Application of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Innovative Method of Treatment for Legionella Control in a Hospital Water Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Setting
4.2. Water Disinfection
4.3. Sample Collection and Detection of Legionella spp.
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Fields, B.S.; Benson, R.F.; Besser, R.E. Legionella and Legionnaires’ disease: 25 years of investigation. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 506–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldrow, L.L.; Tyndall, R.L.; Fliermans, C.B. Application of flow cytometry to studies of pathogenic free-living amoebae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 44, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, A.; Alvarez, J.; Sabria, M.; Carmona, G.; Torner, N.; Oviedo, M.; Cayla, J.; Minguell, S.; Barrabeig, I.; Sala, M.; et al. Factors influencing the case-fatality rate of Legionnaires’ disease. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2009, 13, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baggiani, A.; Casini, B.; Totaro, M.; Aquino, F.; Valentini, P.; Bruni, B.; Porretta, A.; Casalini, F.; Miccoli, M.; Privitera, G. Colonization by Legionella spp. of water networks in residential buildings of the Province of Pisa, Italy. Ann. Ig. 2015, 27, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diederen, B.M. Legionella spp. and Legionnaires’ disease. J. Infect. 2008, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seenivasan, M.H.; Yu, V.L.; Muder, R.R. Legionnaires’ disease in long-term care facilities: Overview and proposed solutions. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2005, 53, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISS. Rapporto Annuale Sulla Legionellosi in Italia 2014. Notiziario dell’Istituto Superiore di Sanità 2015, 28, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, D.J.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Gorman, G.W.; Wilkinson, H.W.; Bibb, W.F.; Hackel, M.; Tyndall, R.L.; Campbell, J.; Feeley, J.C.; Thacker, W.L.; et al. Ten new species of Legionella. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 35, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.J. Classification of Legionellaceae: Status and remaining questions. Israel J. Med. Sci. 1986, 22, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuchta, J.M.; Navratil, J.S.; Shepherd, M.E.; Wadowsky, R.M.; Dowling, J.N.; States, S.J.; Yee, R.B. Impact of Chlorine and Heat on the Survival of Hartmannella vermiformis and Subsequent Growth of Legionella pneumophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1993, 59, 4096–4100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fliermans, C.B. Ecology of Legionella: From data to knowledge with a little wisdom. Microb. Ecol. 1996, 32, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraca, P.W.; Yu, V.L.; Goetz, A. Disinfection of water distribution systems for Legionella: A review of application procedures and methodologies. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1990, 11, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.E.; Stout, J.E.; Yu, V.L. Controlling Legionella in hospital drinking water: An evidence-based review of disinfection methods. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2011, 32, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tablan, O.C.; Anderson, L.J.; Besser, R.; Bridges, C.; Hajjeh, R.; CDC; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Guidelines for preventing health-care-associated pneumonia, 2003: Recommendations of CDC and the Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2004, 53, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Casini, B.; Buzzigoli, A.; Cristina, M.L.; Spagnolo, A.M.; Del Giudice, P.; Brusaferro, S.; Poscia, A.; Moscato, U.; Valentini, P.; Baggiani, A.; et al. Long-term effects of hospital water network disinfection on Legionella and other waterborne bacteria in an Italian università hospital. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristina, M.L.; Spagnolo, A.M.; Casini, B.; Baggiani, A.; Del Giudice, P.; Brusaferro, S.; Poscia, A.; Moscato, U.; Perdelli, F.; Orlando, P. The impact of aerators on water contamination by emerging gram-negative opportunists in at-risk hospital departments. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2014, 35, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilvington, S.; Price, J. Survival of Legionella pneumophila within cysts of Acanthamoeba polyphaga following chlorine exposure. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1990, 68, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, J.; Brown, M.R.; Collier, P.J.; Farrell, I.; Gilbert, P. Relationship between Legionella pneumophila and Acanthamoeba polyphaga: Physiological status and susceptibility to chemical inactivation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barker, J.; Scaife, H.; Brown, M.R. Intraphagocytic growth induces an antibiotic-resistant phenotype of Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob. Agents Chemoter. 1995, 39, 2684–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwachuku, N.; Gerba, C.P. Health effects of Acanthamoeba spp. and its potential for waterborne transmission. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2004, 180, 93–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Storey, M.V.; Ashbolt, J.; Stenström, T.A. Biofilms, thermophilic amoebae and Legionella pneumophila—A quantitative risk assessment for distributed water. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia, M.T.; Jones, S.; Pelaz, C.; Millar, R.D.; Abu Kwaik, Y. Acanthamoeba polyphaga resuscitates viable non-culturable Legionella pneumophila after disinfection; Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, USA. Environ Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel-Frausto, M.S.; Rhomberg, P.; Hollis, R.J.; Pfaller, M.A.; Wenzel, R.P.; Helms, C.M.; Herwaldt, L.A. Persistance of Legionella pneumophila in a Hospital’s Water System: A 13-Year Survey. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 1999, 20, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, J.E.; Yu, V.L. Experiences of the First 16 Hospitals Using Copper–Silver Ionization for Legionella Control: Implications for the Evaluation of Other Disinfection Modalities. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2003, 24, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaturro, M.; Dell’Eva, I.; Helfer, F.; Ricci, M.L. Persistence of the same strain of Legionella pneumophila in the water system of an Italian hospital for 15 years. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2007, 28, 1089–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totaro, M.; Valentini, P.; Casini, B.; Miccoli, M.; Costa, A.L.; Baggiani, A. Experimental comparison of point-of-use filters for drinking water ultrafiltration. J. Hosp. Infect. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministère des Affaires sociales et de la Santé 2002, France, Circulaire DGS/SD7A/SD5C/DHOS/E4 no 2002/243 du 22 avril 2002 relative à la prévention du risque lié aux légionelles dans les établissements de santé).
- Block, S.S. Disinfection, Sterilization, and Preservation, 5rd ed.; Limpicott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- St John, G.; Steinman, H.M. Periplasmic copper-zinc superoxide dismutase of Legionella pneumophila: Role in stationary-phase survival. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 1578–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallolio, L.; Scuderi, A.; Rini, M.S.; Valente, S.; Farruggia, P.; Sabattini, M.A.; Pasquinelli, G.; Acacci, A.; Roncarati, G.; Leoni, E. Effect of Different Disinfection Protocols on Microbial and Biofilm Contamination of Dental Unit Waterlines in Community Dental Practices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2064–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petti, S.; Polimeni, A.; Allen, M.J. Dental unit water treatment with hydrogen peroxide and monovalent silver ions artificially contaminated with freshly isolated pathogens. Ann. Ig. 2015, 27, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ditommaso, S.; Giacomuzzi, M.; Ricciardi, E.; Zotti, C.M. Efficacy of a Low Dose of Hydrogen Peroxide (Peroxy Ag+) for Continuous Treatment of Dental Unit Water Lines: Challenge Test with Legionella pneumophila Serogroup 1 in a Simulated Dental Unit Waterline. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuval, H.; Rachel Yarom, R.; Shenman, R. An innovative method for the control of Legionella infections in the hospital hot water systems with a stabilized hydrogen peroxide silver formulations. Int. J. Infect. Control 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, M.L.; Dell’Eva, I.; Scaturro, M.; Baruchelli, P.; De Ponte, G.; Losardo, M.; Ottaviani, M.; Guizzardi, F. Six-months experience of silver-hydrogen peroxide treatment for Legionella control in two nursing home water sistems. In Legionella: State of the Art 30 Years after Its Recognition; Nicholas, P., Cianciotto, N., Kwaik, Y., Edelstein, P., Fields, B., Geary, D., Harrison, T., Joseph, C., Ratcliff, R., Stout, J., et al., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, S.; Legnani, P.P.; Leoni, E. Plan for the control of Legionella infections in long-term care facilities: Role of environmental monitoring. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2012, 215, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, I.; Ferranti, G.; Mansi, A.; Marcelloni, A.M.; Proietto, A.R.; Saini, N.; Borella, P.; Bargellini, A. Control of Legionella Contamination and Risk of Corrosion in Hospital Water Networks following Various Disinfection Procedures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2959–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, A.; Donaghy, M.; Marley, M.; Othieno, R.; Stevenson, J.; Hyland, J.; Pollock, K.G.; Lindsay, D.; Edwards, G.; Hanson, M.F.; et al. Cluster of Legionnaires disease cases caused by Legionella longbeachae serogroup 1, Scotland, August to September 2013. Euro Surveill. 2013, 18, 20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 11731 Procedura Integrativa al Metodo ISO 11731-2: 2004 Water Quality—Detection and enumeration of Legionella Part 2: “Direct Membrane Filtration Method for Waters with Low Bacterial Counts” in Base Alle Linee Guida per la Prevenzione ed il Controllo Della Legionellosi (79/CSR 7 maggio 2015). Available online: http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail.htm?csnumber=32326 (accessed on 20 January 2016).
