Abstract
A cross-sectional survey was conducted in 2014–2016 in 301 ruminant herds to estimate C. jejuni and C. coli prevalence, and investigate their susceptibility to antimicrobials. Risk of shedding C. jejuni was higher in cattle than sheep (81.2% vs. 45.2%; ORadj = 5.22, p < 0.001), whereas risk of shedding C. coli was higher in sheep than in cattle (19.1% vs. 11.3%; ORadj = 1.71, p = 0.128). Susceptibility to six antimicrobials was determined by broth microdilution using European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) epidemiological cut-off values. C. coli exhibited higher resistance (94.1%, 32/34) than C. jejuni (65.1%, 71/109), and resistance was more widespread in isolates from dairy cattle than beef cattle or sheep. Compared to results obtained 10-years earlier (2003–2005) in a similar survey, an increase in fluoroquinolone-resistance was observed in C. jejuni from beef cattle (32.0% to 61.9%; OR = 3.45, p = 0.020), and a decrease in tetracycline-resistance in C. jejuni from dairy cattle (75.0% to 43.2%; OR = 0.25, p = 0.026). Resistance to macrolides remained stable at low rates and restricted to C. coli from dairy cattle, with all macrolide-resistant C. coli showing a pattern of pan-resistance. Presence of the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated to quinolone and macrolide resistance was confirmed in all phenotypically resistant isolates. The increase in fluoroquinolone resistance is worrisome but susceptibility to macrolides is reassuring.
1. Introduction
Campylobacter is the main cause of food-borne gastroenteritis in industrialized countries and the cause of the most frequently reported zoonosis in the European Union (EU). In 2017, 246,158 confirmed cases of campylobacteriosis in humans were reported in the EU, which accounted to an average notification rate of 64.8 per 100,000 population []. In the Basque Country, notification rate in the same year was 104.2/100,000 inhabitants, mainly concentrating among young patients (40.6% in <5 years-old and 20.6% in 5–14 years-old) []. The sporadic nature of Campylobacter infection causes underreporting and hampers the identification of the infection source []. Although poultry is the principal source for human infection, Campylobacter is also highly prevalent in ruminants worldwide, and there is increasing evidence that the contribution of ruminant Campylobacter to campylobacteriosis in humans is also considerable, with cattle being the second most important reservoir after broilers for C. jejuni human infection and sheep the first for C. coli infections in humans [,]. Contamination of red meat is infrequent [] and does not seem to play a major risk for human infection, but contaminated raw milk is a frequent vehicle of foodborne infection []. In addition, Campylobacter from ruminant feces can contaminate water supplies and fresh products via agricultural run-off water []. Finally, humans can also get infected by contact with animals. Hence, ruminants are important reservoirs for zoonotic campylobacters and source of contamination for the environment and other animals. Antimicrobial resistance is another subject of concern. Antimicrobial therapy is only recommended in systemic and severe Campylobacter infections or in immunocompromised patients. However, the emergence of Campylobacter strains resistant to the antimicrobial agents of choice (macrolides for laboratory-confirmed cases and fluoroquinolones for cases of diarrhea) compromises the therapeutic efficacy [,].
Despite the role of ruminant Campylobacter in human campylobacteriosis [,,], the number of studies that estimate Campylobacter prevalence in ruminants (dairy cattle, beef cattle and sheep) and investigate their susceptibility to antimicrobials is small compared to the large number of studies carried out in poultry. In a previous study (2003–2006) carried out in ruminants in the Basque Country (Northern Spain), 62.1% of cattle herds and 55.0% of sheep flocks were Campylobacter-positive, identifying C. jejuni and C. coli in 21.8% and 5.9% of the farms, respectively []. In that study, all thermotolerant Campylobacter species were targeted and only one isolate per positive farm was identified, so that species like C. hyointestinalis in cattle or C. lanienae in sheep contributed to the high prevalence of the genus Campylobacter []. A few C. jejuni isolates were then characterized for antimicrobial resistance showing high levels of resistance to tetracyclines and quinolones []. Now, 10 years later (2014–2016), a similar number of farms was surveyed but targeting only the main zoonotic species and performing a more exhaustive analysis of isolates with the following objectives: (i) To update herd-level prevalence estimates of C. jejuni and C. coli in ruminant herds in the Basque Country; (ii) to determine the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) profiles of C. jejuni and C. coli; (iii) to compare antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter isolated from ruminants in two studies carried out 10-years apart; and, (iv) to investigate the potential of a highly discriminatory and rapid method for estimating the true prevalence of Campylobacter macrolide-resistance under an apparently low prevalence situation.
