Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Diseased Poultry in Northern China between 2014 and 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Serotyping of Salmonella
2.2. Multilocus Sequence Analysis
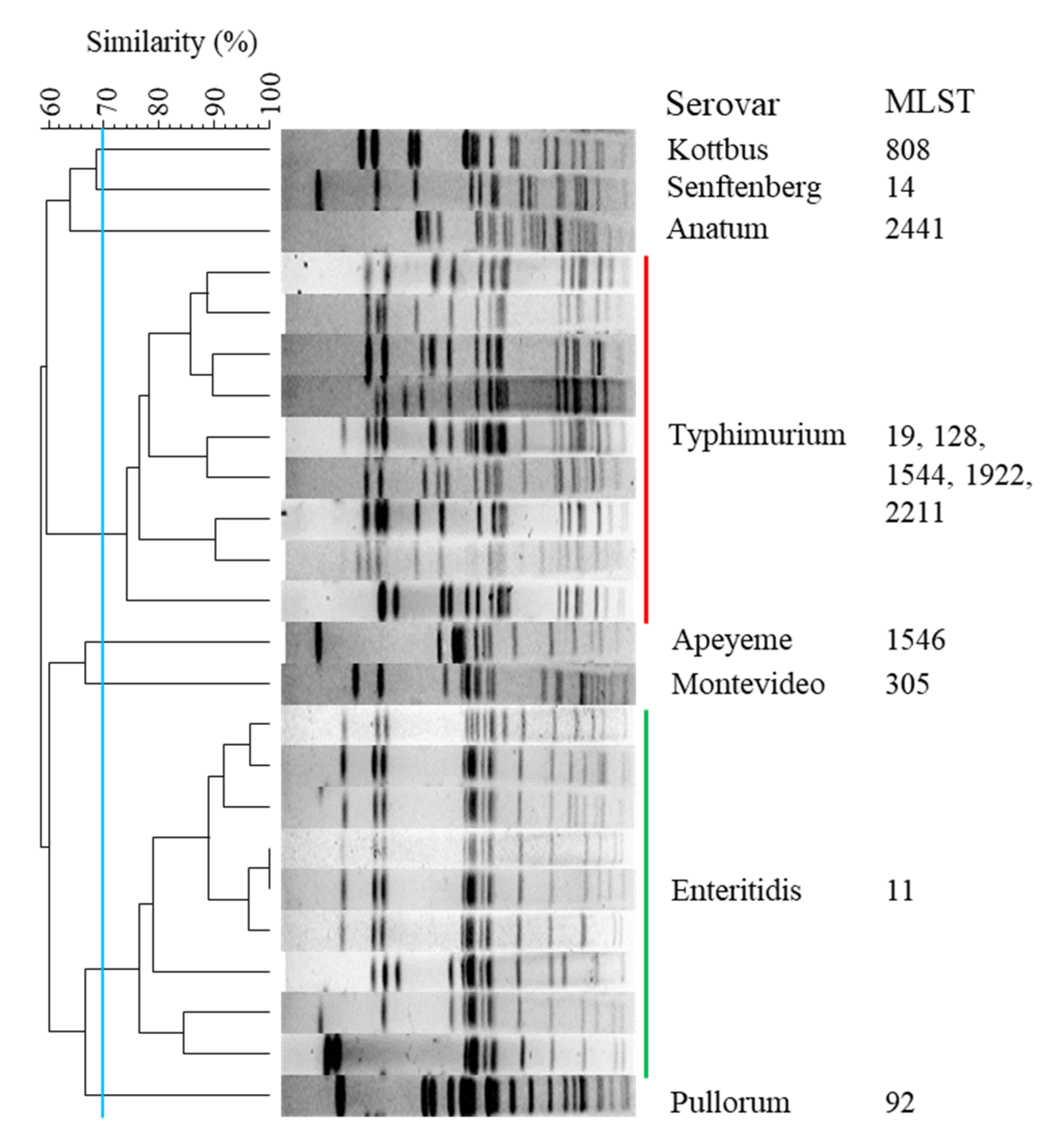
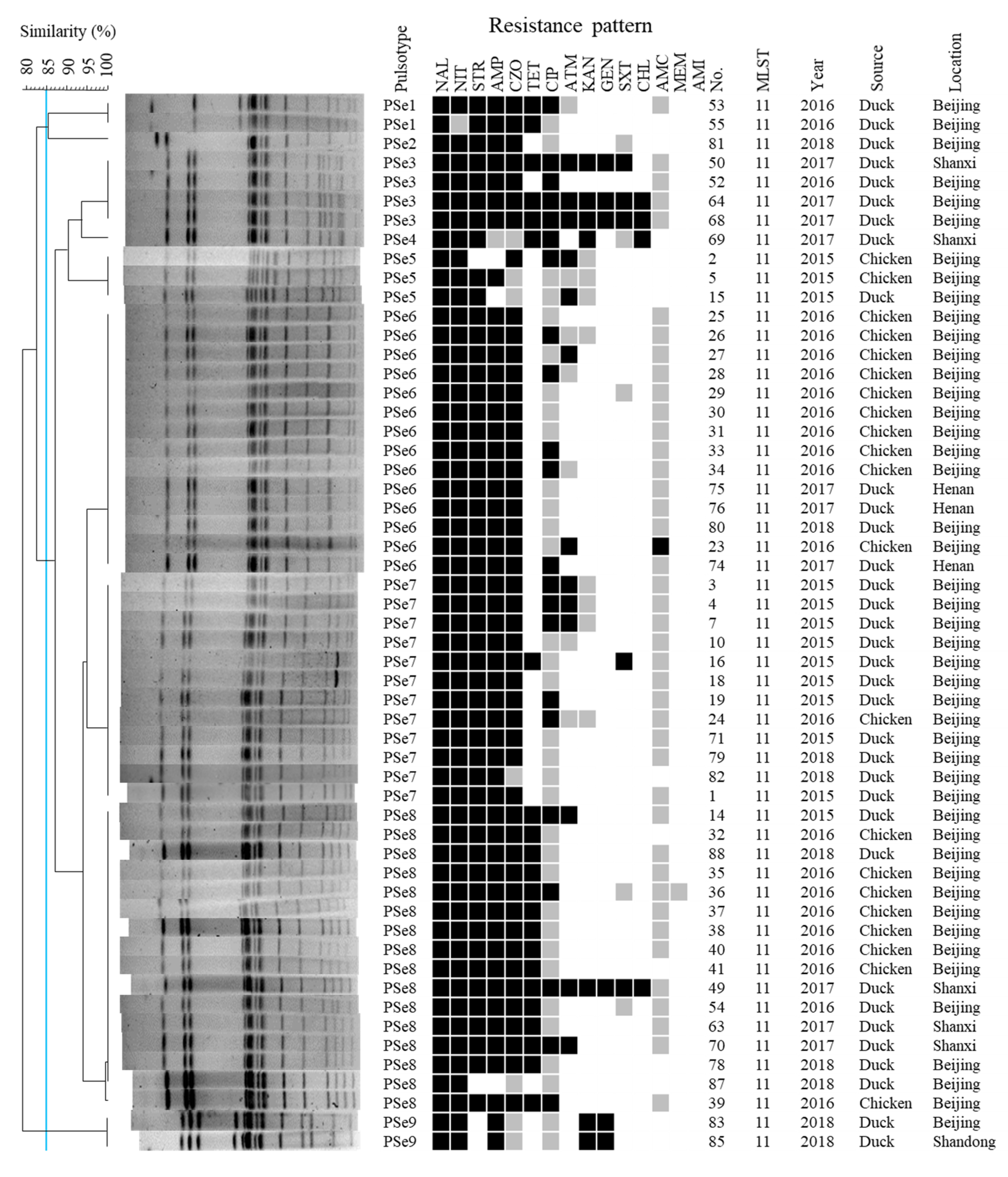
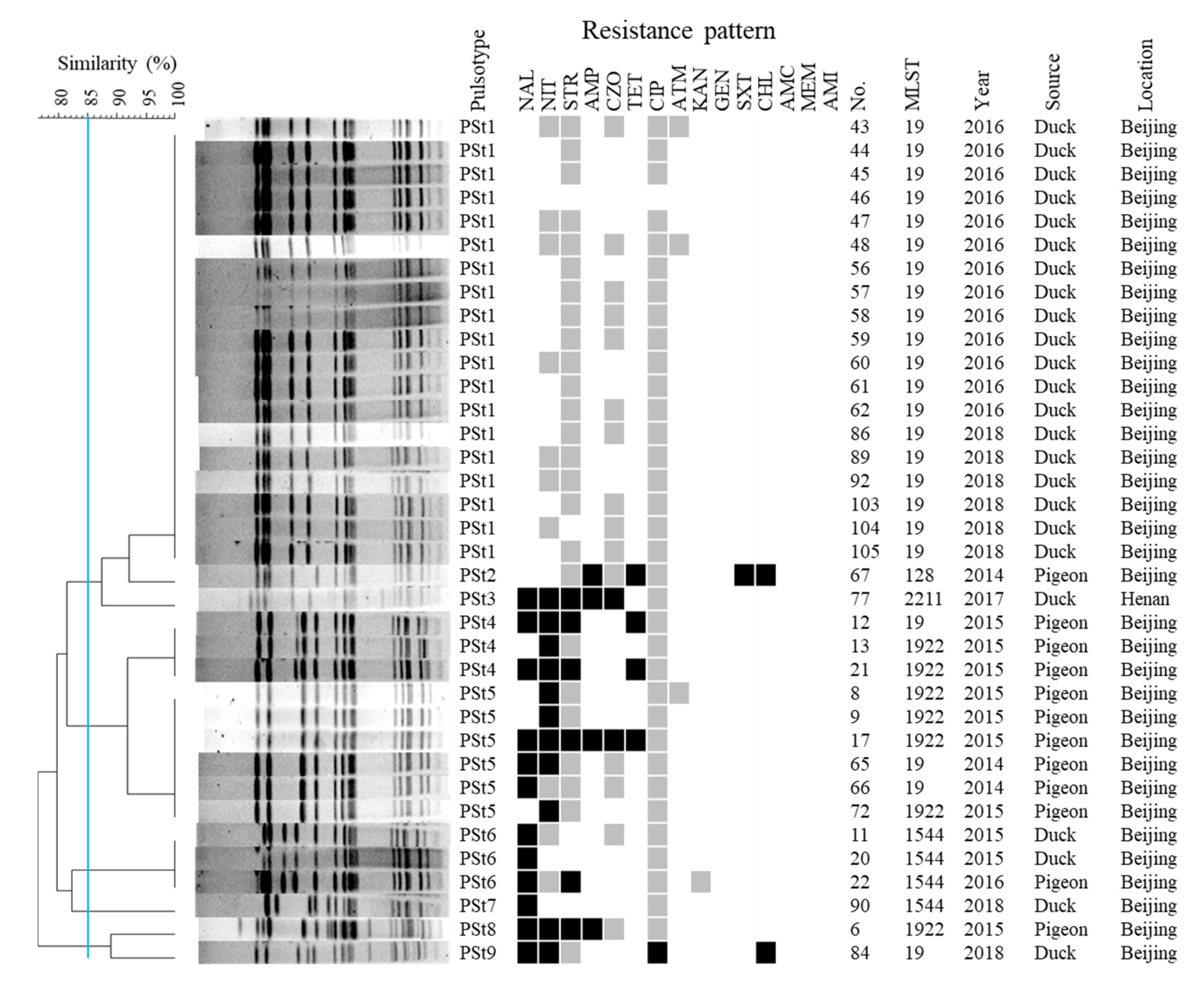
2.3. PFGE Analysis
2.4. Salmonella Isolates Displayed High Levels of Antimicrobial Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Salmonella Isolation and Serotyping
4.2. Multilocus Sequence Typing
4.3. Pulsed-field Gel Electrophoresis
4.4. Antimicrobial Resistance Test
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
References
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M. The global burden of nontyphoidal Salmonella gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.M.J.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.A.; Ward, M.P.; Mor, S.M. Diversity of Salmonella serotypes from humans, food, domestic animals and wildlife in New South Wales, Australia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 DALYs and HALE Collaborators. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1859–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Non-Typhoidal Salmonella Invasive Disease Collaborators. The global burden of non-typhoidal Salmonella invasive disease: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Duan, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.W. Analysis of bacterial foodborne disease outbreaks in China between 1994 and 2005. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 51, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, P.; Mourao, J.; Campos, J.; Peixe, L. Salmonellosis: the role of poultry meat. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chousalkar, K.; Gole, V.C. Salmonellosis acquired from poultry. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 29, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.; Nicolas, G.; Cinardi, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Wint, G.R.W.; Robinson, T.P. Global distribution data for cattle, buffaloes, horses, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens and ducks in 2010. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.W. Current situation and development prospect of China’s pigeon industry. South China Rural Area 2018, 34, 30–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria, M.C.; Soria, M.A.; Bueno, D.J.; Godano, E.I.; Gomez, S.C.; ViaButron, I.A.; Padin, V.M.; Roge, A.D. Salmonella spp. contamination in commercial layer hen farms using different types of samples and detection methods. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 2820–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Shen, J.; Wu, C. Prevalence and characterization of Salmonella species isolated from pigs, ducks and chickens in Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Gao, S.; Chang, Y.; Su, M.; Xie, Y.; Sun, S. Occurrence and Characterization of Salmonella Isolated from Large-Scale Breeder Farms in Shandong Province, China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 8159567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, K.; De Grandis, S.A.; Clarke, R.C.; McEwen, S.A.; Galán, J.E.; Ginocchio, C.; Curtiss, R.; Gyles, C.L. Amplification of an invA gene sequence of Salmonella typhimurium by polymerase chain reaction as a specific method of detection of Salmonella. Mol. Cell. Probes 1992, 6, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A.; Aquilanti, L.; Clementi, F. Salmonellosis associated with mass catering: a survey of European Union cases over a 15-year period. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144, 3000–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.B.; Xiong, L.G.; Tan, M.F.; Li, H.Q.; Yan, H.; Zhang, L.; Yin, D.F.; Kang, Z.F.; Wei, Q.P.; Luo, L.G. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella in Pork, Chicken, and Duck from Retail Markets of China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollin, R. A study of invasiveness of different Salmonella serovars based on analysis of the Enter-net database. Euro. Surveill. 2007, 12, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Tao, J.; Jiao, Y.; Fei, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Pan, Z.; Jiao, X. Phenotypic characteristics and genotypic correlation between Salmonella isolates from a slaughterhouse and retail markets in Yangzhou, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 222, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Zeng, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, H.; et al. Prevalence, Bacterial Load, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella Serovars Isolated From Retail Meat and Meat Products in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ju, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, S. Serotype, antimicrobial susceptibility and genotype profiles of Salmonella isolated from duck farms and a slaughterhouse in Shandong province, China. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, F.; Birch, C.; Davies, R.H. Observations on the distribution and control of Salmonella in commercial duck hatcheries in the UK. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabsch, W.; Andrews, H.L.; Kingsley, R.A.; Prager, R.; Tschape, H.; Adams, L.G.; Baumler, A.J. Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium and its host-adapted variants. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoelzer, K.; Soyer, Y.; Rodriguez-Rivera, L.D.; Cummings, K.J.; McDonough, P.L.; Schoonmaker-Bopp, D.J.; Root, T.P.; Dumas, N.B.; Warnick, L.D.; Grohn, Y.T.; et al. The prevalence of multidrug resistance is higher among bovine than human Salmonella enterica serotype Newport, Typhimurium, and 4,5,12:i:- isolates in the United States but differs by serotype and geographic region. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5947–5959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haesendonck, R.; Rasschaert, G.; Martel, A.; Verbrugghe, E.; Heyndrickx, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Pasmans, F. Feral pigeons: A reservoir of zoonotic Salmonella Enteritidis strains? Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 195, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Xiao, C.; Zeng, H.; Wei, X.; Gu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Prevalence, abundance, serovars and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella isolated from retail raw poultry meat in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Sancho, M.; García-Seco, T.; Porrero, C.; García, N.; Gomez-Barrero, S.; Cámara, J.M.; Domínguez, L.; Álvarez, J. A ten-year-surveillance program of zoonotic pathogens in feral pigeons in the City of Madrid (2005-2014): The importance of a systematic pest control. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 128, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, T.; Murakami, K.; Asai, T.; Etoh, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Kuroki, T.; Horikawa, K.; Fujimoto, S. Multi-locus sequence typing of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Enteritidis strains in Japan between 1973 and 2004. Acta Vet. Scand. 2011, 53, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal, P.; Fresno, M.; Dougnac, C.; Gutierrez, S.; Gornall, V.; Vidal, R.; Vernal, R.; Pujol, M.; Barreto, M.; Gonzalez-Acuna, D.; et al. Genetic and phenotypic evidence of the Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis human-animal interface in Chile. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Yin, K.; Yin, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Tian, Y.; Geng, S.; Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; et al. Analyses of prevalence and molecular typing reveal the spread of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella infection across two breeder chicken farms. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 4374–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, T.; Petridou, E.; Zdragas, A.; Mandilara, G.; Nair, S.; Peters, T.; Chattaway, M.; de Pinna, E.; Passiotou, M.; Vatopoulos, A. Comparative study of all Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis strains isolated from food and food animals in Greece from 2008 to 2010 with clinical isolates. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgia, M.; Bouchrif, B.; Timinouni, M.; Al-Qahtani, A.; Al-Ahdal, M.N.; Cappuccinelli, P.; Rubino, S.; Paglietti, B. Antibiotic resistance determinants and genetic analysis of Salmonella enterica isolated from food in Morocco. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 215, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ktari, S.; Ksibi, B.; Gharsallah, H.; Mnif, B.; Maalej, S.; Rhimi, F.; Hammami, A. Molecular epidemiological characteristics of Salmonella enterica serovars Enteritidis, Typhimurium and Livingstone strains isolated in a Tunisian university hospital. APMIS 2016, 124, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ke, B.; Huang, Y.; He, D.; Li, X.; Liang, Z.; Ke, C. The Molecular Epidemiological Characteristics and Genetic Diversity of Salmonella Typhimurium in Guangdong, China, 2007–2011. PloS ONE 2014, 9, e113145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, W.; Cai, S. Prevalence and Characterization of Monophasic Salmonella Serovar 1,4,[5],12:i:- of Food Origin in China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florez-Cuadrado, D.; Moreno, M.A.; Ugarte-Ruiz, M.; Dominguez, L. Antimicrobial Resistance in the Food Chain in the European Union. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 86, 115–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardsanei, F.; Soltan Dallal, M.M.; Douraghi, M.; Memariani, H.; Bakhshi, B.; Zahraei Salehi, T.; Nikkhahi, F. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence genes and genetic relatedness of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis isolates recovered from human gastroenteritis in Tehran, Iran. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 12, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasquez, C.G.; Macklin, K.S.; Kumar, S.; Bailey, M.; Ebner, P.E.; Oliver, H.F.; Martin-Gonzalez, F.S.; Singh, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Salmonella isolated from poultry farms in southeastern United States. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, X.; Xi, M.; Wang, X.; Xia, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, D.; et al. Molecular characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis on retail raw poultry in six provinces and two National cities in China. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Q.; Wen, G.; Wang, G.; Shao, H.; Zhang, T. Quinolone resistance phenotype and genetic characterization of Salmonella enterica serovar Pullorum isolates in China, during 2011 to 2016. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Liang, B.; Wu, F.; Yang, X.; Ma, Q.; Yang, C.; Hu, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, C.; Alali, W.Q.; Cui, S.; Li, F.; Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Yang, B. Distribution and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Foodborne Salmonella Serovars in Eight Provinces in China from 2007 to 2012 (Except 2009). Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremont, P.A.D.; Weill, F.X. Antigenic Formulae of the Salmonella Serovars, 9th Edn. Paris: WHO Collaborating Center for Reference and Research on Salmonella. Institut Pasteur. 2007, 1, 1–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kidgell, C.; Reichard, U.; Wain, J.; Linz, B.; Torpdahl, M.; Dougan, G.; Achtman, M. Salmonella typhi, the causative agent of typhoid fever, is approximately 50,000 years old. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2002, 2, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribot, E.M.; Fair, M.A.; Gautom, R.; Cameron, D.N.; Hunter, S.B.; Swaminathan, B.; Barrett, T.J. Standardization of pulsed-field gel electrophoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Twenty-fifth Informational Supplement; M100-s25; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
| Serovar | Duck | Chicken | Pigeon | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dead-in-Shell Embryo (n = 1028) | Day-old Hatching (n = 1400) | One- to Four-Week-Old Duck (n = 1307) | Dead-in-Shell Embryo (n = 450) | One- to Four-Week-Old Chicken (n = 15) | Liver or Brain of Dead Pigeon (n = 55) | 4255 | |
| Enteritidis | 1 | - | 33 | 19 | 2 | - | 55 |
| Typhimurium | 2 | - | 22 | - | - | 12 | 36 |
| Apeyeme | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Anatum | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Senftenberg | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 2 |
| Kottbus | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 2 |
| Montevideo | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Pullorum | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| ST of S. Typhimurium | hisD | purE | sucA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | 482 G | 539 G | 81 T | 478 G |
