Abstract
Bee products, in particular honey, propolis and bee venom, are of growing scientific interest due to their broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity. In the face of increasing antibiotic resistance and the limitations of conventional therapies, natural bee-derived substances offer a promising alternative or support for the treatment of infections. This paper summarizes the current state of knowledge on the chemical composition, biological properties and antimicrobial activity of key bee products. The main mechanisms of action of honey, propolis and bee venom are presented, and their potential applications in the prevention and treatment of bacterial, viral and fungal infections are discussed. Data on their synergy with conventional drugs and prospects for use in medicine and pharmacology are also included. The available findings suggest that, with appropriate standardization and further preclinical and clinical analyses, bee products could become an effective support for the treatment of infections, especially those caused by pathogens resistant to standard therapies.
1. Introduction
Honey bees, belonging to the order of Hymenoptera, suborder Apocrita and family Apidae, are insects that play a fundamental role in shaping the balance of ecosystems, contributing to the pollination of a significant part of crop plants around the world [1,2,3,4]. According to estimates, almost 70% of global crop production is dependent on the activity of pollinators, primarily bees, whose functioning ensures stability and biodiversity [2,3,5]. From the perspective of humans, and especially agriculture, the role of bees translates into real economic benefits, which amount to many billions of euros per year. It is estimated that honeybees contribute directly to global agriculture to the amount of about EUR 153 billion per year [1,6]. Unfortunately, in recent decades there has been a steady decline in the numbers of these insects, caused by the impact of numerous biotic (parasites, infectious diseases) and abiotic (climate change, pesticides) factors, which poses a serious challenge to global food security [2,3,6,7].
Bees, in addition to their key role in pollinating plants, are also valued for providing products with high therapeutic potential. Of particular importance among them are honeybees, such as Apis mellifera (found mainly in Europe, America, Africa and Asia) and Apis cerana (from Southeast Asia), which produce a wide range of bee products rich in bioactive compounds, including polyphenols, flavonoids, proteins, organic acids and enzymes. The most important of these include honey, bee pollen, bee bread, royal jelly, propolis and bee venom, valued for centuries for their potential health-promoting properties [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. In the traditions of many cultures, these products have held an important place in phytotherapy for centuries, which is confirmed by historical references to their use in healing wounds, treating skin diseases and digestive system diseases [15,16]. An example would be the use of honey in ancient Egypt to disinfect wounds or propolis in ancient Greece as an antiseptic substance [17,18]. Nowadays, thanks to the development of biological and medical sciences, we are increasingly understanding the mechanisms of action of these natural products, and numerous studies indicate their antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antioxidant properties [3,5,19,20,21].
The importance of the biological properties of bee products is particularly important in the face of the dynamic increase in infections of various etiological origins (bacterial, viral, fungal) [3,5,19,20,21]. In the era of intensive antibiotic therapy and progressive multidrug resistance of pathogens, the search for new, effective and safe treatment assays is a priority for scientists and medical practitioners. An additional challenge is the toxicity of many commonly used synthetic drugs and limitations in their long-term use, which encourages the development of alternative or supportive therapies, including those based on natural substances [22]. The multifaceted effects of bee products make them a promising component in the fight against respiratory and digestive system infections, as well as in the prevention of skin diseases and oral diseases [3,5,19,20,21].
This article aims to discuss and systematize knowledge about the therapeutic potential of bee products in the treatment and prevention of infections of various etiologies. In particular, the mechanisms of action of honey, propolis, pollen, bee bread, royal jelly and venom will be presented, as well as the prospects for their use in combination with conventional pharmacotherapy. Analysis of available studies, while indicating significant limitations and potential risks, will allow for a broader understanding of how bee products can support efforts to combat increasingly frequent and complex health problems associated with infections. In the context of global challenges, such as multidrug resistance of microorganisms or limited access to modern drugs, further research and development of apitherapy is indicated as an important complement to standard medical care.
2. Bee Products and Their Chemical Composition
Bee products play a crucial role in the functioning of the hive, fulfilling a variety of biological and ecological functions [23,24,25]. Honey serves as the primary food source for bees, providing essential carbohydrates [26], while propolis, also known as “bee glue”, is used to seal gaps and protect the colony from pathogens [27]. Bee venom functions as a defense mechanism against predators [28]. The production processes of these substances are complex and depend on the interactions between bees and their environment [23,24,25,26,27,28]. Honey is produced by collecting nectar from flowers, which is then processed and stored in honeycombs [23]. Propolis is gathered by bees from plant resins and subsequently modified through the addition of waxes and enzymes [29]. Bee venom is synthesized in the venom glands of worker bees and deployed in threatening situations [30].
Beyond their medicinal uses, bee products are widely applied in various fields [31,32,33,34]. Honey is valued in cuisine for its flavor and nutritional properties [32], propolis is used in cosmetics due to its antiseptic qualities [33], and beeswax finds application in both industry and craftsmanship [35].
From a chemical perspective, bee products are rich in a wide range of bioactive compounds [36,37,38,39]. Honey consists primarily of simple sugars, but also contains proteins, enzymes, amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and polyphenols [11]. Propolis is a source of flavonoids, phenols, terpenes, and other compounds with antioxidant and antibacterial effects [40,41]. Bee venom contains peptides such as melittin and apamin, as well as enzymes including phospholipase A2, all of which exhibit diverse biological activities [42]. In scientific research, bee products are often used in various formulations [43,44].
Ethanolic and aqueous extracts are commonly employed to isolate bioactive compounds from propolis [43], while supercritical CO2 extraction allows for the acquisition of specific, highly pure fractions [45]. Vacuum and freeze-drying honey [46] and purified peptides from bee venom are also used in studies investigating their biological properties [47]. Standardization of these preparations is essential to ensure the reproducibility of results and the reliability of research [44,48].
2.1. Honey
Honey is a natural product produced by bees from plant-derived raw materials. Honey bees (Apis mellifera) collect nectar or honeydew (sweet secretions of sap-sucking insects) from plants and transform it into mature honey within the hive. Floral nectar typically contains 40–80% water and a significant amount of sucrose, whereas honeydew has a slightly different sugar composition—often richer in complex sugars (e.g., melezitose, raffinose) and with a higher mineral content [36,49]. For this reason, honeydew honey (originating, among others, from coniferous trees such as fir and spruce, as well as from deciduous trees like oaks and lindens) differs from nectar honey in color (it is darker), composition, and health-promoting properties [36,37]. Honeydew honey contains on average about 1% mineral components, whereas typical nectar honey contains only 0.1–0.5% [49]. Furthermore, honeydew honeys are found to contain more oligosaccharides and dextrins, whereas nectar honeys are dominated by simple sugars (glucose and fructose) and disaccharides [38,39]. However, the production process of both honey types is similar—bees concentrate the raw material in the hive and enrich it with enzymes, regardless of whether the source is nectar or honeydew [37,40].
Freshly collected nectar or honeydew is transported in the bee’s honey stomach (the so-called “honey crop”) and undergoes initial enzymatic processing during transport. Forager bees repeatedly detach and pass nectar droplets between one another, adding enzymes and evaporating water in the process [41]. Subsequently, hive bees place the processed liquid into honeycomb cells and accelerate further evaporation of water by vigorously fanning their wings. When the water content drops from approximately 60–80% to around 17–20%, and the sugar concentration reaches saturation, the bees seal the honeycomb cells with wax, protecting the mature honey from absorbing moisture and spoiling [50]. The final product—mature honey—takes the form of a thick, viscous liquid with high sweetness, capable of long-term storage due to its low water content and unique composition [51].
2.1.1. Enzymes of Honey
Enzymes added by bees play a key role in processing plant-derived raw materials into honey [52,53,54,55]. These enzymes originate primarily from the bees’ salivary glands (mainly the hypopharyngeal glands), and partly also from the plants themselves (nectar) and microorganisms present in the raw material [52]. The most important enzyme is invertase (sucrase)—secreted by the bees during nectar transport—which catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose (the dominant sugar in nectar) into two simple sugars: glucose and fructose [53]. As a result, honey mainly contains easily digestible simple sugars, with almost all sucrose being broken down (in ripe honey, the sucrose content is below ~5%) [54]. Another enzyme introduced by bees is α- and β-amylase (diastase), which breaks down any polysaccharides (e.g., starch from pollen grains or honeydew) into dextrins and simpler sugars [55]. Diastase activity is a traditional indicator of honey quality and freshness—this enzyme is quite sensitive to heating and prolonged storage, so its level decreases in overheated or old honey [52].
Another key enzyme is glucose oxidase (GOX), also added by bees during the maturation of honey [56]. This enzyme oxidizes a portion of glucose into gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of oxygen and the FAD cofactor [57]. Gluconic acid lowers the pH of honey (typically to ~3.2–4.5), giving it its characteristic acidity, while hydrogen peroxide is responsible for honey’s so-called “peroxide activity”—its antiseptic and bactericidal properties [58] In fresh, mature honey, the concentration of H2O2 is kept at a safe level thanks to the activity of catalase—an enzyme that breaks hydrogen peroxide down into water and oxygen [52]. Interestingly, catalase enters honey primarily from nectar and pollen, as well as from microorganisms, rather than from the bees themselves [56]. In honeys with high catalase activity (e.g., some honeydew honeys or manuka honey), very low levels of H2O2 are observed, whereas honeys with low catalase activity accumulate more peroxide and display stronger bactericidal peroxide activity [52]. In addition to the aforementioned enzymes, honey also contains others such as phosphatases, lysozyme, β-glucosidase, and plant-derived enzymes, which may continue to modify honey’s composition during maturation [59]. Thanks to the synergistic action of enzymes and the evaporation of water, raw nectar or honeydew is transformed into stable honey, rich in simple sugars, with an acidic pH and the presence of bioactive components [52].
2.1.2. Chemical Composition of Honey
Honey is a mixture of several hundred different chemical compounds, with carbohydrates being the dominant component [32,36,49,60]. On average, the total sugar content in mature honey ranges from 70 to 85% by weight, with the main constituents being monosaccharides: fructose (approximately 30–45%) and glucose (approximately 25–40%) [49]. The fructose-to-glucose ratio is usually >1 (typically in the range of ~1.2–1.7), which makes honey slightly sweeter than sucrose—fructose has a higher sweetness level than glucose [60]. In addition to simple sugars, honey also contains disaccharides (up to around 5–10%, mainly maltose, isomaltose, sucrose, and trehalose), as well as oligosaccharides and dextrins (together up to a few percent) [49]. The exact sugar profile depends on the origin of the honey—honeydew honeys contain more complex sugars (e.g., melezitose, which can crystallize into so-called “cement honey”), whereas nectar honeys are dominated by glucose and fructose [32,36].
The second most important component of honey is water—its content typically ranges from 16 to 20% [61]. The low water activity (aw ~0.5–0.6) is responsible for honey’s long shelf life and its ability to inhibit microbial growth [62]. If the water content exceeds 20%, honey becomes susceptible to fermentation by osmotolerant yeasts, which is why bees carefully regulate this parameter during the maturation process [61,62].
Although sugars and water account for over 90% of honey’s mass [36,49,60,61,62], the remaining small fraction (5–10%) is responsible for many of its unique biological properties [49,52,63,64]. Honey contains organic acids (0.5–1%), primarily gluconic acid (a product of glucose oxidase activity), as well as malic, citric, succinic, and other acids—these are what give honey its acidity (pH ~3.5) [52,64]. Proteins and nitrogenous compounds make up approximately 0.2–0.5% of honey—these include enzymes (invertase, diastase, glucosidase, catalase, phosphatase, and others), free amino acids (over 25 have been identified, with proline—mainly from bee secretions—being the most abundant), and trace amounts of proteins derived from pollen [49]. The content of free amino acids and proteins also affects honey’s tendency to brown (Maillard reactions) during aging and heating [64].
Honey contains small amounts of vitamins, primarily from the B group, including thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (PP), pyridoxine (B6), pantothenic acid (B5), biotin (H), and folic acid (B9), as well as vitamins C, K, and trace amounts of vitamin A [49,65,66]. However, the overall vitamin content is low—typically several dozen milligrams per kilogram of honey—making it an insignificant dietary source of vitamins [65].
Of much greater importance for honey’s biological activity are its phenolic compounds and flavonoids. Although present only in trace concentrations (tenths or hundredths of a percent), these compounds exhibit notable antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects [49,67,68]. The phenolic profile of honey varies with its botanical origin—for instance, buckwheat honey contains rutin and gallic acid, manuka honey is rich in leptosperin and methylglyoxal, while eucalyptus honeys contain ellagic acid [36]. These phenolic acids and flavonoids are regarded as the main contributors to honey’s antioxidant potential and, to a lesser extent, its antimicrobial properties [49,63]. Darker honeys (e.g., buckwheat, honeydew, or heather honey) typically contain higher levels of phen chrysin olics and show stronger antioxidant and antibacterial activities compared to lighter honeys such as acacia [36]. Notably, several flavonoids commonly identified in honey, such as apigenin, chrysin, pinocembrin, eupatilin, myricetin, quercetin and phloretin, have been shown to exert a broad spectrum of biological activities. These include anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, photoprotective, antimicrobial and even anticancer properties, particularly in relation to skin health. Their presence, even at low concentrations, reinforces the therapeutic potential of honey and supports its application beyond simple nutrition [11,69].
Honey also contains approximately 20–30 mineral elements [49,70,71]. Potassium (K) is the predominant mineral, accounting for a significant portion of the ash content. Other minerals include calcium, sodium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, manganese, silicon, and various trace elements [70]. The total ash content ranges from 0.1 to 0.5% in nectar honeys and can reach up to 1% in honeydew honeys [49]. Mineral composition is strongly influenced by the soil conditions where nectar-producing plants grow, which is why it can serve as an indicator of honey’s geographical origin [71]. Although the overall mineral percentage is low, these elements are important for the electrical conductivity of honey (used in the identification of honeydew honeys) and may influence enzymatic activity and product stability [49,70,71].
2.1.3. Forms of Honey Utilized in Research
In laboratory studies on the antimicrobial properties of honey, various forms and preparations of the product are used, with efforts made to ensure proper standardization [72,73,74,75,76,77]. The simplest form is raw honey—taken directly from the comb (after centrifugation and, if necessary, filtration to remove wax) [72]. This type of honey is used, for example, in vitro tests as a complete research sample [72]. It is often dissolved in sterile water or broth to a defined concentration in order to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) or zones of growth inhibition on solid media [49,70,71]. Typical concentrations of honey tested against bacteria range from 5 to 50% (v/v) [75]. Due to its high viscosity and sugar content, it is often necessary to compare the effects with so-called artificial honey—a sugar solution that mimics the sugar composition of natural honey but lacks biologically active components. This allows researchers to determine what portion of the antimicrobial effect is due to osmotic pressure (sugars) and what portion results from honey’s unique bioactive compounds [55]. For example, Mundo et al. demonstrated that artificial honey (a mixture of glucose, fructose, and maltose in concentrations corresponding to natural honey) inhibits bacterial growth significantly less effectively than real honey, confirming the contribution of hydrogen peroxide and other compounds to its antibacterial activity [77].
Recent studies have also demonstrated that specific phenolic compounds present in honey—such as p-coumaric acid, hydroxyphenyl acetic acid, 1H-quinolinone, and abscisic acid—strongly correlate with antimicrobial activity. These molecules may act via multiple mechanisms, including membrane disruption, interference with bacterial DNA replication, or modulation of gene expression. For example, p-coumaric acid, abundant in buckwheat honey, has been shown to inhibit the growth of S. aureus and E. coli. This highlights the importance of not only total phenolic content, but also specific compound composition when evaluating the therapeutic potential of honey [78].
2.2. Propolis
Propolis (bee glue) is a resinous substance collected by bees from plant buds and exudates, which they then use inside the hive to seal gaps and smooth the surfaces of the nest [79]. Thanks to its antimicrobial properties, propolis forms a protective barrier within the hive that limits the growth of bacteria and fungi, helping to maintain a healthy microclimate for the colony [80]. This phenomenon is considered part of the so-called social immunity of honeybee colonies [79]. Bees are also capable of covering the bodies of dead intruders that are too large to remove from the hive with a layer of propolis, effectively mummifying them and preventing the decomposition of their remains [79,81].
Raw propolis typically contains approximately ~50% plant-derived resinous substances, ~30% beeswax, ~10% essential oils, with the remainder made up of pollen and other impurities [29,79,82]. In total, more than 300 different chemical compounds have been identified in propolis [63,64]. The main groups include polyphenols, primarily flavonoids, phenolic acids and their esters, and terpenes [83]. Propolis also contains waxes and aromatic essential oils [79,83,84]. Among the aromatic acids found in propolis are caffeic acid, ferulic acid, and cinnamic acid [85].
