Abstract
An adaptive particle refinement (APR) algorithm has been developed for the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method to augment the resolution of the region of interest to achieve high accuracy and simultaneously reduce the cost of computational resources. It is widely applied in the field of fluid-controlling problems involving large interface deformations, such as the two-phase flow and fluid–structure interaction because this algorithm can capture the interface with high accuracy. Nonetheless, existing APR algorithms widely encounter computational dispersion issues at the interface of regions of different particle resolutions. Moreover, traditional shifting algorithms applied in the APR processes also have difficulties in dealing with particles with different smooth lengths. In this work, an algorithm for fast particle generation was first developed based on the accelerated ray method, which accelerates the discretization of the flow field into particles. Then, a dynamic refinement/coarsening algorithm based on the APR algorithm is proposed to solve the computational dispersion problem that occurs at the refinement/coarsening interfaces. In addition, the shifting algorithm was improved in this work to ensure the particles are always well distributed during numerical calculations and, thus, can efficiently facilitate the adaptive particle refinement/coarsening processes. Comparative analysis indicates that the robust algorithms developed for the SPH method in this work can lead to more precise and reasonable flow fields compared with the conventional SPH adaptive methods.
1. Introduction
Numerous phenomena in hydrodynamic engineering, such as structure entry [1], breakwater wave dissipation [2], ship navigation [3], tidal power generation [4], etc., are usually accompanied by the large deformation of the free liquid surface and dynamic boundaries, etc. The traditional grid-based computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method can encounter issues like mesh entanglement and deformation when addressing these complexities. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH), as a kind of Lagrangian meshless method, has a natural advantage in dealing with these fluid-controlling problems by making up for the deficiencies of the mesh methods. However, uniformly distributed particles are conventionally used by SPH in numerical simulations. It, thus, generates a large number of spatial particles when the computational domain is large, which takes up a lot of the computer’s memory and consumes a lot of computational time. To overcome this problem, two main types of adaptive techniques are proposed. The first one, normally referred to as the variable smooth length technique, is to set different lengths between two neighboring particles to make the particle spacing increase smoothly from the boundary to the core region of the computational domain [5]. It is similar to the practice of refining the grids of the region of interest in the grid method [6]. The variable smooth length technique can distinctly improve the accuracy of the solution. The second one is to apply dynamic refinement and coarsening algorithms to control the resolution of the distributed particles to achieve a high accuracy in the calculation of the computational domain [7].
Inspired by research in astrophysics, Monaghan introduced the concept of the spatially varied resolution, which adjusts the smoothing length according to the number of neighboring particles around the target particle [8]. Then, Nelson and Papaloizou proposed applying this variable smooth length technique to improve the SPH method [9]. In particular, particle spacing is determined by the smoothing length h, and each particle has its adaptive smoothing length hi. By incorporating the gradient of the smoothing length in the momentum equation, an improved SPH model with variable smoothing lengths is derived, which is validated by solving the problem of a one-dimensional shock tube. Another study also improved the SPH model by modifying the SPH momentum equation so that the errors arising from the interaction of particles with different smooth lengths could be reasonably reduced. The rational simulation results of a wedge entering the water were achieved by utilizing this improved SPH model with particles densely arranged around the wedge [10]. However, this SPH method can still cause strong instability in the flow field [11]. It is brought about by the nature of the Lagrange particles in the SPH method, which inevitably induces the movement of particles over time and, thus, causes large gradients of smooth lengths between adjacent particles, ultimately leading to large errors in the kernel approximation. To avoid this problem, some studies have proposed dynamically adjusting the smooth length according to the density [12,13] or the velocity [14] of the target particles. Qiang and Gao proposed an iterative solution to the problem of fully varied smooth lengths to further improve the accuracy of physical interpolation calculations [15]. However, the efficiency of the simulation calculation is greatly affected by the need to iteratively solve the smooth lengths of the particles at each step of the calculations. To improve computational efficiency, the smooth length of the target particle was reasonably adjusted according to the variation in the number and the average smooth length of the neighboring particles [16], thus avoiding the time-consuming iterative solution method.
Some other scholars have utilized dynamic particle refinement and coarsening techniques to enhance the adaptive SPH method. Feldman and Bonet proposed a particle refinement technique that splits a parent particle into several child particles and assigns the corresponding physical properties to the child particles according to the principles of mass and energy conservation [17]. Although the dynamic particle refinement technique allows for large gradients of smooth lengths between particles, the number of particles increases significantly, thus decreasing the efficiency of numerical simulation as it proceeds. Therefore, Vacondio et al. proposed an adaptive SPH method to increase the efficiency of the numerical simulation, which dynamically distributes particles by splitting them at the target region and merging them outside the target region [18]. Wang et al. also proposed a general dynamic particle refinement strategy and, importantly, a new particle refinement criterion for two-phase flow to capture the interface more precisely in fluid–structure interaction (FSI) problems. The calculation results of the wedge entering water showed that the proposed dynamic particle refinement strategy can achieve better accuracy and efficiency [19]. It is notable that the essential disadvantage of the dynamic particle refinement technique is its high cost in computational resources, as the splitting and the merging of particles need to be performed again at the beginning of each computation step. In addition, the merging algorithm is very inefficient, and the conditions for its application are very demanding, making it difficult to be widely adopted. For this reason, Barcarolo et al. avoided using the complex merging process by keeping the split parent particles in the refinement region passively following the fluid and activating them when they left the refinement region [20]. To deal with the instability caused by the interaction of particles with different smooth lengths, Chiron et al. proposed the adaptive particle refinement (APR) technique by referring to the adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) technique from the mesh method [7]. This method makes particles of the same smooth length interact with each other only within its conservation area of uniform spatial resolution. Information between two conservation areas of different spatial resolutions can be exchanged only through the boundary of the conservation area to achieve the coupling of two different resolution regions.
In this work, systematical investigations were carried out based on the dynamic particle refinement and coarsening technique introduced above. Firstly, this work developed an initial point generation algorithm and then applied the accelerated ray method to quickly discretize the particles in the two-dimensional calculation domain. This work innovatively proposes a scheme that dynamically splits parent particles and removes child particles according to the target region based on the adaptive SPH technique proposed by Chiron [3]. We also improved the particle shifting algorithm so that it could efficiently facilitate the adaptive particle refinement and coarsening processes. Finally, the significantly improved adaptive SPH algorithm was verified through two reported cases. This work not only realizes the acceleration of the discretization of the flow field into particles through the accelerated ray method but also solves the computational dispersion problem occurring at the refinement/coarsening interfaces. In addition, the shifting algorithm is simultaneously improved in this work to significantly facilitate the adaptive particle refinement/coarsening processes.
2. Mathematical Model
In the field of computational fluid dynamics, it can be reasonably assumed that the fluid is weakly compressible. Therefore, the incompressible flow can be simulated using the weakly compressible Navier–Stokes equations [21], the Lagrangian form of which is given as follows:
where υ, ρ, v, P, and r denote the kinematic viscosity, the density, the velocity, the pressure, and the position of the investigated fluid, respectively. In addition, the Tait equation [22,23] is often used to establish the relationship between pressure and density when solving hydrodynamic problems, which is provided as follows:
where ρ0 is the density of the fluid when P = 0 and cs is the artificial speed of sound. γ is a constant that is typically set to 7 in the hydrodynamic simulations [24]. To keep the compressibility of the fluid within 1% [25], the artificial speed of sound must be set to at least 10 times the value of umax.
As for the SPH method, a convolution integral on the domain is used to interpolate given physical quantities based on kernel functions. The kernel approximation of the field function at a certain spatial position r can be expressed as follows [26]:
where and h represent the kernel function and the smooth length. Ω is the support domain of the kernel function, which is determined by the smooth length. Since the SPH method discretizes the flow field into particles, each of which carries the physical properties of the fluid, it is not technically possible to use Equation (3) with continuous integration to approximate the field function. Thus, the SPH scheme converts the continuous integral into a discrete summation approximation. Then, Equation (3) can be represented by the kernel particle approximation as follows:
where N is the total number of particles contained in the support domain of particle i, and Vj is the virtual volume of the particle j. The smooth kernel function used in this work is the Wenland kernel function [27], with a ratio of 4 for the smooth length h compared to the particle spacing dx. There are approximately 50 particles in the kernel support domain in the two-dimensional case.
Therefore, the control equations in Equation (3) can be converted into the ones in the form of a weakly compressible SPH as follows:
where m is the mass of the particle. The SPH scheme in antisymmetric and symmetric forms is used for the continuity and momentum equations, respectively, to reduce the errors arising from discontinuities and to ensure better conservation properties [28].
3. Numerical Methodology
3.1. Initial Point Generation
In the two-dimensional case, the generation of boundary points requires first parameterizing the physical boundary curve, which must be of first-order continuity and have good locality to ensure the smoothness of the curve, and changes in the position of a single point only affect the shape of the curve around the control point [29]. In addition, to completely represent the shape of the physical boundary, the spline interpolation function needs to proceed through every node extracted on the physical boundary. Accordingly, this work employs the Catmull–Rom cubic spline for curve parameterization, as depicted below:
where S(u) is the point coordinate, and u is the parametric coordinate ranging from 0 to 1.
Once the parametric equations of the boundary curve are obtained, the discrete points of the boundary curve can be obtained, and the background point system is subsequently generated. To generate the background point system, the fluid domain needs to be determined and completely covered using the background Cartesian points. The coordinates of the background Cartesian points are calculated as follows:
where xstart and ystart denote the coordinates of the point generated at the beginning, ∆x, and ∆y represent the spacings of the background Cartesian points, and Nx and Ny are the number of layers of the background Cartesian point in the x and y directions.
In the background point system, it is necessary to determine the spatial position relationship between the background Cartesian points and the boundary point system. If the background Cartesian points are in the computational domain, they are judged as valid points. The ray method is a commonly used judging algorithm in the two-dimensional case [29,30,31]. Due to the need to perform the judging algorithm through the ray method at least once for each background Cartesian point, when the number of background Cartesian points and boundary nodes is large, the efficiency of determining the positions of the nodes is very low. Therefore, to improve the efficiency of point generation, this work proposes an accelerated ray method, which marks the fluid domain by a set of background grids and defines the attributes of the background grids in advance. The properties of the background Cartesian points are then quickly determined according to the properties of the background grids where the background Cartesian points are located. Taking the boundary of a solid existing within a flow field as an example, the corresponding steps of the accelerated ray method are given as follows.
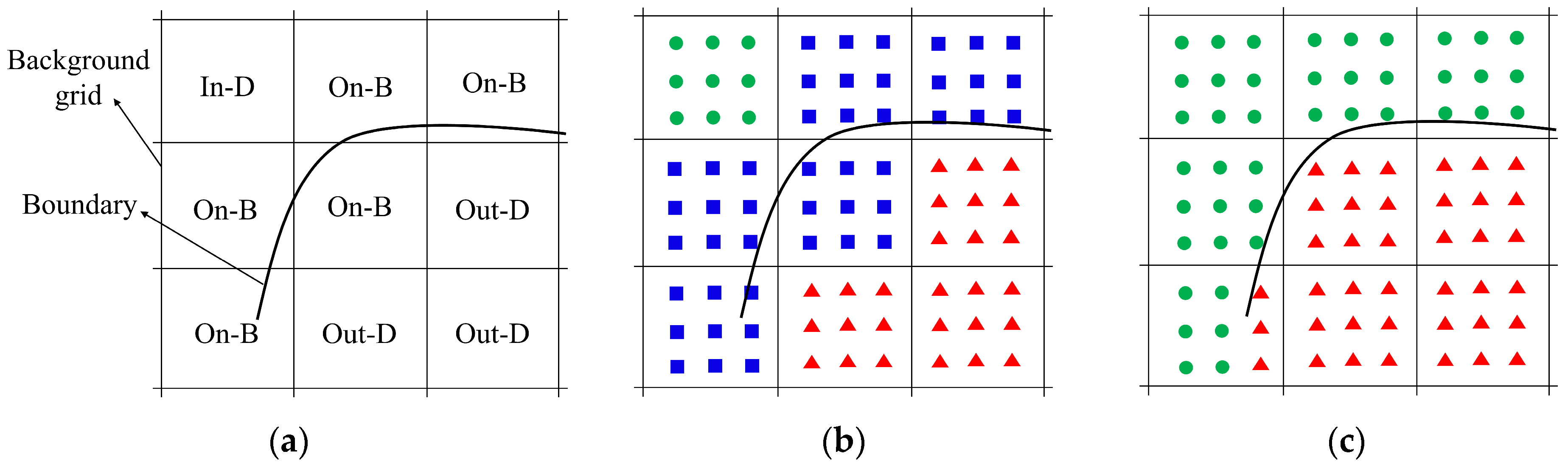
Firstly, the whole flow field is marked by background grids, as shown in Figure 1a. The properties of the background grids in the flow field are defined as In-D, Out-D, and On-B, which are abbreviations of In-domain, Out-of-domain, and On-boundary, respectively. Secondly, the background Cartesian points are then judged according to the properties of the background grid, as shown in Figure 1a. The properties of the background Cartesian points are set to valid, invalid, and to-be-judged according to the properties of the background grids of In-D, Out-D, and On-B. Finally, as shown in Figure 1b, the background Cartesian points whose initial properties are defined as to-be-judged are judged and defined again as valid or invalid by the ray method.
