Abstract
This paper presents an overview of cooperative actuator and sensor systems based on dielectric elastomer (DE) transducers. A DE consists of a flexible capacitor made of a thin layer of soft dielectric material (e.g., acrylic, silicone) surrounded with a compliant electrode, which is able to work as an actuator or as a sensor. Features such as large deformation, high compliance, flexibility, energy efficiency, lightweight, self-sensing, and low cost make DE technology particularly attractive for the realization of mechatronic systems that are capable of performance not achievable with alternative technologies. If several DEs are arranged in an array-like configuration, new concepts of cooperative actuator/sensor systems can be enabled, in which novel applications and features are made possible by the synergistic operations among nearby elements. The goal of this paper is to review recent advances in the area of cooperative DE systems technology. After summarizing the basic operating principle of DE transducers, several applications of cooperative DE actuators and sensors from the recent literature are discussed, ranging from haptic interfaces and bio-inspired robots to micro-scale devices and tactile sensors. Finally, challenges and perspectives for the future development of cooperative DE systems are discussed.
1. Introduction
The development of cooperative systems, in which several entities (or agents) perform a complex task by sharing information with their neighbors and coordinating in a decentralized fashion, represents an attractive and highly challenging goal for researchers working in many areas [1]. Compared to centralized system architectures, the advantages of cooperative solutions include ability to adapt to a great variety of configurations and/or environments, modularity, robustness to failures and disturbances, and a reduced amount of computational effort. The paradigm shift from centralized to cooperative architectures has been made possible by recent technological advances in miniaturized actuators and sensors [2], as well as by the development of reliable and communication paradigms [3] and distributed control algorithms [4]. At the macro-scale, the introduction of cooperative strategies has led to a number of novel concepts and applications, which range from the intelligent management of smart grids [5] and sensor networks [6] to the coordination of teams of autonomous vehicles [7], robots [8], and unmanned aerial vehicles [9], to mention few examples. At the same time, cooperative concepts have also been successfully applied to micro electro-mechanical systems (MEMS), leading to devices in which a complex global task is accomplished via the cooperation of several micro-actuator units. Some relevant examples include arrays of micro-actuators functioning as micro-conveyors [10,11,12,13], micro-manipulators [14,15,16], micro-fluidic systems [17], and reconfigurable structures [18,19].
In macro-scale cooperative systems, the individual behavior of each agent is generally well understood, and most of the technological issues are related to communication and control strategies, as well as energy autonomy. In case of meso- or micro-scale cooperative devices, however, integration and miniaturization efforts also represent highly critical technological challenges [20]. Moreover, even though some authors succeeded in implementing advanced control paradigms in cooperative micro-actuators [21,22,23,24], most such devices are still controlled via centralized or open-loop methods, possibly due to the challenges in miniaturizing the sensing, communication, and online processing units. As a result, the full exploitation of the benefits of cooperative control in micro-actuator systems is still far from being achieved. Examples of micro-actuator application areas that may benefit from new features introduced by cooperative control methods include haptics [25,26], wearables [27], and reconfigurable displays [28].
A potential means to enhance miniaturization while keeping the desired actuation/sensing and cooperative functionalities consists of adopting highly integrated multifunctional transducers based on smart materials. This term refers to active materials capable of modifying their mechanical properties (e.g., geometry, force, stiffness) when subjected to an external stimulus of electrical, magnetic, thermal, or chemical nature [29,30,31]. Thanks to the so-called self-sensing operating mode, smart material transducers are able to work as actuators and sensors at the same time, thus allowing to reduce cost and size of the final device [32,33,34]. Even though most of the state-of-the-art cooperative micro-actuators are driven by conventional technologies (e.g., silicon actuators, microfluidic valves), a number of smart-materials-based prototypes have also been successfully developed. Some notable examples include tactile displays made of shape memory alloy [35], piezoelectric unimorph actuators [36], shape memory polymer flexile tactile displays [37], and artificial skins based of stimuli-responsive hydrogel [38].
Among the many transducers that appear as potential candidates for the design of cooperative micro-actuators, dielectric elastomers (DEs) represent a highly promising alternative [39]. A DE consists of a flexible and highly stretchable capacitor made of polymeric material. Thanks to their large deformability, design scalability, high energy density and efficiency, and dual actuator/sensor behavior, DEs have become a popular technology in various areas of mechatronics, including industrial actuators [40,41], soft robotics [42,43], wearables [44,45], and artificial muscles [46,47]. Despite most of currently developed DE-based devices are stand-alone systems that operate at the macroscopic level [48], these active materials offer many opportunities for the development of innovative small-scale cooperative applications [30,49]. In contrast to other types of cooperative systems based on micro-valves and silicon MEMS technologies, the intrinsic flexibility and large deformability of DE transducers open up new areas of applications, such as intelligent wearables, smart skins, and bio-inspired soft robots.
The goal of this review paper is to provide an overview of recently developed cooperative actuator and sensor systems based on DE technology. Throughout this work, the term cooperative is used to refer to those devices in which many DE units are arranged in an array-like layout, resulting in a fully integrated system where the single elements interact with each other to perform coordinated tasks of various complexity. Potential examples include reconfigurable haptic displays, bio-inspired robots capable of coordinated motion, conveyors of small objects, and wearable sensor surfaces for the detection of local pressure distributions. After describing the basic operating principle of DE transducers and presenting the most common types of DE actuator configurations, a wide variety of cooperative DE systems from the recent literature is presented, focusing on both actuation and sensing applications. Although most of the current cooperative DE systems are developed to operate at the macro-scale, examples of concepts that push the miniaturization limits of the technology will also be highlighted.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the basic operating principle of DE transducers and presents the most common types of actuator configurations used in cooperative applications. A variety of cooperative DE actuators and sensors from the literature are then reviewed in Section 3. Finally, Section 4 outlines future perspective and possible new research directions for cooperative DE systems.
2. Dielectric Elastomer Transducers
This section summarizes the basic operating principle of DE transducers. After describing the basic actuation and sensing principle of the transducer, the most common types of DE layouts encountered in cooperative applications are presented.
2.1. Dielectric Elastomer Material and Operating Principle
A DE basically consist of a thin (typically 20–100 μm) layer of highly elastic dielectric material coated with compliant electrodes on both surfaces. Common materials used as dielectric are acrylics [50], silicones [51], natural rubbers [52], synthetic rubbers [53], and polyurethane [54], while the compliant electrodes can be manufactured via carbon-based compounds [55] or thin metal films [56]. The first documented investigation of DEs is due to Röntgen, who demonstrated their operating principle back in 1880 [57]. The effect was then rediscovered more than one century after by Pelrine and coworkers [58], causing a renovated interest in the technology by the smart materials research community. Over the last two decades, DEs have generated a large amount of basic and applied research, which led to the publications of the first standards in 2015 [59].
To understand the operating principle of a DE actuator (DEA), we consider the sketch provided in Figure 1a in which an undeformed DE membrane is depicted. When an electric voltage difference is applied between the electrodes, charges of opposite signs are stored onto them. The combination of attractive electrostatic forces among charges of opposite signs (i.e., between the two electrodes), and repulsive electrostatic forces among charges on the same sign (i.e., on the same electrode) cause the DE membrane to reduce in thickness and expand in area, as shown in Figure 1b. This electro-mechanical transduction principle can be quantified via the following equation [58]:
where σMax is the Maxwell stress, i.e., the compressive stress that arises as a consequence of the applied voltage (cf. Figure 1b), ϵ0 and ϵr are the vacuum and DE relative permittivity, respectively, while E is the electric field in the material and is given by the ratio between applied voltage v and membrane thickness z. In order to practically understand the effect of Maxwell stress in Equation (1) on the overall material response, Figure 1c reports an example of (in-plane) force-displacement curves of a DE membrane for different applied voltages [60]. As it can be seen, the application of the voltage results into a change of the elastic force. This fact plays a key role when designing a DEA, as it will be discussed in Section 2.2. Furthermore, it can be noticed that the DEA curves also exhibit nonlinearities and a rate-dependent hysteresis because of the complex response of the elastomer.
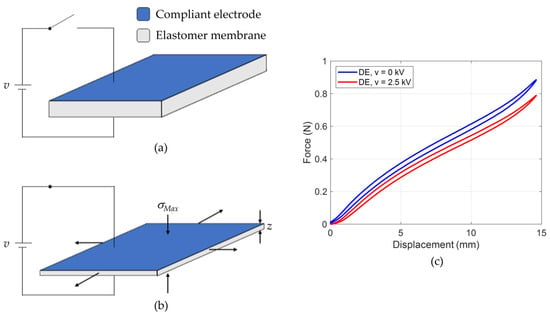
Figure 1.
Operating principle of a DEA, deactivated state (a), activated state (b), and example of force-displacement characteristics for different applied voltages (c).
Other than working as an actuator, a DE membrane can also be used in sensing applications. With respect to the DE sensor (DES) layouts shown in Figure 2a,b, we can express the electrical capacitance via the usual parallel-plate capacitor equation:
where Ci, Ai, and zi represent the capacitance, surface area, and thickness of the DES when being undeformed (i = 0, Figure 2a) and deformed by an external in-plane force (i = 1, Figure 2b), respectively. Since the DE material is incompressible [39], the total volume of elastomer remains constant in both states, i.e., z0A0 = z1A1. Using this fact in conjunction with Equation (2) leads to:
which implies that we can use the change in capacitance to detect geometric changes in the DES membrane thickness or area. An example of experimental capacitance-displacement curve of a DES is shown in Figure 2c, confirming the monotonic relationship between the two quantities.
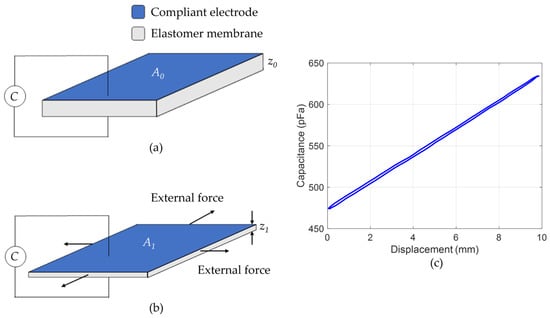
Figure 2.
Operating principle of a DES, undeformed state (a), deformed state (b), and example of capacitance-displacement characteristics (c).
