Evaluation of Mosquito Blood Meals as a Tool for Wildlife Pathogen Surveillance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
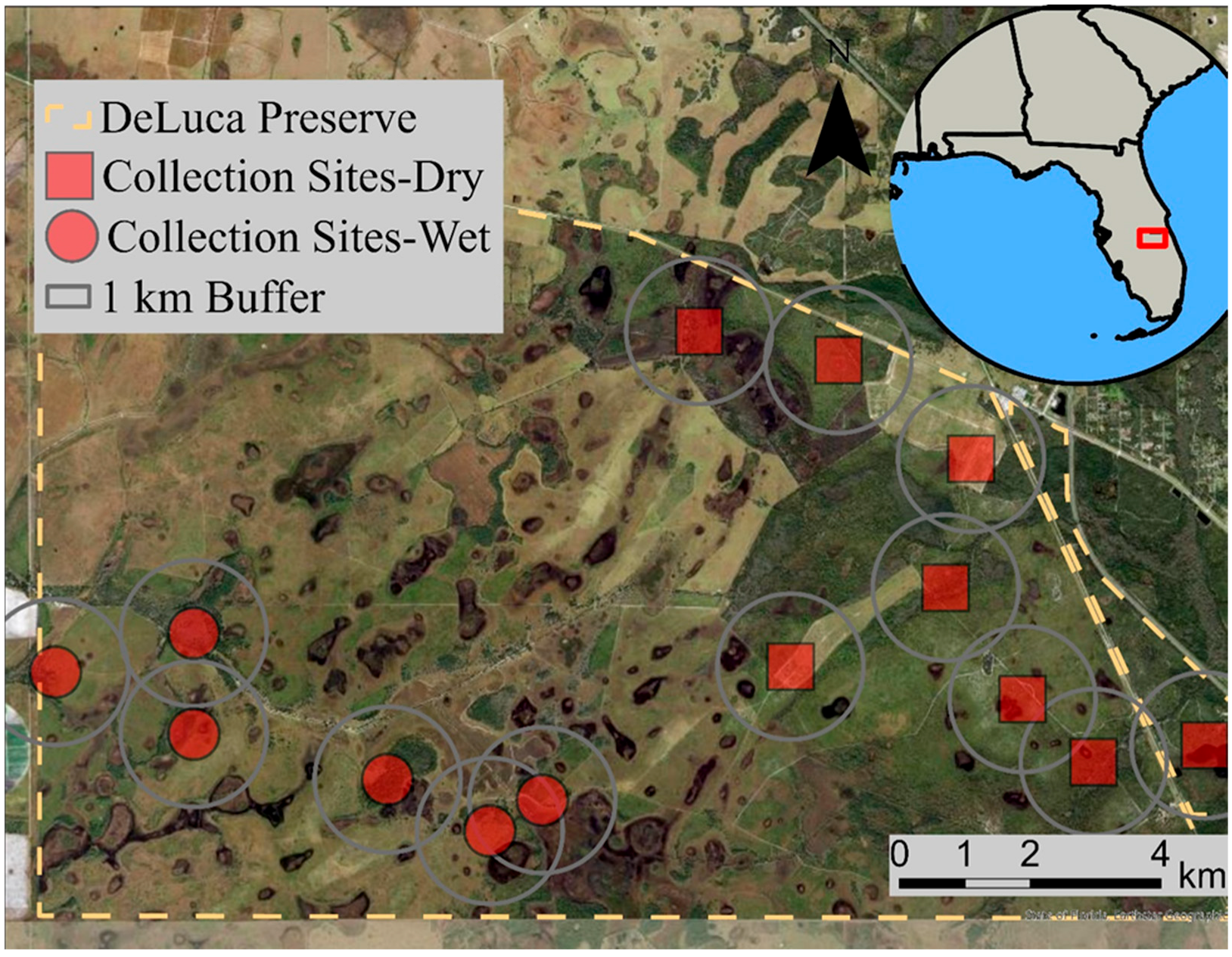
2.1. Mosquito Collection
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction from and Identification of Mosquito Blood Meals
2.3. Molecular-Based Pathogen Detection from Mosquito Blood Meals
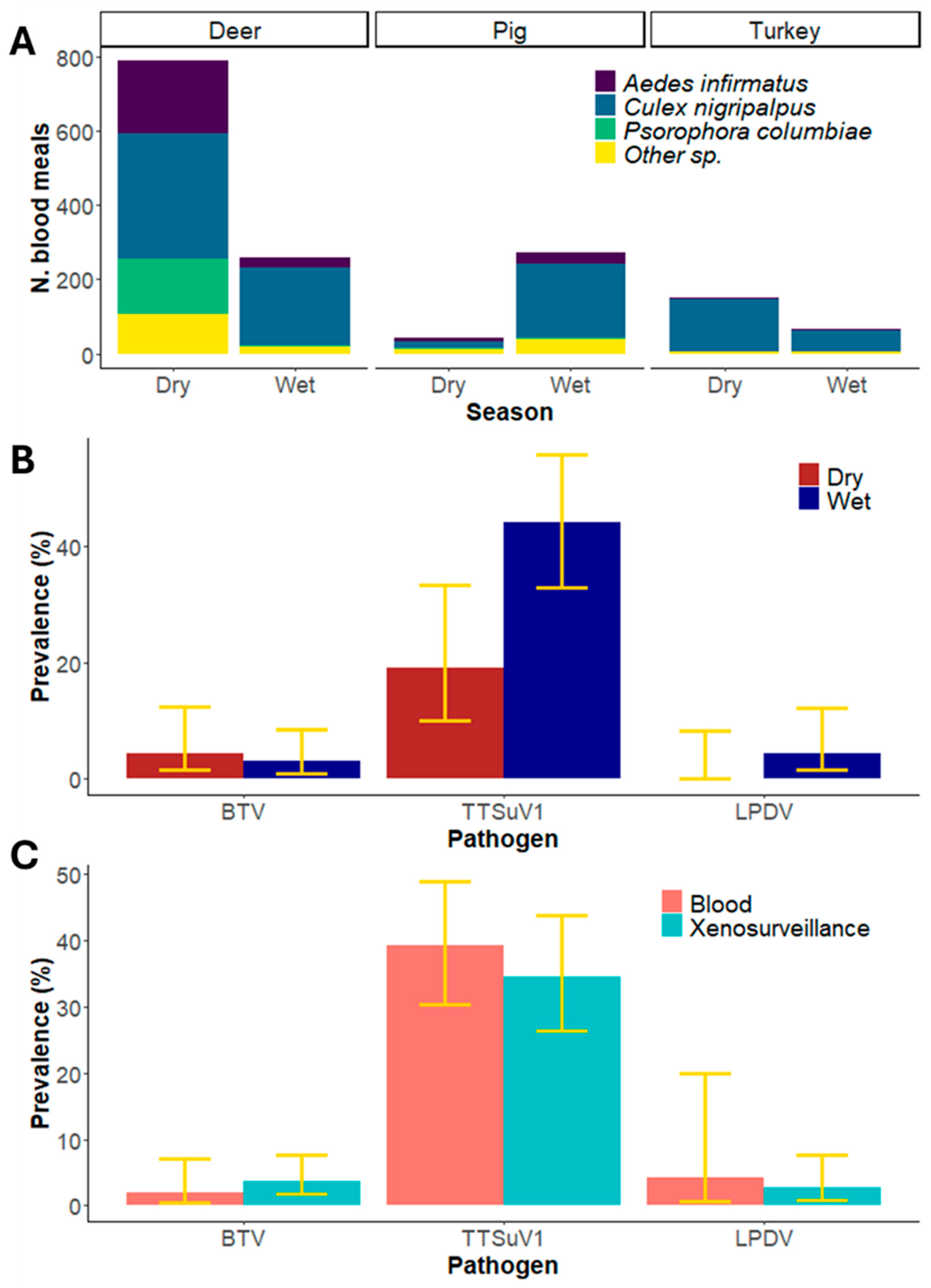
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| TTSuV1 | Torque teno sus virus 1 |
| LPDV | Lymphoproliferative virus |
| BTV | Bluetongue virus |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| USA | United States of America |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| FTA | Flinders Technology Associates |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| TAE | Tris-Acetate-EDTA |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-qPCR | Real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- Schilling, A.-K.; Mazzamuto, M.V.; Romeo, C. A Review of Non-Invasive Sampling in Wildlife Disease and Health Research: What’s New? Animals 2022, 12, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Hannaoui, S.; John, T.R.; Dudas, S.; Czub, S.; Gilch, S. Early and Non-Invasive Detection of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions in Elk Feces by Real-Time Quaking Induced Conversion. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Bangura, U.; Mariën, J.; Douno, M.; Fichet-Calvet, E. Detection of Lassa Virus in Wild Rodent Feces: Implications for Lassa Fever Burden within Households in the Endemic Region of Faranah, Guinea. One Health 2021, 13, 100317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.C.; Murphy, A.; James, P.; Travis, E.; Porter, D.; Sawyer, J.; Cork, J.; Delahay, R.J.; Gaze, W.; Courtenay, O.; et al. Performance of a Noninvasive Test for Detecting Mycobacterium Bovis Shedding in European Badger (Meles meles) Populations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2316–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valente, A.; Jiolle, D.; Ravel, S.; Porciani, A.; Vial, L.; Michaud, V.; Kwiatek, O.; Pedarrieu, A.; Misse, D.; Ferraris, P.; et al. Flying Syringes for Emerging Enzootic Virus Screening: Proof of Concept for the Development of Noninvasive Xenosurveillance Tools Based on Tsetse Flies. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2023, 2023, 9145289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, D.; Christison, K.W.; Stentiford, G.D.; Cook, L.S.J.; Hartikainen, H. Environmental DNA/RNA for Pathogen and Parasite Detection, Surveillance, and Ecology. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štefanić, S.; Grimm, F.; Mathis, A.; Winiger, R.; Verhulst, N.O. Xenosurveillance Proof-of-Principle: Detection of Toxoplasma Gondii and SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Mosquito Blood Meals by (Pan)-Specific ELISAs. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2022, 2, 100076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, C.J.S.; Gyawali, N.; Onn, M.; Shivas, M.; Shearman, D.; Darbro, J.; Wallau, G.; van den Hurk, A.F.; Frentiu, F.; Skinner, E.B.; et al. Mosquito Blood meals Can Be Used to Determine Vertebrate Diversity, Host Preference, and Pathogen Exposure in Humans and Wildlife. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisely, S.M.; Torhorst, C.W.; Atsma, H.; Botero-Cañola, S.; Burkett-Cadena, N.; Reeves, L.E. Xenosurveillance of Wild Pigs Using Mosquito Blood meals. In Proceedings of the Vertebrate Pest Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 11–14 March 2024; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Tshering, C.; Takagi, M.; Deguchi, E. Infection Dynamics of Torque Teno Sus Virus Types 1 and 2 in Serum and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 74, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alger, K.; Bunting, E.; Schuler, K.; Jagne, J.; Whipps, C.M. Diagnosing Lymphoproliferative Disease Virus in Live Wild Turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) Using Whole Blood. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2015, 46, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, J.; Rajko-Nenow, P.; Hicks, H.; Hill, H.; Gubbins, S.; Batten, C. Evaluating the Most Appropriate Pooling Ratio for EDTA Blood Samples to Detect Bluetongue Virus Using Real-Time RT-PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 217, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Tavares, Y.; Carneiro, C.M.; Phillips, C.; Subramaniam, K.; Lednicky, J.; Boughton, R.K.; Pepin, K.M.; Miller, R.S.; VerCauteren, K.C.; et al. Whole Genome Characterization of Torque Teno Sus Virus 1 (TTSuV1) in Wild and Domestic Pigs: Insights into Genetic Classification, Host Differentiation, and Intra-Host Variation. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1585558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Parker, B.; Boughton, R.; Beasley, J.C.; Smyser, T.; Austin, J.D.; Pepin, K.M.; Miller, R.S.; Vercauteren, K.; Wisely, S. Torque Teno Sus Virus 1: A Potential Surrogate Pathogen to Study Pig-Transmitted Transboundary Animal Diseases. Viruses 2024, 16, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, S. TTV, a New Human Virus with Single Stranded Circular DNA Genome. Rev. Med. Virol. 2002, 12, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.M.; Allison, A.B.; Holmes, E.C.; Phillips, J.E.; Bunting, E.M.; Yabsley, M.J.; Brown, J.D. Molecular Surveillance for Lymphoproliferative Disease Virus in Wild Turkeys (Meleagris Gallopavo) from the Eastern United States. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, A.B.; Kevin Keel, M.; Philips, J.E.; Cartoceti, A.N.; Munk, B.A.; Nemeth, N.M.; Welsh, T.I.; Thomas, J.M.; Crum, J.M.; Lichtenwalner, A.B.; et al. Avian Oncogenesis Induced by Lymphoproliferative Disease Virus: A Neglected or Emerging Retroviral Pathogen? Virology 2014, 450–451, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, C.; McDermott, E.; Kopanke, J.; Stenglein, M.; Lee, J.; Mathiason, C.; Carpenter, M.; Reed, K.; Perkins, T.A. Ecological Dynamics Impacting Bluetongue Virus Transmission in North America. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, S.L.; Cheng, A.