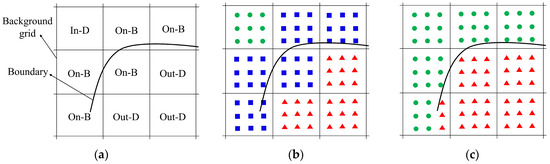
Figure 1.
Schematic of the accelerated ray method: (a) the background grids and their properties; (b) the initial judgment of properties of the background Cartesian points; and (c) the final judgment of properties of the background Cartesian points. The abbreviations In-D, Out-D, and On-B represent the In-domain, Out-of-domain, and On-boundary, respectively. The samples ●, ▲, and ■ denote valid, invalid, and to-be-judged, respectively.
3.2. SPH Adaptive Algorithm
3.2.1. Particle Refinement Algorithm
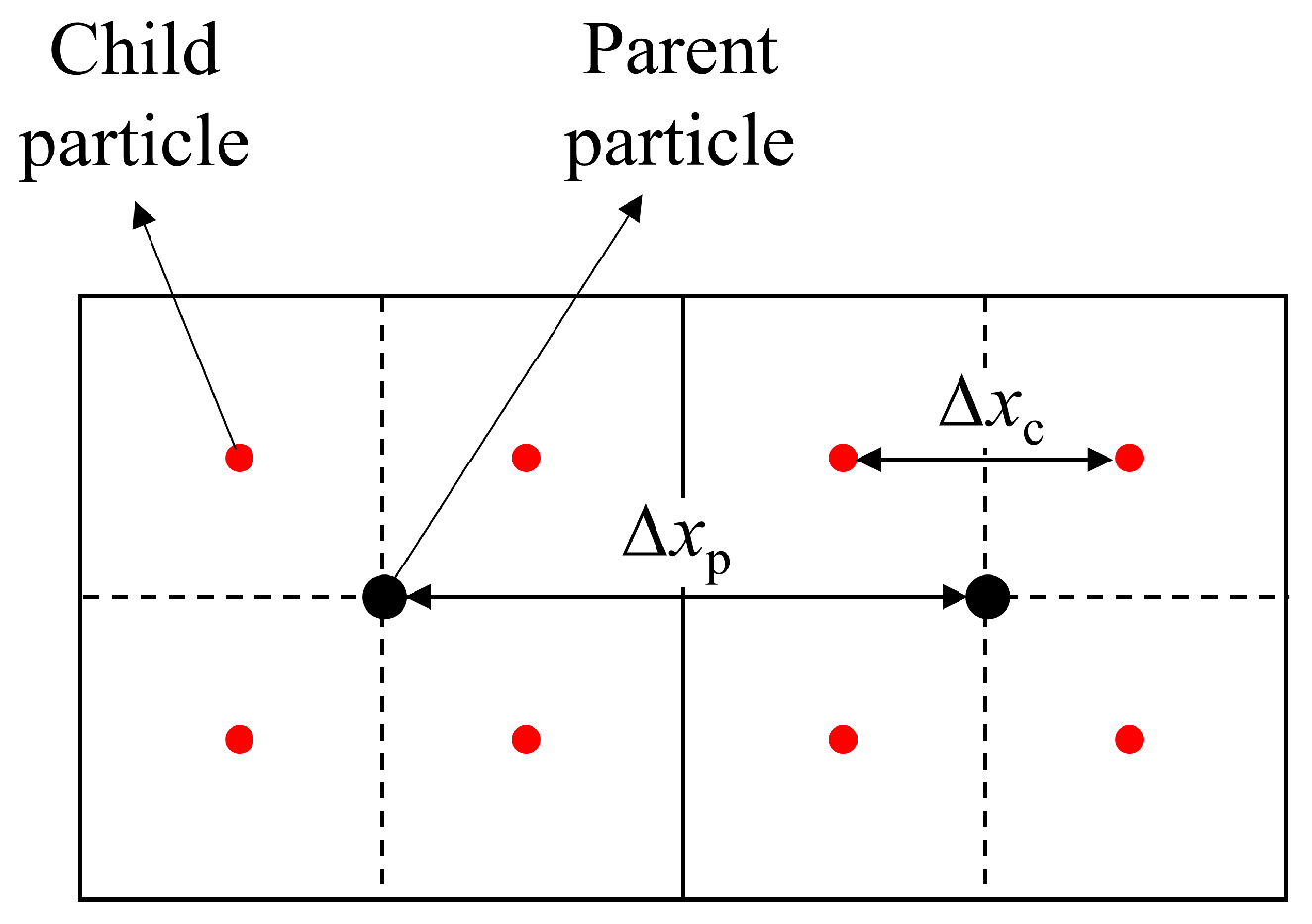
Following the initial generation of fluid particles, the refinement of particles within the region of interest needs to be performed to achieve high accuracy. The refinement algorithm applied in this work was improved based on the one reported by Feldman and Bonet [13]. It splits a parent particle requiring refinement into a number of child particles using a pre-defined square refinement pattern, as shown in Figure 2 [32]. Two parameters, the separation ratio ε and the smoothing ratio ς, are defined to determine the distance between two child particles and the ratio of the smooth length of the child particles to that of the parent particles, respectively. Then, the spacing Δxc and the smooth length hc of the child particles can be calculated according to Equations (8) and (9):
where the subscripts c and p represent the child particle and the parent particle, respectively. The ranges of both the separation ratio ε and the smooth length ratio ς are from 0 to 1. When ε and ς equal 0, it means that the distance between two child particles and the smooth length of the child particles is 0. When ε and ς equal 1, it means that the distance between the two child particles and the smooth length of the child particles are the same as those of the parent particle.
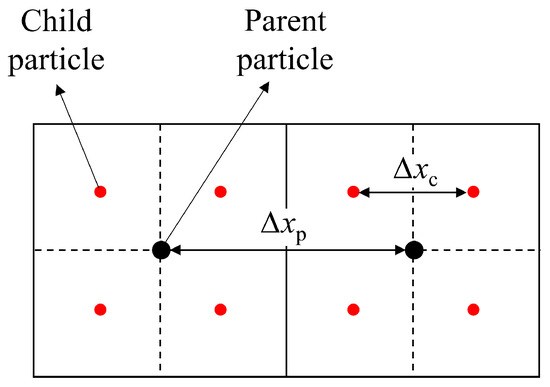
Figure 2.
Schematic of square refinement pattern. The black and the red disks represent the parent and the child particles, respectively.
The distribution of the child particles approximates a uniform Cartesian lattice distribution when ε = 0.5. Then, as for the child particles, the ratio of the smooth length to the spacing can be derived as follows:
This ratio determines the number of particles in the support domain. It is reported that these two refinement parameters need to meet certain restrictive conditions to ensure a minimized error and good stability; that is, ς should change from 0.6 to 0.65 when ε is set as 0.5 [33]. However, this significantly increases the computational load and also runs counter to the goals of the adaptive technique since the number of generated child particles in the support domain is 73% to 120% more than that of the parent particles. This work utilizes a more advanced APR technique, which directly sets two refinement parameters as ε = 0.5 and ς = 0.5 to ensure the same number of neighboring child particles before and after refinement.
In addition to the refinement pattern, the physical properties of the child particles also need to be determined. The physical properties of the child particle, including the mass mc and the velocity uc, are derived from the parent particle below:
where λc is the refinement coefficient related to the refinement pattern. It is set as 0.25 for the square refinement pattern utilized in this work.
The refinement process should satisfy conservations of mass, energy, and momentum, which are provided as Equations (13)–(16), according to Equations (11) and (12).
The conservation of mass, energy, and linear momentum are naturally satisfied, and the conservation of angular momentum is automatically satisfied as for the refinement pattern applied in this work. However, the conservation of angular momentum cannot be satisfied for the asymmetric refinement pattern.
3.2.2. Particle Coarsening Algorithm
The efficiency of the SPH adaptive algorithm can be significantly enhanced through the implementation of coarsening algorithms, which dynamically remove the child particles that move out of the target region. Vacondio et al. proposed a particle coarsening algorithm that allowed two child particles in pairs to be merged into a new parent particle [18]. The mass of the new parent particle was the sum of the masses of the two child particles; the position of the new parent particle was located at the center of the mass of the system composed of the two child particles, and the velocity of the new parent particle was obtained as the velocity at the center of mass of the system composed of the two child particles. Although this particle coarsening algorithm can ensure all the conservation equations above, it comes with a substantial computational cost and requires a more intricate implementation process.
Another particle coarsening algorithm is to retain and inactivate the parent particles after refinement so that they passively follow the flow within the refinement zone and activate upon exiting the refinement zone [20]. Child particles are generated once the parent particle enters the refinement zone and are removed after leaving the refinement zone. Therefore, the statuses of particles over the whole calculation domain are divided into two categories: activated and inactivated. A variable γ is defined to indicate these statuses as follows:
Introducing γ as a weighting function into the kernel particle approximation.
In this case, both the parent and the child particles are involved in the summation of the particles, and the field functions of the inactivated particles are also calculated. However, an irrational state, as shown in Figure 3, may occur when the parent particles enter or leave the refinement region [20]. When a parent particle, represented by the red disk, leaves the refinement region with an activated status, its two child particles, represented by the blue disks, are still kept inside the refinement region, also with an activated status. It causes the total mass of the system to increase transiently. To ensure a smooth transition between the two statutes of activated and inactivated, Barcarolo et al. proposed the concept of a transition zone in which γ varies linearly within the transition zone [20]. When a parent particle leaves the refinement zone and crosses the transition zone, the parameter γ increases linearly from 0 to 1. In contrast, the parameter γ decreases linearly from 1 to 0 as the child particle leaves the refinement zone and crosses the transition zone.
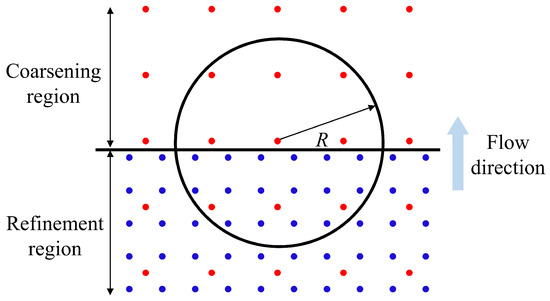
Figure 3.
Illustration of the irrational state related to the particle coarsening procedure [20]. The black horizontal line is the boundary between the refinement and the coarsening regions; the red and the blue disks are the parent particles and the child particles, respectively.
