Abstract
Decreasing the system weight while maintaining the assistance performance can help reduce the metabolic penalty in exosuits. Various researchers have proposed a bi-directional cable-driven actuator that can provide two degrees of freedom (2-DOF) assistance by using a single motor. However, such systems face limitations associated with the controllability of the assistance force. This study proposes a novel cable-driven system, that is, a dual pulley drive, that can provide versatile controllability of 2-DOF cable actuation by using a single motor via a novel moving gear mechanism. The moving gear winds the cable by switching both the side pulleys, which are then used for 2-DOF cable actuation. The spiral springs embedded between the pulley and base shaft work to release the cable. Results of experiments demonstrate that the dual pulley drive provides a versatile range of motion. The proposed system can provide 34.1% of overlapping motion per cable round trip time and support the non-overlapping motion. The preliminary integration of the dual pulley drive to the exosuit confirms that the novel exosuit is considerably lighter than the state-of-the-art exosuit. The calculations indicate that the operating cable speed and force generated using the proposed design are higher than the existing exosuit.
1. Introduction
With rapid technological advancements, robots that can be worn by humans are being actively developed to enhance physical abilities and promote rehabilitation [1]. Robotic exoskeletons are a representative type of wearable robots that consists of a rigid frame. These exoskeletons transmit high assistive force to the wearer through motors or springs [2,3]. An exoskeleton firmly supports a wearer’s body and efficiently assists in tasks involving a considerable physical effort by providing a strong assisting force. However, when a user moves, the heavy frame of the exoskeleton applies significant inertia and weight to the lower extremities. The additional inertia and weight degrade the assistive effect from the exoskeleton and may increase the metabolic rate when the wearer walks normally [3,4,5]. In addition, owing to the rigid structure of the frame, misalignment with the wearers’ joints may occur, thus restricting natural movement and causing discomfort [6,7,8].
Owing to these limitations posed by exoskeletons, lightweight, comfortable, and flexible exosuits have been developed in recent years. An exosuit based on a clothing-type frame and cable-driven method was proposed by a group at Harvard University [9,10,11]. This exosuit does not have a heavy, rigid structure and is thus lightweight while introducing low inertia. Owing to the flexible characteristic of the clothing-type frame, precise alignment with the wearer’s joints is unnecessary, and therefore, the frame is comfortable to use. Moreover, Kim et al. developed a hip extension assistance exosuit to decrease the metabolic rate by 9.3% and 4% while walking and driving, respectively [10].
The abovementioned exosuits are fundamentally lighter than exoskeletons. However, an exosuit relies on actuators and batteries for generating assistive force. Consequently, exosuits incur a significant metabolic penalty owing to the system weight. Most existing exosuits are cable-driven systems that can provide targeted assistance in only one direction with a single actuator. Owing to such system limitations, with the increase in the number of joints and muscles to be supported, the required number of actuators increases, which increases the system weight.
To minimize the number of actuators required in exosuits, several researchers have proposed bi-directional cable-driven actuators (BCDAs), in which two pulleys are attached to one motor in opposite directions, as shown in Figure 1a. One pulley winds the cable when the motor rotates, and the other pulley unwinds the cable. When the motor rotates in reverse, the drive system operates in the opposite manner. Using this method, Asbeck et al. developed an exosuit that uses two sets of BCDAs to assist the bilateral hip extension muscles and bilateral multi-articular muscles (ankle plantarflexion and hip flexion) [12]. Tricomi et al. designed an exosuit that assists bilateral hip flexion muscles with a BCDA and demonstrated that the muscle activity decreases when using the exosuit [13]. Moreover, Kwon et al. and other researchers developed an ankle brace supporting the ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion muscles with a BCDA [14,15,16].
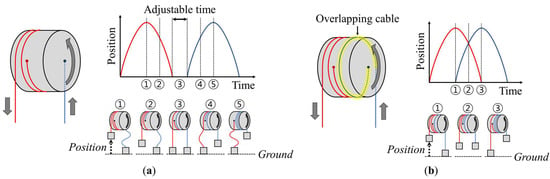
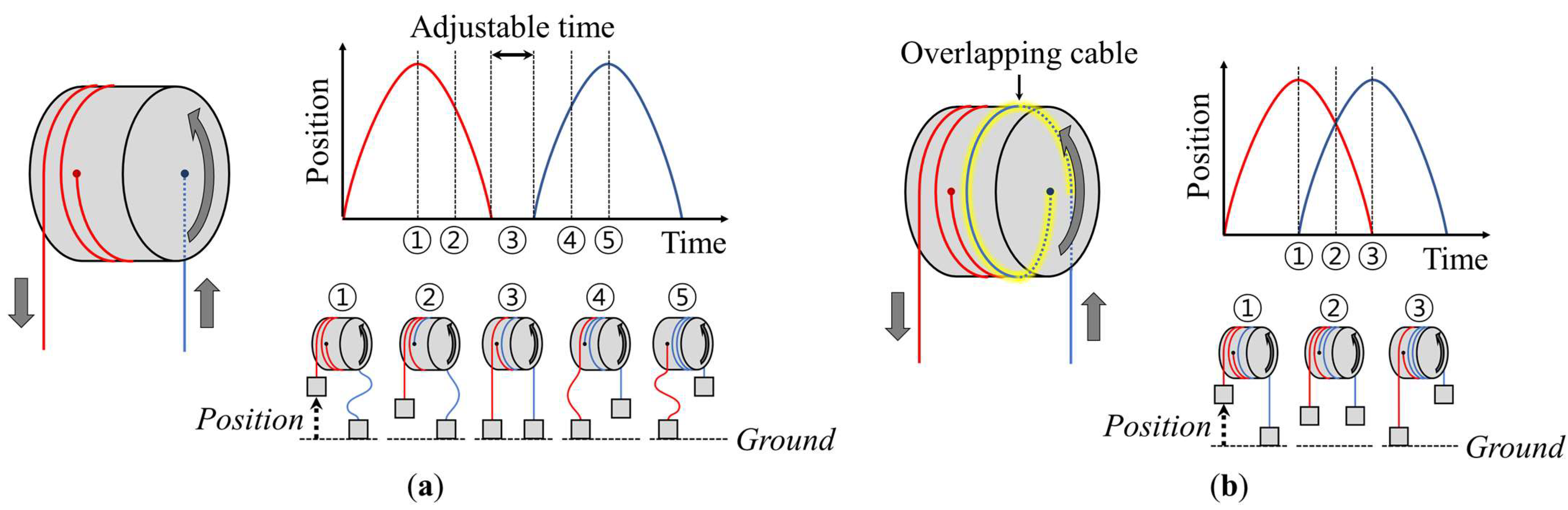
Figure 1.
Conceptual explanation of cable positioning profiles with existing bi-directional cable-driven actuators (BCDAs), for a position a certain distance from the ground: (a) BCDAs with non-overlapping cables can generate all non-overlapping profiles; (b) BCDAs with overlapping cables can generate only one overlapping profile.
Nevertheless, these BCDAs involve several limitations. In general, exosuits provide assistive force to the target muscles by coinciding with the section while activating the target muscles. The human body’s musculoskeletal system is a hyper-redundantly actuated system in which the number of muscles is considerably larger than the degrees of freedom (DOFs). Several co-contractions occur among muscles during movement, and the sections of muscle activation patterns frequently overlap and vary by motion and individuals. Thus, although 2-DOF exosuits have been designed to independently assist two different muscles, 2-DOF assistance typically requires the overlapping of the actuation region for optimal assistance.
One of the main assistance targets for lower extremity exosuits is the hip-joint-related muscle. Several activation periods of muscles, such as the hamstring, which are involved in the movement of the hip joint, overlap in bilateral legs in more than 50% of the gait cycle [17]. In addition, the range of activation periods varies based on the gait velocity and individual. Considering this biological feature of muscles, researchers attempted to optimize the hip extension assistive profiles while walking through human-in-the-loop experiments [18]. The optimal assistive profiles of six out of eight participants occupied over 50% of the gait cycle, necessitating the overlapping of assistance regions for bilateral hip assistance.
