Suicidal Leishmania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Not All Toxins/Antimicrobial Peptides Are Toxic for Leishmania mexicana Promastigotes
2.2. BnSP-7, a Basic Phospholipase A2 from Bothrops pauloensis Venom, Dramatically Reduces Viability of L. mexicana Promastigotes In Vitro
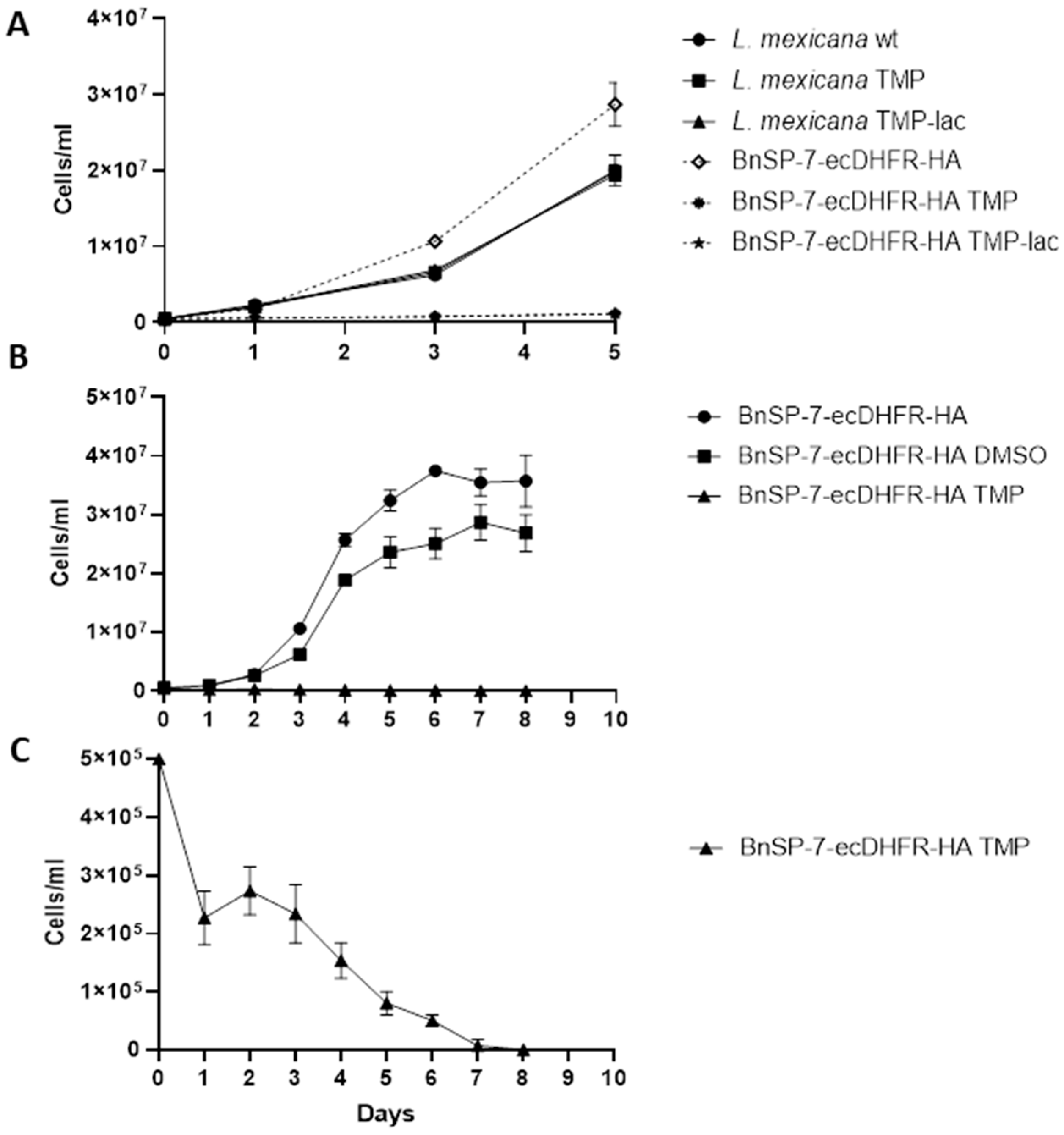
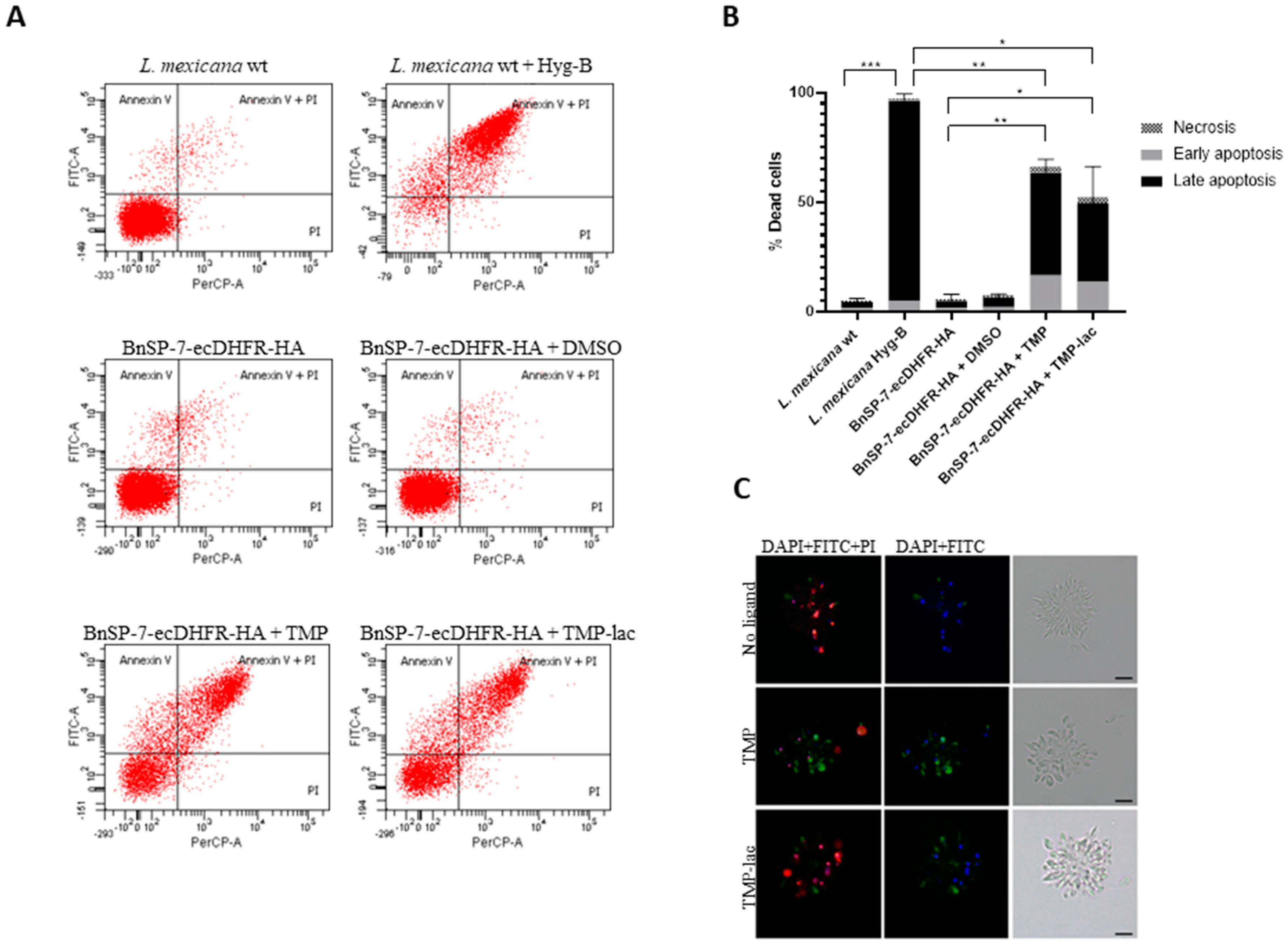
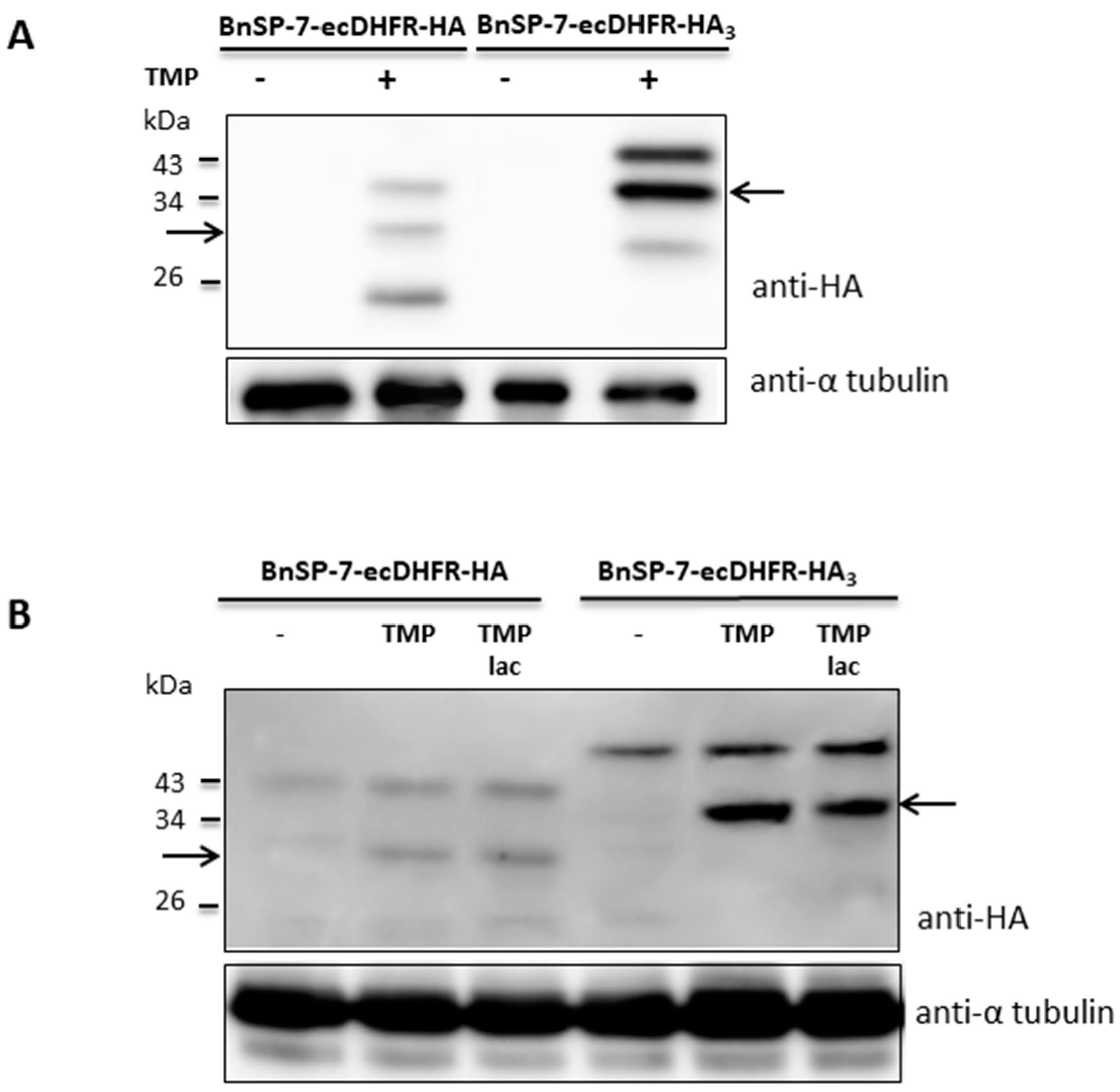
2.3. BnSP-7-ecDHFR-HA System Is Functional in Axenically Differentiated L. mexicana Amastigotes