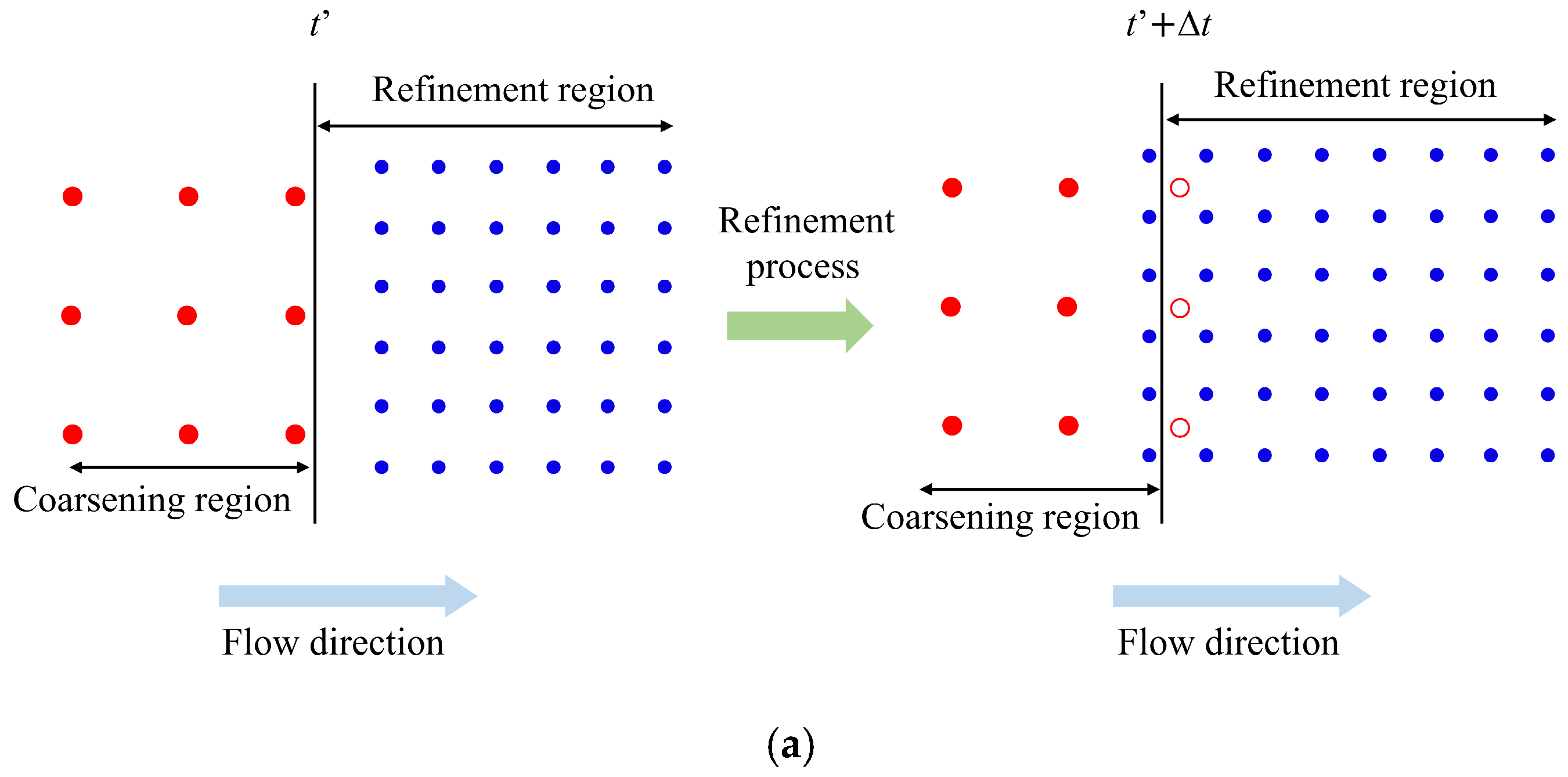
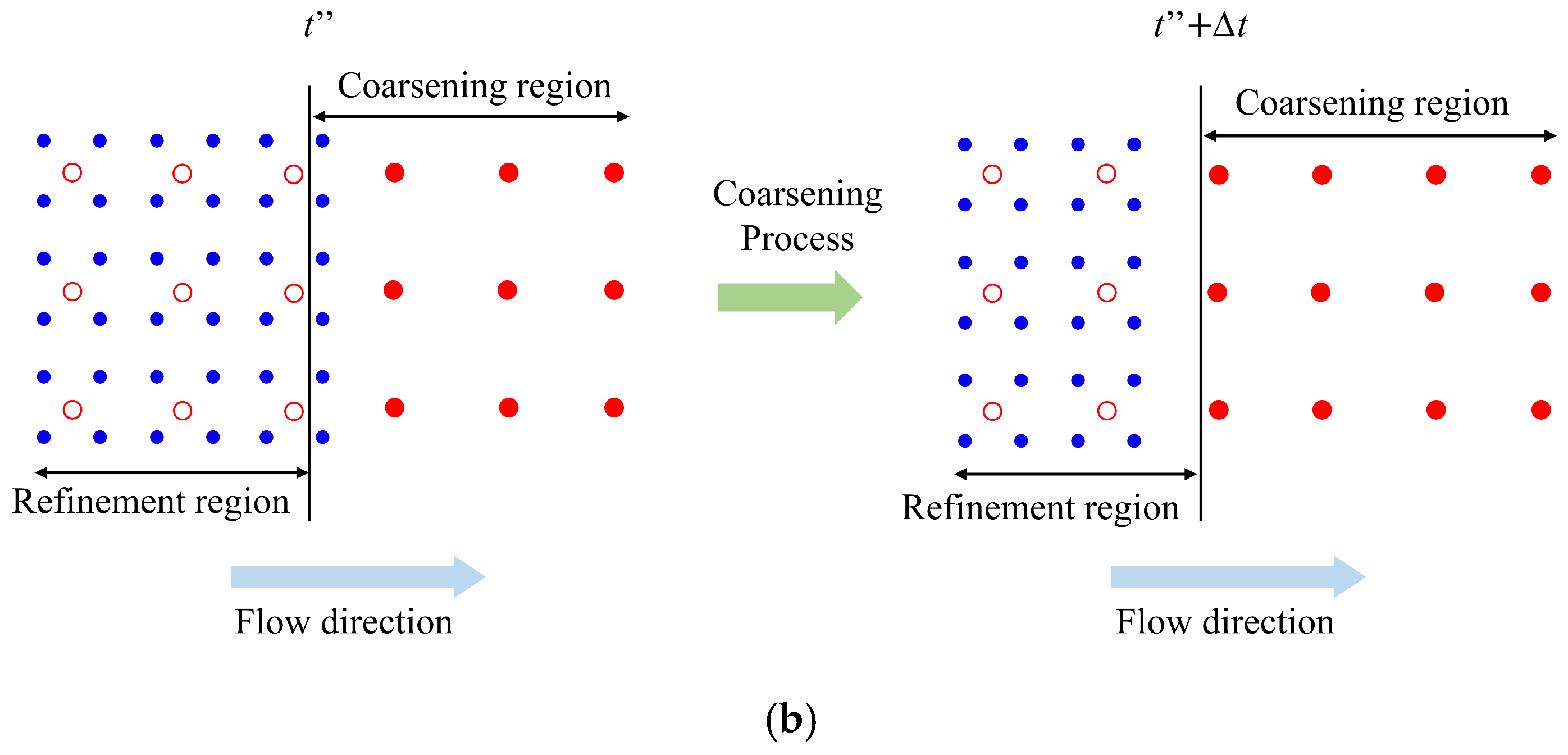
Instead of using the linearly varied γ, this work proposes a new refinement-coarsening technique, as shown in Figure 4, to effectively enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the adaptive SPH method in a more effective way. Generally, the parent particles are represented by red disks in the coarsening region to indicate their activated status and by a red circle in the refinement region to indicate their inactivated status. The child particles are represented by blue disks. When a parent particle flows across the boundary from the coarsening region to the refinement region, as shown in Figure 4a, it is initially activated before the boundary at the time of t’. Once the parent particle enters the refinement region at the time of t’ + Δt, it is inactivated and split into four regular child particles simultaneously. The inactivated parent particles only move with the flow field and are not involved in any calculations. When a parent particle flows across the boundary from the refinement region to the coarsening region, as shown in Figure 4b, it is initially inactivated before the boundary at the time of t”. Once the parent particle enters the coarsening region at the time of t” + Δt, it is activated again, and the corresponding four child particles are removed from the computational domain simultaneously. The proposed refinement-coarsening technique can effectively avoid sudden changes in the mass of the system and shows great advantage in fulfilling the requirements of all the aforementioned conservation equations.
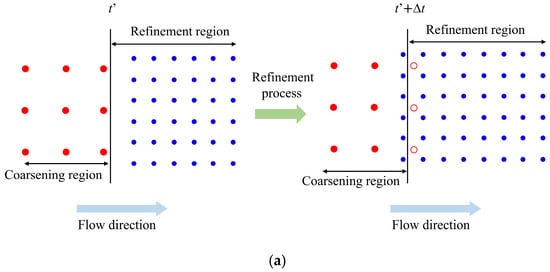
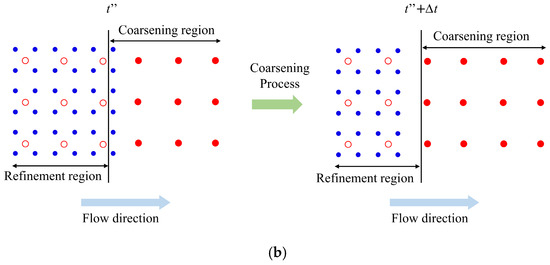
Figure 4.
Illustration of the proposed refinement-coarsening technique: (a) the refinement process; (b) the coarsening process. The black vertical line is the boundary between the refinement and the coarsening regions; the red disks and the red circles represent the activated and inactivated parent particles, respectively; the blue disks represent the child particles.
