Molecular Characterization of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Jiangxi Province: A High Prevalence of Rickettsia, Anaplasma and Ehrlichia in Rhipicephalus microplus in Cattle from Ganzhou City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tick Collection and Identification
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Polymerase Chain Reaction
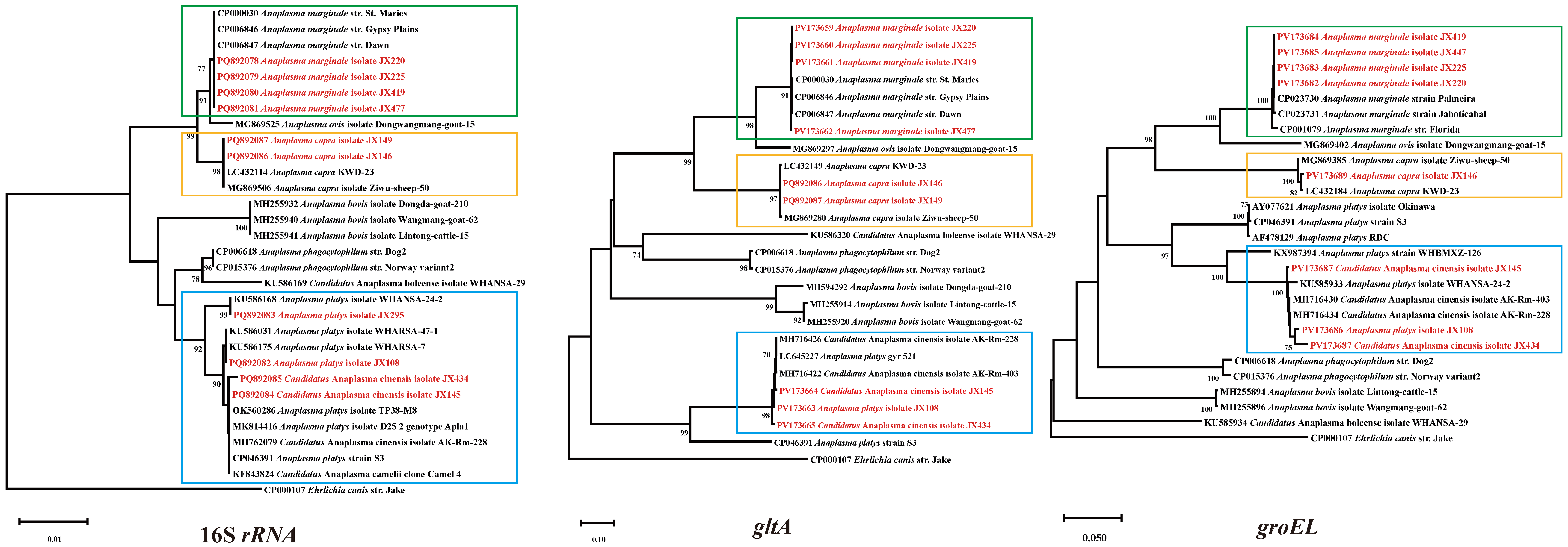
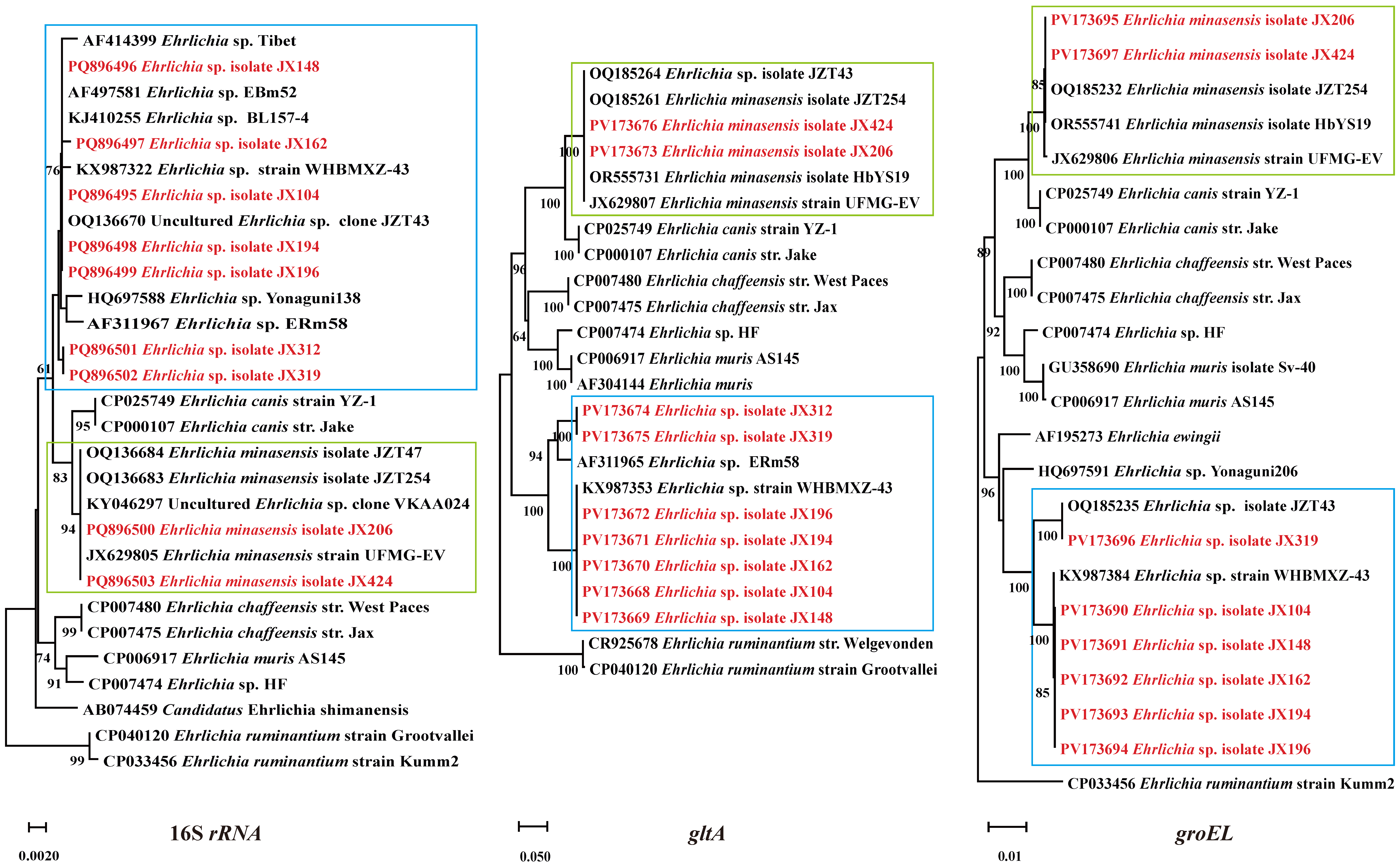
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Tick Identification
3.2. Rickettsia Bacteria Detected in Ticks
3.3. Anaplasma Bacteria Detected in Ticks
3.4. Ehrlichia Bacteria Detected in Ticks
3.5. Co-Infection of Rickettsiales in Ticks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and tick-borne diseases: A one health perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Fuente, J.; Estrada-Pena, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Kocan, K.M.; Sonenshine, D.E. Overview: Ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 6938–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.F.; Jiang, Z.J. Insect Knowl. Fascicle 39. Acari: Ixodidae. In Economic Insects Fauna of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Schetters, T.; Bishop, R.; Crampton, M.; Kopáček, P.; Lew-Tabor, A.; Maritz-Olivier, C.; Miller, R.; Mosqueda, J.; Patarroyo, J.; Rodriguez-Valle, M.; et al. Cattle tick vaccine researchers join forces in CATVAC. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almazán, C.; Moreno-Cantú, O.; Moreno-Cid, J.A.; Galindo, R.C.; Canales, M.; Villar, M.; de la Fuente, J. Control of tick infestations in cattle vaccinated with bacterial membranes containing surface-exposed tick protective antigens. Vaccine 2012, 30, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.P.; Wang, Y.X.; Fan, Z.W.; Ji, Y.; Liu, M.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Li, X.L.; Zhou, S.X.; Li, H.; Liang, S.; et al. Mapping ticks and tick-borne pathogens in China. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narladkar, B.W. Projected economic losses due to vector and vector-borne parasitic diseases in livestock of India and its significance in implementing the concept of integrated practices for vector management. Vet. World 2018, 11, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, D.; Carolino, N.; Gomes, J.; Coelho, A.C.; Espadinha, P.; Pais, J.; Carolino, I. A study of knowledge, attitudes, and practices on ticks and tick-borne diseases of cattle among breeders of two bovine Portuguese autochthonous breeds. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2024, 48, 100989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochlin, I.; Toledo, A. Emerging tick-borne pathogens of public health importance: A mini-review. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, M.; Rymaszewska, A. Expansion of Tick-Borne Rickettsioses in the World. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Bu, F.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, J. Ticks (acari: Ixodoidea: Argasidae, ixodidae) of China. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2010, 51, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmat, M.; Ijaz, M.; Farooqi, S.H.; Ghaffar, A.; Ali, A.; Masud, A.; Saleem, S.; Rehman, A.; Ali, M.M.; Mehmood, K.; et al. Molecular epidemiology, associated risk factors, and phylogenetic analysis of anaplasmosis in camel. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.C.; Zhao, Q.M.; Zhang, P.H.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.M.; Wen, B.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Habbema, J.D. Prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophila and Borrelia burgdorferi in Ixodes persulcatus ticks from northeastern China. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bouyer, D.H.; Stenos, J.; Crocquet-Valdes, P.; Moron, C.G.; Popov, V.L.; Zavala-Velazquez, J.E.; Foil, L.D.; Stothard, D.R.; Azad, A.F.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsia felis: Molecular characterization of a new member of the spotted fever group. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.P.; Tian, J.H.; Lin, X.D.; Ni, X.B.; Chen, X.P.; Liao, Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Dumler, J.S.; Holmes, E.C.; Zhang, Y.Z. Extensive genetic diversity of Rickettsiales bacteria in multiple mosquito species. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafar Bekloo, A.; Ramzgouyan, M.R.; Shirian, S.; Faghihi, F.; Bakhshi, H.; Naseri, F.; Sedaghat, M.; Telmadarraiy, Z. Molecular Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Anaplasma spp. and Ehrlichia spp. Isolated from Various Ticks in Southeastern and Northwestern Regions of Iran. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Niu, Q.; Liu, J.; Han, R.; Guan, G.; Hassan, M.A.; Liu, G.; Luo, J.; Yin, H. A novel zoonotic Anaplasma species is prevalent in small ruminants: Potential public health implications. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlough, J.E.; Madigan, J.E.; DeRock, E.; Bigornia, L. Nested polymerase chain reaction for detection of Ehrlichia equi genomic DNA in horses and ticks (Ixodes pacificus). Vet. Parasitol. 1996, 63, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.P.; Tie, W.F.; Meng, S.; Li, D.; Wang, J.L.; Du, L.Y.; Xie, G.C. Extensive genetic diversity of Anaplasma bovis in ruminants in Xi’an, China. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftis, A.D.; Ross, D.E.; Levin, M.L. Susceptibility of Mice (Mus musculus) to Repeated Infestation with Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) Ticks. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Meng, C.; Gao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, G.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, G.; Wang, W.; et al. Diversity of Rickettsiales in Rhipicephalus microplus Ticks Collected in Domestic Ruminants in Guizhou Province, China. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, J.; Apanaskevich, D.A.; Gutiérrez, R.; Nachum-Biala, Y.; Baneth, G.; Harrus, S. Morphological and molecular identification of Rhipicephalus (boophilus) microplus in Nigeria, West Africa: A threat to livestock health. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 73, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P. Prediction of spatial distribution and epidemic analysis of pathogens of Rhipicephalus microplus. Master’s Thesis, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing, China, 2022; p. 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.H.; Li, K.; Zhang, S.Z.; Xu, Z.J.; Wu, H.X.; Xu, H.B.; Lei, C.L. Tick (acari: Ixodoidea) fauna and zoogeographic division of Jiangxi Province, China. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2023, 14, 102099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byaruhanga, C.; Collins, N.E.; Knobel, D.L.; Khumalo, Z.T.H.; Chaisi, M.E.; Oosthuizen, M.C. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma centrale amongst transhumant cattle in north-eastern Uganda. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hosary, A.; Răileanu, C.; Tauchmann, O.; Fischer, S.; Nijhof, A.M.; Silaghi, C. Epidemiology and genotyping of Anaplasma marginale and co-infection with piroplasms and other Anaplasmataceae in cattle and buffaloes from Egypt. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Dai, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Qin, T. The increasing Prevalence of Japanese Spotted Fever in China: A Dominant Rickettsial Threat. J. Infect. 2025, 90, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qi, W.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; He, L.; Zhao, J. Molecular characterization of tick-borne bacterial and protozoan pathogens in parasitic ticks from Xinjiang, China. Parasites Vectors 2025, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.J.; Ye, R.Z.; Tian, D.; Wang, N.; Gao, W.Y.; Wang, B.H.; Lin, Z.T.; Liu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhu, D.Y.; et al. The first direct detection of spotted fever group Rickettsia spp. Diversity in ticks from Ningxia, northwestern China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2025, 19, e0012729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Tian, J.; Duan, C.; Qin, X.; Guo, Y.; Chen, G.; Lei, F.; et al. Circulation of multiple Rickettsiales bacteria in ticks from Sichuan province, Southwest China. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 183, 106313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badillo-Viloria, M.; Mattar, S.; Remesar, S.; de la Rosa-Jaramillo, S.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Miranda, J.; Portillo, A.; Cervera-Acedo, C.; Oteo, J.A.; Cano-Terriza, D. Rickettsia spp. and Anaplasmataceae Ticks Domest. Anim. North. Colombia. Zoonoses Public Health 2025, 72, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, C.S.; Félix, M.L.; Domínguez, A.L.; Araúz, D.; Venzal, J.M. Molecular screening of tick-borne microorganisms in ticks from rural areas of Panama, with the first record of Ehrlichia minasensis in Rhipicephalus microplus from Central America. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Pan, K.; Teng, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Ren, H.; Yi, L.; He, J.; Cai, K.; Qin, T. Molecular detection reveals diverse tick-borne bacterial and protozoan pathogens in two tick species from Yingshan County of Hubei Province, China in 2021–2022. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1298037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Ticks and Tickborne Bacterial Diseases in Humans: An Emerging Infectious Threat. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 897–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahara, F.; Koga, K.; Sawada, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Shigemi, F.; Suto, T.; Tsuboi, Y.; Ooya, A.; Koyama, H.; Uchiyama, T.; et al. The First Report of the Rickettsial Infections of Spotted Fever Group in Japan: Three Clinical Cases. Kansenshogaku Zasshi 1985, 59, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Z.; Gong, P.; Wang, W.; Zhao, N.; Jin, X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, X.; Wen, B.; et al. Clinical Forms of Japanese Spotted Fever from Case-series Study, Zigui county, Hubei province, China, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Song, M.; Wei, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q. Characterization of rickettsiae in ticks in northeastern China. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, X.M.; Du, J.; Zhang, X.A.; Cui, N.; Yang, Z.D.; Xue, X.J.; Zhang, P.H.; Cao, W.C.; Liu, W. Candidatus Rickettsia xinyangensis as cause of Spotted Fever Group Rickettsiosis, Xinyang, China, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.W.; Simpson, C.F.; Gaskin, J.M. Cyclic thrombocytopenia induced by a Rickettsia-like agent in Dogs. J. Infect. Dis. 1978, 137, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, R.G.; Mascarelli, P.E.; Havenga, L.N.; Naidoo, V.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Co-infection with Anaplasma platys, Bartonella henselae and Candidatus Mycoplasma haematoparvum in a veterinarian. Parasites Vectors 2013, 6, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraga-Alvarado, C.M.; Qurollo, B.A.; Parra, O.C.; Berrueta, M.A.; Hegarty, B.C.; Breitschwerdt, E.B. Case report: Molecular Evidence of Anaplasma platys infection in Two Women from Venezuela. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocan, K.M.; de la Fuente, J.; Blouin, E.F.; Garcia-Garcia, J.C. Anaplasma marginale (Rickettsiales: Anaplasmataceae): Recent advances in defining host-pathogen adaptations of a tick-borne Rickettsia. Parasitology 2004, 129, S285–S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.B.; Jusi, M.M.G.; Freschi, C.R.; Ramos, I.A.S.; Mendes, N.S.; Bressianini do Amaral, R.; Gonçalves, L.R.; André, M.R.; Machado, R.Z. High genetic diversity and superinfection by Anaplasma marginale strains in naturally infected angus beef cattle during a clinical anaplasmosis outbreak in southeastern Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2022, 13, 101829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, P.; Geale, D.W. A review of bovine anaplasmosis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2011, 58, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zheng, Y.C.; Ma, L.; Jia, N.; Jiang, B.G.; Jiang, R.R.; Huo, Q.B.; Wang, Y.W.; Liu, H.B.; Chu, Y.L.; et al. Human infection with a novel tick-borne Anaplasma species in China: A surveillance study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.T.; Ye, R.Z.; Liu, J.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, W.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Cui, X.M.; Cao, W.C. Epidemiological and phylogenetic characteristics of emerging Anaplasma capra: A systematic review with modeling analysis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2023, 115, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, G.; Wang, X.; Ni, X.; Zhou, E.M. Molecular identification and characterization of Anaplasma capra and Anaplasma platys-like in Rhipicephalus microplus in Ankang, Northwest China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumler, J.S.; Barbet, A.F.; Bekker, C.P.; Dasch, G.A.; Palmer, G.H.; Ray, S.C.; Rikihisa, Y.; Rurangirwa, F.R. Reorganization of genera in the families rickettsiaceae and anaplasmataceae in the order rickettsiales: Unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‘HGE agent’ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 2145–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, D.M.; Araujo, J.P., Jr.; Nakazato, L.; Bard, E.; Cabezas-Cruz, A. Complete Genome Sequence of an Ehrlichia minasensis Strain Isolated from Cattle. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00161-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajadhar, A.A.; Lobanov, V.; Scandrett, W.B.; Campbell, J.; Al-Adhami, B. A novel Ehrlichia genotype detected in naturally infected cattle in North America. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 173, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweygarth, E.; Schöl, H.; Lis, K.; Cabezas Cruz, A.; Thiel, C.; Silaghi, C.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Passos, L.M. In vitro culture of a novel genotype of Ehrlichia sp. from Brazil. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60 (Suppl. 2), 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Zweygarth, E.; Aguiar, D.M. Ehrlichia minasensis, an old demon with a new name. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 828–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ticks | Coinfection | Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rickettsia | Anaplasma | Ehrlichia | ||
| Rhipicephalus microplus | R. japonica | A. marginale | 2 | |
| Ca. R. jingxinensis | A. marginale | 1 | ||
| Ca. R. jingxinensis | A. platys | 1 | ||
| R. japonica | Ehrlichia sp. | 4 | ||
| Ca. R. jingxinensis | Ehrlichia sp. | 4 | ||
| Ca. R. jingxinensis | E. minasensis | 1 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Yang, M.; Teng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liang, J.; Zou, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, N.; Qin, T. Molecular Characterization of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Jiangxi Province: A High Prevalence of Rickettsia, Anaplasma and Ehrlichia in Rhipicephalus microplus in Cattle from Ganzhou City, China. Pathogens 2025, 14, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080770
He J, Yang M, Teng Z, Wang P, Liang J, Zou Y, Wang W, Zhao N, Qin T. Molecular Characterization of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Jiangxi Province: A High Prevalence of Rickettsia, Anaplasma and Ehrlichia in Rhipicephalus microplus in Cattle from Ganzhou City, China. Pathogens. 2025; 14(8):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080770
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jia, Meng Yang, Zhongqiu Teng, Peng Wang, Junrong Liang, Yusheng Zou, Wen Wang, Na Zhao, and Tian Qin. 2025. "Molecular Characterization of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Jiangxi Province: A High Prevalence of Rickettsia, Anaplasma and Ehrlichia in Rhipicephalus microplus in Cattle from Ganzhou City, China" Pathogens 14, no. 8: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080770
APA StyleHe, J., Yang, M., Teng, Z., Wang, P., Liang, J., Zou, Y., Wang, W., Zhao, N., & Qin, T. (2025). Molecular Characterization of Tick-Borne Pathogens in Jiangxi Province: A High Prevalence of Rickettsia, Anaplasma and Ehrlichia in Rhipicephalus microplus in Cattle from Ganzhou City, China. Pathogens, 14(8), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14080770