-C.; de Oliveira Viadanna, P.H.; Subramaniam, K.; Craft, W.F.; Iredale, M.E.; Wisely, S.; Campos Krauer, J.C. Mycobacterium Kansasii Infection in a Farmed White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in Florida, USA. Animals 2024, 14, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsma, H.I. Mosquito Blood Meal Analysis for Biodiversity Monitoring at a Florida Preserve. Master’s Thesis, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, D.F.; Myers, R.L.; Ewel, J.J. Ecosystems of Florida. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 1991, 118, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett-Cadena, N.D.; Eubanks, M.D.; Unnasch, T.R. Preference of Female Mosquitoes for Natural and Artificial Resting Sites. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2008, 24, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkett-Cadena, N.D. A Wire-Frame Shelter for Collecting Resting Mosquitoes. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2011, 27, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlichting, P.E.; Boughton, R.K.; Anderson, W.; Wight, B.; VerCauteren, K.C.; Miller, R.S.; Lewis, J.S. Seasonal Variation in Space Use and Territoriality in an Invasive Large Mammal (Sus scrofa). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darsie, R.F.; Ward, R.A. Identification and Geographical Distribution of the Mosquitoes of North America, North of Mexico, 2nd ed.; University Press of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 9780813027845. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, L.E.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D. Extracting DNA from Preserved Mosquito Blood Meals. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2024, 2024, pdb.prot108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truett, G.E.; Heeger, P.; Mynatt, R.L.; Truett, A.A.; Walker, J.A.; Warman, M.L. Preparation of PCR-Quality Mouse Genomic DNA with Hot Sodium Hydroxide and Tris (HotSHOT). Biotechniques 2000, 29, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, L.E.; Gillett-Kaufman, J.L.; Kawahara, A.Y.; Kaufman, P.E. Barcoding Blood Meals: New Vertebrate-Specific Primer Sets for Assigning Taxonomic Identities to Host DNA from Mosquito Blood Meals. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankamp, B.; Byrd-Leotis, L.A.; Lopareva, E.N.; Woo, G.K.S.; Liu, C.; Jee, Y.; Ahmed, H.; Lim, W.W.; Ramamurty, N.; Mulders, M.N.; et al. Improving Molecular Tools for Global Surveillance of Measles Virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 58, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segalés, J.; Martínez-Guinó, L.; Cortey, M.; Navarro, N.; Huerta, E.; Sibila, M.; Pujols, J.; Kekarainen, T. Retrospective Study on Swine Torque Teno Virus Genogroups 1 and 2 Infection from 1985 to 2005 in Spain. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 134, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alger, K.; Bunting, E.; Schuler, K.; Whipps, C.M. Risk Factors for and Spatial Distribution of Lymphoproliferative Disease Virus (Lpdv) in Wild Turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) in New York State, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2017, 53, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernike, K.; Hoffmann, B.; Beer, M. Simultaneous Detection of Five Notifiable Viral Diseases of Cattle by Single-Tube Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 217, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viadanna, P.H.O.; Surphlis, A.; Cheng, A.-C.; Dixon, C.E.; Meisner, S.; Wilson, K.N.; White, Z.S.; DeRuyter, E.; Logan, T.D.; Krauer, J.M.C.; et al. A Novel Bluetongue Virus Serotype 2 Strain Isolated from a Farmed Florida White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus) Arose from Reassortment of Gene Segments Derived from Co-Circulating Serotypes in the Southeastern USA. Virus Genes 2024, 60, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, E.B. Probable Inference, the Law of Succession, and Statistical Inference. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1927, 22, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribasterra, M.G.; Orange, J.P.; Dinh, E.T.N.; Peters, C.; Peters, R.M.; Goodfriend, O.; Wisely, S.M.; Blackburn, J.K. Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease Virus and Bluetongue Virus Seroprevalence in Wild White-Tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in Florida, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentenac, H.; Valenzuela-Sánchez, A.; Haddow-Brown, N.; Delgado, S.; Azat, C.; Cunningham, A.A. Accounting for Bias in Prevalence Estimation: The Case of a Globally Emerging Pathogen. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herm, R.; Tummeleht, L.; Jürison, M.; Vilem, A.; Viltrop, A. Trace Amounts of African Swine Fever Virus DNA Detected in Insects Collected from an Infected Pig Farm in Estonia. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Gao, Z.; Wu, S.; Bao, W. Preliminary Analysis of Whether Mosquitoes Can Carry and Transmit African Swine Fever. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wisely, S.M.; Torhorst, C.W.; Botero-Cañola, S.; Atsma, H.; Burkett-Cadena, N.D.; Reeves, L.E. Evaluation of Mosquito Blood Meals as a Tool for Wildlife Pathogen Surveillance. Pathogens 2025, 14, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080792
Wisely SM, Torhorst CW, Botero-Cañola S, Atsma H, Burkett-Cadena ND, Reeves LE. Evaluation of Mosquito Blood Meals as a Tool for Wildlife Pathogen Surveillance. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080792
Chicago/Turabian StyleWisely, Samantha M., Carson W. Torhorst, Sebastian Botero-Cañola, Hannah Atsma, Nathan D. Burkett-Cadena, and Lawrence E. Reeves. 2025. "Evaluation of Mosquito Blood Meals as a Tool for Wildlife Pathogen Surveillance" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080792
APA StyleWisely, S. M., Torhorst, C. W., Botero-Cañola, S., Atsma, H., Burkett-Cadena, N. D., & Reeves, L. E. (2025). Evaluation of Mosquito Blood Meals as a Tool for Wildlife Pathogen Surveillance. Pathogens, 14(8), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080792