Moreover, the overlapping range among individuals was noted to be different. The optimal assistive profiles of two out of eight participants occupied less than 50% of the gait cycle, necessitating the non-overlapping of assistance regions for bilateral hip assistance. Therefore, the ideal actuator for exosuits must operate in both overlapping and non-overlapping profiles and adjust the range of overlap.
Figure 1a shows an existing BCDA that can perform most types of assistive operations, in which the sections supported by cables on both sides do not overlap. A profile with overlapping assistive sections cannot be driven in this configuration. As shown in Figure 1b, by overlapping the cables of the two pulleys, the assistant profile can be overlapped. However, because the overlapping length is fixed, only one type of fixed overlapping profile can be driven. In this context, adjusting the length of the overlapping cable each time to correct the extent of overlapping of the assistive profiles to respond to changes in the target user or motion may be challenging. Consequently, a novel BCDA with high controllability of assistive profiles on both sides must be established, changing the overlapping shapes and extents and supporting non-overlapping profiles.
To this end, this study proposes a dual pulley drive, a novel type of BCDA that can ensure versatile controllability of assistive forces and support the overlapping and non-overlapping motions of both legs with a single motor. The system converts and rotates two pulleys with one motor through a moving gear mechanism that moves and rotates gears according to the direction of rotation of the motor. Additionally, a spiral spring is installed inside the pulley. The moving gear winds up the spring together with the cable. When the gear is separated from the pulley, the cable is unloaded by the elastic force of the spring.
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 explains the structure and operating principle of the dual pulley drives along with the mechanisms for implementing the dual pulley drive, such as the moving gear mechanism, feeder mechanism, and spiral spring design. Section 3 describes the testing of the cable position through marker tracking and comparison with the existing cable-driven actuator. Section 4 summarizes the contributions of this research and describes how future studies can overcome the limitations of dual pulley drives. In addition, Supplementary Material, Video S1, is attached to help understand the overall explanation and tests.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. System Configuration
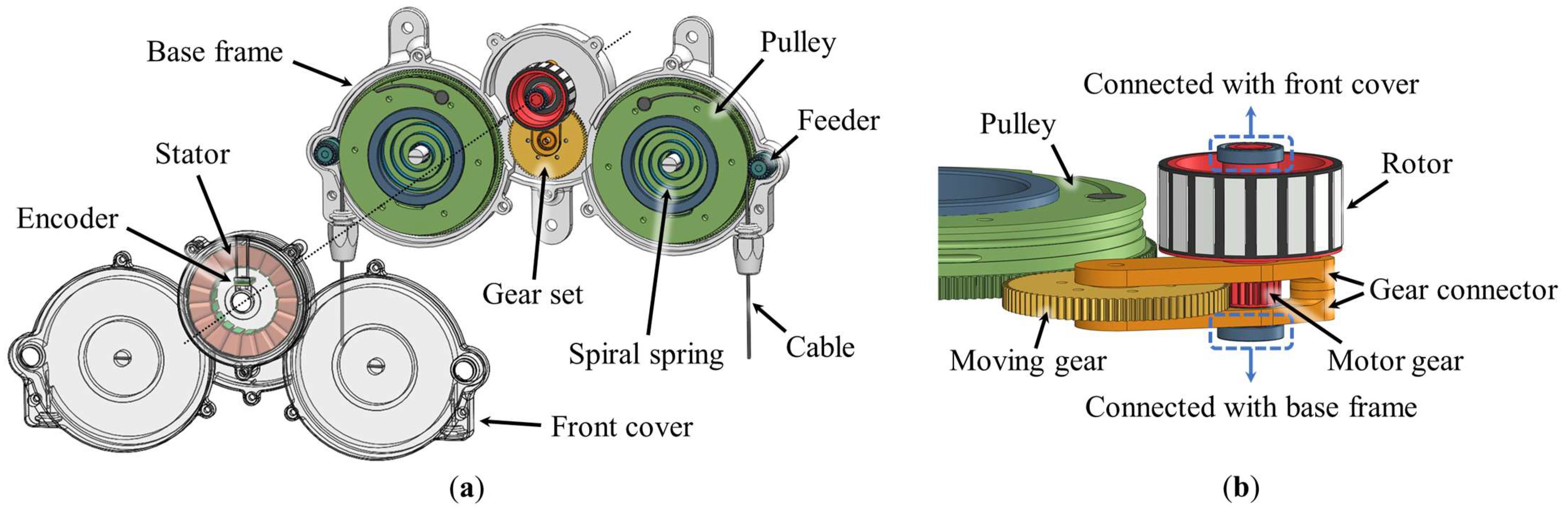
Figure 2 shows the various parts of a dual pulley drive, including a motor with a stator, a rotor, and an encoder to generate the driving torque. Pulleys with a gear, motor gear, moving gear, feeders, and spiral springs transmit the driving torque to the cable. Housings with a base frame and front cover constitute the base structure.
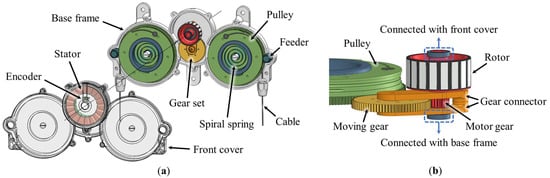
Figure 2.
Structure of the dual pulley drive, prepared in 3D CAD: (a) exploded view of dual pulley drive; (b) detailed view of the gear set.
The stator is fixed to the front cover, and the rotor is fixed to the motor gear. The motor gear and moving gear are assembled with the gear connector, as shown in Figure 2b. Both ends of the motor gear shaft are connected to the front cover and base frame. However, the moving gear shaft is not connected to the housing. Thus, when the rotor rotates the motor gear, the motor gear rotates the moving gear and simultaneously moves it in the trajectory of pendulum motion based on the axis of the motor gear. When the moving gear moves and engages with the pulley gear, the pulley is rotated by the rotational force of the moving gear. The moving gear alternately rotates both the side pulleys according to the rotation direction of the motor. The motion and principle of the mechanism are explained in Section 2.2 and Section 2.3.
The two pulleys are installed on the two shafts extruding from the base frame. The spiral springs are coupled to the shafts on the base frame and inside the pulley. The feeder is connected to the gear on the pulley to decrease the friction between the cable and base frame when the cable is released. The principle and experimental analysis of the feeder are described in Section 2.4.