In general, the performance of a DE are strongly dependent on the adopted material. For instance, while acrylic elastomers are able to sustain reversible deformations up to 400–500% and exhibit a relatively low elastic modulus (on the order of 20 kPa), they are also subject to high electro-mechanical losses which, in turn, results in inefficient and slow operations [53,61]. On the other hand, silicone elastomers are more rigid (on the order of 100–1000 kPa) and can sustain deformations up to 100%, but are significantly faster (>50 times), exhibit smaller losses, and have a longer (>100 times) cyclic lifetime [62,63]. Another important aspect is represented by the compliant electrodes, which are used to apply a high voltage. Since the elastomer can undergo very large deformations, the electrode must also be capable of high stretchability and compliance, while exhibiting at the same time low mechanical degradation and resistivity [56,64]. Commonly, these features are achieved with carbon-based materials, such as carbon powder [65], carbon grease [66], or carbon black [67], whose manufacturing can be systematically addressed via inkjet printing [68], screen printing [55], or dip-coating processes [69]. While this process usually results in electrodes thickness on the order of 5 μm and sheet resistances of 50 kΩ/□, it has recently been shown that ultrathin (10 nm) sputter-deposited metallic electrodes result in a sheet resistance on the order of 0.5 kΩ/□, and are able to withstand a strain up to 200% while remaining electrically conductive [70]. Nanoscale electrodes, in conjunction with laser-structuring methods [71], open up the possibility of using DE transducers in micro-scale applications.
2.2. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators Configurations
The Maxwell stress described by Equation (1) represents the main physical principle that enables the use of DE in actuator applications. The main advantages of DEAs include large deformations, high compliance and flexibility, low power consumption (on the order of mW), high energy density and efficiency, broad bandwidth (from DC up to several kHz), lightweight, and low cost [39]. The intrinsic multi-functionalities of DE transducers makes it possible to use them as actuators and sensors at the same time, by exploiting the so-called self-sensing mode. In this way, one can reconstruct the DEA displacement [34,72,73,74] or force [75] via online processing of electrical quantities only (e.g., electric voltage and current), and eventually use this information to implement a sensorless control system [76,77,78]. Major drawbacks of DEA technology include the need to generate a high voltage on the order of several kV (for membrane thickness within the range 20–100 μm) to produce a meaningful actuation. This, in turn, results into high electric fields which are close to the breakdown strength of the material [79,80], negatively affecting the lifetime of the device. In addition, the strong nonlinearities of the material, in combination with the large deformations, makes their accurate modeling and control a highly challenging task [81,82].
The high flexibility of DEAs makes it possible to generate a variety of layouts and actuation modes [83]. It can be noted that the Maxwell stress principle shown in Figure 1 can be exploited to generate two different actuation modes, i.e., thickness contraction and membrane expansion. Those two modes are exploited to develop different types of DEAs.
The thickness reduction mode can be naturally used to develop contractile actuators. Since the absolute thickness reduction of a single DE layer is on the order of few micrometers, one generally achieves a macroscopic stroke by stacking together several layers, which are then activated simultaneously with the same high voltage signal [84,85]. A sketch showing the layout and principle of such actuators is reported in Figure 3a. Stack DEAs allow to simply tune the actuation stroke and force by changing the number of layers and the electrode surface areas, thus they appear as highly scalable. Other advantages of this topology include high compactness and energy density. In general, stack DEAs are preferred when one needs to generate higher forces rather than large stroke.
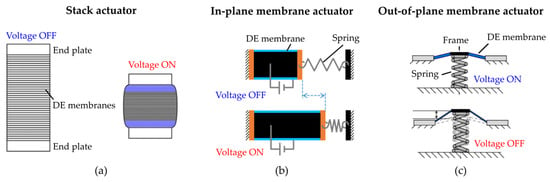
Figure 3.
Different types of DEAs: stack actuator (a), in-plane membrane actuator (b), out-of-plane membrane actuator (c).
At the same time, the electrode area expansion mode can be also exploited as a means for an actuation. In this case, differently from the stack actuator case, the motion is an elongation rather than a contraction. Membrane DEAs can be further divided into two sub-categories, i.e., in-plane actuators and out-of-plane actuators. On the one hand, when an in-plane membrane DEA is electrically activated, its motion is always restricted to a two-dimensional plane, see Figure 3b. Examples of in-plane membrane DEAs include strips [86,87], uniaxial rolls [88,89], and lozenge-shaped [90]. On the other hand, the motion of out-of-plane membrane DEAs is not constrained to a two-dimensional plane, thanks to the adoption of design solutions that generate external forces directed orthogonally to the elastomer, see the example in Figure 3c. Examples in this category include cones [91,92,93], double-cones [91,94,95], and bending structures [96,97]. A wide variety of actuation patterns can be realized through membrane actuators, depending on the type of geometry and pre-loading condition to which the membrane is subjected. Membrane actuators are preferred when one needs to generate a larger stroke, possibly in combination with a complex motion pattern, even though stacking concepts can be used also in this case to multiply the amount of force [98].
In order to generate a meaningful actuation stroke, a membrane DEA is usually combined with a mechanical biasing system which provides a pre-load force. It is remarked that the role of such a biasing system is fundamental in determining the performance of the actuator [99], and can lead to an increase in stroke up to one order of magnitude given the same DE membrane layout and applied voltage [86]. To understand why, we notice that at equilibrium the force of the DE membrane and the one of the biasing system must be equal. Graphically, such equilibrium condition can be obtained by plotting the biasing system force-displacement curve on top of the DE membrane characteristics, and checking for the corresponding intersection points. In particular, the intersections between the biasing curve and the low/high voltage DE curve correspond to the equilibrium position when the DE is deactivated/activated; thus, their inspection allows to readily estimate the stroke. Figure 4 provides several examples of commonly adopted biasing systems, together with the corresponding force-displacement curves for prediction of the stroke. As it can be seen, conventional biasing solutions, such as hanging masses [88,100], linear springs [101,102], pressurized air [103,104], or a second DE membrane [105,106] leads to a relatively small actuation stroke. In contrast, the use of negative-stiffness types of springs results in a significantly larger amount of stroke, since the resulting change in slope allows the biasing system curve to fit between the two DEA characteristics (note that the slope of the biasing curve appears as positive even though the stiffness is negative, since we are plotting the bias curve with respect to the DE deformation, not the biasing one). In the literature, this type of negative-stiffness biasing has been achieved in several ways, e.g., via bi-stable beams [91,99], attracting permanent magnets [107], compliant [92] as well as spring-based mechanisms [108], or buckling polymeric domes [109].
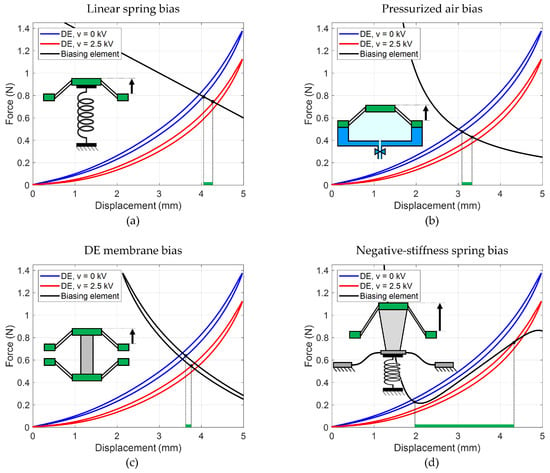
Figure 4.
Examples of biasing elements used in membrane DEAs: linear spring (a), pressurized air (b), a second DE membrane (c), and negative-stiffness spring (d). In each case, the green segment quantifies the resulting actuation stroke.
3. Dielectric Elastomer Applications in Cooperative Actuator and Sensor Systems
The unique combination of large strain, scalability, high energy density, low power consumption, low cost, and self-sensing has made DE technology highly attractive for the realization of cooperative actuator and sensor systems. A prototypical example of such device is shown in Figure 5. Here, several DE elements are arranged in an array-like layout, and can be operated either as actuators or as sensors (or, eventually, as self-sensing actuators capable of executing both modes at the same time). The synergistic coordination among the various taxels enables complex tasks that are not achievable with individual actuators. Possible examples include wearable haptic interfaces capable of recognizing different touch inputs from the user and sending them wave patterns accordingly, reconfigurable displays, and micro-conveyors. Clearly, a system as the one in Figure 5 requires a synergistic combination of system design, miniaturization, microfabrication, as well as modeling and cooperative control to enable intelligent self-sensing operations.
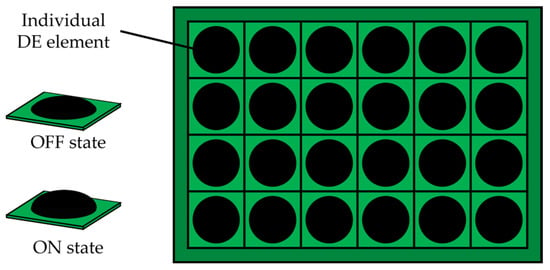
Figure 5.
A prototypical example of cooperative DE actuator/sensor system.
3.1. Towards Meso- and Micro-Scale Dielectric Elastomer Actuators
Over the last two decades, progresses in DE micromachining [110,111,112,113] have made possible to systematically scale size and accuracy of DEAs to the mm and sub mm scale [114]. As an example, Carpi et al. presented in [115] a bio-inspired lens having a size similar to human eyes (7.6 mm diameter), and capable of actively adjusting its focal length of about 26%, see Figure 6a. The same group proposed in [116] a hydrostatically coupled bubble-like DEA for tactile displays, having a size of about 6 mm capable of producing an out-of-plane displacement of 18% and stresses up to 2.2 kPa under a static actuation at 2.25 kV. A similar concept was presented by Kim et al. in [117], in the context of a button-like haptic actuator application. This completely transparent DEA is about 5 mm large, and exhibits a stroke of ~1 mm when actuated via 3 kV. Hau et al. [118] presented a high-speed micro-positioning stage consisting of 2 DEAs arranged in agonist–antagonist configuration, shown in Figure 6b, which can produce a stroke of 40 μm with a maximum error of 2 μm when operating at a frequency of 60 Hz. A method to fabricate miniaturized DEAs embedded between gold electrodes was proposed by Soulimane et al. in [119], resulting in a controllable actuation of 2 μm. More DEA-based micro-fluidic actuators have also been presented in [120,121,122,123].
It has been remarked how one of the main impediments to DEA miniaturization is the high voltage needed to drive the elastomer. Equation (1) implies that, by either increasing the material permittivity or reducing the membrane thickness, the same amount of actuation stress can be obtained with a smaller input voltage [66]. By pursuing the path of thickness reduction, several authors have developed DE micro-actuators capable of operating below the 1 kV threshold. In [124], Ren et al. proposed a high-lift micro aerial robot that weighs about 150 g and achieves a high lift-to-weight ratio of 3.7, see Figure 6c. Actuation is provided by means of 20-layer DEA membrane with each layer being 10 μm thick, which is operated via 630 V at a frequency of 400 Hz. In [125], Rosset et al. developed and characterized a DEA micro-actuator based on a 30 μm thick layer with compliant electrodes based on metal ion implantation, which exhibits a displacement of ~100 μm when operated at ~500 V. A remarkable milestone in DEA miniaturization was achieved by Poulin et al. [126], who developed a pad printing method to produce 3 μm thick DEA, which, in turn, can be operated at 245 V while maintaining an actuation strain on the order of 7.5%. A picture of the resulting actuator is shown in Figure 6d.