2. Results
2.1. Campylobacter Herd Prevalence
The proportion of herds positive to C. jejuni and/or C. coli was 78.8% (82/104) of beef cattle, 86.6% (71/82) of dairy cattle and 54.8% (63/115) of sheep flocks, the difference in proportions being statistically significant between cattle and sheep (p < 0.001) (Figure 1). C. jejuni was the most frequently detected species, present in 85.4% of dairy cattle herds, 77.9% of beef cattle herds, and 45.2% of sheep flocks, whereas C. coli was found in 17.1% of dairy cattle herds, 6.7% of beef cattle herds and 19.1% of sheep flocks. In 10.0% (30/301) of the tested herds/flocks both C. jejuni and C. coli were detected. Univariate analysis did not identify any significant explanatory variables associated to Campylobacter shedding. Multivariate analysis using host species (cattle vs. sheep) as principal explanatory variable for C. jejuni herd prevalence showed that cattle presented significantly higher risk of shedding C. jejuni than sheep (ORadj = 5.22 (3.11–8.89), p < 0.001), and also when considering the farm system as the principal variable and comparing beef cattle and dairy cattle with sheep separately (dairy cattle vs. sheep: ORadj = 7.07 (3.46–14.43), p < 0.001; beef cattle vs. sheep: ORadj = 4.27 (2.36–7.70), p < 0.001). No associations were found between C. jejuni or C. coli shedding and any of the other variables tested. Risk of shedding C. coli was non-significantly higher in sheep than in cattle (ORadj = 1.71 (0.86–3.40), p = 0.128). However, no differences were found between dairy and beef cattle.
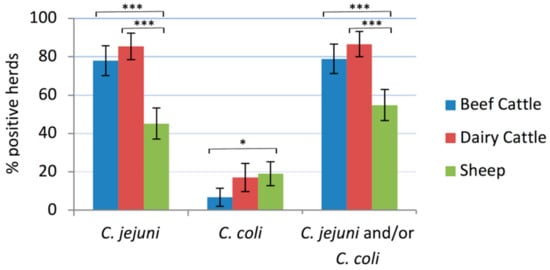
Figure 1.
Prevalence of Campylobacter-positive herds/flocks in each host. The error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals (*, p ≤ 0.05; ***, p ≤ 0.001).
2.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests
Sensitivities to six antimicrobials (four classes) were determined by broth microdilution for 109 C. jejuni isolates and 34 C. coli isolates; distributions of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are shown in Table 1. Isolates susceptible to all antimicrobials tested, accounted for a total of 28.0%. Except for ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid, resistance against all other antimicrobials was significantly more widespread among C. coli than C. jejuni isolates (Figure 2) and the magnitude of this difference was higher in isolates from cattle than sheep, and higher in dairy cattle than beef cattle or sheep (Table 2). Overall, 65.1% (71/109) of C. jejuni and 94.1% (32/34) of C. coli isolates showed resistance to at least one of the six antimicrobial agents tested. C. coli exhibited higher resistance to tetracycline (76.5%), streptomycin (67.6%) and quinolones (64.7%), whereas in C. jejuni resistance to quinolones (60.6%) was the most common followed by resistance to tetracycline (38.5%) (Table 1). Resistance to quinolones was always present as resistance to both ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid. Resistance to aminoglycosides varied depending on the antimicrobial agent and the Campylobacter species. Thus, whereas all C. jejuni were susceptible to gentamicin, 3.7% were resistant to streptomycin; in the case of C. coli, resistance to gentamicin was moderate (11.8%) but very high for streptomycin (67.7%). Finally, resistance to erythromycin (macrolide) was low (8.8%) and only detected in C. coli isolated from dairy cattle herds. No relationship was found between host species or farm system and resistance against each of the antimicrobial agents tested in neither C. jejuni nor C. coli isolates. However, MIC values for C. jejuni susceptible to gentamicin and streptomycin were higher in sheep than in cattle isolates (p = 0.040 and p = 0.009, respectively), whereas MICs for C. coli resistant to ciprofloxacin and tetracycline were higher in cattle than in sheep isolates (p = 0.011 and p = 0.029, respectively).

Table 1.
Microbiological resistance (percentage) and distribution of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for the 109 C. jejuni and 34 C. coli isolates.
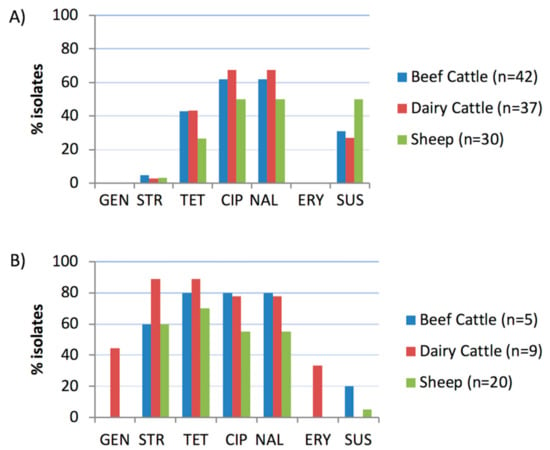
Figure 2.
Proportion of isolates resistant to each antimicrobial agent tested: (A) C. jejuni; (B) C. coli. GEN, gentamicin; STR, streptomycin; TET, tetracycline; CIP, ciprofloxacin; NAL, nalidixic acid; ERY, erythromycin; SUS, susceptible to all six antimicrobials.

Table 2.
Odds ratio (OR) of association between resistance to each antimicrobial and Campylobacter species for each host, determined with simple logistic regression analysis using C. jejuni as reference.