2.2. Working Principle
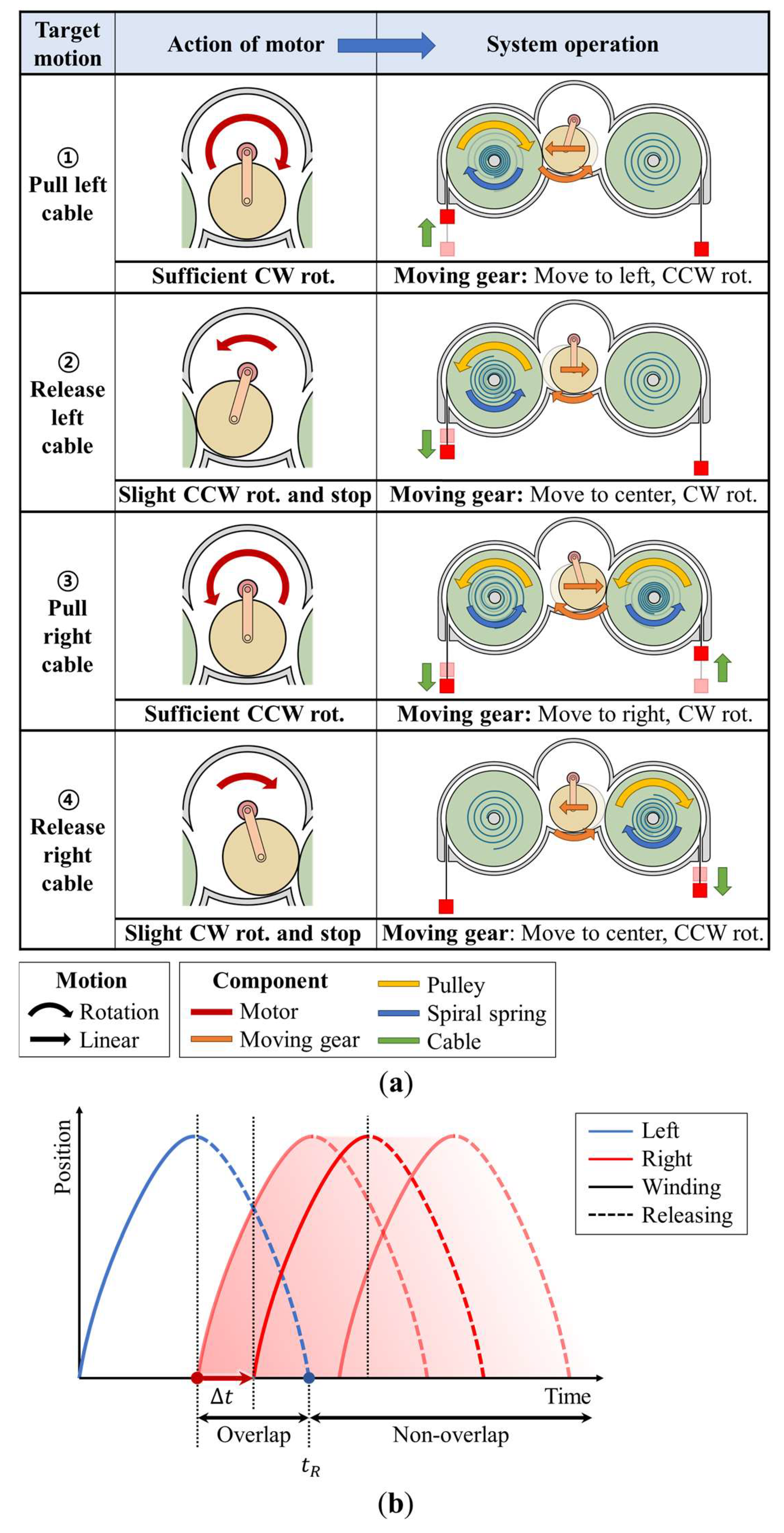
The dual pulley drive rotates the two pulleys on the left and right sides by moving and rotating the moving gear to the left and right, according to the rotation of a single motor. In Figure 3a, the first column shows the target motion of the system, and the second column illustrates the actions of the motor for generating the target motion. Based on the motor operation, the third column shows the resultant system operation (moving gear, pulley, spiral spring, and cable). The drive system operates sequentially from the first row to the last row in a driving cycle.
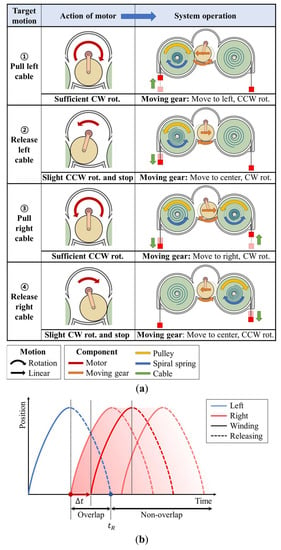
Figure 3.
Process flow of the operation of a dual pulley drive: (a) working principle according to sequential target motions; (b) method for adjusting the gap in two motion profiles.
The target motion in the first row pertains to the pulling of the left cable. For this motion, the motor must rotate sufficiently clockwise. Subsequently, the motor gear applies force to the moving gear in the clockwise direction on the part engaged with the moving gear. Owing to this applied force, the moving gear moves to the left, thereby rotating counterclockwise. In combination with the left pulley, the moving gear rotates the left pulley in the clockwise direction and pulls the left cable. The target assistive force can be generated by connecting the cable to the exosuit and pulling it at the desired speed and stroke. The rotation of the pulley simultaneously winds the left spiral spring installed in the pulley.
The next target motion, illustrated in the second row, is the release of the left cable. In this case, the motor rotates slightly counterclockwise and halts for a certain duration Δt. Owing to the force applied by the motor gear to the moving gear in the counterclockwise direction, the moving gear is pulled out from the left pulley. Because the motor rotates slightly, the moving gear moves to the center and stops. When the moving gear is pulled out of the left pulley, the left pulley rotates counterclockwise owing to the elastic force of the spiral spring coupled to the left pulley, thereby releasing the left cable without the aid of the motor.
The subsequent target motions involve the pulling and releasing of the right cable (presented in the third and fourth rows, respectively). The operating principles of the motor and system are the same as those for the motions presented in the first and second rows, except that the right-side pulley is in use. Therefore, the motor and system operation directions of action are opposite to those in the first and second rows.
By repeating this driving cycle, the position of both cables can be driven, as shown in Figure 3b. During the operation, the extent of overlapping of both the position profiles varies by Δt, which is the latency in the motor action, as explained in the second and fourth rows. When Δt is larger than , which is the time the cable takes to be released by the spiral spring, the system drives the cable movement on both sides without any overlapping, as indicated in Figure 1a. Conversely, when Δt is smaller than , the system operates with the overlapping movements of both cables, as shown in Figure 1b. Furthermore, Δt can be adjusted to any value greater than or equal to zero through motor control. Adjusting Δt allows the amount of overlap of both the cable actuation profiles to be varied.
2.3. Analysis of the Moving Gear Mechanism
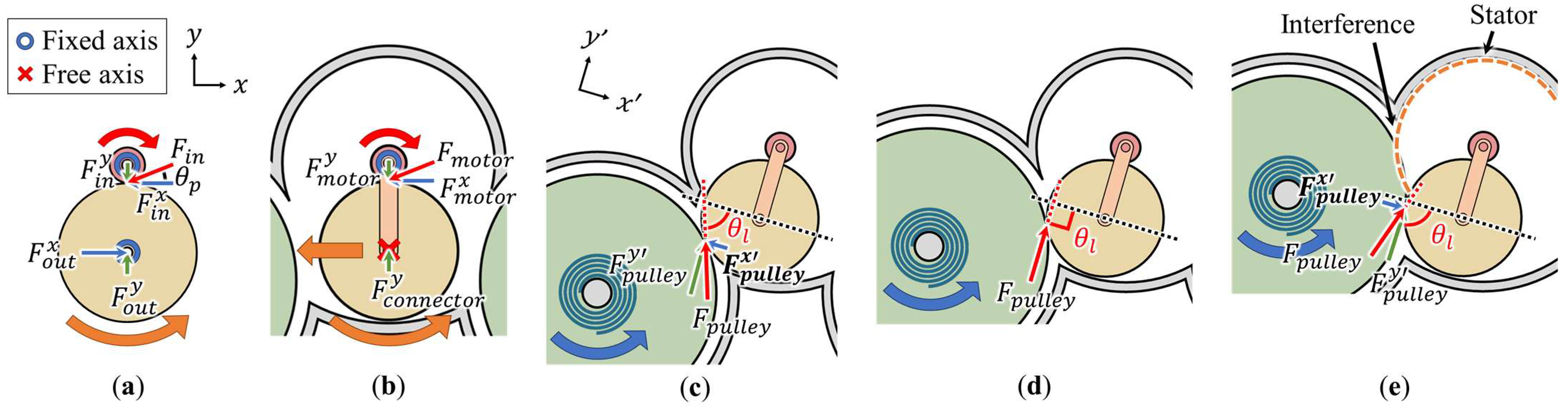
In general, gear shafts are fixed in mechanisms, as shown in Figure 4a. When the input gear rotates, force is transmitted to the output gear in a specific direction of the pressure angle . The transmitted force is eliminated by the reaction forces of the output gear shaft, as:
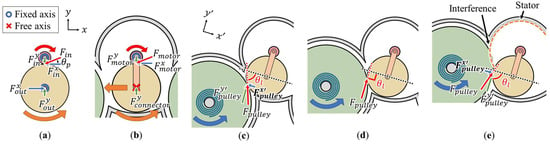
Figure 4.
Moving gear mechanism and free body diagram of (a) general gear rotation, (b) moving gear rotation, and (c–e) rotation according to the angle formed by the pressure angle direction between the gears (red dotted line) and moving direction of the moving gear (black dotted line) ((c) acute angle, (d) right angle, (e) obtuse angle).
