Development of Novel Hydraulic 3D Printed Actuator Using Electrorheological Fluid for Robotic Endoscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
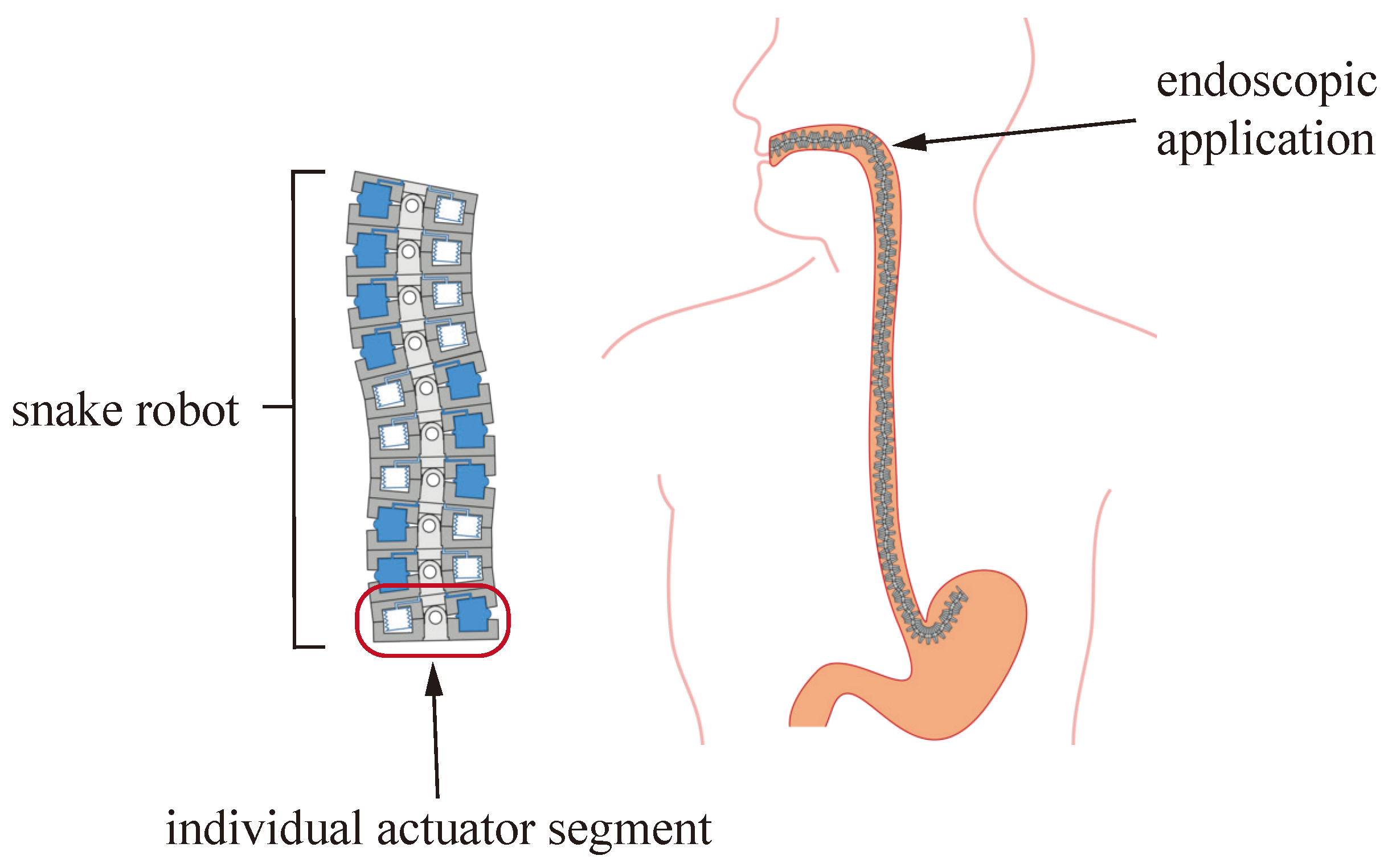
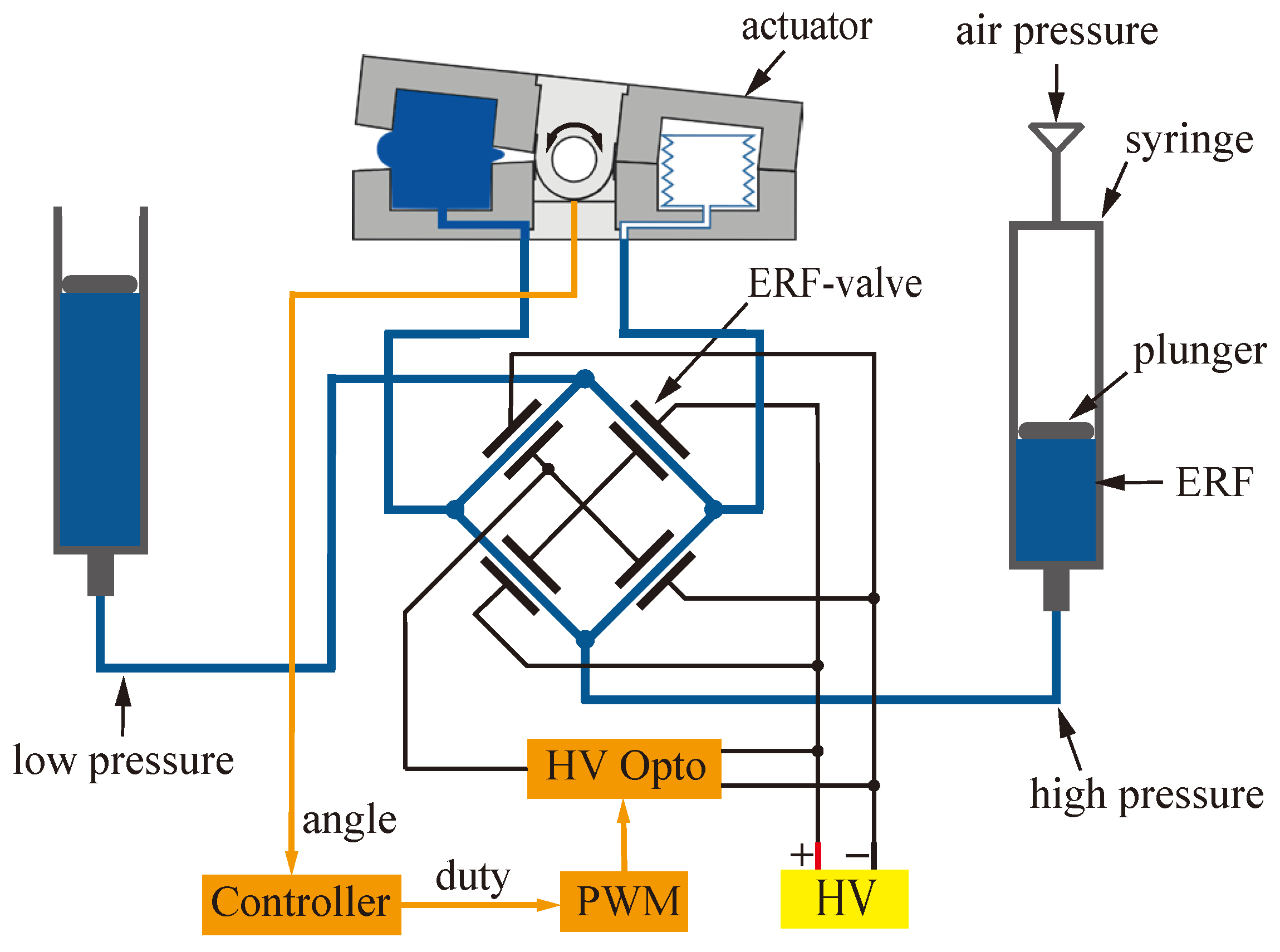
1.1. Actuation Concept
- Development of a suitable manufacturing process for miniaturized and pressure-tight ERF hydraulics.
- Integration of a suitable sensor for measuring the actuator rotation.
- Establishment of a control system to maneuver the actuator module to a desired position.
