Identifying Candidate Genetic Markers of CDV Cross-Species Pathogenicity in African Lions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequences
2.2. SNPs Differentiating Clinical and Subclinical CDV Strains in East Africa
2.3. Evolutionary Processes Acting on CDV Genomes
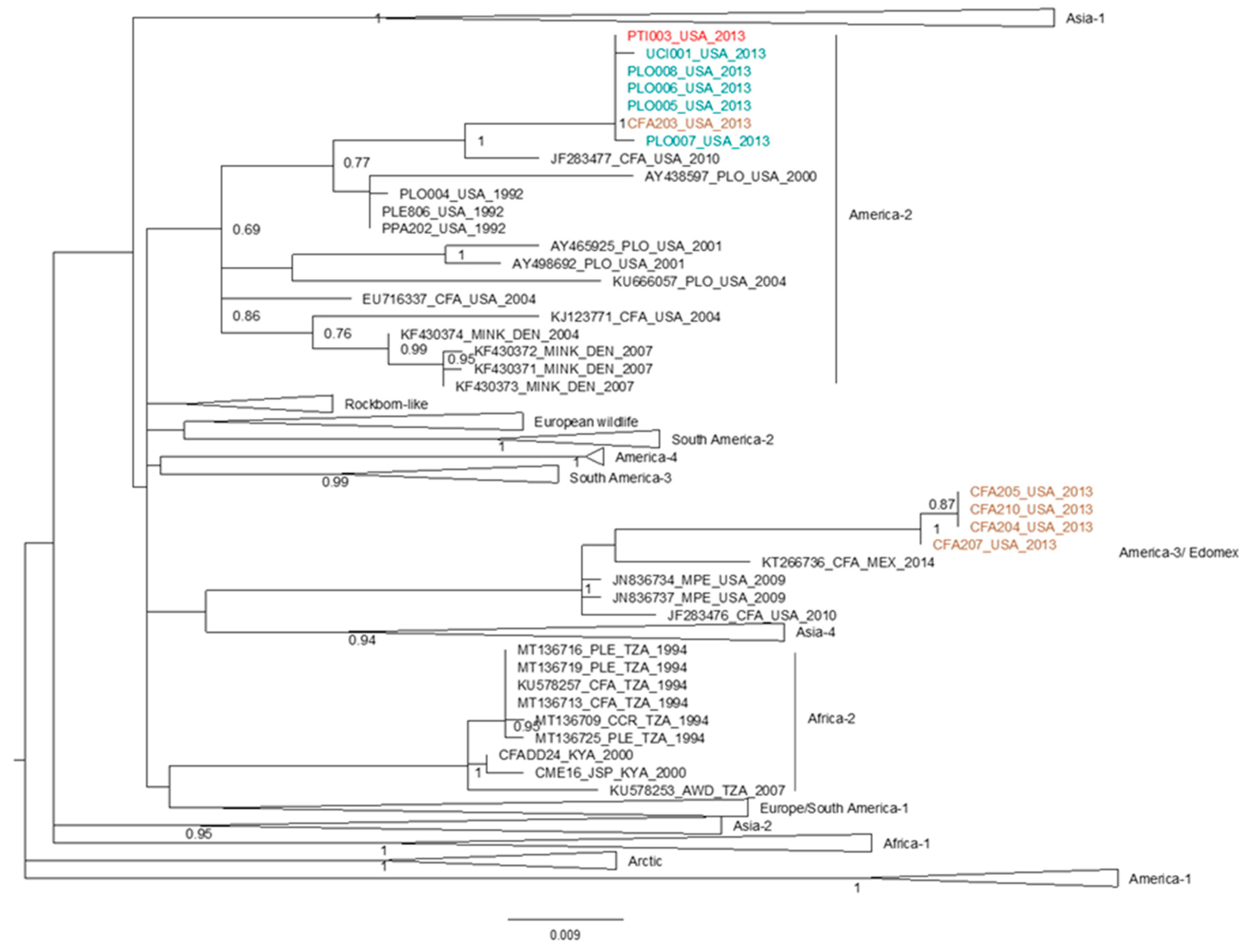
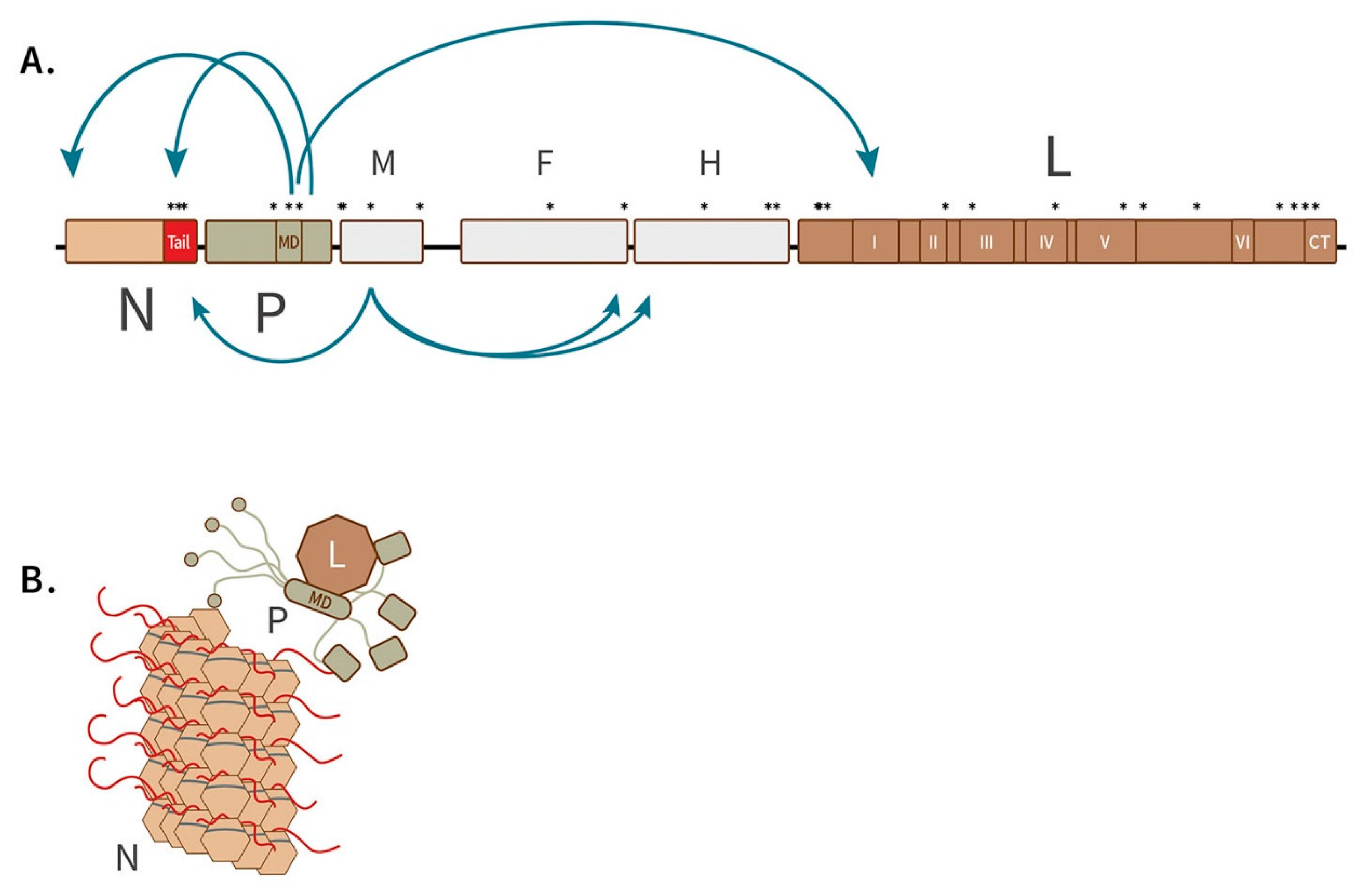
2.4. Phylogenetic Analyses and Distribution of Mutations at Candidate Markers
3. Discussion
3.1. Candidate Loci Associated with CDV Pathogenicity in Lions in East Africa
3.2. SNPs at Candidate Loci Occur in Multiple, Independent Distemper Outbreaks in Lions
3.3. Mutations at Candidate Loci Occur Primarily in the RNP Complex and Matrix Protein
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Specimens
5.2. Sequencing
5.2.1. Whole-Genome Sequencing
5.2.2. RT-PCR and Sanger Sequencing
5.3. Identifying Loci Differentiating Clinical and Subclinical CDV Strains in East Africa
5.4. Evolutionary Analyses
5.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Ruiz-Saenz, J. Diversity of susceptible hosts in canine distemper virus infection: A systematic review and data synthesis. BMC Veter. Res. 2016, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.E.; Appel, M.J. Canine Distemper. In Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1990; pp. 226–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Miyazawa, T.; Chen, M.-C.; Kuo, T.-F.; Lin, J.A.; Mikami, T.; Kai, C.; Takahashi, E. Seroprevalence of Canine Distemper Virus in Cats. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2001, 8, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, T.M. Ferrets. In Manual of Exotic Pet Practice; Saunders Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009; pp. 345–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, L.; Terio, K.A.; Kock, R.; Mlengeya, T.; Roelke, M.E.; Dubovi, E.; Summers, B.; Sinclair, A.R.E.; Packer, C. Climate Extremes Promote Fatal Co-Infections during Canine Distemper Epidemics in African Lions. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, K.A.; Kat, P.W.; Frank, L.G.; Holekamp, K.E.; Smale, L.; House, C.; Appel, M.J.G. Evidence of canine distemper virus infection among free-ranging spotted hyenas (Crocuta crocuta) in the Masai Mara, Kenya. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 1995, 26, 201–206. Available online: http://www.jstor.org/stable/20095463 (accessed on 4 March 2011).