Then, only a net moment that rotates the output gear remains. In contrast, in the moving gear mechanism, the shaft of the moving gear, which is the output gear, is not fixed, as shown in Figure 4b. In this case, the force transmitted in the pressure angle direction through the motor gear, which is the input gear, acts differently than that in general mechanisms. The y-axis component of the force received by the moving gear is canceled by the reaction of the gear connector, as:
However, the moment and force in the x-axis direction are not canceled, leading to the simultaneous movement and rotation of the moving gear.
Therefore, the moving gear mechanism simultaneously generates the movement and rotation of the moving gear via only the rotation of the motor gear, without any additional driving source. This configuration simplifies the design and enables 2-DOF driving with a single motor. However, the underactuated controllability of operation can potentially lead to failure in controlling the moving gear, leading to system/operational failure. Thus, we consider two possible failure modes and examine the countermeasures for each mode.
The first failure mode may occur owing to the elastic force generated by the spiral spring inside the pulley when the moving gear is engaged with the pulley gear. This failure may occur in the direction in which the elastic force of the spring interferes with the separation of the pulley and moving gear or leads to an unintentional separation based on the pressure angle transmitted from the pulley gear to the moving gear.
To prevent such failures, as shown in Figure 4c–e, the angle formed by the pressure angle direction between the gears (black dotted line) and the moving direction of the moving gear (red dotted line) must be considered. Here, is the force transmitted from the pulley gear to the moving gear. The angle can be categorized into acute, right, and obtuse angles.
Moreover, the can be divided into component forces and . When is acute, as shown in Figure 4c, acts in the direction opposite to that in which the moving gear is pulled out of the pulley. Therefore, must not be acute because may prevent the moving gear from exiting the pulley. When is obtuse, as shown in Figure 4e, acts in the direction in which the moving gear is detached from the pulley. Therefore, must not be obtuse because may cause the moving gear to not come off the pulley. Moreover, as shown in Figure 4e, from a design perspective, as increases, the pulley approaches the motor gear, which may lead to interference between the pulley and stator, causing operational issues. When is 90°, no operational failures occurred in the moving gear mechanism, and the design is simplified.
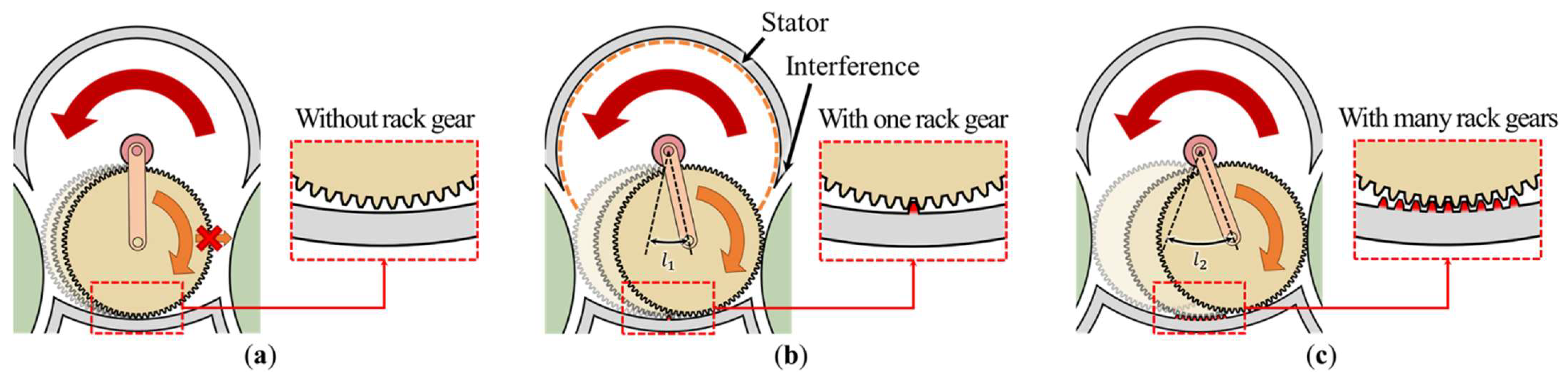
The second failure mode may occur when the moving gear only rotates without moving to the pulley on the other side. Theoretically, the moving gear must move to the left and right when the motor rotates. However, as shown in Figure 5a, the moving gear may remain idle without engaging with the pulley owing to manufacturing errors, such as inferior bearing performance, inadequate machining precision, or unexpected external forces.
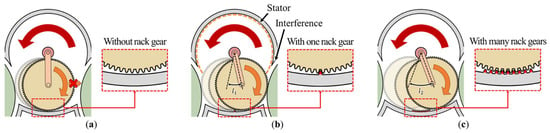
Figure 5.
Rack gear design to minimize the distance of the moving gear: (a) without the rack gear, the moving gear rotates without moving to the pulley on the other side; (b) with one rack gear, the moving gear moves to the other pulley by distance ; (c) with many rack gears, the moving gear moves to the other pulley by distance (larger than ).
To prevent such failures, a rack gear can be introduced on the path of the moving gear, as shown in Figure 5b,c. To install the rack gear, a gap must be incorporated between the moving gear and rack gear to avoid interference when the moving gear engages with the pulley gear. Notably, with the additional rack gears, the moving gear moves over a larger distance and period, as shown in Figure 5c. Therefore, only one rack gear is installed at the center of the housing, as shown in Figure 5b. The moving gear engages with the rack gear as soon as it is pulled out of the left pulley and moves to the pulley on the other side without idling.
In the final stage of the moving gear mechanism design, the reduction gear ratio must be selected by considering the design aspects to prevent the two failure modes. As shown in Figure 5b, when the moving gear is too small, interference between the stator and pulley may occur owing to it approaching the motor gear and pulley gear.
Furthermore, the target specifications of the actuation system must be considered to select the gear ratio. In this study, considering the size and weight of the actuation system after implementation, we selected the RI 60 motor (T-Motor, Nanchang, China), with a peak torque of 1.63 Nm. The target cable force was 300 N, equal to the assistive force of the state-of-the-art hip exosuit designed by Harvard University [19]. In general, the gear ratio must be selected to satisfy the target force. Thus, the ratio of the motor gear, moving gear, and pulley gear was set as 1:4:8.5, with the cable force exceeding 300 N in a pulley with a diameter of 80 mm, and no design interference was observed.