- Ministero della Salute. Linee Guida per la Prevenzione ed il Controllo Della Legionellosi. 2015. Available online: http://www.iss.it/binary/iss4/cont/C_17_pubblicazioni_2362 (accessed on 20 January 2016).
- European Working Group for Legionella Infections. Sequence-Based Identification of Legionella Using the Macrophage Infectivity Potentiator (mip) Gene; Health Protection Agency: London, UK, 2013; Available online: http://www.hpa.org.uk/web/HPAweb&HPAwebStandard/HPAweb_C/1195733805138 (accessed on 28 March 2013).
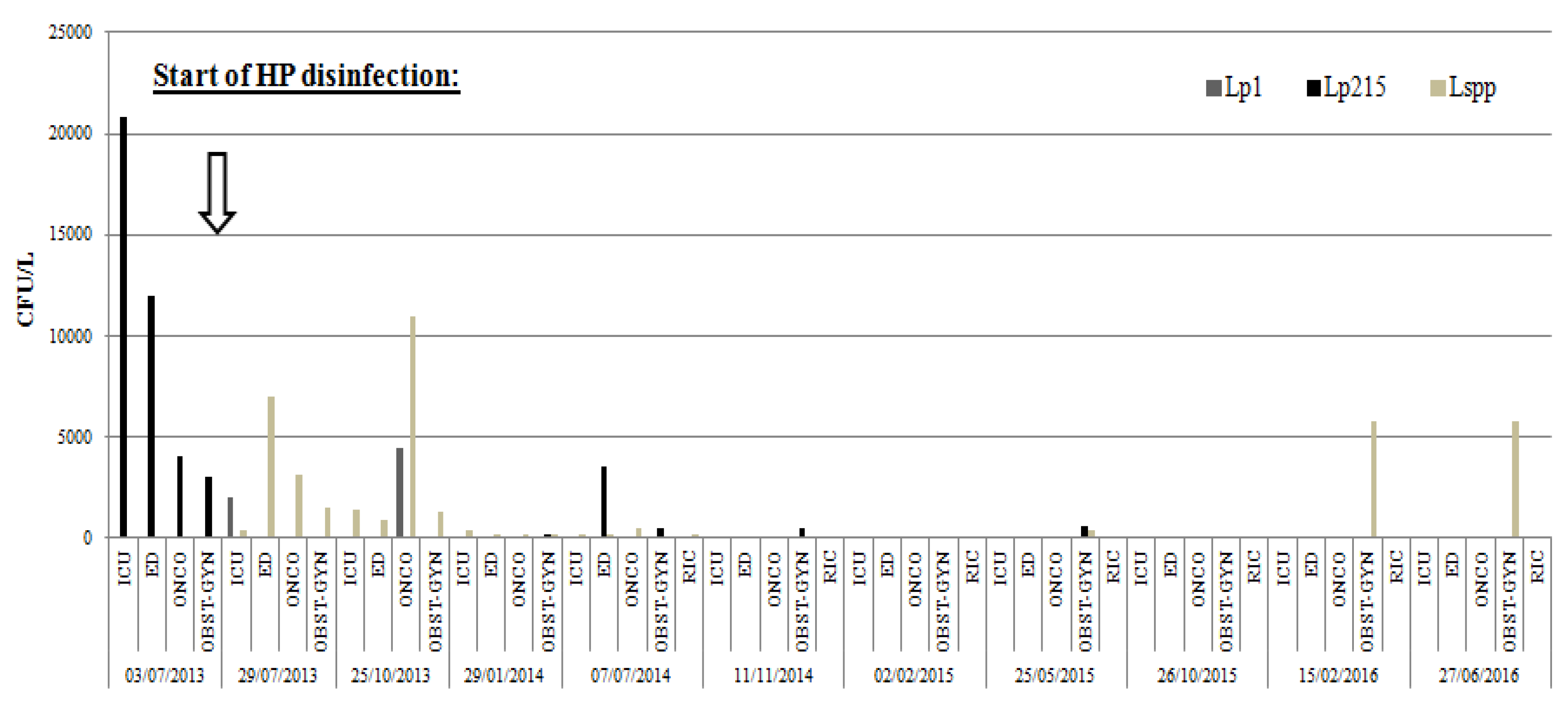
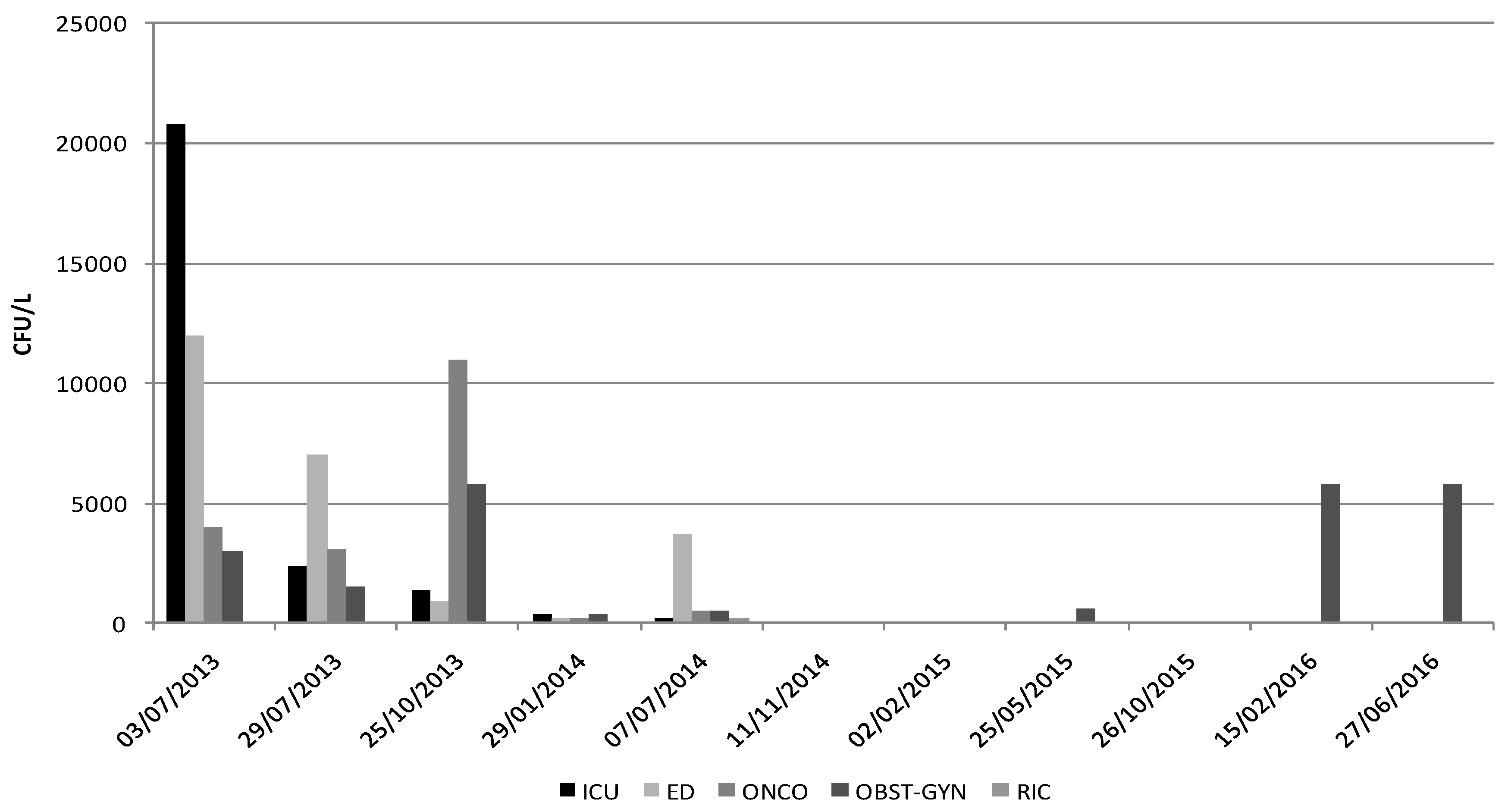
| p-Values | T0 3 July 2013 | T1 29 July 2013 | T2 25 October 2013 | T3 29 January 2014 | T4 7 July 2014 | T5 11 November 2014 | T6 2 February 2015 | T7 25 May 2015 | T8 26 October 2015 | T9 15 February 2016 | T10 27 January 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0—3 July 2013 | 1 | 0.670 | 0.790 | 0.136 | 0.241 | 0.003 * | 0.003 * | 0.012 * | 0.003 * | 0.003 * | 0.033 * |
| T1—29 July 2013 | 0.670 | 1 | 0.873 | 0.286 | 0.456 | 0.011 * | 0.011 * | 0.038 * | 0.011 * | 0.011 * | 0.088 |
| T2—25 October 2013 | 0.790 | 0.873 | 1 | 0.220 | 0.365 | 0.007 * | 0.007 * | 0.025 * | 0.007 * | 0.007 * | 0.062 |
| T3—29 January 2014 | 0.136 | 0.286 | 0.220 | 1 | 0.749 | 0.136 | 0.136 | 0.311 | 0.136 | 0.136 | 0.522 |
| T4—7 July 2014 | 0.241 | 0.456 | 0.365 | 0.749 | 1 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.183 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.337 |
| T5—11 November 2014 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.136 | 0.070 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.631 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.394 |