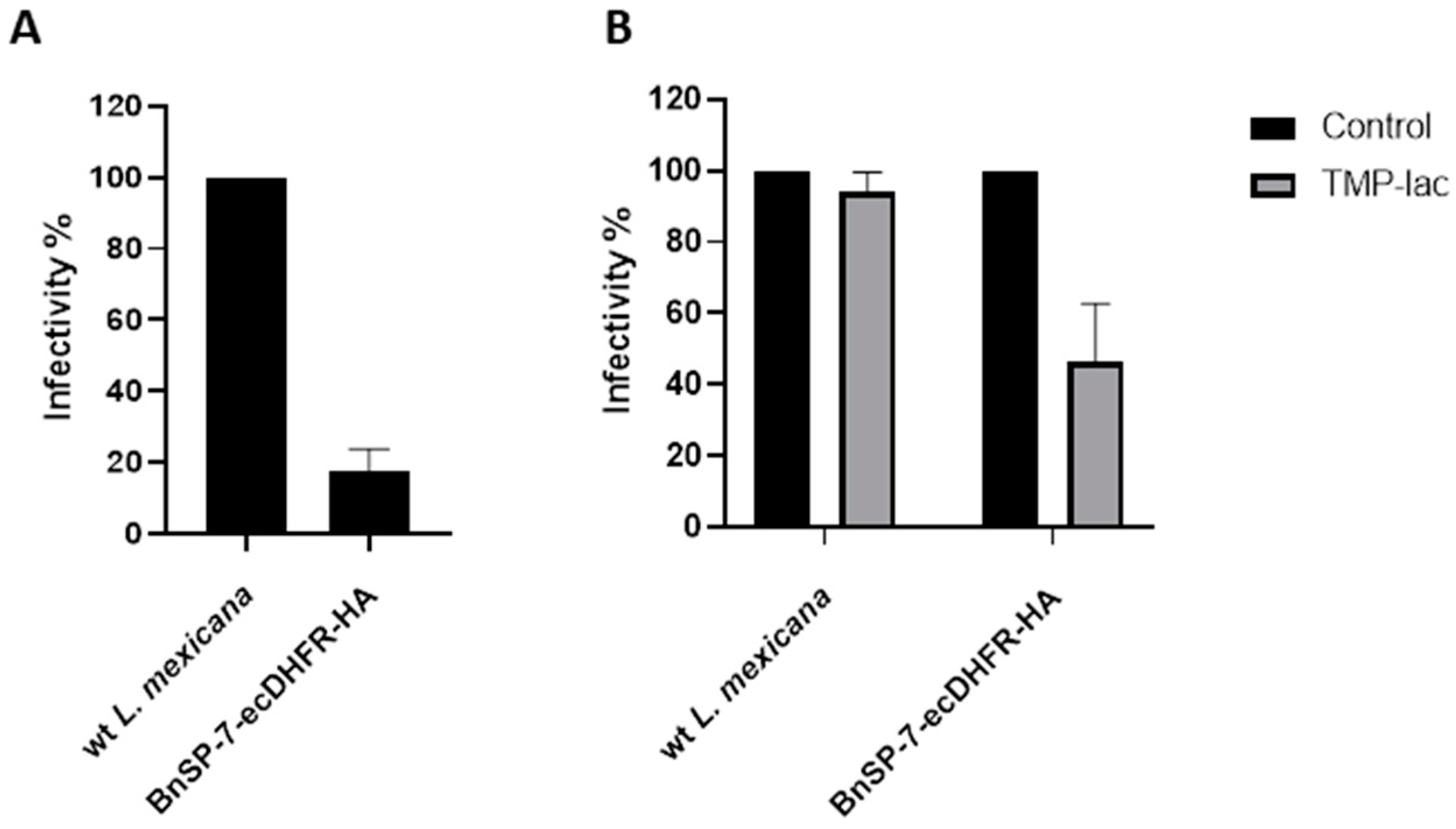
2.4. The BnSP-7-ecDHFR-HA-expressing L. mexicana Are Attenuated in Macrophage Infections
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Axenic Cultivation of Leishmania mexicana
4.2. Genetic Manipulations
4.3. Growth Kinetics and Differentiation
4.4. Apoptosis Assays
4.5. Immunoblotting, Immunoprecipitation, and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.6. Macrophage Infection
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bruschi, F.; Gradoni, L. The Leishmaniases: Old Neglected Tropical Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; p. 245. [Google Scholar]
- Maslov, D.A.; Opperdoes, F.R.; Kostygov, A.Y.; Hashimi, H.; Lukeš, J.; Yurchenko, V. Recent advances in trypanosomatid research: Genome organization, expression, metabolism, taxonomy and evolution. Parasitology 2019, 146, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostálová, A.; Volf, P. Leishmania development in sand flies: Parasite-vector interactions overview. Parasites Vectors 2012, 5, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podinovskaia, M.; Descoteaux, A. Leishmania and the macrophage: A multifaceted interaction. Future Microbiol. 2015, 10, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Leishmaniasis: Stuation and Trends. Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/gho/neglected_diseases/leishmaniasis/en/ (accessed on 24 January 2020).
