First Survey on the Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Positive Human Patients from 2015 to 2024 in Sardinia, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Laboratory Investigations
Indirect Immunofluorescence
2.4. GIS-Based Survey of Patients’ Positive Distribution Sites
2.5. Seroprevalence Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Laboratory Investigations
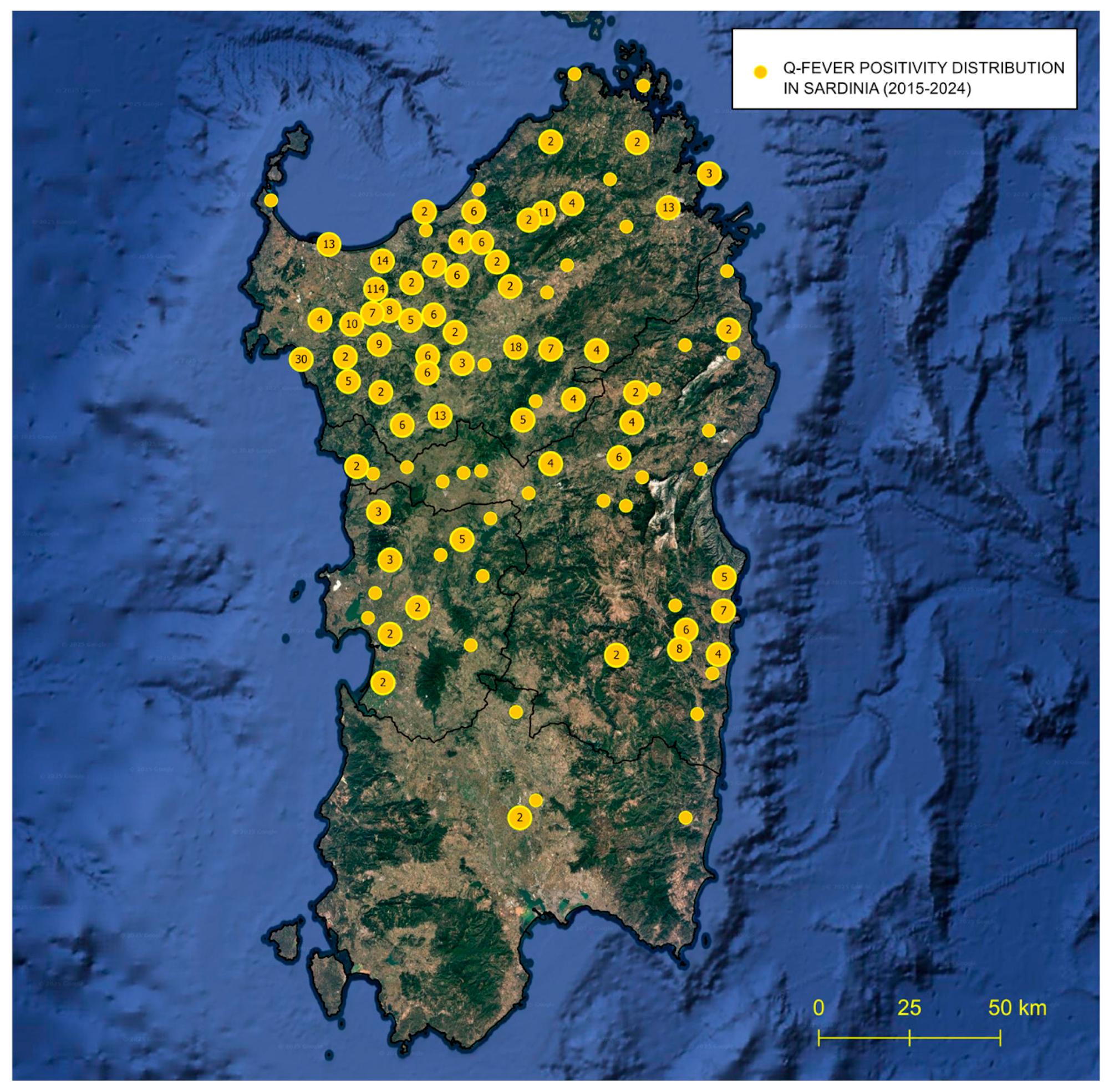
3.2. GIS-Based Survey of Patients’ Positive Distribution Sites
3.3. Seroprevalence Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bielawska-Drózd, A.; Cieślik, P.; Mirski, T.; Bartoszcze, M.; Knap, J.P.; Gaweł, J.; Zakowska, D. Q Fever-Selected Issues. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Omsland, A.; Beare, P.A.; Hill, J.; Cockrell, D.C.; Howe, D.; Hansen, B.; Samuel, J.E.; Heinzen, R.A. Isolation from Animal Tissue and Genetic Transformation of Coxiella burnetii are Facilitated by an Improved Axenic Growth Medium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3720–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, C.; Mélenotte, C.; Mediannikov, O.; Ghigo, E.; Million, M.; Edouard, S.; Mege, J.-L.; Maurin, M.; Raoult, D. From Q Fever to Coxiella burnetii Infection: A Paradigm Change. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 115–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrick, E.H. “Q” Fever, a New Fever Entity: Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Laboratory Investigation. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1983, 5, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masala, G.; Porcu, R.; Sanna, G.; Chessa, G.; Cillara, G.; Chisu, V.; Tola, S. Occurrence, Distribution, and Role in Abortion of Coxiella burnetii in Sheep and Goats in Sardinia, Italy. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 99, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisu, V.; Loi, F.; Foxi, C.; Chessa, G.; Masu, G.; Rolesu, S.; Masala, G. Coexistence of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Ticks Collected from Their Hosts in Sardinia: An Update. Acta Parasitol. 2020, 65, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Körner, S.; Makert, G.R.; Ulbert, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Mertens-Scholz, K. The Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Hard Ticks in Europe and Their Role in Q Fever Transmission Revisited—A Systematic Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 655715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebani, V.V. Coxiella burnetii Infection in Cats. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, M.; Afonso, A.; Neubauer, H.; Needham, H.; Thiery, R.; Rodolakis, A.; Roest, H.; Stark, K.; Stegeman, J.; Vellema, P.; et al. Q Fever in Humans and Farm Animals in Four European Countries, 1982 to 2010. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelakis, E.; Raoult, D. Q Fever. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, J.G.; Flint, N.; Smith, E.G.; Tunnicliffe, W.S.; Fletcher, T.J.; Hammond, K.; Ward, D.; Marmion, B.P. Post-Infection Fatigue Syndrome Following Q Fever. QJM 1998, 91, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenollar, F.; Fournier, P.E.; Carrieri, M.P.; Habib, G.; Messana, T.; Raoult, D. Risks Factors and Prevention of Q Fever Endocarditis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Million, M.; Raoult, D. No Such Thing as Chronic Q Fever. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canevari, J.T.; Firestone, S.M.; Vincent, G.; Campbell, A.; Tan, T.; Muleme, M.; Cameron, A.W.N.; Stevenson, M.A. The Prevalence of Coxiella burnetii Shedding in Dairy Goats at the Time of Parturition in an Endemically Infected Enterprise and Associated Milk Yield Losses. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, H.K.; Priestley, R.A.; Kersh, G.J. Q Fever: A Troubling Disease and a Challenging Diagnosis. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2021, 43, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, M.; Dalai, S.C.; Venkatasubrahmanyam, S.; Eisenberg, N.; Robinson, B.D.; Westblade, L.F.; Marks, K.M. Diagnosis and Genotyping of Coxiella burnetii Endocarditis in a Patient with Prosthetic Pulmonary Valve Replacement Using Next-Generation Sequencing of Plasma Microbial Cell-Free DNA. