Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Potentiates Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles
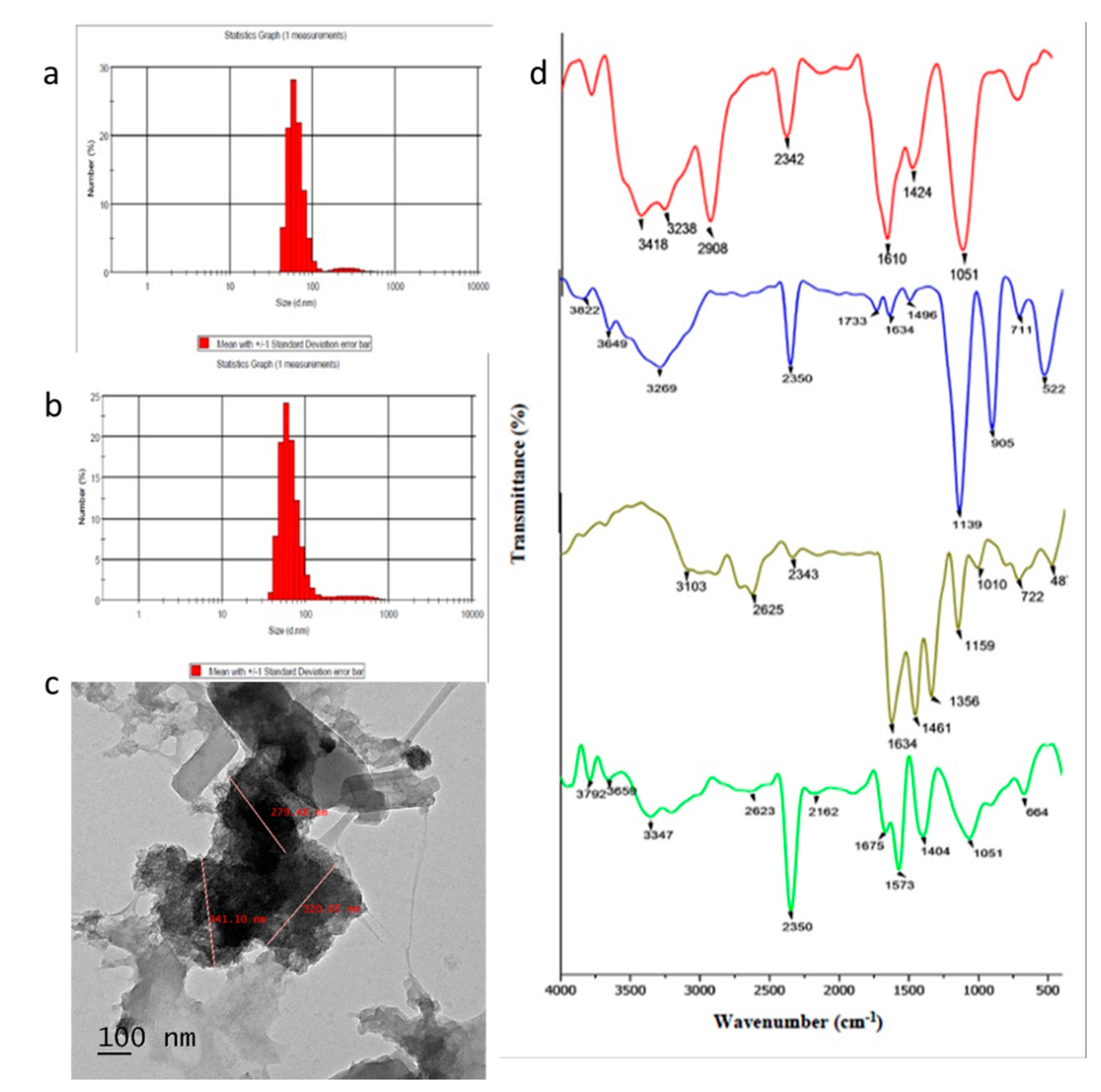
2.3. Physical Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.4. Determination of the Loading Efficiency and Drug Release of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
2.5. Determination Sub-Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (Sub-MIC) of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
2.6. In Vitro Anti-Biofilm Assays of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
2.6.1. Microtiter Plate (MTP) Assay for Biofilm Disruption and Inhibition
2.6.2. Microscopic Examination of Biofilm
2.6.3. Exopolysaccharide (EPS) Quantification and Microbial Adhesion to Hydrocarbon (MATH) Assay
2.6.4. Growth Curve Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
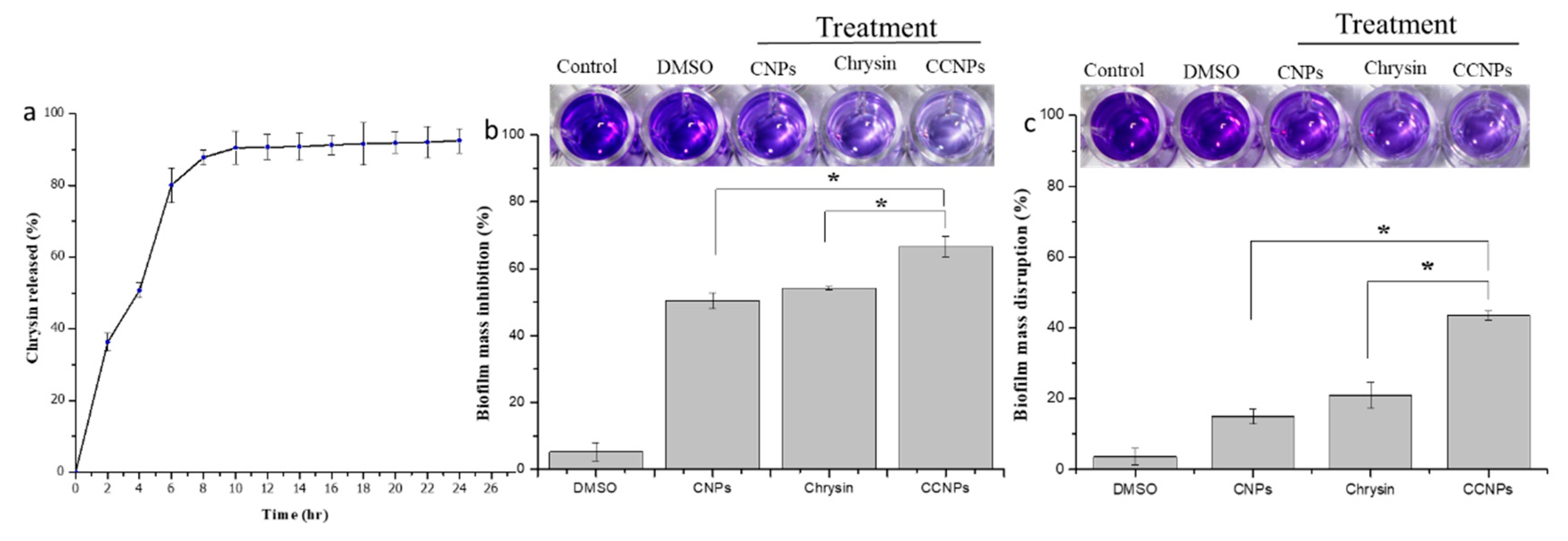
3.2. Loading Efficiency and Release Kinetics of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
3.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Sub-MIC of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
3.4. In Vitro Anti-Biofilm Activity of Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan NPs
3.4.1. Crystal Violet Staining Assay for Biofilm Formation and Disruption
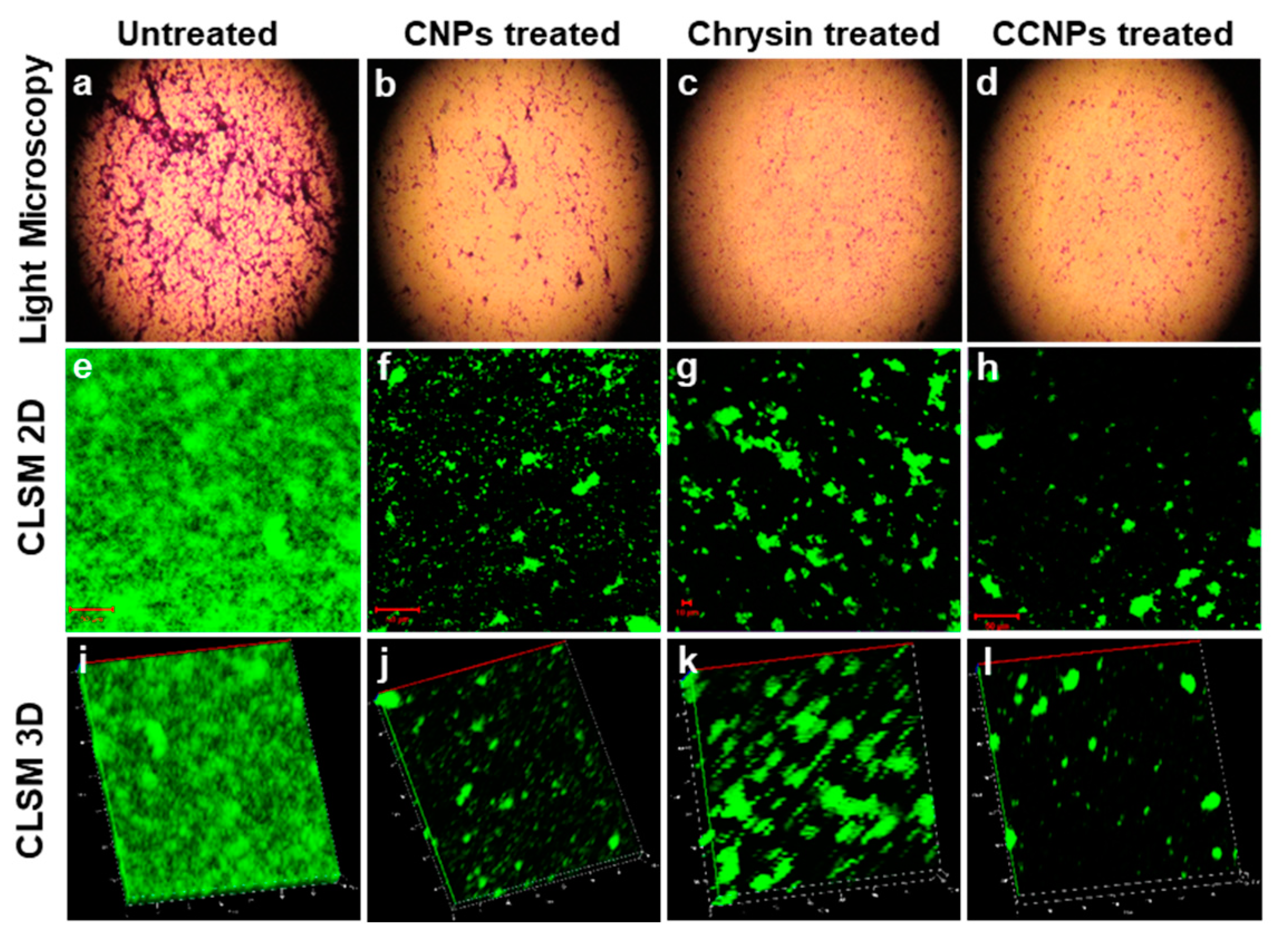
3.4.2. Microscopic Examination of Biofilm
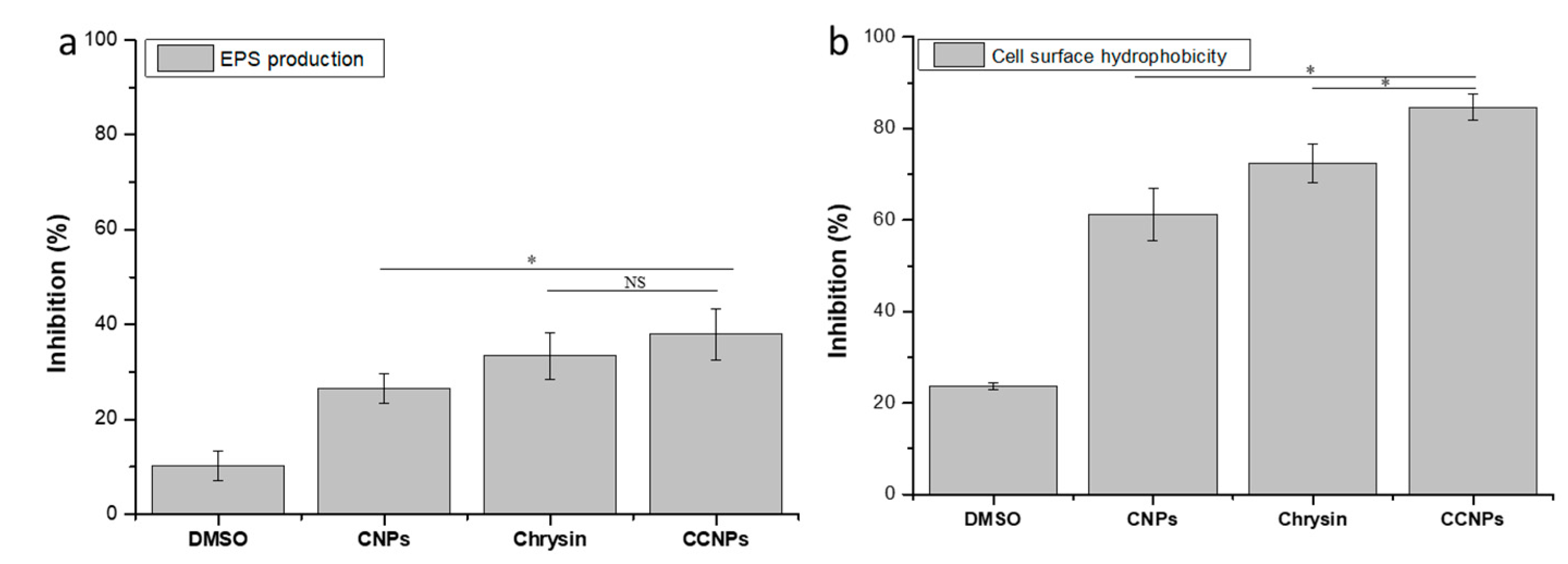
3.4.3. Exopolysaccharide (EPS) Quantification and Microbial Adhesion to Hydrocarbon (MATH) Assay
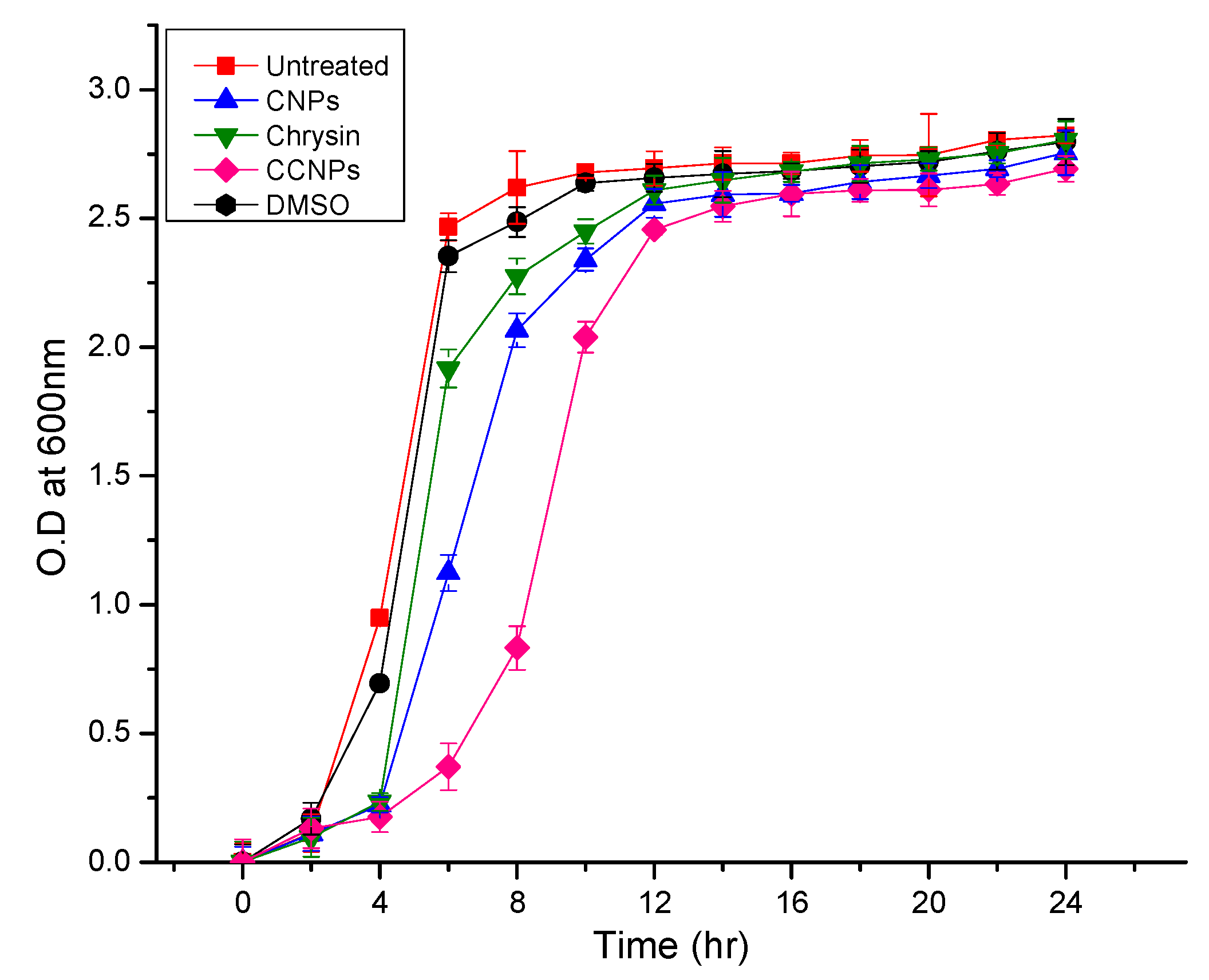