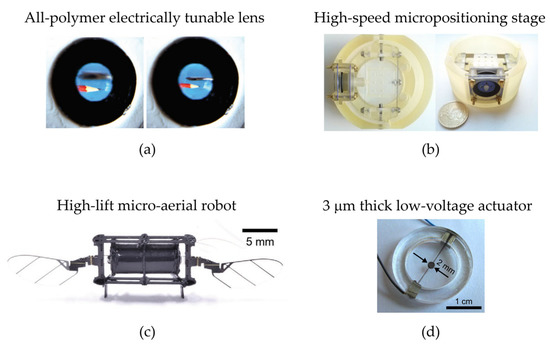
Figure 6.
Examples of meso- and micro-scale DEAs: (a) All-polymer electrically tunable lens [115], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2011; (b) High-speed micro-positioning stage [118], reproduced with permission from IEEE, copyright 2017; (c) High-lift micro-aerial robot [124], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2022; (d) 3 μm thick low-voltage actuator [126], reproduced with permission from AIP Publishing, copyright 2015.
All the devices and micro-actuators mentioned above, however, make use of DEAs as stand-alone transducers. The subsequent sections will present cooperative systems in which multiple DEA/DES units are combined together in an array-like fashion.
3.2. Cooperative Dielectric Elastomer Actuators
3.2.1. One-Dimensional Arrays
The simplest types of cooperative DEAs are represented by macro-scale one-dimensional arrays. An example of such a system is the object of investigation of the DECMAS project, which aims at developing fully polymeric intelligent arrays of DEA elements that can be used, e.g., in intelligent wearables and soft robotics. The key elements of the DECMAS project are the multi-stable polymeric domes shown in Figure 7a, which are used as biasing elements for the individual DEA units. In this way, a large stroke can be obtained without the need to use pressurized air or metal beams, making the overall concept significantly easier to miniaturize while keeping it flexible [109]. The potential for miniaturization is also enhanced by the adoption of ultrathin (10 nm) and highly stretchable sputter-deposited metallic electrodes [70]. By means of model-based optimization, it was possible to optimize the design of the biasing domes and, in turn, achieve a fully polymeric DEA capable of a stroke on the order of 3 mm for an actuator with a radius of 20 mm [109], see Figure 7b. Current research studies focus on the characterization [127] and modeling [82] of the electro-mechanical coupling effects occurring when many of those elements are placed onto a common elastic substrate in an array configuration (cf. Figure 7c), as well as on the development of laser-structuring electrode techniques for enabling local activation of the DEAs [71]. A picture of the first prototype of 1-by-3 actuator array is shown in Figure 7d.
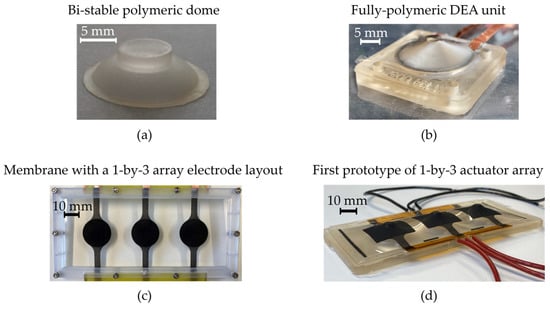
Figure 7.
Fully polymeric DEA array developed in the context of the DECMAS project: (a) Bi-stable polymeric dome; (b) Fully polymeric DEA unit; (c) Silicone membrane with a screen-printed 1-by-3 electrode layout; (d) First prototype of 1-by-3 actuator array.
Another example of a 1D array of DEAs was presented by Yu et al. in [128], reported in Figure 8a. Here, a 1-by-4 array of DEAs, each one having a size of 160 mm × 135 mm and characterized by a different pre-stretch, is used to achieve a broadband tunable resonator. In particular, the amount of pre-stretch and applied DC voltage can be used to tune the natural frequency of each DEA and, in turn, the attenuation bandwidth of each resonator. The synergy among the four elements allows the combination of the attenuation bandwidth of each individual DEA, leading to an increase in the effective bandwidth by a factor of 10, with a bandwidth tunability up to 14%. An untethered 1-by-10 array of feel-through haptic elements was presented in [129], based on a 18 μm thick silicone DEA membrane, see Figure 8b. The device can be worn on the user’s fingertip, and can generate perceivable vibrations up to 500 Hz when operated below 500 V. Lotz et al. presented in [113] a fabrication technique for silicone-based miniaturized stacked DEAs, and used it to develop a 1-by-8 array operating as a microfluidic pump, where every actuator contains 30 layers of 50 μm each and has a total length of 40 mm. The periodic activation of the DEAs causes the wall of the pump to undergo a periodic motion, which, in turn, propels the fluid at a flowrate of 12 μL/min under a maximum pressure of 0.4 kPa. A similar actuator was then used in [130] to develop a fluidic micro-mixer, shown in Figure 8c. Here, three 1-by-4 arrays of stacked DEAs were used to activate two pumping chambers and one mixing chamber, distributed over a 33 mm × 25 mm layout. In [131], Schlatter et al. presented a multi-material inkjet printing method for integrated and soft multifunctional machines, and used it to develop a 1 DEA flexible peristaltic pump with six integrated actuators capable of pumping up to 13.8 μL/min when operating at 1 Hz and 3.8 kV, see Figure 8d.
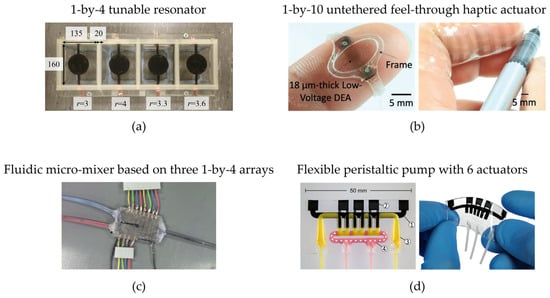
Figure 8.
Examples 1D DE arrays: (a) 1-by-4 tunable resonator [128]; (b) 1-by-10 untethered fee-through haptic actuator [129], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2020; (c) Fluidic micro-mixer based on three 1-by-4 arrays [130], reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd., copyright 2018; (d) Flexible peristaltic pump with 6 integrated actuators [131].
3.2.2. Cooperative Bio-Inspired Robots
Different types of 1D array concepts have also been proposed for the development of bio-inspired DEA conveyors. O’Brien et al. presented in [132] modeling and experimental validation of a 1-by-4 array of acrylic-based bending DEA, with the aim of replicating the generation of travelling waves generated by ctenophores. By implementing a coordinated mechano-sensitivity concept, in which the motion of one element triggers the actuation of the subsequent one via a capacitance measurement, the authors succeeded in propelling tubes of various materials and sizes, i.e., a 13.9 g and 10.11 mm diameter Teflon tube and an 18.63 g and 4.77 mm diameter brass tube. In [133], a different concept of cilia array conveyor was presented based on a DE matrix and dielectric barium titanate nanoparticles. A transportation experiment showed how the array of cilia can drive a cargo at an average speed of 30 mm/min when operating at a frequency of 2.25 Hz with a voltage of 20 kV. A compliant slug drive capable of generating travelling waves for object micro-transportation by taking inspiration from the motion of invertebrate animals was presented by Schlatter et al. in [131], see Figure 9a. The slug drive has an area of 25 cm2 and contains 28 integrated DEAs, each one having an area of 0.126 mm2. The authors showed how the slug drive allows conveying a 15 mm long, 0.26 g plastic object, achieving a travelling speed of 6.1 μm/s when using a 3.5 kV, 0.2 Hz square wave driving signal.
The generation of travelling waves through cooperation of several DEAs has also been used to achieve bio-inspired robotic locomotion. Zhao et al. [134] presented the design of a soft creeping robot consisting of a 1-by-4 array of elliptic frames, which can deform under high voltage application thanks to the use of DEAs. The cooperative activation of each actuation unit allows each one of the four segments to switch between an elliptical and a circular shape, leading to a forward peristaltic motion. Although the results are preliminary, they show the high potential of cooperative DEAs for the achievement of complex actuation patterns. An annelid-like peristaltic crawling robot based on a 1-by-4 array of acrylic DEAs operating in bending mode was proposed by Lu et al. in [135], shown in Figure 9b. The developed robot is 150 mm long, weights 8 g, and achieves a forward or backward motion with a maximum speed of 11.5 mm/s and a maximum speed/mass ratio of 86.23 mm/min∙g thanks to the cooperative coordination of all the actuated segments. A multi-segment annular soft robot driven by acrylic DEAs was presented by Li et al. in [136]. The system layout corresponds to a circle with 6 DEA segments distributed along its circumference, as shown in Figure 9c. The resulting actuator weights less than 1 g, has a diameter of ~50 mm, and can achieve a variety of motion patterns (i.e., rolling, creeping, and peristalsis) thanks to the synergistic activation of different combinations of DEA units. Pfeil et al. [137] presented a bio-inspired worm-like crawling robot, consisting of a 1-by-3 serial connection of silicone-based cylindrical DEAs with additional textile reinforcement. Relative elongations of 2.4% and generated forces of 0.29 N were achieved, which, in turn, resulted into a locomotion speed of 28 mm/min. A bio-inspired robot capable of mimicking the crawling motion of a caterpillar was presented in [138]. A 1-by-6 array of DEAs is powered through a DE-based electronic oscillator, which automatically generated the coordinated periodic signals that were needed to set the robot in motion. A speed up to 50 mm/min is achieved with a driving voltage of 4 kV. A different concept of walking hexapod robot is presented by Nguyen et al. in [139], also reported in Figure 9d. Here, a silicone-based double-cone silicone DEA with a patterned electrode is used to generate different motions of the robot legs. In particular, by activating different combinations of electrode segments, translation along both in-plane axes as well as rotation of the robotic leg can be achieved. By properly coordinating and synchronizing those three motion modes on the six legs of the robots, the authors successfully demonstrated the ability of the robot to move at an average speed of 30 mm/s (about 12 body lengths/min).
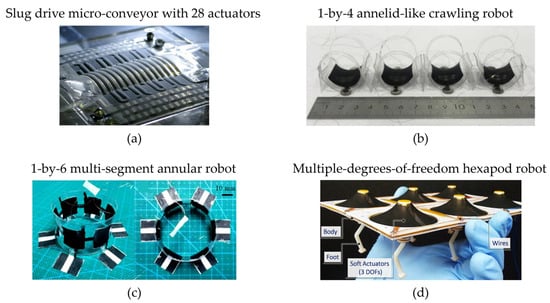
Figure 9.