- Creel, S.; Creel, N.M.; Munson, L.; Sanderlin, D.; Appel, M.J.G. Serosurvey for selected viral diseases and demography of African wild dogs in Tanzania. J. Wildl. Dis. 1997, 33, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Messling, V.; Milosevic, A.; Cattaneo, R. Tropism illuminated: Lymphocyte-based pathways blazed by lethal morbillivirus through the host immune system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14216–14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawatsky, B.; Wong, X.X.; Hinkelmann, S.; Cattaneo, R.; Von Messling, V. Canine Distemper Virus Epithelial Cell Infection Is Required for Clinical Disease but Not for Immunosuppression. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3658–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyce, R.S.; Delpeut, S.; Richardson, C.D. Dog nectin-4 is an epithelial cell receptor for canine distemper virus that facilitates virus entry and syncytia formation. Virology 2013, 436, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, E.; Ruiz-Jarabo, C.M.; Domingo, E. Evolution of Cell Recognition by Viruses. Sci. N. Y. 2001, 292, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasik, B.R.; Muñoz-Rojas, A.R.; Okamoto, K.W.; Miller-Jensen, K.; E Turner, P. Generalized selection to overcome innate immunity selects for host breadth in an RNA virus. Evolution 2016, 70, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Miura, R.; Barrett, T.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Kai, C. Rinderpest Virus Phosphoprotein Gene Is a Major Determinant of Species-Specific Pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6676–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, G.; Kawaoka, G.N.A.Y. Host Range Restriction and Pathogenicity in the Context of Influenza Pandemic. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisder, S.; Möckel, N.; Eisenhardt, D.; Genersch, E. In vivo evolution of viral virulence: Switching of deformed wing virus between hosts results in virulence changes and sequence shifts. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 4612–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.; Qing, K.; Kwon, H.J.; Mah, C.; Srivastava, A. Impaired Intracellular Trafficking of Adeno-Associated Virus Type 2 Vectors Limits Efficient Transduction of Murine Fibroblasts. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Furuse, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kamigaki, T.; Oshitani, H. Evolution of the M gene of the influenza A virus in different host species: Large-scale sequence analysis. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Deng, G.; Song, J.; Tian, G.; Suo, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Bu, Z.; Kawaoka, Y.; Chen, H. Two amino acid residues in the matrix protein M1 contribute to the virulence difference of H5N1 avian influenza viruses in mice. Virology 2009, 384, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Shaw, M.A.; Goodman, S.J. Pathogen evolution and disease emergence in carnivores. Proc. Biol. Sci. R. Soc. 2007, 274, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolin, V.M.; Wibbelt, G.; Michler, F.U.F.; Wolf, P.; East, M.L. Susceptibility of carnivore hosts to strains of canine distemper virus from distinct genetic lineages. Veter. Microbiol. 2012, 156, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terio, K.; Craft, M.E. Canine Distemper Virus (CDV) in Another Big Cat: Should CDV Be Renamed Carnivore Distemper Virus? mBio 2013, 4, e-00702-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, Y.; Uema, M.; Miura, R.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Yoneda, K.; Kai, C. Prevalence of Canine Distemper Virus, Feline Immunodeficiency Virus and Feline Leukemia Virus in Captive African Lions (Panthera leo) in Japan. J. Veter. Med Sci. 2004, 66, 1587–1589. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15644613 (accessed on 1 December 2017). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nagao, Y.; Nishio, Y.; Shiomoda, H.; Tamaru, S.; Shimojima, M.; Goto, M.; Une, Y.; Sato, A.; Ikebe, Y.; Maeda, K. An Outbreak of Canine Distemper Virus in Tigers (Panthera tigris): Possible Transmission from Wild Animals to Zoo Animals. J. Veter. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsauer, S.; Bay, G.; Meli, M.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Lutz, H. Seroprevalence of Selected Infectious Agents in a Free-Ranging, Low-Density Lion Population in the Central Kalahari Game Reserves in Botswana. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McDermid, K.R.; Snyman, A.; Verreynne, F.J.; Carroll, J.P.; Penzhorn, B.L.; Yabsley, M.J. Surveillance for viral and parasitic pathogens in a vulnerable African lion (Panthera leo) population in the Northern Tuli Game Reserve, Botswana. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, K.C.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Dubovi, E.J.; Frank, L.G.; Munson, L.; Wagner, A.P.; Woodroffe, R. Rabies Virus and Canine Distemper Virus in Wild and Domestic Carnivores in Northern Kenya: Are Domestic Dogs the Reservoir? EcoHealth 2012, 9, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driciru, M.; Siefert, L.; Prager, K.C.; Dubovi, E.; Sande, R.; Princee, F.; Friday, T.; Munson, L. A Serosurvey of Viral Infections in Lions (Panthera leo), from Queen Elizabeth National Park, Uganda. J. Wildl. Dis. 2006, 42, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, M.J.G.; Yates, R.A.; Foley, G.L.; Bernstein, J.J.; Santinelli, S.; Spelman, L.H.; Miller, L.D.; Arp, L.H.; Anderson, M.; Barr, M.; et al. Canine Distemper Epizootic in Lions, Tigers, and Leopards in North America. J. Veter. Diagn. Investig. 