| T6—2 February 2015 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.136 | 0.070 | 1.000 | 1 | 0.631 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.394 |
| T7—25 May 2015 | 0.012 | 0.038 | 0.025 | 0.311 | 0.183 | 0.631 | 0.631 | 1 | 0.631 | 0.631 | 0.709 |
| T8—26 October 2015 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.136 | 0.070 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.631 | 1 | 1.000 | 0.394 |
| T9—15 February 2016 | 0.003 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.136 | 0.070 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.631 | 1.000 | 1 | 0.394 |
| T10—27 June 2016 | 0.033 | 0.088 | 0.062 | 0.522 | 0.337 | 0.394 | 0.394 | 0.709 | 0.394 | 0.394 | 0 |
| 3 July 2013 | 29 July 2013 | 25 October 2013 | 29 January 2014 | 7 July 2014 | 11 November 2014 | 2 February 2015 | 25 May 2015 | 26 October 2015 | 15 February 2016 | 27 June 2016 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICU | |||||||||||
| Iron Ions (µg/L Fe) | 140 | n.a | 300 | 140 | 120 | 210 | <40 | 50 | 184 | 80 | n.a |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 2.74 | 1.62 | 2.75 | 3.92 | 4.18 | 2.6 | <0.5 | 1.13 | n.a | 0.66 | < 0.5 |
| ONCO | |||||||||||
| Iron Ions (µg/L Fe) | 180 | n.a | 230 | 50 | 70 | 230 | 40 | <40 | 144 | <40 | n.a |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 6.73 | 0.85 | 0.73 | 1.34 | 0.36 | 2.68 | <0.5 | <0.5 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 1.42 |
| 3 July 2013 | 29 July 2013 | 25 October 2013 | 29 January 2014 | 7 July 2014 | 11 November 2014 | 2 February 2015 | 25 May 2015 | 26 October 2015 | 15 February 2016 | 27 June 2016 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED | |||||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | 48.1 | 42.6 | 37.6 | 42.4 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 42.5 | 42.7 | 40 | 46.3 |