The composition of propolis depends on the source of resins collected by bees, which varies according to local flora and geographical region [84,86,87,88]. In temperate climates (e.g., in Europe), bees mainly gather propolis from the buds of poplar trees (Populus spp.), which is why European propolis (typically brown) is rich in flavonoids and other polyphenols characteristic of poplar exudates [29]. In contrast, Brazil is known for its so-called “green” propolis, derived from the plant Baccharis dracunculifolia, which is distinguished by a high content of prenylated derivatives of cinnamic acid (e.g., artepillin C) [89]. Meanwhile, “red propolis”, found for instance in Cuba, is produced from the resins of plants such as Clusia spp., and contains characteristic polyprenylated benzophenones not found in temperate-zone propolis [90].
Propolis shows strong antimicrobial activity. Numerous studies have confirmed the efficacy of this natural product against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, viruses, as well as pathogenic fungi [91,92]. It also possesses high antioxidant potential, owing to the presence of numerous polyphenolic compounds capable of neutralizing free radicals [85], propolis has well-documented anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to the inhibition of inflammatory mediators and modulation of the body’s immune response [93].
In scientific research on propolis, the most commonly used preparation is the ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP), which effectively extracts biologically active components [79]. Alternatively, non-alcoholic extracts, such as glycerine-based ones, are also used, although they differ in composition and activity from EEP [94]. To analyze the individual components of propolis, researchers also isolate phenolic fractions or specific pure compounds, for example, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE), to study their individual biological effects [95].
2.3. Bee Venom
Bee venom (apitoxin) plays a key role within the bee colony, primarily as a defensive agent protecting the hive from intruders [30,96,97]. Worker honeybees possess stingers connected to venom glands, and when threatened, they inject a dose of venom into the target—an effective defense mechanism [30]. Components of the venom (e.g., melittin) cause an immediate, sharp pain in the attacked organism [97], which deters predators and intruders from continuing their assault [30]. There are also reports suggesting that venom may play an additional role in maintaining colony health, antimicrobial peptides derived from bee venom have been detected on wax combs and bee bodies, suggesting a possible contribution of venom to bee social immunity [96].
Chemically, bee venom is a complex mixture of biologically active compounds. Over 80% of its mass is water, while the remainder consists of a diverse range of components, including proteins (enzymes), peptides, biogenic amines, and other substances [30,42,98]. The main component of bee venom is the peptide melittin, which makes up approximately 50–60% of its dry mass [42]. Other peptides are also present, such as apamin (~2%), a neurotoxin that blocks Ca2+ —dependent potassium channels in nerve cells, and the mast cell degranulating peptide (~2%), which has anti-inflammatory properties [98]. Important enzymatic components include phospholipase A2 (approximately 10–12%) [42] and hyaluronidase (approximately 1–3%) [42]. Phospholipase A2 hydrolyses phospholipids in cell membranes and, in combination with melittin, causes significant membrane damage [99], while hyaluronidase degrades hyaluronic acid in host tissues, increasing their permeability and facilitating the spread of venom [100]. Both enzymes are considered among the most potent allergens in bee venom [30]. Bee venom also contains small amounts of biogenic amines such as histamine and catecholamines (dopamine and noradrenaline) [101]. Histamine increases capillary permeability and intensifies the inflammatory response, whereas catecholamines raise blood pressure and accelerate heart rate, which helps to distribute the venom more rapidly throughout the victim’s body [30].
Melittin, the main component of bee venom, is a polypeptide made up of 26 amino acids, positively charged and amphipathic in nature [102]. By binding to the lipids of cell membranes, melittin forms pores (~4 nm in diameter), leading to cell lysis [103]. As a result, melittin exhibits strong cytolytic activity, causing, among other effects, haemolysis (the destruction of red blood cells) due to membrane damage [104]. Numerous preclinical studies have also confirmed its anticancer properties—melittin inhibits growth and induces death in cancer cells across various models (including melanoma, lung cancer, glioma, and leukemia) [102,105,106,107,108]. Cancer cells have been observed to be more sensitive to melittin than healthy cells, suggesting a degree of selectivity in its action [102]. The mechanisms underlying its anticancer effect include the induction of apoptosis and disruption of key signaling pathways that regulate cancer cell survival and proliferation [109]. In addition, melittin displays immunomodulatory properties—for instance, it inhibits NF-κB activity and reduces the release of pro-inflammatory mediators (e.g., TNF-α), thereby helping to alleviate inflammatory responses [110,111].
Research on bee venom faces several significant challenges. One of them is obtaining sufficient quantities of the raw material with standardized quality. The most commonly used assay involves electrically stimulating bees to sting a special collection membrane [112]. This technique avoids killing the bees but may result in the loss of certain volatile components (e.g., histamine) during collection [30]. An alternative approach is the extraction of venom directly from the venom gland; however, material obtained this way is often contaminated with fragments of bee tissue and tends to be of lower purity [113]. Another major challenge is the risk of severe allergic reactions [30]. Bee stings are among the most common causes of anaphylaxis—it is estimated that approximately 8% of the population experiences anaphylactic shock following a sting [104]. The main allergen in bee venom is phospholipase A2, but melittin and hyaluronidase also possess strong allergenic properties [114]. The risk of a sudden allergic reaction is a serious limitation to the potential therapeutic use of bee venom [30,114].
3. Antimicrobial Activity of Bee Products
3.1. Characterization of Microbial Infection
Human infections are caused by a diverse array of bacterial and fungal pathogens, which collectively exact a massive toll on global health. Bacterial infections alone were associated with an estimated 7.7 million deaths in 2019—roughly one in eight of all deaths worldwide. A recent systematic analysis identified 33 bacterial species or genera as the predominant causes of these deaths [115]. Among these, five pathogens—Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa—accounted for about 55% of bacterial infection fatalities. These exemplify the major taxonomic groups of bacterial pathogens: Gram-positive cocci and Gram-negative rods are common causes of human disease. Other important groups include the Mycobacteria; notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis remains a leading single-agent killer, causing ~1.4 million deaths in 2021, with especially high burdens in low-resource regions [116]. In 2019, over 6 million deaths were attributed to just three syndromes caused by bacteria, reflecting the enormous number of severe bacterial infections occurring globally each year [115].
Fungal pathogens, also contribute substantially to human morbidity and mortality. Fungi are ubiquitous in the environment and an estimated 3–5 million species are able to cause disease in humans [117]. The pathogenic fungi belong primarily to the phyla Ascomycota and Basidiomycota, and species from four genera—Aspergillus, Candida, Cryptococcus, and Pneumocystis. These fungi cause the majority of life-threatening invasive fungal infections. For example, Candida yeasts (especially C. albicans and related species) are the most common cause of invasive mycoses such as candidemia, while Aspergillus fumigatus and relatives cause invasive aspergillosis in immunosuppressed hosts [118]. Cryptococcus neoformans causes cryptococcal meningitis, and Pneumocystis jirovecii causes pneumonia in immunocompromised people. An estimated >150 million people develop serious fungal diseases annually. Global deaths due to fungal infections are now estimated at approximately 1.5–1.6 million per year [117].
Both bacteria and fungi are increasingly developing resistance to antimicrobial therapies, undermining our ability to treat infections. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in bacteria has reached crisis levels globally. In 2019, an estimated 4.95 million deaths were associated with drug-resistant bacterial infections, including 1.27 million deaths directly attributable to AMR [119]. Common pathogens that were once readily treatable now possess strains resistant to multiple antibiotic classes. For instance, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) has spread worldwide in hospitals and communities [120] and was responsible for over 100,000 deaths in 2019. Similarly, multi-drug-resistant E. coli and K. pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii resistant to nearly all β-lactams, and fluoroquinolone-resistant P. aeruginosa are causing difficult to treat infections. These six leading drug-resistant bacteria together accounted for about 930,000 deaths attributable to AMR in 2019 [119]. These trends underscore that decades of antibiotic usage have accelerated the evolution of resistance [121]. Bacteria acquire resistance genes via mutations or horizontal gene transfer, enabling them to neutralize drugs, alter drug targets or expel drugs. The result is that infections which were once routine to cure can become resistant, necessitating last-line therapies or leaving no effective treatment [122]. Without concerted action, the spread of multidrug-resistant bacteria threatens to reverse the success of combating microbial infections the availability of antibiotic treatment allowed.
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity of Honey
The antimicrobial activity of honey has been recognized since the late XIX century [123]. Modern research has shown it exhibits significant activity against many bacteria and other microorganism species. Due to the difference in chemical composition based on the nectar or honeydew source [124] the effectiveness of local honeys can significantly differ between each other.
It has been established that honey’s antibacterial effect is the result of two pathways. The peroxide dependent pathway is the result of the presence of glucose oxidase in honey. This enzyme, by catalyzing the oxidation of glucose to β-gluconolactone, produces hydrogen peroxide—H2O2 [125], which has a directly bactericidal effect, causing oxidative damage to cell structures [126], and degradation of DNA [127]. It has been show that this mechanism is the major contributor to the antibacterial effect, with the notable exception of manuka honey [128]. The rest of the antibacterial effect of honey is ascribed to the peroxide independent pathway, which is the result of various other physiochemical properties of the substance. The high sugar content resulting in high osmolality causes cellular dehydration due to osmotic pressure [72]. The typical pH of honey, 3.2–4.5 [63], is outside the range well tolerated by most common bacterial pathogens [129].
Proteins other than glucose oxidase may also play a significant role, the main royal jelly protein 2 and defensin 1, both present in honey, have significant antimicrobial activity [130,131]. Phenolic, as well as flavonoid content of honey has also been correlated to its effects against bacteria [132,133]. It has to be noted that due to the range of possible chemical compositions of different honeys, there exists significant variance in the contributions of these compounds to the general effect [134]. One example of it is methylglyoxal—a bioactive compound found in Manuka honey, which has been of particular interest to researchers due to its antioxidant and antibacterial properties [135,136]. The honey is produced from nectar of Leptospermum scoparium, containing dihydroxyacetone [137] which is non-enzymatically converted to methylglyoxal during the honey’s maturation process. This compound has been shown to be the main cause of the Manuka honey’s non-peroxide antibacterial activity exceeding that of other products of this type [134,138].
Honey also has been shown to exhibit significant antifungal activity [134]. While the antifungal mechanisms are comparatively less researched compared to the antibacterial, it is understood that both peroxide dependent and independent pathways play a role [139]. In addition, the flavonoid content has been shown to contribute to the effect, resulting in significant research utilizing the flavonoid extract of honey against Candida spp. and other fungal pathogens [140].
It must be noted that honey in its typical form is limited to topical treatment, hence the need to utilize extracts, potentially expanding the uses of the substance to other routes of administration. In topical treatment, honey and honey based product has been particularly researched for wound treatment [141], as it exhibits significant activity against common pathogens in wound infection [142] (Table 1).

Table 1.
Selection of articles on the antimicrobial effect of honey.
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of Propolis
In recent years, propolis has been the subject of extensive into its potential role in medicine from many perspectives, with its antimicrobial activity being one shown a particular interest [157] (Table 2). The analysis of that property has its challenges—the form of propolis most often used is an ethanol extract, requiring higher scrutiny towards the results due to bactericidal effect of the solvent itself. This can be mitigated by utilizing DMSO in sub-inhibitory concentration as a solvent after evaporating the extract as described by Wieczyńska et al. [158]. The extract has also been shown to exhibit irregular diffusion into agar mediums, as shown by Bosio et al. [159], causing, in particular, the results of disc diffusion assays to be potentially unreliable.
Despite these limitations, it has been shown that propolis has both a direct and indirect mechanism of antibacterial activity. Propolis composition varies significantly geographically, a wide array of its biological properties is accredited to its phenolic and flavonoid content [160,161], but as described by Bouchelaghem et al. [162] a direct correlation cannot be assumed in all cases. Artepillin C, one of the antioxidant phenolic compounds whose high content is a defining characteristic of Brazilian green propolis, is a significant contributor to its bacteriostatic effect [163,164]. Prenylflavonoid constituents of propolis found in Australia [165], Taiwan and Japan [166], propolins present a significant contribution to the inhibitory activity against Gram-positive strains of bacteria. Different propolins found in the same propolis sample exhibit synergistic and inhibitory interaction towards each other’s antibacterial activity [92]. Other flavonoids also present significant activity against bacteria, apigenin [36] and pinocembrin [167] isolated from Chilean propolis exhibited ability to not only effectively inhibit growth of S. mutans, but also completely prevent biofilm formation [168]. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) is a compound found commonly in propolis [169], capable of inhibiting growth of S. aureus, B. subtilis and P. aeruginosa [170]. In Australian propolis, the inhibitory effect against S. aureus has been ascribed to C-geranyl flavonoids and triterpenoids ability to interact with the cell wall of Gram-positive bacteria [165].
Propolis has also been shown to exhibit significant antifungal properties, in particular against yeast and filamentous fungi capable of causing human infection. One of the primary mechanisms of antifungal activity has been determined to be disruption of fungal cell membrane by binding to membrane sterols [171], inhibition of cell wall synthesis by CAPE [172], and disruption of the cell’s redox balance by polyphenols, causing oxidative stress induction [173].
Due to the dynamic increase in infections with multidrug resistant bacteria [119], the perspective of utilizing propolis against bacterial strains such as methicillin resistant S. aureus has been of particular interest to researchers. Propolis has been shown to be an effective inhibitor of staphylococci growth and one not affected by antibiotic resistance mechanisms of pathogens [174,175]. Additionally, propolis exhibits ability to disrupt biofilm formation [176], downregulate expression of virulence related genes [177]. While the mechanism of antibacterial activity against S. aureus is not yet fully understood, it has been shown that propolis induces changes in cell wall and membrane structure of the bacteria [177]. This mechanism is also a potential explanation for another useful phenomenon—some propolis samples have been shown to have strong synergistic interactions with many antibiotics [178], in particular ones inhibiting cell wall synthesis [175], such as β-lactams and glycopeptides. Australian propolis has been found to reduce expression of genes responsible for β-lactam resistance in MRSA [81].

Table 2.
Selection of articles on the antimicrobial effect of propolis.
Table 2.
Selection of articles on the antimicrobial effect of propolis.