1994, 6, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, D.L.; Zurbriggen, A.; Lutz, H.; Pospischil, A. Distemper: Not a new disease in lions and tigers. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 1997, 4, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelke-Parker, M.; Munson, L.; Packer, C.; Kock, R.; Cleaveland, S.; Carpenter, M.; O’Brien, S.; Pospischil, A.; Hofmann-Lehmann, R.; Lutz, H.; et al. A canine distemper virus epidemic in Serengeti lions (Panthera leo). Nature 1996, 379, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, R.; Chalmers, W.S.K.; Mwanzia, J.; Chillingworth, C.; Wambua, J.; Coleman, P.G.; Baxendale, W. Canine distemper antibodies in lions of the Masai Mara. Veter. Rec. 1998, 142, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Phillips, S.; Davidson-Phillips, P.; Canning, G.; Schroder, B.; Swart, J.; Burger, A. Canine Distemper Virus Management in Lions (Panthera leo) on Welgevonden Game Reserve. Afr. J. Wildl. Res. 2019, 49, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budaszewski, R.D.F.; Streck, A.F.; Weber, M.N.; Siqueira, F.M.; Guedes, R.L.M.; Canal, C.W. Influence of vaccine strains on the evolution of canine distemper virus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 41, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.Z.; Liu, X.P.; Li, S.S. Cross-species recombination in the haemagglutinin gene of canine distemper virus. Virus Res. 2008, 136, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.M.; Ho, C.H.; Chiang, M.J.; Sanno-Duanda, B.; Chung, C.S.; Lin, M.Y.; Shi, Y.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C.; Liao, P.C.; et al. Phylodynamic analysis of the canine distemper virus hemagglutinin gene. BMC Veter. Res. 2015, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G. Homologous recombination is a force in the evolution of canine distemper virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, E.; Newell, T.K.; Dyer, N.; Wilkes, R.P. Phylogenetic analysis of the wild-type strains of canine distemper virus circulating in the United States. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckworth, J.K.; Davis, B.W.; Dubovi, E.; Fountain-Jones, N.; Packer, C.; Cleaveland, S.; Craft, M.E.; Eblate, E.; Schwartz, M.; Mills, L.S.; et al. Cross-species transmission and evolutionary dynamics of canine distemper virus during a spillover in African lions of Serengeti National Park. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolin, V.M.; Olarte-Castillo, X.A.; Osterrieder, N.; Hofer, H.; Dubovi, E.; Mazzoni, C.J.; Brunner, E.; Goller, K.V.; Fyumagwa, R.D.; Moehlman, P.D.; et al. Canine distemper virus in the Serengeti ecosystem: Molecular adaptation to different carnivore species. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 2111–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolin, V.M.; Osterrieder, K.; Von Messling, V.; Hofer, H.; Anderson, D.; Dubovi, E.; Brunner, E.; East, M.L. Antagonistic Pleiotropy and Fitness Trade-Offs Reveal Specialist and Generalist Traits in Strains of Canine Distemper Virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seimon, T.A.; Miquelle, D.G.; Chang, T.Y.; Newton, A.L.; Korotkova, I.; Ivanchuk, G.; Lyubchenko, E.; Tupikov, A.; Slabe, E.; McAloose, D. Canine Distemper Virus: An Emerging Disease in Wild Endangered Amur Tigers (Panthera tigris altaica). mBio 2013, 4, e00410–e00413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Shan, F.; Zhou, X.; Li, B.; Zhai, J.Q.; Zou, S.Z.; Wu, M.F.; Chen, W.; Zhai, S.L.; Luo, M. Outbreak and genotyping of canine distemper virus in captive Siberian tigers and red pandas. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Raha, T.; Shaila, M.S. Effect of single amino acid mutations in the conserved GDNQ motif of L protein of Rinderpest virus on RNA synthesis in vitro and in vivo. Virus Res. 2004, 99, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas, J.M.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Sanjuán, R. The Fitness Effects of Synonymous Mutations in DNA and RNA Viruses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novella, I.; Zárate, S.; Metzgar, D.; Ebendick-Corpus, B. Positive Selection of Synonymous Mutations in Vesicular Stomatitis Virus. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 342, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepin, K.M.; Domsic, J.; McKenna, R. Genomic evolution in a virus under specific selection for host recognition. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2008, 8, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourimant, J.; Thakkar, V.D.; Cox, R.M.; Plemper, R.K. Viral evolution identifies a regulatory interface between paramyxovirus polymerase complex and nucleocapsid that controls replication dynamics. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sourimant, J.; Plemper, R.K. Organization, Function, and Therapeutic Targeting of the Morbillivirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Complex. Viruses 2016, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, G.V. Genome Packaging and Host-Pathogen Interactions in Paramyxovirus Assembly and Budding. Ph.D. Thesis, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, August 2016. Available online: https://etda.libraries.psu.edu/catalog/0v838057gLaine2005 (accessed on 11 August 2020).