3.2.3. APR Technology
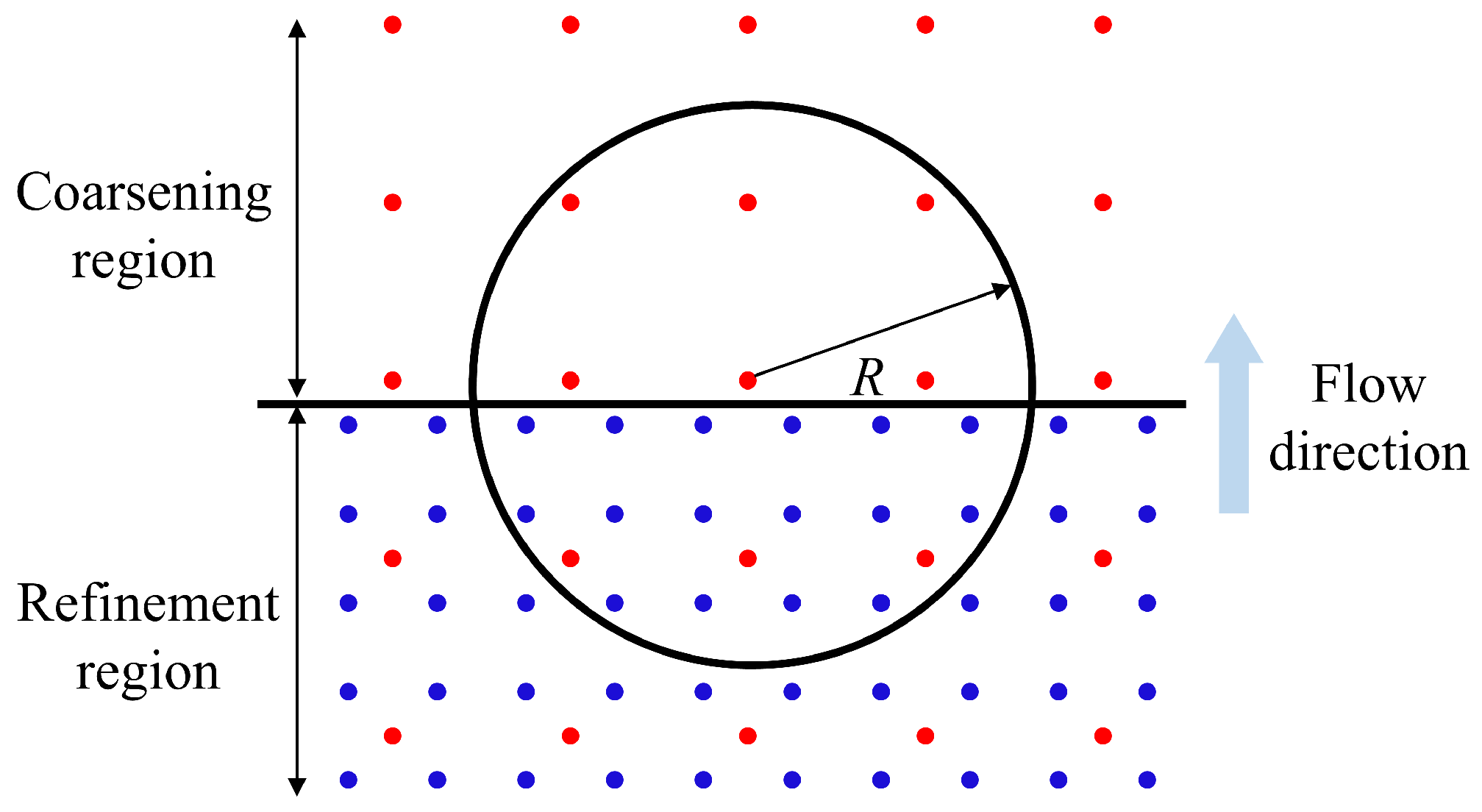
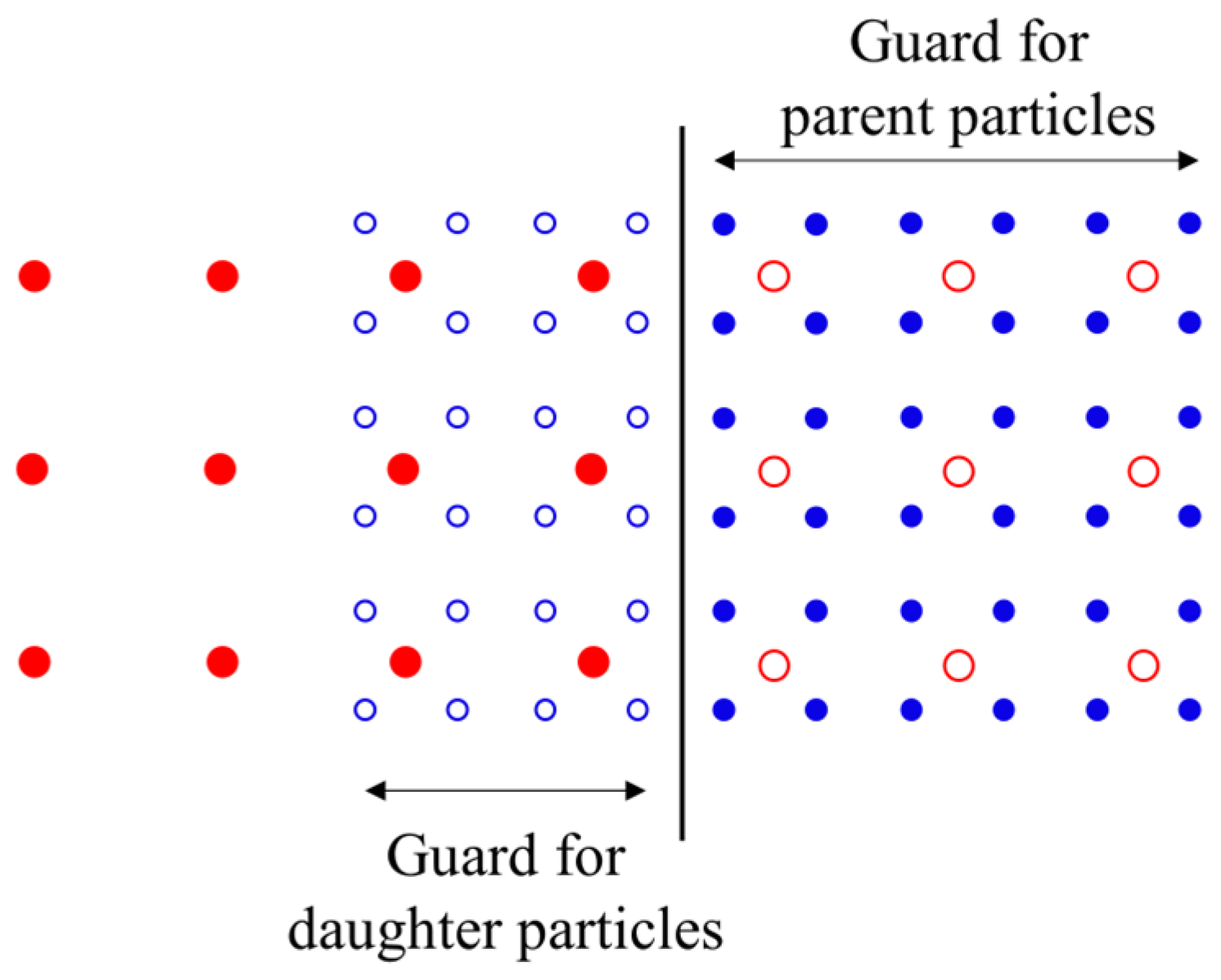
According to the algorithm of the APR technique, particles possessing identical smoothing lengths within a region of consistent spatial resolution can interact directly, whereas particles with distinct smoothing lengths in two separate regions cannot directly interact. Information exchange occurs exclusively through the guard area, which serves to connect the two regions of varying resolutions. As shown in Figure 5, the guard area acts as a boundary between two regions with different levels of refinement.
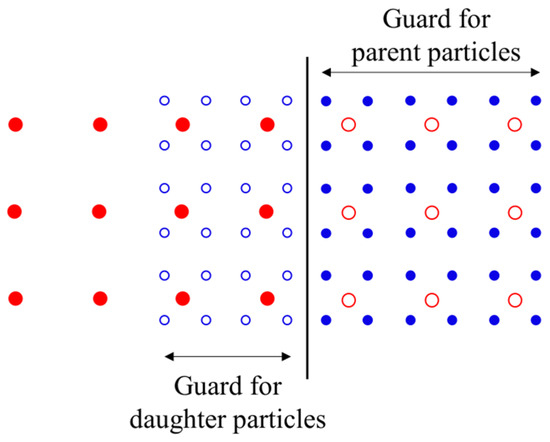
Figure 5.
Schematic of the guard area for APR. The black vertical line is the boundary between the refinement and the coarsening regions; the red disks and the red circles represent the activated and inactivated parent particles, respectively; the blue disks and the blue circles represent the activated and inactivated child particles, respectively. All the solid disks are involved in SPH calculations, while all the circles are not. The circles only passively follow the fluid.
In SPH calculations, two neighboring regions of different resolutions indirectly interact with each other through particles in the guard area. The field function f of the particles in the guard area is interpolated from the fluid as follows:
where denotes the approximation of the field function f for particles in the guard area. Interpolations are carried out at the start of each time step, and values of the field functions of the neighboring particles are assigned equally to the particles in the guard area through Equation (20). As shown in Figure 5, the field functions of the particles in the guard area are obtained via interpolations of the field functions of the activated particles so that two guard areas with different refinement levels are generated besides the boundary. Since only particles with the same refinement level can be calculated interactively, computational errors induced by the gradient of smooth length are avoided.
Since the traditional shifting algorithm can only deal with the flow where the particles are uniformly distributed, it causes erroneous displacement corrections for particles with different smooth lengths. In this work, the shifting algorithm is improved by adjusting the displacement correction equation as follows:
where is the concentration gradient of the particle, is the diffusion coefficient, and is the time step. When the displacement correction is applied to the particles in the guard area, the lack of a complete support domain for the protected particles leads to the incorrect calculation of the concentration gradient of the particle. It causes the particles in the guard area to spread into the fluid, which significantly disrupts the distribution of the particles in the guard area and, thus, affects the calculation of the flow field in the refinement region. Therefore, the displacement correction proposed in this work is only applied to the particles in the non-guard area. In addition, the particles in the guard area only passively move with the fluid and are regenerated at every time step to maintain a uniform distribution.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. A Viscous Flow Passing around a Rectangular Cylinder
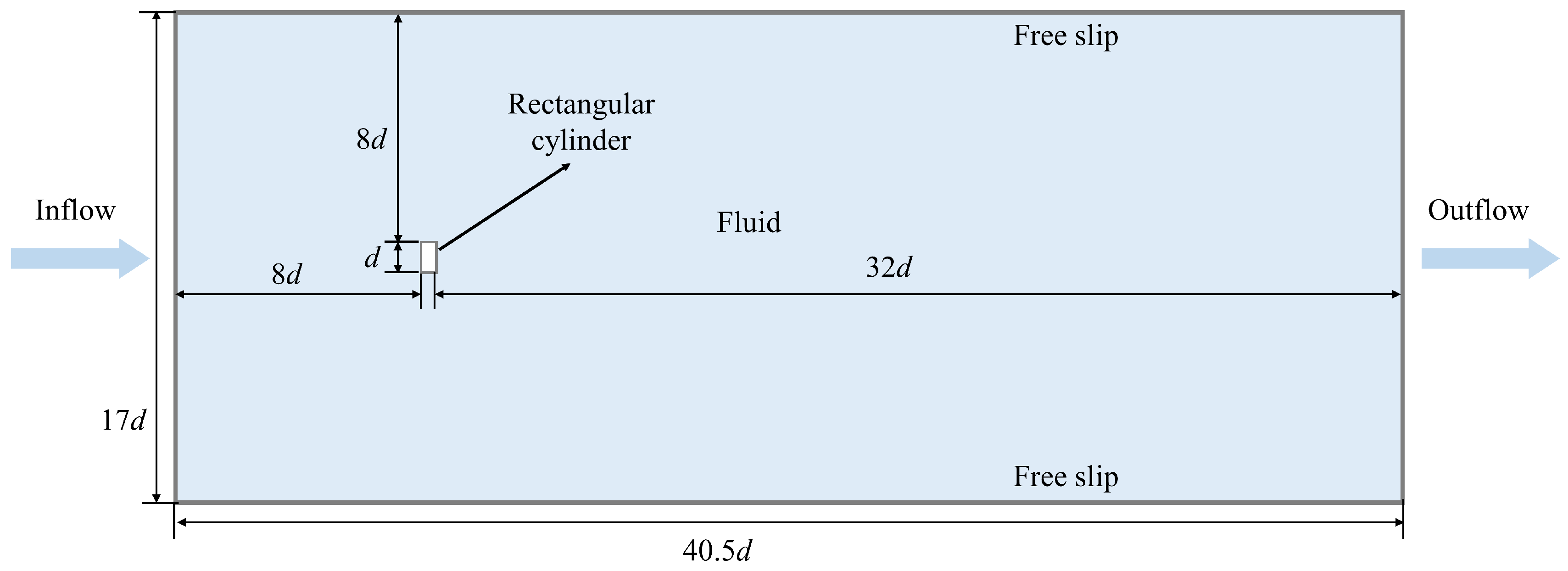
In this section, a case study of a viscous flow passing around a rectangular cylinder, representing a kind of blunt-headed body, is conducted to test the accuracy of the improved adaptive SPH model in this work. The geometry in this case study involves sharp corners, and the conventional SPH model commonly produces stretching instabilities when dealing with flow fields near these sharp corners. Therefore, this work demonstrates the superiority of the proposed adaptive SPH algorithm, first by figuring out the flow field of the viscous flow passing around a rectangular cylinder. The calculation domain set in this work, as shown in Figure 6, is consistent with the one reported in Ref. [34]. The gravity force is ignored, and the Reynolds number Re = ud/υ is set as 200. An initial flow field with uniformly distributed particles is generated by applying the accelerated ray method. Along with the proceeding simulation, the whole calculation domain is divided into three regions with three particle resolutions, d/Δx = 25, d/Δx = 50, and d/Δx = 100, through the adaptive SPH method.
