Design and Analysis of a High-Speed Slotless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering Air-Gap Airflow
Abstract
1. Introduction
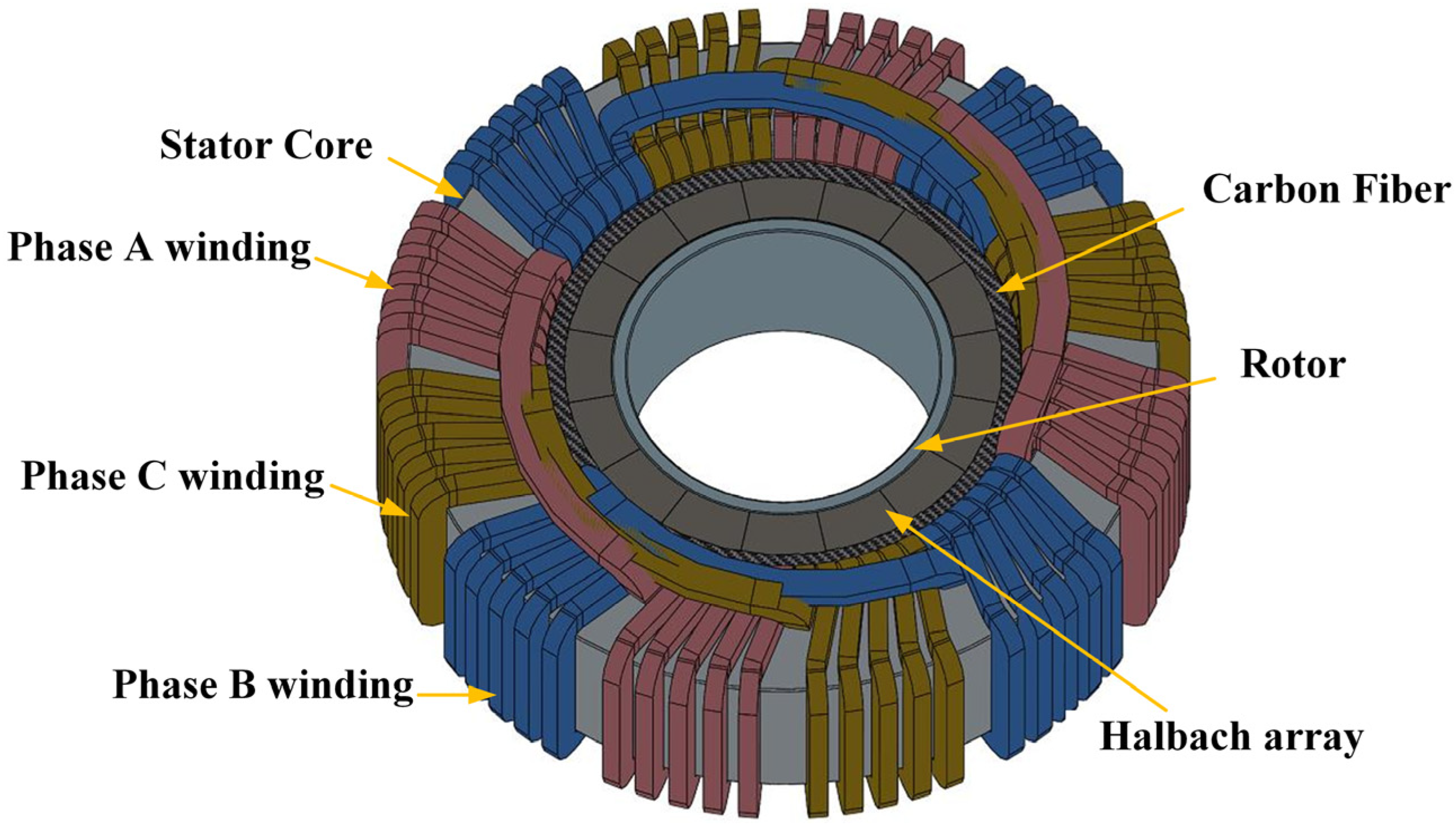
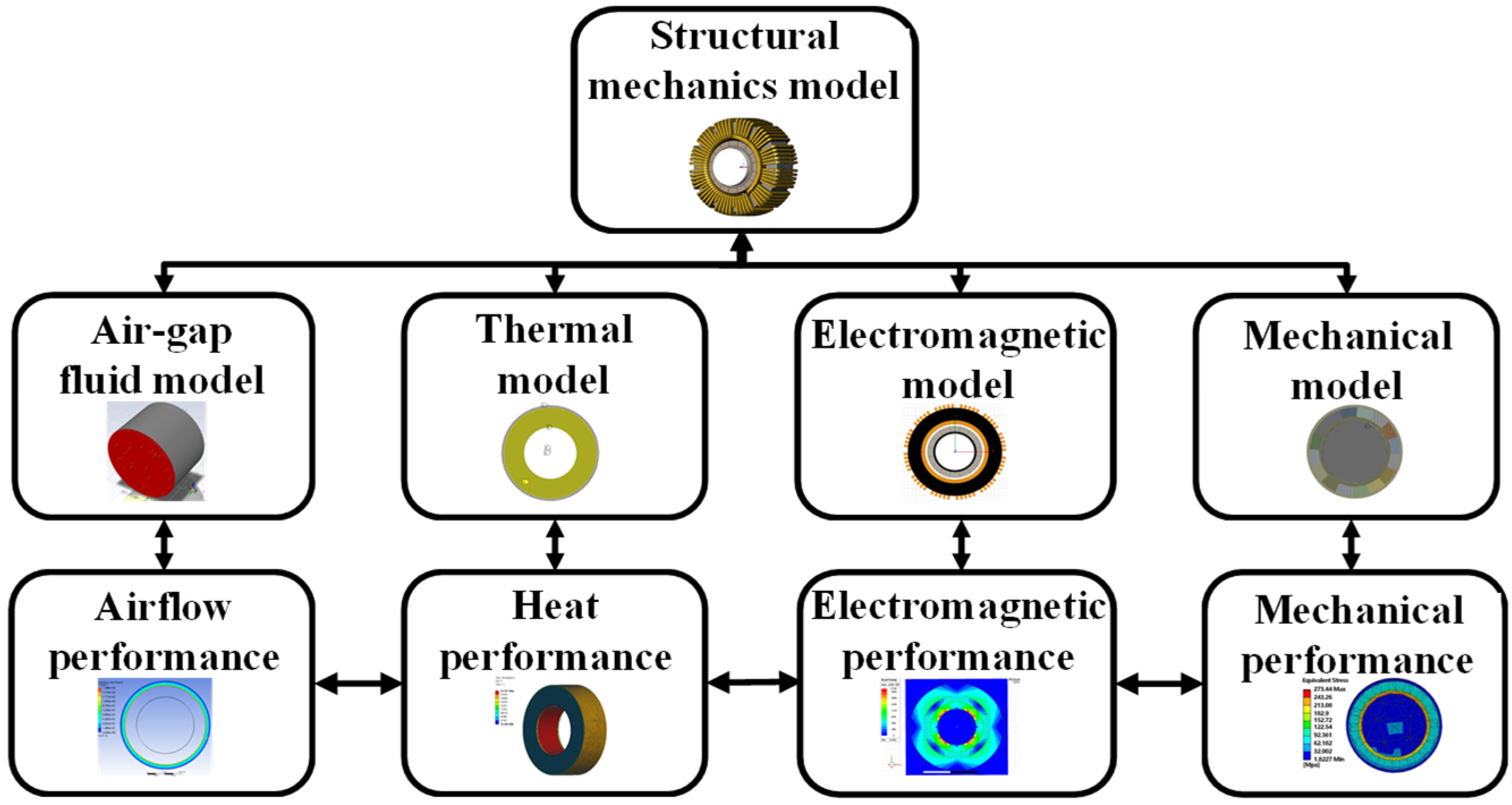
2. Multi-Physical Field in HSSPMSM
3. Multi-Physical Design and Analysis of the HSSPMSM Considering Air-Gap Airflow
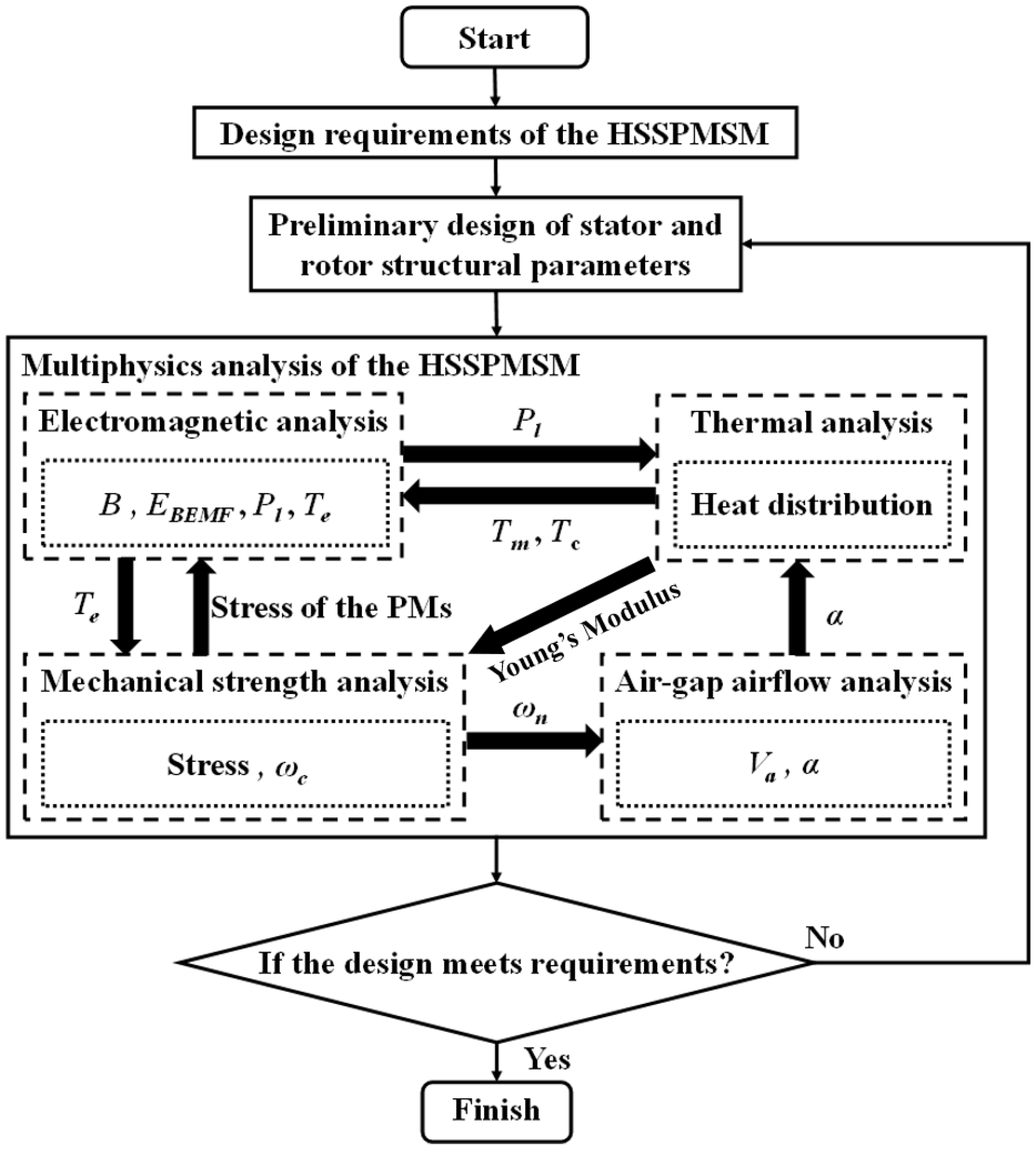
3.1. Motor Design Process
3.2. Initial Dimensions Determination
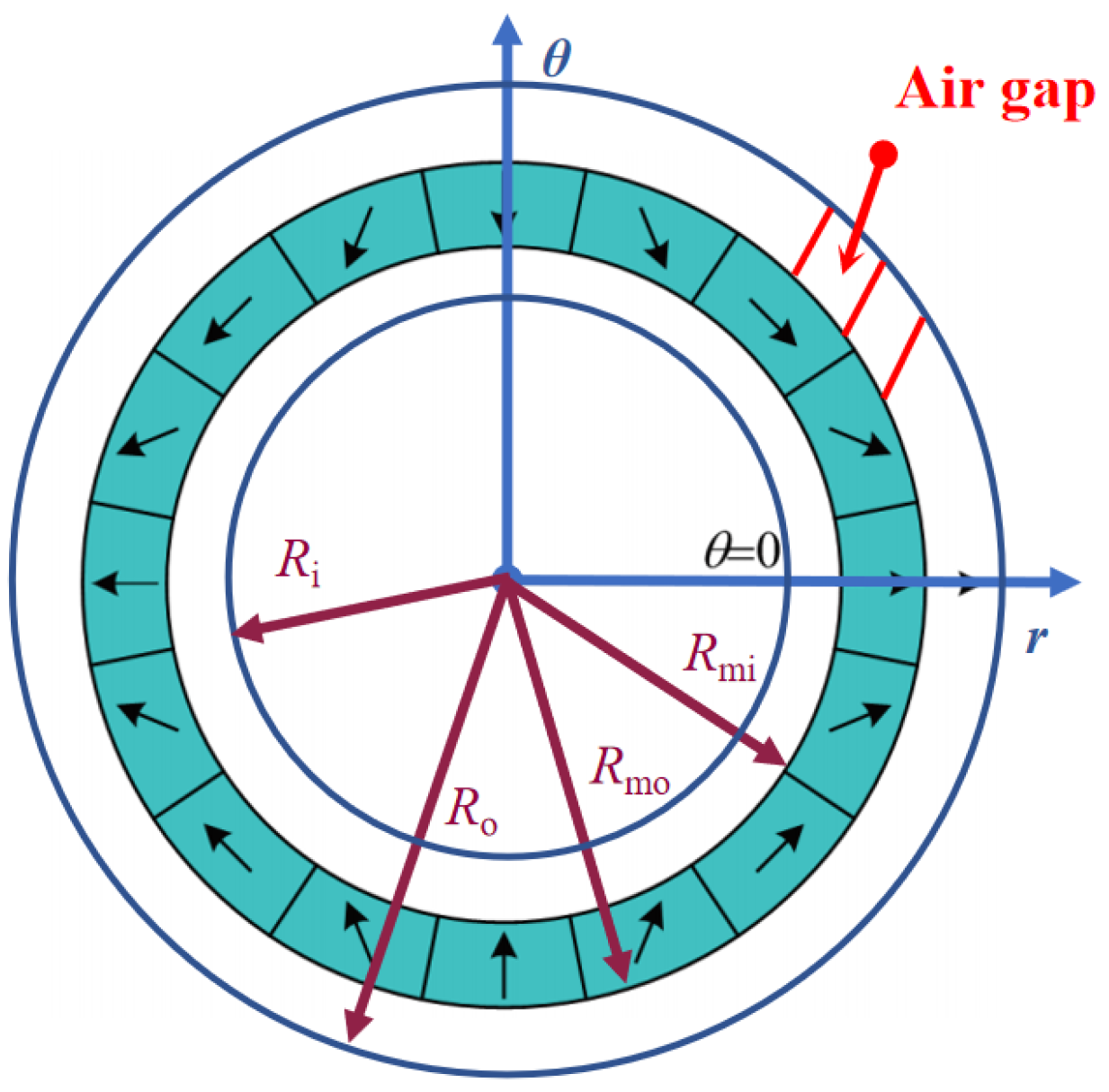
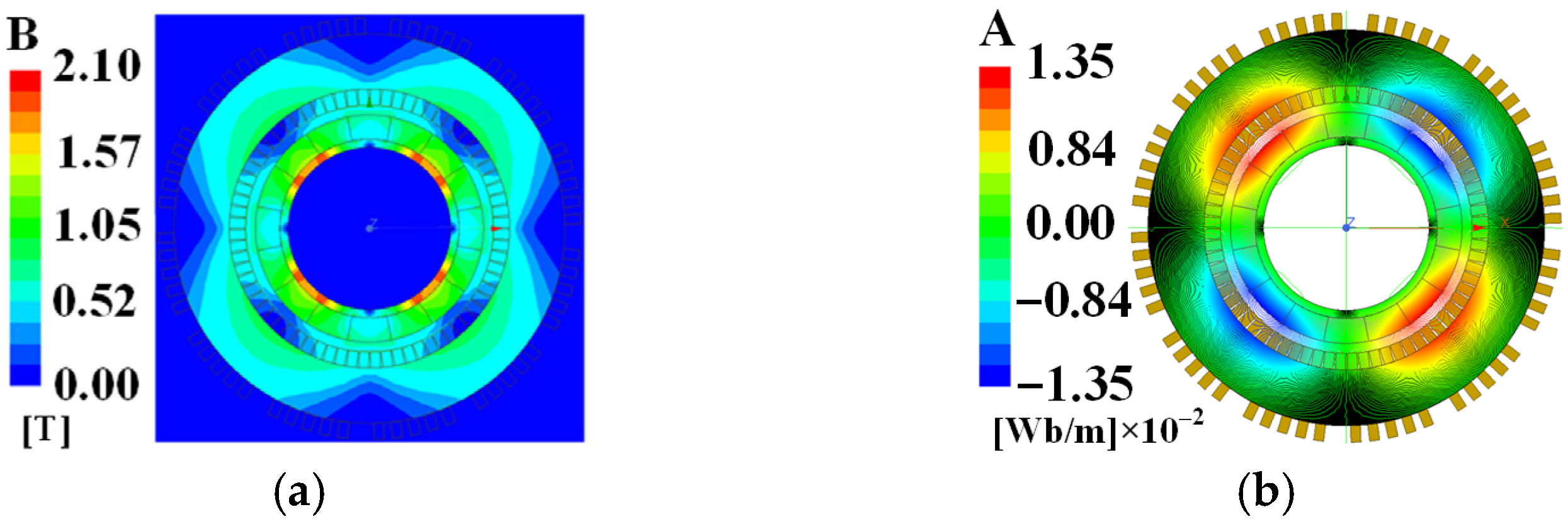
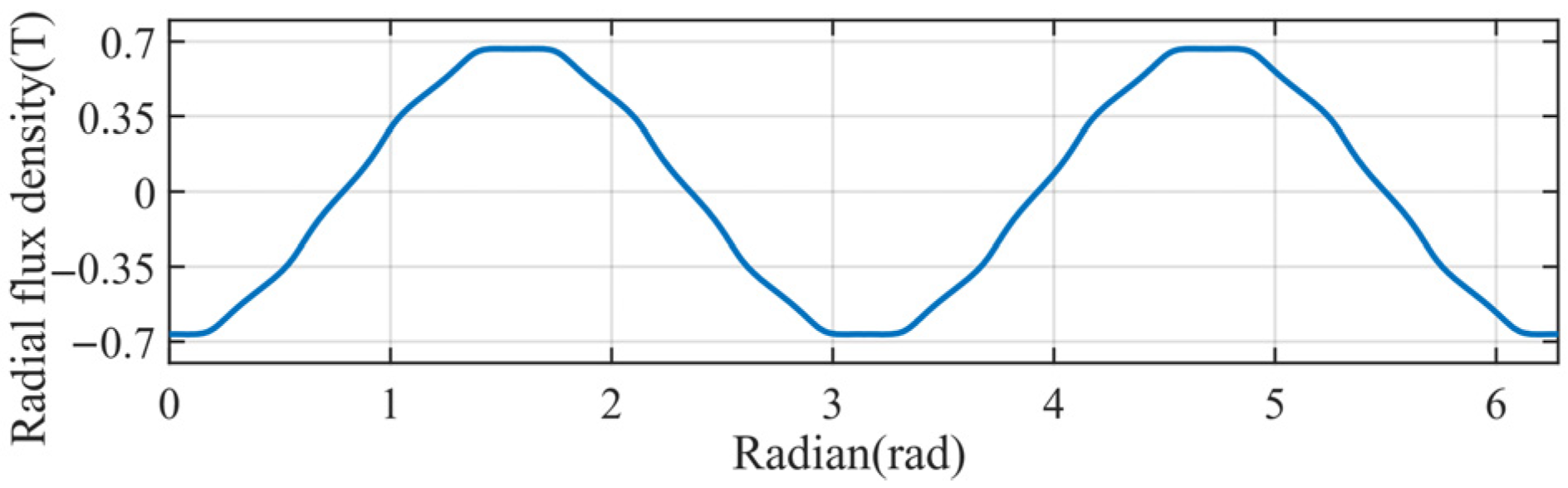
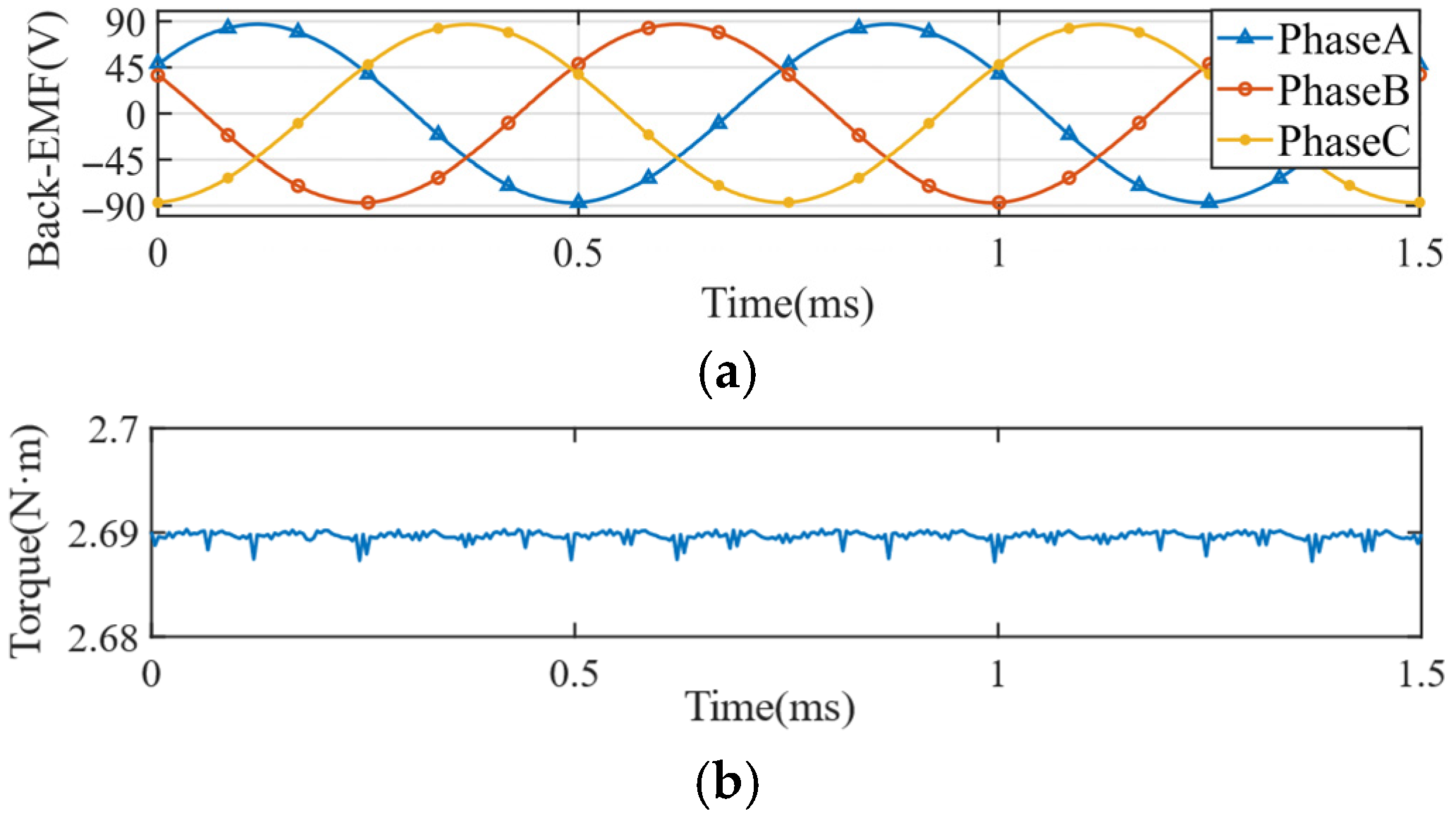
3.3. Electromagnetic Analysis of the HSSPMSM
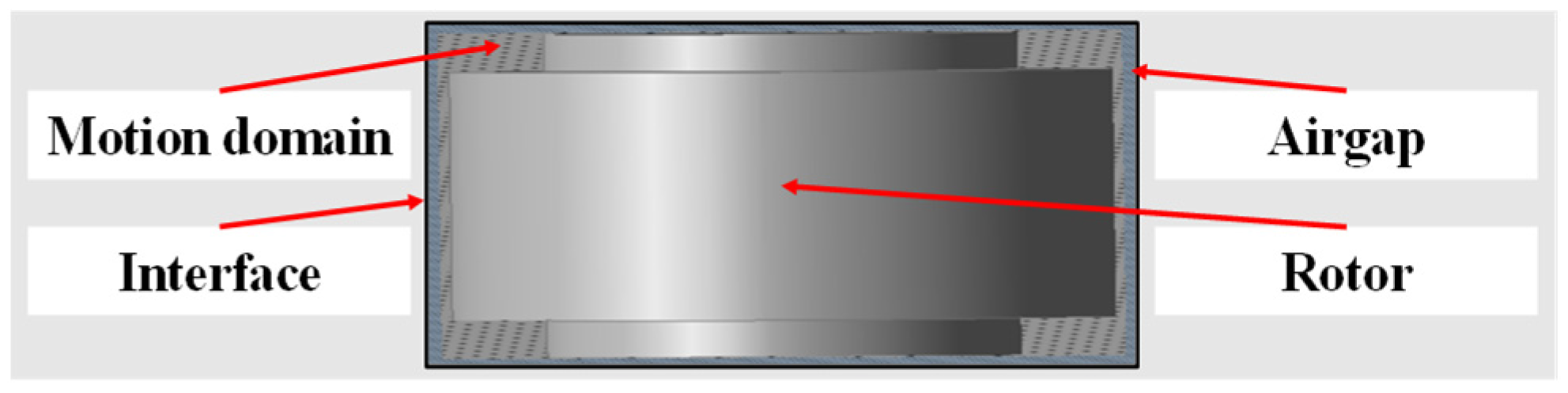
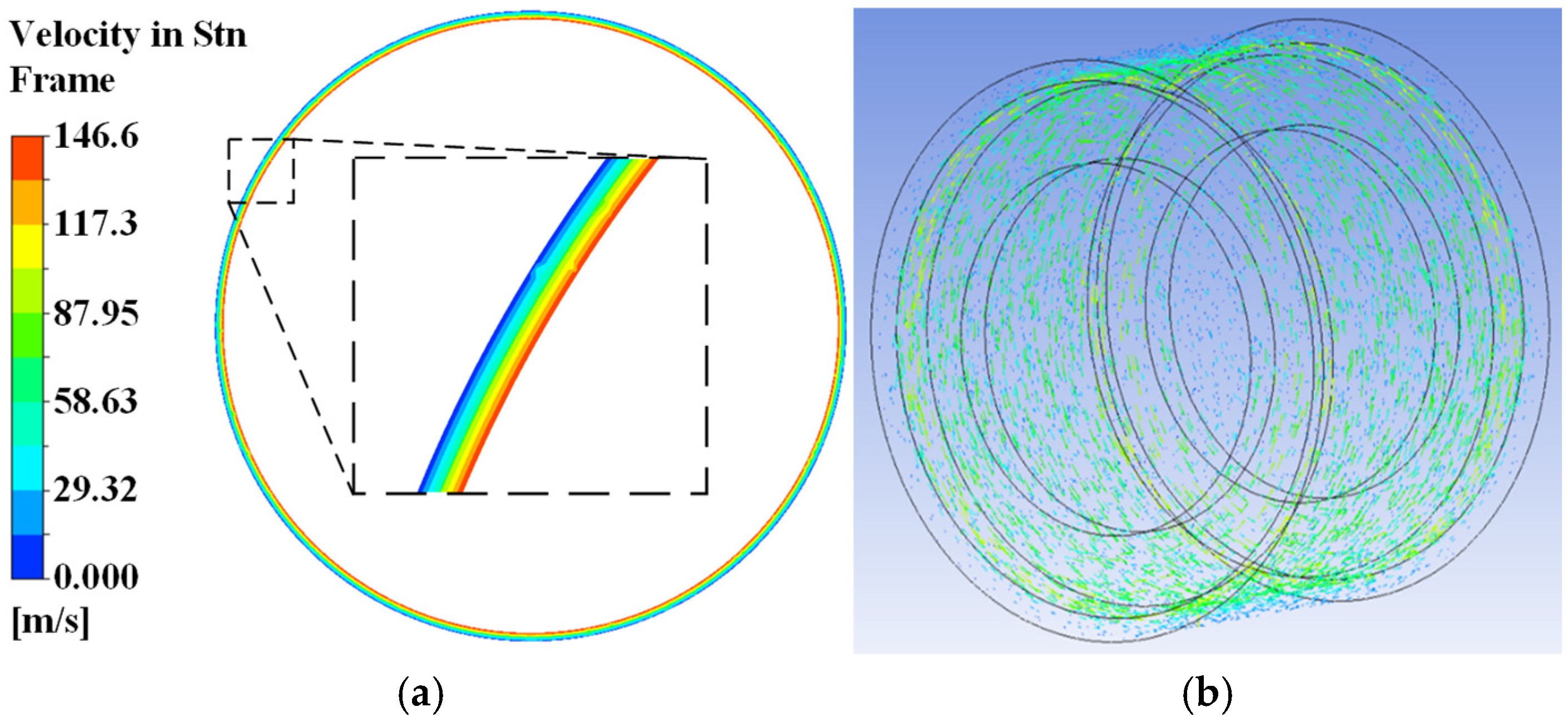
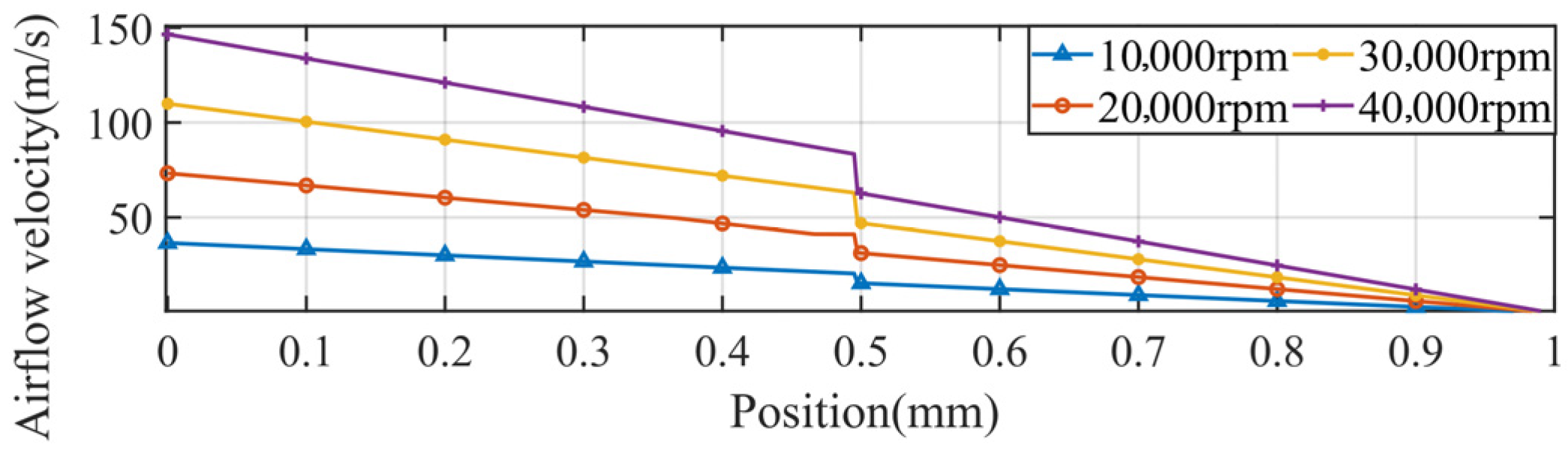
3.4. Airflow–Thermal Analysis of the HSSPMSM
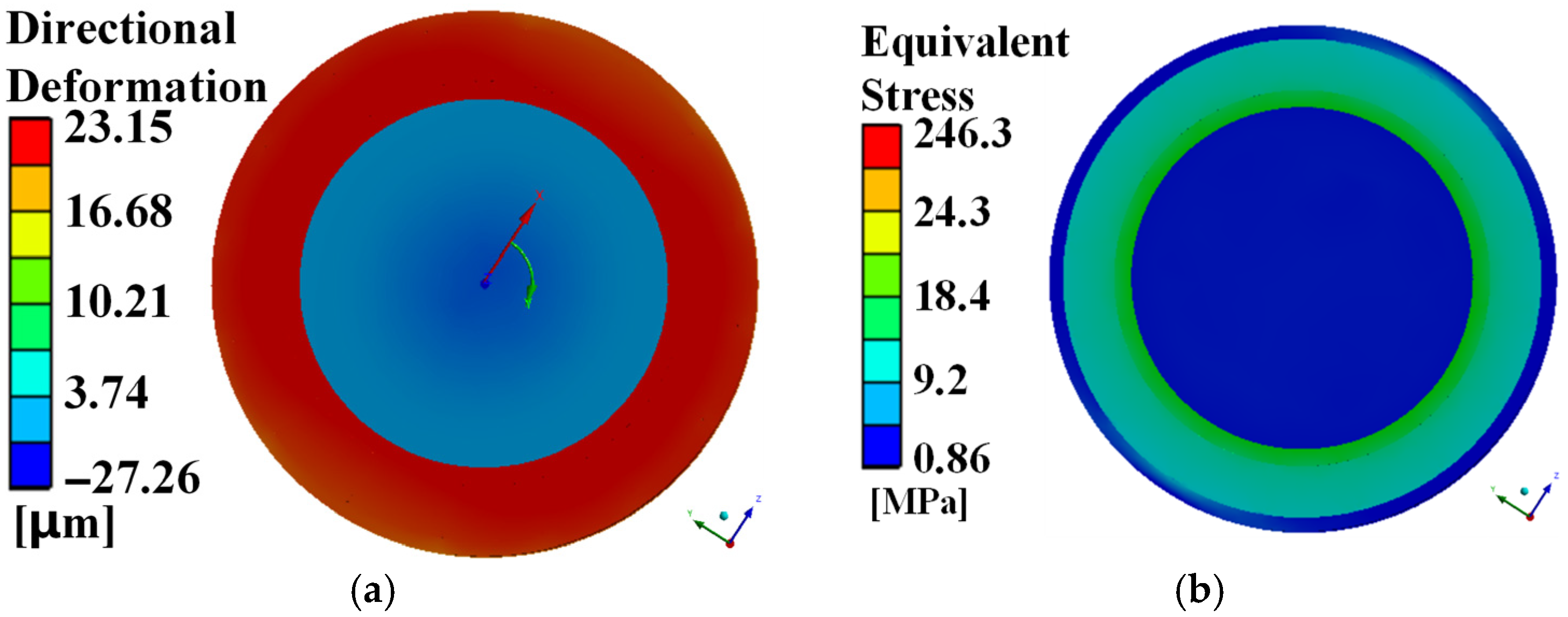
3.5. Mechanical Strength Analysis of the HSSPMSM
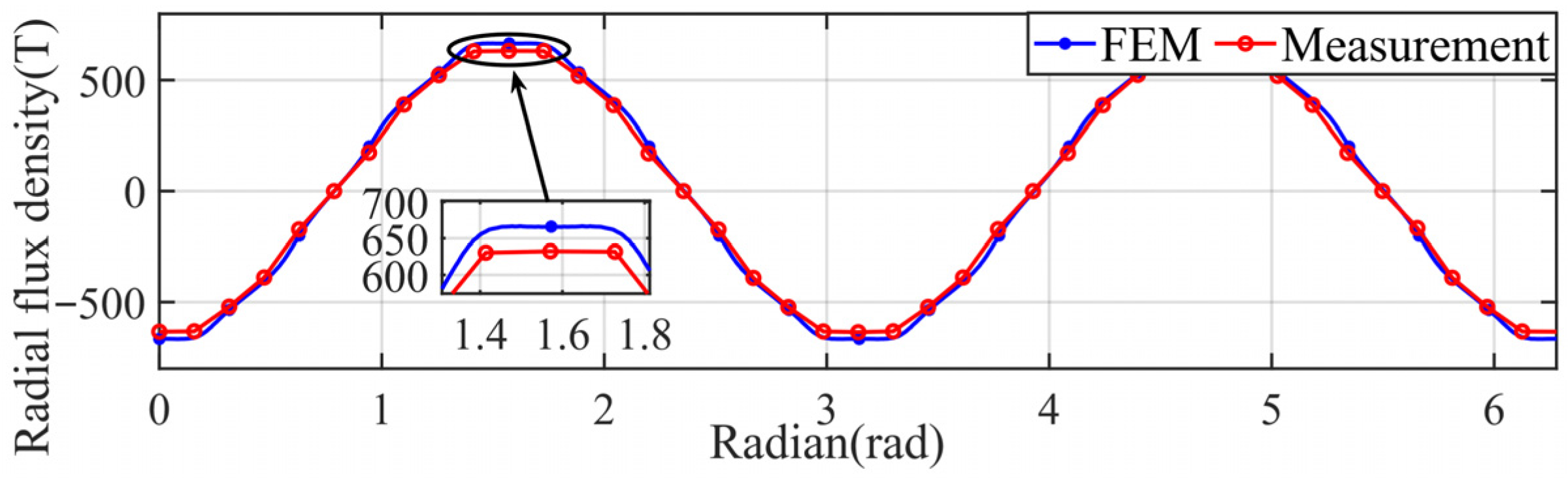
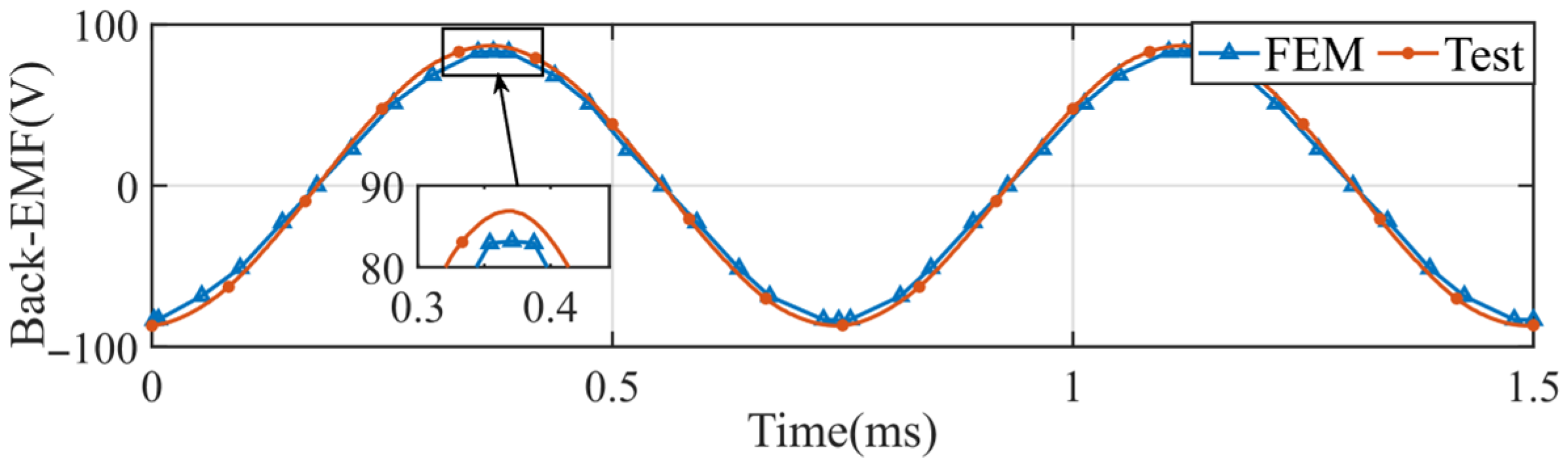
4. Experiment Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.W.; Liu, M.Y. High-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor iron loss calculation method considering multiphysics