| Material | Microorganism | Assay | Key Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol extract of Brazilian propolis | Clinical isolates: 210 of S. aureus, 48 of MRSA and 162 of MSSA | In vitro-agar dilution assay | The MIC50 and MIC 90 remained similar for all analyzed strains. Both MSSA and MRSA ATCC strains being inhibited by EEP at 1420 µg/mL concentration, showing that the mechanism of resistance to methicillin does not affect the antimicrobial effect of propolis against S. aureus. | [174] |
| Ethanol extract of Polish propolis | S. epidermidis strains isolated from blood samples and ATCC 35983 | In vitro-Tissue culture plate assay, broth dilution assay | The extract exhibited significant antibacterial effect against S. epidermidis. EEP reduced bacterial biofilm formation at concentrations above 1/8 MIC, while concentrations lower than 0.025 mg/mL increased biofilm formation. | [179] |
| Ethanol extracts of propolis from Yangpyeong, Boryung, Cheorwon and Yeosu | S. aureus ATCC 25923, B. subtilis ATCC 15523, S. typhimurium ATCC 13311 C. albicans ATCC 10231 | In vitro-disc diffusion assay, induced lipoperoxidation | Comparison of inhibition zones has shown the Yeosu and Cheorwon propolis extracts to have the strongest antimicrobial effect. These samples contained highest total polyphenol and flavonoid content and antioxidant activity. | [164] |
| Italian propolis dry extract dissolved in broth with DMSO and Tween 80 | Clinical isolates from respiratory tract infections: S. aureus, β-hemolytic streptococci, S. pneumoniae, M. catarrhalis, H. influenzae, K. pneumoniae, E. coli, P. mirabilis, P. aeruginosa and C. albicans strains | In vitro-broth microdilution assay. | MIC values show propolis as an effective agent against most tested strains, except for Enterobacteriaceae, for which inhibitory effect was only achieved at high concentrations. MIC of propolis against S. pneumoniae, M catarrhalis and H. influenzae strains is within range of the respective MBC values. Bactericidal effect was shown against all isolates at 4xMIC concentration, except S. pyogenes. | [180] |
| Ethanol extracts of Turkish propolis from different areas of Marmara region | Clinical isolates: E. coli, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, beta-hemolytic streptococci | In vitro-agar dilution assay | Analyzed samples’ MIC values showed significant difference in antibacterial effect between samples, especially against Gram-negative bacteria. The sample with the stronger antibacterial effect contained 3 chemical components not found in the less effective sample: 3-methyl-2 butenol, diethyl succinate and phenyl-ethyl alcohol. | [181] |
| Ethanol extracts of propolis samples from different regions of Turkey | S. Enteritidis ATC 13076 and L. monocytogenes ATCC 1462 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay | All samples showed strong antibacterial effect on both species at 1:10 dilution, no viable bacteria were determined after incubation. Against L. monocytogenes, at 1:100 dilution 8 samples had a bactericidal effect, 11 an inhibitory effect and 6 no effect. Against S. enteritidis, 5 samples had a weak inhibitory effect and 20 no effect. | [182] |
| Methanol extract of Chinese red propolis | S. aureus ATC 25923 (methicillin sensitive), ATC 43300 (methicillin resistant) | In vitro-agar diffusion assay, broth microdilution assay, intracellular protein and nucleic acid leakage assay, metabolomic analysis, | Extract showed significant antibacterial effect against MSSA and MRSA, disrupting the cell wall, cell membrane and inducing changes in cell morphology. Metabolomic analysis showed enrichment of 12 pathways in MSSA and 9 in MRSA after treatment with the extract. Expression of genes related to biofilm formation, autolysis, cell wall synthesis and virulence of MRSA was found to be downregulated. | [177] |
| Ethanol, methanol, DME and aqueous extracts of Taiwanese green propolis | S. aureus BCRC 10780, BCRC 10781, BCRC 101451, methicillin resistant S. aureus ATCC 43300, B. subtilis BCRC 10675, L. monocytogenes BCRC 14845, E. coli BCRC 10675, P. aeruginosa BCRC 10944, P. larvae BCRC 14187 | In vitro-microdilution assay | Comparable levels of antibacterial activity were exhibited by all extracts apart from the aqueous, which was unable to inhibit growth. None of the extracts inhibited growth of E. coli. Propolin C exhibited the lowest MIC value against Gram-positive strains. None of the tested propolis samples and propolin isolates inhibited growth of E. coli or P. aeruginosa. Out of the tested propolin combinations, twofold concentration of propolin C with propolin D exhibited highest antibacterial activity, higher than pure propolin C or total propolis extract. | [92] |
| Methanol extracts of Chilean propolis from the Región del Maule | S. aureus ATCC 25923, methicillin-resistant S. aureus ATCC 43300, E. coli ATCC 25922 and 3 clinically isolated strains, clinically isolated stains of S. enteritidis, Salmonella spp., Y. enterocolitica, Pseudomonas spp. and P. mirabilis. | In vitro-broth microdilution assay | Samples showed significant variance in antibacterial activity beyond the expected effect of total phenolic and flavonoid content. The highest level of activity was exhibited by central valley propolis samples. The strains most susceptible to the activity of propolis extracts were E. coli, Y. enterocolitica and S. enteritidis. | [183] |
| Ethanol extract of Italian propolis and bud poplar resins | P. aeruginosa P1232 expressing the luciferase gene and P. aeruginosa PAO1 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay, static biofilm assay, swimming motility, swarming motility and twitching motility analysis | Both extracts exhibited comparable levels of bacteriostatic activity. At sub-MIC concentration both extracts inhibited biofilm formation and swimming motility. Bud poplar resin sample increased swarming motility, while neither sample affected twitching motility of the bacteria. | [184] |
| Ethanol, n-hexane, ethyl acetate and n-butanol extracts of Pacific propolis from the Guadalcanal Province | clinical isolates of methicillin resistant S. aureus, methicillin sensitive S. aureus ATC 9144, P. aeruginosa ATCC 25668 | In vitro-agar dilution assay | Ethanol extracts exhibited the strongest antibacterial activity, showing bacteriostatic effect against all tested MRSA and MSSA strains. No samples inhibited the growth of P. aeruginosa. Four prenylflavanones were reported in Solomon Island propolis for the first time, propolins C and D exhibiting strong anti-MRSA activity. | [185] |
| Polyphenol-rich extract of Chilean propolis, isolated polyphenols | Clinically isolated S. mutans strains | In vitro-well microdilution assay, evaluation biofilm formation with fluorescence microscopy | Polyphenol mixture exhibited antibacterial activity comparable to chlorhexidine. Apigenin and pinocembrin had the lowest MIC values against S. mutans out of the isolated polyphenols. All samples inhibited biofilm formation, with apigenin and pinocembrin disrupting the biofilm structural integrity. | [168] |
| Ethanol extract of Brazilian green propolis | P. gingivalis ATCC 33277, W83, W50 and YH522, P. nigrescens ATCC 33563, F. nucleatum 20, ATCC 23726, A. actinomycetemcomitans (serotype b) Y4, ATCC 29522, P. loescheii ATCC 15930, Streptococcus spp. ATCC 33397, 51100, 10558, 6245, UA159, 9759, 10556, 6715, E. coli BW25113, S. oralis No. 10 | In vitro-well microdilution assay, biofilm formation assay, membrane permeability analysis, | Extract exhibited stronger antibacterial effect against P. gingivalis, than against other oral bacteria. Extracts had a rapid bactericidal effect caused by disruption of cell membrane and bleb formation. The active compounds were determined as artepillin C, baccharin, and ursolic acid. Formation of biofilm was inhibited at sub-MIC concentrations. | [186] |
| Magnetite nanoparticles functionalized with ethanol extract of Moroccan propolis in combination with chloramphenicol | Methicillin sensitive S. aureus ATC 6538, clinical isolates of methicillin resistant S. aureus | In vitro-well microdilution assay | Functionalized magnetite nanoparticles exhibited strong antibacterial effect against both methicillin sensitive and resistant S. aureus. Nanoparticles with both the propolis extract and chloramphenicol exhibited complete inhibition of bacterial growth after 2 h in 2 MRSA strains. The mechanism of action was determined to be the disruption of cell wall structure and cytoplasm leakage. | [187] |
| Ethanol extract of Italian propolis in combinations with antibiotics | Clinically isolated strains: S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. hominis strains, S. haemolyticus, S. warnerii, S. capitis, S. auricularis, S. faecalis, S. viridans, S. β-haemolyticus, S. pneumoniae | In vitro-agar dilution assay, lipase test, coagulase test, propidium iodide uptake test, adherence test | Extract exhibited strong antimicrobial activity, caused by membrane disruption. It inhibited virulence factors, reducing lipase activity and completely suppressing coagulase activity in Staphylococcus spp. All tested antibiotics apart from erythromycin and ceftriaxone exhibited synergistic effect with the propolis extract, especially ampicillin, gentamicin and streptomycin MIC90 values were reduced up to 250 times. | [188] |
| Ethanol extracts of Polish propolis | clinically isolated coagulase positive S. aureus strains and reference S. aureus strains, methicillin sensitive ATCC 25923 and methicillin resistant ATCC 43300 | In vitro-disk diffusion assay, broth microdilution assay | Polish propolis exhibited antibacterial activity against both MSSA and MRSA. Significant synergistic effects were observed in combinations with cefoxitin, clindamycin, tetracycline, tobramycin, linezolid, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, penicillin and erythromycin, while no synergism was found with ciprofloxacin and chloramphenicol. | [178] |
| Ethanol extract of commercial Brazilian propolis and a commercial antimicrobial containing gentamicin and amoxicillin | Staphylococcus strains isolated from Brazilian cattle | In vitro-broth microdilution assay | Extract at ½ MBC exhibited strong synergistic effect with the antibiotics, lowering the MIC and MBC values against Staphylococcus spp. of both gentamicin and amoxicillin by a factor of 10. | [189] |
| Ethanol extracts of Brazilian and Bulgarian propolis | S. typhi standard serovar 00238 | In vitro-agar dilution assay | Both extracts showed significant antibacterial activity, the Brazilian sample showed a bacteriostatic activity, while the Bulgarian sample exhibited a bactericidal one. No synergy between the propolis samples and tested antibiotics was found. | [190] |
| Ethanol extract of Australian propolis | Methicillin resistant S. aureus ATCC 43300 | In vitro-disc diffusion assay, resazurin microdilution assay, nucleic acid leakage assay, propidium iodide staining assay, resistance reversal assessment | Extract exhibited activity against methicillin resistant S. aureus, disrupting cell wall and membrane. At ½ MIC and 1MIC concentrations respectively, the extract significantly reduced the expression of PBP2a and activity of β-lactamase, inhibiting the main mechanisms of antibiotic resistance found in MRSA. At ½ MIC formation of the bacterial biofilm was inhibited. | [176] |
| Ethanol extract of propolis (Sigma P8904) | Methicillin resistant S. aureus ATCC 33591 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay In vivo-rabbit nasal colonization model, examination of polymorphonuclear leukocyte count | Both the propolis extract drops and topical mupirocin treatment significantly inhibited colonization at MIC concentration. Group receiving both treatments produced the least bacteria from nasal cultures, as well as the lowest PMNL count. | [191] |
| Ethanol extracts of German, Irish and Czech propolis, Aqueous extract of German propolis | Reference strains: Gram-positive, gram-negative, Candida spp. Clinically isolated: methicillin resistant S. aureus strain, K. pneumoniae strains and Candida spp. strains | In vitro-broth microdilution assay, checkerboard dilution assay, time-kill assay, | All evaluated extracts exhibited significant antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin and vancomycin resistant strains. Against Gram-negative bacteria, the ethanol extracts were shown to be moderately effective, except for P. aeruginosa which proved resistant. Against Candida spp. Irish and Czech samples exhibited a fungicidal effect, while German samples were fungistatic. Irish propolis exhibited strong synergistic activity with vancomycin, oxacillin and levofloxacin against S. pyogenes, MRSA and vancomycin resistant Enterococcus. | [175] |
| Ethanol extract of Chinese propolis | Methicillin resistant S. aureus ATCC 43300 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay, checkerboard assay, nucleic acid leakage assay, live/dead staining assay, β-lactamase activity test | The combinations of the propolis extract with ampicillin and oxacillin exhibited strong synergistic effect in antibacterial activity against MRSA. Resistance reversal analysis showed that at ¼ MIC the extract reduced expression of PBP2a and the β-lactamase activity. Extract also caused cell wall and membrane damage. | [192] |
| Korean propolis in composite nanoemulsion with PVA and chitosan | Methicillin resistant S. aureus ATCC 33591, C. perfingens NCTC 8237 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay, assessment of biofilm formation In vivo-rat wound infection model | Composite exhibited antibacterial properties against both strains comparable to azithromycin in vitro. At high concentrations of propolis, the composite effectively inhibited biofilm formation, causing its complete destruction. The in vivo study showed the propolis composite to have an ameliorative effect, accelerating wound curing and decreasing MRSA infection. | [193] |
| Ethanol extracts of Australian propolis | S. aureus ATCC 25923, K. pneumoniae ATCC 13883, C. albicans ATCC 10231 | In vitro-agar diffusion assay, broth microdilution assay | Extracts exhibited bactericidal activity against S. aureus, no activity against Gram-negative or yeast strains was detected. The effect against staphylococci was determined to be the result of C-geranyl flavonoids and triterpenoids in the propolis | [165] |
| Ethanol extracts of Greek and Cypriot propolis | S. dysenteriae NCTC 2966, S. typhimurium NCTC 12023, E. aerogenes NCTC 10006, Y. enterocolitica NCTC 10460, E. coli NCTC 09001, S. aureus NCTC 6571, ATCC 25923 S. epidermidis NCTC 11047, B. cereus NCTC 7464, ATCC 9139, L. monocytogenes NCTC 10357, ATCC 7644, C. tropicalis ATCC 13801 C. albicans ATCC 10231, L. bulgaricus ACA-DC 101 L. fermentum F 12, L. casei LC 14, L. delbrueckii LDD-C1, L. plantarum LP 101, La. helveticus LH 09 | In vitro-agar diffusion assay | Extracts exhibited a broader spectrum of antimicrobial activity than nisin. Tested samples had the strongest antibacterial properties against Gram-positive strains. Lactobacillus spp. strains were resistant to the activity, indicating selectivity beneficial for probiotic preservation. | [194] |
| Ethanol extracts of Anatolian propolis | S. mutans ATCC 25175, S. aureus 6538-P, S. sobrinus ATCC 33478, S. epidermidis ATCC 12228, E. faecalis ATCC 29212, M. luteus ATCC 9341. P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, E. coli ATCC 11230, S. typhimurium CCM 5445, E. aerogenes ATCC 13048, C. albicans ATCC 10231, C. tropicalis ATCC 665 and C. krusei ATCC 6258 | In vitro-broth macrodilutions assay | All extracts exhibited a potent antibacterial effect against Gram-positive bacteria. Less activity was achieved against Gram-negative strains, especially P. aeruginosa and S. typhimurium. The sample from Bursa proved the most effective, strongly inhibiting Candida spp. and oral pathogens, suggesting clinical potential in dental care. Total flavonoid content was shown to be correlated with antimicrobial potency of propolis | [195] |
| Ethanol extracts of Serbian propolis | S. epidermidis ATCC 14990, S. aureus ATCC 25923, S. sciuri ATCC 29062, E. faecalis ATCC 29212, B. subtilis, L. monocytogenes SLCC 2375. E. coli ATCC 25922, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853. S. marscenscens, P. stuartii, C. guilliermondii, C. parapsilosis, C. albicans | In vitro-agar diffusion assay, agar dilution assay, synergy disc diffusion assay | Extracts exhibited strong antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria and fungi, while Gram-negative species were not inhibited. Antimicrobial effect of propolis was not affected by antibiotic resistance. At subinhibitory concentrations extracts exhibited strong synergism with ceftriaxone against K. pneumoniae and nystatin against C. albicans. | [196] |
| Ethanol extracts of Brazilian and Bulgarian green propolis | S. typhi standard serovar 00238 | In vitro-agar dilution assay, synergism assay | Extracts of Brazilian propolis exhibited bacteriostatic activity while extracts of Bulgarian propolis were bactericidal to S. typhi. Synergism study showed significant increase in antibacterial effect of β-lactam antibiotics when combined with either propolis sample at sub-MIC concentrations | [197] |
| Ethanol extracts of green propolis | C. albicans ATCC 443-805-2, C. parapsilosis ATCC 726-42-6, C. tropicalis ATCC 1036-09-2 | In vitro-disc diffusion assay, biofilm formation assay | Extract exhibited dose-dependent growth inhibition of all tested Candida spp. Biofilm formation was significantly inhibited at low concentration of the extract | [198] |
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity of Bee Venom
In recent years, bee venom has gathered scientific interest for its potent antimicrobial effects against bacteria and fungi [19] (Table 3). While compositions of bee venom from different sources vary, it has been shown that this activity is largely caused by the activity of peptides and enzymes present in the substance [199].
One of the best researched of them, melittin, a small 26-amino-acid cationic peptide that constitutes around half of apitoxins dry weight [200]. It is α-helical and amphipathic in character, which allows it to bind and insert into the lipid bilayer, creating pores and allowing leakage of cytosolic content and ions [201]. Such loss of membrane integrity leads to rapid lysis of the cell. The effectiveness of this mechanism against bacteria has been shown to be dependent on the cell envelope structure—due to lack of outer membrane, Gram-positive bacteria exhibit greater sensitivity to the cytolytic activity of melittin than Gram-positive bacteria [47], which while still susceptible to effect, often require significantly higher concentrations to be affected [47]. Similar to bacteria, fungal cell membranes can be disrupted by melittin. Fungal membranes contain ergosterol and a higher proportion of negatively charged lipids compared to mammalian membranes, making them good targets for cationic peptides [202]. Melittin has been shown to directly permeabilize yeast cell membranes, causing leakage of vital contents. For instance, melittin exhibits fungicidal activity against Candida albicans by causing the cells to rapidly lose membrane integrity and viability [203]. Whole BV is often even more potent: one study reported BV completely inhibited growth of Trichophyton mentagrophytes within 5 min at 15–30 µg/mL, while the standard antifungal drug fluconazole was ineffective [204]. A very promising aspect of BV components is their synergistic interaction with existing antibiotics. In synergy assays, melittin drastically lowers the MIC of various antibiotics against resistant bacteria. For example, melittin combined with oxacillin was bactericidal against MRSA that oxacillin alone was not able to affect [205]. Another study found that a combination of melittin and doripenem reduced the required concentrations of each > 60-fold against MDR A. baumannii. Similar synergy was seen for melittin with colistin and with ceftazidime against P. aeruginosa [206]. Beyond membrane damage, melittin can trigger apoptotic-like cell death in fungi. Researchers have observed that Candida albicans cells exposed to sub-lytic doses of melittin exhibit symptoms of apoptosis: DNA fragmentation, phosphatidylserine externalization on the cell membrane, and activation of caspase-like proteases [207]. Melittin treatment led to a surge in intracellular ROS, which in turn caused mitochondrial dysfunction in C. albicans. Specifically, melittin disrupts the fungal mitochondrial membrane, leading to release of calcium ions and activation of a caspase-dependent death pathway [208].