3.4.4. Growth Curve Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mu, H.; Guo, F.; Niu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Duan, J. Chitosan Improves Anti-Biofilm Efficacy of Gentamicin through Facilitating Antibiotic Penetration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22296–22308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lister, J.L.; Horswill, A.R. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: Recent developments in biofilm dispersal. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, N.K.; Mazaitis, M.J.; Costerton, J.W.; Leid, J.G.; Powers, M.E.; Shirtliff, M.E. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Virulence 2011, 2, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, P.Y.; Toh, Y.S. Anti-biofilm agents: Recent breakthrough against multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Wozniak, D.J.; Stoodley, P.; Hall-Stoodley, L. Prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2015, 13, 1499–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anari, E.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Zarghami, N. Chrysin-loaded PLGA-PEG nanoparticles designed for enhanced effect on the breast cancer cell line. Artif. Cells NanoMed. Biotechnol. 2015, 44, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Babu, K.; Hari Babu, T.; Srinivas, P.V.; Hara Kishore, K.; Murthy, U.S.N.; Rao, J.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel C (7) modified chrysin analogues as antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, X.; He, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, H. Synthetic derivatives of chrysin and their biological activities. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Malik, D.; Kaur, G. Enhanced Dissolution and Antioxidant Activity of Chrysin Nanoparticles Employing Co-Precipitation as a Technique. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2016, 3, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.F.; Jia, J.F.; Guo, X.K.; Zhao, Y.P.; Chen, D.S.; Guo, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.L. Reduced Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation in the presence of chitosan-coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. NanoMed. 2016, 11, 6499–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Isacchi, B.; Righeschi, C.; Guccione, C.; Bergonzi, M.C. Flavonoids Loaded in Nanocarriers: An Opportunity to Increase Oral Bioavailability and Bioefficacy. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 1212–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Zou, X. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampino, A.; Borgogna, M.; Blasi, P.; Bellich, B.; Cesàro, A. Chitosan nanoparticles: Preparation, size evolution and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 455, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, B.; Guo, J.; Hu, Y.; Su, Z. Water-Soluble Chitosan Nanoparticles Inhibit Hypercholesterolemia Induced by Feeding a High-Fat Diet in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 