Metagenomic Analysis of Infectious F-Specific RNA Bacteriophage Strains in Wastewater Treatment and Disinfection Processes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Metagenomic and Taxonomic Analyses
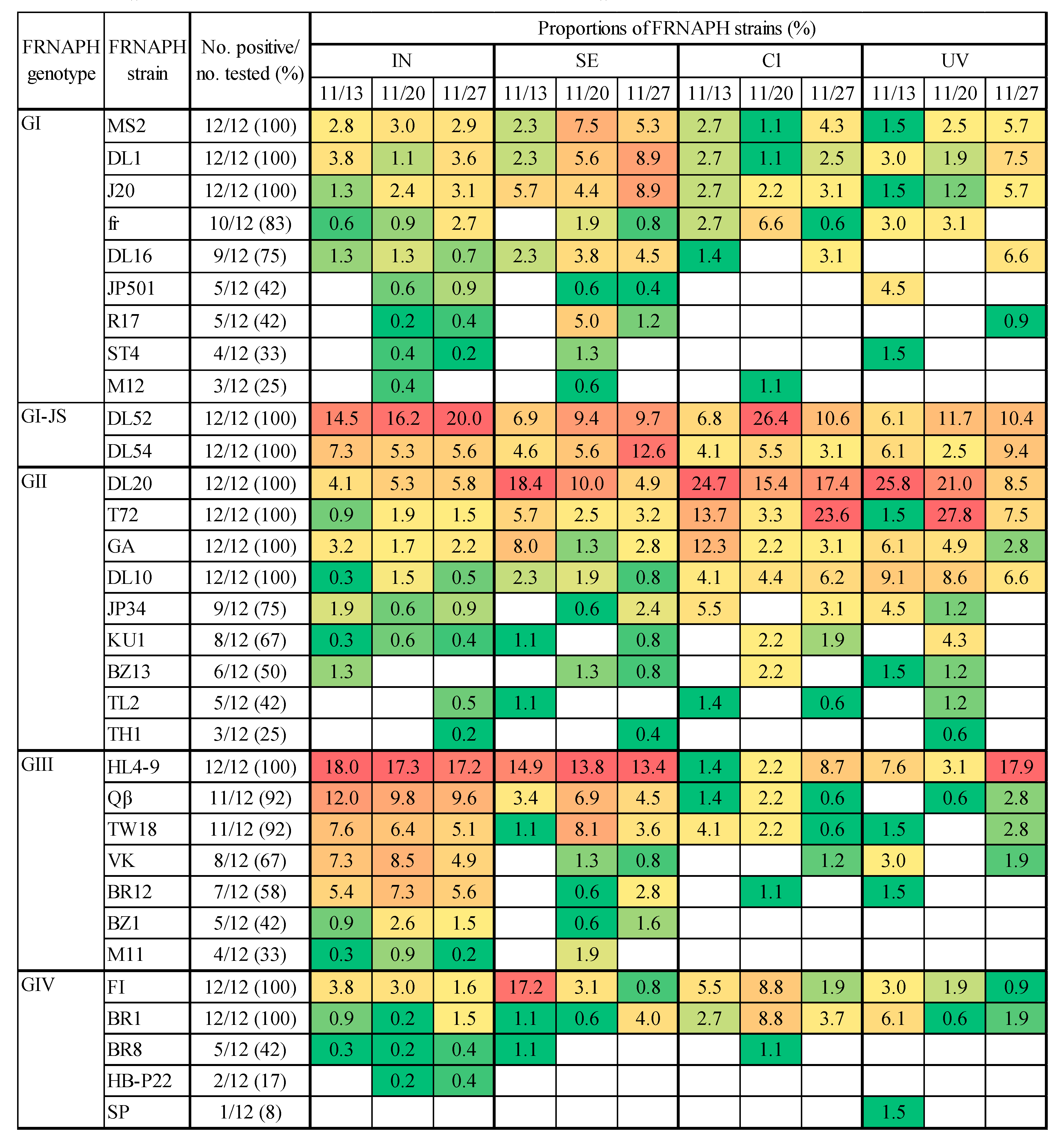
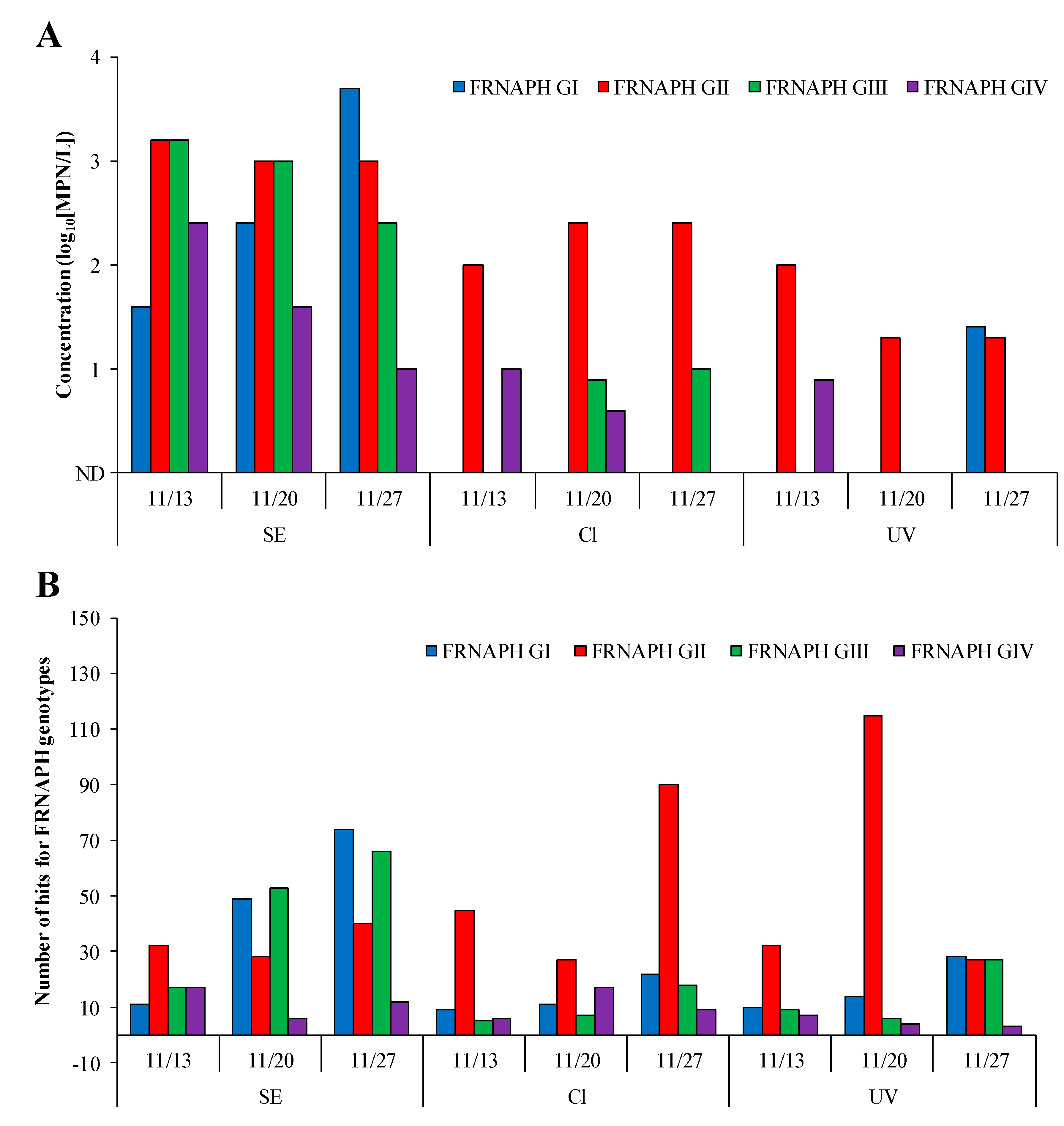
2.2. Detection of Infectious FRNAPH Strains in Wastewater Treatment and Disinfection Processes
2.3. Comparison of IC–RT-PCR–MPN and IC–NGS Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Wastewater Samples
4.2. Samples Disinfected Using Chlorine or Ultraviolet Light
4.3. IC–NGS Analysis of Infectious FRNAPH Strains
4.4. IC–RT-PCR–MPN Analysis of Infectious FRNAPH Genotypes
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IAWPRC Study Group on Health Related Water Microbiology. Bacteriophages as model viruses in water quality control. Water Res. 1991, 25, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabow, W.O.K. Bacteriophages: Update on application as models for viruses in water. Water SA 2001, 27, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, S.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Ozawa, S.; Hall, A.J.; Lee, B.Y. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PLoS ONE. 2016, 11, e0151219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelaar, A.; Van Olphen, M.; Drost, Y. F-specific RNA bacteriophages are adequate model organisms for enteric viruses in fresh water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 2956–2962. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartard, C.; Leclerc, M.; Rivet, R.; Maul, A.; Loutreul, J.; Banas, S.; Boudaud, N.; Gantzer, C. F-specific RNA bacteriophages, especially members of subgroup II, should be reconsidered as good indicators of viral pollution of oysters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Suwa, M.; Shigemura, H. Occurrence and reduction of F-specific RNA bacteriophage genotypes as indicators of human norovirus at a wastewater treatment plant. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Otagiri, M.; Morita, H.; Kitajima, M. Genogroup distribution of F-specific coliphages in wastewater and river water in the Kofu basin in Japan. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 54, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Fujino, S.; Otagiri, M. Distinct behaviors of infectious F-specific RNA coliphage genogroups at a wastewater treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 520, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Kitajima, M.; Katayama, H. Occurrence and reduction of human viruses, F-specific RNA coliphage genogroups and microbial indicators at a full-scale wastewater treatment plant in Japan. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniesa, M.; Payan, A.; Moce-Llivina, L.; Blanch, A.R.; Jofre, J. Differential persistence of F-specific RNA phage subgroups hinders their use as single tracers for faecal source tracking in surface water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, M.; Durán, A.E.; Jofre, J. Comparative resistance of phage isolates of four genotypes of F-specific RNA bacteriophages to various inactivation processes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 3702–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Blatchley, E.R., III; Shen, C.; Scheible, O.K.; Robinson, J.P.; Ragheb, K.; Bergstrom, D.E.; Rokjer, D. Validation of large-scale, monochromatic UV disinfection systems for drinking water using dyed microspheres. Water Res. 2008, 42, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijnen, W.A.M.; Beerendonk, E.F.; Medema, G.J. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo)cysts in water: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.D.; Cooper, E.M.; Casanova, L.; Sobsey, M.D.; Genthner, F.J. A reverse transcription-PCR assay to distinguish the four genogroups of male-specific (F+) RNA coliphages. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 159, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.D.; Cooper, E.M.; Calci, K.R.; Genthner, F.J. Design and assessment of a real time reverse transcription-PCR method to genotype single-stranded RNA male-specific coliphages (Family Leviviridae). J. Virol. Methods 2011, 173, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.D.; Snellgrove, W.C.; Genthner, F.J.; Division, G.E.; Breeze, G. Genomic sequences of two novel Levivirus single-stranded RNA coliphages (Family Leviviridae): Evidence for recombination in environmental strains. Viruses 2012, 1548–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, K.; Sakurai, T.; Hirashima, A.; Katsuki, M.; Ando, A.; Watanabe, I. Distribution of ribonucleic acid coliphages in South and East Asia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miyake, T.; Shiba, T.; Sakurai, T.; Watanabe, I. Isolation and properties of two new RNA phages SP and FI. Jpn. J. Microbiol. 1969, 13, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartard, C.; Rivet, R.; Banas, S.; Gantzer, C. Occurrence of and sequence variation among F-specific RNA bacteriophage subgroups in feces and wastewater of urban and animal origins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6505–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlet, J.; Gaboriaud, F.; Duval, J.F.L.; Gantzer, C. Aggregation and surface properties of F-specific RNA phages: Implication for membrane filtration processes. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2769–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudaud, N.; Machinal, C.; David, F.; Fréval-Le Bourdonnec, A.; Jossent, J.; Bakanga, F.; Arnal, C.; Jaffrezic, M.P.; Oberti, S.; Gantzer, C. Removal of MS2, Qβ and GA bacteriophages during drinking water treatment at pilot scale. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2651–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dika, C.; Ly-Chatain, M.H.; Francius, G.; Duval, J.F.L.; Gantzer, C. Non-DLVO adhesion of F-specific RNA bacteriophages to abiotic surfaces: Importance of surface roughness, hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 435, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaper, M.; Jofre, J.; Uys, M.; Grabow, W.O.K. Distribution of genotypes of F-specific RNA bacteriophages in human and non-human sources of faecal pollution in South Africa and Spain. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, D.; Long, S.C.; Sobsey, M.D. Evaluation of F+ RNA and DNA coliphages as source-specific indicators of fecal contamination in surface waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 73, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogorzaly, L.; Tissier, A.; Bertrand, I.; Maul, A.; Gantzer, C. Relationship between F-specific RNA phage genogroups, faecal pollution indicators and human adenoviruses in river water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Hewitt, J.; Rivera-Aban, M.; Greening, G.E. Detection and characterization of F+ RNA bacteriophages in water and shellfish: Application of a multiplex real-time reverse transcription PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2008, 149, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haramoto, E.; Kitajima, M.; Katayama, H.; Asami, M.; Akiba, M.; Kunikane, S. Application of real-time PCR assays to genotyping of F-specific phages in river water and sediments in Japan. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3759–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourmelon, M.; Caprais, M.P.; Mieszkin, S.; Marti, R.; Wéry, N.; Jardé, E.; Derrien, M.; Jadas-Hécart, A.; Communal, P.Y.; Jaffrezic, A.; et al. Development of microbial and chemical MST tools to identify the origin of the faecal pollution in bathing and shellfish harvesting waters in France. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4812–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieszkin, S.; Caprais, M.P.; Le Mennec, C.; Le Goff, M.; Edge, T.A.; Gourmelon, M. Identification of the origin of faecal contamination in estuarine oysters using Bacteroidales and F-specific RNA bacteriophage markers. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 115, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalupo, P.G.; Calgua, B.; Zhao, G.; Hundesa, A.; Wier, A.D.; Katz, J.P.; Grabe, M.; Hendrix, R.W.; Girones, R.; Wang, D.; et al. Raw sewage harbors diverse viral populations. MBio 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, H.; Zhang, R.; Angly, F.E.; Nakamura, S.; Hong, P.Y.; Yasunaga, T.; Kamagata, Y.; Liu, W.T. Metagenomic analysis of DNA viruses in a wastewater treatment plant in tropical climate. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibby, K.; Peccia, J. Identification of viral pathogen diversity in sewage sludge by metagenome analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aw, T.G.; Howe, A.; Rose, J.B. Metagenomic approaches for direct and cell culture evaluation of the virological quality of wastewater. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 210, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, A.; Hanamoto, S.; Shirasaka, Y.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H. Quantitative distribution of infectious F-specific RNA phage genotypes in surface waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4244–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Tasaki, S.; Hata, A.; Yamashita, N.; Tanaka, H. Evaluation of virus reduction at a large-scale wastewater reclamation plant by detection of indigenous F-specific RNA bacteriophage genotypes. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bömer, M.; Rathnayake, A.I.; Visendi, P.; Sewe, S.O.; Paolo, J.; Sicat, A.; Silva, G.; Kumar, P.L.; Seal, S.E. Tissue culture and next-generation sequencing: A combined approach for detecting yam (Dioscorea spp.) viruses. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2019, 105, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haft, D.H.; Tovchigrechko, A. High-speed microbial community profiling. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 793–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.F.; Ng, C.; Nshimyimana, J.P.; Loh, L.L.; Gin, K.Y.H.; Thompson, J.R. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) for assessment of microbial water quality: Current progress, challenges, and future opportunities. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahn, R.O. Potassium iodide as a chemical actinometer for 254 nm radiation: Use of iodate as an electron scavenger. Photochem. Photobiol. 1997, 66, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, R.O.; Stefan, M.I.; Bolton, J.R.; Goren, E.; Shaw, P.S.; Lykke, K.R. Quantum yield of the iodide-iodate chemical actinometer: Dependence on wavelength and concentrations. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003, 78, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FRNAPH Genotype | FRNAPH Strain | Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI | MS2 | Sewage | [14,15,16] |
| M12 | Sewage | [14,15,16] | |
| DL1 | River water | [14,15,16] | |
| DL2 | Bay water | [14,15,16] | |
| DL13 | Oyster | [14,15,16] | |
| DL16 | Bay water | [14,15,16] | |
| J20 | Chicken litter | [14,15,16] | |
| ST4 | Unknown | [14,15,16] | |
| R17 | Sewage | [14,15,16] | |
| Fr | Dung hill | [14,16] | |
| JP501 | Sewage | [17] | |
| GI-JS | DL52 | Bay water | [16] |
| DL54 | Bay water | [16] | |
| GII | GA | Sewage | [14,15,16,17] |
| KU1 | Sewage | [14,15,16,17] | |
| DL10 | Mussel | [14,15,16] | |
| DL20 | Clam | [14,15,16] | |
| T72 | Bird | [14,15,16] | |
| BZ13 | Sewage | [17] | |
| TL2 | Sewage | [17] | |
| JP34 | Sewage | [17] | |
| TH1 | Sewage | [17] | |
| GIII | Qβ | Human feces | [14,15,17] |
| BR12 | Creek water | [14,15] | |
| BZ1 | Sewage | [14,15] | |
