Abstract
Tick infestation represents a significant constraint on livestock productivity in Saudi Arabia; however, there remains a substantial gap in research addressing tick species diversity, distribution, and their direct effects on milk production. This study aimed to morphologically and molecularly identify tick species infesting dairy cattle, quantify the impact of tick infestation on milk yield and composition, and contribute to the limited understanding of tick ecology and its economic implications in the region. Ticks were collected from infested cows and identified morphologically using taxonomic keys. Molecular identification was performed via PCR amplification of the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) gene. Milk production and quality parameters were assessed in tick-infested and healthy cows in Hafar Al-Batin, Eastern Saudi Arabia. Morphological and genetic analyses confirmed Hyalomma anatolicum as the predominant tick species in the study area, with COI sequences showing high similarity to regional isolates. Tick-infested cows exhibited substantial reductions in milk yield, fat, calcium, and potassium levels, indicating significant metabolic disruptions. Blood biochemical analysis revealed elevated levels of liver enzymes [aspartate aminotransferase (AST) increased by 238.6%, gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) by 155.7%], renal markers [creatinine increased by 788.9%, urea by 130.0%], and electrolyte imbalances [serum calcium decreased by 39.5%, potassium by 45.2%]. Hematological findings included increased white blood cell (WBC) and red blood cell (RBC) counts by 44.9% and 124.7%, respectively, along with a 53.1% decrease in hemoglobin (HGB), suggesting a systemic inflammatory response and possible anemia. This study is among the first to genetically confirm the presence of H. anatolicum in Hafar Al-Batin using molecular tools, thereby enhancing the accuracy of species-level identification and highlighting the physiological impact of tick burden on dairy productivity.
1. Introduction
Ticks are the most economically important ectoparasites affecting livestock health and productivity, especially in tropical and subtropical regions [1]. The most common genus in Saudi Arabia is Hyalomma spp., which is widely distributed in arid areas where environmental conditions favor tick proliferation. Dairy cows in such regions are at high risk of tick infestations, which not only cause injury due to blood feeding but also exert indirect impacts by transmitting tick-borne diseases such as those caused by Theileria, Babesia, and Anaplasma species [2]. These infections result in systemic illness, reduced weight gain, and significant losses in milk yield and quality [3].
Ticks belong to the subclass Acari, class Arachnida, and are grouped into two families of veterinary importance: Ixodidae (hard ticks) and Argasidae (soft ticks). Among these, Ixodidae is considered more medically and economically significant due to its widespread distribution and critical role in disease transmission [4]. The dominant tick genera infesting livestock in Saudi Arabia include Hyalomma, Rhipicephalus, Amblyomma, and Boophilus [5]. Hyalomma anatolicum and H. dromedarii are particularly common in cattle and camels [6]. H. anatolicum is a known vector for Theileria annulata, the causative agent of tropical theileriosis in cattle, while H. dromedarii is generally associated with camels and is capable of transmitting Coxiella burnetii and Anaplasma spp. [7].
Accurate tick species identification is essential for effective disease surveillance and control programs. Classical morphological tools, based on external characteristics such as scutal patterns, genital aperture, and coxal structures, are commonly employed. However, significant intraspecific variation and morphological similarities between closely related species make these methods challenging and sometimes unreliable [8]. Molecular tools, including polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA sequencing—particularly targeting the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) gene—have improved species-level accuracy and have been successfully applied in Saudi Arabia to identify Hyalomma spp. infesting camels and cattle [4,9].
In dairy cattle, tick infestations not only cause visible skin damage and discomfort but also result in substantial economic losses. Blood-sucking ticks contribute to anemia, stress, and immunosuppression, leading to reduced milk yield, lower milk quality, increased treatment costs, and potential culling of chronically infected animals [10,11]. Milk quality is a critical indicator of animal welfare and farm profitability [12].
Furthermore, minerals such as calcium and phosphorus (Ca and P) are essential for milk secretion and skeletal integrity, while magnesium and potassium (Mg and K) are crucial for nerve transmission and enzyme activation. Several studies have reported that parasitic infestations may disrupt the metabolic functions required for normal milk production [13,14]. Notably, biochemical disturbances such as hypocalcemia (low calcium), hypokalemia (low potassium), and elevated liver enzymes—including aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT)—have been documented in infested animals [15]. Additionally, an increased somatic cell count (SCC), a key indicator of udder health, is frequently observed [16], signifying inflammatory or infectious processes [17,18]. These physiological disruptions can negatively impact mammary gland function and alter milk composition, including fat and protein content [19,20].