| pH (pH units) | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.6 |
| conductivity (µS/cm) | 1394 | 1365 | 761 | 880 | 865 | 886 | 945 | 911 | 895 | 906 | 927 |
| HP (mg/L) | n.a. | 25 | 25 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| ICU | |||||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | 45.7 | 44 | 41 | 44.5 | 47.2 | 44.5 | 35 | 46 | 44 | 43.7 | 47.5 |
| pH (pH units) | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.7 |
| conductivity (µS/cm) | 1398 | 1380 | 790 | 882 | 869 | 885 | 923 | 904 | 892 | 907 | 923 |
| HP (mg/L) | n.a. | 25 | 25 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| ONCO | |||||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | 49.4 | 49 | 47.8 | 49.5 | 49.4 | 49.2 | 49 | 49.9 | 45.6 | 47.4 | 48.8 |
| pH (pH units) | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.7 |
| conductivity (µS/cm) | 1399 | 1364 | 804 | 880 | 869 | 887 | 944 | 903 | 894 | 907 | 925 |
| HP (mg/L) | n.a. | 25 | 25 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| OBST-GYN | |||||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | 47.8 | 48 | 49.5 | 49.2 | 48.7 | 49.7 | 49.5 | 46 | 48 | 46.5 | 49.4 |
| pH (pH units) | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.5 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.7 |
| conductivity (µS/cm) | 1398 | 1361 | 807 | 876 | 864 | 885 | 945 | 902 | 893 | 902 | 924 |
| HP (mg/L) | n.a. | 25 | 25 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
| RIC | |||||||||||
| Temperature (°C) | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 50.1 | 50.4 | 51 | 50.8 | 45.6 | 51.4 | 53.7 |
