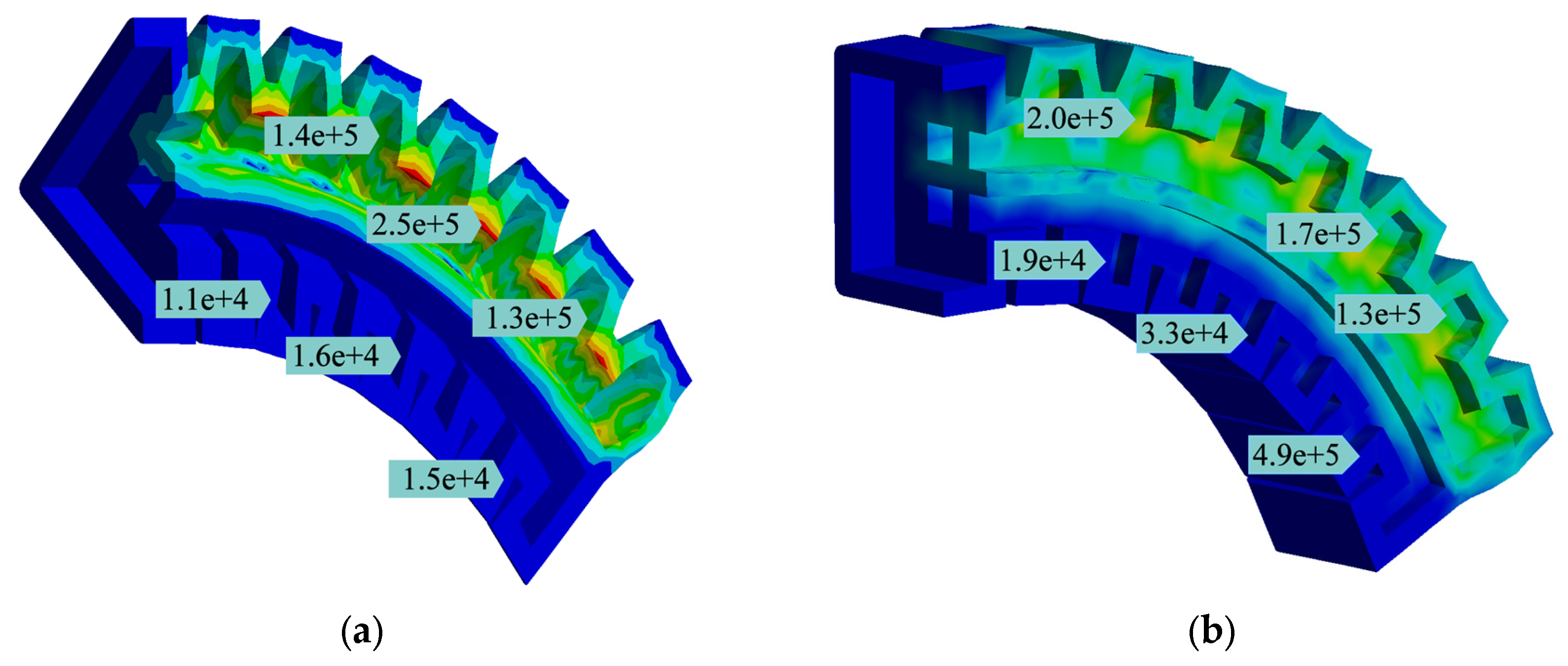
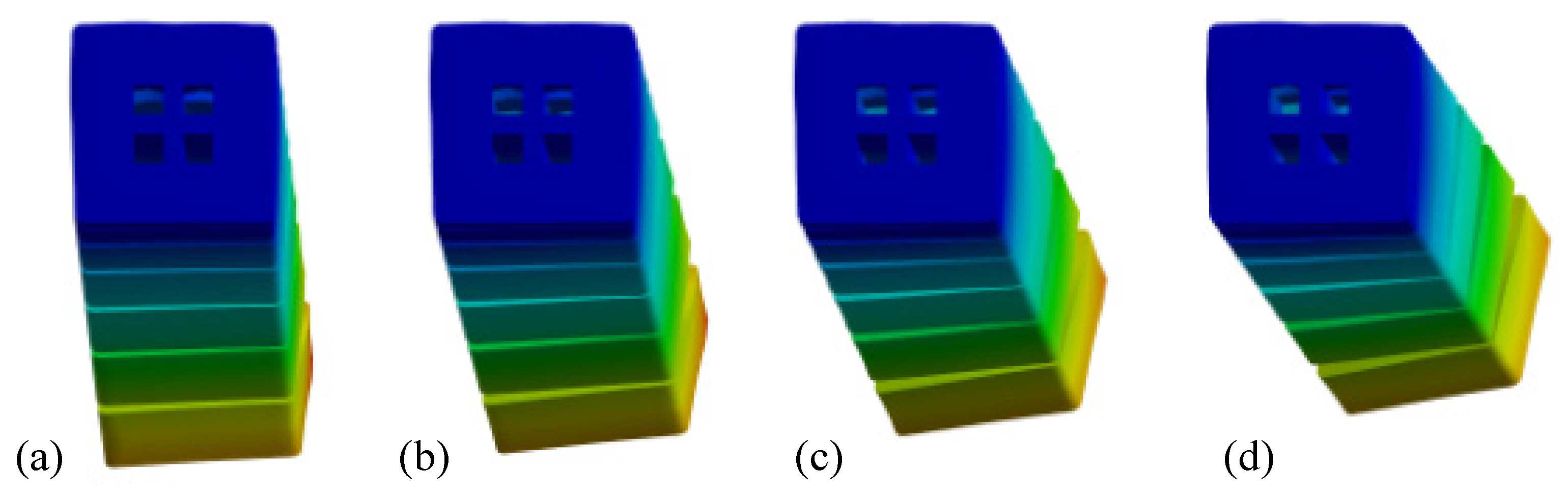
2.2. Finite-Element Analysis
3. Theoretical Model of Bending Deformation
- (1)
- Due to the presence of gaps between chambers, the compression deformation of non-inflated chambers during bending is negligible. Consequently, the silicone reaction force from these chambers will be neglected.
- (2)
- The bending deformation of the soft actuator is assumed to be unaffected by its own weight, and the silicone material is treated as incompressible.
- (3)
- The work performed by the internal air pressure within the chambers is entirely converted into stored potential energy of the actuator.
- (4)
- Throughout the deformation process of the soft actuator, the silicone body undergoes uniform deformation. Thus, the central angle corresponding to each PneuNet unit is considered to maintain an identical value. Therefore, the overall central angle of the soft actuator’s bending deformation can be regarded as the sum of the individual bending central angles of all PneuNet units. The overall angle can be expressed aswhere n denotes the effective PneuNet unit count; owing to the connector in the first unit, n = 7 is used for the present actuator.