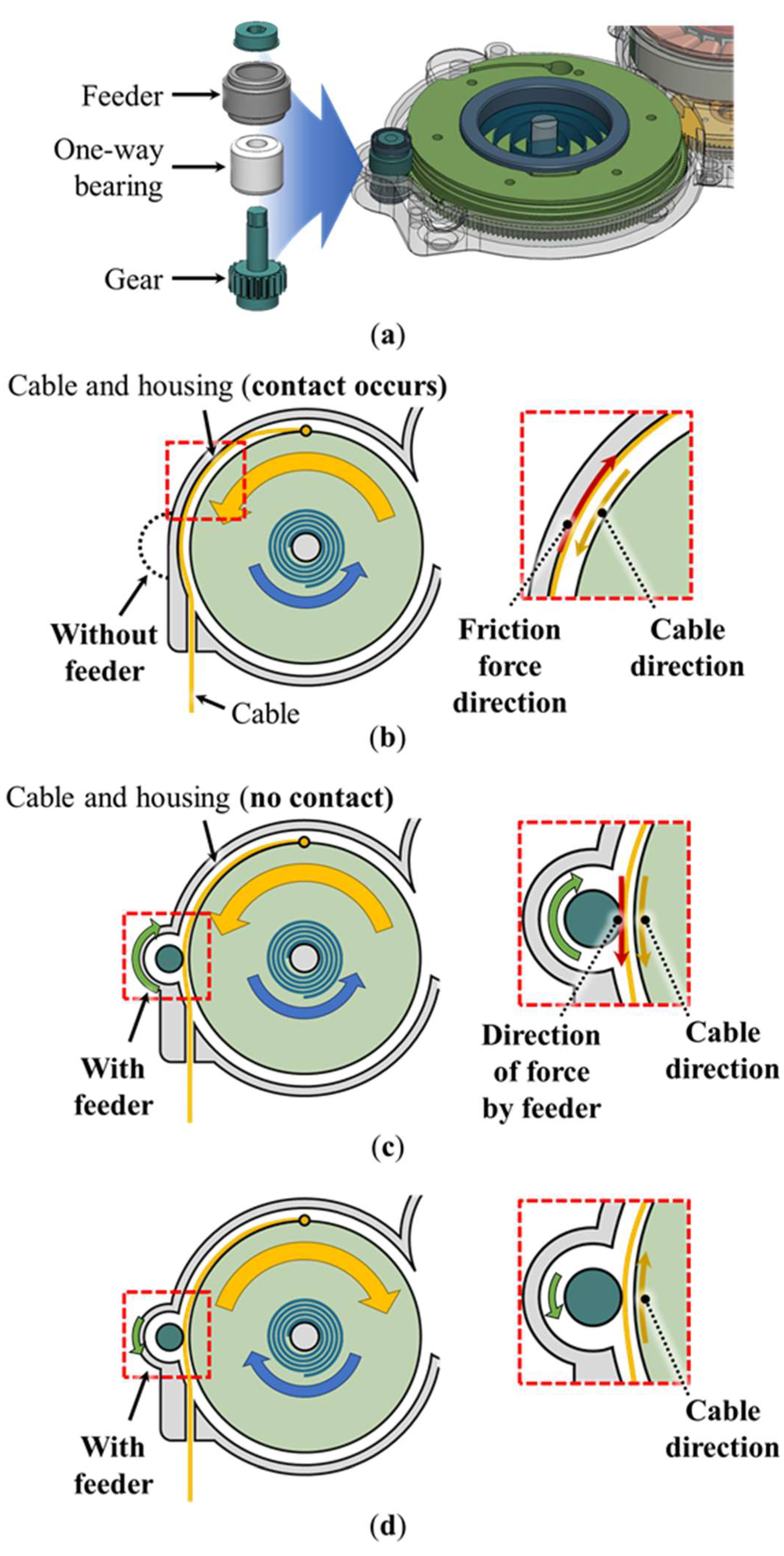
2.4. Feeder Mechanism
Typical cable-driven actuators wind and release the cable using the motor. Because these systems release the cable through high motor power, it is unnecessary to decrease the friction between the cable and housing in the design. In contrast, the dual pulley drives wind the cable through motor power and release the cable through the elasticity of the spiral spring. Therefore, greater friction between the cable and housing corresponds to a higher elasticity required to release the cable, resulting in energy consumption, for instance, in the form of elasticity associated with storing energy by deforming the spring when the motor rotates to wind the cable. Therefore, the spring force must be minimized to decrease the friction between the cable and housing.
The feeder mechanism can effectively decrease the friction by ensuring that the feeder turns with the pulley when the pulley turns by the spring. As shown in Figure 6a, the feeder mechanism consists of a feeder, one-way bearing, and gear. As shown in Figure 6b, the general cable-driven actuator generates friction because the cable contacts the housing when released. However, as shown in Figure 6c, when the feeder is installed closer to the pulley than to the housing, the cable contacts the feeder instead of the housing, thereby eliminating the friction generated in the case shown in Figure 6b. Moreover, the feeder gear is connected to the pulley gear and rotated in the direction opposite to that of the pulley when the pulley rotates. By setting a higher gear ratio (1:8.5) than the ratio of the radius between the feeder and pulley (1:6.67), the feeder rotation can be designed to be faster than the cable release, with the linear velocity of the feeder surface being higher than that of the pulley, thereby generating a force in the cable-release direction. This phenomenon occurs at the point of contact between the cable and feeder.
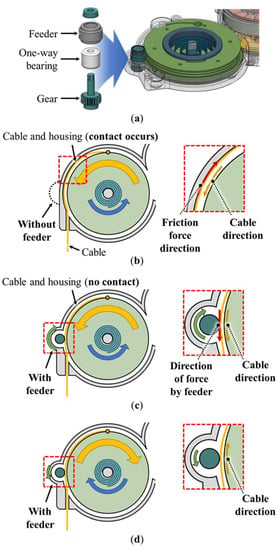
Figure 6.
Feeder mechanism design: (a) components of the feeder mechanism; (b) pulley without the feeder (the frictional force acts in the direction opposite to the cable-release direction); (c) pulley with the feeder (the force associated with the feeder acts in the same direction as the cable-release direction); (d) pulley with the feeder (free rotation in the cable-winding direction).
In addition, the one-way bearing installed inside the feeder is designed to transmit the torque in one direction and rotate freely in the other direction. Therefore, as shown in Figure 6d, when the pulley rotates in the cable-winding direction, the feeder does not push the cable into the system owing to the free rotation. Consequently, the use of the one-way bearing can help prevent the generation of the frictional force when the cable is wound.
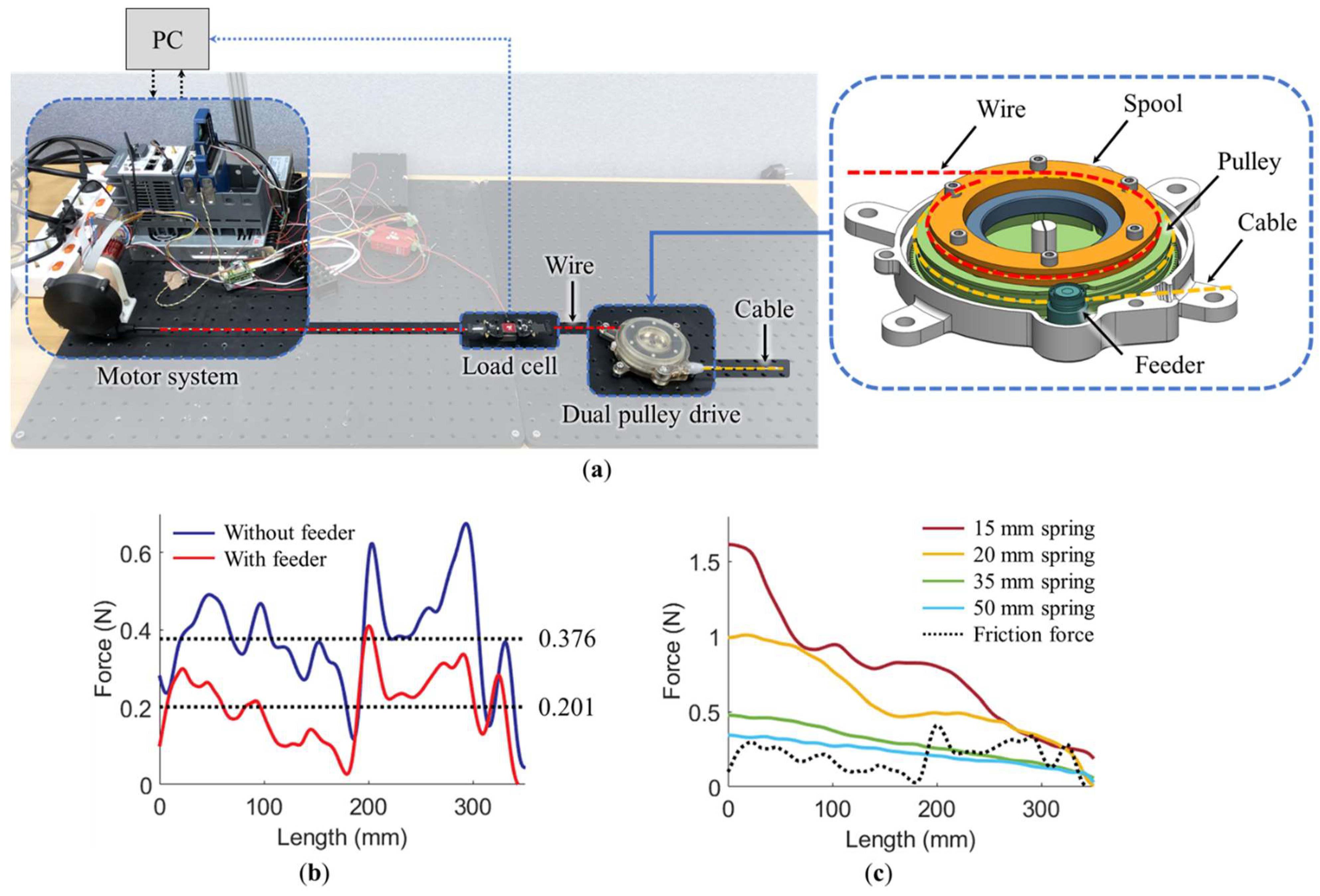
To verify the effect of the feeder, the friction of the model with and without the feeder was compared. As shown in Figure 7a, the pulley part of the dual pulley drive, combined with the spool, was fixed on the surface plate. The wire of the spool was connected to the motor system through a load cell (LSB205, Futek, MI, USA). When the EC 4-pole 30 brushless motor (#305013, Maxon, Switzerland) with the planetary gearhead (#326664, Maxon, Switzerland) pulled the wire (with the wire wound in the spool and the cable wound in the pulley), the cable released as the pulley rotated. The friction between the cable and housing was measured using a load cell. The wire was pulled at a low velocity of 5 mm/s to eliminate the inertia of the pulley. The motor position and velocity were controlled using a system engineering software (LabView 2019, National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) and a real-time controller (CompactRio, National Instruments, USA), combined with a motor driver (Gold Solo Twitter, Elmo Motion Control, Petach Tikva, Israel). The test results are shown in Figure 7b. The average and maximum friction of the model with the feeder was 0.201 N and 0.41 N, respectively. The average and maximum friction of the model without the feeder were 0.376 N and 0.675 N, respectively. Thus, the average and maximum friction decreased by 47% and 39%, respectively, through the addition of the feeder mechanism.