Examples of DEA bio-inspired robots: (a) Slug drive micro-conveyor with 28 integrated actuators [131]; (b) 1-by-4 annelid-like peristaltic crawling robot [135], reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd., copyright 2020; (c) 1-by-6 multi-segment annular soft robot [136], reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd., copyright 2018; (d) Multiple-degrees-of-freedom walking hexapod robot [139], reproduced with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2017.
3.2.3. Two-Dimensional Arrays for Out-of-Plane Actuation
Two-dimensional cooperative DEA concepts, capable of operating both out-of-plane and in-plane, have also been explored by several authors. Chen et al. [140] developed a 3-by-3 array of acrylic DEAs. Each actuator operates out of plane, is biased via pressurized air at 2 kPa, and has a circular shape with a radius of 10 mm. A model-based design technique is adopted to suppress the snap-through instability of the device, thus allowing continuous actuation of each element. The authors showed that by modulating the high voltage signals applied to each DEA, the array can be programmed to achieve different desired configurations. An optically addressable and stretchable DEA matrix was presented by Hajiesmaili and Clarke in [141], see Figure 10a. By integrating percolating networks of zinc oxide nanowires into the soft elastomer array, the authors showed the possibility of achieving a localized control of each DEA in a 6-by-6 array. A micro-actuator concept for microfluidic is discussed in [30]. Here, a 7-by-7 array of DEAs operating in enhanced thickness mode is presented, in which localized patterns of out-of-plane bumps can be created upon electrical activation. A 9-by-9 array of DEA-based varifocal micro-lenses was proposed by Wang et al. in [142]. The array, shown in Figure 10b, has a total size of is 40 mm × 40 mm, while the diameter of each actuator element is of 1 mm. The DEA is based on a 1 mm thick acrylic membrane, which is activated at 5 kV. The authors show how the device enables tunability of the focal length from 950 mm to infinity. A concept for enhancing the performance of cooperative DEAs through the use of a fractal interconnection architecture was presented by Burugupally et al. in [143], see Figure 10c. Here, the authors presented bi-dimensional arrays of various sizes in which DEAs are arranged alternatively onto a common substrate. The actuators are based on a 100 μm thick acrylic DE membrane, and undergo a radial expansion when activated. The most complex design comprises 25 actuators having a diameter of 1.8 mm each, arranged alternatingly on a square frame. In-plane displacements on the order of 0.1 mm are achieved for a voltage of about 5 kV.
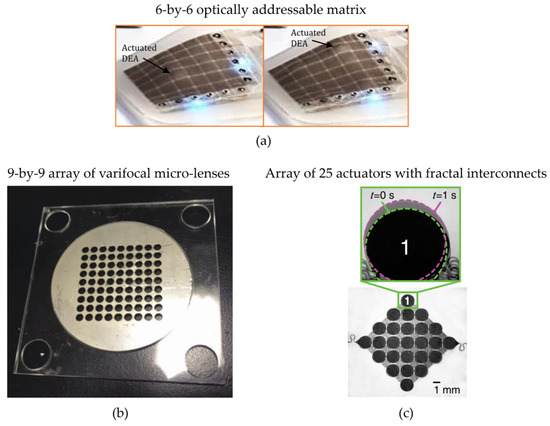
Figure 10.
Examples of two-dimensional DEA arrays operating out of plane: (a) 6-by-6 optically addressable matrix [141], reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2022; (b) 9-by-9 array of varifocal micro-lenses [142]; (c) Array of distributed electrodes with fractal interconnects architecture [143], reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd., copyright 2021.
3.2.4. Two-Dimensional Arrays for in-Plane Actuation
While the previously discussed concepts of two-dimensional arrays operate out of plane, several authors also investigated the possibility of generating a cooperative in-plane actuation via DEA systems. A concept of a two-dimensional array of hollow DEA cylinders is presented in [144]. By means of finite element simulations, the authors studied the propagation of an acoustic wave, and confirmed that adjusting the DEA voltage enables an effective tuning of the acoustic band gap of the device. No experimental validation was presented.
A soft-wave handling system capable of transporting fragile and soft objects was proposed by Wang et al. in [145]. The system consists of a 4-by-4 array of hydrostatically coupled acrylic DEA units, each one having a diameter of 55 mm. By concurrent activation of different DEA elements with phase-shifted 1 Hz sinusoidal waves, the authors were able to generate a travelling wave that set a rolling ball in motion. Although the proposed systems exhibit a high potential for future DEA-based conveyor systems, the authors acknowledge the high losses of the adopted acrylic material as one of the limiting factor for the actuator performance.
Akbari and Shea investigated the use of in-plane operating micro-arrays of DEAs to provide in-plane mechanical actuation to cell cultures. The first generation of those devices, shown in Figure 11a, is based on a 30 μm thick silicone membrane consists of an 8-by-9 array of 0.1 mm × 0.2 mm DEA elements capable of a strain of 4.7% at 2.9 kV [146]. A second generation of cell stretcher, always based on the same type of DE membrane, is made of 0.1 mm × 0.1 mm DEA elements and can produce a strain of 37% when driven at 3.6 kV [147]. An expanded view of the micro-actuator grid is reported Figure 11b. Those devices represent some of the most remarkable examples of micro-scale cooperative DEA systems.

Figure 11.
Examples of two-dimensional DEA arrays operating in plane: (a) First generation cell stretcher based on a 8-by-9 array with of 0.1 mm × 0.2 mm micro-actuators [146], reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd., copyright 2012; (b) Second generation cell stretcher based on 0.1 mm × 0.2 mm micro-actuators [147], reproduced with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2012.
3.2.5. Two-Dimensional Arrays for Haptics and Wearables
Two-dimensional cooperative DEAs have also found natural applications in the field of haptics. Matysek et al. [148] presented a concept for a tactile display consisting of a 3-by-3 array of 1 mm × 1 mm DEA taxels. Each actuator is based on a stack of 25 μm thick silicone elastomer layers. Marette et al. developed in [111] a 4-by-4 array of independently controllable circular DEAs, each one characterized by a diameter of 4 mm and a thickness of 17 μm. Each DEA produces a stroke of 0.25 mm when activated via a 1.4 kV driving voltage, which is switched by using high-voltage metal-oxide thin-film transistors that can be switched with a 30 V gate voltage. The tactile display operates under pneumatic bias at 50 mbar, and can still generate a stroke even when bent to a 5 mm radius of curvature, as shown in Figure 12a. A bidirectional haptic display, which combines a 4-by-4 array of DEAs with a 5-by-5 array of resistive sensors, was proposed by Phung et al. in [149]. The device is 130 mm long × 130 mm wide × 13 mm high. The design is based on rigidly coupled double-cone DEAs made of a 50 μm thick silicone elastomer, operated at a driving voltage of 3.5 kV. The device reaches frequencies up to 300 Hz, providing 0.52 mm of displacement and 0.6 N of normal force. The device can also measure normal forces up to 6 N and the position of touches, and use this information to control the corresponding tactile actuator units. A 2-by-3 tactile display is presented in [150] and also shown in Figure 12b. The device makes use of the liquid coupling between touch spot and DEA to transmit the tactile sensation to the user. The radius of each actuator is 4 mm, while the radius of the touching spot is limited to 1.5 m. A 90 μm thick silicone film is chosen to fabricate the actuators, operated up to a voltage of 7 kV. Displacements of about 240–120 μm at 3–10 Hz are achieved, with forces large enough to simulate the sensation of touch.
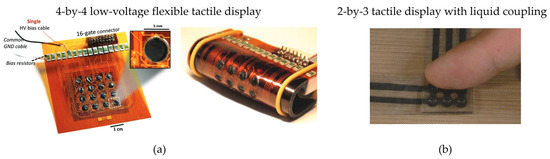
Figure 12.
Examples of two-dimensional DEA arrays for tactile displays: (a) 4-by-4 flexible array of low-voltage actuators [111], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2017; (b) 2-by-3 tactile display based on liquid coupling [150], reproduced with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2014.
In the area of wearables, Lee et al. [151] presented a textile-embedded haptic display consisting of a 3-by-5 array of circular DEAs. Each actuator unit has a diameter of 20 mm and is on the skin of the user via a cylindrical polymer indenter. The overall display has a thickness of 7 mm and a weight of 60 g; thus, can be easily worn on the user’s forearm. A multi-layered actuator design permits the use of driving voltages of 1 kV only, while ensuring, at the same time, a bandwidth of 240 Hz. A wearable tactile communicator, consisting of a 2-by-2 array of circular DEAs embedded in a wearable armband, is proposed by Zhao et al. in [152]. Each actuator consists of a 10-layer silicone DEA with a hollow cylindrical shape, having an outer radius of 5 mm. A free displacement of ~60 mm and a blocking force of ~30 mN are obtained at a frequency of 300 Hz, considering a driving frequency of 300 Hz.
3.2.6. Two-Dimensional Arrays for Refreshable Braille Displays
Several authors have also investigated the use of DE technology to develop refreshable Braille displays. A 2-by-8 array concept for a refreshable Braille display was discussed in [30]. Each Braille dot has a diameter of 1.5 mm and a relative spacing distance of 2.3 mm. Actuation is provided by spring-biased circular DEAs having a diameter of 2 mm, each one resulting in forces up to 25 g. Chakraborti et al. [153] developed a 2-by-3 Braille matrix of refreshable dots. The actuation is provided by silicone-based thin-walled DEA tubes, having outer and inner diameters of 0.51 mm and 0.94 mm, respectively, and a length of 20 mm. A steady displacement of 1 mm and a response time of 0.1 s are achieved with a driving voltage of 1 kV. Qu et al. [154] also proposed a 2-by-3 refreshable Braille display based on DEAs. The device operates under pneumatic bias, adopts 0.25 mm thick acrylic membranes as elastomer. The total size of the device is of 30 mm × 22 mm × 16 mm, while the diameter of the single Braille dot is of 2 mm. An actuation displacement larger than 0.6 mm is achieved for a biasing pressure of 4 kPa and a driving voltage of 3.25 kV. The ability of this prototype in reproducing different letters is illustrated in Figure 13a. A prototype of a 2-by-4 refreshable Braille display was presented by Frediani et al. in [155], based on acrylic DEAs, see Figure 13b. Each actuator unit has the size of about 1.5 mm, and is capable of out-of-plane displacements of ~ 750 μm. In this case, electrical insulation with the user’s finger is achieved via hydrostatic coupling with a passive membrane, which acts as a bias for the DEA.