- Oliveira, L.F.; Schubach, A.O.; Martins, M.M.; Passos, S.L.; Oliveira, R.V.; Marzochi, M.C.; Andrade, C.A. Systematic review of the adverse effects of cutaneous leishmaniasis treatment in the New World. Acta Trop. 2011, 118, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvan, H.; Moafi, M. An overview on Leishmania vaccines: A narrative review article. In Veterinary Research Forum; Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Urmia University: Urmia, Iran, 2015; Volume 6, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, L.I.; Zhang, W.W.; Ranasinghe, S.; Matlashewski, G. Leishmanization revisited: Immunization with a naturally attenuated cutaneous Leishmania donovani isolate from Sri Lanka protects against visceral leishmaniasis. Vaccine 2013, 31, 1420–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamesipour, A.; Dowlati, Y.; Asilian, A.; Hashemi-Fesharki, R.; Javadi, A.; Noazin, S.; Modabber, F. Leishmanization: Use of an old method for evaluation of candidate vaccines against leishmaniasis. Vaccine 2005, 23, 3642–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handman, E. Leishmaniasis: Current status of vaccine development. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedzierski, L. Leishmaniasis vaccine: Where are we today? J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2010, 2, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, A.M.M.; Lanza, J.S.; Tunes, L.G.; Fiuza, J.A.; Roy, G.; Orfano, A.D.S.; de Carvalho, A.T.; Frezard, F.; Barros, A.L.B.; Murta, S.M.F.; et al. Growth arrested live-attenuated Leishmania infantum KHARON1 null mutants display cytokinesis defect and protective immunity in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, R.; Dagur, P.K.; Selvapandiyan, A.; McCoy, J.P.; Salotra, P.; Duncan, R.; Nakhasi, H.L. Live attenuated Leishmania donovani p27 gene knockout parasites are nonpathogenic and elicit long-term protective immunity in BALB/c mice. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvapandiyan, A.; Dey, R.; Nylen, S.; Duncan, R.; Sacks, D.; Nakhasi, H.L. Intracellular replication-deficient Leishmania donovani induces long lasting protective immunity against visceral leishmaniasis. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 1813–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Madhubala, R. Genetically engineered ascorbic acid-deficient live mutants of Leishmania donovani induce long lasting protective immunity against visceral leishmaniasis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solana, J.C.; Ramirez, L.; Corvo, L.; de Oliveira, C.I.; Barral-Netto, M.; Requena, J.M.; Iborra, S.; Soto, M. Vaccination with a Leishmania infantum HSP70-II null mutant confers long-term protective immunity against Leishmania major infection in two mice models. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyombwe, A.; Olivier, M.; Ouellette, M.; Papadopoulou, B. Selective killing of Leishmania amastigotes expressing a thymidine kinase suicide gene. Exp. Parasitol. 1997, 85, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghedin, E.; Charest, H.; Zhang, W.W.; Debrabant, A.; Dwyer, D.; Matlashewski, G. Inducible expression of suicide genes in Leishmania donovani amastigotes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 22997–23003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davoudi, N.; Tate, C.A.; Warburton, C.; Murray, A.; Mahboudi, F.; McMaster, W.R. Development of a recombinant Leishmania major strain sensitive to ganciclovir and 5-fluorocytosine for use as a live vaccine challenge in clinical trials. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Samant, M.; Khare, P.; Misra, P.; Dutta, S.; Kolli, B.K.; Sharma, S.; Chang, K.P.; Dube, A. Photodynamic vaccination of hamsters with inducible suicidal mutants of Leishmania amazonensis elicits immunity against visceral leishmaniasis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Weiss, L.M.; Huang, H. Inducible suicide vector systems for Trypanosoma cruzi. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podesvova, L.; Huang, H.; Yurchenko, V. Inducible protein stabilization system in Leishmania mexicana. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2017, 214, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.C.; Figueira, M.M.; Lopes, D.S.; de Souza, D.L.; Izidoro, L.F.; Ferro, E.A.; Souza, M.A.