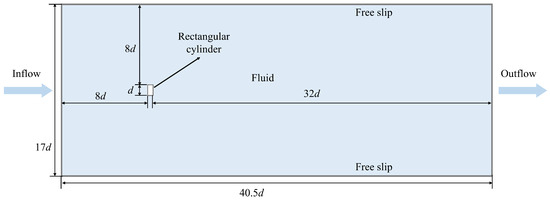
Figure 6.
Schematic of the calculation domain of a viscous flow passing around a rectangular cylinder.
Usually, there is a wide zone of negative pressure behind an object when a viscous flow passes around the object. As shown in Figure 7a, the negative pressure induces significant tensile instabilities [35] and unphysical cavitation behind the object [36] by applying the conventional adaptive algorithms of the SPH method. Another problem is that the traditionally applied shifting algorithm of the SPH method normally results in diffusions of particles between regions with different resolutions, which blurs the boundaries between different regions, as shown in Figure 7b.
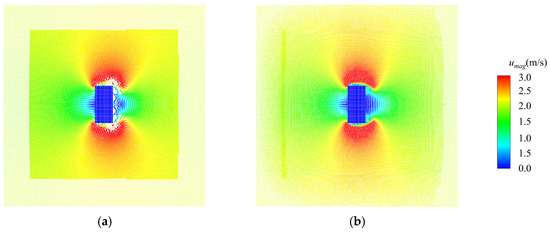
Figure 7.
Common problems caused by the traditionally applied SPH method are as follows: (a) tensile instability and (b) diffusion of particles between regions with different resolutions.
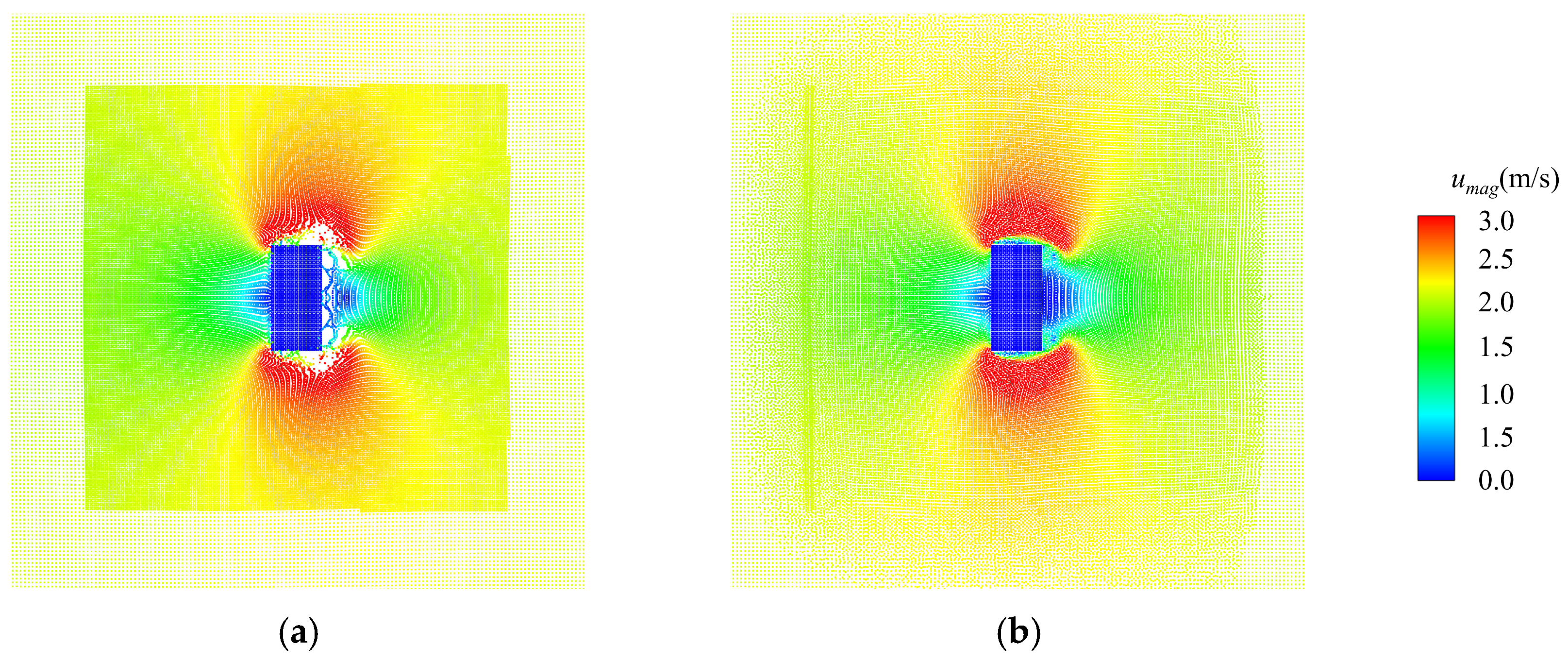
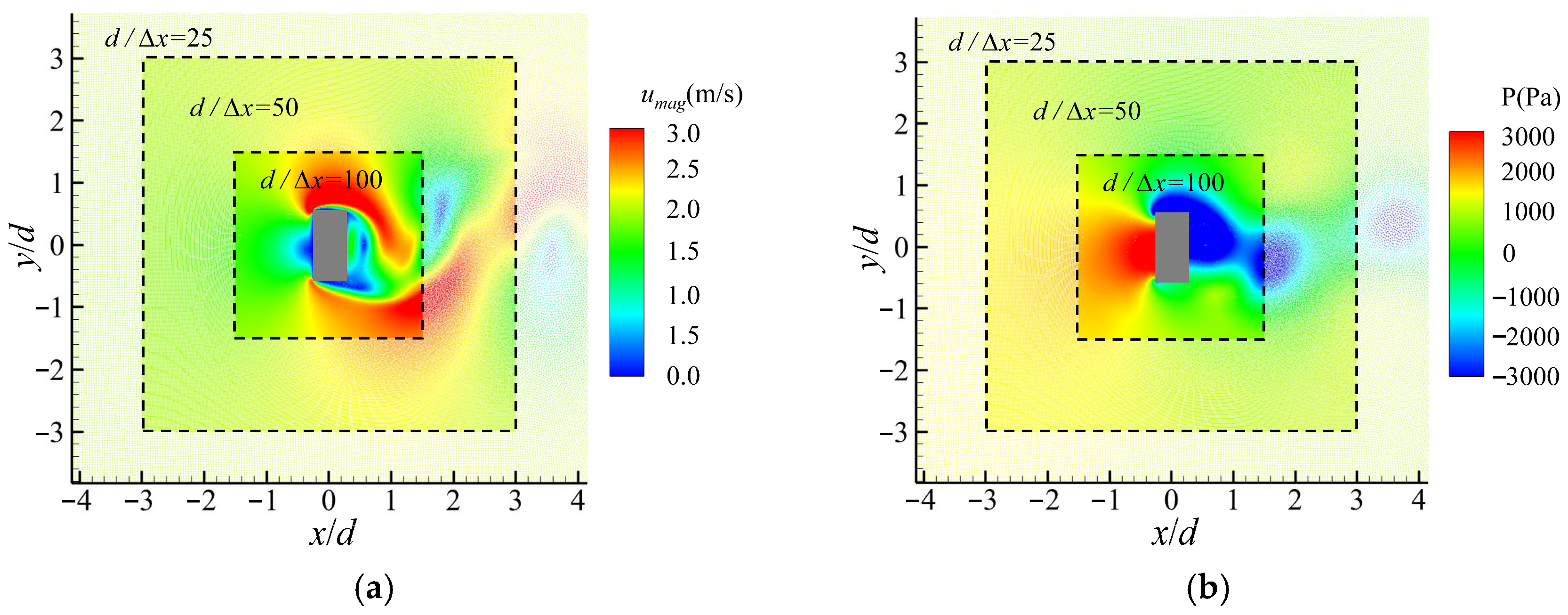
All these problems can be effectively figured out by applying the adaptive algorithms improved in this work, as shown in Figure 8. It displays contour plots of the pressure and the velocity when the lift reaches the maximum value. The boundaries between regions with different resolutions are highlighted by dashed boxes. As shown in this figure, reasonable pressure and velocity are achieved, and they vary rationally and smoothly over regions with different resolutions. Most importantly, no tensile instabilities or diffusions of particles between regions with different resolutions occur.
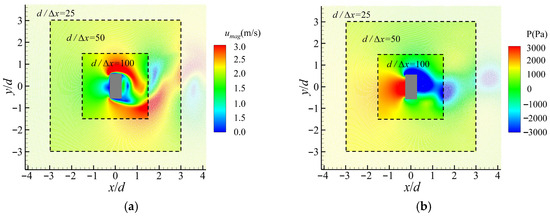
Figure 8.
Simulation results of a viscous flow passing around a rectangular cylinder by applying adaptive algorithms improved in this work: (a) the contour plot of the pressure and (b) the contour plot of velocity. Dashed boxes are added to highlight the boundaries between regions with different resolutions.