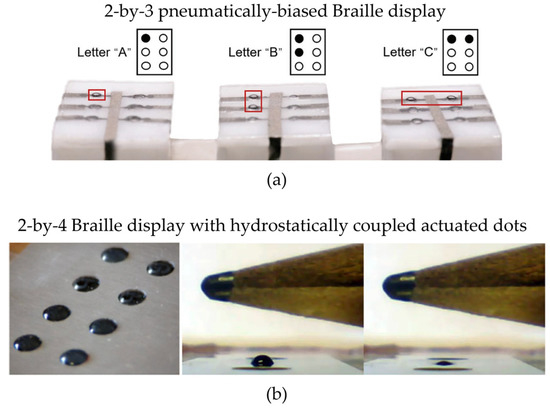
Figure 13.
Examples of two-dimensional DEA arrays for refreshable Braille displays: (a) 2-by-3 pneumatically biased Braille display [154], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2020; (b) 2-by-4 Braille display with hydrostatically coupled actuated dots [155], reproduced with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2018.
3.2.7. Three-Dimensional Reconfigurable Structures
All concepts presented so far permit the achievement of cooperative actuation by means of an array of actuators distributed on a surface, all operating either in plane or out of plane. Few authors have proposed more advanced concepts of cooperative reconfigurable structures based on DE technology. An example of reconfigurable 3D meso-structured driven by DEAs is introduced in [156]. The developed 3D meso-structures can be morphed into several distinct geometries, which are based on 100 μm thick circular DEAs made of acrylic materials. By combining theoretical and experimental studies, the authors are able to develop a large variety (~30) of actuated 3D structures, one of which shown in Figure 14a. Sun et al. presented in [157] an origami-inspired 3D folding actuator based on DEAs. The actuation is based on bending elements driven by circular (~10 mm diameter) DEAs of acrylic material, which are able to generate a bending angle of 120° and 90° when activated with 5.5 kV and 4 kV, respectively. Those two types of bending are then used to develop actuators capable of folding in pyramidal and cubic shapes, respectively, also shown in Figure 14b. The authors demonstrated how the bending actuator can be used to develop gripping and locking functions.
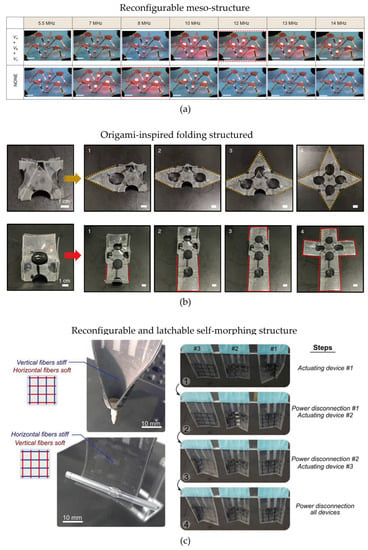
Figure 14.
Examples of three-dimensional DEA reconfigurable structures: (a) 3D reconfigurable meso-structure [156]; (b) 3D origami-inspired folding actuator [157]; (c) Reconfigurable and latchable shape-morphing structure [158], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2020.
The idea of combining cooperative DE actuation and bi-stability was also explored in the literature. In [158], Aksoy and Shea proposed a reconfigurable and latchable soft structure that combines layers of DEAs and shapes memory polymers. Joule heating allows reducing the stiffness of the shape memory polymers by two orders of magnitude. Actuation of DEAs allows then the structure to bend along the selected soft axis, thus allowing it to dynamically tune the orientation and location of soft and hard regions. Cooling down the shape memory polymers causes them to become stiff again, thus permitting them to lock in place the shape of the structure without requiring further DEA activation. This mechanism allows the development of several types of complex shapes, as illustrated in Figure 14c, which can be kept in place without requiring additional energy consumption. Tip-bending angles up to 300° and blocking forces over 27 mN can be achieved with a driving force of 5 kV. The authors then demonstrate how this concept allows the development of grippers for grasping objects of various shapes. A similar principle was also used by Meng et al. in [159] to develop a bending structure. Here, a bending angle of 50° is achieved with an activation voltage of 6 kV for the DEA, and a heating up to 50 °C for the shape memory polymer.
3.3. Cooperative Dielectric Elastomer Sensors
Although the main focus of this paper is on actuators, in this section we present a few relevant examples of DE applications in the area of cooperative sensors. In this context, one usually leverages on the large deformations of DE transducers to reconstruct large deformation or pressure patterns localized over a 1D or 2D region. An example of a one-dimensional DES array was presented by Xu et al. in [160], shown in Figure 15a. The device consists of a 1-by-4 array of silicone DES elements. By means of a capacitance reconstruction method built upon a multi-frequency technique, the deformed element within the array is detected using only a single-data acquisition channel.
A 2-by-2 array of silicone-based DESs was proposed by Zhang et al. [161], also reported in Figure 15b. The sensor module allows the detection of the location and magnitude of compressive forces applied on a surface area of 15 mm × 15 mm. By embedding an air chamber in the sensor, the authors achieved an increase in sensitivity by a factor of ~20, with a corresponding a detection range of 382 kPa. A further example of 2-by-2 DES array suitable for tactile sensing applications was proposed by Ham et al. in [162]. The device has a size of 10 mm × 10 mm × 3 mm and can conform to curved surfaces, such as a robotic arm or a prosthetic hand. The sensor array has a dynamic range of 500 kPa in the normal direction, can provide tactile information with a frequency up to 100 Hz, and is robust to electromagnetic interference during contacts thanks to the use of active shielding. A further example soft tactile sensor based on acrylic DE was presented by Kadooka et al. in [163]. The device comprises a DEA module, based on an unimorph-type structure that undergoes a bending upon high voltage application, and three 2-by-2 arrays of DES element. The total size of the device is 15 mm x 35 mm, while the area of each sensor is ~1.2 mm2, and the footprint of each 2-by-2 element equals ~ 8 mm2. Dome-shaped bumps positioned over the DES array permit the redistribution of tactile forces, allowing the proper scaling up of the magnitude of the sensed load. The recorded resolution equals 27 mN for normal forces and 67 mN for shear forces, respectively, for a maximum applied force of 5 N.
Zhu et al. [164] proposed an example of a multi-modal sensor, consisting of a 4-by-4 array of silicone DES, see Figure 15c. A multi-layer structure was used, comprising a top protection layer (0.1 mm thick), a first sensor layer (0.6 mm thick) used to measure the applied pressor, a second underlying sensor array (2.4 mm thick) enabling localization features, and a passive substrate (1.9 mm thick). A digital acquisition system was used to identify the unique location of each taxel. A 4-by-4 DES grid was presented by Meyer et al. in [165], shown in Figure 15d. The DES taxels were based on a 50 mm thick silicone membrane on which four rows and four columns of electrode lines were screen-printed to enable the eight required electrical connections. The resulting structure was a fully polymeric and highly stretchable membrane, with 16 taxels each one having a size of 10 mm × 10 mm, for a total array size of 65 mm × 65 mm. Different types of load distributions applied on the grid, corresponding to out-of-plane displacements up to 4 mm, are effectively estimated via a commercially available integrated circuit for capacitance estimation.
A similar sensor array concept was also proposed by Lee et al. [166], this time based on a 5-by-5 grid applied on a silicone DE film with micro-pores, see Figure 15e. The device size equals 33 mm × 33 mm, while the size of the single-sensing element equaled 5 mm × 4.45 mm. The device allows reconstructing localized pressures below 0.02 kPa with a high sensitivity of 1.18 kPa−1, and a fast response time of 150 ms. A further example of a 5-by-5 DEs array was proposed by Kwon et al. in [167]. Due to the presence of 3D micro-pores in the DES layer, the sensitivity of the device can be dramatically increased while maintaining the large deformation features. The sensor is characterized by a sensitivity of 0.6 kPa−1 for pressures below 5 kPa, and has a maximum range of 130 kPa, which makes it suitable for tactile sensing applications. The effectiveness of the sensor in detecting spatially distributed pressure patterns shaped as alphabetic letters is also demonstrated. Kyaw et al. [168] proposed a 5-by-5 array for a pressure-sensitive electronic skin, shown in Figure 15f. Each electrode has a size of 3 mm × 3 mm, for a total active sensing area of ~500 mm2. The device is able to sense pressures up to 40 kPa with a sensitivity of ~0.01 kPa−1. Compared to silicone-based DES, the adopted Ecoflex material is characterized by a higher accuracy due to a higher linearity in its response. A deformable interface for human-touch recognition was developed by Larson et al. [169]. Here, a concept is developed named Orbtouch in which a 5-by-5 soft array of DES is integrated onto a deformable bubble-like structure. The overall circular membrane has a radius of 45 mm and is 2 mm thick, while each taxel has a size of 5 mm × 5 mm, and spacing among neighboring elements is also equal to 5 mm. A convolutional neutral network is used to classify the sensing information from the various channels in the array, allowing, in turn, to localize interactions with the interface with an accuracy of 97.6%. The authors showed the flexibility and effectiveness of the concept by letting users play Tetris with it.
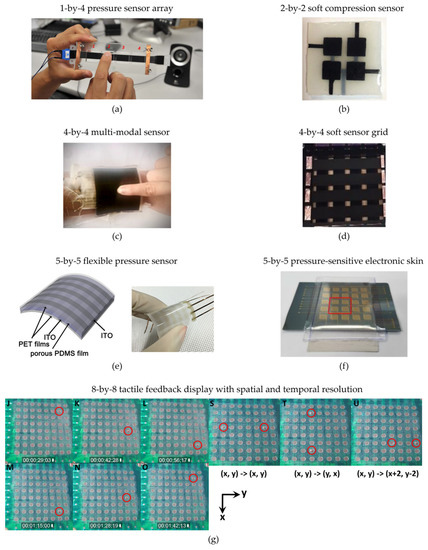
Figure 15.
Examples of arrays of DES: (a) 1-by-4 pressure sensor array [160], reproduced with permission from John Wiley and Sons, copyright 2015; (b) 2-by-2 soft compression sensor [161], reproduced with permission from IOP Publishing Ltd., copyright 2016; (c) 4-by-4 multi-modal sensor for simultaneous detection of amplitude and location of touch pressure [164]; (d) 4-by-4 soft sensor grid [165], reproduced with permission from SPIE, copyright 2020; (e) 5-by-5 flexible pressure sensor [166], reproduced with permission from Elsevier, copyright 2016; (f) 5-by-5 pressure-sensitive electronic skin [168], reproduced with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry, copyright 2017; (g) 8-by-8 tactile feedback display with spatial and temporal resolution [170], reproduced with permission from Springer Nature, copyright 2013.