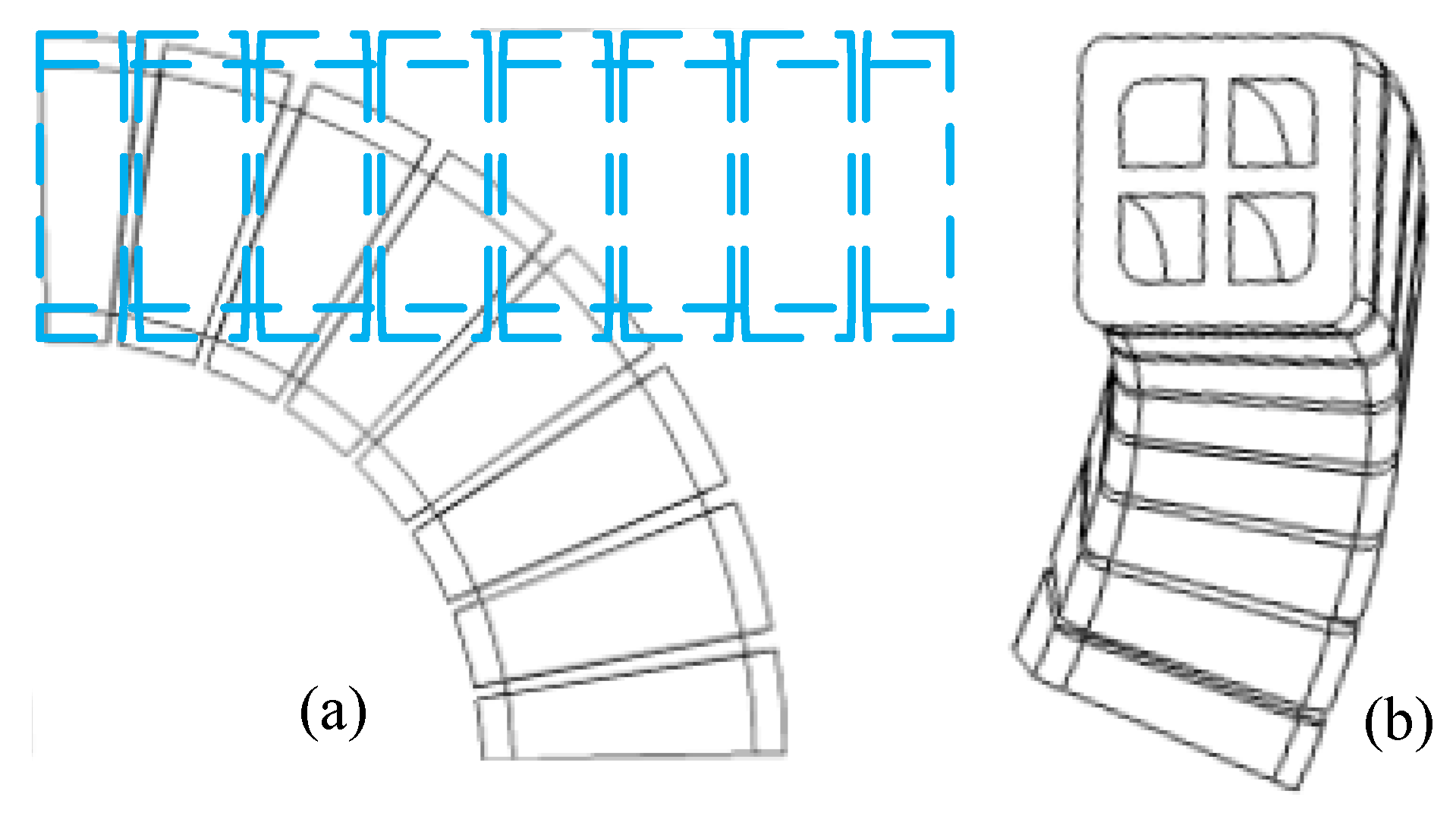
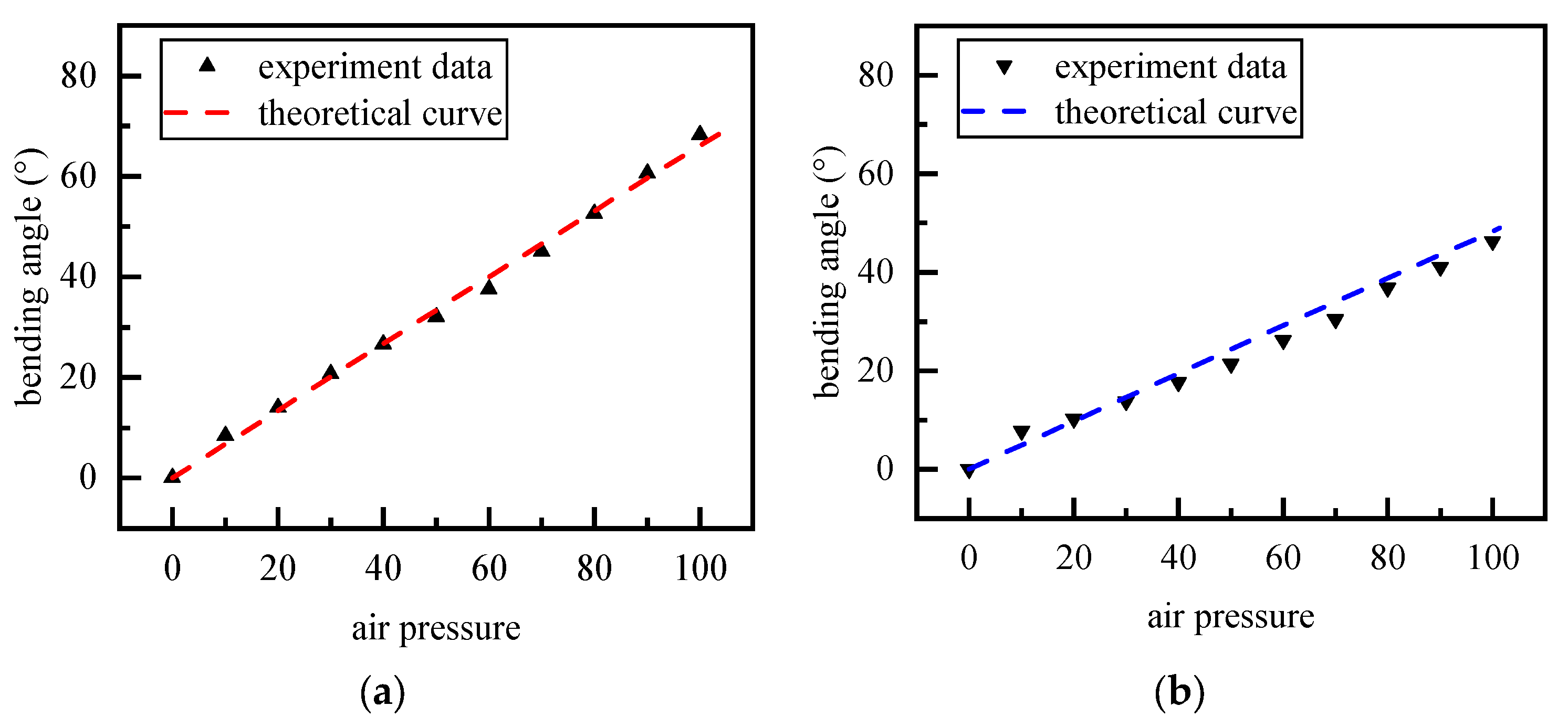
3.1. Bending with Two Adjacent Chambers Inflated
3.2. Bending with One Chamber Inflated
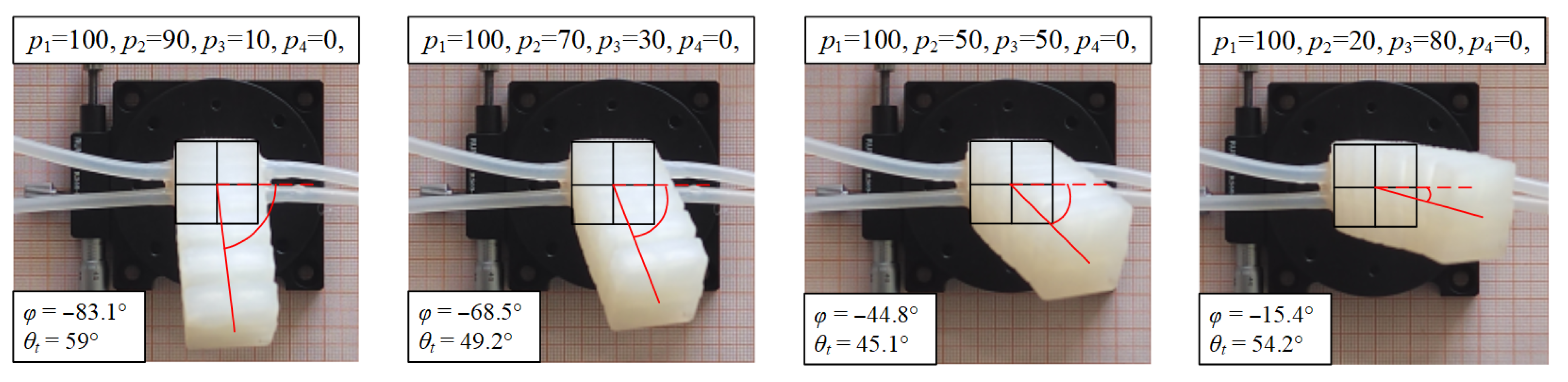
3.3. Empirical Derivation of Inflation Deformation in Any Chamber
4. Fabrication and Test of the Multimodal Actuator
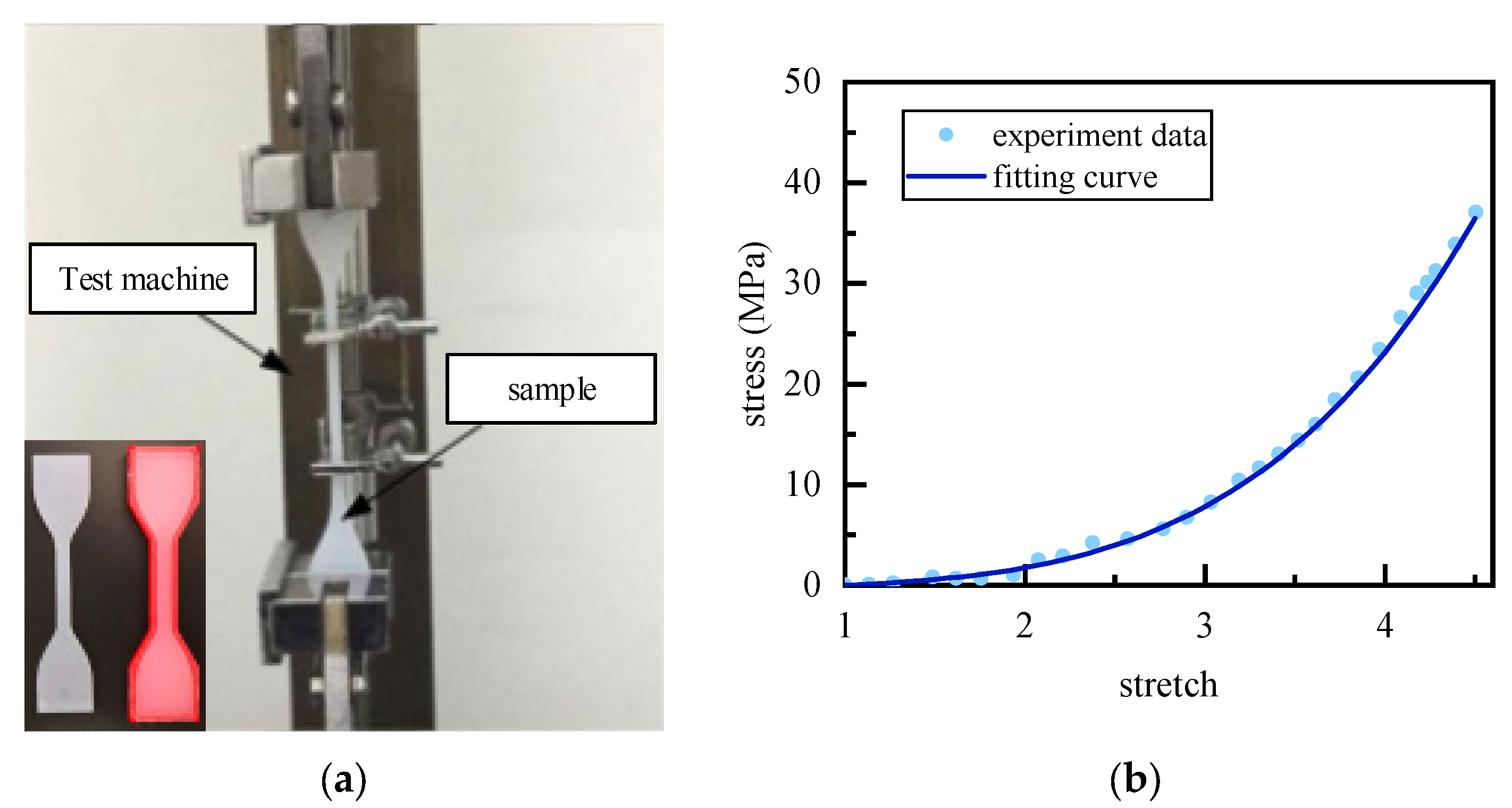
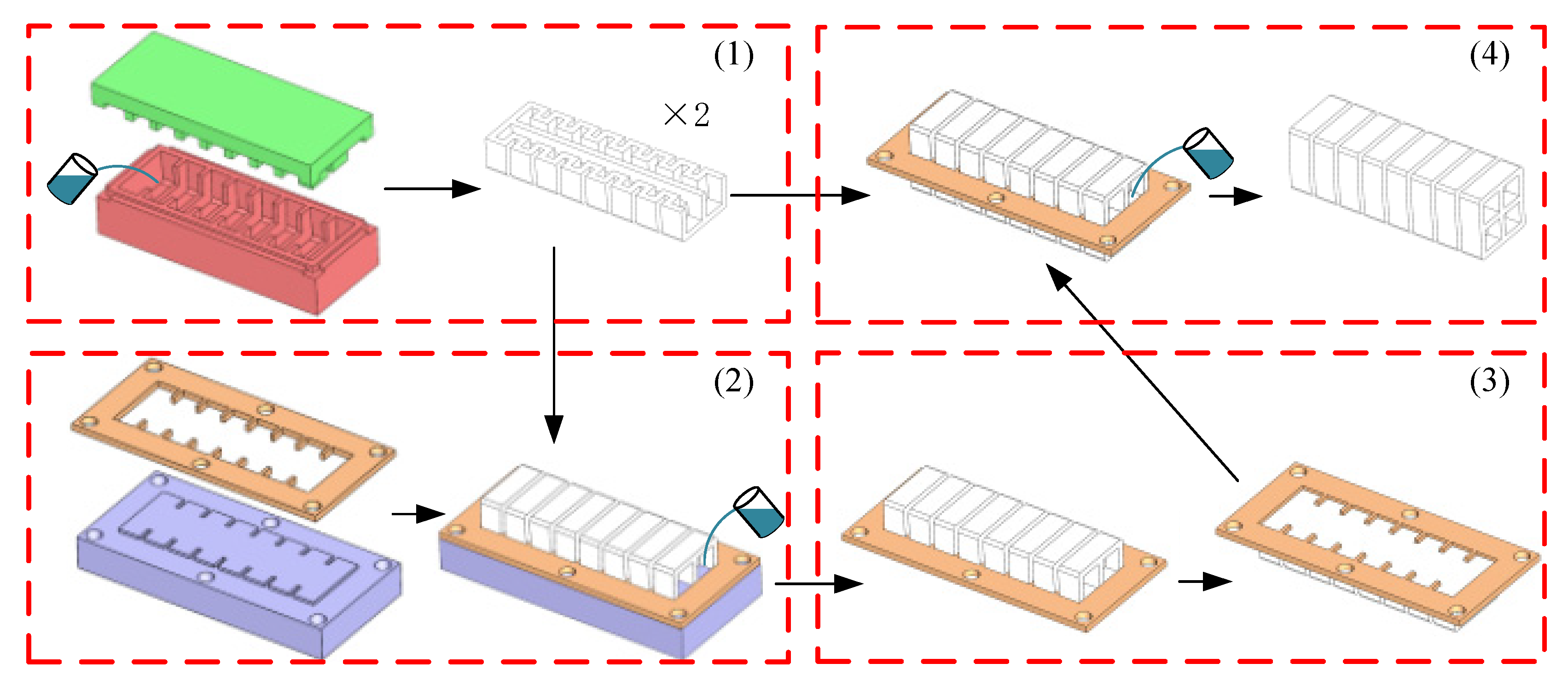
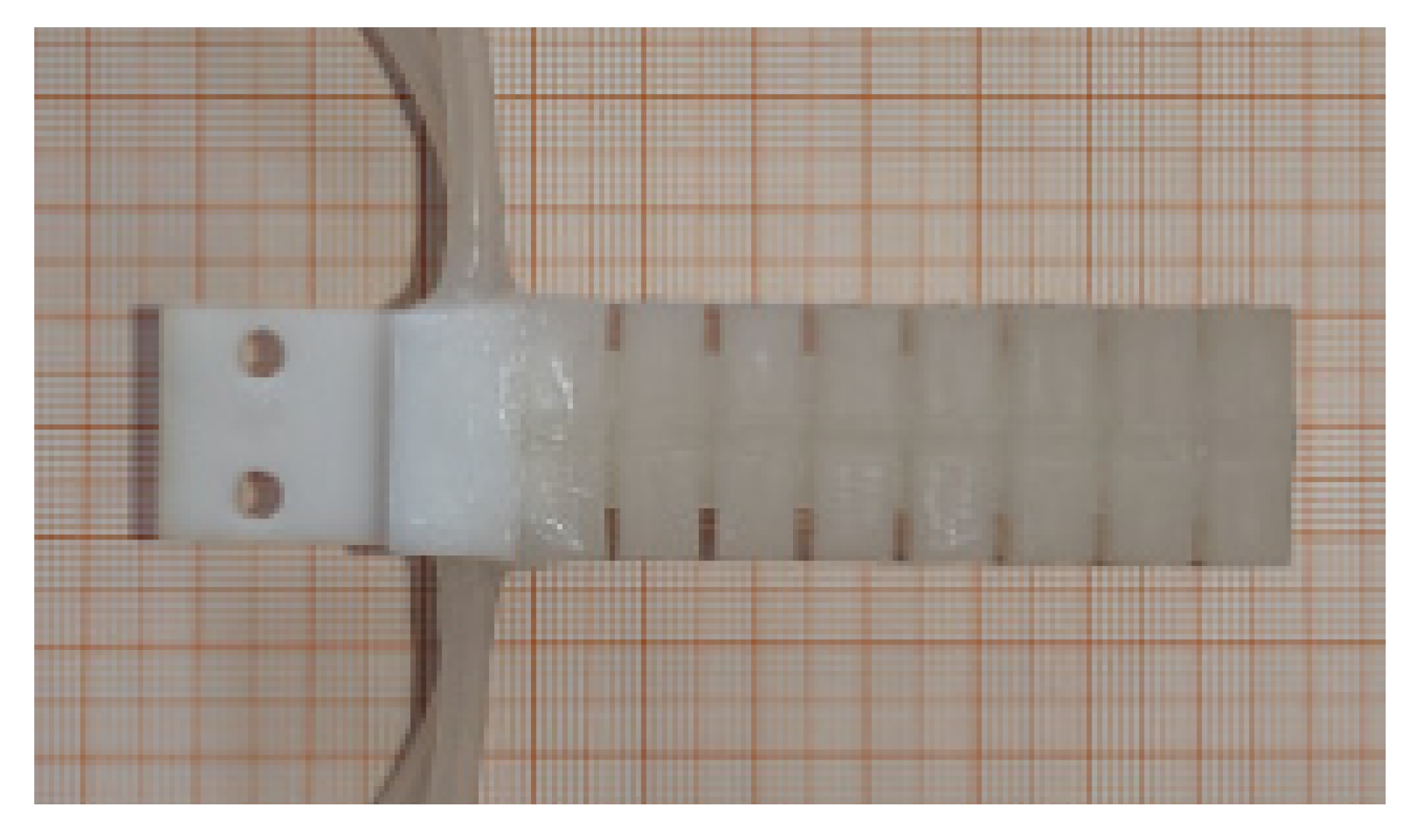
4.1. Fabrication
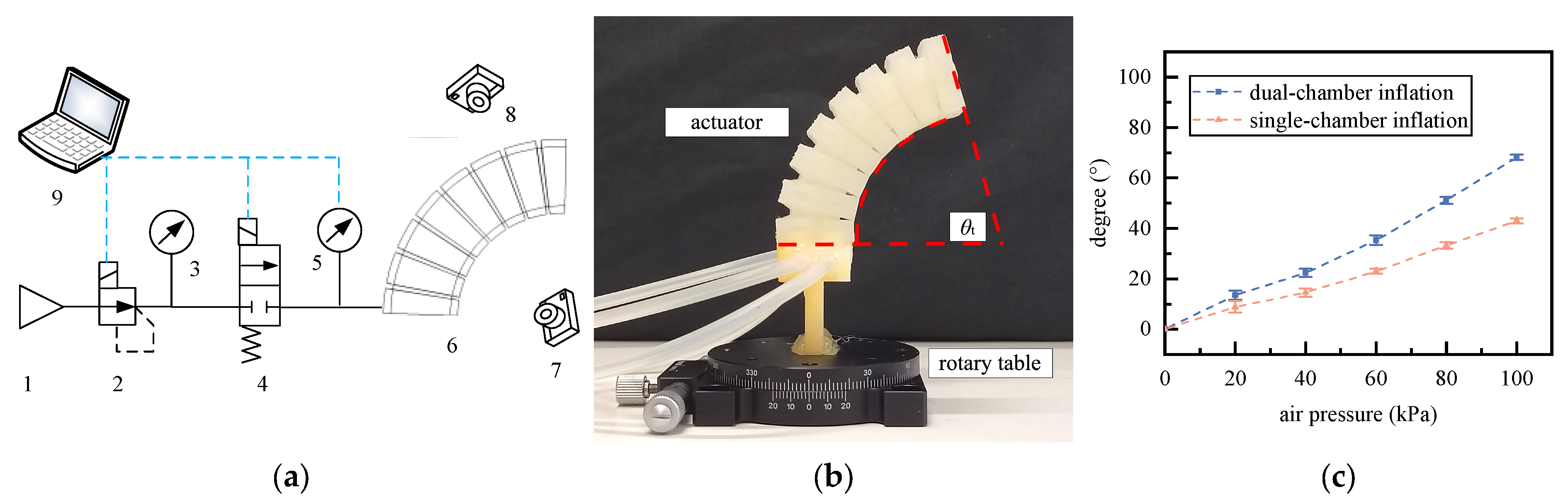
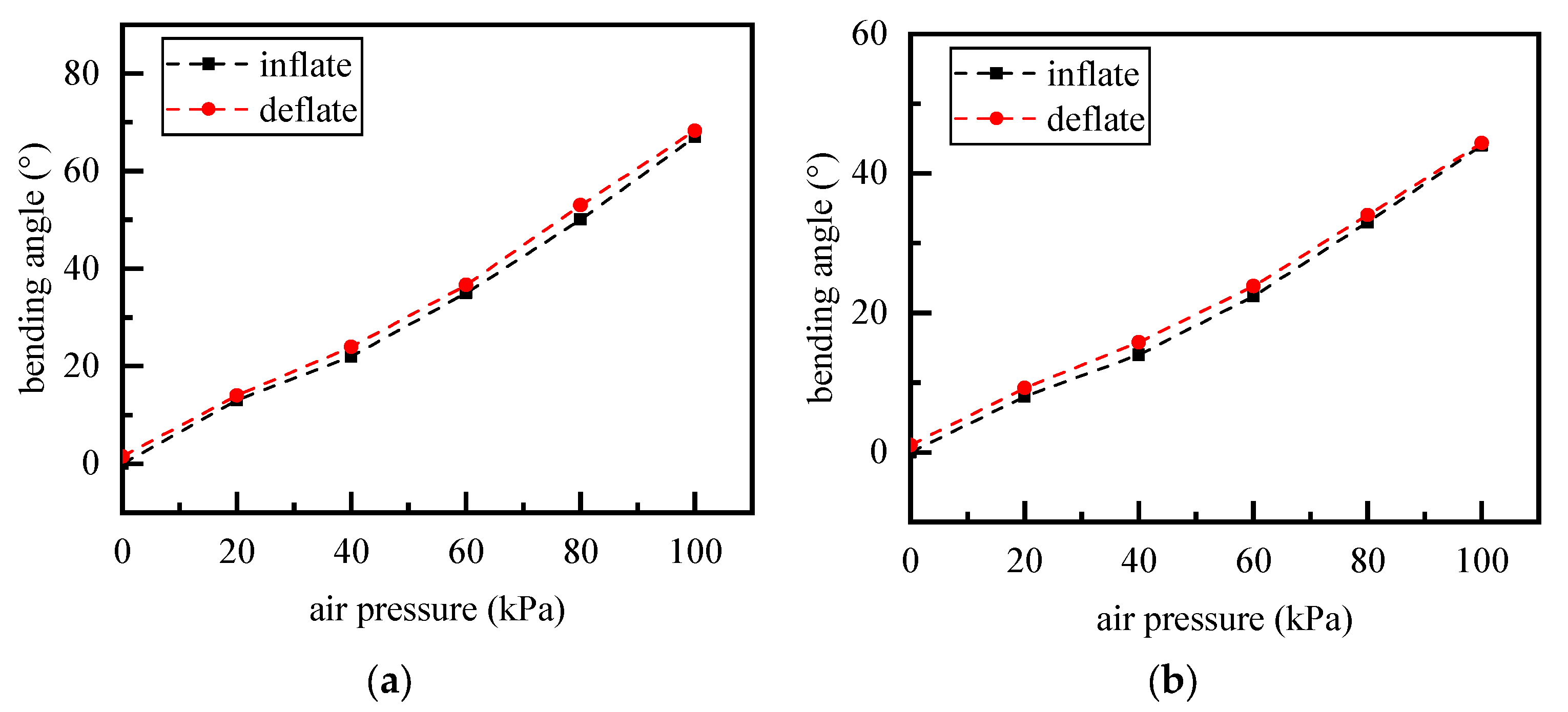
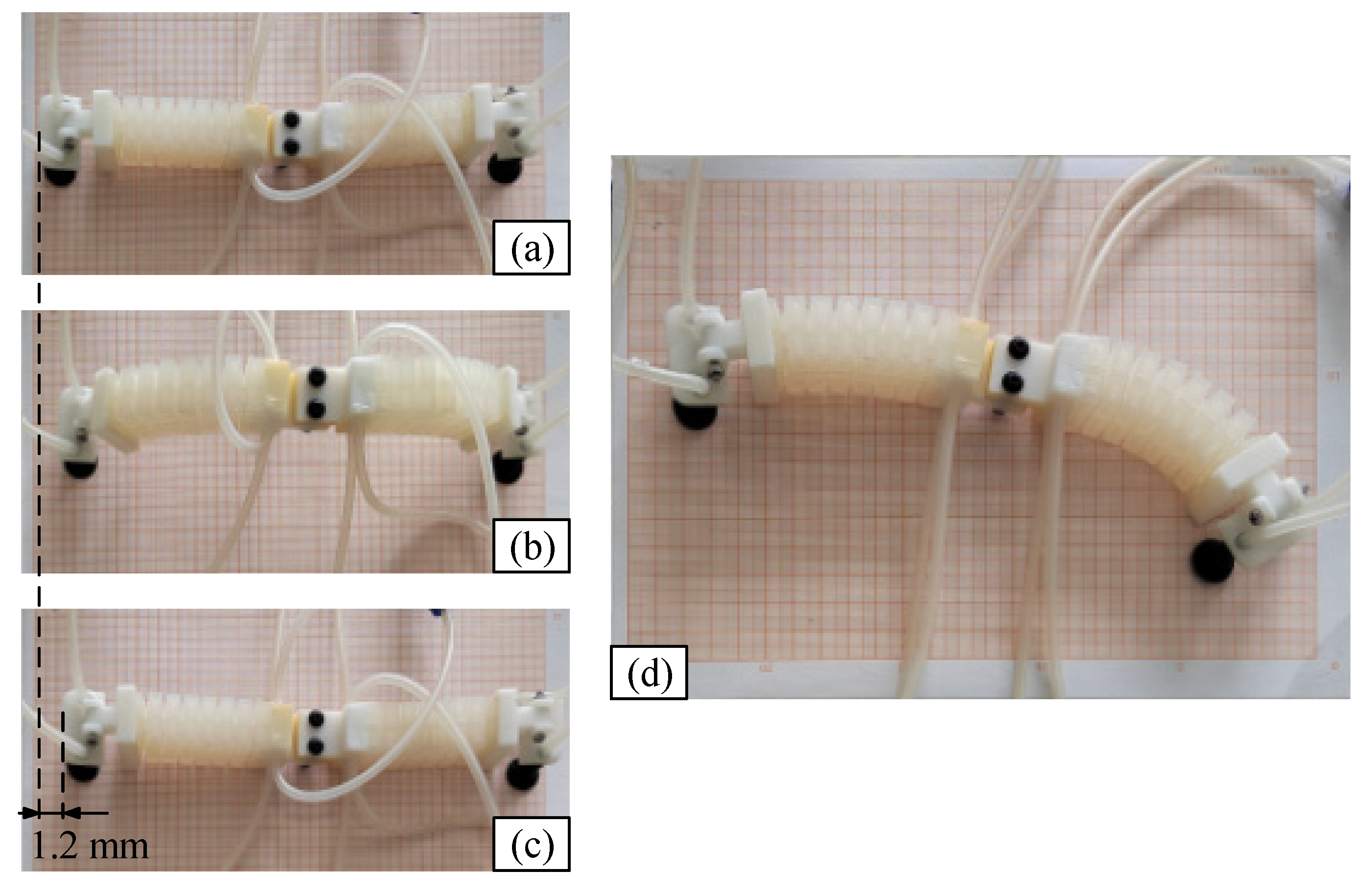
4.2. Static Characteristic Test
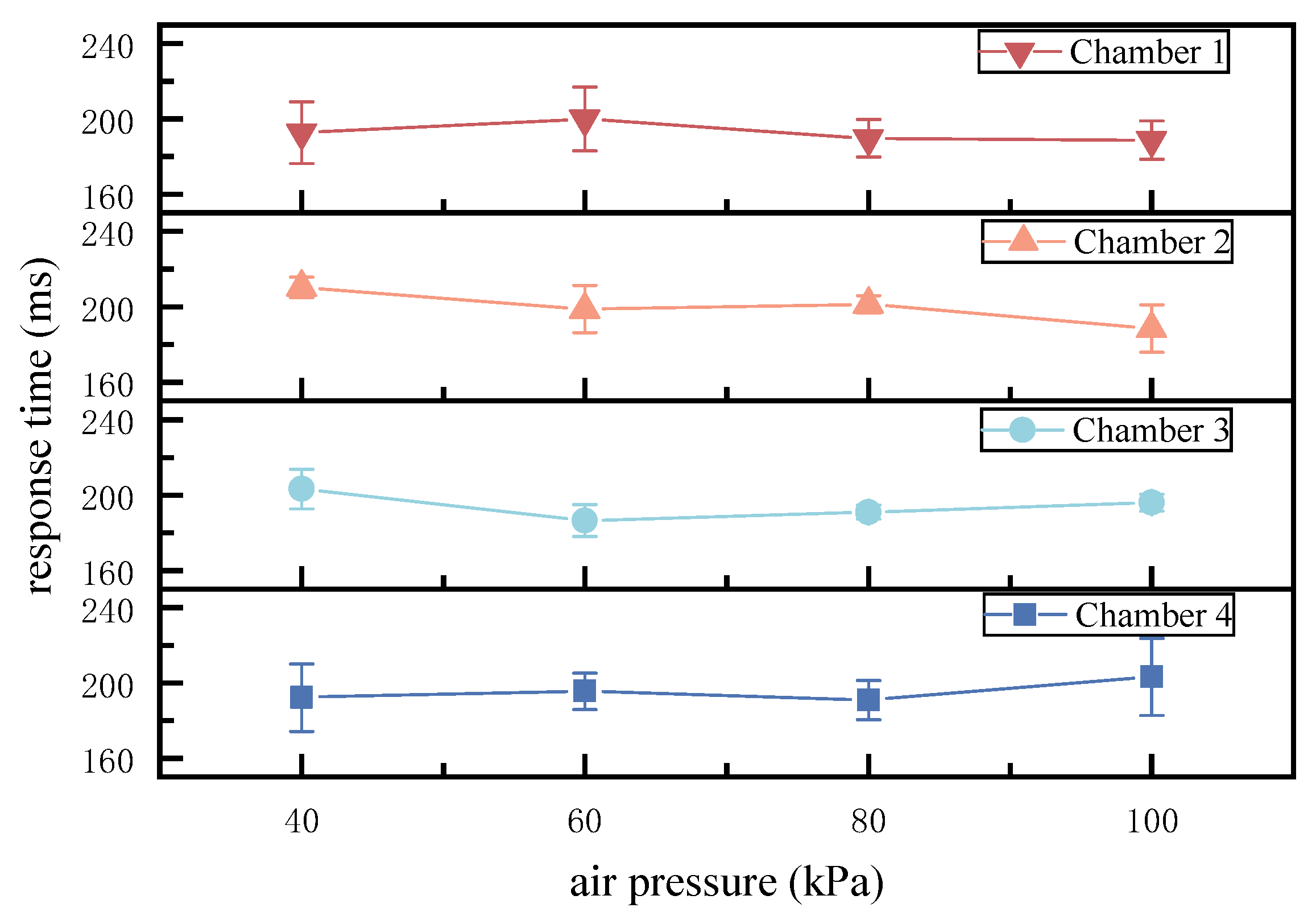
4.3. Dynamic Characteristic Test
5. Applications of the Multimodal Soft Actuator
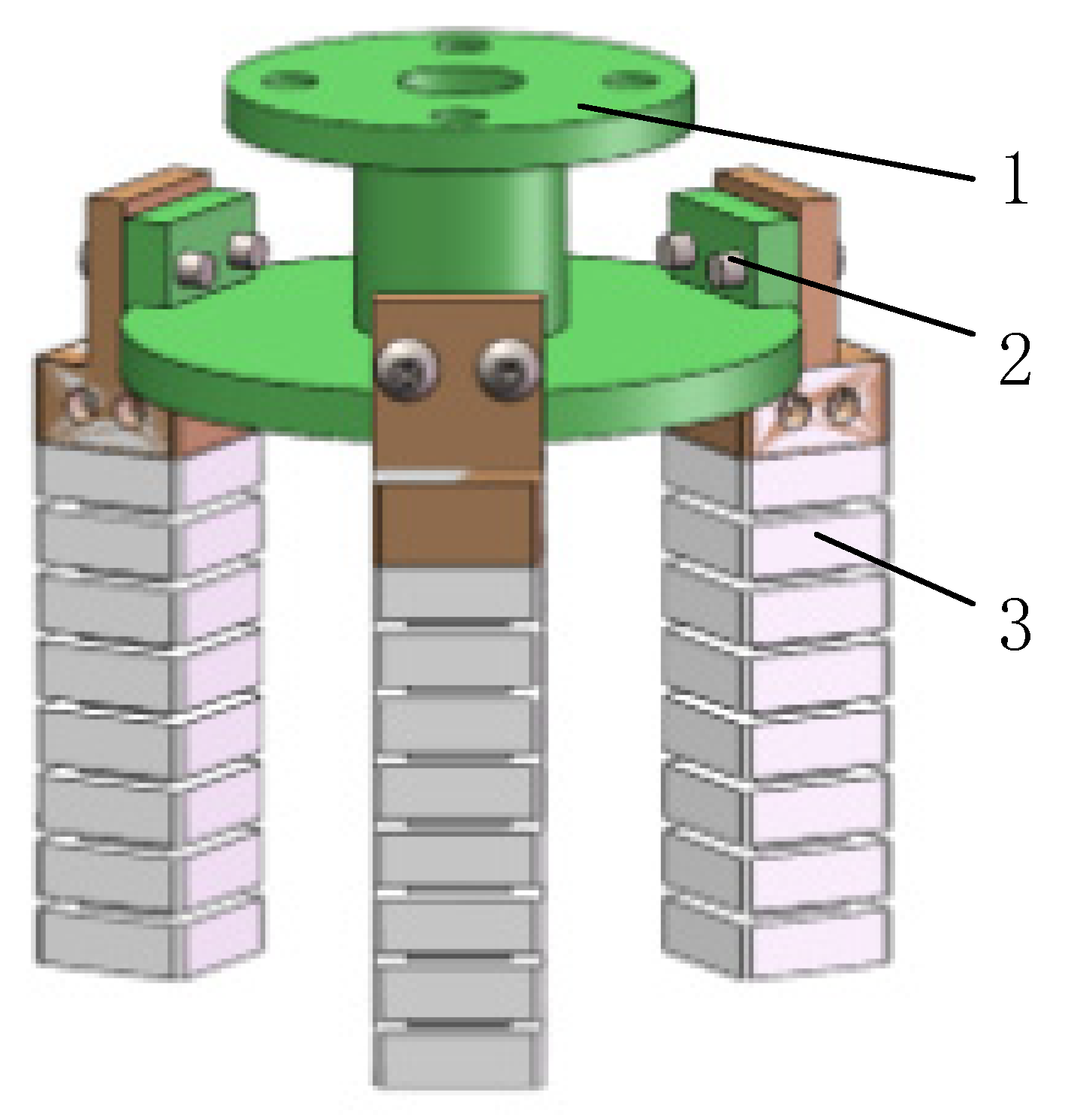
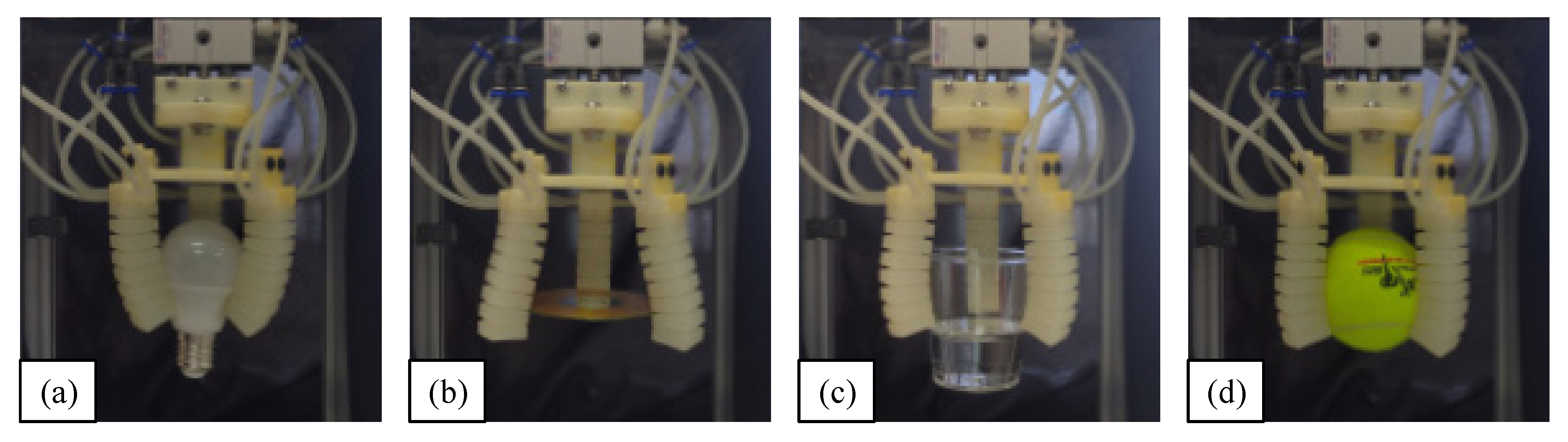
5.1. Soft-Gripper Application
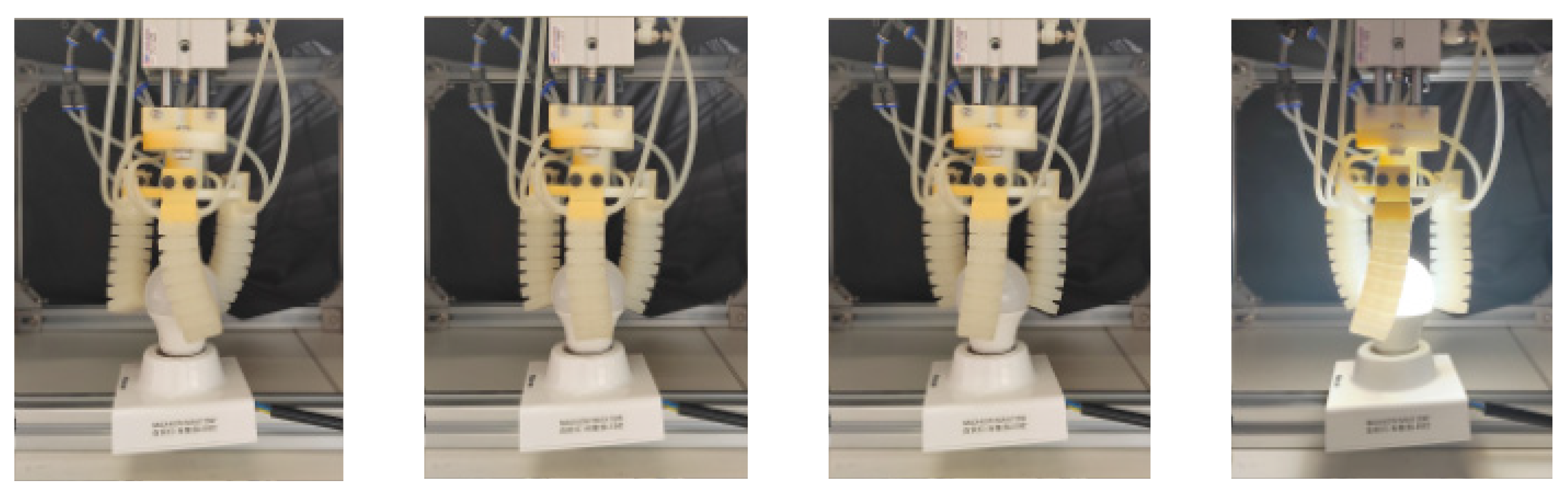
5.2. Soft-Robot Application
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
8. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Ren, L.; Chen, Y.; Niu, S.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Bio-Inspired Soft Grippers Based on Impactive Gripping. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-P.; Romario, Y.S.; Bhat, C.; Hentihu, M.F.R.; Zeng, X.-C.; Ramezani, M. Design and fabrication of multi-material pneumatic soft gripper using newly developed high-speed multi-material vat photopoly-merization 3D printer. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, F.; Frohn-Sörensen, P.; Engel, B.; Manns, M. Applicability of models to predict the bending behavior of soft pneumatic grippers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 138, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, T.; Pang, M.; Yang, X.; Qi, Y.; Xia, L.; Qian, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, L.; et al. Research progress in fluid actuation technology of soft robot. Chin. J. Nat. 2023, 45, 217–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, S.; Zhang, D.; Shi, M.; Dai, W.; Wang, S. Design and Basic Performance Analysis of a Bionic Finger Soft Actuator with a Dual-Chamber Composite Structure. Actuators 2025, 14, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ji, C.; Dou, M.; Wang, X. Bio-G inspired Design and Research on Light Ductile Soft Grippers. China Mech. Eng. 2023, 34, 595–602. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ilievski, F.; Mazze, A.D.; Shepherd, R.F.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Robotics for Chemists. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherda, R.F.; Ilievskia, F.; Choi, W.; Morin, S.A.; Stokes, A.A.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Multigait soft robot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20400–20403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Li, X. A Soft Robotic Tongue—Mechatronic Design and Surface Reconstruction. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosadegh, B.; Polygerinos, P.; Polygerinos, P.; Keplinger, C.; Wennstedt, S.; Shepherd, R.F.; Gupta, U.; Shim, J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J.; et al. Pneumatic Networks for Soft Robotics that Actuate Rapidly. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2163–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Mei, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, G.; He, L.; Wang, Y. A finger-inspired pneumatic network actuator based on rigid-flexible coupling structure for soft robotic grippers. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2024, 17, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, S.; Mathias, K.A.; Kim, T.-W. 3D-Printed soft pneumatic actuators: Enhancing flexible gripper capabilities. ROBOMECH J. 2025, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y. Passive Particle Jamming and Its Stiffening of Soft Robotic Grippers. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.M. A novel approach to enhancing smart stiffness of soft robotic gripper fingers for wider grasping capability. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2025, 9, 553–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, J.; Zhou, P.