The distribution of the AMR profiles resulting from the combination of the antimicrobials tested varied according to Campylobacter species, but only C. coli isolates presented different profiles according to host (Figure 3). Resistance to both quinolones and tetracycline, which was present in 33.9% of C. jejuni and 58.8% of C. coli isolates, was the combination most commonly found. Multidrug resistance (MDR), defined as resistance to three or more classes of antimicrobial agents, was present in significantly higher proportions (odds ratio (OR) = 20.72, p < 0.001) in C. coli (44.1%, 15/34) than in C. jejuni (3.7%, 4/109) isolates and, albeit at different levels, this trend was observed in each host (Figure 4). Thus, MDR was more likely to occur in C. coli than in C. jejuni, being the odds ratios much higher in cattle than sheep (OR = 45.60 vs. 12.43), and considerably higher in dairy cattle (OR = 72.00) (Table 2). Among C. jejuni isolates, no difference in MDR related to host was detected, and among C. coli, MDR was marginally more frequent in isolates from cattle than sheep (OR = 4.20 (0.98–17.95), p = 0.053). The most common MDR pattern was to CIP-NAL-STR-TET (Figure 3). All three C. coli isolates resistant to erythromycin were also resistant to all other antimicrobials tested. Overall, dairy cattle were the host species that harbored the highest percentage of multidrug resistant Campylobacter isolates (15.2%) at similar levels as sheep (14.0%), whereas beef cattle had the lowest (10.6%) (Figure 4).
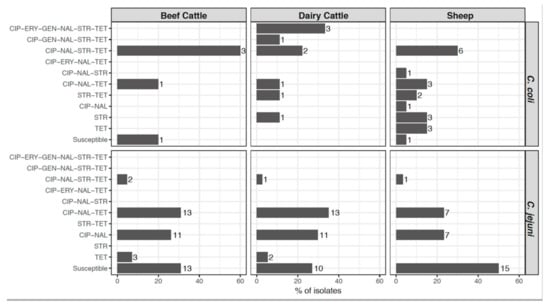
Figure 3.
Distribution of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) patterns according to Campylobacter species and host. Percentage of each AMR pattern was calculated for each Campylobacter species in each host, and numbers beside the bars represent the number of isolates. CIP, ciprofloxacin; ERY, erythromycin; GEN, gentamicin; NAL, nalidixic acid; STR, streptomycin; TET, tetracycline.
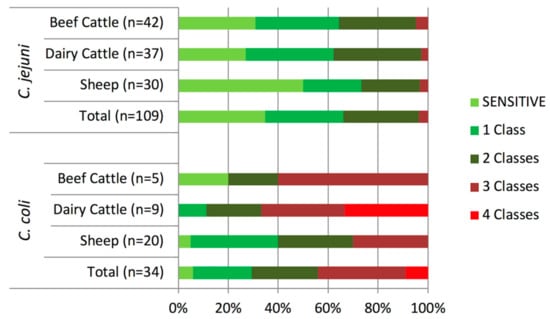
Figure 4.
Distribution of isolates resistant to 1–4 classes of antimicrobial agents according to Campylobacter species and host.
2.3. Real-Time PCR Discrimination of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Associated to Quinolone and Macrolide Resistance
Sequencing analysis demonstrated the analytical specificity of the newly developed TaqMan assay to detect the point mutation C257T in the gyrA gene of quinolone-resistant C. coli. The results obtained with the real-time PCR SNP discrimination assays were in fully agreement with the phenotypic antimicrobial sensitivity test results. Thus, all C. jejuni (66) and C. coli (24) isolates that were phenotypically resistant to ciprofloxacin and nalidixic acid contained the C257T mutation in the gyrA gene. However, one C. coli isolate from a sheep farm failed to give any hybridization results when analyzed with the C. coli-specific gyrA SNP detection real-time PCR, but provided a resistant profile when using the C. jejuni-specific gyrA SNP assay. Sequencing analysis of the gyrA gene demonstrated that this isolate had a typical C. jejuni gyrA allele. The SNP mutation associated to resistance to macrolides (A2075G in the 23S rRNA genes) was found in the only three C. coli isolates that were phenotypically resistant to erythromycin. In all three isolates, MIC values were far above the highest concentration tested (>128 mg/L) and therefore far higher than the MIC epidemiological cut-off value.
2.4. Isolation of Macrolide-Resistant Campylobacter Using a PCR-Based Screening Method Followed by Selective Isolation
Macrolide-resistant Campylobacter was only isolated from one dairy cattle herd when directly picking colonies from the CASA® plate without selective isolation. When DNA extracted from CASA® cultures that tested C. jejuni and/or C. coli-positive were screened by real-time PCR for the macrolide-resistance associated SNP, another three dairy cattle herds tested positive, and in two of them erythromycin-resistant C. coli strains were confirmed after selective isolation in erythromycin-containing media; in the third herd no isolates could be recovered. Hence, prevalence of dairy cattle shedding macrolide-resistant Campylobacter was 3.7% (3/82) of herds.