As a final example of more complex sensor layout, Vishniakou et al. [170] developed a tactile feedback display with spatial and temporal resolutions based on an 8-by-8 array of circular DES, reported in Figure 15g. The array is based on an acrylic elastomer and is capable of distributed-pressure sensing with a spatial resolution of 3 mm. The same device can also be operated as an actuator, exhibiting a maximum out-of-plane displacement of ~150 μm under an applied voltage of 4 kV and a blocking force on the order of 10 mN. The estimated sensitivity is of about 15 kPa.
4. Conclusions
This paper presented an overview of cooperative actuator and sensor systems based on soft dielectric elastomer technology. DE transducers make it possible to develop cooperative arrays of actuators with improved lightweight, flexibility, controllability, and energy consumption compared to alternative technologies (e.g., pneumatics), thus enabling applications such as wearable soft robots and sensors, haptic interfaces, or reconfigurable structures. The provided overview showed how cooperative DE technology has allowed the development of a variety of systems, which range from coordinated micropumps and bio-inspired crawling robots to bi-dimensional reconfigurable structures, soft conveyors haptic interfaces, refreshable Braille displays, and wearable tactile sensors. The surge of publications in this field over the last few years suggests that the interest in cooperative DE actuator and sensor technology will steadily increase in the near future.
Even though the presented prototypes have succeeded in showcasing the potential of DE technology for a variety of applications, many practical limitations still exist. In general, the corresponding taxel size is on the meso- (order of mm2) rather than micro-scale, and only few prototypes succeeded in delivering actuation in the sub mm regime, e.g., [146,147]. Therefore, additional effort in both design and manufacturing is still needed to effectively scale the systems at the micro-scale level. Additionally, most current devices are based on a limited number of elements per array, each one producing a relatively small stroke compared to the potential DE large deformation. This is essentially due to limitations in current microfabrication methods for both DE membrane and electrodes, lack of bias systems suitable for miniaturization (e.g., pneumatic), as well as challenges in miniaturizing the control and sensing electronics. In this sense, the multi-stable polymeric domes presented in [109] may offer a great potential means for future miniaturization of cooperative DEAs with large stroke. Finally, it is worth noting that almost the totality of the current devices are controlled via centralized feedforward approaches rather than by means of feedback cooperative strategies, without taking advantage of the DE self-sensing functionalities. This may be partially due to the highly nonlinear and hysteretic behavior of such materials, which complicates the design of control and self-sensing algorithms. In principle, by properly exploiting self-sensing, each individual actuator unit can autonomously reconstruct information on its current electromechanical state based on simplified sensing hardware, i.e., local measurements of voltage and current, and use this information to perform a desired cooperative task in a fully autonomous and fault-tolerant way. Some examples include the generation of a specific shape, the propagation of a dynamic motion pattern (e.g., a wave as in [132]), or the transportation of an object on a path by avoiding damaged taxels. This concept, although highly attractive, is still largely unexploited in current cooperative DE systems. As a result, the full potential and intelligence offered by the technology are yet to be realized. Once those novel design and control concepts are developed, it will be possible to develop the next generation of fully autonomous, intelligent, and fault-tolerant DE cooperative micro-actuator/-sensor systems.
Funding
This research was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation), Priority Program SPP 2206 “Cooperative Multistage Multistable Microactuator Systems” (Projects: RI3030/2-1, SCHU1609/7-1, SE704/9-1).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Butenko, S.; Murphey, R.; Pardalos, P.M. Cooperative Control: Models, Applications and Algorithms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, S.A.; Jourdain, R.P.J.; Zhang, Q.; Dorey, R.A.; Bowen, C.R.; Willander, M.; Wahab, Q.U.; Willander, M.; Al-hilli, S.M.; Nur, O.; et al. New materials for micro-scale sensors and actuators: An engineering review. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2007, 56, 1–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, C.L.P. A survey of communication/networking in Smart Grids. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2012, 28, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ren, W. On the Control of Multi-Agent Systems: A Survey. Found. Trends® Syst. Control 2019, 6, 339–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, A.; Velotto, G.; Zobaa, A.F. A Decentralized and Cooperative Architecture for Optimal Voltage Regulation in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4593–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwari, N.; Ash, J.N.; Kyperountas, S.; Hero, A.O.; Moses, R.L.; Correal, N.S. Locating the nodes: Cooperative localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, B. Development and Evaluation of a Cooperative Vehicle Intersection Control Algorithm Under the Connected Vehicles Environment. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2012, 13, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Hussein, A.; Elmogy, A. Multi-Robot Task Allocation: A Review of the State-of-the-Art; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, P.R.; Swaroop, D.; Howlett, J.K.; Pachter, M.; Fowler, J.M. Complexity in UAV Cooperative Control. In Proceedings of the 2002 American Control Conference, Anchorage, AK, USA, 8–10 May 2002; pp. 1831–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, G.J.; Delettre, A.; Zeggari, R.; Yahiaoui, R.; Manceau, J.-F.; Le Fort-Piat, N. Micropositioning and Fast Transport Using a Contactless Micro-Conveyor. Micromachines 2014, 5, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Hassine, A.; Terrien, J.; Lamarque, F.; Prelle, C. Development of a Control Module for a Digital Electromagnetic Actuators Array. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 4788–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataka, M.; Legrand, B.; Buchaillot, L.; Collard, D.; Fujita, H. Design, Fabrication, and Operation of Two-Dimensional Conveyance System with Ciliary Actuator Arrays. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2009, 14, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, S.; Fujita, H. A conveyance system using air flow based on the concept of distributed micro motion systems. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1994, 3, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luntz, J.E.; Messner, W.; Choset, H. Distributed Manipulation Using Discrete Actuator Arrays. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2001, 20, 553–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui, R.; Zeggari, R.; Malapert, J.; Manceau, J.-F. A MEMS-based pneumatic micro-conveyor for planar micromanipulation. Mechatronics 2012, 22, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, A.; Biegelsen, D.; Cheung, P.; Fromherz, M.; Goldberg, D.; Jackson, W.; Preas, B.; Reich, J.; Swartz, L.-E. Motion Control of Planar Objects Using Large-Area Arrays of Mems-Like Distributed Manipulators. Micromechatronics 2000, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vandelli, N.; Wroblewski, D.; Velonis, M.; Bifano, T. Development of a MEMS Microvalve Array for Fluid Flow Control. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1998, 7, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellers, M.C.; Pulskamp, J.S.; Bedair, S.S.; Rudy, R.Q.; Kierzewski, I.M.; Polcawich, R.G.; Bergbreiter, S.E. Piezoelectric actuator array for motion-enabled reconfigurable RF circuits. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers-2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (Transducers), Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; pp. 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baz, D.; Piranda, B.; Bourgeois, J. A Distributed Algorithm for a Reconfigurable Modular Surface. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Parallel & Distributed Processing Symposium Workshops, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 19–23 May 2014; pp. 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, J.; Goldstein, S.C. Distributed Intelligent MEMS: Progresses and Perspectives. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 9, 1057–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutoustous, K.; Laurent, G.J.; Dedu, E.; Matignon, L.; Bourgeois, J.; Le Fort-Piat, N. Distributed Control Architecture for Smart Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 2018–2024. [Google Scholar]
- Konishi, S.; Fujita, H. System design for cooperative control of a microactuator array. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1995, 42, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matignon, L.; Laurent, G.J.; Le Fort-Piat, N.; Chapuis, Y.-A. Designing Decentralized Controllers for Distributed-Air-Jet MEMS-Based Micromanipulators by Reinforcement Learning. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2010, 59, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuta, Y.; Chapuis, Y.-A.; Mita, Y.; Fujita, H. Design, Fabrication, and Control of MEMS-Based Actuator Arrays for Air-Flow Distributed Micromanipulation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 912–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; De Vittorio, M.; Petroni, S. Advanced MEMS Technologies for Tactile Sensing and Actuation. MEMS Fundam. Technol. Appl. 2013, 351–380. [Google Scholar]
- Chouvardas, V.G.; Miliou, A.N.; Hatalis, M.K. Tactile Display Applications: A State of the Art Survey. In Proceedings of the 2nd Balkan Conference in Informatics, Ohrid, Macedon, 26–28 September 2005; pp. 290–303. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez, R. Wearable Assistive Devices for the Blind. In Wearable and Autonomous Biomedical Devices and Systems for Smart Environment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 331–349. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm, E.; Schwarz, T.; Jaworek, G.; Voigt, A.; Rapp, B.E. Towards Displaying Graphics on a Cheap, Large-Scale Braille Display; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 662–669. [Google Scholar]
- Munasinghe, K.C.; Bowatta, B.G.C.T.; Abayarathne, H.Y.R.; Kumararathna, N.; Maduwantha, L.K.A.H.; Arachchige, N.M.P.; Amarasinghe, Y.W.R. New MEMS based micro gripper using SMA for micro level object manipulation and assembling. In Proceedings of the 2016 Moratuwa Engineering Research Conference (MERCon), Moratuwa, Sri Lanka, 5–6 April 2016; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluh, R.D.; Pelrine, R.; Prahlad, H.; Heydt, R. Electroactive Polymers: An Emerging Technology for MEMS; Janson, S.W., Henning, A.K., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5344, pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jui Tay, C.; Quan, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Lee, C. Piezoelectric MEMS Energy Harvester for Low-Frequency Vibrations With Wideband Operation Range and Steadily Increased Output Power. Artic. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2011, 20, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, K. Demonstration of self-sensing in Shape Memory Alloy actuated gripper. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Control (ISIC), Hyderabad, India, 28–30 August 2013; pp. 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.N.; Seethaler, R.J. Sensorless Position Control for Piezoelectric Actuators Using A Hybrid Position Observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2014, 19, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, G.; Naso, D.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. A Self-Sensing Approach for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators Based on Online Estimation Algorithms. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineta, T.; Yanatori, H.; Hiyoshi, K.; Tsuji, K.; Ono, Y.; Abe, K. Tactile display MEMS device with SU8 micro-pin and spring on SMA film actuator array. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 2031–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Hishinuma, Y.; Yang, E.-H. Piezoelectric Unimorph Microactuator Arrays for Single-Crystal Silicon Continuous-Membrane Deformable Mirror. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, N.; Zarate, J.J.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Flexible haptic display with 768 independently controllable shape memory polymers taxels. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 323–326. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, A.; Paschew, G. Optoelectrothermic Control of Highly Integrated Polymer-Based MEMS Applied in an Artificial Skin. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; De Rossi, D.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.E.; Sommer-Larsen, P. Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers: Fundamentals, Materials, Devices, Models and Applications of an Emerging Electroactive Polymer Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. Development and Experimental Characterization of a Pneumatic Valve Actuated by a Dielectric Elastomer Membrane. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 085023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loverich, J.J.; Kanno, I.; Kotera, H. Concepts for a new class of all-polymer micropumps. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.-Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, L.-M.; Zhu, X. A survey on dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2017, 12, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Review of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators and their Applications in Soft Robots. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2021, 3, 2000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Li, M.; Mei, T.; McCoul, D.; Qin, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, J. Wearable stretch sensors for motion measurement of the wrist joint based on dielectric elastomers. Sensors 2017, 17, 2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, C.R.; Kauffman, J.L. Towards wearable tremor suppression using dielectric elastomer stack actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 30, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Lochmatter, P.; Wissler, M. An arm wrestling robot driven by dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, S306–S317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.D.; Pei, Q.; Stanford, S.; Oh, S.; Eckerle, J.; Full, R.J.; Rosenthal, M.A.; Meijer, K. Smart Structures and Materials. In Proceedings of the SPIE’S 9th Annual International Symposium on Smart Structures and Materials, San Diego, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2002; Volume 4695, pp. 126–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.F.; Cui, C.Y.; Guo, H.; Chen, B.C.; Zhang, X.M. Advances in dielectric elastomer actuation technology. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 1512–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrisnan, B.; Smela, E. Challenges in the Microfabrication of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators; Bar-Cohen, Y., Ed.; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010; Volume 7642, pp. 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, L.; Gabor, K.; Silvain, M. Characterization of dielectric elastomer actuators based on a hyperelastic film model. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 135, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.; Dunn, J.; Seelecke, S. Experimental characterization of the hysteretic and rate-dependent electromechanical behavior of dielectric electro-active polymer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 094014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltseis, R.; Keplinger, C.; Koh, S.J.A.; Baumgartner, R.; Goh, Y.F.; Ng, W.H.; Kogler, A.; Tröls, A.; Foo, C.C.; Suo, Z.; et al. Natural rubber for sustainable high-power electrical energy generation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 27905–27913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Agostini, L.; Moretti, G.; Fontana, M.; Vertechy, R. Dielectric elastomer materials for large-strain actuation and energy harvesting: A comparison between styrenic rubber, natural rubber and acrylic elastomer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, K.; Li, J. Electro-mechanical performance of polyurethane dielectric elastomer flexible micro-actuator composite modified with titanium dioxide-graphene hybrid fillers. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolt, B.; Hodgins, M.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. Effect of screen printing parameters on sensor and actuator performance of dielectric elastomer (DE) membranes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 265, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Flexible and stretchable electrodes for dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 110, 281–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röntgen, W.C. Ueber die durch Electricität bewirkten Form- und Volumenänderungen von dielectrischen Körpern. Ann. Der Phys. Und Chem. 1880, 247, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Joseph, J. Electrostriction of polymer dielectrics with compliant electrodes as a means of actuation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 64, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Anderson, I.; Bauer, S.; Frediani, G.; Gallone, G.; Gei, M.; Graaf, C.; Jean-Mistral, C.; Kaal, W.; Kofod, G.; et al. Standards for dielectric elastomer transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 105025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, G.; Loew, P.; Agostini, L.; Fontana, M.; Seelecke, S. A lumped parameter model for strip-shaped dielectric elastomer membrane transducers with arbitrary aspect ratio. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 115030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shian, S.; Huang, J.; Zhu, S.; Clarke, D.R. Optimizing the Electrical Energy Conversion Cycle of Dielectric Elastomer Generators. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6617–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, S.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wissler, M.; Löwe, C.; Kovacs, G. A comparison between silicone and acrylic elastomers as dielectric materials in electroactive polymer actuators. Polym. Int. 2009, 59, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Agostini, L.; Moretti, G.; Berselli, G.; Fontana, M.; Vertechy, R. Fatigue life performances of silicone elastomer membranes for dielectric elastomer transducers: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, Denver, CO, USA, 3–7 March 2019; Volume 10966, pp. 158–167. [Google Scholar]
- Youn, J.-H.; Jeong, S.M.; Hwang, G.; Kim, H.; Hyeon, K.; Park, J.; Kyung, K.-U. Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Soft Robotics Applications and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Joseph, J.; Heydt, R.; Pei, Q.; Chiba, S. High-field deformation of elastomeric dielectrics for actuators. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2000, 11, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romasanta, L.J.; Lopez-Manchado, M.A.; Verdejo, R. Increasing the performance of dielectric elastomer actuators: A review from the materials perspective. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 188–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgins, M.; Seelecke, S. Systematic experimental study of pure shear type dielectric elastomer membranes with different electrode and film thicknesses. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 095001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlatter, S.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H. Inkjet Printing of Carbon Black Electrodes for Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. In SPIE Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10163, pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Klug, F.; Solano-Arana, S.; Hoffmann, N.J.; Schlaak, H.F. Multilayer dielectric elastomer tubular transducers for soft robotic applications. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubertus, J.; Neu, J.; Croce, S.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S.; Schultes, G. Nanoscale Nickel-Based Thin Films as Highly Conductive Electrodes for Dielectric Elastomer Applications with Extremely High Stretchability up to 200%. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 39894–39904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubertus, J.; Croce, S.; Neu, J.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S.; Schultes, G. Electromechanical characterization and laser structuring of Ni-based sputtered metallic compliant electrodes for DE applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference and Exhibition on New Actuator Systems and Applications, online, 17–19 February 2021; pp. 321–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, K.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, H.R. A self-sensing dielectric elastomer actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 143, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisby, T.A.; O’Brien, B.M.; Anderson, I.A. Self sensing feedback for dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 193703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffstadt, T.; Griese, M.; Maas, J. Online identification algorithms for integrated dielectric electroactive polymer sensors and self-sensing concepts. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, G.; Fugaro, F.; Naso, D.; Seelecke, S. Simultaneous Self-Sensing of Displacement and Force for Soft Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, G.; Naso, D.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Closed loop control of dielectric elastomer actuators based on self-sensing displacement feedback. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 035034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffstadt, T.; Maas, J. Sensorless force control for dielectric elastomer transducers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 30, 1419–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, G.; Serafino, P.; Naso, D.; Seelecke, S. Towards Sensorless Soft Robotics: Self-Sensing Stiffness Control of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2020, 36, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, D.; Haus, H.; Matysek, M.; Frohnapfel, B.; Tropea, C.; Schlaak, H.F. The dielectric breakdown limit of silicone dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 052905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasolt, B.; Welsch, F.; Jank, M.; Seelecke, S. Effect of actuation parameters and environment on the breakdown voltage of silicone dielectric elastomer films. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 094002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Z. Theory of dielectric elastomers. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2010, 23, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, S.; Neu, J.; Moretti, G.; Hubertus, J.; Schultes, G.; Rizzello, G. Finite element modeling and validation of a soft array of spatially coupled dielectric elastomer transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 084001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiesmaili, E.; Clarke, D.R. Dielectric elastomer actuators. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 151102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, G.; Düring, L.; Michel, S.; Terrasi, G. Stacked dielectric elastomer actuator for tensile force transmission. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2009, 155, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, J.; Tepel, D.; Hoffstadt, T. Actuator design and automated manufacturing process for DEAP-based multilayer stack-actuators. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2839–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, S.; Bruch, D.; Rizzello, G.; Motzki, P.; Seelecke, S. Silicone based dielectric elastomer strip actuators coupled with nonlinear biasing elements for large actuation strains. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 074003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.W.; Chi, H.J.:; Jung, K.M.; Koo, J.C.; Jeon, J.W.; Lee, Y.; Nam, J.-D.; Ryew, Y.; Choi, H.-R. A Face Robot Actuated With Artificial Muscle Based on Dielectric Elastomer. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2005, 19, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunze, J.; Prechtl, J.; Bruch, D.; Fasolt, B.; Nalbach, S.; Motzki, P.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Design, Manufacturing, and Characterization of Thin, Core-Free, Rolled Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Actuators 2021, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamani, A.; Grissom, M.; Rahn, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q. Wound roll dielectric elastomer actuators: Fabrication, analysis and experiments. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, IROS, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; Volume 13, pp. 2587–2592. [Google Scholar]
- Moretti, G.; Sarina, L.; Agostini, L.; Vertechy, R.; Berselli, G.; Fontana, M. Styrenic-rubber dielectric elastomer actuator with inherent stiffness compensation. Actuators 2020, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follador, M.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B. Design of a compact bistable mechanism based on dielectric elastomer actuators. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berselli, G.; Vertechy, R.; Vassura, G.; Parenti-Castelli, V. Optimal Synthesis of Conically Shaped Dielectric Elastomer Linear Actuators: Design Methodology and Experimental Validation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, G.; Hodgins, M.; Naso, D.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Modeling of the effects of the electrical dynamics on the electromechanical response of a DEAP circular actuator with a mass-spring load. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 094003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbach, S.; Banda, R.M.; Croce, S.; Rizzello, G.; Naso, D.; Seelecke, S. Modeling and Design Optimization of a Rotational Soft Robotic System Driven by Double Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Chen, G.; Nie, Z.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Toward broad optimal output bandwidth dielectric elastomer actuators. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2022, 65, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofod, G.; Wirges, W.; Paajanen, M.; Bauer, S. Energy minimization for self-organized structure formation and actuation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 081916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGough, K.; Ahmed, S.; Frecker, M.; Ounaies, Z. Finite element analysis and validation of dielectric elastomer actuators used for active origami. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 094002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, S.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. A novel dielectric elastomer membrane actuator concept for high-force applications. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2018, 23, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgins, M.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Experimental comparison of bias elements for out-of-plane DEAP actuator system. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 094016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, J. Artificial muscles for jaw movements. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2016, 6, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lochmatter, P.; Kunz, A.; Kovacs, G. Spring roll dielectric elastomer actuators for a portable force feedback glove. In Proceedings of the Smart Structures and Materials 2006: Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD), San Diego, CA, USA, 26 February–2 March 2006; Volume 6168, pp. 505–516. [Google Scholar]