814606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahreini, E.; Aghaiypour, K.; Abbasalipourkabir, R.; Mokarram, A.R.; Goodarzi, M.T.; Saidijam, M. Preparation and nanoencapsulation of l-asparaginase II in chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles and in vitro release study. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.H.; Chitra, E.; Ramamurthy, S.; Siddalingam, R.P.; Yuen, K.H.; Ambu, S.P.; Davamani, F. Chitosan-propolis nanoparticle formulation demonstrates anti-bacterial activity against Enterococcus faecalis biofilms. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174888. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Yan, W.; Xu, Z.; Ni, H. Formation mechanism of monodisperse, low molecular weight chitosan nanoparticles by ionic gelation technique. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 90, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumari, J.; Busi, S.; Vasu, A.C.; Reddy, P. Facile green synthesis of baicalein fabricated gold nanoparticles and their antibiofilm activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 107, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilk, S.; Sağlam, N.; Özgen, M.; Korkusuz, F. Chitosan nanoparticles enhances the anti-quorum sensing activity of kaempferol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Raveendran, S.; Ferreira, J.M.F.; Kannan, S. In Situ Impregnation of Silver Nanoclusters in Microporous Chitosan-PEG Membranes as an Antibacterial and Drug Delivery Percutaneous Device. Langmuir 2016, 3, 