2.5. Changes in Campylobacter Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Two Studies Carried Out 10-Years Apart
Comparison of results from this study (2014–2016) and those from the study carried out 10 years earlier (2003–2005) showed a significant increase in the proportion of fluoroquinolone resistance in C. jejuni isolates from beef cattle (61.9% in 2014–2016 vs. 32.0% in 2003–2005; OR= 3.45 (1.21–9.83), p = 0.020). However, resistance to tetracyclines in C. jejuni from dairy cattle decreased from 75.0% to 43.2% (OR = 0.25 (0.08 – 0.85), p = 0.026). In C. coli, no significant changes were observed in the proportion of isolates resistant to each antimicrobial, but MIC values among isolates susceptible to erythromycin were significantly lower in the present study (p < 0.001), particularly in isolates from beef cattle (p = 0.034).
2.6. Campylobacter coli Strain Characterization by Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
MLST analysis of 34 C. coli isolates resulted in 13 ST-types, 12 of them belonging to clonal complex (CC)-828 and another (ST-8857) not assigned to any recognized CC, and described in this study for the first time. The most common ST type (ST-827) accounted for 38.2% of the C. coli isolates typed, and was the most prevalent type in sheep (11/20 isolates; 55.0%) but not in cattle (2/14; 14.3%). All macrolide resistant isolates belonged to ST-2097, a ST-type associated to the three macrolide-resistant C. coli isolates plus another MDR C. coli (CIP-NAL-GEN-STR-TET) isolated also from dairy cattle.
3. Discussion
This cross-sectional study provided estimates of C. jejuni and C. coli herd prevalence in dairy cattle, beef cattle and sheep in the Basque Country, along with a collection of representative strains and their corresponding antimicrobial resistance profiles. Results showed a widespread distribution of both zoonotic Campylobacter species in ruminants, prevalence being higher than that reported in a study carried out in the same region in 2003–2005 [], an apparent increase that can most likely be ascribed to changes in methodology rather than reflect a real increment. Still, similarly high Campylobacter herd level prevalence has been reported in other studies [,,]. Also consistently with other studies in ruminants [,], we found that cattle presented significantly higher risk of shedding C. jejuni than sheep, while risk of shedding C. coli was non-significantly higher in sheep than in cattle. This situation might reflect differences in the epidemiology of C. jejuni and C. coli. In this sense, increasing evidence suggests that sources and epidemiology of C. coli and C. jejuni infections are different. Thus, whereas sheep are associated to only 2.5%–24% of C. jejuni human infections [,], 41% of human C. coli clinical cases were attributed to sheep, a proportion similar to that assigned to chicken (40%) and lower than that attributed to cattle (14%) []. The higher prevalence of C. coli in sheep flocks as described here might explain the significant contribution of sheep to human infection with C. coli. On the other hand, it has been suggested that strains isolated from sheep belonged to genotypes that commonly cause disease in humans. Here, half of the strains from sheep belonged to ST-827, one of the genotypes most frequently found in humans []. Our MLST results also confirmed the low diversity of C. coli STs of ruminant origin compared to C. jejuni [] or compared to C. coli from swine or poultry []. All but one belonged to the same clonal complex (CC-828) but still, one novel ST was described here (ST-8857). Interestingly, one C. coli isolate from a sheep farm (ST-5380) showed a typical C. jejuni gyrA sequence suggestive of genome introgressed from C. jejuni as previously described for other C. coli strains belonging to CC-828 [].
Regarding AMR, differences in methodology and results interpretation hamper comparisons among studies available in the bibliography. Here, EU harmonized methods were used, MICs were determined by broth microdilution, and European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) epidemiological cut-off values were used to determine microbiological resistance []. In this study, resistance against all antimicrobials tested except quinolones was more widespread in C. coli than in C. jejuni in all three host species, as was MDR. An overall higher resistance in C. coli than C. jejuni has already been reported in different hosts and for different antibiotics [,,,,]. Overall, the highest resistance levels were found for fluoroquinolones (61.5%) followed by tetracycline (47.6%). This represented an increase in the proportion of C. jejuni isolates resistant to fluoroquinolones in beef cattle between the two studies carried out 10-years apart but a decrease in resistance to tetracyclines in dairy cattle. In fact, resistance to tetracycline was much lower than that reported for C. jejuni isolated from calves in Spain (83.3%) within the EU survey on AMR in zoonotic and indicator bacteria in 2017 []. Although overall sales have decreased in the last years, tetracyclines have been used in livestock for many years and in 2016 still accounted for the largest sales (ca. 32% of total sales) in the EU and Spain []. This would explain the high levels of tetracycline resistance often reported in Campylobacter from food-producing animals []. The high frequency of fluoroquinolone resistance observed in this study is worrisome, while susceptibility to macrolides is reassuring. Increased resistance of Campylobacter to fluoroquinolones has been reported worldwide [,], but the levels of fluoroquinolone resistance in both C. jejuni and C. coli observed in the present study were higher than those found in ruminants in other EU countries [,,], though lower than resistance rates described for poultry and pigs in Spain [,]. Use of fluoroquinolones is much higher in Spain than the European average []. In a survey carried out among veterinary clinicians in the region (unpublished results), fluoroquinolones were mentioned to be mostly used for diarrhea and respiratory diseases in cattle, similar to data reported elsewhere for Spain []. Although the gyrA mutation associated to fluoroquinolone resistance has been described to impose certain fitness burden on Campylobacter [], once fluoroquinolone resistant Campylobacter is prevalent it can persist for years even in the absence of antibiotic selection pressure so that a reversal in resistance trend might be difficult to achieve []. Resistance to macrolides was significantly lower and only detected in C. coli isolated from dairy cattle and at similar levels to those reported elsewhere [,,] and in the study carried out 10-years earlier. This is most probably due to the comparatively infrequent use of macrolides in ruminants and the highest fitness cost associated to resistance []. Also reassuring was the fact that MIC values among isolates susceptible to erythromycin were significantly lower in the present study than 10 years before. However, macrolide-resistant isolates from both studies were resistant to high concentrations of erythromycin (>128 mg/L) and in most cases co-resistant to fluoroquinolones, tetracycline and aminoglycosides. This pattern of MDR has been associated to the presence of a transferable chromosomal MDR genomic island (MDRGI) that contains the rRNA methylase erm(B) gene []. Resistance to aminoglycosides was found in a very small proportion of C. jejuni isolates, lower than that reported in the EU for cattle isolates []. In C. coli resistance to aminoglycosides was higher, reaching similar levels to those reported in isolates from pigs []. Thus, combined resistance to critically important antimicrobials was absent in C. jejuni, but all C. coli isolates resistant to erythromycin were also resistant to fluoroquinolones.