- He, T.; Cui, L.; Chen, C.; Suo, Z. Nonlinear deformation analysis of a dielectric elastomer membrane–spring system. Smart Mater. Struct. 2010, 19, 085017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Li, T.; Baumgartner, R.; Suo, Z.; Bauer, S. Harnessing snap-through instability in soft dielectrics to achieve giant voltage-triggered deformation. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Keplinger, C.; Baumgartner, R.; Bauer, S.; Yang, W.; Suo, Z. Giant voltage-induced deformation in dielectric elastomers near the verge of snap-through instability. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2013, 61, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordi, C.; Michel, S.; Kovacs, G.; Ermanni, P. Scaling of planar dielectric elastomer actuators in an agonist-antagonist configuration. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 161, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; De Rossi, D. Hydrostatically Coupled Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 15, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loew, P.; Rizzello, G.; Seelecke, S. A novel biasing mechanism for circular out-of-plane dielectric actuators based on permanent magnets. Mechatronics 2018, 56, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Chen, L.; Hill, T.L.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. Exploiting Bistability for High-Performance Dielectric Elastomer Resonators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 27, 5994–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, J.; Hubertus, J.; Croce, S.; Schultes, G.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Fully Polymeric Domes as High-Stroke Biasing System for Soft Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 695918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, P.; Rosset, S.; Koster, S.; Stauffer, J.; Mikhaïlovc, S.; Dadras, M.; de Rooij, N.-F.; Shea, H. Microactuators based on ion implanted dielectric electroactive polymer (EAP) membranes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 131, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marette, A.; Poulin, A.; Besse, N.; Rosset, S.; Briand, D.; Shea, H. Thin Film Transistors: Flexible Zinc-Tin Oxide Thin Film Transistors Operating at 1 kV for Integrated Switching of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators Arrays. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, A.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H. Fully printed 3 microns thick dielectric elastomer actuator. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20–24 March 2016; Volume 9798, pp. 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lotz, P.; Matysek, M.; Schlaak, H.F. Fabrication and Application of Miniaturized Dielectric Elastomer Stack Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ouyang, G.; Chen, X.; Jakobsen, H. Engineering Electroactive Dielectric Elastomers for Miniature Electromechanical Transducers. Polym. Rev. 2017, 57, 369–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; Turco, S.; De Rossi, D. Bioinspired Tunable Lens with Muscle-Like Electroactive Elastomers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4152–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; Tarantino, S.; De Rossi, D. Millimetre-scale bubble-like dielectric elastomer actuators. Polym. Int. 2009, 59, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.; Kang, J.; Lee, C.; Kwon, H.Y.; Hwang, S.; Moon, H.; Koo, J.C.; Nam, J.-D.; Hong, B.H.; Choi, J.-B.; et al. A transparent and stretchable graphene-based actuator for tactile display. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 145501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau, S.; Rizzello, G.; Hodgins, M.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Design and control of a high-speed positioning system based on dielectric elastomer membrane actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulimane, S.; Pinon, S.; Shih, W.P.; Camon, H. Dielectric Elastomer Micro Actuator Made In Micromachining Technology: Finite Element Modelling and Deformation Measurement. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimpin, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Kasagi, N. Microelectrostrictive actuator with large out-of-plane deformation for flow-control application. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2007, 16, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.; McCoul, D.; Sollier, E.; Ruggiero, T.; Niu, X.; Pei, Q.; Di Carlo, D. Electro-adaptive microfluidics for active tuning of channel geometry using polymer actuators. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2013, 14, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Fujikawa, T.; Kazoe, Y.; Kitamori, T. An active valve incorporated into a microchip using a high strain electroactive polymer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 184, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Ghazali, F.A.; Mah, C.K.; AbuZaiter, A.; Chee, P.S.; Mohamed Ali, M.S. Soft dielectric elastomer actuator micropump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 263, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Kim, S.; Ji, X.; Zhu, W.; Niroui, F.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. A High-Lift Micro-Aerial-Robot Powered by Low-Voltage and Long-Endurance Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, S.; Niklaus, M.; Dubois, P.; Shea, H.R. Mechanical characterization of a dielectric elastomer microactuator with ion-implanted electrodes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 144, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, A.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Printing low-voltage dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 244104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, J.; Croce, S.; Willian, T.; Hubertus, J.; Schultes, G.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Distributed Electro-Mechanical Coupling Effects in a Dielectric Elastomer Membrane Array. Exp. Mech. 2022, 63, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lu, Z.; Cui, F.; Cheng, L.; Cui, Y. Tunable acoustic metamaterial with an array of resonators actuated by dielectric elastomer. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2017, 12, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Liu, X.; Cacucciolo, V.; Civet, Y.; El Haitami, A.; Cantin, S.; Perriard, Y.; Shea, H. Untethered Feel-Through Haptics Using 18-µm Thick Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Arana, S.; Klug, F.; Mößinger, H.; Förster-Zügel, F.; Schlaak, H.F. A novel application of dielectric stack actuators: A pumping micromixer. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 074008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlatter, S.; Grasso, G.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H. Inkjet Printing of Complex Soft Machines with Densely Integrated Electrostatic Actuators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 2000136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.; Gisby, T.; Calius, E.; Xie, S.; Anderson, I. FEA of Dielectric Elastomer Minimum Energy Structures as a Tool for Biomimetic Design. In SPIE Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2009; Volume 7287, pp. 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, B.; Li, S.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gu, Z.; Wang, S. Artificial Asymmetric Cilia Array of Dielectric Elastomer for Cargo Transportation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 42979–42984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Niu, J.; Liu, L.; Yu, J. A Soft Creeping Robot Actuated by Dielectric Elastomer. In SPIE Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9056, pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.J.; Wang, K.; Hu, T.T. Development of an annelid-like peristaltic crawling soft robot using dielectric elastomer actuators. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2020, 15, 046012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.B.; Zhang, W.M.; Zou, H.X.; Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G. Multisegment annular dielectric elastomer actuators for soft robots. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 115024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeil, S.; Henke, M.; Katzer, K.; Zimmermann, M.; Gerlach, G. A Worm-Like Biomimetic Crawling Robot Based on Cylindrical Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, E.-F.M.; Schlatter, S.; Anderson, I.A. Soft Dielectric Elastomer Oscillators Driving Bioinspired Robots. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Phung, H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Jung, H.; Choi, H.R. Multiple-degrees-of-freedom dielectric elastomer actuators for soft printable hexapod robot. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2017, 267, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Cao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.F. Programmable Deformations of Networked Inflated Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiesmaili, E.; Clarke, D.R. Optically addressable dielectric elastomer actuator arrays using embedded percolative networks of zinc oxide nanowires. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 3110–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hayakawa, T.; Ishikawa, M. Dielectric-elastomer-based fabrication method for varifocal microlens array. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 31708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burugupally, S.P.; Koppolu, B.; Danesh, N.; Lee, Y.; Indeewari, V.; Li, B. Enhancing the performance of dielectric elastomer actuators through the approach of distributed electrode array with fractal interconnects architecture. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 064002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-P.; Chen, L.-W.; McGough, K.; Ahmed, S. The tunable acoustic band gaps of two-dimensional phononic crystals with a dielectricelastomer cylindrical actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 17, 015011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Hong, J.; Wang, M.Y. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators for Soft Wave-Handling Systems. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Shea, H.R. Microfabrication and characterization of an array of dielectric elastomer actuators generating uniaxial strain to stretch individual cells. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 045020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Shea, H.R. An array of 100 m × 100 m dielectric elastomer actuators with 80% strain for tissue engineering applications. Sens. Actuators A 2012, 186, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matysek, M.; Lotz, P.; Winterstein, T.; Schlaak, H.F. Dielectric elastomer actuators for tactile displays. In Proceedings of the World Haptics 2009-Third Joint EuroHaptics conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Online, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 290–295. [Google Scholar]
- Phung, H.; Hoang, P.T.; Jung, H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, C.T.; Choi, H.R. Haptic Display Responsive to Touch Driven by Soft Actuator and Soft Sensor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 2495–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Phung, H.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, U.K.; Nguyen, C.T.; Moon, H.; Koo, J.C.; Choi, H.R. Design analysis and fabrication of arrayed tactile display based on dielectric elastomer actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 205, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Cohen, A.J.; Vogt, D.M.; Kollosche, M.; Lansberry, G.; Mengüç, Y.; Israr, A.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J. A Wearable Textile-Embedded Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Haptic Display. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Hussain, A.M.; Israr, A.; Vogt, D.M.; Duduta, M.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J. A Wearable Soft Haptic Communicator Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, P.; Toprakci, H.A.K.; Yang, P.; Di Spigna, N.; Franzon, P.; Ghosh, T. A compact dielectric elastomer tubular actuator for refreshable Braille displays. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 179, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Ma, X.; Shi, B.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; et al. Refreshable Braille Display System Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Dielectric Elastomer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2006612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frediani, G.; Busfield, J.; Carpi, F. Enabling portable multiple-line refreshable Braille displays with electroactive elastomers. Med. Eng. Phys. 2018, 60, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, H.; Guo, X.; Ji, Z.; Li, G.; Liang, Y.; Xue, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, F.; et al. Electro-mechanically controlled assembly of reconfigurable 3D mesostructures and electronic devices based on dielectric elastomer platforms. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020, 7, 342–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, M.; Yang, Y.; Su, J.; Wong, T.; Xu, K.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; et al. Origami-inspired folding assembly of dielectric elastomers for programmable soft robots. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2022, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, B.; Shea, H. Reconfigurable and Latchable Shape-Morphing Dielectric Elastomers Based on Local Stiffness Modulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Qiu, Y.; Hou, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Bistable dielectric elastomer actuator with directional motion. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 330, 112889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Tairych, A.; Anderson, I.A. Where the rubber meets the hand: Unlocking the sensing potential of dielectric elastomers. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, J. A soft compressive sensor using dielectric elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 035045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.; Huh, T.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.-O.; Park, S.; Cutkosky, M.R.; Bao, Z. Porous Dielectric Elastomer Based Flexible Multiaxial Tactile Sensor for Dexterous Robotic or Prosthetic Hands. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, in press. [CrossRef]
- Kadooka, K.; Imamura, H.; Taya, M. Tactile Sensor Integrated Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Simultaneous Actuation and Sensing. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9798, pp. 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Giffney, T.; Aw, K. A Dielectric Elastomer-Based Multimodal Capacitive Sensor. Sensors 2022, 22, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.; Lenz, S.; Gratz-Kelly, S.; Motzki, P.; Nalbach, S.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G. Experimental Characterization of a Smart Dielectric Elastomer Multi-Sensor Grid. In SPIE Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) XXII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11375, pp. 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Kim, C.; Lee, S.D. Low-cost flexible pressure sensor based on dielectric elastomer film with micro-pores. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 240, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Lee, T.-I.; Shim, J.; Ryu, S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.-S.; Park, I. Highly Sensitive, Flexible, and Wearable Pressure Sensor Based on a Giant Piezocapacitive Effect of Three-Dimensional Microporous Elastomeric Dielectric Layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16922–16931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyaw, A.K.K.; Loh, H.H.C.; Yan, F.; Xu, J. A polymer transistor array with a pressure-sensitive elastomer for electronic skin. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 12039–12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, C.; Spjut, J.; Knepper, R.; Shepherd, R. A Deformable Interface for Human Touch Recognition Using Stretchable Carbon Nanotube Dielectric Elastomer Sensors and Deep Neural Networks. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishniakou, S.; Lewis, B.W.; Niu, X.; Kargar, A.; Sun, K.; Kalajian, M.; Park, N.; Yang, M.; Jing, Y.; Brochu, P.; et al. Tactile Feedback Display with Spatial and Temporal Resolutions. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).