Despite the evident impact of tick infestations on dairy production, comprehensive studies correlating blood and milk parameters with tick burden remain scarce in Saudi Arabia. Current literature tends to emphasize regional tick distribution and pathogen detection without integrating animal productivity data. Addressing this research gap is essential for designing targeted control strategies and minimizing financial losses in the dairy sector.
The influence of tick infestation on milk yield, milk composition (fat, protein, calcium, and potassium), SCC, as well as blood indices (selected hematological and biochemical parameters) is studied in this paper. The study will be useful to provide scientific evidence on the cross-effects of ectoparasite infestation during dairying under Saudi Arabian conditions by studying the physiological as well as productive responses in dairy cows over 8 weeks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The study was conducted at Haleeba Dairy Farm, located in Hafar Al-Batin, Eastern Saudi Arabia (Latitude 28.3468° N, Longitude 45.9235° E), during March and April 2024. The region is characterized by an arid desert climate, with average daily temperatures ranging between 35 °C and 40 °C, and relative humidity levels between 8% and 12%, according to the Saudi National Center for Meteorology (https://ncm.gov.sa, accessed on 1 May 2025). To contextualize regional occurrence, we compiled published records of Hyalomma distribution in Saudi Arabia and the UAE (Supplementary Table S1).
2.2. Animal Selection, Housing, and Study Design
Thirty Jersey lactating adult dairy cows (4–6 years of age and 550–570 kg body weight) were randomly selected from a free-grazing herd that had routine exposure to ticks under natural field conditions. Prior to the start of the experiment, all animals underwent clinical examination by a licensed veterinarian to assess their tick infestation status. The cows in this study did not exhibit any clinical manifestation of bacterial, viral, helminthic, or protozoal infections. Based on this assessment, cows were divided into two groups:
Group I (Tick Infested Group): 15 cows presented ticks on the body, especially at the ears, udder, axilla, and tail. Ticks were recognized by direct visual assay by a veterinarian. Group II (Negative control): 15 healthy cows with no evidence of ticks or infestation.
To ensure standardized conditions and prevent further tick exposure during the experimental period, all selected cows were transferred to individual pens and maintained under controlled conditions. Each pen was physically isolated, and strict hygiene and biosecurity protocols were implemented to minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
Tick control measures, including manual removal, acaricide application, and regular inspection, were applied exclusively to the healthy control group to preserve their tick-free status. In contrast, the tick-infested group received no treatment during the study in order to monitor the natural progression of tick burden and its physiological impact over time.
All cows were fed a standard diet of hay and silage with ad libitum access to water. Feeding, housing, and milking practices were identical across groups to minimize confounding variables.
2.3. Tick Collection and Species Identification
Ticks were collected daily over an eight-week period (Supplementary Table S2, per-cow daily counts) by examining the entire body surface of each cow in the tick-infested group (Group I), with particular attention to predilection sites such as the ears, neck, dewlap, axillae, udder, perineum, and tail. Adult ticks were carefully removed using blunt forceps and placed into sterile containers filled with 70% ethanol. Each container was clearly labeled with the date and time of collection. The collected ticks were transported daily to the laboratory for morphological species identification (Daily tick counts per cow). In total, 250 adult were recovered across the study (Supplementary Table S3) were collected from Group I and examined under a stereomicroscope using standard taxonomic keys and morphological descriptions [21,22,23,24]. No ticks were detected or removed from the control group (Group II) during the study period.
2.4. Molecular Identification
2.4.1. DNA Extraction from Ticks
Six adult ticks were randomly selected from six different cows (out of the fifteen tick-infested animals) for molecular identification. Before DNA extraction, ticks were thoroughly washed to eliminate surface contaminants and microorganisms. Each tick was immersed in a 5% sodium hypochlorite solution for 5 min, followed by five consecutive washes in deionized distilled water, each lasting 5 min. After the final rinse, the ticks were preserved in 70% ethanol according to Binetruy et al. (2019) and Hoffman et al. (2020) [25,26], and the collection tubes were labeled with the corresponding date and cow number.
In the laboratory, each tick was manually crushed, and genomic DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood & Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), following the manufacturer’s protocol. The extracted DNA was stored at −20 °C until further analysis.
2.4.2. PCR Amplification of the DNA COI Gene
For tick identification, primers targeting the COI region of mitochondrial DNA were used as described by [27]. The primer sequences are as follows. LCO1490 (Forward): 5′-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGATATTGG-3′; HCO2198 (Reverse): 5′-TAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAAAAATCA-3′.