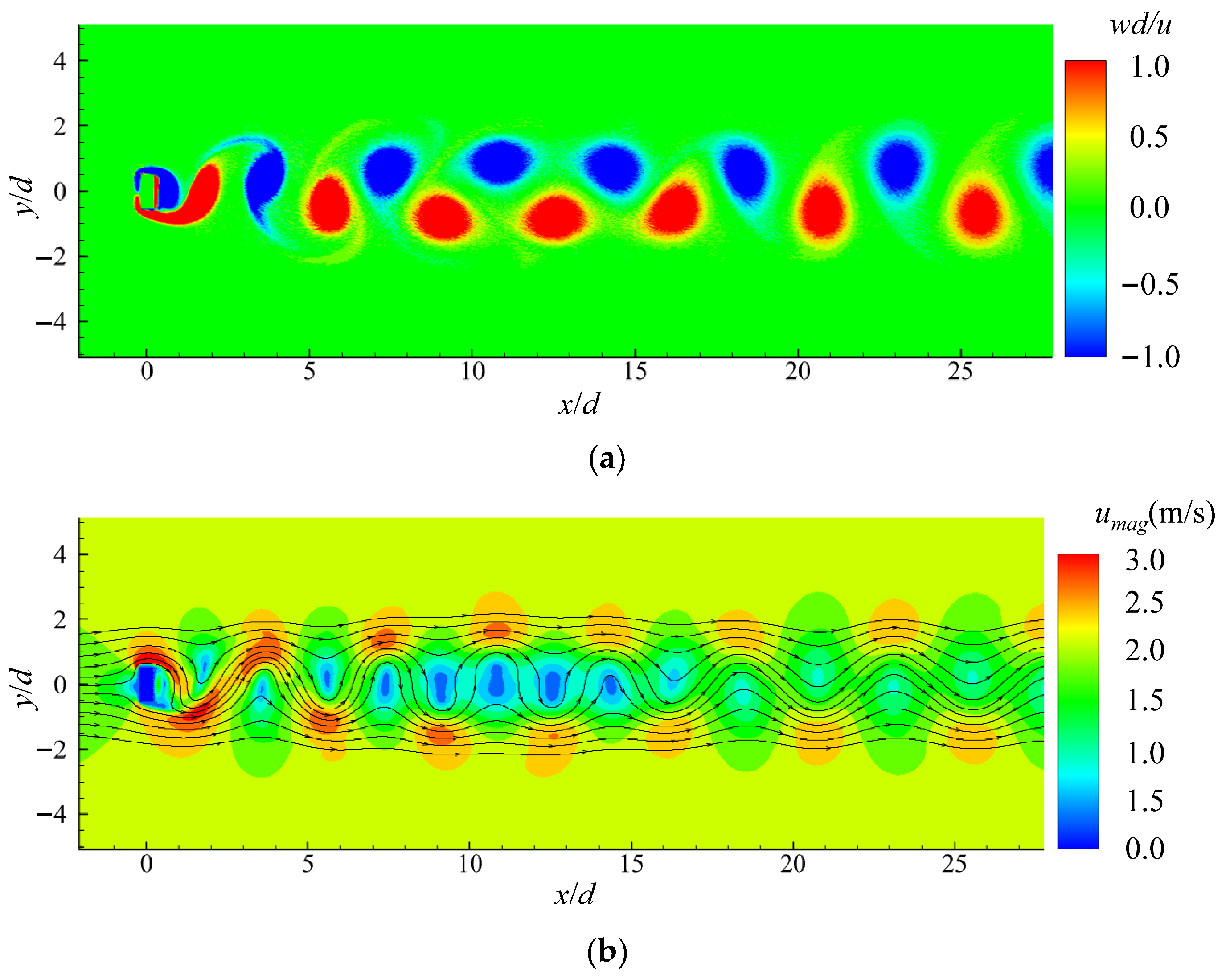
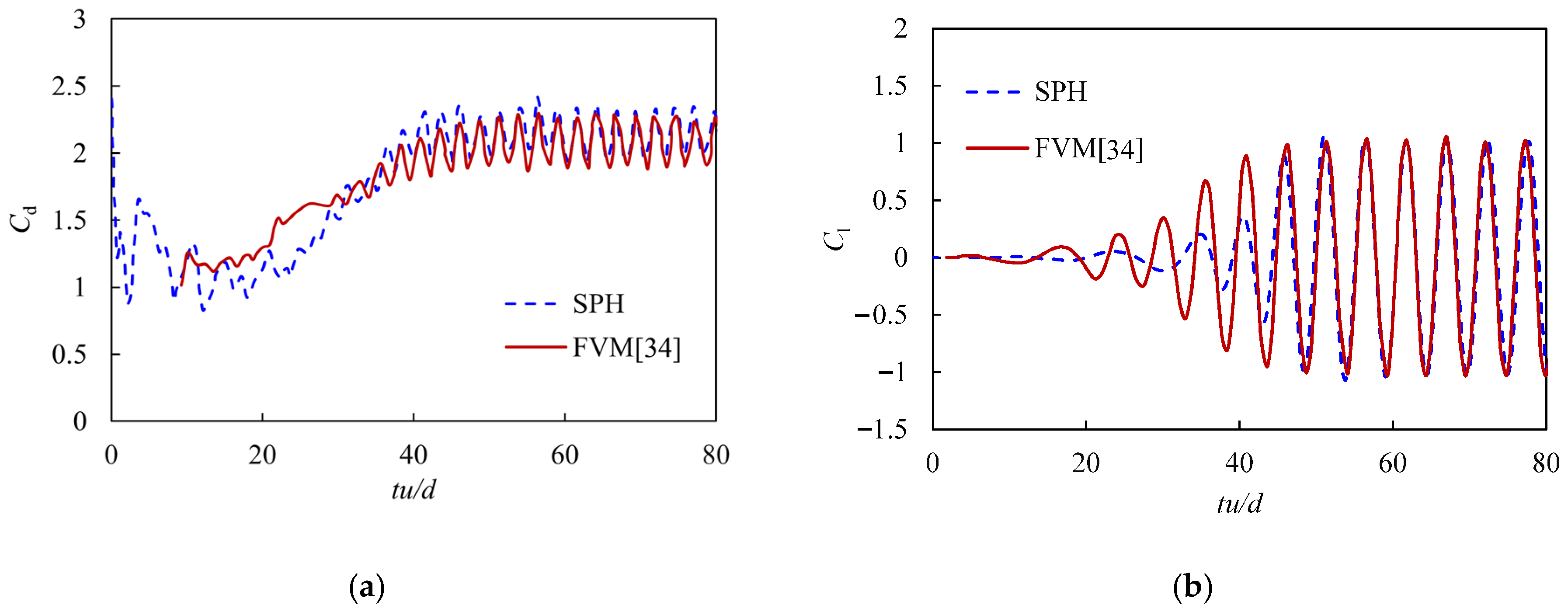
The vortex and the flow field of the viscous flow passing around a rectangular cylinder at Re = 200 are calculated and given in Figure 9. It can be seen that after the flow field fully developed, a periodic vortex-shedding phenomenon occurred behind the square column, forming a Karmen vortex street. The corresponding time histories of the lift and drag coefficients were derived and are compared with that achieved using the Finite Volume Method (FVM) [34], as shown in Figure 10. The satisfactory agreements of the curves of the lift and drag coefficients in the periodic regime demonstrate that the improved adaptive algorithms can effectively capture the transportation features in this case study. Furthermore, Table 1 also compares the results of the mean of the drag coefficient Cd.mean and the root mean square of the lift coefficient Cl.rms calculated from this work and the reported work in Ref. [34]. As can be seen from the table, the errors between this work and the reported work are only 2.39% and 9.25%, corresponding to Cd.mean and Cl.rms. It proves that the improved adaptive SPH model in this work can stably and accurately deal with problems such as the viscous flow passing around blunt-headed bodies.
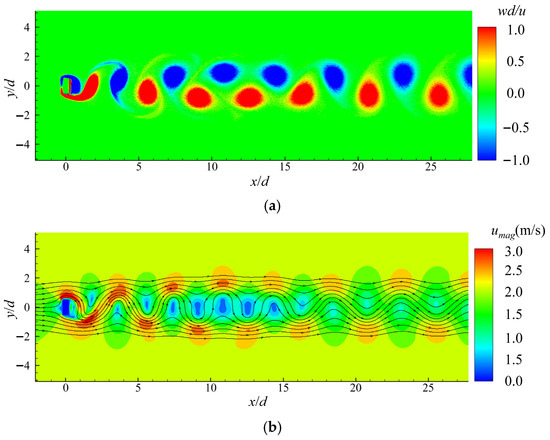
Figure 9.
(a) The vortex and (b) the flow field of the viscous flow passing around a rectangular cylinder at Re = 200.
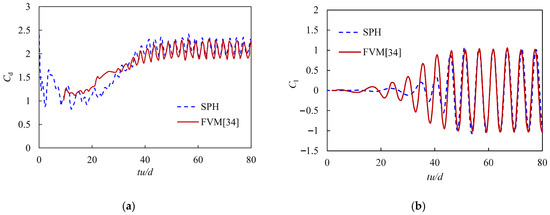
Figure 10.
Comparison of the time histories of (a) the drag coefficient Cd and (b) the lift coefficient Cl between the improved SPH method and the reported FVM.

Table 1.
Comparison of the mean of the drag coefficient, Cd.mean, and the root mean square of the lift coefficient, Cl.rms, calculated from this work and the reported work in Ref. [34].
4.2. A Free Body Sinking in a Fluid
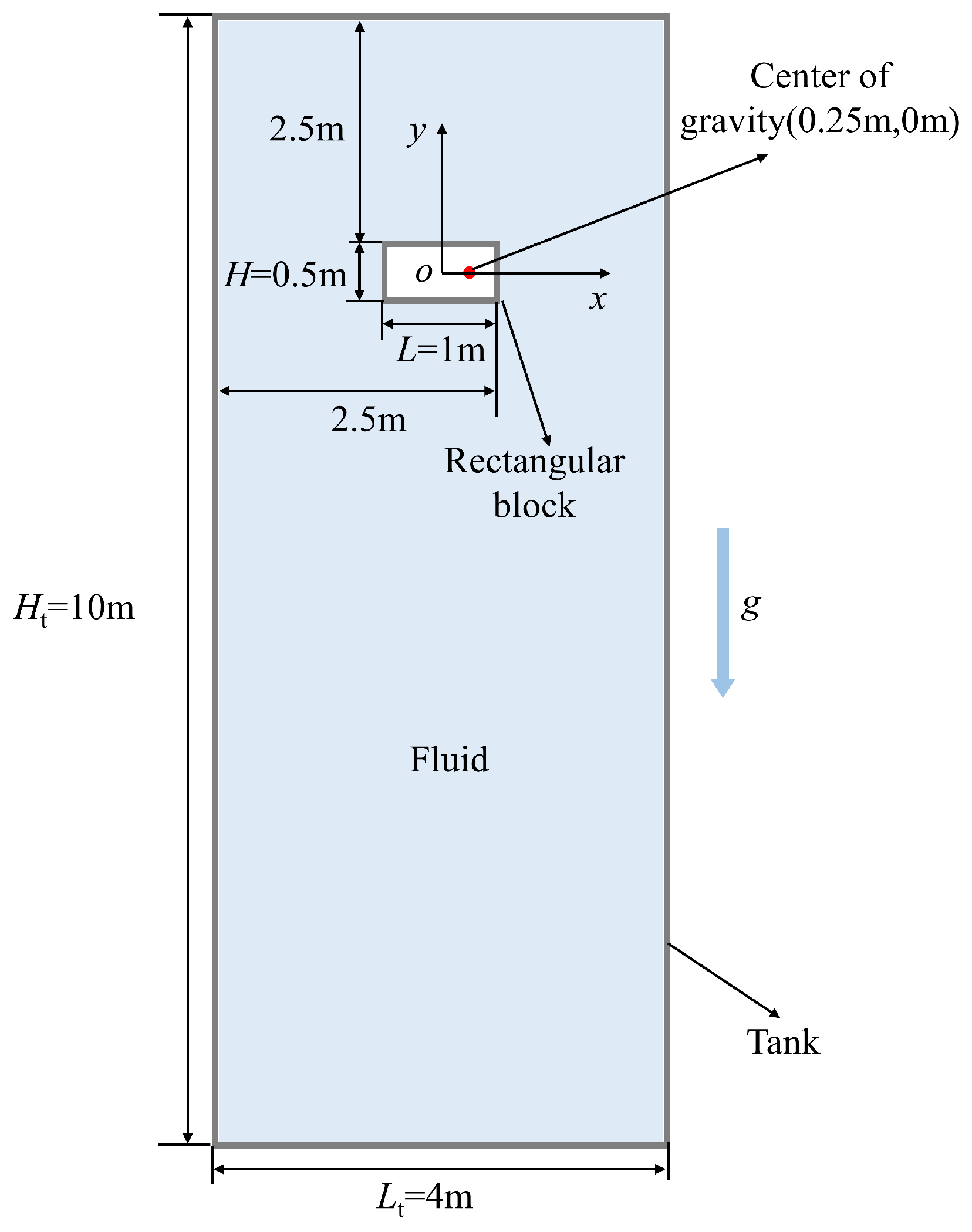
In this section, a case study of a free body sinking in a fluid with a moving refinement domain was conducted to validate the effectiveness of the dynamic adaptive SPH method developed in this work. As shown in Figure 11, a rectangular block with dimensions of 0.5 m in height H and 1 m in width L was submerged in a fluid-filled tank with dimensions of 10 m in height Ht and 4 m in width Lt. The origin of these coordinates is located at the centroid of the rectangular block and the center of gravity of the rectangular block (xco, yco) is located at (0.25 m, 0 m). The densities of the fluid and the rectangular block are set as ρf = 1.0 kg/m3 and ρb = 2.0 kg/m3, respectively. The gravity g is 1.0 m2/s, the initial velocity of the rectangular block is 0 m/s, and the kinematic viscosity of the fluid ν is 0.002 m2/s. In this validation case, the variations in the center of gravity and the roll angle θ(z) of the rectangular block were analyzed.

Figure 11.
Schematic of a free body sinking in a fluid.
A particle-independent test was carried out first based on three different particle resolutions, L/Δx = 50, L/Δx = 100, and L/Δx = 200, which was also used to verify the capability and assess the accuracy of the adaptive algorithm with the dynamic refinement and coarsening of the particles. Two refinement-coarsening sets were provided, including a refinement region with a particle resolution of L/Δx = 100 surrounded by a coarsening region with a particle resolution of L/Δx = 50, i.e., L/Δx = 100–50 and a refinement region with a particle resolution of L/Δx = 200 surrounded by a coarsening region with a particle resolution of L/Δx = 100, i.e., L/Δx = 200–100.