factors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5360–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dietz, D.; An, J. Manufacture and testing of a magnetically suspended 0.5-kWh flywheel energy storage system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 6152–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.J.; Liu, K.; Wei, J.B.; Wang, H.Z. Multirate model predictive current control of a permanent magnet synchronous machine for a flywheel energy storage system. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11579–11591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Tian, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X. Design and Analysis of an Integrated Modular Motor Drive for More Electric Aircraft. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Mecrow, B.C.; Atkinson, G.J.; Bennett, J.W.; Atkinson, D.J. Overview of Electric Motor Technologies Used for More Electric Aircraft (MEA). IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3523–3531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Han, Y. Integrated Modular Motor Drive Design with GaN Power FETs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 3198–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.P.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, S.; Liao, X.L.; Wang, T.; He, X.R.; Zhang, J.S. Design and analysis of the high-speed permanent magnet motors: A review on the state of the art. Machines 2022, 10, 549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.D.; Chen, Y.S. Influence of radial force harmonics with low mode number on electromagnetic vibration of PMSM. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.L.; Gómez, D.J.; Villar, I.; López-de-Heredia, A.; Etxeberria-Otadui, I. Improved analytical multiphysical modeling of a surface PMSM. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jannot, X.; Vannier, J.C.; Marchand, C.; Gabsi, M.; Saint-Michel, J.; Sadarnac, D. Multiphysic Modeling of a High-Speed Interior Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine for a Multiobjective Optimal Design. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2011, 26, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, T.K.; Shin, K.H.; Lee, J.I.; Cho, H.W.; Choi, J.Y. Electro-mechanical characteristics analysis and experimental study of PMSM according to rotor eccentricity. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8103205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiki, P. Multiphysics Design of a V-Shape IPM Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Tasnim, K.N.; Choi, S.; Kwak, S.; Arafat, A. Designing High-Power Ultra-High-Speed Motor Using a New Multiphysics Multi-Objective Optimization Method for Mechanical Antenna Applications. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 106305–106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.; Foley, I.; Staton, D.A.; Goss, J.E. Multi-physics analysis of a high torque density motor for electric racing cars. In Proceedings of the 2015 EEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.D.; Wang, X.J.; Gerada, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C.A.; Wang, Y.L. Multi-physics and multi-objective optimization of a high speed PMSM for high performance applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 54, 8106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wan, B.; Lei, G.; Tian, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. Multiobjective and Multiphysics Design Optimization of a Switched Reluctance Motor for Electric Vehicle Applications. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3294–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansompel, H.; Leijnen, P.; Sergeant, P. Multiphysics analysis of a stator construction method in yokeless and segmented armature axial flux PM machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.X.; Xu, Y.L.; Zhang, W.J. Multiphysics analysis of flywheel energy storage system based on cup winding permanent magnet synchronous machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 2684–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.X.; Liu, C.H.; Feng, K.; Zhao, H.; Yu, J.C. Field prediction and validation of a slotless segmented-Halbach permanent magnet synchronous machine for more electric aircraft. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 6, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Balachandran, T.; Sirimanna, S.; Salk, N.; Yoon, A.; Xiao, P.; Macks, J.; Yu, Y.X.; Liu, S.N.; Schuh, J.; et al. Detailed design and prototyping of a high power density slotless PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, Z. Analytical Modeling of Surface-Mounted PM Machines Accounting for Magnet Shaping and Varied Magnet Property Distribution. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 8101511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Huang, X.; Cao, J. Thermal analysis of high speed motor based on flow field calculation considering tooth-slots effects. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Beijing, China, 20–23 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xyptras, J.; Hatziathanassiou, V. Thermal analysis of an electrical machine taking into account the iron losses and the deep-bar effect. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziathanassiou, V.; Xypteras, J.; Archontoulakis, G. Electrical-thermal coupled calculation of an asynchronous machine. Arch. Elektrotech. 1994, 77, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahfarokhi, P.S.; Podgornovs, A.; Kallaste, A.; Cardoso, A.J.M.; Belahcen, A.; Vaimann, T.; Asad, B.; Tiismus, H. Determination of heat transfer coefficient from housing surface of a totally enclosed fan-cooled machine during passive cooling. Machines 2021, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





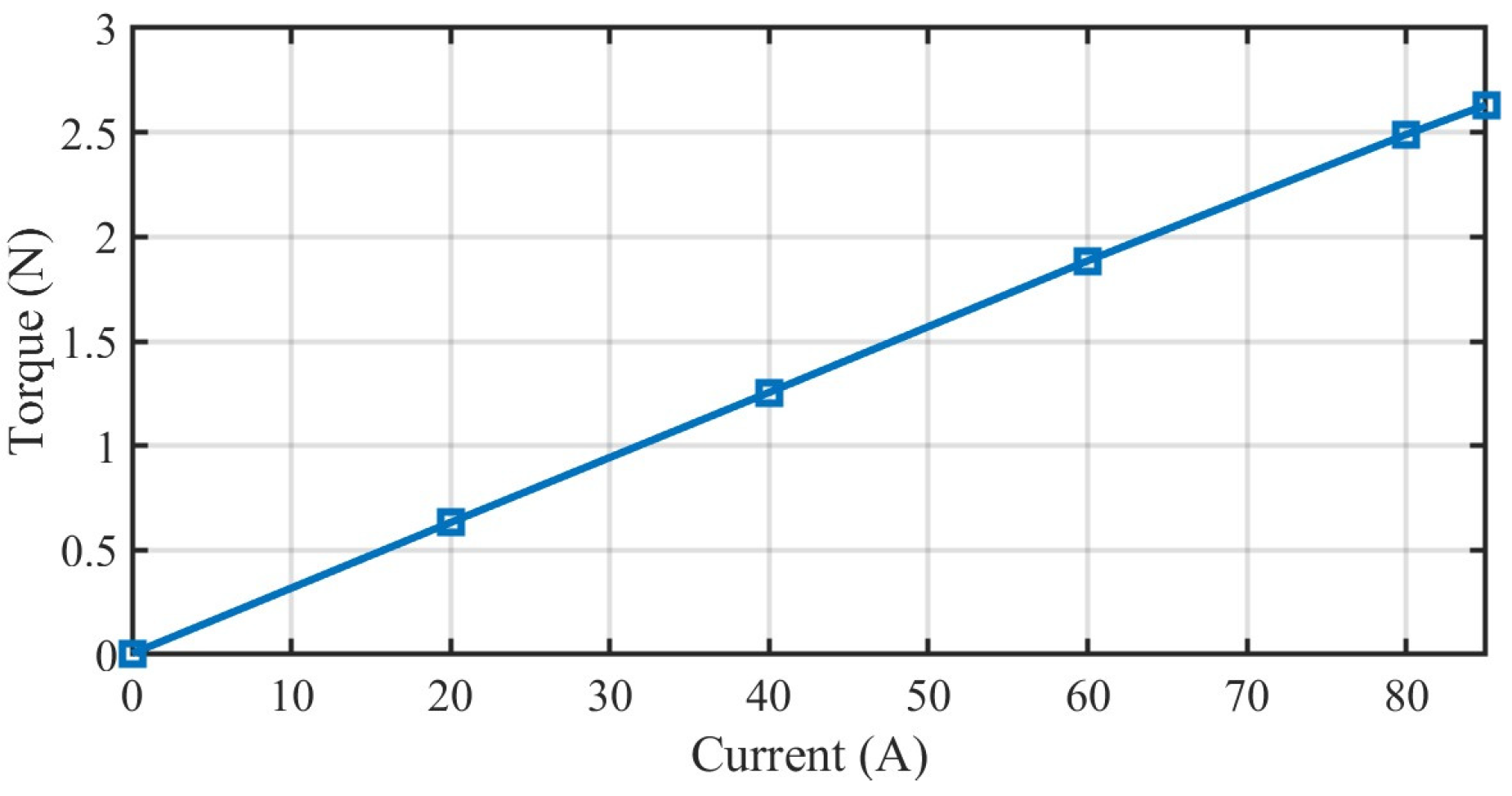
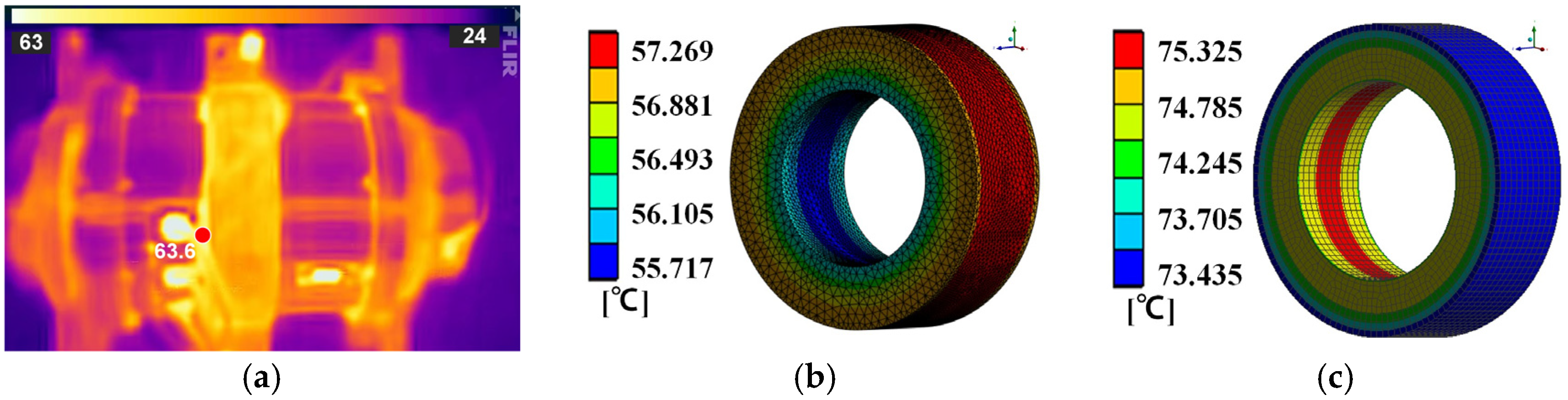
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| PN | rated power | >10 kW |
| nN | rated speed | >40,000 rpm |
| Im | maximum winding current | <85 A |
| Te | maximum output torque | >2.5 N∙m |
| To | maximum allowable operating temperature | <70 °C |
| Udc | DC supply voltage | <110 V |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Pi | iron core loss | 26.31 W |