| 128 | - | - | - | 478 C |
| 1544 | - | 539 A | - | - |
| 1922 | 482 A | - | - | - |
| 2211 | - | - | 81 C | - |
| Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns | Isolates no. |
|---|---|
| Susceptible to all tested antimicrobials | 26 |
| NAL | 7 |
| NIT | 4 |
| NAL-STR | 1 |
| NAL-TET | 1 |
| NAL-NIT | 2 |
| NAL-STR-KAN | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-CHL | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-ATM | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP | 2 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-ATM | 1 |
| AMP-TET-SXT-CHL | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-TET-STR | 2 |
| NAL-NIT-CIP-CHL | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-CZO-CIP-ATM | 1 |
| NAL-STR-AMP-CZO-TET | 1 |
| NAL-NIT- STR-AMP-CZO | 14 |
| NAL-NIT-AMP-KAN-GEN | 2 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-CIP | 8 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-TET | 12 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-CIP-ATM | 3 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-TET-SXT | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-ATM-AMC | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-TET-CIP-FAZ | 3 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-TET-CIP-KAN-CHL | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-TET-CIP-ATM | 2 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-TET-CIP-ATM-KAN-GEN-SXT | 1 |
| NAL-NIT-STR-AMP-CZO-TET-CIP-ATM-KAN-GEN-SXT-CHL | 3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Su, J. Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Diseased Poultry in Northern China between 2014 and 2018. Pathogens 2020, 9, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020095
Wang J, Li J, Liu F, Cheng Y, Su J. Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Diseased Poultry in Northern China between 2014 and 2018. Pathogens. 2020; 9(2):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jun, Jinxin Li, Fengli Liu, Yongyou Cheng, and Jingliang Su. 2020. "Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Diseased Poultry in Northern China between 2014 and 2018" Pathogens 9, no. 2: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020095
APA StyleWang, J., Li, J., Liu, F., Cheng, Y., & Su, J. (2020). Characterization of Salmonella enterica Isolates from Diseased Poultry in Northern China between 2014 and 2018. Pathogens, 9(2), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020095