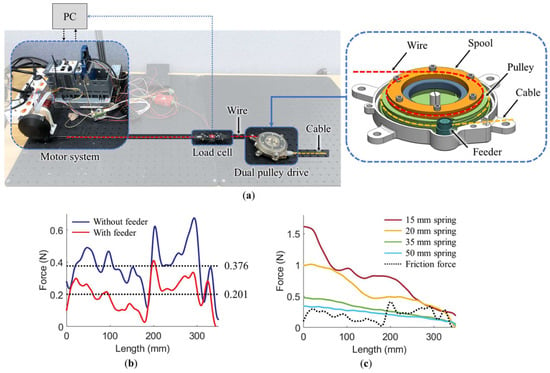
Figure 7.
Tests conducted on the feeder mechanism and spring elasticity: (a) test bench for the feeder mechanism; (b) friction with and without the feeder; (c) spring elasticities of 15 mm, 20 mm, 35 mm, and 50 mm. A second-order Butterworth low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 0.2 Hz was used to obtain the data (b,c).
2.5. Spiral Spring Design
To ensure that the spring released the cable, the spring elasticity was required to exceed the friction measured in the feeder mechanism test described in Section 2.4. The moment of the spiral spring was calculated using Equation [20], as follows:
in which M(N) is the spring moment when the spring rotates N turns, E is the elastic modulus of the spring material, B is the spring width, t is the spring thickness, and L is the spring length. A spiral spring that could be installed in the pulley was purchased to optimize the spring performance. Because L was the easiest design parameter to be adjusted according to Equation (4), springs with several lengths (15 mm, 20 mm, 35 mm, and 50 mm) were used, and their elasticities were compared.
To measure the spring elasticity, the cable of the pulley was removed, and the spring was installed in the pulley, as shown in Figure 7a. The motor system pulled the wire at 5 mm/s (equal to that used in the feeder test) using the test bench. The spring elasticities were measured using a load cell. Figure 7c shows the spring elasticity test results, in which the black dotted line represents the cable friction of the model with the feeder. The elasticities of the 35 mm and 50 mm springs did not exceed the cable friction, whereas those of the 15 mm and 20 mm springs did exceed the cable friction. To minimize the energy loss of the motor while driving, the spring elasticity was required to be minimized. Thus, the 20 mm spring was selected.
3. Results
A prototype of the dual pulley drive was manufactured, and the cable position profiles of several overlapping conditions were verified through marker tracking. Additionally, the benefits of implementing the exosuit on the dual pulley drive were highlighted through a comparison with the state-of-the-art exosuit [10].
3.1. Versatile Controllability of the Motion Profile
A prototype of the dual pulley drive was manufactured for the cable position profile test. The total system weight was 0.82 kg, and the maximum size was 250 mm × 36 mm × 120 mm (width × depth × length). The precision components related to the gears, e.g., the gear set, pulley, and feeder, were made of Al 7075. The components related to the housing (that did not require high hardness values) were prepared using VeroClear (Objet30 Pro, Stratasys, Rehovot, Israel). The other parts (requiring appropriate hardness to support loads) were made of carbon fiber (Mark Two, Markforged, Watertown, MA, USA).
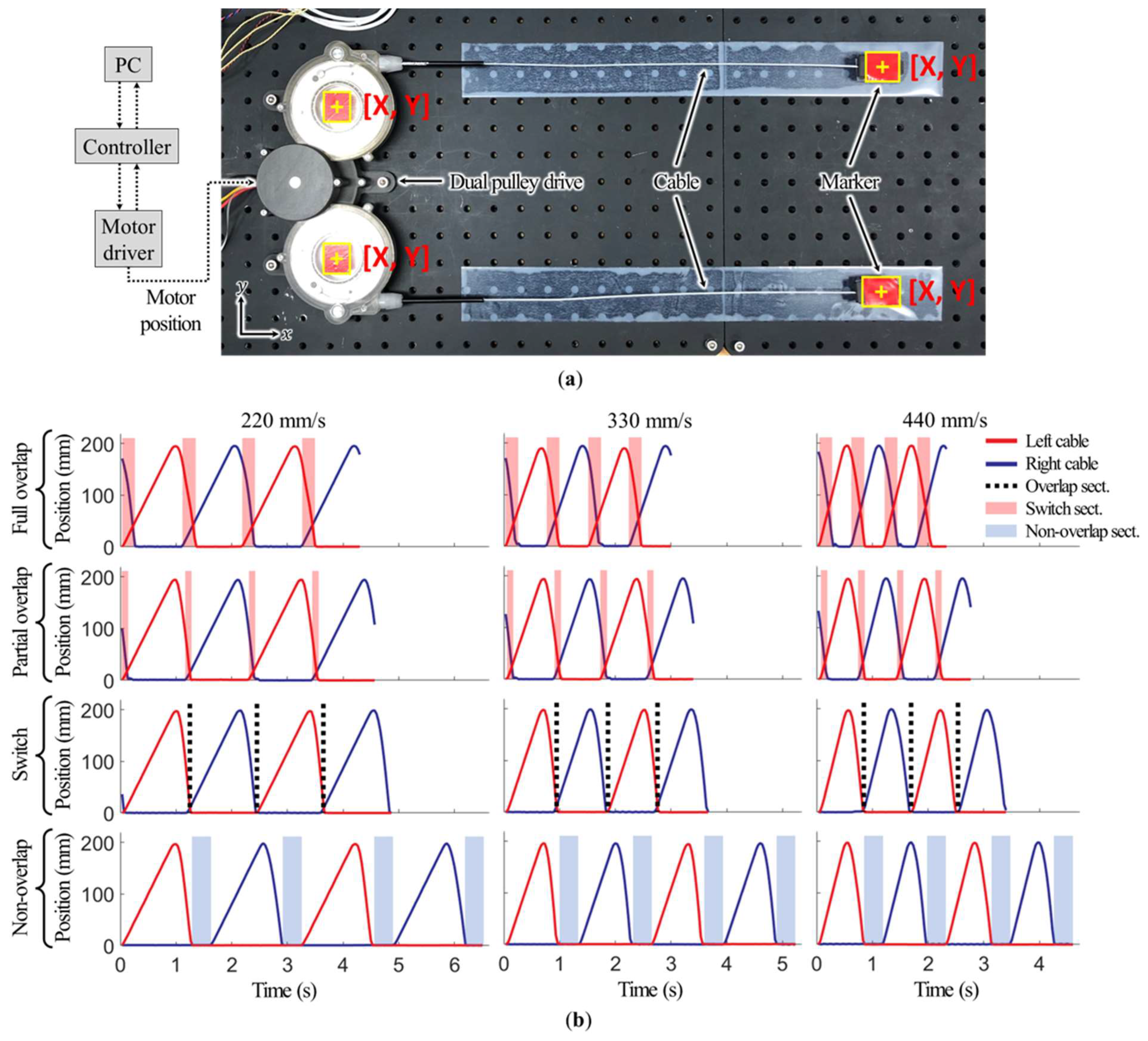
As shown in Figure 8a, the dual pulley drive was fixed on a surface plate. The motor actuated the motion of several cable position profiles. The cable position was measured by the markers attached to the ends of both cables. The motor driver was connected to a real-time controller (CompactRio, National Instruments, USA), and the motor was controlled to implement the motions as explained in Section 2.2 by using LabView. Marker tracking was performed using the engineering software MATLAB R2021a (MathWorks, Portola Valley, CA, USA). First, the hue saturation value (HSV) range of the marker was determined using the Color Thresholder app in MATLAB. As shown in Figure 8a, each frame of the test video was read using VideoReader and the read function. The marker was tracked after converting the frame to HSV data by using the rgb2hsv function, based on basic MATLAB functions. The cable position was determined as the distance from the cable position in the fully released condition. The absolute length was calculated based on the fixed distance of markers on the front cover.