| Pc | copper loss | 300 W |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| αδ | the inner surface of the stator | 241.35 W/m2·°C |
| αs | the end-face of the rotor | 22.22 W/m2·°C |
| αr | the end-face of the stator | 28.07 W/m2·°C |
| αh | the outer surface of the housing | 22.00 W/m2·°C |
| Component | Material | Value |
|---|---|---|
| iron core | 10JNEX900 | 11.6 W/m·°C |
| winding | copper | 396.7 W/m·°C |
| motor housing | aluminum alloy | 160 W/m·°C |
| air gap | air | 0.025 W/m·°C |
| Halbach array | N45UH | 7 W/m·°C |
| rotor | stainless steel | 16.3 W/m·°C |
| rotor | electrical pure iron of steel 1008 | 36 W/m·°C |
| insulation | thermal glue | 1.2 W/m·°C |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| np | number of pole pairs | 2 |
| Ri | radius of the main shaft | 25 mm |
| Rmi | inner radius of the Halbach array | 27.5 mm |
| Rmo | outer radius of the Halbach array | 35 mm |
| Ro | inner radius of the stator | 42 mm |
| δ | length of the air gap | 3.5 mm |
| Br | remanence | 1.358 T |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| np | number of pole pairs | 2 |
| Ri | radius of the main shaft | 24 mm |
| Rmi | inner radius of the Halbach array | 28 mm |
| Rmo | outer radius of the Halbach array | 35 mm |
| Ro | inner radius of the stator | 42 mm |
| δ | length of the air gap | 3.5 mm |
| Br | remanence | 1.358 T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, H.-J.; Lin, Z.-Q.; Cao, G.-Z.; Guo, M.-H.; Huang, S.-D. Design and Analysis of a High-Speed Slotless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering Air-Gap Airflow. Actuators 2025, 14, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110530
Hu H-J, Lin Z-Q, Cao G-Z, Guo M-H, Huang S-D. Design and Analysis of a High-Speed Slotless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering Air-Gap Airflow. Actuators. 2025; 14(11):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110530
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Hong-Jin, Ze-Qiang Lin, Guang-Zhong Cao, Ming-Hong Guo, and Su-Dan Huang. 2025. "Design and Analysis of a High-Speed Slotless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering Air-Gap Airflow" Actuators 14, no. 11: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110530
APA StyleHu, H.-J., Lin, Z.-Q., Cao, G.-Z., Guo, M.-H., & Huang, S.-D. (2025). Design and Analysis of a High-Speed Slotless Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Considering Air-Gap Airflow. Actuators, 14(11), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110530