Finally, the PCR-based screening method followed by selective isolation in erythromycin-containing media developed here allowed the isolation of macrolide-resistant C. coli in two herds that had tested negative when using non-selective isolation. Results demonstrated the usefulness of the method in providing more reliable estimates of macrolide-resistance than procedures that analyze a single colony per sample and likely underestimate the real prevalence. Under a low prevalence situation, PCR screening followed by selective isolation provides the processability needed to carry out extensive antimicrobial surveillance. Here it was only applied to macrolides, but a similar approach could also be used to screen for C. jejuni and C. coli quinolone resistance prevalence in regions where expected resistance levels were not as high as those found here.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sampling Design
A cross-sectional survey was carried out to estimate the prevalence of C. jejuni and C. coli in cattle herds and sheep flocks in the Basque Country (Northern Spain). Cattle included both dairy and beef herds, and sheep were of the Latxa dairy breed. Details on general husbandry systems for beef cattle, dairy cattle and sheep in the region were reported elsewhere []. Briefly, while dairy cattle are mostly housed in pens, beef cattle and sheep are managed under a semi-intensive system where animals graze in farmland pastures in spring and part of the summer, and in communal mountain pastures from the middle of July until the end of November, and are housed in winter. In all cases, animals of all ages are raised in the herd (suckler herds), and intensive feedlot systems are not used in the region. The census of beef cattle, dairy cattle and sheep farms was obtained from the Department of Agriculture of the Basque Government. The number of herds to sample was then calculated separately for each animal category for an expected herd prevalence of 50%, a 95% confidence level and an accuracy of 10% using Win Episcope 2.0. A sample size of 25 animals per herd was selected after estimating a within-herd prevalence of 10% and a level of confidence of at least 90% in detecting a positive.
Sampling was carried out throughout the year, and a total of 301 herds (115 dairy sheep, 104 beef and 82 dairy cattle) were visited once between February 2014 and June 2016. Rectal fecal samples from 25 animals randomly selected per herd were collected with a gloved hand, and a 25 g-pool was prepared (1 g per animal per pool) for microbiological analyses. Sample collection was carried out by veterinary clinicians as part of the usual health monitoring procedures performed on farms, strictly following Spanish ethical guidelines and animal welfare regulations (Real Decreto 53/2013). The collection of this material, being considered as routine veterinary practice, did not require the approval of the Ethics Committee for Animal Experimentation. Informed oral consent was obtained from the farm owners at the time of sample collection.
4.2. Campylobacter Isolation and Identification
For the isolation of thermophilic Campylobacter spp., 25 g of pooled rectal fecal samples were diluted 1/10 in Preston broth, homogenized and incubated for 18±2 h at 42 ℃ for enrichment. Suspensions (0.1 mL) were then subcultured onto a Chromogenic-Campylobacter Selective Agar (CASA® Agar, Biomerieux) and incubated at 42 ℃ in a microaerobic atmosphere (5% O2, 10% CO2, 85% N2) for 48–72 h. To confirm the presumptive Campylobacter and identify the species present in the pool of feces, DNA was extracted from a loopful of bacterial culture (InstaGene, BioRad, CA, USA) and screened for the presence of C. jejuni and C. coli in a multiplex real-time PCR (TaqMan® Campylobacter Multiplex assay, ThermoFisher Diagnostics). Individual colonies were then tested using the same multiplex real-time PCR to confirm their identity and were stored for further characterization.
4.3. Antimicrobial Resistance: Broth Microdilution Tests and SNP Discrimination by Real-Time PCR
Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) were determined by broth microdilution using Sensititre® MIC Susceptibility Plate (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) containing two-fold serial dilutions of six antimicrobial agents (gentamicin, streptomycin, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, nalidixic acid and erythromycin) following recommendations by the Commission Decision 2013/652/EU. MIC results were interpreted using epidemiological cut-off values (ECOFF) as developed by the European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST, http://www.eucast.org) to define microbiological resistance.