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y. High-force soft pneumatic actuators based on novel casting method for robotic applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 306, 111957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.J.; Baek, S.G.; Oh, D.J.; Beak, J.M.; Koo, J.C. ILC-driven control enhancement for integrated MIMO soft robotic system. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2024, 17, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Guo, Z. A Novel Pneumatic Soft Gripper with a Jointed Endoskeleton Structure. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. A Bioinspired Stress-Response Strategy for High-Speed Soft Grippers. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Su, J.; Liu, J.; Cao, C.; Yuan, H. A minimally designed soft crawling robot for robust locomotion in unstructured pipes. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2022, 17, 056001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Goswami, D.; Martinez, R.V. Elastic Energy Storage Enables Rapid and Programmable Actuation in Soft Machines. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1906603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Domel, A.G.; An, N.; Green, C.; Gong, Z.; Wang, T.; Knubben, E.M.; Weaver, J.C.; Bertoldi, K.; Wen, L. Octopus Arm-Inspired Tapered Soft Actuators with Suckers for Improved Grasping. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, K.; Qian, M. An Octopus-Inspired Bionic Flexible Gripper for Apple Grasping. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Pei, C.; Jin, Z.; Sun, Y. Design and Grasping Force Modeling for a Soft Robotic Gripper with Multi-stem Twining. J. Bionic Eng. 2023, 20, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. Design and Motion Analysis of a Wheel-walking Bionic Soft Robot. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 55, 27–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.-Q.; Li, W.-H.; Li, J.-H.; Zhou, H.-L.; Deng, Z.-C. Tuning stiffness with granular chain structures for versatile soft robots. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, J.; Hu, W.; Huang, H.; Zhou, F. Multimodal Soft Robot for Complex Environments Using Bionic Omnidirectional Bending Actuator. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 193827–193844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.; Yang, P.; Cao, T.; Liao, H. Worm-Like Soft Robot for Complicated Tubular Environments. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Liang, C. Modeling and Experimental Study of Multichambered Composite. J. Tianjin Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2025, 58, 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Drotman, D.; Jadhav, S.; Karimi, M.; de Zonia, P.; Tolley, M.T. 3D Printed Soft Actuators for a Legged Robot Capable of Navigating Unstructured Terrain. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mustaza, S.M.; Elsayed, Y.; Lekakou, C.; Saaj, C.; Fras, J. Dynamic Modeling of Fiber-Reinforced Soft Manipulator: A Visco-Hyperelastic Material-Based Continuum Mechanics Approach. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marechal, L.; Balland, P.; Lindenroth, L.; Petrou, F.; Kontovounisios, C.; Bello, F. Toward a common framework and database of materials for soft robotics. Soft Robot. 2021, 8, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Actuator | Number of Chambers | Workspace | Fabrication Simplicity | Key Feature/Application | Control Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shepherd [8] | 5 chambers | Planar Bending | Complex | Multi-gait locomotion, connected in series, | Medium (Sequential) |
| Yu [11] | 2 chambers | Planar Bending | Simple | Multi segment bending; connected in series, | Low |
| Drotman [29] | 3 independent actuators in parallel | Omnidirectional bending | Simple | Large volume, small curvature, connected in parallel | High (Parallel Control) |
| Mustaza [30] | 3 chambers | Omnidirectional bending | Medium | Fiber-reinforced, large volume, small curvature | High (Fiber Coupling) |
| Huang [26] | 4 chambers | Omnidirectional bending | Complex | Strip-shaped without gaps, crawling robot | Medium (No Gaps) |