- Laine, D.; Bourhis, J.M.; Longhi, S.; Flacher, M.; Cassard, L.; Canard, B.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Rabourdin-Combe, C.; Valentin, H. Measles virus nucleoprotein induces cell-proliferation arrest and apoptosis through NTAIL–NR and NCORE–FcγRIIB1 interactions, respectively. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M.; Krumm, S.A.; Thakkar, V.D.; Sohn, M.; Plemper, R.K. The structurally disordered paramyxovirus nucleocapsid protein tail domain is a regulator of the mRNA transcription gradient. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, V.D.; Cox, R.M.; Sawatsky, B.; Budaszewski, R.D.F.; Sourimant, J.; Wabbel, K.; Makhsous, N.; Greninger, A.L.; Von Messling, V.; Plemper, R.K. The Unstructured Paramyxovirus Nucleocapsid Protein Tail Domain Modulates Viral Pathogenesis through Regulation of Transcriptase Activity. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e2064-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cortay, J.C.; Gerlier, D. Measles virus protein interactions in yeast: New findings and caveats. Virus Res. 2003, 98, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, T.; Kaushik, R.; Shaila, M.S. Phosphoprotein P of Rinderpest virus binds to plus sense leader RNA: Regulation by phosphorylation. Virus Res. 2004, 104, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Messling, V.; Svitek, N.; Cattaneo, R. Receptor (SLAM [CD150]) Recognition and the V Protein Sustain Swift Lymphocyte-Based Invasion of Mucosal Tissue and Lymphatic Organs by a Morbillivirus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6084–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, M.S.; Menonna, J.P.; Cook, S.D.; Dowling, P.C.; Udem, S.A. Canine Distemper Virus L Gene: Sequence and Comparison with Related Viruses. Virology 1993, 193, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Li, Z.; Jenni, S.; Rahmeh, A.A.; Morin, B.M.; Grant, T.; Grigorieff, N.; Harrison, S.C.; Whelan, S.P. Structure of the L Protein of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus from Electron Cryomicroscopy. Cell 2015, 162, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dochow, M.; Krumm, S.A.; Crowe, J.E.; Moore, M.L.; Plemper, R.K. Independent Structural Domains in Paramyxovirus Polymerase Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6878–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Najjar, F.; Schmitt, A.P.; Dutch, R.E. Paramyxovirus Glycoprotein Incorporation, Assembly and Budding: A Three Way Dance for Infectious Particle Production. Viruses 2014, 6, 3019–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naim, H.Y.; Ehler, E.; Billeter, M.A. Measles virus matrix protein specifies apical virus release and glycoprotein sorting in epithelial cells. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3576–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzel, E.; Anderson, D.E.; Castan, A.; Von Messling, V.; Maisner, A. Canine Distemper Virus Matrix Protein Influences Particle Infectivity, Particle Composition, and Envelope Distribution in Polarized Epithelial Cells and Modulates Virulence. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7162–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, M.; Sheffy, B.E.; Percy, D.H.; Gaskin, J.M. Canine distemper virus in domesticated cats and pigs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1974, 35, 803–806. Available online: https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/19742225506 (accessed on 4 March 2011).
- Harder, T.C.; Kenter, M.; Vos, H.; Siebelink, K.; Huisman, W.; Van Amerongen, G.; Orvell, C.; Barrett, T.; Appel, M.J.G.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Canine distemper virus from diseased large felids: Biological properties and phylogenetic relationships. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, K.M.; Lass, S.; Pulliam, J.R.C.; Read, A.F.; Lloyd-Smith, J.O. Identifying genetic markers of adaptation for surveillance of viral host jumps. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.; Soutyrina, S.V.; Seryodkin, I.V.; Sulikhan, N.; Uphyrkina, O.V.; Goncharuk, M.; Matthews, L.; Cleaveland, S.; Miquelle, D. Canine distemper virus as a threat to wild tigers in Russia and across their range. Integr. Zool. 2015, 10, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keahy, V. (In-Sync Exotics, Wylie, TX, USA). Personal communication, 2018.