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Rodrigues, V.M.; Yoneyama, K.A. BnSP-7 toxin, a basic phospholipase A2 from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom, interferes with proliferation, ultrastructure and infectivity of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis. Parasitology 2013, 140, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermes, I.; Haanen, C.; Steffens-Nakken, H.; Reutelingsperger, C. A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J. Immunol. Methods 1995, 184, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlamadinger, D.E.; Gable, J.E.; Kim, J.E. Toxins and antimicrobial peptides: Interactions with membranes. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2009, 7397, 73970J. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Karamycheva, S.; Zhang, D.; Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Antimicrobial peptides, polymorphic toxins, and self-nonself recognition systems in Archaea: An untapped armory for intermicrobial conflicts. MBio 2019, 10, e00715-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukša, J.; Ravoitytė, B.; Konovalovas, A.; Aitmanaitė, L.; Butenko, A.; Yurchenko, V.; Serva, S.; Servienė, E. Different metabolic pathways are involved in response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to L-A and M viruses. Toxins 2017, 9, e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, A.; Brodersen, D.E.; Mitarai, N.; Gerdes, K. Toxins, targets, and triggers: An overview of toxin-antitoxin biology. Mol. Cell 2018, 70, 768–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Cerdan, R.; Radulescu, O. Drug discovery in infectious diseases. In Comprehensive Analysis of Parasite Biology: From Metabolism to Drug Discovery; Selzer, P.M., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; Volume 7, p. 549. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Aksoy, S. An antimicrobial peptide with trypanocidal activity characterized from Glossina morsitans morsitans. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fieck, A.; Hurwitz, I.; Kang, A.S.; Durvasula, R. Trypanosoma cruzi: Synergistic cytotoxicity of multiple amphipathic anti-microbial peptides to T. cruzi and potential bacterial hosts. Exp. Parasitol. 2010, 125, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cordero, J.J.; Lozano, J.M.; Cortes, J.; Delgado, G. Leishmanicidal activity of synthetic antimicrobial peptides in an infection model with human dendritic cells. Peptides 2011, 32, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, M.A.; Kindrachuk, J.; Marr, A.K.; Jenssen, H.; Pante, N.; Elliott, M.R.; Napper, S.; Hancock, R.E.; McMaster, W.R. Effect of BMAP-28 antimicrobial peptides on Leishmania major promastigote and amastigote growth: Role of leishmanolysin in parasite survival. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epand, R.M.; Vogel, H.J. Diversity of antimicrobial peptides and their mechanisms of action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1462, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenssen, H.; Hamill, P.; Hancock, R.E. Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantel, H.; Sinha, B.; Domschke, W.; Peters, G.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Janicke, R.U. alpha-Toxin is a mediator of Staphylococcus aureus-induced cell death and activates caspases via the intrinsic death pathway independently of death receptor signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Hobaugh, M.R.; Shustak, C.; Cheley, S.; Bayley, H.; Gouaux, J.E. Structure of staphylococcal alpha-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science 1996, 274, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Angulo, Y.; Sasa, M.; Gutierrez, J.M. The phospholipase A2 homologues of snake venoms: Biological activities and their possible adaptive roles. Protein Pept. Lett. 2009, 16, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Lomonte, B. Phospholipase A2 myotoxins from Bothrops snake venoms. Toxicon 1995, 33, 1405–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, C.E.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B. Identification of the myotoxic site of the Lys49 phospholipase A(2) from Agkistrodon piscivorus piscivorus snake venom: Synthetic C-terminal peptides from Lys49, but not from Asp49 myotoxins, exert membrane-damaging activities. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabner, A.N.; Alfonso, J.; Kayano, A.M.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Santos, A.P.A.D.; Caldeira, C.A.S.