PCR amplification was performed in a 25 μL reaction mixture containing approximately 80 ng of extracted tick DNA, 10 pmol of each primer, and 12.5 μL of 2× PCR Master Mix (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Reactions were carried out in a Multigene™ thermocycler (Labnet International, Inc., Edison, NJ, USA) under the following cycling conditions: an initial denaturation at 98 °C for 3 min; followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 58 °C for 30 s, and elongation at 72 °C for 1 min; and a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min.
PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis using 2% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under a UV transilluminator.
2.4.3. DNA Sequencing and GenBank Accession Numbers and Phylogenetic Analysis
To identify the species of the collected ticks, six of the amplified PCR products were sent for sequencing at Life Technologies (USA). Sequence alignment and similarity analysis were performed using the NCBI BLAST tool (2.16.0). Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the Maximum Likelihood method and the Tamura–Nei model (MEGA) version 6.0 software to evaluate the evolutionary relationships. The obtained COI gene sequences from the identified ticks were deposited in GenBank, and the confirmed H. anatolicum sequences were assigned accession numbers PQ613621—PQ613626.
2.5. Blood Samples for Blood Parasite Examination
Blood samples were collected from the tail vein of the examined cows into tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and subsequently transported to the laboratory. Thin blood smears were prepared from each sample, fixed with methanol, and stained with Giemsa stain following the protocol described by Feldman et al. (2000) [28]. The stained slides were examined under an oil immersion lens (×100 magnification), and intraerythrocytic parasites were identified according to the criteria described by Soulsby (1982) [29].
2.6. Milk Yield Evaluation
Milk samples were collected to assess both the quantity and quality of milk from tick-infested and tick-free (control) cows over a two-month period. Samples were taken twice daily (at 04:00 AM and 04:00 PM) and stored in sterile, leak-proof vials. All sample collections were performed by the same staff member to minimize inter-observer variation. For each cow, daily milk production (liters per cow per day) was recorded for 8 consecutive weeks (tick-infested vs. tick-free controls; morning vs. afternoon). The raw, per-cow, per-milking data for week 1to week 8 are provided in Supplementary Table S4. For all weeks, we then computed weekly group means for each group and milking time; this averaging naturally reduces apparent variability within groups [30]. As expected, aggregation at the group–week level reduces the apparent within-group variability. Control cows, all of the same breed (Jersey) and maintained under standardized feeding, housing, and milking conditions, exhibited stable physiological status throughout the study. In contrast, the tick-infested group displayed greater variability, reflecting physiological stress and individual differences in response to infestation.
To evaluate the relationship between tick infestation and milk yield, a linear regression model was applied. The model used week number (1–8) as the independent variable and mean milk yield (L) as the dependent variable. Separate regression models were fitted for morning and afternoon milk yields in tick-infested cows. The regression equation was expressed as follows:
where Y represents milk yield (L), X represents the week number, β0 is the intercept, β1 is the slope (change in milk yield per week), and ϵ is the error term.
Y = β0 + β1X + ϵ
Chemical and Mineral Analysis of Cow’s Milk
Milk composition was determined using samples collected from all cows during the morning milking session over eight weeks. Upon collection, samples were placed into sterile, labeled tubes, stored at 4 °C, and transported to the analytical laboratory within four hours to preserve their physicochemical properties [31].
To assess milk composition, a method was used to measure mineral concentrations, particularly calcium and potassium, using quantitative spectroscopic techniques [30]. Protein and fat contents were determined using a volumetric chemistry analyser, according to standard protocols Supplementary Table S5 [32,33].
SCC was determined using the Direct Microscopic Count (DMC) method. Milk smears were stained with methylene blue, and ten microscopic fields per sample were examined under oil immersion [34]. SCC was calculated using the following formula:
The reading method for samples was double-blind for both samples (duplicate analysis).
2.7. Blood Sampling and Biochemical Measurement
Jugular blood samples were aseptically collected from each cow using 10 mL sterile test tubes and immediately divided into two equal parts. One 5 mL portion was placed in a tube without EDTA for hematological analysis, while the other 5 mL was placed in a tube containing EDTA as an anticoagulant for serum analysis under sterile and controlled conditions. All procedures for blood collection and handling were performed in accordance with established veterinary hematology standards [35].
2.7.1. Serum Blood Biochemistry Analysis
Serum samples were allowed to clot at room temperature for 30–45 min and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 min. The separated serum was carefully transferred into sterile Eppendorf tubes and stored at −20 °C until further analysis.