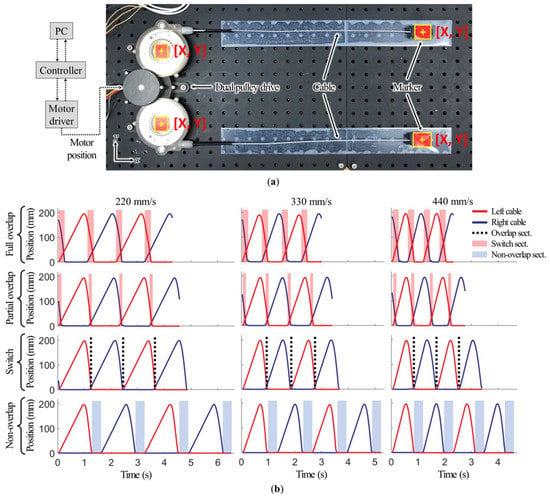
Figure 8.
Cable position profile test: (a) test bench for marker tracking; (b) test result profiles.
The cable position was verified in four conditions: full overlap of the two profiles (∆t = 0); partial overlap of the profiles (∆t = 0.1); switching of the profiles (∆t = 0.2); and no overlap of the profiles (∆t = 0.6). The test was conducted at three cable velocities (200 mm/s, 300 mm/s, and 400 mm/s).
Figure 8b illustrates the test results. The dual pulley drive created 12 cable position profiles corresponding to four profile overlapping conditions and three velocities. The cable round trip time was 1.3 s, 0.96 s, and 0.82 s at velocities of 200 mm/s, 300 mm/s, and 400 mm/s, respectively. The average overlapping time was 0.28 s in the condition with a full overlap of the profiles. The error range, determined from an SEM analysis, was 0.006 s, indicating that the dual pulley drive could support overlapping motions of 21.5%, 29.2%, and 34.1% at velocities of 200 mm/s, 300 mm/s, and 400 mm/s, respectively, per round trip time and operate without any problems in the remaining three conditions (partial overlap, switching, and no overlap) by increasing ∆t.
3.2. Comparison with the State-of-the-Art Exosuit
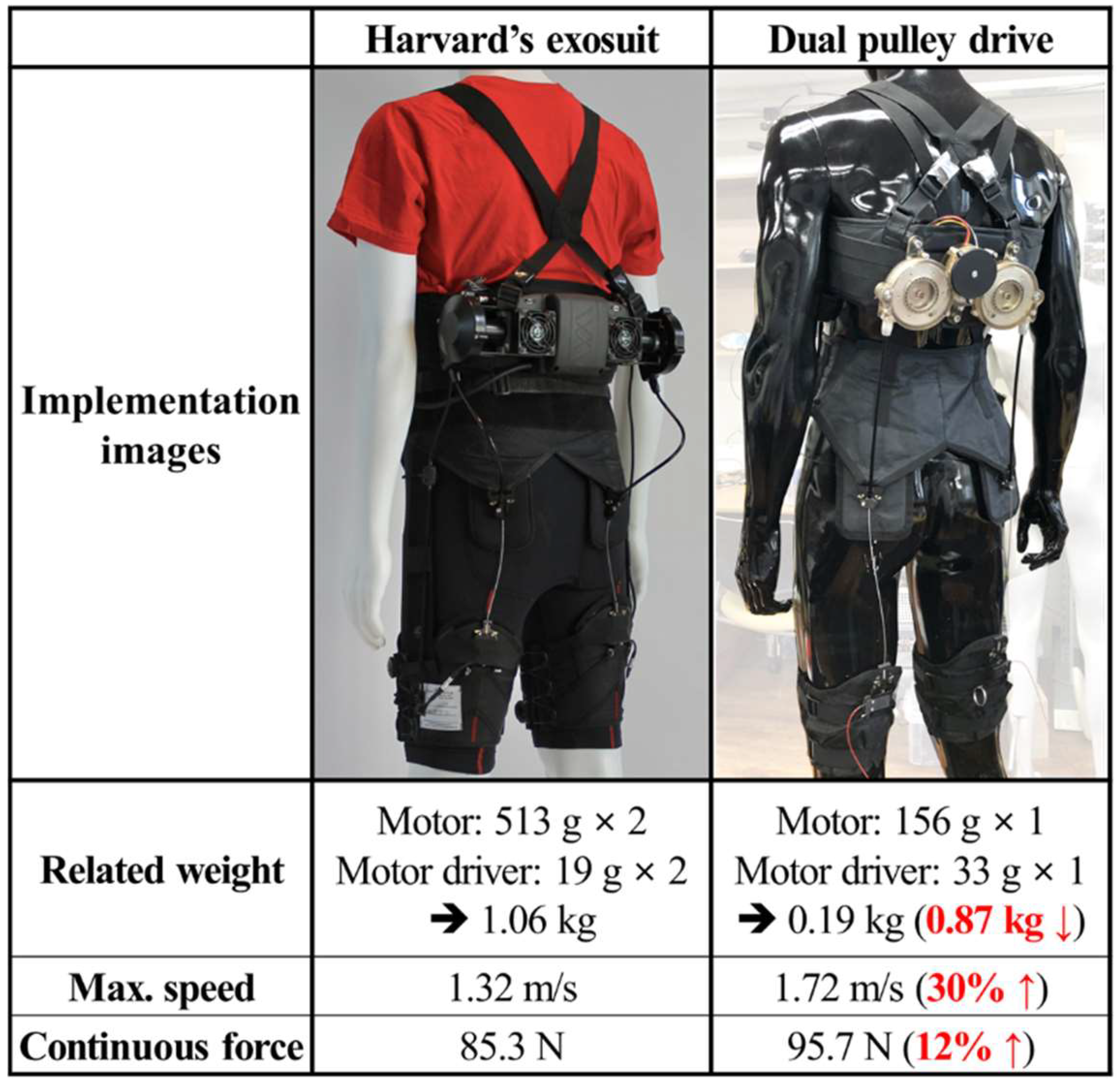
The expected advantages of the dual pulley drive incorporated in an exosuit were highlighted through a comparison with the actuation system of the exosuit developed by Harvard University [10]. Because the dual pulley drive was not fully implemented in the exosuit, only the motor-related components, which underwent significant changes when the dual pulley drive was applied, were compared.
Figure 9 presents the images of the integrated suits and compares the two actuators. The actuator of the existing exosuit consists of two sets of motors and two sets of 18.6 g motor drivers (Gold Twitter, Elmo Motion Control, Israel). Each 300 g EC 4-pole 30 brushless motor (#305013, Maxon, Switzerland) is connected to a 213 g planetary gearhead (#326664, Maxon, Switzerland). The total weight of the motor-related components of the existing exosuit is 1063.2 g. The dual pulley drive consists of a 155.9 g frameless torque motor (RI 60, T-Motor, Nanchang, China) and a 32.5 g motor driver (Gold Solo Twitter, Elmo Motion Control, Petah Tikva, Israel). The total weight of the motor-related components of the dual pulley drive is 188.4–874.8 g, lower than that of the existing exosuit.