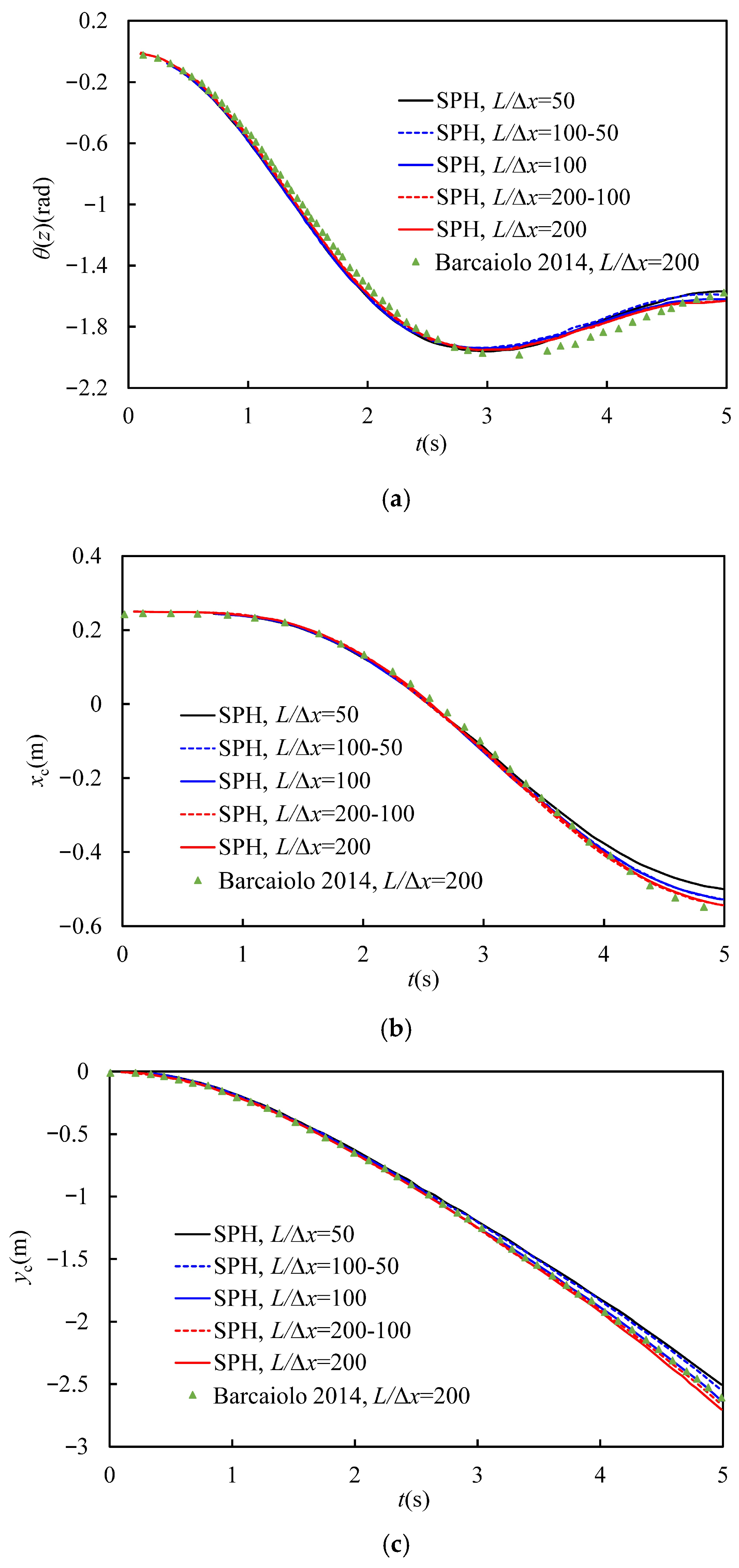
Figure 12 shows the evolution of the roll angle and the center of gravity with the time from t = 0.0 s to t = 5.0 s. First, the calculations converged gradually as the particle resolution increased from L/Δx = 50 to L/Δx = 200. Second, the evolution trends obtained from the refinement-coarsening sets showed growing agreement with the ones achieved from the cases of uniform particle resolutions when increasing particle resolutions. Third, the evolution trends obtained from the refinement-coarsening set of L/Δx = 200–100 displayed a satisfied consistency with the one achieved from the work reported in Ref. [20]. The corresponding quantitative comparison of the roll angle θ(z) and the displacement of the center of gravity of the rectangular block, xco−xc, and yco−yc, at t = 5.0 s between L/Δx = 200–100 and the Ref. [20] is provided in Table 2. It shows that the errors of θ(z), xco−xc, and yco−yc are relatively small at 4.46%, 2.44%, and 2.69%, respectively, indicating that the adaptive algorithm developed in this work can accurately figure out the problems with moving boundaries.

Figure 12.
Evolution of selected parameters of the rectangular block sinking in a fluid: (a) the roll angle θ(z), (b) the horizontal coordinate of the center of gravity of the rectangular block xc, and (c) the vertical coordinate of the center of gravity of the rectangular block yc [20].

Table 2.
Comparison of the roll angle and the displacement of the center of gravity of the rectangular block at t = 5.0 s between L/Δx = 200–100 and the Ref. [20].
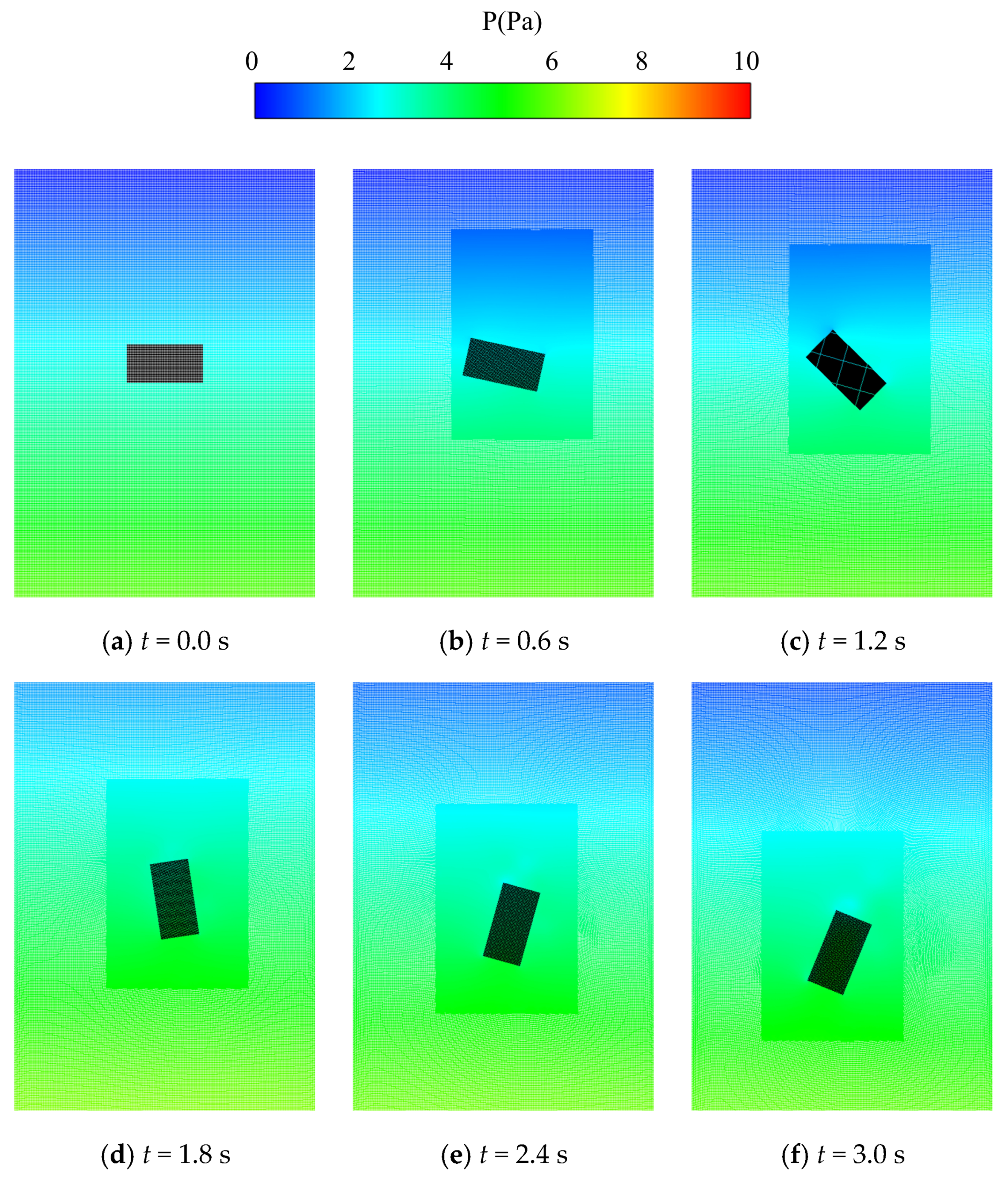
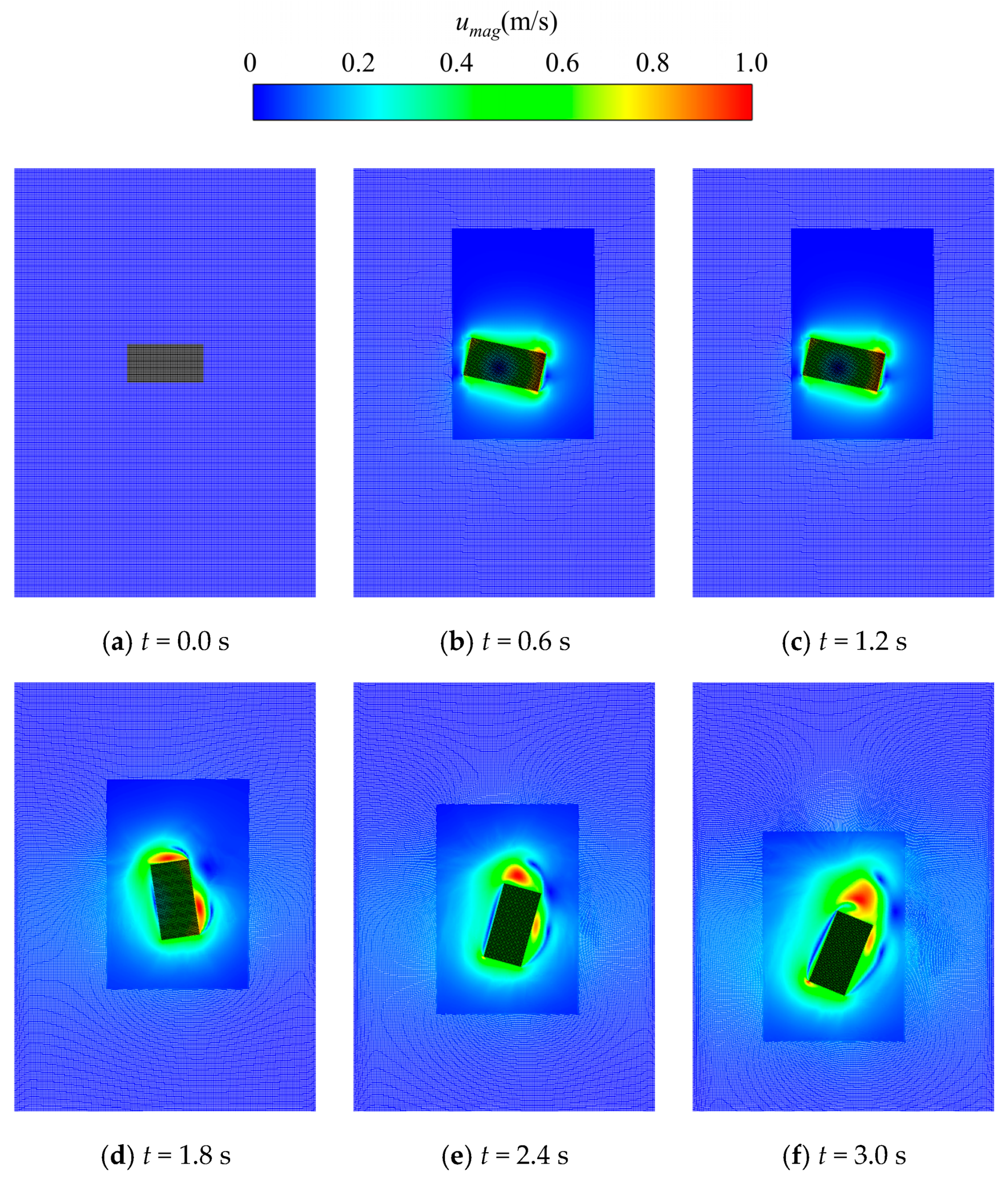
Figure 13 and Figure 14 illustrate the evolution of the pressure and the velocity when the rectangular block sinks into the fluid, respectively. Since vortexes shed from the rectangular block as it sinks, the flow field at the upper and the lower regions of the rectangular block varies more significantly and spreads more widely than that at the left and right regions. Therefore, this work applies a rectangular refinement region, with the longer edge being placed in the vertical direction in the simulation domain. As depicted in the figures, reasonable contour plots of pressure and velocity were obtained and then distributed rationally and smoothly in the dynamically varied refinement and coarsening regions.