Serum biochemical parameters were determined using automated analyzers following the manufacturers’ protocols. The following parameters were measured: liver enzymes (AST and GGT). Renal function markers: creatinine and urea, and electrolytes (calcium (Ca) and potassium (K).
AST, GGT, urea, and creatinine levels were measured using an automated chemistry analyzer (Mindray BS-240) [36]. Serum calcium was also quantified using the BS-200 Chemistry Analyzer (Mindray Medical International Ltd., Shenzhen, China) [37,38], while potassium concentrations were measured using the Ion-Selective Electrode (ISE) method on the Blood Analyzer L platform [39].
All reagents used were of analytical reagent grade, and internal quality control procedures were implemented for each batch to ensure the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of the results. Serum biochemistry data are provided in Supplementary Table S6.
2.7.2. Hematological Analysis
Blood samples for hematological examination were collected into tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) to prevent coagulation. After gentle inversion to ensure homogeneity, the samples were analyzed immediately to avoid cellular degradation, following the procedure described by [35]. All hematological parameters were measured using the Mindray BC-2800 Vet, an automated veterinary hematology analyzer [40]. The parameters assessed included white blood cell (WBC) count, red blood cell (RBC) count, hemoglobin concentration (HGB), and hematocrit (HCT). All hematological analyses were performed within two hours of sample collection to prevent artifacts and ensure data accuracy. Hematology data are provided in Supplementary Table S7.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics (Version 20.0). The mean, standard deviation (SD), and standard error percentage (SE%) were calculated for all measured variables. The Shapiro–Wilk test was used to assess the normality of the data (n = 15 per group); all datasets met the assumption of normal distribution (p > 0.05), allowing the use of parametric tests.
Differences between tick-infested and non-infested (healthy) cows in milk yield (morning and evening), blood biochemical parameters (AST, GGT, urea, and creatinine), hematological indices (WBC, RBC, HGB, and HCT), and SCC were evaluated using independent sample t-tests. The homogeneity of variances between groups for the same parameters, indicative of biological response consistency, was assessed using F-tests.
A week-by-week comparison of milk yield was performed using two-sample t-tests for each week (1–8), and F-tests were conducted to determine differences in variance across weeks within groups. To evaluate changes in milk production over time within each group, one-way ANOVA was applied, followed by Tukey’s HSD post-hoc test to identify significant differences between weeks.
Linear regression analysis was conducted separately for tick-infested and healthy cows to model trends in milk yield over time. Regression coefficients (β), coefficients of determination (R2), and associated p-values were reported.
All statistical tests were two-tailed, and p-values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The specific statistical tests applied are indicated in the respective figure legends.
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Identification of Ticks
A total of 250 adult ticks were collected from cows in Group I (tick-infested group) over the eight-week study period for species-level identification. No ticks were detected or removed from the control group (Group II) during daily inspections. The specimens were curated and examined under a dissecting stereomicroscope and morphologically identified using standard taxonomic keys.
All examined specimens exhibited external morphological features characteristic of the genus Hyalomma and were identified as H. anatolicum. Species identification was based on a combination of diagnostic traits, including the genital aperture, mouthparts, scutal ornamentation, and configuration of the leg coxae, consistent with published descriptions.
In male specimens, key diagnostic features included a well-defined hexagonal basis capituli, cervical field depression, short lateral grooves, and two posterior ridges on the scutum. Identification was further supported by the alignment of the subanal plates with the adanal plates along their long axis (Figure 1B). The ventral aspect of coxa I displayed prominent internal and external spurs, whereas coxae II and III exhibited only external spurs, and coxa IV lacked clear internal spurs. The mouthparts were robust and anteriorly directed, with a hexagonal basis capituli visible dorsally—another distinguishing feature of H. anatolicum (Figure 1A).
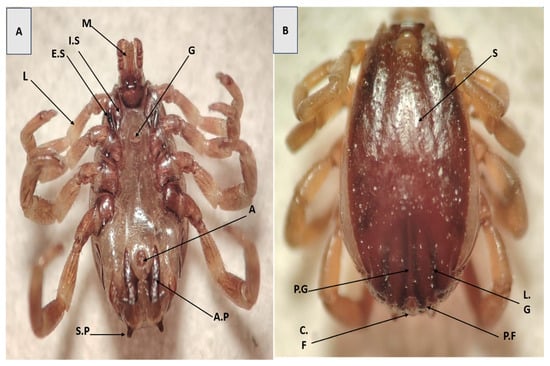
Figure 1.