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Gomez, A.; Grabner, F.P.; Cardoso, F.F.; et al. BmajPLA2-II, a basic Lys49-phospholipase A2 homologue from Bothrops marajoensis snake venom with parasiticidal potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passero, L.F.; Laurenti, M.D.; Tomokane, T.Y.; Corbett, C.E.; Toyama, M.H. The effect of phospholipase A2 from Crotalus durissus collilineatus on Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis infection. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, J.J.; Kayanoa, A.M.; Garay, A.F.G.; Simoes-Silva, R.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Vourliotis, S.; Soares, A.M.; Calderon, L.A.; Gomez, M.C.V. Isolation, biochemical characterization and antiparasitic activity of BmatTX-IV, a basic Lys49-phospholipase A2 from the venom of Bothrops mattogrossensis from Paraguay. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basmaciyan, L.; Berry, L.; Gros, J.; Azas, N.; Casanova, M. Temporal analysis of the autophagic and apoptotic phenotypes in Leishmania parasites. Microb. Cell 2018, 5, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingärtner, A.; Kemmer, G.; Muller, F.D.; Zampieri, R.A.; dos Santos, M.G.; Schiller, J.; Pomorski, T.G. Leishmania promastigotes lack phosphatidylserine but bind annexin V upon permeabilization or miltefosine treatment. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braten, O.; Livneh, I.; Ziv, T.; Admon, A.; Kehat, I.; Caspi, L.H.; Gonen, H.; Bercovich, B.; Godzik, A.; Jahandideh, S.; et al. Numerous proteins with unique characteristics are degraded by the 26S proteasome following monoubiquitination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4639–E4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.A.; Tetley, L. Leishmania mexicana: Induction of metacyclogenesis by cultivation of promastigotes at acidic pH. Exp. Parasitol. 1993, 76, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, P.A. Axenic culture of Leishmania amastigotes. Parasitol. Today 1993, 9, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishemgulova, A.; Kraeva, N.; Hlavacova, J.; Zimmer, S.L.; Butenko, A.; Podesvova, L.; Lestinova, T.; Lukes, J.; Kostygov, A.; Votypka, J.; et al. A putative ATP/GTP binding protein affects Leishmania mexicana growth in insect vectors and vertebrate hosts. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeva, N.; Ishemgulova, A.; Lukeš, J.; Yurchenko, V. Tetracycline-inducible gene expression system in Leishmania mexicana. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 198, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeva, N.; Butenko, A.; Hlaváčová, J.; Kostygov, A.; Myškova, J.; Grybchuk, D.; Leštinová, T.; Votýpka, J.; Volf, P.; Opperdoes, F.; et al. Leptomonas seymouri: Adaptations to the dixenous life cycle analyzed by genome sequencing, transcriptome profiling and co-infection with Leishmania donovani. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeva, N.; Leštinová, T.; Ishemgulova, A.; Majerová, K.; Butenko, A.; Vaselek, S.; Bespyatykh, J.; Charyyeva, A.; Spitzová, T.; Kostygov, A.Y.; et al. LmxM.22.0250-encoded dual specificity protein/lipid phosphatase impairs Leishmania mexicana virulence in vitro. Pathogens 2019, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AMP/Toxin | Source | Mass (kDa) | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alpha-toxin | Staphylococcus aureus | 35.9 | plasma membrane permeabilization |
| Attacin-A | Glossina morsitans morsitans | 21.7 | plasma membrane permeabilization |
| BnSP-7 | Bothrops pauloensis | 13.7 | plasma membrane permeabilization |
| Cathelicidin-5 (BMAP-28) | Bos taurus | 17.6 | plasma membrane permeabilization |
| Cecropin-A | Hyalophora cecropia | 6.9 | plasma membrane permeabilization |
| Exotoxin-A | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 69 | elongation factor-2 inhibition |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Podešvová, L.; Leštinová, T.; Horáková, E.; Lukeš, J.; Volf, P.; Yurchenko, V. Suicidal Leishmania. Pathogens 2020, 9, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020079
Podešvová L, Leštinová T, Horáková E, Lukeš J, Volf P, Yurchenko V. Suicidal Leishmania. Pathogens. 2020; 9(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020079
Chicago/Turabian StylePodešvová, Lucie, Tereza Leštinová, Eva Horáková, Julius Lukeš, Petr Volf, and Vyacheslav Yurchenko. 2020. "Suicidal Leishmania" Pathogens 9, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020079
APA StylePodešvová, L., Leštinová, T., Horáková, E., Lukeš, J., Volf, P., & Yurchenko, V. (2020). Suicidal Leishmania. Pathogens, 9(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020079