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, Version 7.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.P.; Murrell, B.; Golden, M.; Khoosal, A.; Muhire, B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Rybicki, E. RDP: Detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padidam, M.; Sawyer, S.; Fauquet, C.M. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 1999, 265, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K.; Williamson, C. A Modified Bootscan Algorithm for Automated Identification of Recombinant Sequences and Recombination Breakpoints. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2005, 21, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.M. Analyzing the mosaic structure of genes. J. Mol. Evol. 1992, 34, 126–129. Available online: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/BF00182389.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2020). [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: Computer simulations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13757–13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, M.J.; Armstrong, J.S.; Gibbs, A.J. Sister-Scanning: A Monte Carlo procedure for assessing signals in recombinant sequences. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W. Not So Different After All: A Comparison of Methods for Detecting Amino Acid Sites Under Selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Pond, S.L.K. Detecting Individual Sites Subject to Episodic Diversifying Selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pond, S.L.K.; Frost, S.D.W.; Muse, S.V. HyPhy: Hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 676–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delport, W.; Poon, A.F.Y.; Frost, S.D.W.; Pond, S.L.K. Datamonkey 2010: A suite of phylogenetic analysis tools for evolutionary biology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2455–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posada, D. jModelTest: Phylogenetic Model Averaging. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2008, 25, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Position (nt) | Gene | Amino Acid/Gene | Subclinical | Clinical | Synonymous or Nonsynonymous | AA-Subclinical | AA-Clinical |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 132 | N | 9 | A | G | non | T | A |
| 470 | N | 121 | A | G | syn | - | - |
| 1361 | N | 418 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 1382 | N | 425 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 1458 | N | 451 | T | C | non | F | L |
| 1505 | N | 466 | C | A | syn | - | - |
| 1914 * | P/V/C | 38/38/31 | A | C | non/non/non | Q/Q/K | H/H/T |
| 2200 * | P/V/C | 134/134/126 | G | A | non/non/syn | G/G/- | S/S/- |
| 2638 | P/V | 280/280 | A | G | non | K/K | E/R |
| 2832 | P | 344 | A/G | C | syn | - | - |
| 2934 | P | 378 | G | A | syn | - | - |
| 3292 | P | 498 | T | C | non | Y | H |
| 3410 | P-M UTR | n.a. | A | T | n.a. | - | - |
| 3457 | M | 9 | A | G | non | Q | R |
| 3461 | M | 10 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 3821 | M | 130 | G | A | syn | - | - |
| 4436 | M | 335 | C | T | syn | - | - |
| 4900 | M-F UTR | n.a. | A | G | n.a. | - | - |
| 5001 | FSP | 23 | C | T | non | H | Y |
| 5226 | F | 98 | G | A | non | A | T |
| 5978 | F | 348 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 6058 | F | 375 | G | A | non | R | Q |
| 6694 | F | 587 | T | C | non | V | A |
| 6710 | F | 592 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 6905 | F | 657 | C | A | syn | - | - |
| 6974 | F-H UTR | n.a. | T | C | n.a. | - | - |
| 7088 | H | 4 | T | C | non | Y | H |
| 7167 | H | 30 | A | G | non | Q | R |
| 7870 | H | 264 | A | T | syn | - | - |
| 8320 | H | 414 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 8634 | H | 519 | G | T | non | R | I |
| 8723 | H | 549 | T | C | non | Y | H |
| 9210 | L | 61 | A | C | non | M | L |
| 9290 | L | 87 | C | T | syn | - | - |
| 9308 | L | 93 | C | T | non | L | F |
| 9428 | L | 133 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 10844 | L | 605 | T/C | G | syn | - | - |
| 11159 | L | 710 | C | T | syn | - | - |
| 12170 | L | 1047 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 12986 | L | 1319 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 13142 | L | 1371 | A | G | syn | - | - |