TaqMan real-time PCR assays were used to detect point mutations associated to macrolide (A2075G mutation in the 23S rRNA genes) and quinolone (C257T in the gyrA gene, Thr-86-Ile) resistance. Primers and probes used for C. jejuni (macrolide and quinolone) and C. coli (macrolide) were as described before []. To detect point mutations associated to quinolone resistance (C257T in the gyrA gene) in C. coli, new primers and probes targeting a 101 bp fragment of the gyrA gene of C. coli were designed in this study (Table 3). PCR reactions and cycling conditions were as previously described []. The analytical specificity of the newly developed TaqMan assay to detect the point mutation C257T in the gyrA gene of C. coli was confirmed by sequencing analysis of the gyrA gene amplicon of control strains generated with the primers described in Table 3.

Table 3.
Primers and probes used to detect point mutations associated to macrolide (A2075G mutation in the 23S rRNA genes) and quinolone (C257T in the gyrA gene, Thr-86-Ile) resistance in C. jejuni and C. coli, and gyrA sequencing.
4.4. PCR-Based Screening Method for the Isolation of Macrolide-Resistant Campylobacter
In order to increase chances of isolation of macrolide-resistant Campylobacter (whose prevalence was expected to be very low), a PCR-based screening method followed by selective isolation in media containing erythromycin was assessed. Thus, DNA was extracted from a loopful of bacterial culture grown in CASA® agar (see Section 4.2) from all samples identified as C. jejuni and/or C. coli-positive and screened with the macrolide SNP real-time PCR assay as described above but using only the probe that detects the resistant SNP (G in nt 2075 of the 23S rRNA gene). All samples that tested PCR-positive were then selectively isolated in Preston broth supplemented with erythromycin (4mg/L, 18±2 h at 42 ℃), and individual colonies (presumptive macrolide-resistant colonies) were identified to the species level by real-time PCR and MICs were determined as above.
4.5. Assessment of Changes in Campylobacter Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Two Studies Carried Out 10-Years Apart
Antimicrobial resistance profiles were available for a 53 C. jejuni isolates from a similar study carried out in the region in 2003–2005 (Oporto et al., 2009). As part of this study, MIC values and presence of point mutation associated to quinolone and macrolide resistance were determined for a further 32 C. jejuni and 17 C. coli isolates from that previous study. Statistical analyses of the results from both studies were performed as described below (Section 4.7).
4.6. Campylobacter coli Strain Characterization by Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
C. coli DNA was extracted from pure cultures using InstaGene (Bio-Rad, Berkeley, CA, USA) and subjected to multilocus sequence typing (MLST) of seven housekeeping genes (aspA, glnA, gltA, glyA, pgm, tkt and uncA) as previously described [,]. The sequences obtained were queried against the Campylobacter MLST database PubMLST (http://pubmlst.org/campylobacter/), developed by Keith Jolley and Man-Suen Chan and sited at the University of Oxford, for type (ST) and clonal complex (CC) assignation. Novel STs were submitted to the Campylobacter MLST database for assignation of new numbers.
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Herd-level prevalences were expressed as the percentage of herds/flocks that tested positive in each farm system out of all herds/flocks that were examined in the respective farm system, with 95% confidence intervals adjusted for the population size, using the software EpiInfo2. Variables selected to check for statistical differences in shedding prevalence of each pathogen (i.e., thermophilic Campylobacter, C. jejuni, C. coli) were categorized as follows: Host species (cattle, sheep); farm system (beef cattle, dairy cattle and sheep); sampling season (spring, summer, autumn, winter), geographical location of the farm (oceanic, continental); and presence of other species in the farm such us cattle, sheep, goats, horses (presence, absence). First, univariate logistic regressions were conducted to explore the unadjusted association between herd positivity and variables. Only significant factors (p ≤ 0.20; likelihood-ratio test) were included for further multivariate logistic regression analysis. Test of overall significance (chunk test) was performed to assess any possible effect modifiers that could bias the magnitude of associations, and interactions with a value of p > 0.05 were excluded until no significant difference between the full and the reduced models was observed. To identify confounding variables, the measure of association was estimated before and after adjusting for the potential confounder, and variables causing change of ≥ 10% in the estimated measure were retained. Adjusted odds ratios (ORadj) were used as the measure of association between positivity and the explanatory variable, and were expressed with their confidence interval at 95% (95% CI).
Simple logistic regression tests were performed to determine associations between resistance against the antimicrobial agents tested and host species (sheep vs. cattle) or farm system (beef cattle, dairy cattle and sheep). The same approach was also used to investigate whether resistance against each antimicrobial agent was more likely to be present on either C. jejuni or C. coli, stratifying the dataset by host species or farm system. Linear regression analyses were performed to compare log2 transformed MIC values among host species and farm system, performing independent tests for susceptible and resistant isolates. Results from this study (2014–2016) and those from the study carried out 10 years earlier (2003–2005) were also compared. Qualitative assessment (resistant or susceptible outcome) was done with logistic regression and quantitative comparisons (log2 MIC, mg/L) with linear regression. In all cases, regression analyses were performed separately for C. jejuni and C. coli and for each specific antimicrobial agent. All analyses were conducted in Stata/IC version 13.1 statistical software (StataCorp LP) and figures were elaborated with Microsoft Excel and with ggplot2 package of R statistical software (v.3.3.2).