| This work | 4 chambers | Omnidirectional bending | Medium | Gaps between PneuNet, gripper and crawling robot | Low |
| Symbol | Description | Value (mm) | Symbol | Description | Value (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | Length of chamber | 7 | b3 | Depth of gap | 4 |
| b1 | Thickness of strain layer | 2 | e2 | Width of chamber | 2.5 |
| b2 | Thickness of constraint layer | 2 | L | Length | 62.5 |
| e1 | Width of gap | 1.5 | d | Width | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Zhu, H.; Chen, G.; Cao, J.; Yuan, J.; Wu, K. A Four-Chamber Multimodal Soft Actuator and Its Application. Actuators 2025, 14, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14120602
Yang J, Zhu H, Chen G, Cao J, Yuan J, Wu K. A Four-Chamber Multimodal Soft Actuator and Its Application. Actuators. 2025; 14(12):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14120602
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jiabin, Helei Zhu, Gang Chen, Jianbo Cao, Jiwei Yuan, and Kaiwei Wu. 2025. "A Four-Chamber Multimodal Soft Actuator and Its Application" Actuators 14, no. 12: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14120602
APA StyleYang, J., Zhu, H., Chen, G., Cao, J., Yuan, J., & Wu, K. (2025). A Four-Chamber Multimodal Soft Actuator and Its Application. Actuators, 14(12), 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14120602