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2019, 6, ofz242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masala, G.; Porcu, R.; Daga, C.; Denti, S.; Canu, G.; Patta, C.; Tola, S. Detection of Pathogens in Ovine and Caprine Abortion Samples from Sardinia, Italy, by PCR. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2007, 19, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisu, V.; Loi, F.; Mura, L.; Tanda, A.; Chessa, G.; Masala, G. Molecular Detection of Theileria Sergentii/Orientalis/Buffeli and Ehrlichia Canis from Aborted Ovine and Caprine Products in Sardinia, Italy. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Cafiso, A.; Cialini, C.; Olivieri, E.; Allievi, C.; Pintore, E.; Garippa, G.; Manfredi, M.T.; Bazzocchi, C. Serological and Molecular Insights into Tick-Borne Pathogens in Wild Donkeys from an Unexplored Mediterranean Nature Reserve. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2025, 7, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisu, V.; Zobba, R.; Masala, G.; Chessa, G.; Giua, L.; Bianco, P.; Cacciotto, C.; Bazzoni, E.; Alberti, A. Emergence of Novel Anaplasma Species in the Mediterranean Area. Animals 2025, 15, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeykoon, A.M.H.; Clark, N.J.; Soares Magalhaes, R.J.; Vincent, G.A.; Stevenson, M.A.; Firestone, S.M.; Wiethoelter, A.K. Coxiella burnetii in the Environment: A Systematic Review and Critical Appraisal of Sampling Methods. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolesu, S.; Loi, F.; Cappai, S.; Coccollone, A.; Cataldi, M.; Usala, P.; Podda, A.; Deliperi, S.; Oppia, P.; Natale, A.; et al. Description and Typology of Dairy Sheep Farm Management Profiles in Sardinia. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 164, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pexara, A.; Solomakos, N.; Govaris, A. Q Fever and Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Domestic Ruminants. Vet. Ital. 2018, 54, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanda, V.; Chiarenza, G.; Giacchino, I.; Migliore, S.; Di Bella, S.; La Russa, F.; Vaglica, V.; D’Agostino, R.; Arcuri, F.; Sciacca, C.; et al. Molecular and Serological Findings in Sheep During Two Coxiella burnetii Outbreaks in Sicily (Southern Italy). Animals 2024, 14, 3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, A.; Trotta, A.; Bono, F.; Corrente, M.; Buonavoglia, D. Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Dairy Cattle and Buffalo from Southern Italy. Vet. Ital. 2021, 56, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menadi, S.E.; Mura, A.; Santucciu, C.; Ghalmi, F.; Hafsi, F.; Masala, G. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Coxiella burnetii Infection in Cattle in Northeast Algeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 52, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissot-Dupont, H.; Torres, S.; Nezri, M.; Raoult, D. Hyperendemic Focus of Q Fever Related to Sheep and Wind. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuño Mateo, F.J.; Noval Menéndez, J.; Campoamor Serrano, M.T.; del Valle Prieto, A. Acute Q fever in Asturias. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2002, 202, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brouqui, P.; Dupont, H.T.; Drancourt, M.; Berland, Y.; Etienne, J.; Leport, C.; Goldstein, F.; Massip, P.; Micoud, M.; Bertrand, A. Chronic Q Fever. Ninety-Two Cases from France, Including 27 Cases without Endocarditis. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, D.; Giura, R.; Colombo, M.C.; Antonelli, P.; Gramegna, M.; Gandola, O.; Gridavilla, G. Q Fever in Como, Northern Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pustahija, T.; Medić, S.; Vuković, V.; Lozanov-Crvenković, Z.; Patić, A.; Štrbac, M.; Jovanović, V.; Dimitrijević, D.; Milinković, M.; Kosanović, M.L.; et al. Epidemiology of Q Fever in Southeast Europe for a 20-Year Period (2002–2021). J. Epidemiol Glob. Health 2024, 14, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, F.; Vitale, N.; Ballardini, M.; Borromeo, V.; Luzzago, C.; Chiavacci, L.; Mandola, M.L. Q Fever Seroprevalence and Risk Factors in Sheep and Goats in Northwest Italy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2016, 130, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, M.K.; Tsaras, K.; Billinis, C.; Gourgoulianis, K.I.; Papagiannis, D. Q Fever in Greece and Factors of Exposure: A Multiregional Seroprevalence Study. Cureus 2024, 16, e69501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaroulaki, A.; Ragiadakou, D.; Kouris, G.; Papadopoulos, B.; Chaniotis, B.; Tselentis, Y. Ticks, Tick-Borne Rickettsiae, and Coxiella burnetii in the Greek Island of Cephalonia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1078, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadinezhad, M.; Mounesan, L.; Doosti-Irani, A.; Behzadi, M.Y. The Prevalence of Q Fever in the Eastern Mediterranean Region: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Epidemiol. Health 2022, 44, e2022097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, C.C.; Nichols Heitman, K.; Bestul, N.C.; Kersh, G.J. Acute and Chronic Q Fever National Surveillance—United States, 2008–2017. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccò, M.; Baldassarre, A.; Corrado, S.; Marchesi, F. Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Occupational Settings: A Meta-Analysis of Italian Studies. Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 3, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Q Fever—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/q-fever-annual-epidemiological-report-2019 (accessed on 21 July 2025).
- Satta, G.; Chisu, V.; Cabras, P.; Fois, F.; Masala, G. Pathogens and Symbionts in Ticks: A Survey on Tick Species Distribution and Presence of Tick-Transmitted Micro-Organisms in Sardinia, Italy. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisu, V.; Foxi, C.; Mannu, R.; Satta, G.; Masala, G. A Five-Year Survey of Tick Species and Identification of Tick-Borne Bacteria in Sardinia, Italy. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Castro, L.; Zuddas, C.; Ortega, N.; Serrano, E.; Salinas, J.; Castellà, J.; Castillo-Contreras, R.; Carvalho, J.; Lavín, S.; Mentaberre, G. On the Possible Role of Ticks in the Eco-Epidemiology of Coxiella burnetii in a Mediterranean Ecosystem. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Techniques | n° (%) Positive | n° (%) Negative | n° (%) Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFI-IgG | 656 (15.2) | 1424 (33.0) | 2080 (48.3) |
| IFI-IgM | 38 (0.9) | 2192 (50.9) | 2230 (51.7) |
| Total (%) | 694 (16.0) | 3616 (83.9) | 4310 (100) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santucciu, C.; Giordo, M.P.; Tanda, A.; Chessa, G.; Senes, M.; Masu, G.; Masala, G.; Chisu, V. First Survey on the Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Positive Human Patients from 2015 to 2024 in Sardinia, Italy. Pathogens 2025, 14, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080790
Santucciu C, Giordo MP, Tanda A, Chessa G, Senes M, Masu G, Masala G, Chisu V. First Survey on the Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Positive Human Patients from 2015 to 2024 in Sardinia, Italy. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080790
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantucciu, Cinzia, Maria Paola Giordo, Antonio Tanda, Giovanna Chessa, Matilde Senes, Gabriella Masu, Giovanna Masala, and Valentina Chisu. 2025. "First Survey on the Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Positive Human Patients from 2015 to 2024 in Sardinia, Italy" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080790
APA StyleSantucciu, C., Giordo, M. P., Tanda, A., Chessa, G., Senes, M., Masu, G., Masala, G., & Chisu, V. (2025). First Survey on the Seroprevalence of Coxiella burnetii in Positive Human Patients from 2015 to 2024 in Sardinia, Italy. Pathogens, 14(8), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080790