5. Conclusions
This study showed a widespread distribution of C. jejuni and C. coli in ruminants, with cattle as the main reservoir of C. jejuni and sheep of C. coli, thus highlighting the importance of non-poultry reservoirs for Campylobacter infection. AMR was significantly more prevalent among C. coli than C. jejuni isolates, and higher in isolates from dairy cattle than beef cattle or sheep. An increase in fluoroquinolone resistance was observed, highlighting the need to promote prudent use of these antimicrobials. Resistance to macrolides, the antibiotic of choice for the treatment of Campylobacter-associated diarrhea (especially in infants), remained stable at low rates and restricted to C. coli, which was reassuring. Still, antimicrobial surveillance in campylobacters from livestock is needed for early detection of emerging resistance, and the PCR-based screening method developed here proved to be a valuable tool to achieve the processability required for the analysis of a relatively large number of samples.
Author Contributions
Sample and data collection and laboratory analysis: B.O. & M.O. Statistical analysis: M.O. Interpretation of results and writing of the manuscript: A.H. & M.O. Design and coordination of the study and final drafting of the manuscript: A.H. All authors contributed in reviewing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Basque Government. M.O. is the recipient of a predoctoral fellowship from the Basque Government (Departamento de Desarrollo Económico e Infraestructuras, Ekonomiaren Garapen eta Lehiakortasun Saila, Eusko Jaurlaritza).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the veterinary staff from the Diputaciones Forales de Gipuzkoa, Bizkaia and Araba, and the farmers for their collaboration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5500. [Google Scholar]
- Anonymous. Informe 2017: Salud Pública y Adicciones; Servicio Central de Publicaciones del Gobierno Vasco: Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Ivarsson, S.; Löfdahl, M.; Nauta, M.J. Estimating the true incidence of campylobacteriosis and salmonellosis in the European Union, 2009. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Dallas, J.F.; Strachan, N.J.C.; MacRae, M.; McCarthy, N.D.; Wilson, D.J.; Gormley, F.J.; Falush, D.; Ogden, I.D.; Maiden, M.C.J.; et al. Campylobacter genotyping to determine the source of human infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, F.; Sproston, E.; Rotariu, O.; MacRae, M.; Sheppard, S.K.; Bessell, P.; Smith-Palmer, A.; Cowden, J.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Forbes, K.J.; et al. Elucidating the aetiology of human Campylobacter coli infections. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs-Reitsma, W.; Wagenaar, J. Campylobacter in the food supply. In Campylobacter; Nachamkin, I., Szymanski, C., Blaser, M., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-1-55581-437-3. [Google Scholar]
- Heuvelink, A.E.; van Heerwaarden, C.; Zwartkruis-Nahuis, A.; Tilburg, J.J.H.C.; Bos, M.H.; Heilmann, F.G.C.; Hofhuis, A.; Hoekstra, T.; de Boer, E. Two outbreaks of campylobacteriosis associated with the consumption of raw cows’ milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 134, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.G.; Price, L.; Ahmed, R.; Woodward, D.L.; Melito, P.L.; Rodgers, F.G.; Jamieson, F.; Ciebin, B.; Li, A.; Ellis, A. Characterization of waterborne outbreak–associated Campylobacter jejuni, Walkerton, Ontario. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luangtongkum, T.; Jeon, B.; Han, J.; Plummer, P.; Logue, C.M.; Zhang, Q. Antibiotic resistance in Campylobacter Emergence, transmission and persistence. Future Microbiol. 2009, 4, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, K.; Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance mechanisms among Campylobacter. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 340605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mughini Gras, L.; Smid, J.H.; Wagenaar, J.A.; de Boer, A.G.; Havelaar, A.H.; Friesema, I.H.M.; French, N.P.; Busani, L.; van Pelt, W. Risk factors for campylobacteriosis of chicken, ruminant, and environmental origin: A combined case-control and source attribution analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullner, P.; Spencer, S.E.F.; Wilson, D.J.; Jones, G.; Noble, A.D.; Midwinter, A.C.; Collins-Emerson, J.M.; Carter, P.; Hathaway, S.; French, N.P. Assigning the source of human campylobacteriosis in New Zealand: A comparative genetic and epidemiological approach. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2009, 9, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oporto, B.; Esteban, J.I.; Aduriz, G.; Juste, R.A.; Hurtado, A. Prevalence and strain diversity of thermophilic campylobacters in cattle, sheep and swine farms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oporto, B.; Hurtado, A. Emerging thermotolerant Campylobacter species in healthy ruminants and swine. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oporto, B.; Juste, R.A.; Hurtado, A. Phenotypic and genotypic antimicrobial resistance profiles of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from cattle, sheep, and free-range poultry faeces. Int. J. Microbiol. 2009, 2009, 456573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englen, M.D.; Hill, A.E.; Dargatz, D.A.; Ladely, S.R.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter in US dairy cattle. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.; Menzies, P.; Reid-Smith, R.J.; Avery, B.P.; Mcewen, S.A.; Moon, C.S.; Berke, O. Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter spp. isolated from Ontario sheep flocks and associations between antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotariu, O.; Dallas, J.F.; Ogden, I.D.; MacRae, M.; Sheppard, S.K.