1.2. Related Work
2. Materials and Methods
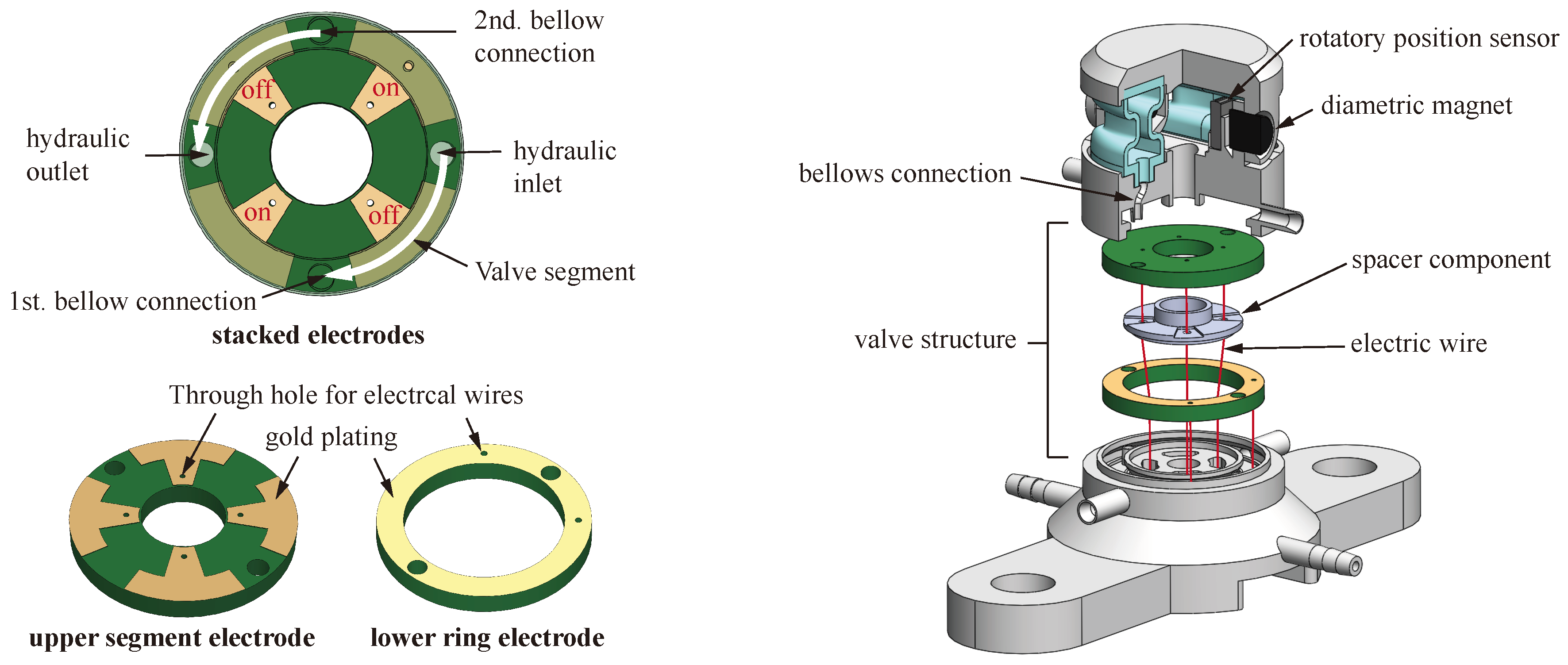
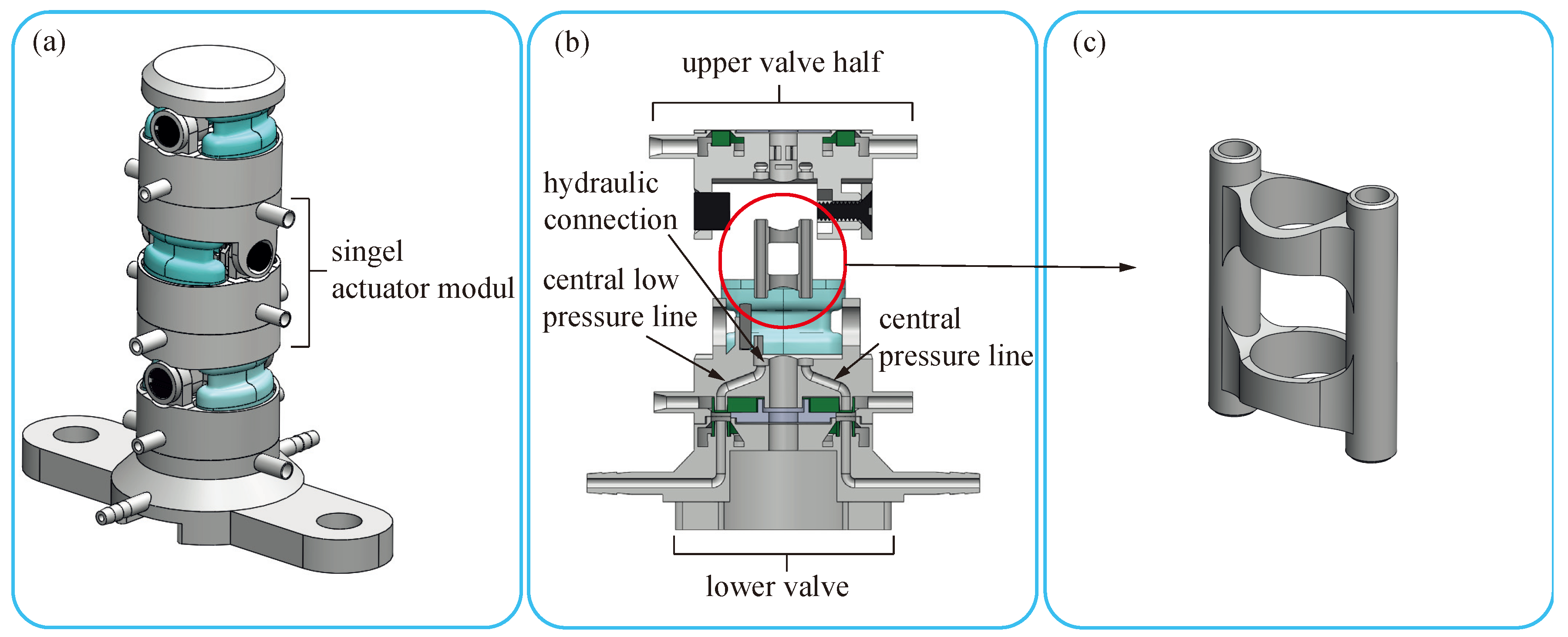
2.1. Actuator Design
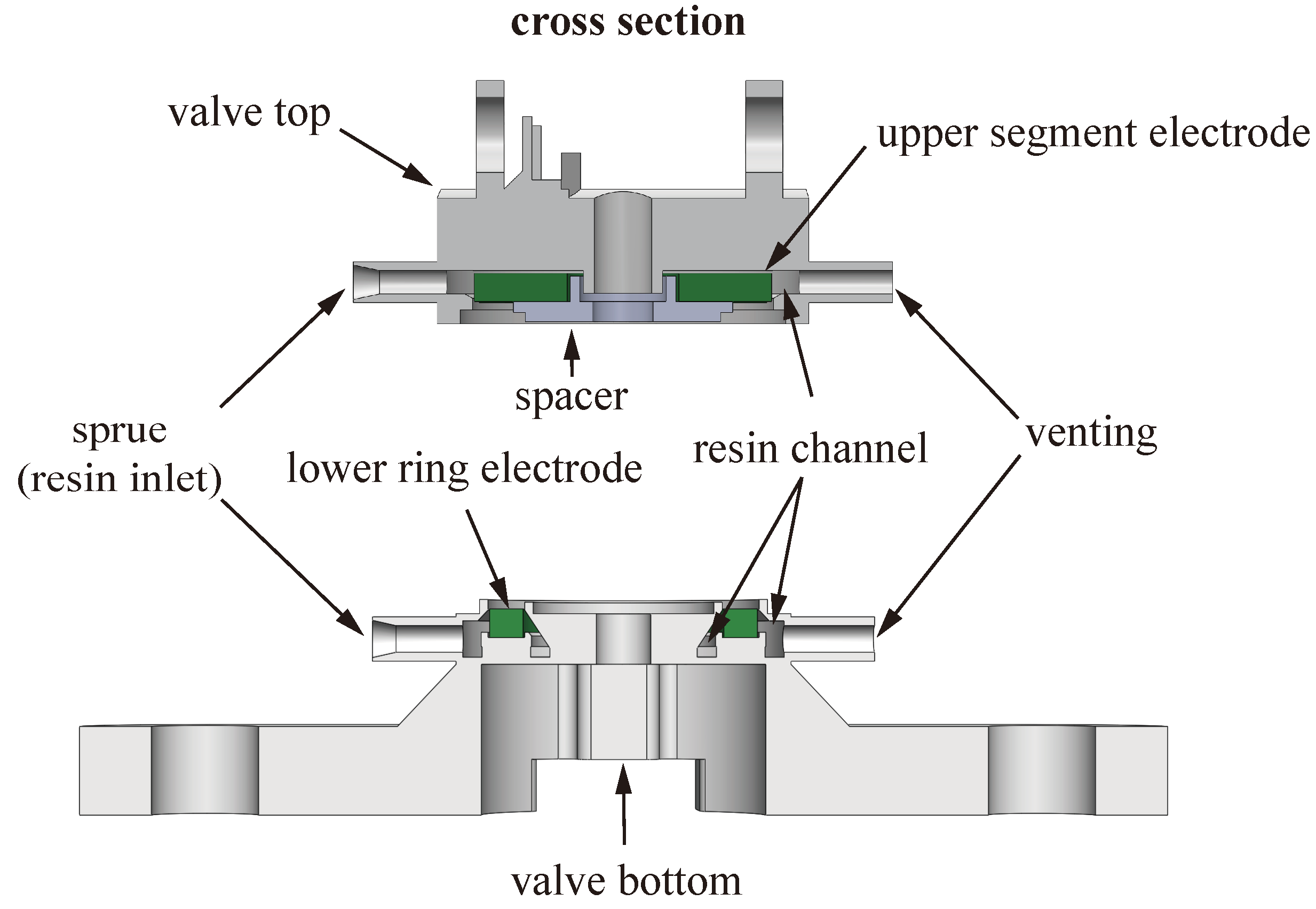
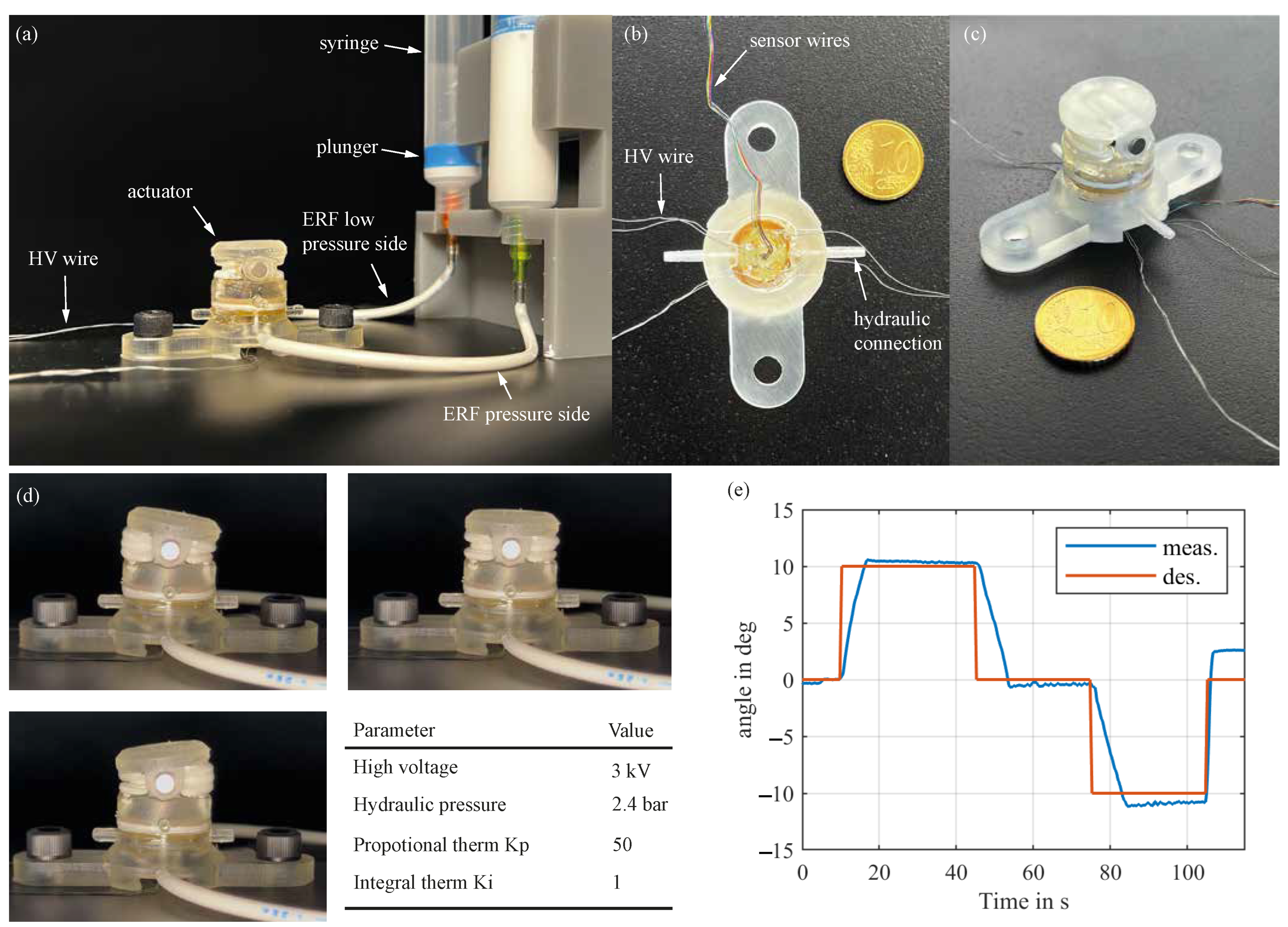
2.2. Actuator Fabrication
3. Experiments
Experiment Setup
4. Results
5. Discussion
- Further miniaturization development to achieve a maximum outer diameter of 10 mm
- Development of integrable and long-term stable bellows
- Serial connection of multiple actuators to form a snake-like robot
- Control of the assembled snake robot.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fatikow, S. Mikroroboter und Mikromontage: Aufbau, Steuerung und Planung von Flexiblen Mikroroboterbasierten Montagestationen, softcover reprint of the hardcover 1st edition 2000 ed.; B.G. Teubner: Stuttgart/Leipzig, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Janocha, H. Unkonventionelle Aktoren; Oldenbourg Verlag: Oldenbourg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfarth, M. Hydraulic miniature actuators controlled by electrorheological fluid. In Proceedings of the ACTUATOR 2018—16th International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuators and Drive Systems, Conference Proceedings, Bremen, Germany, 25–27 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liljebäck, P. Snake Robots: Modelling, Mechatronics, and Control, 1st ed.; Advances in Industrial Control Ser; Springer London Limited: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Hong, N.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S. Soft robot review. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhawary, H.; Zivanovic, A.; Davies, B.; Lampérth, M. A review of magnetic resonance imaging compatible manipulators in surgery. Proc. Inst. Mech. Engineers. Part H J. Eng. Med. 2006, 220, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, Y.; Amirat, Y.; Fried, G. Modeling and Control of a Continuum Style Microrobot for Endovascular Surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2011, 27, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumori, K.; Endo, S.; Kanda, T.; Kato, N.; Suzuki, H. A Bending Pneumatic Rubber Actuator Realizing Soft-bodied Manta Swimming Robot. In Proceedings of the Proceedings 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; IEEE: Toulouse, France, 2007; pp. 4975–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzani, T.; Gerboni, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Menciassi, A. A bioinspired soft manipulator for minimally invasive surgery. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2015, 10, 035008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, J. A review of soft manipulator research, applications, and opportunities. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 281–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzani, T.; Cianchetti, M.; Gerboni, G.; de Falco, I.; Menciassi, A. A Soft Modular Manipulator for Minimally Invasive Surgery: Design and Characterization of a Single Module. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanov, E.; Nguyen, T.D.; Burgner-Kahrs, J. Tendon-driven continuum robots with extensible sections—A model-based evaluation of path-following motions. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2021, 40, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.R.; Krebs, H.I. An Electrorheological Fluid Actuator for Rehabilitation Robotics. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 2156–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusho, J.; Zhang, G.; Sakaguchi, M. Vibration Suppression Control of Robot Arms Using a Homogeneous-Type Electrorheological Fluid. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 25 April 1997; IEEE: Toulouse, France, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zatopa, A.; Walker, S.; Menguc, Y. Fully Soft 3D-Printed Electroactive Fluidic Valve for Soft Hydraulic Robots. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virta, A.; Timonen, J.V.; Ras, R.H.; Zhou, Q. Force sensing using artificial magnetic cilia. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vilamoura, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoshi, T.; Yoshida, K.; in Eom, S.; Yokota, S. Proposal of a multiple ER microactuator system using an alternating pressure source. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 2015, 222, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helios Klinikum Aue. Ablauf Einer Magenspiegelung—Gastroskopie. Available online: https://www.helios-gesundheit.de/kliniken/aue/unser-angebot/unsere-fachbereiche/gastroenterologie-hepatologie/patientenwissen-ablauf-gastroskopie/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- HUBS. Auswahl des Richtigen 3D-Druckverfahrens: Entscheidungshilfen und Allgemeine Richtlinien, die Sie bei der Auswahl des Richtigen 3D-Druckverfahrens für Ihre Anwendung Unterstützen. Available online: https://www.hubs.com/de/wissensbasis/auswahl-3d-druckverfahren/ (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Formlabs. Wie Sie den Richtigen 3D-Industriedrucker Auswählen. Available online: https://formlabs.com/de/blog/industrielle-3d-drucker/ (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Lachmayer, R. Additive Manufacturing Quantifiziert; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fomlabs. Elastic Resin: Ein Widerstandsfähiges, Weiches und Flexibles 3D-Druckmaterial. Available online: https://formlabs.com/de/blog/elastic-resin-silikon-3d-druck/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- KG Rubberpoint. Roh- & Zusatzstoffe. Available online: https://www.kgk-rubberpoint.de/roh-zusatzstoffe/oberflaechenaktivierung-reicht-aus-281.html (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- 3M. Klebstoff- und Klebebandlösungen: Oberflächenenergie Kategorisieren. Available online: https://www.3mdeutschland.de/3M/de_DE/kleben-und-verbinden/schulung-weiterbildung/die-wissenschaft-des-klebens/oberflaechenenergie-kategorisieren/ (accessed on 6 September 2023).
- University of Michigan. Control Tutorials for Matlab & Simulink. Available online: https://ctms.engin.umich.edu/CTMS/index.php?example=Introduction§ion=ControlPID (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Su, H.; Kwok, K.W.; Cleary, K.; Iordachita, I.; Cavusoglu, M.C.; Desai, J.P.; Fischer, G.S. State of the Art and Future Opportunities in MRI-Guided Robot-Assisted Surgery and Interventions. Proc. IEEE. Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 110, 968–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frishman, S.; Kight, A.; Pirozzi, I.; Coffey, M.C.; Daniel, B.L.; Cutkosky, M.R. Enabling In-Bore MRI-Guided Biopsies With Force Feedback. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2020, 13, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Attributes | FDM | MMJ | SLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Printing process | Filament Extrusion | Material Droplets | Photopolymerization |
| Tolerances | ±0.5% | ±0.1–±0.2% | ±0.1–±0.2% |
| Material layering | applying | applying and curing | applying and layer penetrating laser curing |
| Post-processing process | Low | High | Medium |
| Stop printing (to insert parts) | Yes | Yes | No |
| Costs | Low | High | Medium |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadi, F.; Holthausen, J.; Stallkamp, J.; Siegfarth, M. Development of Novel Hydraulic 3D Printed Actuator Using Electrorheological Fluid for Robotic Endoscopy. Actuators 2024, 13, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040119
Sadi F, Holthausen J, Stallkamp J, Siegfarth M. Development of Novel Hydraulic 3D Printed Actuator Using Electrorheological Fluid for Robotic Endoscopy. Actuators. 2024; 13(4):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040119
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadi, Fabian, Jan Holthausen, Jan Stallkamp, and Marius Siegfarth. 2024. "Development of Novel Hydraulic 3D Printed Actuator Using Electrorheological Fluid for Robotic Endoscopy" Actuators 13, no. 4: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040119
APA StyleSadi, F., Holthausen, J., Stallkamp, J., & Siegfarth, M. (2024). Development of Novel Hydraulic 3D Printed Actuator Using Electrorheological Fluid for Robotic Endoscopy. Actuators, 13(4), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/act13040119