Phospholipase A2: PLA2 on its own has relatively modest antibacterial effects compared to melittin –reported minimum inhibitory concentrations of PLA2 are typicallu much higher than those of melittin [209]. However, PLA2’s activity dramatically increases in the presence of melittin. Melittin-induced membrane pores and deformations expose the inner phospholipids of bacterial membranes, providing access for PLA2 to its substrate [210]. This cooperative action results in complete membrane disintegration. PLA2 likely contributes to antifungal action as well by digesting fungal membrane phospholipids [211]. Fungi have an outer cell wall made of glucans and chitin and melittin can penetrate this cell wall, after which PLA2 can reach the membrane. The enzymatic breakdown of membrane lipids by PLA2, together with melittin’s pore formation, leads to cell lysis [210]. Other minor peptides in BV, such as secapin, may have auxiliary antibacterial effects or could potentiate the action of melittin. MCD peptide, for instance, causes release of histamine from host mast cells, which might indirectly create an inflammatory environment unfavorable for pathogens [212]. Some BV peptides also exhibit protease inhibition or other activities that could stress bacteria. However, detailed mechanisms for these lesser components are less documented, and their roles are presumably supportive [207].

Table 3.
Selection of articles on the antimicrobial effect of bee venom.
Table 3.
Selection of articles on the antimicrobial effect of bee venom.
| Material | Microorganism | Assay | Key Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial bee venom samples | E. coli k-12 ATCC 47074, P. putida ATCC 7000008, P. fluorescens NCIMB 9046 | In vitro-bacterial viability assay | Venom samples exhibited a strong inhibitory effect on E. coli, with viability decreasing proportionally to the increase in venom concentration. Antibacterial activity against P. putida, while present, did not increase with concentration beyond 225 µg/mL. No effect against P. fluorescens was observed. Cell membrane damage and pore formation were determined as the mechanism of action. | [213] |
| Commercial bee venom and in natura samples, melittin and phospholipase A2 | S. salivarius ATCC 25975, S. sobrinus ATCC 33478, S. mutans ATCC 25175, S. mitis ATCC 49452, S. sanguinis ATCC 10556, L. casei ATCC 11578, E. faecalis ATCC 4082 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay | Both commercial and in natura apitoxins exhibited strong antimicrobial effects. Phospholipase A2 did not inhibit growth of tested strains, except for L. casei, which was inhibited at high concentrations. Melittin exhibited the highest level of activity against all tested strains. | [209] |
| Bee venom and melittin samples from A. dorsata, A. mellifera, A. florea, and A. cerana species | S. aureus TISTR 517, S. epidermidis DMST 15505, methicillin-resistant S. aureus DMST 20625, B. subtilis DMST 15896, M. luteus DMST 15503, K. pneumoniae DMST 8216, S. typhimurium DMST 562, and E. coli ATCC 25922, C. albicans TISTR 5554 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay | All tested venom and melittin samples exhibited low to none antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria strain. The inhibitory effect against Gram-positive bacteria, while present against all strains, did not show significant differences between the venom samples and their respective melittin activity, except for A. dorsata venom which inhibited MRSA growth stronger than melittin. A. mellifera and A. cerana venoms inhibited C. albicans growth, despite yeast proving resistant to all tested melittins. | [47] |
| Collected bee venom | Clinical isolates of S. agalactiae, S. gordonii, S. epidermidis, S. bovis S. aureus, methicillin resistant S. aureus. S. pneumonia laboratory strain. | In vitro-broth microdilution assay In vivo-mouse infection model | Bee venom exhibited strong antibacterial activity against all tested strains. While active against MRSA strains, in vivo administration of bee venom enhanced MRSA propagation. Melittin exhibited a superior effect on survivability of MRSA infected mouse compared to bee venom. | [214] |
| Bee venom and isolated melittin | S. aureus ATCC 13464, ATCC 14558, ATCC 19095, ATCC 23235, methicillin resistant S. aureus clinical isolates | In vitro-resazurin microdilution assay. | Both venom and melittin exhibited similar potent antibacterial effect against tested S. aureus strains. Neither apitoxin nor melittin affected bacterial enterotoxin production. Both apitoxin and melittin enhanced the activity of oxacillin. Exposure of MRSA strains to apitoxin and melittin caused extensive morphological changes to the bacteria. | [205] |
| Synthetic melittin | Clinical isolates: S. aureus and P. aeruginosa. S. aureus ATCC 25923, ATCC 29213, P aeruginosa PAO1 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay, biofilm formation test, synergy assay | It was show melittin, alone and in combination with conventional antibiotics has a strong antibacterial effect against tested MDR pathogens as well as their mature biofilms. Synergistic effect with antibiotics at low concentrations was demonstrated. | [206] |
| Bee venom from 5 apiaries in Equador | S. enterica and L. monocytogenes strains, including S. enterica CECT 4395 and L. monocytogenes CECT 934 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay | All apitoxins exhibited similar antibacterial effects against Salmonella spp. strains. Inhibitory activity was significantly stronger against L. monocytogenes strains. | [215] |
| Bee venom extracts in DMSO | isolates from wastewater near hospitals—P. mendicina, K. pneumonia and E. coli MDR strains | In vitro-disc diffusion assay, agar dilution assay | Apitoxin exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against Gram-negative bacteria. All tested antibiotics had increased effectiveness when combined with bee venom, independently of the strain of bacteria. | [216] |
| Bee venom loaded on chitosan nanoparticles | clinically isolated strains: K. ohmeri, C. neoformans and C. albicans ATCC90023 reference strain | In vitro-agar well diffusion assay, yeast-hypheal transition study | The bee venom loaded nanoparticles exhibited significantly higher levels of antifungal activity against C. neoformans and C. albicans than free nanoparticles. The nanoparticles effectively inhibited the formation of biofilm of all isolates. Disruption of yeast-hypheal transition was determined in all isolates. | [217] |
| Bee venom loaded on chitosan nanoparticles | E. coli ATCC 8739, P. aeruginosa ATCC 9027, B. subtilis ATCC 6633, S. aureus ATCC 7984 | In vitro-agar well diffusion assay, broth macrodilution assay | The bee venom loaded nanoparticles exhibited an inhibitory stronger than that of either free nanoparticles or bee venom against all tested strains. Bactericidal effect was improved by bee venom loading only against S. aureus. | [218] |
| Collected bee venom | Methicillin resistant S. aureus CCARM 3366, CCARM 3708 | In vitro-broth microdilution assay, checkerboard assay | Bee venom exhibited a strong antibacterial effect against tested MRSA strains. Significant synergistic effects have been determined in combinations of bee venom with gentamycin ant vancomycin. | [219] |
5. Wound Treatment—A Promising Use of Bee Products in Medicine
Wounds resulting from burns, injuries, incisions, or medical procedures involve disruption of the skin continuity and disruption of the body’s natural barrier exposes tissues to colonization by various microorganisms, increasing the risk of infection [271]. Physiological wound healing aims to restore tissue integrity, but effective regeneration of the skin tissue remains a serious problem, as complications that occur during this process can lead to health consequences. The wound healing process in the body consists of many biochemical and cellular reactions and is divided into several stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling [272]. Hemostasis is defined as the immediate response to injury and involves vasoconstriction and clot formation to limit blood loss. In the inflammatory phase occurs the infiltration of neutrophils and macrophages which eliminate cellular debris and pathogens. The initiation of tissue regeneration begins with the proliferation phase through fibroblast activity, angiogenesis and keratinocyte migration. The final remodeling phase involves the reorganization of collagen fibers and wound scarring [272,273].
The oldest report documenting the use of bee products as a medical agent came from Egypt 4000 years ago [274]. Modern studies provide increasing evidence to support the efficacy of bee products in promoting and accelerating wound healing [275]. For example, Takzaree et al. [276] showed that local application of thyme honey affected key processes such as shortening the inflammatory phase, stimulating the formation of granulation tissue, promoting angiogenesis, early onset of cell proliferation, remodeling, and ultimately accelerating the healing of open wounds in rats [276]. The therapeutic properties of honey result not only from its widely described antimicrobial effects but also from its physicochemical characteristics [276]. One of the most meaningful properties of honey is its influence on maintaining a moist wound environment. This wet environment prevents scab formation, alleviates necrotic changes in the dermis, and increases the migration of keratinocytes to the lesion surface, accelerating re-epithelialization [277,278]. In addition, the high sugar content contributes to the osmotic effect, which inhibits bacterial growth and attracts water and lymph to the wound area, contributing to better nutrition of the damaged tissue and strengthening the immune response. In addition, the low pH of honey provides an acidic microenvironment that promotes fibroblast activity and epithelial regeneration. In turn, the high viscosity of honey provides a protective barrier against external contamination, reducing the risk of microbial penetration [279]. Interestingly, in addition to many reports on the ability of honey in supporting superficial wound care, its effectiveness as a skin graft fixative in patients with burns has also been described. It has been shown [280] that using of honey not only reduced the frequency of infections and pain reported by patients but also improved the adhesion of the split-thickness graft and overall healing results.
The properties of propolis make it a promising agent for the treatment of wounds of various origins like infected wounds, acute injuries, but also thermal wounds (burns and frostbite), as summarized Yang et al. [281]. The therapeutic effect of propolis is not only related to its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activity but also its analgesic effect conditioned by the presence of the flavonoid—chrysin [31,274]. Moreover, propolis has been shown to promote the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes and fibroblasts, which supports the regeneration of the epidermis and dermis, while reducing excessive scar formation [282]. Studies have shown that propolis has an effect at various stages of the healing process—from the inflammatory to tissue remodeling. Propolis has been shown to inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, or IL-6 [283], but also to increase the level of anti-inflammatory cytokines [283] and growth factors such as VEGF [284], which promotes the formation of new tissue. Importantly, propolis does not have a toxic effect on skin cells and rare allergic reactions, which makes it a safe therapeutic agent for topical use [33]. The clinical use of propolis has been confirmed, among others, in the treatment of diabetic foot ulcers [285]. A randomized controlled trial showed that local application of propolis significantly shortened the healing time of wounds and reduced the degree of infection in patients with type II diabetes [286]. Similar effects in the treatment of diabetic wounds were also obtained in the study of the effect of bee venom. Hozzein et al. [287] reported that bee venom treatment improved wound closure in mice with type I diabetes, restored antioxidant enzyme activity, normalized chemokine levels, and protected wound macrophages from apoptosis. This indicates the immunomodulatory and cytoprotective effects of bee venom under oxidative stress, which is typical for chronic wounds in patients with diabetes [288].
Positive results have also been demonstrated with bee pollen. Olczyk et al. [289] reported that using bee pollen ointment had a positive effect on the healing of burn wounds while improving the general condition of the animals in a pig model, and showed strong antimicrobial properties, preventing secondary infections. The therapeutic effects of royal jelly have been well described in the context of many diseases, including diabetic foot ulcers [290]. Although the effect of this product on wound healing is not fully understood, available data suggest significant pro-regenerative properties. Kim et al. [291] conducted a study in which they assessed the effect of royal jelly on human fibroblasts in vitro because the migration of these cells is one of the initial phenomena during the formation of new skin tissue. The results showed that royal jelly increased fibroblast migration and influenced the expression of signaling lipids involved in the wound healing process, indicating a potential role in initiating skin repair [291]. Promising results were obtained by Alvarez et al. [292] in a study in which the effect of royal jelly extracellular vesicles (RJEV) on wound healing was assessed in a mouse model. As a result, RJEV was shown to have antibacterial activity and significantly accelerated the initial wound closure process [292].
The current state of knowledge indicates that combining different bee products produces a synergistic effect in the wound healing process. Andritoiu et al. [293] conducted a study evaluating the efficacy of an ointment based on honey, propolis, drone brood homogenate and a mixture of these substances on different types of wounds: incisions, excisions and burn wounds, in an animal model. The results showed that all the products used accelerated wound shrinkage and re-epithelialization, and the best results were observed after using an ointment containing a combination of all apitherapeutics. In addition, it was shown that combining bee products with other natural agents also has beneficial effects. For example, Javadi et al. [294] showed that the best therapeutic properties on wound healing in rats were obtained after using a mixture of honey and Nigella sativa seed oil compared to using each of these substances separately. Also, a study by Bayir et al. [295] showed that the use of a dressing impregnated with beeswax, olive oil, and butter in a rat model of second-degree burns improved the regeneration of the dermis and epidermis, increased fibroblast activation and keratinization, and had a positive effect on wound contraction [295]. The above data indicates that using the synergistic effect of bee products and other natural substances has therapeutic potential as a comprehensive approach to wound treatment.
6. Obstacles on the Way to Implementing Bee Product Treatments in the Current Medical Landscape
Medicinal use of honey is generally considered safe [19]. It has been shown although it has been shown that about 5% of patients treated with topical medical honey report pain at the application site, more than with conventional dressings [296]. On the other hand, serious adverse effects from honey are rare, there are no severe systemic reactions to medical-grade honey reported in the literature. Propolis is a well-known contact sensitizer, and allergic reactions are a significant concern. Repeated topical or oral exposure can lead to sensitization in susceptible individuals. Allergic manifestations include contact cheilitis, oral mucositis, perioral eczema, labial edema, and even dyspnea in severe cases. Patch test studies have shown that 1–6% of adults tested exhibit sensitivity to propolis; higher rates have been reported in certain populations like children with eczema [297]. Systemic effects such as acute renal failure [298] associated with high dose propolis ingestion have been reported. Bee venom therapy carries the most serious safety risks. Bee venom is a complex mixture of peptides and enzymes that can trigger profound immunological reactions. Allergic and anaphylactic reactions are the paramount concerns. A comprehensive 2015 systematic review of 145 studies found that systemic adverse reactions occurred in about 14% of patients undergoing bee venom therapy, including numerous cases of anaphylaxis, with some requiring emergency epinephrine and steroids. There has been at least one documented fatality directly attributed to bee venom apitherapy [299]. Apart from anaphylaxis, other severe adverse events recorded include hemolysis and even a case of Guillain–Barré syndrome and an irreversible nerve injury [300]. Repeated exposure also carries the risk of sensitization: someone may develop an allergy after multiple bee venom treatments [299]. Overall, the clinical risk-benefit profile of bee venom is problematic, the unpredictable severity of reactions has thus far limited its acceptance in mainstream infection management. In the context of treating infections, where safer alternatives exist, the threshold for tolerating venom’s risks is especially high.
Traditionally venom delivered by the bee’s own mechanism or by subcutaneous injections of collected venom [301]. Using live bee stings is not precise in dosage, as each bee may inject a slightly different amount of venom and the process cannot be standardized clinically [302]. Injections with purified venom allow precise dosing, but venom proteins are prone to degradation, so they are often lyophilized and reconstituted fresh for use [303]. Another pharmacologic issue is maintaining potency during storage. Honey can lose enzymatic activity if improperly stored [304], propolis extracts can undergo chemical changes that not only reduce efficacy but may increase allergenicity [297] and dried bee venom can lose some volatile components over time [305]. Unlike single-compound drugs, bee products have multiple active constituents that work in concert [19] and their metabolites could be different from the parent compounds that showed activity in vitro.
Bee products can inadvertently contain harmful contaminants from the environment. Honey and propolis can accumulate pesticide residues and heavy metals from flowers and sap if hives are near polluted areas. Studies have shown that propolis can serve as a bioindicator of environmental pollution. Propolis from industrial or mining regions often contains elevated concentrations of lead, cadmium or arsenic [306]. Propolis and pollen products, if not properly processed, might carry fungal spores or bacteria from the hive. To be medicinal grade, these products must be processed in sterile conditions or sterilized without degrading active ingredients [307].
7. Conclusions
This review highlights the significant potential of bee products to support and complement modern therapies for the treatment of infectious diseases. Honey, propolis and bee venom show a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity (Figure 1), including efficacy against multi-drug resistant (MDR) microorganisms, making them a promising target for further research. Their synergy with conventional antibiotics and their documented use in wound healing strengthen the position of apitherapeutics in regenerative and infectious medicine. Despite the existing regulatory and technological barriers, the integration of bee preparations into modern therapeutic strategies can provide significant health benefits. Further clinical trials and the development of standardized formulations are needed to fully exploit the therapeutic potential of these natural substances.
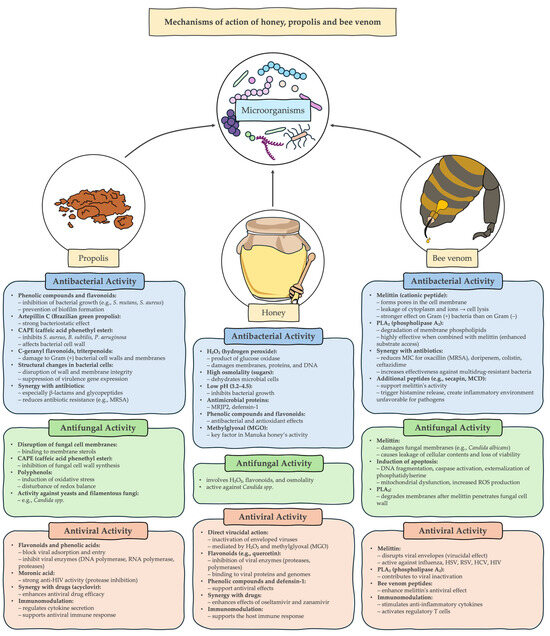
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of action of honey, propolis and bee venom.