| 13233 | L | 1402 | A | C | non | - | - |
| 13524 | L | 1499 | A | G | non | I | V |
| 13886 | L | 1619 | C | T | syn | - | - |
| 14132 | L | 1701 | A | G | syn | - | - |
| 15056 | L | 2009 | T | C | syn | - | - |
| 15185 | L | 2052 | C | T | syn | - | - |
| 15203 | L | 2058 | A | C | syn | - | - |
| 15326 | L | 2099 | T | A | syn | - | - |
| Acc. No. | # | Species | Country | Year | Clade | RDP pval | GC pval | BS pval | MC pval | Ch pval | SS pval | 3Seq pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB462810 | 1 ^ | CFA | Japan | nd | Asia-2 | 9.95 × 10−28 | 4.86 × 10−26 | 4.93 × 10−23 | 4.67 × 10−8 | 8.28 × 10−8 | 0.000173 | 1.32 × 10−11 |
| AB462810 | 2 | CFA | Japan | nd | Asia-3 | 7.74 × 10−28 | 1.01 × 10−26 | 3.87 × 10−21 | 5.43 × 10−7 | 5.32 × 10−7 | 3.00 × 10−8 | 1.32 × 10−11 |
| AB474397 | 1 ^ | CFA | Japan | nd | Asia-4 | 9.95 × 10−28 | 4.86 × 10−26 | 4.93 × 10−23 | 4.67 × 10−8 | 8.28 × 10−8 | 0.000173 | 1.32 × 10−11 |
| AB474397 | 2 | CFA | Japan | nd | Asia-5 | 7.74 × 10−28 | 1.01 × 10−26 | 3.87 × 10−21 | 5.43 × 10−7 | 5.32 × 10−7 | 3.00 × 10−8 | 1.32 × 10−11 |
| AY443350 | 1 ^ | PLO | USA | 2000 | Amer-2 | 3.23 × 10−12 | 5.27 × 10−18 | 4.42 × 10−16 | 1.00 × 10−11 | 7.02 × 10−13 | 3.73 × 10−16 | 2.21 × 10−16 |
| AY443350 | 2 ^ | PLO | USA | 2000 | Amer-2 | 2.34 × 10−12 | 0.007073 | 2.08 × 10−11 | 3.85 × 10−15 | 0.000116 | 4.74 × 10−7 | 6.62 × 10−12 |
| AY445077 | 1 ^ | PLO | USA | 1998 | Amer-1 * | 3.16 × 10−19 | 6.42 × 10−13 | 1.90 × 10−16 | 1.32 × 10−9 | 3.47 × 10−9 | 1.09 × 10−10 | 6.62 × 10−12 |
| AY445077 | 2 ~ | PLO | USA | 1998 | Amer-1 * | 6.21 × 10−8 | 8.26 × 10−8 | 4.02 × 10−5 | 0.020799 | 0.005608 | NS | 1.04 × 10−5 |
| AY466011 | 1 | PLO | USA | 1998 | Amer-1 * | 3.16 × 10−19 | 6.42 × 10−13 | 1.90 × 10−16 | 1.32 × 10−9 | 3.47 × 10−9 | 1.09 × 10−10 | 6.62 × 10−12 |
| AY466011 | 2 ~ | PLO | USA | 1998 | Amer-1 * | 6.21 × 10−8 | 8.26 × 10−8 | 4.02 × 10−5 | 0.020799 | 0.005608 | NS | 1.04 × 10−5 |
| AY542312 | 1 ^ | PLO | USA | 1998 | Amer-1 * | 3.16 × 10−19 | 6.42 × 10−13 | 1.90 × 10−16 | 1.32 × 10−9 | 3.47 × 10−9 | 1.09 × 10−10 | 6.62 × 10−12 |
| AY542312 | 2 ~ | PLO | USA | 1998 | Amer-1 * | 6.21 × 10−8 | 8.26 × 10−8 | 4.02 × 10−5 | 0.020799 | 0.005608 | NS | 1.04 × 10−5 |
| AY649446 | 1 ^ | PLO | USA | 2001 | Amer-2 | 4.64 × 10−11 | 1.04 × 10−14 | 1.03 × 10−8 | 0.000218 | 0.000172 | 0.01701 | 9.42 × 10−9 |
| AY649446 | 2 ^~ | PLO | USA | 2001 | Amer-2 | NS | 0.003004 | 0.004893 | 9.18 × 10−5 | 0.000131 | 8.85 × 10−16 | NS |
| HQ540293 | 1 | FOX | China | 2006 | Asia-1 | 3.89 × 10−71 | 4.39 × 10−69 | 4.91 × 10−63 | 4.81 × 10−18 | 1.78 × 10−17 | 2.67 × 10−17 | 1.99 × 10−11 |
| JX681125 | 1 | FOX | China | 2006 | Asia-1 | 3.89 × 10−71 | 4.39 × 10−69 | 4.91 × 10−63 | 4.81 × 10−18 | 1.78 × 10−17 | 2.67 × 10−17 | 1.99 × 10−11 |
| KJ123771 | 1 ~ | CFA | USA | 2004 | Amer-2 | NS | 0.000126 | 2.35 × 10−9 | 2.23 × 10−7 | 2.14 × 10−8 | 1.41 × 10−15 | 2.58 × 10−10 |
| KJ994343 | 1 | NPR | Canada | 2013 | Asia-1 | 7.52 × 10−33 | 1.95 × 10−31 | 1.98 × 10−26 | 1.42 × 10−5 | 1.12 × 10−5 | 3.55 × 10−6 | 1.99 × 10−11 |
| KJ994343 | 2 ^~ | NPR | Canada | 2013 | Asia-1 | 1.06 × 10−9 | 1.69 × 10−10 | 2.39 × 10−6 | 5.91 × 10−8 | 1.80 × 10−8 | 2.53 × 10−5 | 9.47 × 10−8 |
| KJ994343 | 3 ~ | NPR | Canada | 2013 | Asia-1 | 1.31 × 10−7 | 0.000298 | 1.72 × 10−5 | 0.012219 | 0.040604 | NS | 6.46 × 10−5 |
| KJ994343 | 4 | NPR | Canada | 2013 | Asia-1 | 0.003985 | NS | 0.012217 | 2.17 × 10−6 | 2.50 × 10−6 | NS | 7.89 × 10−8 |
| KJ994343 | 5 ~ | NPR | Canada | 2013 | Asia-1 | 2.93 × 10−5 | 5.18 × 10−5 | 6.73 × 10−7 | 0.003271 | 0.001688 | 0.000122 | 0.039698 |
| WGS Position (nt) | Gene | AA | Sub-Clinical AA | Clinical AA | Functional Domains | Putative Function | Virus Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1361 | N | 418 * | - | - | N-tail, box 1 | Binds unidentified host receptor suppressing immune cell proliferation | Transcription & replication |
| 1458 | N | 451 | F | L | N-tail | Binds P recruiting RdRp complex to prevent slipping during transcription & replication | Transcription & replication |
| 1505 | N | 466 | - | - | N-tail | Binds P recruiting RdRp complex to prevent slipping during transcription & replication | Transcription & replication |