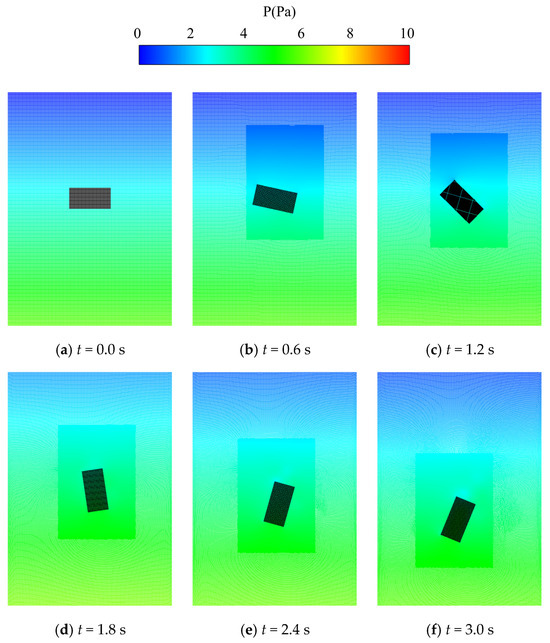
Figure 13.
Evolution of the pressure when the rectangular block sinks in the fluid.
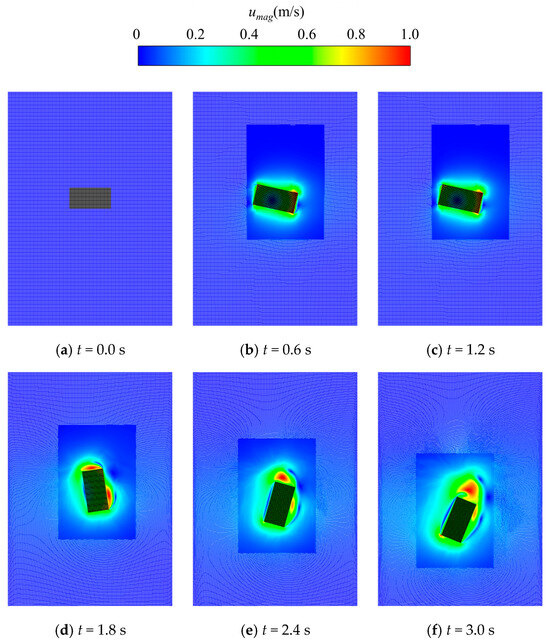
Figure 14.
Evolution of the velocity when the rectangular block sinks into the fluid.
In addition, conventional adaptive techniques normally induce unreasonable pressure peaks at the junctions between the refinement and the coarsening regions [37] due to the interaction of particles in different regions with different particle resolutions. It is still impossible to eliminate the discontinuity and distributions of the pressure between two different regions, even with the use of the buffer method proposed by Barcarolo et al. [20]. However, the upgraded adaptive algorithm reestablished in this work improves the dynamic refinement and coarsening of particles using the concept of guard areas to avoid the interaction of particles with different smooth lengths. This novel approach successfully eliminates pressure perturbations at the boundary of different refinement regions, and thus, stable, and continuous pressure and velocity fields are achieved, as shown in Figure 13 and Figure 14.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this work systematically investigates and reestablishes the SPH adaptive algorithm, the details of which are listed below:
- (1)
- A novel point generation algorithm based on the accelerated ray method is proposed, where the boundary is parameterized using Catmull–Rom cubic splines, and background Cartesian points are composed of particles within the flow field. The new point generation algorithm accelerates the discretization of the flow field into particles.
- (2)
- An improved dynamic particle refinement/coarsening algorithm based on the APR technique has been developed to solve the computational dispersion problem at the boundary between regions with different particle resolutions.
- (3)
- The shifting algorithm was improved in this work to ensure the particles are always well distributed during numerical calculations and, thus, efficiently facilitate the adaptive particle refinement/coarsening processes.
Two case studies were conducted to validate the high capabilities of the reestablished SPH adaptive algorithm to deal with the problems of viscous flows passing around blunt-headed bodies and the flows within dynamically moving refinement regions. The comparative analysis between the results obtained from this study and the literature demonstrates that the improved robust SPH adaptive algorithm in this study offers distinct advantages in generating a more precise flow field when compared to traditional SPH adaptive methods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Z.; methodology, J.Z. and Y.D.; software, J.Z., Y.D. and Y.J.; validation, Y.D. and Y.J.; investigation, W.W. and W.L.; data curation, W.W. and Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.W. and Y.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z. and W.L.; visualization, W.L.; supervision, Z.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the State Key Laboratory of Hydrodynamics [grant numbers 61422030302]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 52106246]; and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [grant numbers BK20200687]. And the APC was funded by the State Key Laboratory of Hydrodynamics [grant numbers 61422030302].
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Hydrodynamics [grant numbers 61422030302]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 52106246]; and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [grant numbers BK20200687].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Dong, L.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yao, B.; Lian, L. Numerical Study on the Water Entry of a Freely Falling Unmanned Aerial-Underwater Vehicle. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Qiao, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T. Numerical Study on Wave Dissipation and Mooring Force of a Horizontal Multi-Cylinder Floating Breakwater. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Ojeda, H.R.; Oyuela, S.; Sosa, R.; Otero, A.D.; Pérez Arribas, F. Fishing Vessel Bulbous Bow Hydrodynamics—A Numerical Reverse Design Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Woo, S.B. A numerical approach to the treatment of submerged water exchange processes through the sluice gates of a tidal power plant. Renew. Energy 2023, 219, 119408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Børve, S.; Omang, M.; Trulsen, J. Regularized smoothed particle hydrodynamics with improved multi-resolution handling. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 208, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S. SPH Liquid Simulation Method Based on Adaptive Smooth Length. Master’s Thesis, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, L.; Oger, G.; Leffe, M.D.; Touzé, D.L. Analysis and improvements of Adaptive Particle Refinement (APR) through CPU time, accuracy and robustness considerations. J. Comput. Phys. 2018, 354, 552–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 30, 543–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.P.; Papaloizou, J.C. Variable smoothing lengths and energy conservation in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1994, 270, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, G.; Doring, M.; Alessandrini, B.; Ferrant, P. Two-dimensional SPH simulations of wedge water entries. J. Comput. Phys. 2006, 213, 803–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.; Oger, G.; Touzé, D.L.; Guibert, D. Validation of a conservative variable-resolution SPH scheme including ∇h terms. In Proceedings of the 6th international SPHERIC Workshop (SPHERIC 2011), Hambourg, Germany, 8–10 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Attwood, R.E.; Goodwin, S.P.; Whitworth, A.P. Adaptive smoothing lengths in SPH. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 464, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kitsionas, S.; Whitworth, A.P. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics with particle splitting, applied to self-gravitating collapse. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 330, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olejnik, M.; Szewc, K.; Pozorski, J. SPH with dynamical smoothing length adjustment based on the local flow kinematics. J. Comput. Phys. 2017, 348, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, H.F.; Gao, W.R. SPH method with fully variable smoothing lengths and implementation. Chin. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 5, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Kong, S.C. Adaptive resolution for multiphase smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2019, 239, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, J.; Bonet, J. Dynamic refinement and boundary contact forces in SPH with applications in fluid flow problems. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Eng. 2007, 72, 295–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacondio, R.; Rogers, B.D.; Stansby, P.K.; Mignosa, P.; Feldman, J. Variable resolution for SPH: A dynamic particle coalescing and splitting scheme. Comput. Method. Appl. M. 2013, 256, 132–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.Y. A dynamic particle refinement strategy in Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics for Fluid-Structure Interaction problems. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2019, 100, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcarolo, D.A.; Touzé, D.L.; Oger, G.; Vuyst, F.D. Adaptive particle refinement and derefinement applied to the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. J. Comput. Phys. 2014, 273, 640–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Z.; Xu, F.; Yang, Y.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.Y. A GPU-accelerated adaptive particle refinement for multi-phase flow and fluid-structure coupling SPH. Ocean Eng. 2023, 279, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shen, L.; Nguyen, G.D.; El-Zein, A.; Maggi, F. A smoothed particle hydrodynamics framework for modelling multiphase interactions at meso-scale. Comput. Mech. 2018, 62, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, J.J. Simulating Free Surface Flows with SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 1994, 110, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ouyang, J.; Jiang, T. Simulation of complex filling process based on the generalized Newtonian fluid model using a corrected SPH scheme. Comput. Mech. 2012, 49, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Wang, S.P.; Peng, Y.X.; Zhang, A.M. A novel coupled Riemann SPH–RKPM model for the simulation of weakly compressible fluid–structure interaction problems. Ocean Eng. 2022, 266, 112447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, J.P.; Weißenfels, C.; Wriggers, P. Free surface tension in incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamcis (ISPH). Comput. Mech. 2020, 65, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Lu, L.G.; Lu, W.G. The numerical investigation of spreading process of two viscoelastic droplets impact problem by using an improved SPH scheme. Comput. Mech. 2014, 53, 977–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colagrossi, A.; Antuono, M.; Touzé, D.L. Theoretical considerations on the free-surface role in the smoothed-particle-hydrodynamics model. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 79, 056701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C. Physically Based Modeling and Simulation of 1D Flexible Parts Deformation with Constraints. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Q. Research on Algorithms of Computational Geometry in GIS. Master’s Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J. 3D Solid Modeling and Boolean Operation Modeling Technique. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- López, Y.R.; Roose, D. Dynamic refinement for fluid flow simulations with SPH. In Proceedings of the II International Conference on Particle-Based Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, Barcelona, Spain, 26–28 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- López, Y.R.; Roose, D.; Morfa, C.R. Dynamic particle refinement in SPH: Application to free surface flow and non-cohesive soil simulations. Comput. Mech. 2013, 51, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Colagrossi, A.; Durante, D.; Graziani, G. Simulating 2D viscous flow around geometries with vertices through the Diffused Vortex Hydrodynamics method. Comput. Method. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2016, 302, 147–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swegle, J.W.; Hicks, D.L.; Attaway, S.W. Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Stability Analysis. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 116, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, S.; Colagrossi, A.; Antuono, M.; Colicchio, G.; Graziani, G. An accurate SPH modeling of viscous flows around bodies at low and moderate Reynolds numbers. J. Comput. Phys. 2013, 245, 456–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcarolo, D.A. Improvement of the Precision and the Efficiency of the SPH Method: Theoretical and Numerical Study. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Centrale de Nantes, Nantes, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).