8. Methodology of the Literature Search
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in the PubMed database to identify scientific papers on the antimicrobial properties of honey, propolis, and bee venom. No time limits were applied to ensure a complete review of the available data. The search strategy included a combination of terms related to bee products and their biological activity, mechanisms of action, and potential use in combating infections.
The search was based on the following phrases: (honey OR propolis OR bee venom) AND (antimicrobial OR antibacterial OR antiviral OR antifungal OR anti-infective OR antimicrobial resistance OR pathogen inhibition OR biofilm inhibition) AND (mechanism of action OR biological activity OR therapeutic application OR pharmacological properties OR infection treatment OR synergistic effect).
Additionally, extended queries were used, such as: (honey OR propolis OR bee venom) AND (drug resistance OR antibiotic resistance OR multidrug-resistant pathogens OR alternative therapy OR natural antimicrobials). To enhance the completeness of the review, results from Google Scholar were also included and a hand search of journals in the fields of microbiology, pharmacology, apitherapy and natural medicine was performed.
The selection process was conducted independently by two researchers. In the case of papers with similar topics or results, priority was given to the most up-to-date ones, containing reliable data on the chemical composition, mechanisms of action and antimicrobial properties of honey, propolis and bee venom, as well as their potential use in the treatment of infections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.N.-R., A.G.-G., R.H., M.K., F.L. and D.B.; data curation, M.K. and C.A.; data interpretation, R.H., F.L. and D.B.; visualization, R.H. and F.L.; writing—original draft preparation, F.L., R.H., M.K., D.B. and P.N.-R.; writing—review and editing, P.N.-R.; supervision, P.N.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elshafiey, E.H.; Shetaia, A.A.; El-Wahed, A.A.A.; Algethami, A.F.; Musharraf, S.G.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Zhao, C.; Masry, S.H.D.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; et al. Overview of Bee Pollination and Its Economic Value for Crop Production. Insects 2021, 12, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsadila, C.; Amoroso, C.; Mossialos, D. Microbial Diversity in Bee Species and Bee Products: Pseudomonads Contribution to Bee Well-Being and the Biological Activity Exerted by Honey Bee Products: A Narrative Review. Diversity 2023, 15, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotti, E.; Sansonno, L.; Prosdocimi, E.M.; Vacchini, V.; Hamdi, C.; Cherif, A.; Gonella, E.; Marzorati, M.; Balloi, A. Microbial Symbionts of Honeybees: A Promising Tool to Improve Honeybee Health. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 716–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelli, L.; Branchiccela, B.; Romero, H.; Zunino, P.; Antúnez, K. Seasonal Dynamics of the Honey Bee Gut Microbiota in Colonies Under Subtropical Climate: Seasonal Dynamics of Honey Bee Gut Microbiota. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribière, C.; Hegarty, C.; Stephenson, H.; Whelan, P.; O’Toole, P.W. Gut and Whole-Body Microbiota of the Honey Bee Separate Thriving and Non-Thriving Hives. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallai, N.; Salles, J.M.; Settele, J.; Vaissière, B.E. Economic Valuation of the Vulnerability of World Agriculture Confronted with Pollinator Decline. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, S.; Nastasa, A.; Chapman, A.; Kwong, W.K.; Foster, L.J. The Honey Bee Gut Microbiota: Strategies for Study and Characterization. Insect Mol. Biol. 2019, 28, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasupuleti, V.R.; Sammugam, L.; Ramesh, N.; Gan, S.H. Honey, Propolis, and Royal Jelly: A Comprehensive Review of Their Biological Actions and Health Benefits. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1259510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampieri, F.; Quiles, J.L.; Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Orantes-Bermejo, F.J.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. Bee Products: An Emblematic Example of Underutilized Sources of Bioactive Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6833–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, M.; Giampieri, F.; Cianciosi, D.; Ansary, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Gil, E.; Forbes-Hernández, T. The Roles of Strawberry and Honey Phytochemicals on Human Health: A Possible Clue on the Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Prevention of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Phytomedicine 2021, 86, 153170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P.; Zhang, J.; Bravo Lamas, L.; Martínez Flórez, S.; Agudo Toyos, P.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Associated Health Benefits: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Cordero, M.; Gasparrini, M.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Mazzoni, L.; Afrin, S.; Beltrán-Ayala, P.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; et al. Activation of AMPK/Nrf2 Signalling by Manuka Honey Protects Human Dermal Fibroblasts against Oxidative Damage. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 25, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amessis-Ouchemoukh, N.; Maouche, N.; Otmani, A.; Terrab, A.; Madani, K.; Ouchemoukh, S. Evaluation of Algerian’s Honey in Terms of Quality and Authenticity Based on the Melissopalynology and Physicochemical Analysis and Their Antioxidant Powers. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 14, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, S.; Giampieri, F.; Cianciosi, D.; Pistollato, F.; Ansary, J.; Pacetti, M.; Amici, A.; Reboredo-Rodríguez, P.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Quiles, J.L.; et al. Strawberry Tree Honey as a New Potential Functional Food. Part 1: Strawberry Tree Honey Reduces Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation and Colony Formation Ability, Inhibits Cell Cycle and Promotes Apoptosis by Regulating EGFR and MAPKs Signaling Pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 57, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriele, G.; Parri, E.; Felicioli, A.; Sagona, S.; Pozzo, L.; Biondi, C.; Domenici, V.; Pucci, L. Phytochemical Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Tuscan Bee Pollen of Different Botanic Origins. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2015, 27, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, J.A.G.; de Melo, I.L.P.; Granato, D.; Araújo, E.; da Silva de Freitas, A.; Barth, O.M.; Sattler, A.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Impact of Origin on Bioactive Compounds and Nutritional Composition of Bee Pollen from Southern Brazil: A Screening Study. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; Khalifa, S.A.M.; El-Wahed, A.A.; Gao, R.; Guo, Z.; Tahir, H.E.; Zhao, C.; Du, M.; Farag, M.A.; Musharraf, S.G.; et al. Honeybee Products: An Updated Review of Neurological Actions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 101, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Krishnan, K.T.; Salleh, N.; Gan, S.H. Biological and Therapeutic Effects of Honey Produced by Honey Bees and Stingless Bees: A Comparative Review. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainu, F.; Masyita, A.; Bahar, M.A.; Raihan, M.; Prova, S.R.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Simal-Gandara, J. Pharmaceutical Prospects of Bee Products: Special Focus on Anticancer, Antibacterial, Antiviral, and Antiparasitic Properties. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Albujja, M.; Bakar, M.F.A. Honey and Its Nutritional and Anti-Inflammatory Value. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asma, S.T.; Bobiş, O.; Bonta, V.; Acaroz, U.; Shah, S.R.A.; Istanbullugil, F.R.; Arslan-Acaroz, D. General Nutritional Profile of Bee Products and Their Potential Antiviral Properties against Mammalian Viruses. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Dong, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Processing Technologies for Bee Products: An Overview of Recent Developments and Perspectives. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 727181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, K.E.; Frost, E.A.; Remnant, E.J.; Schell, K.R.; Cokcetin, N.N.; Carter, D.A. The Role of Honey in the Ecology of the Hive: Nutrition, Detoxification, Longevity, and Protection against Hive Pathogens. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 954170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Didamony, S.E.; Gouda, H.I.A.; Zidan, M.M.M.; Amer, R.I. Bee Products: An Overview of Sources, Biological Activities and Advanced Approaches Used in Apitherapy Application. Biotechnol. Rep. 2024, 44, e00862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Plutino, M.; Lucini, L.; Aromolo, R.; Martinelli, E.; Souto, E.B.; Santini, A.; Pignatti, G. Bee Products: A Representation of Biodiversity, Sustainability, and Health. Life 2021, 11, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaloni, L.S.; Kristl, J.; Domingues, C.E.C.; Gregorc, A. An Overview of the Nutritional Requirements of Honey Bees (Apis Mellifera Linnaeus, 1758). Insects 2025, 16, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, S.I.; Ullah, A.; Khan, K.A.; Attaullah, M.; Khan, H.; Ali, H.; Bashir, M.A.; Tahir, M.; Ansari, M.J.; Ghramh, H.A.; et al. Composition and Functional Properties of Propolis (Bee Glue): A Review. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehbe, R.; Frangieh, J.; Rima, M.; El Obeid, D.; Sabatier, J.-M.; Fajloun, Z. Bee Venom: Overview of Main Compounds and Bioactivities for Therapeutic Interests. Molecules 2019, 24, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagh, V.D. Propolis: A Wonder Bees Product and Its Pharmacological Potentials. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 2013, 308249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Oliveira, I.S.; Jenkins, T.P.; Argemí, L.; Sørensen, C.V.; Ahmadi, S.; Barbosa, J.E.; Laustsen, A.H. Bee Updated: Current Knowledge on Bee Venom and Bee Envenoming Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek-Górecka, A.; Górecki, M.; Rzepecka-Stojko, A.; Balwierz, R.; Stojko, J. Bee Products in Dermatology and Skin Care. Molecules 2020, 25, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, A.; Chamunorwa, J.P.; Erlwanger, K.H. Nutraceutical Values of Natural Honey and Its Contribution to Human Health and Wealth. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sakhawy, M.; Salama, A.; Tohamy, H.-A.S. Applications of Propolis-Based Materials in Wound Healing. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 316, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Perużyńska, M.; Kucharska, E.; Kucharski, Ł.; Jakubczyk, K.; Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P.; Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J.; Droździk, M.; Majtan, J. Assessment of in Vitro Skin Permeation and Accumulation of Phenolic Acids from Honey and Honey-Based Pharmaceutical Formulations. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2025, 25, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanov, S. Beeswax: Production, Properties, Composition, Control; Bee Product Science Publishing: Muehlethurnen, Switzerland, 2009; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Grabek-Lejko, D.; Miłek, M.; Dżugan, M. The Comparison of the Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Antiviral Potential of Polish Fir Honeydew and Manuka Honeys. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraglio, S.K.T.; Silva, B.; Bergamo, G.; Brugnerotto, P.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Fett, R.; Costa, A.C.O. An Overview of Physicochemical Characteristics and Health-Promoting Properties of Honeydew Honey. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 44–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, M.; Martín-Alvarez, P.J.; Polo, M.C.; de Lorenzo, C.; Gonzalez, M.; Pueyo, E. Changes in the Free Amino Acid Contents of Honeys During Storage at Ambient Temperature. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9099–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Beer, T. Physico-Chemical Quality Assessment of Honey from Different Floral and Geographical Origin. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kieliszek, M.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M.; Wojtczuk, M.; Roszko, M.; Bryła, M.; Petkoska, A.T. Recent Advances and Opportunities Related to the Use of Bee Products in Food Processing. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 2051–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenbaum, M.R.; Calla, B. Honey as a Functional Food for Apis Mellifera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 185–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaacoub, C.; Wehbe, R.; Roufayel, R.; Fajloun, Z.; Coutard, B. Bee Venom and Its Two Main Components-Melittin and Phospholipase A2-As Promising Antiviral Drug Candidates. Pathogen 2023, 12, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šuran, J.; Cepanec, I.; Mašek, T.; Radić, B.; Radić, S.; Tlak Gajger, I.; Vlainić, J. Propolis Extract and Its Bioactive Compounds-From Traditional to Modern Extraction Technologies. Molecules 2021, 26, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, M.; Bonikowski, R.; Dżugan, M. The Effect of Extraction Conditions on the Chemical Profile of Obtained Raw Poplar Propolis Extract. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 6709–6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.H.d.O.; Machado, B.A.S.; Barreto, G.d.A.; Anjos, J.P.d.; Fonseca, L.M.d.S.; Santos, A.A.B.; Pessoa, F.L.P.; Druzian, J.I. Supercritical Extraction of Red Propolis: Operational Conditions and Chemical Characterization. Molecules 2020, 25, 4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedic, N.; Gojak, M.; Zlatanović, I.; Rudonja, N.; Lazarevic, K.; Dražić, M.; Gligorević, K.; Pajić, M. Study of Vacuum and Freeze Drying of Bee Honey. Therm. Sci. 2020, 24, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitip, J.; Mookhploy, W.; Khorndork, S.; Chantawannakul, P. Comparative Study of Antimicrobial Properties of Bee Venom Extracts and Melittins of Honey Bees. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contieri, L.S.; de Souza Mesquita, L.M.; Sanches, V.L.; Viganó, J.; Martinez, J.; da Cunha, D.T.; Rostagno, M.A. Standardization Proposal to Quality Control of Propolis Extracts Commercialized in Brazil: A Fingerprinting Methodology Using a UHPLC-PDA-MS/MS Approach. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczyńska, A.; Żak, N. Polyphenols as the Main Compounds Influencing the Antioxidant Effect of Honey-A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, E. Honey: A Comprehensive Survey; William Heinemann Ltd.: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson, S.W.; Human, H.; Pirk, C.W.W. Honey Bees Save Energy in Honey Processing by Dehydrating Nectar before Returning to the Nest. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaerjani, W.M.A.; Abu-Melha, S.; Alshareef, R.M.H.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Ghramh, H.A.; Al-Shehri, B.M.A.; Bajaber, M.A.; Khan, K.A.; Alrooqi, M.M.; Modawe, G.A.; et al. Biochemical Reactions and Their Biological Contributions in Honey. Molecules 2022, 27, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossano, R.; LaRocca, M.; Polito, T.; Perna, A.M.; Padula, M.C.; Martelli, G.; Riccio, P. What Are the Proteolytic Enzymes of Honey and What They Do Tell Us? A Fingerprint Analysis by 2-D Zymography of Unifloral Honeys. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borutinskaite, V.; Treigyte, G.; Čeksteryte, V.; Kurtinaitiene, B.; Navakauskiene, R. Proteomic Identification and Enzymatic Activity of Buckwheat (Fagopyrum Esculentum) Honey Based on Different Assays. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 57, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- CXS 12-1981; Standard for Honey. Codex Alimentarius International Food Standards: Rome, Italy, 1981; Revised 2019 1981.