| 2638 ¥ | P/V | 280 * | K | E/R | PNT/V-Zbd | P - binds L - essential co-factor of transcription and replication/V - interrupts host innate immune response, virulence factor | Transcription & replication |
| 2832 | P | 344 | - | - | PMD | L binding site - essential co-factor of transcription and replication | Transcription & replication |
| 2934 | P | 378 | - | - | PMD | L binding site - essential co-factor of transcription and replication | Transcription & replication |
| 3457 | M | 9 | Q | R | M - NTD | Matrix general - modulates fusion and budding, binds F, H, RNP, and cellular actin, assembles components at surface | Assembly & fusion |
| 3461 | M | 10 | - | - | M - NTD | Matrix general - modulates fusion and budding, binds F, H, RNP, and cellular actin, assembles components at surface | Assembly & fusion |
| 3821 | M | 130 | - | - | M - NTD | Matrix general - modulates fusion and budding, binds F, H, RNP, and cellular actin, assembles components at surface | Assembly & fusion |
| 4436 | M | 335 | - | - | M - CTD | Matrix general - modulates fusion and budding, binds F, H, RNP, and cellular actin, assembles components at surface | Assembly & fusion |
| 5978 | F | 348 | - | - | F1 | Extracellular domain of glycoprotein, mediates fusion with host cell, interacts with H | Fusion |
| 6905 | F | 657 | - | - | F tail | Cytoplasmic tail interacts with M at cell surface during fusion and budding | Assembly & fusion |
| 7870 | H | 264 | - | - | no data | No data | Host receptor binding |
| 8634 | H | 519 | R | I | SLAM binding | Host immune cell recognition and entry | Host receptor binding |
| 8723 | H | 549 * | Y | H | SLAM binding | Host immune cell recognition and entry | Host receptor binding |
| 9290 * | L | 87 | - | - | LRI | No data | Transcription & replication |
| 9308 | L | 93 †,∞ | L | F | LRI | No data | Transcription & replication |
| 9428 | L | 133 | - | - | LRI | No data | Transcription & replication |
| 10844 | L | 605 | - | - | CRII | Polymerase activity | Transcription & replication |
| 11159 | L | 710 | - | - | CRIII | Catalytic center for polymerization, i.e., transcription and replication of vRNA | Transcription & replication |
| 12170 | L | 1047 * | - | - | CRIV | mRNA capping, essential for translation and immune escape | Transcription & replication |
| 12986 | L | 1319 * | - | - | CRV | Methylation of viral mRNA | Transcription & replication |
| 13233 | L | 1402 † | N | H | Connector | spacing the catalytic domains, may interact with P to stabilize conformation of RdRp complex | Transcription & replication |
| 13886 | L | 1619 ‡ | - | - | Connector | Spacing the catalytic domains, may interact with P to stabilize conformation of RdRp complex | Transcription & replication |
| 14132 | L | 1701 | - | - | Linker | Separates regions of the L | Transcription & replication |
| 15056 | L | 2009 | - | - | Mtase | Methylation of viral mRNA | Transcription & replication |
| 15203 | L | 2058 † | A | C | Mtase | Methylation of viral mRNA | Transcription & replication |
| 15326 | L | 2099 | - | - | Mtase | Methylation of viral mRNA | Transcription & replication |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weckworth, J.K.; Davis, B.W.; Roelke-Parker, M.E.; Wilkes, R.P.; Packer, C.; Eblate, E.; Schwartz, M.K.; Mills, L.S. Identifying Candidate Genetic Markers of CDV Cross-Species Pathogenicity in African Lions. Pathogens 2020, 9, 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110872
Weckworth JK, Davis BW, Roelke-Parker ME, Wilkes RP, Packer C, Eblate E, Schwartz MK, Mills LS. Identifying Candidate Genetic Markers of CDV Cross-Species Pathogenicity in African Lions. Pathogens. 2020; 9(11):872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110872
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeckworth, Julie K., Brian W. Davis, Melody E. Roelke-Parker, Rebecca P. Wilkes, Craig Packer, Ernest Eblate, Michael K. Schwartz, and L. Scott Mills. 2020. "Identifying Candidate Genetic Markers of CDV Cross-Species Pathogenicity in African Lions" Pathogens 9, no. 11: 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110872
APA StyleWeckworth, J. K., Davis, B. W., Roelke-Parker, M. E., Wilkes, R. P., Packer, C., Eblate, E., Schwartz, M. K., & Mills, L. S. (2020). Identifying Candidate Genetic Markers of CDV Cross-Species Pathogenicity in African Lions. Pathogens, 9(11), 872. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9110872