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Gormley, F.J.; Forbes, K.J.; Strachan, N.J.C. Spatiotemporal homogeneity of Campylobacter subtypes from cattle and sheep across northeastern and southwestern Scotland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6275–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sproston, E.L.; Ogden, I.D.; MacRae, M.; Dallas, J.F.; Sheppard, S.K.; Cody, A.J.; Colles, F.M.; Wilson, M.J.; Forbes, K.J.; Strachan, N.J.C. Temporal variation and host association in the Campylobacter population in a longitudinal ruminant farm study. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6579–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oporto, B.; Juste, R.A.; López-Portolés, J.A.; Hurtado, A. Genetic diversity among Campylobacter jejuni isolates from healthy livestock and their links to human isolates in Spain. Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Didelot, X.; Jolley, K.A.; Darling, A.E.; Pascoe, B.; Meric, G.; Kelly, D.J.; Cody, A.; Colles, F.M.; Strachan, N.J.C.; et al. Progressive genome-wide introgression in agricultural Campylobacter coli. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahlmeter, G.; Brown, D.F.J.; Goldstein, F.W.; MacGowan, A.P.; Mouton, J.W.; Österlund, A.; Rodloff, A.; Steinbakk, M.; Urbaskova, P.; Vatopoulos, A. European harmonization of MIC breakpoints for antimicrobial susceptibility testing of bacteria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 52, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englen, M.D.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Ladely, S.R.; Dargatz, D.A. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Campylobacter from feedlot cattle. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 99, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Châtre, P.; Haenni, M.; Meunier, D.; Botrel, M.A.; Calavas, D.; Madec, J.Y. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from cattle between 2002 and 2006 in France. J. Food Prot. 2010, 73, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bywater, R.; Deluyker, H.; Deroover, E.; de Jong, A.; Marion, H.; McConville, M.; Rowan, T.; Shryock, T.; Shuster, D.; Thomas, V.; et al. A European survey of antimicrobial susceptibility among zoonotic and commensal bacteria isolated from food-producing animals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2004, 54, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017. EFSA J. 2019, 17, 5598. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency; European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 30 European Countries in 2016 (EMA/275982/2018); European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, W.; Mosci, R.E.; Wengert, S.L.; Vargas, C.V.; Rust, S.R.; Bartlett, P.C.; Grooms, D.L.; Manning, S.D. Comparing the genetic diversity and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Campylobacter jejuni recovered from cattle and humans. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sproston, E.L.; Wimalarathna, H.M.L.; Sheppard, S.K. Trends in fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter. Microb. Genomics 2018, 4, e00198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, R.; Kittl, S.; Overesch, G.; Kuhnert, P. Genotypes and antibiotic resistance of bovine Campylobacter and their contribution to human campylobacteriosis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Jöbstl, D.; Sofka, D.; Iwersen, M.; Drillich, M.; Hilbert, F. Multilocus sequence typing and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter jejuni isolated from dairy calves in Austria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish Integrated Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring and Research Programme (DANMAP). Use of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Food Animals, Food and Humans in Denmark 2016; National Food Institute, Technical University of Denmark and Statens Serum Institut: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017; Available online: www.danmap.org (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Food, E.; Authority, S. The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2016. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5182. [Google Scholar]
- De Briyne, N.; Atkinson, J.; Borriello, S.P.; Pokludová, L. Antibiotics used most commonly to treat animals in Europe. Vet. Rec. 2014, 175, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeitouni, S.; Kempf, I. Fitness cost of fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni. Microb. Drug Resist. 2011, 17, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Deng, F.; Shen, Z.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, J. Emergence of multidrug-resistant Campylobacter species isolates with a horizontally acquired rRNA methylase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5405–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, A.; Ocejo, M.; Oporto, B. Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes shedding in domestic ruminants and characterization of potentially pathogenic strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 210, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zirnstein, G.; Helsel, L.; Li, Y.; Swaminathan, B.; Besser, J. Characterization of gyrA mutations associated with fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter coli by DNA sequence analysis and MAMA PCR. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2000, 190, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingle, K.E.; Colles, F.M.; Wareing, D.R.A.; Ure, R.; Fox, A.J.; Bolton, F.E.; Bootsma, H.J.; Willems, R.J.L.; Urwin, R.; Maiden, A.M.C.J. Multilocus sequence typing system for Campylobacter jejuni. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.G.; On, S.L.W.; Wang, G.; Fontanoz, S.; Lastovica, A.J.; Mandrell, R.E. Extended multilocus sequence typing system for Campylobacter coli, C. lari, C. upsaliensis, and C. helveticus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 2315–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).