- Nolan, V.C.; Harrison, J.; Cox, J.A. Dissecting the Antimicrobial Composition of Honey. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.; Thornburg, R.W. Tobacco Nectarin I. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36726–36733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizerra, F.C.; Da Silva, P.I.; Hayashi, M.A.F. Exploring the Antibacterial Properties of Honey and Its Potential. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Campbell, L.T.; Blair, S.E.; Carter, D.A. The Effect of Standard Heat and Filtration Processing Procedures on Antimicrobial Activity and Hydrogen Peroxide Levels in Honey. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.A.; Klein, P. Determination of Sugars in Honey by Liquid Chromatography. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 18, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, P.M.; Gauche, C.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Honey: Chemical Composition, Stability and Authenticity. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirife, J.; Zamora, M.C.; Motto, A. The Correlation between Water Activity and % Moisture in Honey: Fundamental Aspects and Application to Argentine Honeys. J. Food Eng. 2006, 72, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.D.; Mandal, S. Honey: Its Medicinal Property and Antibacterial Activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starowicz, M.; Ostaszyk, A.; Zieliński, H. The Relationship between the Browning Index, Total Phenolics, Color, and Antioxidant Activity of Polish-Originated Honey Samples. Foods 2021, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayeh, W.A.; Cook, C.; Wright, G.A. B-Vitamins Influence the Consumption of Macronutrients in Honey Bees. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 804002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkova, M.A.; Budnikova, N.V.; Paramzina, I.A. Water-Soluble Vitamins in Honeys of Various Botanical Origin and Their Change during Storage of Honey. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 845, 012116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril-Sánchez, A.L.; Quintero-Salazar, B.; Dublán-García, O.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Relationship with Antioxidant Activity, Botanical Origin, and Color. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaśkiewicz, K.; Szczęsna, T.; Jachuła, J. How Phenolic Compounds Profile and Antioxidant Activity Depend on Botanical Origin of Honey—A Case of Polish Varietal Honeys. Molecules 2025, 30, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoone, P.; Oladejo, T.O.; Kassym, L.; McDougall, G.J. Honey Phytochemicals: Bioactive Agents With Therapeutic Potential for Dermatological Disorders. Phytotherapy Res. 2024, 38, 5741–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanjwani, M.F.; Channa, F.A. Minerals Content in Different Types of Local and Branded Honey in Sindh, Pakistan. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Florek, M.; Wolanciuk, A.; Barłowska, J.; Litwińczuk, Z. Concentration of Minerals in Nectar Honeys from Direct Sale and Retail in Poland. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 186, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molan, P.C. The Antibacterial Activity of Honey: 1. The Nature of the Antibacterial Activity. Bee World 1992, 73, 5–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molan, P.C. The Antibacterial Activity of Honey: 2. Variation in the Potency of the Antibacterial Activity. Bee World 1992, 73, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.L.; Molan, P.C.; Reid, G.M. A Survey of the Antibacterial Activity of Some New Zealand Honeys. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1991, 43, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, R.A.; Halas, E.; Molan, P.C. The Efficacy of Honey in Inhibiting Strains of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa From Infected Burns. J. Burn. Care Rehabil. 2002, 23, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasaudi, S. The Antibacterial Activities of Honey. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, P.G.G.; Lemos, T.L.G.; Bizerra, A.M.C.; Arriaga, A.M.C.; Ferreira, D.A.; Santiago, G.M.P.; Braz-Filho, R.; Costa, J.G.M. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Ursolic Acid and Derivatives. Molecules 2014, 19, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLoone, P.; Zhumbayeva, A.; Yunussova, S.; Kaliyev, Y.; Yevstafeva, L.; Verrall, S.; Sungurtas, J.; Austin, C.; Allwood, J.W.; McDougall, G.J. Identification of components in Kazakhstan honeys that correlate with antimicrobial activity against wound and skin infecting microorganisms. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devequi-Nunes, D.; Machado, B.A.S.; Barreto, G.d.A.; Silva, J.R.; Silva, D.F.d.; Rocha, J.L.C.d.; Brandão, H.N.; Borges, V.M.; Umsza-Guez, M.A. Chemical Characterization and Biological Activity of Six Different Extracts of Propolis through Conventional Methods and Supercritical Extraction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bava, R.; Puteo, C.; Lombardi, R.; Garcea, G.; Lupia, C.; Spano, A.; Liguori, G.; Palma, E.; Britti, D.; Castagna, F. Antimicrobial Properties of Hive Products and Their Potential Applications in Human and Veterinary Medicine. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone-Finstrom, M.; Spivak, M. Propolis and Bee Health: The Natural History and Significance of Resin Use by Honey Bees. Apidologie 2010, 41, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Lim, K.; Praphawilai, P.; Danmek, K.; Maitip, J.; Vit, P.; Wu, M.-C.; Ghosh, S.; Jung, C.; Burgett, M.; et al. Exploring the Functional Properties of Propolis, Geopropolis, and Cerumen, with a Special Emphasis on Their Antimicrobial Effects. Foods 2023, 12, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurek-Górecka, A.; Rzepecka-Stojko, A.; Górecki, M.; Stojko, J.; Sosada, M.; Świerczek-Zięba, G. Structure and Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenols Derived from Propolis. Molecules 2013, 19, 78–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, C.F.; Katouli, M.; Grkovic, T.; Vu, H.; Quinn, R.J.; Heard, T.A.; Carvalho, C.; Manley-Harris, M.; Wallace, H.M.; Brooks, P. Anti-Staphylococcal Activity of C-Methyl Flavanones from Propolis of Australian Stingless Bees (Tetragonula Carbonaria) and Fruit Resins of Corymbia Torelliana (Myrtaceae). Fitoterapia 2014, 95, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, M.; Sip, A.; Mrówczyńska, L.; Broniarczyk, J.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Ratajczak, I. Biological Activity and Chemical Composition of Propolis from Various Regions of Poland. Molecules 2022, 28, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidorov, V.A.; Maslowiecka, J.; Szoka, L.; Pellizzer, N.; Miranda, D.; Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Zambrzycka, M.; Swiecicka, I. Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Argentinian Propolis of Four Species of Stingless Bees. Molecules 2022, 27, 7686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velikova, M.; Bankova, V.; Marcucci, M.C.; Tsvetkova, I.; Kujumgiev, A. Chemical Composition and Biological Activity of Propolis from Brazilian Meliponinae. Z. Naturforschung C J. Biosci. 2000, 55, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramón-Sierra, J.; Peraza-López, E.; Rodríguez-Borges, R.; Yam-Puc, A.; Madera-Santana, T.; Ortiz-Vázquez, E. Partial Characterization of Ethanolic Extract of Melipona Beecheii Propolis and in Vitro Evaluation of Its Antifungal Activity. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salatino, A.; Salatino, M.L.F.; Negri, G. How Diverse Is the Chemistry and Plant Origin of Brazilian Propolis? Apidologie 2021, 52, 1075–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccinelli, A.L.; Lotti, C.; Campone, L.; Cuesta-Rubio, O.; Campo Fernandez, M.; Rastrelli, L. Cuban and Brazilian Red Propolis: Botanical Origin and Comparative Analysis by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Photodiode Array Detection/Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6484–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudoit, A.; Mertz, C.; Chillet, M.; Cardinault, N.; Brat, P. Antifungal Activity of Brazilian Red Propolis Extract and Isolation of Bioactive Fractions by Thin-Layer Chromatography-Bioautography. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Ye, S.-R.; Ting, C.; Yu, Y.-H. Antibacterial Activity of Propolins from Taiwanese Green Propolis. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulhendri, F.; Lesmana, R.; Tandean, S.; Christoper, A.; Chandrasekaran, K.; Irsyam, I.; Suwantika, A.A.; Abdulah, R.; Wathoni, N. Recent Update on the Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Propolis. Molecules 2022, 27, 8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronica, G.; Reddy, B.V.T.; Chowdary Birapu, U.K.; Jadadoddi, R.K.; Kumar, R.H.; Saikiran, K.V. Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Triple Antibiotic Paste and Propolis Extract Using Three Different Vehicles as Intracanal Medicament: An in Vitro Study. J. Dr. YSR Univ. Health Sci. 2024, 13, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szliszka, E.; Krol, W. Polyphenols Isolated from Propolis Augment TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 731940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baracchi, D.; Francese, S.; Turillazzi, S. Beyond the Antipredatory Defence: Honey Bee Venom Function as a Component of Social Immunity. Toxicon 2011, 58, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guan, S.-M.; Sun, W.; Fu, H. Melittin, the Major Pain-Producing Substance of Bee Venom. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Han, S.M.; Park, K.-K. Therapeutic Effects of Apamin as a Bee Venom Component for Non-Neoplastic Disease. Toxins 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Xie, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; Su, S.; Yao, H. Pharmacological Effects and Mechanisms of Bee Venom and Its Main Components: Recent Progress and Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1001553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buku, A. Mast Cell Degranulating (MCD) Peptide: A Prototypic Peptide in Allergy and Inflammation. Peptides 1999, 20, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.; Giralt, E. Three Valuable Peptides from Bee and Wasp Venoms for Therapeutic and Biotechnological Use: Melittin, Apamin and Mastoparan. Toxins 2015, 7, 1126–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.; Sorolla, A.; Wang, E.; Golden, E.; Woodward, E.; Davern, K.; Ho, D.; Johnstone, E.; Pfleger, K.; Redfern, A.; et al. Honeybee Venom and Melittin Suppress Growth Factor Receptor Activation in HER2-Enriched and Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Lu, X.; Deng, Z.; Xiao, S.; Yuan, B.; Yang, K. How Melittin Inserts into Cell Membrane: Conformational Changes, Inter-Peptide Cooperation, and Disturbance on the Membrane. Molecules 2019, 24, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Q.; Sun, C.; Xu, N.; Liu, W. The Current Landscape of the Antimicrobial Peptide Melittin and Its Therapeutic Potential. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1326033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Tao, T.; Ren, Q.; Xie, S.; Gao, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, C. Key Genes Are Associated with the Prognosis of Glioma, and Melittin Can Regulate the Expression of These Genes in Glioma U87 Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 7033478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Janik, E.; Gorniak, L.; Synowiec, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Sitarek, P.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.N.; Baek, S.B.; Jung, H.J. Bee Venom and Its Peptide Component Melittin Suppress Growth and Migration of Melanoma Cells via Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK Pathways. Molecules 2019, 24, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Chen, Z. Melittin Exerts an Antitumor Effect on Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F.; Khan, M.A.; Kumar, R.; Upadhyay, T.K. An Updated Review Summarizing the Anticancer Efficacy of Melittin from Bee Venom in Several Models of Human Cancers. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, A.; Mehlawat, K.; Tripathi, K.; Pareek, A.; Chaudhary, S.; Ratan, Y.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Chuturgoon, A. Melittin as a Therapeutic Agent for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Mechanistic Insights, Advanced Delivery Systems, and Future Perspectives. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1510693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Kim, K.-H.; Lee, W.-R.; Han, S.-M.; Park, K.-K. Protective Effect of Melittin on Inflammation and Apoptosis in Acute Liver Failure. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.-G.; Kim, I.-S.; Lee, H.-D. Standardization of the Manufacturing Process of Bee Venom Pharmacopuncture Containing Melittin as the Active Ingredient. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2018, 2018, 2353280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Junior, R.S.; Sciani, J.M.; Marques-Porto, R.; Junior, A.L.; Orsi, R.D.O.; Barraviera, B.; Pimenta, D.C. Africanized Honey Bee (Apis Mellifera) Venom Profiling: Seasonal Variation of Melittin and Phospholipase A2 Levels. Toxicon 2010, 56, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotka, A.K.; Franklin, R.M.; Adkinson, N.F.; Valentine, M.; Baer, H.; Lichtenstein, L.M. Allergy to Insect Stings. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1976, 57, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Aguilar, G.R.; Sharara, F.; Mestrovic, T.; Gray, A.P.; Weaver, N.D.; Wool, E.E.; Han, C.; Hayoon, A.G.; et al. Global Mortality Associated with 33 Bacterial Pathogens in 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, J.; You, S.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y. Global Prevalence and Burden of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis from 1990 to 2019. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongomin, F.; Gago, S.; Oladele, R.O.; Denning, D.W. Global and Multi-National Prevalence of Fungal Diseases—Estimate Precision. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambugala, K.M.; Daranagama, D.A.; Tennakoon, D.S.; Jayatunga, D.P.W.; Hongsanan, S.; Xie, N. Humans vs. Fungi: An Overview of Fungal Pathogens against Humans. Pathogens 2024, 13, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. MRSA Virulence and Spread. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsitch, M.; Samore, M.H. Antimicrobial Use and Antimicrobial Resistance: A Population Perspective. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoj, K.; Phukan, M.M.; Kumar, R.; Jamir, L.; Roy, V.K.; Pankaj, P.P. Therapeutic Applications of Honey: Traditional and Contemporary Approaches in Human Health Management. In Honey in Food Science and Physiology; Kumar, R., Hajam, Y.A., Bala Dhull, S., Giri, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 1–31. ISBN 978-981-97-3565-5. [Google Scholar]
- Husband, S.; Cankar, K.; Catrice, O.; Chabert, S.; Erler, S. A Guide to Sunflowers: Floral Resource Nutrition for Bee Health and Key Pollination Syndromes. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1552335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, I.R. The Sugars of Honey. In Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry; Tipson, R.S., Horton, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1970; Volume 25, pp. 285–309. [Google Scholar]
- Clifford, D.P.; Repine, J.E. Hydrogen Peroxide Mediated Killing of Bacteria. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1982, 49, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudzynski, K.; Abubaker, K.; Laurent, M.; Castle, A. Re-Examining the Role of Hydrogen Peroxide in Bacteriostatic and Bactericidal Activities of Honey. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwakman, P.H.S.; te Velde, A.A.; de Boer, L.; Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.M.J.E.; Zaat, S.A.J. Two Major Medicinal Honeys Have Different Mechanisms of Bactericidal Activity. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razmi, N.; Lazouskaya, M.; Pajcin, I.; Petrovic, B.; Grahovac, J.; Simic, M.; Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Stojanovic, G.M. Monitoring the Effect of pH on the Growth of Pathogenic Bacteria Using Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, H.G.; Deng, Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, K.S.; Jin, B.R. Major Royal Jelly Protein 2 Acts as an Antimicrobial Agent and Antioxidant in Royal Jelly. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojka, M.; Valachova, I.; Bucekova, M.; Majtan, J. Antibiofilm Efficacy of Honey and Bee-Derived Defensin-1 on Multispecies Wound Biofilm. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailli, A.; Zibouh, K.; Eddamsyry, B.; Drioiche, A.; Fetjah, D.; Ayyad, F.Z.; Mothana, R.A.; Hawwal, M.F.; Radi, M.; Tarik, R.; et al. Physicochemical Characterization of Moroccan Honey Varieties from the Fez-Meknes Region and Their Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties. Metabolites 2024, 14, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, S.; Riihinen, K.; Kauhanen, J.; Tikkanen-Kaukanen, C. Antimicrobial Activity of Different Finnish Monofloral Honeys against Human Pathogenic Bacteria. APMIS 2013, 121, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlock, O.; Dolan, A.; Athman, R.; Power, A.; Gethin, G.; Cowman, S.; Humphreys, H. Comparison of the Antimicrobial Activity of Ulmo Honey from Chile and Manuka Honey against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavric, E.; Wittmann, S.; Barth, G.; Henle, T. Identification and Quantification of Methylglyoxal as the Dominant Antibacterial Constituent of Manuka (Leptospermum scoparium) Honeys from New Zealand. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokcetin, N.N.; Pappalardo, M.; Campbell, L.T.; Brooks, P.; Carter, D.A.; Blair, S.E.; Harry, E.J. The Antibacterial Activity of Australian Leptospermum Honey Correlates with Methylglyoxal Levels. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.D.; Pappalardo, L.; Bishop, J.; Brooks, P.R. Dihydroxyacetone Production in the Nectar of Australian Leptospermum Is Species Dependent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11133–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnaimat, S.; Wainwright, M.; Al’Abri, K. Antibacterial Potential of Honey From Different Origins: A Comparsion With Manuka Honey. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2012, 1, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar]