10305–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viszwapriya, D.; Prithika, U.; Deebika, S.; Balamurugan, K.; Pandian, S.K. In vitro and in vivo antibiofilm potential of 2,4-Di- tert -butylphenol from seaweed surface associated bacterium Bacillus subtilis against group A streptococcus. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 191, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumari, J.; Meena, H.; Gangatharan, M.; Busi, S. Green synthesis of anisotropic gold nanoparticles using hordenine and their antibiofilm efficacy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. IET NanoBiotechnol. 2017, 11, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Kong, J.; Dong, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, K.; Wu, L.; Hou, C.; Liang, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, Y. Baicalein attenuates the quorum sensing-controlled virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and relieves the inflammatory response in P. aeruginosa-infected macrophages by downregulating the MAPK and NFkB signal-transduction pathways. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Archana, D.; Singh, B.K.; Dutta, J.; Dutta, P.K. In vivo evaluation of chitosan–PVP–titanium dioxide nanocomposite as wound dressing material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Pu, Y.; Lai, Y.; He, B.; Gu, Z. Nanoparticles generated by PEG-Chrysin conjugates for efficient anticancer drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T.; Azimi-Nezhad, M. Protective effects of chrysn against Drugs and Toxic agents. Dose-Response 2017, 15, 1559325817711782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.L.; Qi, W.; Han, F.; Shao, J.Z.; Gao, J.Q. Toxicity evaluation of biodegradable chitosan nanapariclesu sing a zebrafish embryo model. Int. J. NanoMed. 2011, 6, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siddhardha, B.; Pandey, U.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Pala, R.; Syed, A.; Bahkali, A.H.; Elgorban, A.M. Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Potentiates Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020115
Siddhardha B, Pandey U, Kaviyarasu K, Pala R, Syed A, Bahkali AH, Elgorban AM. Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Potentiates Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens. 2020; 9(2):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020115
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiddhardha, Busi, Uday Pandey, K. Kaviyarasu, Rajasekharreddy Pala, Asad Syed, Ali H. Bahkali, and Abdallah M. Elgorban. 2020. "Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Potentiates Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus aureus" Pathogens 9, no. 2: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020115
APA StyleSiddhardha, B., Pandey, U., Kaviyarasu, K., Pala, R., Syed, A., Bahkali, A. H., & Elgorban, A. M. (2020). Chrysin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles Potentiates Antibiofilm Activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Pathogens, 9(2), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020115