| VK | Sewage | [14,15,17] | |
| TW18 | Sewage | [14,15,17] | |
| HL4-9 | Hog lagoon | [14,15] | |
| M11 | Unknown | [14,15] | |
| MX1 | Sewage | [14,15,17] | |
| GIV | SP | Siamang gibbon | [14,15,17,18] |
| FI | Infant | [14,15,17,18] | |
| BR1 | Creek water | [14,15] | |
| BR8 | Creek water | [14,15] | |
| HB-P22 | Bird | [14,15] | |
| HB-P24 | Bird | [14,15] | |
| NL95 | Calf | [14,15] |
| Date (Month/Day) | Sample 2 | No. of Total Reads | No. of Contigs | No. of Hits for FRNAPHs (Ratio) | No. of Hits for Bacteria (Ratio), [No. of Hits for Salmonella enterica (ratio)] 3 | No. of not Hit Contigs (Ratio) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11/13 | IN | 1,135,519 | 1218 | 317 (26%) | 584 (48%), [380 (65%)] | 200 (16%) |
| SE | 1,080,326 | 537 | 87 (16%) | 343 (64%), [261 (76%)] | 66 (12%) | |
| Cl | 887,593 | 611 | 73 (12%) | 476 (78%), [414 (87%)] | 30 (5%) | |
| UV | 1,278,120 | 732 | 66 (9%) | 608 (83%), [548 (90%)] | 41 (6%) | |
| 11/20 | IN | 1,070,341 | 1299 | 468 (36%) | 570 (44%), [459 (81%)] | 196 (15%) |
| SE | 1,019,493 | 614 | 160 (26%) | 310 (50%), [220 (71%)] | 95 (15%) | |
| Cl | 1,033,979 | 776 | 91 (12%) | 591 (76%), [532 (90%)] | 52 (7%) | |
| UV | 1,025,377 | 821 | 162 (20%) | 577 (70%), [505 (88%)] | 36 (4%) | |
| 11/27 | IN | 4,092,357 | 18,941 | 551 (3%) | 10,471 (55%), [2521 (24%)] | 6859 (36%) |
| SE | 4,900,897 | 4344 | 247 (6%) | 2537 (58%), [1825 (72%)] | 1151 (26%) | |
| Cl | 5,035,503 | 4370 | 161 (4%) | 3484 (80%), [3217 (92%)] | 497 (11%) | |
| UV | 4,102,143 | 2319 | 106 (5%) | 1655 (71%), [1416 (86%)] | 497 (21%) |
| Parameter 1 | Units | Range | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IN 2 | SE 2 | ||
| pH | - | 7.1–7.3 | 6.8–6.9 |
| CODcr | mg/L | 120–140 | 11–14 |
| SS | mg/L | 47–78 | 4.7–6.7 |
| Turbidity | NTU | 37–44 | 1.2–2.8 |
| T-N | mg/L | 31–34 | 15–17 |
| T-P | mg/L | 9.4–9.6 | 4.8–5.2 |
| NH4+-N | mg/L | 20–24 | 0.12–0.27 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Suwa, M.; Shigemura, H. Metagenomic Analysis of Infectious F-Specific RNA Bacteriophage Strains in Wastewater Treatment and Disinfection Processes. Pathogens 2019, 8, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040217
Lee S, Suwa M, Shigemura H. Metagenomic Analysis of Infectious F-Specific RNA Bacteriophage Strains in Wastewater Treatment and Disinfection Processes. Pathogens. 2019; 8(4):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Suntae, Mamoru Suwa, and Hiroyuki Shigemura. 2019. "Metagenomic Analysis of Infectious F-Specific RNA Bacteriophage Strains in Wastewater Treatment and Disinfection Processes" Pathogens 8, no. 4: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040217
APA StyleLee, S., Suwa, M., & Shigemura, H. (2019). Metagenomic Analysis of Infectious F-Specific RNA Bacteriophage Strains in Wastewater Treatment and Disinfection Processes. Pathogens, 8(4), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040217