- de Groot, T.; Janssen, T.; Faro, D.; Cremers, N.A.; Chowdhary, A.; Meis, J.F. Antifungal Activity of a Medical-Grade Honey Formulation against Candida Auris. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candiracci, M.; Citterio, B.; Piatti, E. Antifungal Activity of the Honey Flavonoid Extract against Candida Albicans. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Waili, N.; Salom, K.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A. Honey for Wound Healing, Ulcers, and Burns; Data Supporting Its Use in Clinical Practice. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 766–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusby, P.E.; Coombes, A.L.; Wilkinson, J.M. Bactericidal Activity of Different Honeys against Pathogenic Bacteria. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghramh, H.A.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Kilany, M. Study of Anticancer, Antimicrobial, Immunomodulatory, and Silver Nanoparticles Production by Sidr Honey from Three Different Sources. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, V.M.; Cooper, R.A.; Molan, P.C. The Antibacterial Activity of Honey against Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 56, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hau-Yama, N.E.; Magaña-Ortiz, D.; Oliva, A.I.; Ortiz-Vázquez, E. Antifungal Activity of Honey from Stingless Bee Melipona Beecheii against Candida Albicans. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 59, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainol, M.I.; Mohd Yusoff, K.; Mohd Yusof, M.Y. Antibacterial Activity of Selected Malaysian Honey. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.; Cooper, R. Improving Antibiotic Activity against Wound Pathogens with Manuka Honey In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuś, P.M.; Szweda, P.; Jerković, I.; Tuberoso, C.I.G. Activity of Polish Unifloral Honeys against Pathogenic Bacteria and Its Correlation with Colour, Phenolic Content, Antioxidant Capacity and Other Parameters. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantakee, K.; Tragoolpua, Y. Activities of Different Types of Thai Honey on Pathogenic Bacteria Causing Skin Diseases, Tyrosinase Enzyme and Generating Free Radicals. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koc, A.N.; Silici, S.; Ercal, B.D.; Kasap, F.; Hörmet-Öz, H.T.; Mavus-Buldu, H. Antifungal Activity of Turkish Honey against Candida Spp. and Trichosporon Spp.: An in Vitro Evaluation. Sabouraudia 2009, 47, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzen, R.D.; Zinck Leth-Espensen, J.; Jansson, T.; Nielsen, D.S.; Lund, M.N.; Matzen, S. The Antibacterial Effect In Vitro of Honey Derived from Various Danish Flora. Dermatol. Res. Pr. 2018, 2018, 7021713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamala, T.R.; Shri Jyothi, Y.P.; Saibaba, P. Antibacterial effect of honey on the in vitro and in vivo growth of Escherichia coli. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeleke, S.B.; Dauda, B.E.N.; Tijani, J.O. Nutritional Analysis and Antibacterial Effect of Honey on Bacterial Wound Pathogens. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 6, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Ewnetu, Y.; Lemma, W.; Birhane, N. Antibacterial effects of Apis mellifera and stingless bees honeys on susceptible and resistant strains of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 319Mama, M.; Teshome, T.; Detamo, J. Antibacterial Activity of Honey against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: A Laboratory-Based Experimental Study. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, 7686130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, J.; Kianmehr, A.; Mustafa, M.R.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral Activity of Baicalein and Quercetin against the Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16785–16795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Carvalho, R.; Baltazar, F.; Almeida-Aguiar, C. Propolis: A Complex Natural Product with a Plethora of Biological Activities That Can Be Explored for Drug Development. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczy, A.; Weøgowiec, J.; Ckiewicz, O.W.; Czarny, A.; Kulbacka, J.; Nowakowska, D.; Gancarz, R.; Wilk, K.A. Antimicrobial Activity, Cytotoxicity And Total Phenolic Content Of Different Extracts Of Propolis From The West Pomeranian Region In Poland. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2017, 74, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Bosio, K.; Avanzini, C.; D’Avolio, A.; Ozino, O.; Savoia, D. In Vitro Activity of Propolis against Streptococcus Pyogenes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.F.M.; de Souza, M.C.; Matta, S.R.; de Andrade, M.R.; Vidal, F.V.N. Correlation Analysis between Phenolic Levels of Brazilian Propolis Extracts and Their Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities. Food Chem. 2006, 99, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, M.L.F.; Ribeiro, P.R.; Franco, R.L.P.; Hilhorst, H.W.M.; de Castro, R.D.; Fernandez, L.G. Metabolite Profiling, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Brazilian Propolis: Use of Correlation and Multivariate Analyses to Identify Potential Bioactive Compounds. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchelaghem, S.; Das, S.; Naorem, R.S.; Czuni, L.; Papp, G.; Kocsis, M. Evaluation of Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents, Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities of Hungarian Propolis Ethanolic Extract against Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2022, 27, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, R.S.; De Mendonça, S.; Mendes, P.B.; Paulino, N.; Mimica, M.J.; Lagareiro Netto, A.A.; Lira, I.S.; López, B.G.-C.; Negrão, V.; Marcucci, M.C. Artepillin C and Phenolic Compounds Responsible for Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of Green Propolis and Baccharis Dracunculifolia DC. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 911–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.M.; Noh, D.O.; Cho, S.Y.; Suh, H.J.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, J.M. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities of Propolis from Several Regions of Korea. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, C.F.; Simpson, J.B.; Powell, D.; Brooks, P. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Honeybee (Apis Mellifera Ligustica) Propolis from Subtropical Eastern Australia. Sci. Nat. 2015, 102, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumazawa, S.; Nakamura, J.; Murase, M.; Miyagawa, M.; Ahn, M.-R.; Fukumoto, S. Plant Origin of Okinawan Propolis: Honeybee Behavior Observation and Phytochemical Analysis. Naturwiss. 2008, 95, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, W.; Miao, Y.; Liang, C.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Yin, L.; Geng, Y.; Chen, D.; et al. A Study of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Pinocembrin against Multidrug-Resistant Aeromonas Hydrophila. Int. Microbiol. Off. J. Span. Soc. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloz, J.J.; Alvear, M.; Salazar, L.A. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Activity against Streptococcus Mutans of Individual and Mixtures of the Main Polyphenolic Compounds Found in Chilean Propolis. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7602343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankova, V. Chemical Diversity of Propolis Makes It a Valuable Source of New Biologically Active Compounds. J. ApiProd. ApiMed. Sci. 2009, 1, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, N.; Kakino, Y.; Iwai, K.; Mochida, K.; Fujita, T. In Vitro Antibacterial, Antimutagenic and Anti-Influenza Virus Activity of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Esters. Biocontrol Sci. 2005, 10, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gucwa, K.; Kusznierewicz, B.; Milewski, S.; Van Dijck, P.; Szweda, P. Antifungal Activity and Synergism with Azoles of Polish Propolis. Pathogens 2018, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possamai Rossatto, F.C.; Tharmalingam, N.; Escobar, I.E.; d’Azevedo, P.A.; Zimmer, K.R.; Mylonakis, E. Antifungal Activity of the Phenolic Compounds Ellagic Acid (EA) and Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE) against Drug-Resistant Candida Auris. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M.; Alam, R.; Łochyńska, M. Antifungal Properties of Chemically Defined Propolis from Various Geographical Regions. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamplona-Zomenhan, L.C.; Pamplona, B.C.; da Silva, C.B.; Marcucci, M.C.; Mimica, L.M.J. Evaluation of the in Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of an Ethanol Extract of Brazilian Classified Propolis on Strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, I.; Zimmermann, S.; Reichling, J.; Wink, M. Antimicrobial Activities of European Propolis Collected from Various Geographic Origins Alone and in Combination with Antibiotics. Medicines 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, B.; Xuan, H. Australian Propolis Ethanol Extract Exerts Antibacterial Activity against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by Mechanisms of Disrupting Cell Structure, Reversing Resistance, and Resisting Biofilm. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1651–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Margarita, G.E.; Wu, D.; Yuan, W.; Yan, S.; Qi, S.; Xue, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, L. Antibacterial Activity of Chinese Red Propolis against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA. Molecules 2022, 27, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtyczka, R.D.; Dziedzic, A.; Idzik, D.; Kepa, M.; Kubina, R.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Smoleń-Dzirba, J.; Stojko, J.; Sajewicz, M.; Wasik, T.J. Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates to Propolis Extract Alone or in Combination with Antimicrobial Drugs. Molecules 2013, 18, 9623–9640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtyczka, R.D.; Kȩpa, M.; Idzik, D.; Kubina, R.; Kabała-Dzik, A.; Dziedzic, A.; Wąsik, T.J. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Polish Propolis against Biofilm Forming Staphylococcus Epidermidis Strains. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 590703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Mombelli, B.; Vecchi, E.D.; Tocalli, M.C.F.L.; Gismondo, M.R. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Propolis Dry Extract. J. Chemother. 2000, 12, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, N.; Hazir, S.; Baser, K.H.; Kürkçüoglu, M. Antibacterial Activity and Chemical Composition of Turkish Propolis. Z. Fur Naturforschung Sect. C. J. Biosci. 2001, 56, 1112–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temiz, A.; Şener, A.; Tüylü, A.Ö.; Sorkun, K.; Salih, B. Antibacterial Activity of Bee Propolis Samples from Different Geographical Regions of Turkey against Two Foodborne Pathogens, Salmonella Enteritidis and Listeria Monocytogenes. Turk. J. Biol. 2011, 35, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nina, N.; Quispe, C.; Jiménez-Aspee, F.; Theoduloz, C.; Feresín, G.E.; Lima, B.; Leiva, E.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Antibacterial Activity, Antioxidant Effect and Chemical Composition of Propolis from the Región Del Maule, Central Chile. Molecules 2015, 20, 18144–18167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, S.; Piccioni, M.; Pagiotti, R.; Pietrella, D. Antibiofilm and Antioxidant Activity of Propolis and Bud Poplar Resins versus Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 5163575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghukumar, R.; Vali, L.; Watson, D.; Fearnley, J.; Seidel, V. Antimethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Activity of ‘Pacific Propolis’ and Isolated Prenylflavanones. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimasu, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Sakai, N.; Yagi, A.; Hirayama, S.; Morinaga, Y.; Furukawa, S.; Nakao, R. Rapid Bactericidal Action of Propolis against Porphyromonas Gingivalis. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Guendouz, S.; Lyoussi, B.; Lourenço, J.P.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Miguel, M.G.; Barrocas Dias, C.; Manhita, A.; Jordao, L.; Nogueira, I.; Faleiro, M.L. Magnetite Nanoparticles Functionalized with Propolis against Methicillin Resistant Strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 102, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scazzocchio, F.; DAuria, F.D.; Alessandrini, D.; Pantanella, F. Multifactorial Aspects of Antimicrobial Activity of Propolis. Microbiol. Res. 2006, 161, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Silva, W.E.; Junior, W.D.F.; da Rosa, P.R.; de Moraes Peixoto, R.; Tenorio, J.A.B.; da Silva, T.M.S.; da Costa, M.M. In Vitro Activity of Propolis: Synergism in Combination with Antibiotics against Staphylococcus Spp. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Orsi, R.O.; Fernandes, A.; Bankova, V.; Sforcin, J.M. Antibacterial Effects of Brazilian and Bulgarian Propolis and Synergistic Effects with Antibiotics Acting on the Bacterial DNA and Folic Acid. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onlen, Y.; Duran, N.; Atik, E.; Savas, L.; Altug, E.; Yakan, S.; Aslantas, O. Antibacterial Activity of Propolis Against MRSA and Synergism with Topical Mupirocin. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2007, 13, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, J.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Wei, F.; Xuan, H. Antibacterial Activity of Chinese Propolis and Its Synergy with β-Lactams against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Braz. J. Microbiol. Publ. Braz. Soc. Microbiol. 2022, 53, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarjani, K.M.; Yehia, H.M.; Badr, A.N.; Ali, H.S.; Al-Masoud, A.H.; Alhaqbani, S.M.; Alkhatib, S.A.; Rady, A.M.; Abdel-Maksoud, M. Antimicrobial Impact of a Propolis/PVA/Chitosan Composite and Its Prospective Application against Methicillin Resistance Bacterial Infection. Front. Nanotechnol. 2024, 6, 1387933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Konteles, S.J.; Troullidou, E.; Mourtzinos, I.; Karathanos, V.T. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity and Antimicrobial Properties of Propolis Extracts from Greece and Cyprus. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzel, A.; Sorkun, K.; Onçağ, O.; Cogŭlu, D.; Gençay, O.; Salih, B. Chemical Compositions and Antimicrobial Activities of Four Different Anatolian Propolis Samples. Microbiol. Res. 2005, 160, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanović, S.; Antić, N.; Dakić, I.; Švabić-Vlahović, M. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Propolis and Synergism between Propolis and Antimicrobial Drugs. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, R.d.O.; Sforcin, J.M.; Funari, S.R.C.; Fernandes Junior, A.; Bankova, V. Synergistic Effect of Propolis and Antibiotics on the Salmonella Typhi. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, C.R.F.; Assunção Borges, K.R.; Alves, R.d.N.S.; Teles, A.M.; Pimentel Rodrigues, I.V.; da Silva, M.A.C.N.; Nascimento, M.d.D.S.B.; Bezerra, G.F.d.B. Highly Efficient Antibiofilm and Antifungal Activity of Green Propolis against Candida Species in Dentistry Materials. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpena, M.; Nuñez-Estevez, B.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Bee Venom: An Updating Review of Its Bioactive Molecules and Its Health Applications. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH PubChem. Melitten. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Melitten (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Raghuraman, H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Melittin: A Membrane-Active Peptide with Diverse Functions. Biosci. Rep. 2007, 27, 189–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliaš, D.; Tóth Hervay, N.; Gbelská, Y. Ergosterol Biosynthesis and Regulation Impact the Antifungal Resistance and Virulence of Candida Spp. Stresses 2024, 4, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-B. Antifungal Activity of Bee Venom and Sweet Bee Venom against Clinically Isolated Candida Albicans. J. Pharmacopuncture 2016, 19, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kwon, O.; An, H.-J.; Park, K.K. Antifungal Effects of Bee Venom Components on Trichophyton Rubrum: A Novel Approach of Bee Venom Study for Possible Emerging Antifungal Agent. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Pereira, A.F.; Albano, M.; Bérgamo Alves, F.C.; Murbach Teles Andrade, B.F.; Furlanetto, A.; Mores Rall, V.L.; Delazari Dos Santos, L.; de Oliveira Orsi, R.; Fernandes Júnior, A. Influence of Apitoxin and Melittin from Apis Mellifera Bee on Staphylococcus aureus Strains. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 141, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Esmaeili Gouvarchin Ghaleh, H.; Ranjbar, R. Antibiofilm Effect of Melittin Alone and in Combination with Conventional Antibiotics toward Strong Biofilm of MDR-MRSA and-Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Seedi, H.; El-Wahed, A.A.; Yosri, N.; Musharraf, S.G.; Chen, L.; Moustafa, M.; Zou, X.; Al-Mousawi, S.; Guo, Z.; Khatib, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Properties of Apis Mellifera’s Bee Venom. Toxins 2020, 12, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.G. Melittin Triggers Apoptosis in Candida Albicans through the Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Mitochondria/Caspase-Dependent Pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 355, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leandro, L.F.; Mendes, C.A.; Casemiro, L.A.; Vinholis, A.H.; Cunha, W.R.; De Almeida, R.; Martins, C.H. Antimicrobial Activity of Apitoxin, Melittin and Phospholipase A2 of Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) Venom against Oral Pathogens. An. Da Acad. Bras. De. Cienc. 2015, 87, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damianoglou, A.; Rodger, A.; Pridmore, C.; Dafforn, T.R.; Mosely, J.A.; Sanderson, J.M.; Hicks, M.R. The Synergistic Action of Melittin and Phospholipase A2 with Lipid Membranes: Development of Linear Dichroism for Membrane-Insertion Kinetics. Protein Pept. Lett. 2010, 17, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo, L.A.; Lan, C.-Y.; Agabian, N.M.; Larios, S.; Lomonte, B. Fungicidal Activity of a Phospholipase-A2-Derived Synthetic Peptide Variant against Candida Albicans. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. Publ. Soc. Esp. Quimioter. 2007, 20, 330–333. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.Y.; Yoon, H.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Jin, B.R. Secapin, a Bee Venom Peptide, Exhibits Anti-Fibrinolytic, Anti-Elastolytic, and Anti-Microbial Activities. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 63, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haktanir, I.; Masoura, M.; Mantzouridou, F.T.; Gkatzionis, K. Mechanism of Antimicrobial Activity of Honeybee (Apis Mellifera) Venom on Gram-Negative Bacteria: Escherichia Coli and Pseudomonas Spp. AMB Express 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Jang, A.Y.; Lin, S.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.; Park, K.; Han, S.-M.; Yeo, J.-H.; Seo, H.S. Melittin, a Honeybee Venom-Derived Antimicrobial Peptide, May Target Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6483–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas, A.; Arteaga, V.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Miranda, J.M.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Five Apitoxins from Apis Mellifera on Two Common Foodborne Pathogens. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyad, A.M.; Ali, S.F.; Elkalamawy, I.M.; Radwan, T.E. Synergistic Effect of the Bee Venom with Traditional Antibiotics on Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria. Egypt. J. Med. Microbiol. 2025, 34, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Didamony, S.E.; Kalaba, M.H.; El-Fakharany, E.M.; Sultan, M.H.; Sharaf, M.H. Antifungal and Antibiofilm Activities of Bee Venom Loaded on Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach for Combating Fungal Human Pathogens. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnosary, M.E.; Aboelmagd, H.A.; Habaka, M.A.; Salem, S.R.; El-Naggar, M.E. Synthesis of Bee Venom Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for Anti-MERS-COV and Multi-Drug Resistance Bacteria. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.M.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, I.P.; Woo, S.O.; Kim, S.G.; Jang, H.R.; Pak, S.C. Antibacterial Activity and Antibiotic-Enhancing Effects of Honeybee Venom against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2016, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannis, T.; Dimitriou, T.G.; Didaras, N.A.; Mossialos, D. Antiviral Activity of Bee Products. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 2867–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNAIDS. Fact Sheet 2024. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_en.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- WHO. The Global Health Observatory—HIV. Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/hiv-aids (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- WHO. Influenza (Seasonal). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal) (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Nayak, J.; Hoy, G.; Gordon, A. Influenza in Children. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, A.; Galwankar, S. Seasonal influenza: Waiting for the next pandemic. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2009, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. COVID-19 Epidemiological Update—24 December 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update---24-december-2024 (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Menkir, T.F.; Chin, T.; Hay, J.A.; Surface, E.D.; De Salazar, P.M.; Buckee, C.O.; Watts, A.; Khan, K.; Sherbo, R.; Yan, A.W.C.; et al. Estimating internationally imported cases during the early COVID-19 pandemic. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. WHO Sounds Alarm on Viral Hepatitis Infections Claiming 3500 Lives Each Day. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/09-04-2024-who-sounds-alarm-on-viral-hepatitis-infections-claiming-3500-lives-each-day (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Watanabe, K.; Rahmasari, R.; Matsunaga, A.; Haruyama, T.; Kobayashi, N. Anti-Influenza Viral Effects of Honey in Vitro: Potent High Activity of Manuka Honey. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behbahani, M. Anti-HIV-1 Activity of Eight Monofloral Iranian Honey Types. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabek-Lejko, D.; Miłek, M.; Sidor, E.; Puchalski, C.; Dżugan, M. Antiviral and Antibacterial Effect of Honey Enriched with Rubus spp. as a Functional Food with Enhanced Antioxidant Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyar, A.; Ayazi, P.; Shaftaroni, M.R.; Oveisi, S.; Dalirani, R.; Esmaeili, S. The Effect of Adding Honey to Zinc in the Treatment of Diarrhea in Children. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2022, 3, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obossou, E.K.; Shikamoto, Y.; Hoshino, Y.; Kohno, H.; Ishibasi, Y.; Kozasa, T.; Taguchi, M.; Sakakibara, I.; Tonooka, K.; Shinozuka, T.; et al. Effect of manuka honey on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 6, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, M.; Grabek-Lejko, D.; Stępień, K.; Sidor, E.; Mołoń, M.; Dżugan, M. The enrichment of honey with Aronia melanocarpa fruits enhances its in vitro and in vivo antioxidant potential and intensifies its antibacterial and antiviral properties. Food Funct. 2021, 19, 8920–8931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkhadle, N.I.; Mohamud, R.; Mat Jusoh, T.N.A.; Shueb, R.H. In vitro Evaluation of Anti-Chikungunya Virus Activities of Tualang Honey. Trop. Biomed. 2021, 1, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, K.; Ceylan, E.; Derelioğlu, G. Determination of Chestnut Honey Consumption Characteristics as a Traditional Treatment Method and Its Effect on Protection from COVID-19. Complement. Med. Res. 2022, 3, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Han, S.M.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, J.G. The protective effect of Tilia amurensis honey on influenza A virus infection through stimulation of interferon-mediated IFITM3 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, E.B.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, B.; Han, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, H.M.; Choi, J.G. Castanea crenata honey reduces influenza infection by activating the innate immune response. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1157506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, B.; Kim, S.G.; Na, S.J.; Go, Y.; Choi, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Han, S.M.; Choi, J.G. Korean Chestnut Honey Suppresses HSV-1 Infection by Regulating the ROS-NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 11, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoff, K.; Devant, J.M.; Hansman, G. Natural extracts, honey, and propolis as human norovirus inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2022, 1, 8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.B.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.E.; Na, S.J.; Han, S.M.; Woo, S.O.; Choi, H.M.; Moon, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, J.G. Hovenia dulcis Thunb. Honey Exerts Antiviral Effect Against Influenza A Virus Infection Through Mitochondrial Stress-Mediated Enhancement of Innate Immunity. Antioxidants 2025, 1, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vynograd, N.; Vynograd, I.; Sosnowski, Z. A Comparative Multi-Centre Study of the Efficacy of Propolis, Acyclovir and Placebo in the Treatment of Genital Herpes (HSV). Phytomedicine 2000, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Duran, G.G.; Duran, N.; Jenedi, K.; Bolgul, B.S.; Miraloglu, M.; Muz, M. Antiviral Activity of Hatay Propolis Against Replication of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and Type 2. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münstedt, K. Bee Products and the Treatment of Blister-like Lesions around the Mouth, Skin and Genitalia Caused by Herpes Viruses—A Systematic Review. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019, 43, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Hino, A.; Tsutsumi, A.; Yong, K.P.; Watanabe, W.; Kurokawa, M. Anti-Influenza Virus Activity of Propolis in Vitro and Its Efficacy against Influenza Infection in Mice. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2008, 19, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilhelmova-Ilieva, N.M.; Nikolova, I.N.; Nikolova, N.Y.; Petrova, Z.D.; Trepechova, M.S.; Holechek, D.I.; Todorova, M.M.; Topuzova, M.G.; Ivanov, I.G.; Tumbarski, Y.D. Antiviral Potential of Specially Selected Bulgarian Propolis Extracts: In Vitro Activity against Structurally Different Viruses. Life 2023, 13, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.A.D.; Menezes, M.d.A.; de Souza, S.P.; Galvão, E.B.d.S.; Berretta, A.A.; Caldas, J.; Teixeira, M.B.; Gomes, M.M.D.; Damiani, L.P.; Bahiense, B.A.; et al. Standardized Brazilian Green Propolis Extract (EPP-AF®) in COVID-19 Outcomes: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serkedjieva, J.; Manolova, N.; Bankova, V. Anti-Influenza Virus Effect of Some Propolis Constituents and Their Analogues (Esters of Substituted Cinnamic Acids). J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, J.; Chang, F.R.; Wang, H.K.; Park, Y.K.; Ikegaki, M.; Kilgore, N.; Lee, K.H. Anti-AIDS Agents. 48.(1) Anti-HIV Activity of Moronic Acid Derivatives and the New Melliferone-Related Triterpenoid Isolated from Brazilian Propolis. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1278–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, Z.; Rubinstein, A.; Golodner, M.; Elmaliah, M.; Mizrachi, Y. Suppression of HIV-1 Replication by Propolis and Its Immunoregulatory Effect. Drugs Exp. Clin. Res. 1997, 23, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silva-Beltrán, N.P.; Galvéz-Ruíz, J.C.; Ikner, L.A.; Umsza-Guez, M.A.; de Paula Castro, T.L.; Gerba, C.P. In vitro antiviral effect of Mexican and Brazilian propolis and phenolic compounds against human coronavirus 229E. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2023, 12, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Beltrán, N.P.; Balderrama-Carmona, A.P.; Umsza-Guez, M.A.; Souza Machado, B.A. Antiviral effects of Brazilian green and red propolis extracts on Enterovirus surrogates. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 23, 28510–28517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhalefa, N.; Khaliel, S.; Tahoon, A.; Shaban, H.; Magouz, A.; Ghabban, H.; Lokman, M.S.; Elmahallawy, E.K. In vitro investigation of the antiviral activity of propolis and chitosan nanoparticles against the genotype VII Newcastle disease virus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 947641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sberna, G.; Biagi, M.; Marafini, G.; Nardacci, R.; Biava, M.; Colavita, F.; Piselli, P.; Miraldi, E.; D’Offizi, G.; Capobianchi, M.R.; et al. In vitro Evaluation of Antiviral Efficacy of a Standardized Hydroalcoholic Extract of Poplar Type Propolis Against SARS-CoV-2. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 799546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, V.; Miceli, M.; Pagliuca, C.; Bianco, O.; Castaldo, L.; Izzo, L.; Cozzolino, M.; Zannella, C.; Oglio, F.; Polcaro, A.; et al. Modulation of innate immunity related genes resulting in prophylactic antimicrobial and antiviral properties. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 1, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cora, M.; Buruk, C.K.; Ünsal, S.; Kaklikkaya, N.; Kolayli, S. Chemical Analysis and in Vitro Antiviral Effects of Northeast Türkiye Propolis Samples against HSV-1. Chem. Biodivers. 2023, 8, e202300669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosari, M.; Noureddini, M.; Khamechi, S.P.; Najafi, A.; Ghaderi, A.; Sehat, M.; Banafshe, H.R. The effect of propolis plus Hyoscyamus niger L. methanolic extract on clinical symptoms in patients with acute respiratory syndrome suspected to COVID-19: A clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2021, 7, 4000–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça, R.Z.; Nascimento, R.M.; Fernandes, A.C.O.; Silva, P.I., Jr. Antiviral action of aqueous extracts of propolis from Scaptotrigona aff. postica (Hymenoptera; Apidae) against Zica, Chikungunya, and Mayaro virus. Sci. Rep. 2024, 1, 15289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangboonruang, S.; Semakul, N.; Sookkree, S.; Kantapan, J.; Ngo-Giang-Huong, N.; Khamduang, W.; Kongyai, N.; Tragoolpua, K. Activity of Propolis Nanoparticles against HSV-2: Promising Approach to Inhibiting Infection and Replication. Molecules. 2022, 8, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Guo, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z. Phytochemical Constituents of Propolis Flavonoid, Immunological Enhancement, and Anti-porcine Parvovirus Activities Isolated From Propolis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 857183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, H.; Mady, F.M.; Sarhan, H.A.; Rateb, H.S.; Alaaeldin, E. Optimization and evaluation of propolis liposomes as a promising therapeutic approach for COVID-19. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.B.; Lee, B.H.; Nikapitiya, C.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, C.J. Inhibitory Effects of Bee Venom and Its Components against Viruses in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.; El-Bitar, A.M.H.; Hotta, H. Potent Virucidal Activity of Honeybee “Apis Mellifera” venom against Hepatitis C Virus. Toxicon 2020, 188, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, J.L.; Jallouk, A.P.; Campbell, N.; Ratner, L.; Wickline, S.A. Cytolytic Nanoparticles Attenuate HIV-1 Infectivity. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfiky, A.A.; Elasmy, N.M.; Salama, W.H.; Morsy, A.T.A. Antiviral Effect Of The Egyptian Bee Venom (Bv) And Its Fraction (Pla2) On Influenza Virus: In-Vitro Study. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2020, 50, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Chowdhury, J.P. Antiviral Attributes of Bee Venom as a Possible Therapeutic Approach against SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Futur. Virol. 2023, 18, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.I.; Mohamed, A.F.; Amer, M.A.; Hammad, K.M.; Riad, S.A. Monitoring of the antiviral potential of bee venom and wax extracts against Adeno-7 (DNA) and Rift Valley fever virus (RNA) viruses models. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2015, 1, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Chaturvedi, P.K.; Chun, S.N.; Lee, Y.G.; Ahn, W.S. Honeybee venom possesses anticancer and antiviral effects by differential inhibition of HPV E6 and E7 expression on cervical cancer cell line. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 4, 1675–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Maksoud, E.A.; Rady, M.H.; Mahmoud, A.G.T.; Hamza, D.; Seadawy, M.G.; Essa, E.E. Potential therapeutic biomolecules of hymenopteran venom against SARS-CoV-2 from Egyptian patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 1, 15363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praphawilai, P.; Kaewkod, T.; Suriyaprom, S.; Panya, A.; Disayathanoowat, T.; Tragoolpua, Y. Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Melittin Peptides Derived from Apis mellifera and Apis florea Venom. Insects 2024, 15, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almadani, Y.H.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Davison, P.G.; Murphy, A.M. Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, J.M.; Sorg, H. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Eur. Surg. Res. Eur. Chir. Forsch. Rech. Chir. Eur. 2012, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landén, N.X.; Li, D.; Ståhle, M. Transition from Inflammation to Proliferation: A Critical Step during Wound Healing. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3861–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nader, R.A.; Mackieh, R.; Wehbe, R.; El Obeid, D.; Sabatier, J.M.; Fajloun, Z. Beehive Products as Antibacterial Agents: A Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jull, A.B.; Cullum, N.; Dumville, J.C.; Westby, M.J.; Deshpande, S.; Walker, N. Honey as a Topical Treatment for Wounds. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD005083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takzaree, N.; Hassanzadeh, G.; Rouini, M.R.; Manayi, A.; Hadjiakhondi, A.; Majidi Zolbin, M. Evaluation of the Effects of Local Application of Thyme Honey in Open Cutaneous Wound Healing. Iran. J. Public Health 2017, 46, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kafaween, M.A.; Alwahsh, M.; Hilmi, A.B.M.; Abulebdah, D.H. Physicochemical Characteristics and Bioactive Compounds of Different Types of Honey and Their Biological and Therapeutic Properties: A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mieles, J.Y.; Vyas, C.; Aslan, E.; Humphreys, G.; Diver, C.; Bartolo, P. Honey: An Advanced Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleeging, C.C.; Wagener, F.A.; de Rooster, H.; Cremers, N.A. Revolutionizing non-conventional wound healing using honey by simultaneously targeting multiple molecular mechanisms. Drug Resist. Updat. 2022, 62, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, H.; Moradi, S. Honey: A Skin Graft Fixator Convenient for Both Patient and Surgeon. Indian J. Surg. 2015, 77, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Pi, A.; Yan, L.; Li, J.; Nan, S.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Y. Research Progress on Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Propolis on Wound Healing. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 5798941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderas-Cordero, D.; Canales-Alvarez, O.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Cabrera-Wrooman, A.; Canales-Martinez, M.M.; Rodriguez-Monroy, M.A. Anti-Inflammatory and Histological Analysis of Skin Wound Healing through Topical Application of Mexican Propolis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xool-Tamayo, J.; Chan-Zapata, I.; Arana-Argaez, V.E.; Villa-de la Torre, F.; Torres-Romero, J.C.; Araujo-Leon, J.A.; Aguilar-Ayala, F.J.; Rejón-Peraza, M.E.; Castro-Linares, N.C.; Vargas-Coronado, R.F.; et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Mayan Propolis. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2020, 18, 2058739220935280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Song, S.-Y.; Park, E.-H.; Kim, E.; Oh, G.C.; Choo, E.H.; Hwang, B.-H.; Chang, K.; Oak, M.-H. Beneficial Effects of Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester on Wound Healing in a Diabetic Mouse: Role of VEGF and NO. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujica, V.; Orrego, R.; Fuentealba, R.; Leiva, E.; Zúñiga-Hernández, J. Propolis as an Adjuvant in the Healing of Human Diabetic Foot Wounds Receiving Care in the Diagnostic and Treatment Centre from the Regional Hospital of Talca. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 2507578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshaw, F.R.; Bolton, T.; Nube, V.; Hood, A.; Veldhoen, D.; Pfrunder, L.; McKew, G.L.; Macleod, C.; McLennan, S.V.; Twigg, S.M. Topical Application of the Bee Hive Protectant Propolis Is Well Tolerated and Improves Human Diabetic Foot Ulcer Healing in a Prospective Feasibility Study. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2014, 28, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hozzein, W.N.; Badr, G.; Badr, B.M.; Allam, A.; Ghamdi, A.A.; Al-Wadaan, M.A.; Al-Waili, N.S. Bee Venom Improves Diabetic Wound Healing by Protecting Functional Macrophages from Apoptosis and Enhancing Nrf2, Ang-1 and Tie-2 Signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 103, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Du, C.; Song, P.; Chen, T.; Rui, S.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deng, W. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Diabetic Wound Healing. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8852759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olczyk, P.; Koprowski, R.; Kaźmierczak, J.; Mencner, L.; Wojtyczka, R.; Stojko, J.; Olczyk, K.; Komosinska-Vassev, K. Bee Pollen as a Promising Agent in the Burn Wounds Treatment. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 8473937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siavash, M.; Shokri, S.; Haghighi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Shahtalebi, M.A.; Farajzadehgan, Z. The Efficacy of Topical Royal Jelly on Diabetic Foot Ulcers Healing: A Case Series. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2011, 16, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Yun, H.; Park, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, K.-G.; Han, S.-M.; Cho, Y. Royal Jelly Enhances Migration of Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Alters the Levels of Cholesterol and Sphinganine in an in Vitro Wound Healing Model. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2010, 4, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, S.; Contreras-Kallens, P.; Aguayo, S.; Ramírez, O.; Vallejos, C.; Ruiz, J.; Carrasco-Gallardo, E.; Troncoso-Vera, S.; Morales, B.; Schuh, C.M.A.P. Royal Jelly Extracellular Vesicles Promote Wound Healing by Modulating Underlying Cellular Responses. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 31, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andritoiu, C.V.; Lungu, C.; Danu, M.; Ivanescu, B.; Andriescu, C.E.; Vlase, L.; Havarneanu, C.; Iurciuc (Tincu), C.E.; Popa, M. Evaluation of the Healing Effect of Ointments Based on Bee Products on Cutaneous Lesions in Wistar Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadi, S.M.R.; Hashemi, M.; Mohammadi, Y.; MamMohammadi, A.; Sharifi, A.; Makarchian, H.R. Synergistic Effect of Honey and Nigella Sativa on Wound Healing in Rats. Acta. Cir. Bras. 2018, 33, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayir, Y.; Un, H.; Ugan, R.A.; Akpinar, E.; Cadirci, E.; Calik, I.; Halici, Z. The Effects of Beeswax, Olive Oil and Butter Impregnated Bandage on Burn Wound Healing. Burn. J. Int. Soc. Burn. Inj. 2019, 45, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ran, X. Efficacy and Safety of Honey Dressings in the Management of Chronic Wounds: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaiah, N.D.; Suryakanth, D.B. Propolis and Allergic Reactions. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Lin, J.-L.; Yang, C.-W.; Yu, C.-C. Acute Renal Failure Induced by a Brazilian Variety of Propolis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, e125–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Jeon, E.J.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, J.C.; Shin, J.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, I.W.; Choi, B.W. A Fatal Case of Intravascular Coagulation after Bee Sting Acupuncture. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2012, 4, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherniack, E.P.; Govorushko, S. To Bee or Not to Bee: The Potential Efficacy and Safety of Bee Venom Acupuncture in Humans. Toxicon 2018, 154, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X.-R.; Lin, L.-T.; Xiao, L.-Y.; Zhou, P.; Shi, G.-X.; Liu, C.-Z. Bee Venom Therapy: Potential Mechanisms and Therapeutic Applications. Toxicon 2018, 148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, M.J.; Tveten, M.S.; Egen, N.B. Rate and Quantity of Delivery of Venom from Honeybee Stings. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1994, 93, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, D.C.; Braga, M.R.B.; de Abreu, R.M.M.; Blank, S.; Bridts, C.H.; De Clerck, L.S.; Devreese, B.; Ebo, D.G.; Ferris, T.J.; Hagendorens, M.M.; et al. Standard Methods for Apis Mellifera Venom Research. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickavasagam, G.; Saaid, M.; Lim, V. Impact of Prolonged Storage on Quality Assessment Properties and Constituents of Honey: A Systematic Review. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 811–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, H.M.; El-Bassiony, M.N.; El-Bolok, D.M.R.; Mohamed, W.F.I. Antibacterial Activities of Honeybee Venom Produced under Different Storage Conditions. J. Plant Prot. Pathol. 2020, 11, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laconi, A.; Tolosi, R.; Mughini-Gras, L.; Mazzucato, M.; Ferrè, N.; Carraro, L.; Cardazzo, B.; Capolongo, F.; Merlanti, R.; Piccirillo, A. Beehive Products as Bioindicators of Antimicrobial Resistance Contamination in the Environment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 823, 151131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkırım, A.; Küçüközmen, B.; Çelemli, Ö.G. Impact of Sterilization Process on Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Propolis. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 58, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).