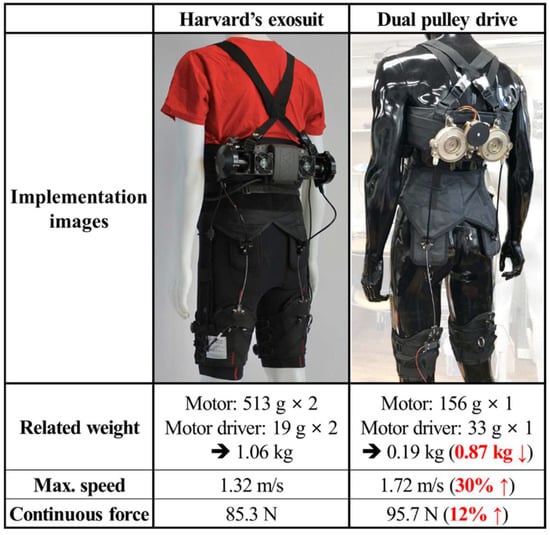
Figure 9.
Comparison of the dual pulley drive and state-of-the-art exosuit developed by Harvard University.
Moreover, the maximum speed and continuous force of the cable of the two actuators were calculated by referring to datasheets. The peak force was not considered in the calculation because it was not available in the datasheet and is considerably influenced by the cooling condition and other factors. The maximum speed of the exosuit actuator was 16,100 rpm, and the continuous torque was 95.6 mNm. The reduction ratio of the gear head was 51:1, and the efficiency was calculated to be 70% based on the datasheet. Therefore, the max speed of the cable was 1.32 m/s, and the continuous force was 85.3 N for an 80 mm diameter pulley.
The maximum speed of the dual pulley drive motor was 3495 rpm, and the continuous torque was 0.57 Nm. The reduction ratio between the motor gear and pulley gear was 8.5:1. When the gear efficiency of the dual pulley drive was assumed to be 89% (minimum efficiency of the spur gear), the contribution of the motor gear to the pulley gear efficiency was 79% [21]. Therefore, the maximum speed of the cable was 1.72 m/s, and the continuous force was 95.7 N based on the 80 mm diameter pulley. Therefore, the dual pulley drive outperformed the existing exosuit in terms of both the cable force and speed.
4. Conclusions
This study was aimed at establishing a dual pulley drive that offers versatile controllability by operating in overlapping and non-overlapping conditions with a single motor, based on a moving gear mechanism different from that adopted in the existing BCDAs. The weight of the dual pulley drive is lower than that of the actuation unit of a state-of-the-art exosuit. Moreover, the manufacturing cost and control complexity are decreased owing to the use of fewer motors. According to the motion profile test, the dual pulley drive can operate in various profiles, ranging from non-overlapping to a maximum overlap of 34.1% at different velocities.
Nevertheless, the dual pulley drive involves certain limitations. Because the dual pulley drive is an underactuated system in which two pulleys are controlled with a single motor, the control strategy must be optimized to enable more accurate control. Future work can be aimed at enhancing the control accuracy in the underactuated region by implementing an algorithm to determine the positions of the moving gear and both cables by using additional sensors or incorporating dynamics models for the estimation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/act11050135/s1, Video S1: Dual pulley drive configuration and test video.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R. and G.L.; methodology, J.R. and G.L.; software, J.R., S.Y. and G.L.; validation, J.R., S.Y. and G.L.; formal analysis, J.R.; investigation, J.R.; resources, G.L.; data curation, J.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.R. and G.L.; writing—review and editing, J.R., S.Y. and G.L.; visualization, J.R.; supervision, G.L.; project administration, G.L.; funding acquisition, G.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2021R1A4A3030268) and R&D Program for Forest Science Technology (No. 2021364B10-2123-BD01), provided by the Korea Forest Service (Korea Forestry Promotion Institute). The work of J. Ryu was supported by the Chung-Ang University Graduate Research Scholarship of 2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ding, Y. Control and Optimization of Soft Exosuit to Improve the Efficiency of Human Walking. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Esquenazi, A.; Talaty, M.; Packel, A.; Saulino, M. The ReWalk powered exoskeleton to restore ambulatory function to individuals with thoracic-level motor-complete spinal cord injury. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.J.; Endo, K.; Herr, H. A quasi-passive leg exoskeleton for load-carrying augmentation. Int. J. Hum. Robot. 2007, 4, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, R.C.; Modica, J.R.; Kram, R.; Goswami, A. The effects of adding mass to the legs on the energetics and biomechanics of walking. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, J.M.; Gregorczyk, K.N.; Bensel, C.K.; Hasselquist, L.; Obusek, J.P. The effects of a lower body exoskeleton load carriage assistive device on limits of stability and postural sway. Ergonomics 2008, 51, 1515–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, H. Exoskeletons and orthoses: Classification, design challenges and future directions. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2009, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiele, A. Ergonomics of exoskeletons: Objective performance metrics. In Proceedings of the World Haptics 2009—Third Joint EuroHaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Stienen, A.H.; Hekman, E.E.; Van Der Helm, F.C.; Van Der Kooij, H. Self-aligning exoskeleton axes through decoupling of joint rotations and translations. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2009, 25, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Karavas, N.; Quinlivan, B.T.; LouiseRyan, D.; Perry, D.; Eckert-Erdheim, A.; Murphy, P.; Goldy, T.G.; Menard, N.; Athanassiu, M.; et al. Autonomous multi-joint soft exosuit for assistance with walking overground. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 2812–2819. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, G.; Heimgartner, R.; Arumukhom Revi, D.; Karavas, N.; Nathanson, D.; Galiana, I.; Eckert-Erdheim, A.; Murphy, P.; Perry, D.; et al. Reducing the metabolic rate of walking and running with a versatile, portable exosuit. Science 2019, 365, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Kim, J.; Panizzolo, F.A.; Zhou, Y.M.; Baker, L.M.; Galiana, I.; Malcolm, P.; Walsh, C.J. Reducing the metabolic cost of running with a tethered soft exosuit. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaan6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbeck, A.T.; Schmidt, K.; Galiana, I.; Wagner, D.; Walsh, C.J. Multi-joint soft exosuit for gait assistance. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 6197–6204. [Google Scholar]
- Tricomi, E.; Lotti, N.; Missiroli, F.; Zhang, X.; Xiloyannis, M.; Müller, T.; Crea, S.; Papp, E.; Krzywinski, J.; Vitiello, J.; et al. Underactuated soft hip exosuit based on adaptive oscillators to assist human locomotion. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 7, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Park, J.H.; Ku, S.; Jeong, Y.; Paik, N.J.; Park, Y.L. A soft wearable robotic ankle-foot-orthosis for post-stroke patients. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2547–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Kim, I.; Baek, Y.S. Design of a 2DOF ankle exoskeleton with a polycentric structure and a bi-directional tendon-driven actuator controlled using a PID neural network. Actuators 2021, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.M.; Pei, X.; Hou, T.G.; Fan, Y.B.; Yang, X.; Herr, H.M.; Yang, X.B. An untethered cable-driven ankle exoskeleton with plantarflexion-dorsiflexion bidirectional movement assistance. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2020, 21, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.G.; Agostini, V.; Knaflitz, M.; Bonato, P. Muscle activation patterns during level walking and stair ambulation. Appl. EMG Clin. Sports Med. 2012, 8, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Kim, M.; Kuindersma, S.; Walsh, C.J. Human-in-the-loop optimization of hip assistance with a soft exosuit during walking. Sci. Robot. 2018, 3, eaar5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Heimgartner, R.; Lee, G.; Karavas, N.; Perry, D.; Ryan, D.L.; Eckert-Erdheim, A.; Murphy, P.; Choe, D.K.; Galiana, I.; et al. Autonomous and portable soft exosuit for hip extension assistance with online walking and running detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 5473–5480. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, H. Spring Designer’s Handbook; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Petrescu, R.V.; Aversa, R.; Akash, B.; Bucinell, R.; Corchado, J.; Apicella, A.; Petrescu, F.I. Gears-part I. Am. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 10, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).