| pH (pH units) | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.6 |
| conductivity (µS/cm) | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 870 | 886 | 948 | 906 | 896 | 907 | 926 |
| HP (mg/L) | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casini, B.; Aquino, F.; Totaro, M.; Miccoli, M.; Galli, I.; Manfredini, L.; Giustarini, C.; Costa, A.L.; Tuvo, B.; Valentini, P.; et al. Application of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Innovative Method of Treatment for Legionella Control in a Hospital Water Network. Pathogens 2017, 6, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6020015
Casini B, Aquino F, Totaro M, Miccoli M, Galli I, Manfredini L, Giustarini C, Costa AL, Tuvo B, Valentini P, et al. Application of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Innovative Method of Treatment for Legionella Control in a Hospital Water Network. Pathogens. 2017; 6(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasini, Beatrice, Francesco Aquino, Michele Totaro, Mario Miccoli, Irio Galli, Laura Manfredini, Carlo Giustarini, Anna Laura Costa, Benedetta Tuvo, Paola Valentini, and et al. 2017. "Application of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Innovative Method of Treatment for Legionella Control in a Hospital Water Network" Pathogens 6, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6020015
APA StyleCasini, B., Aquino, F., Totaro, M., Miccoli, M., Galli, I., Manfredini, L., Giustarini, C., Costa, A. L., Tuvo, B., Valentini, P., Privitera, G., & Baggiani, A. (2017). Application of Hydrogen Peroxide as an Innovative Method of Treatment for Legionella Control in a Hospital Water Network. Pathogens, 6(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens6020015