(A) Ventral and (B) dorsal surfaces of H. anatolicum (Male). (M) Mouth part; (L) Leg; (E.S) External spur; (I.S) Internal spur; (G) Genital aperture; (A) Anus; (A.P) Adanal platesas; (S.P) Subanal platesas; (S) Scutum; (P.G) Posteromedium groove; (L.G) Lateral grooves; (C.F) Central festoon; (P.F) Paracentral festoons.
In female specimens, diagnostic traits included a U-shaped genital aperture, steep scutal grooves, pale leg banding, small porose areas, and a hexagonal basis capituli (Figure 2A). The dorsal shield exhibited a complete set of festoons—small, rectangular grooves along the posterior margin of the body—which is a notable characteristic of the genus and aids in species-level identification (Figure 2B).

Figure 2.
(A) Ventral and (B) dorsal surfaces of H. anatolicum (Female). (M) Mouth part; (G) Genital aperture; (A) Anus; (P.G) Posteromedium groove; (S.G) Scapular grooves; (S) Scutum; (P) Punctation; (S.P) Scutum posterior.
3.2. Molecular Characterization of Tick Infestations
We successfully amplified the COI gene sequences from six adult tick samples using PCR. One adult tick was selected from each of six different cows (out of the fifteen tick-infested individuals) for molecular identification. These ticks had been morphologically identified as H. anatolicum based on consistent diagnostic features observed across the population. DNA extraction and PCR amplification targeting the mitochondrial COI gene were conducted to confirm species identity. The PCR amplicon was approximately 366 bp in length (Figure 3), and subsequent sequence analysis validated the morphological identification. The resulting sequences exhibited high similarity to previously reported H. anatolicum sequences from the region, as documented in GenBank (accession numbers PQ613621–PQ613626).
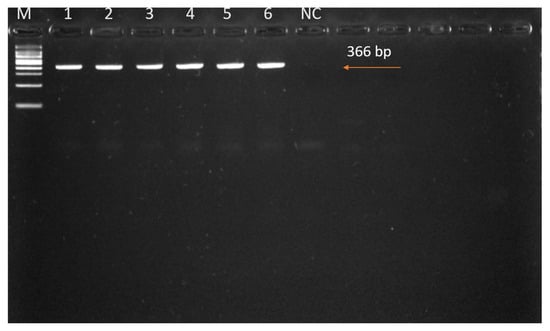
Figure 3.
PCR amplification of the mitochondrial COI gene from DNA extracted from Hyalomma spp. Lane M: 100 bp DNA ladder; Lanes 1–6: amplified tick DNA samples; Lane NC: no-template negative control. The expected amplicon size of ~366 bp is indicated. No bands were observed in the NC lane, confirming the absence of contamination.
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
A Neighbor-Joining (NJ) tree was initially constructed based on the mitochondrial COI gene sequences obtained from the six tick samples analyzed in this study. The resulting sequences showed a high degree of similarity (>99%) with H. anatolicum reference sequences from Turkey (GenBank accession no. MW546283), China (OQ415528), and also H. excavatum (Figure 4).

Figure 4.
The phylogenetic tree using the NJ method in MEGA version 6.0 based on the mitochondrial COI gene sequences of Hyalomma spp. Sequences generated in this study (PQ613621–PQ613626) are highlighted in blue and represent H. anatolicum specimens collected in Saudi Arabia. These sequences clustered closely with reference H. anatolicum isolates from Turkey and China, supporting species-level identification. Rhipicephalus annulatus (KJ410769) was used as the outgroup. Bootstrap values > 70% are shown at the branch nodes.
3.4. Hemoparasite Detection
Microscopically, intraerythrocytic piroplasms morphologically consistent with Theileria spp. were detected in Giemsa-stained blood smears from 2 out of the 15 tick-infested cows. In contrast, blood smears from the healthy control group showed no detectable hemoparasites (Figure 5).
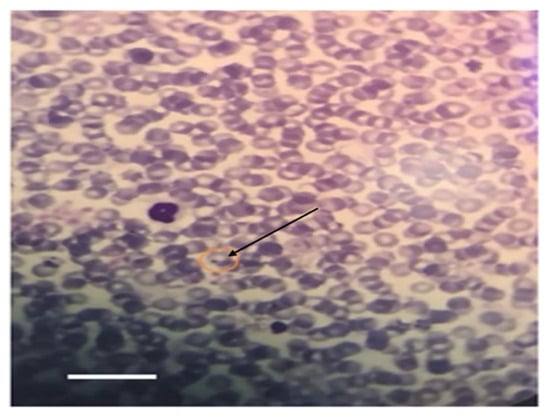
Figure 5.
Giemsa-stained blood smear from a tick-infested cow showing an intraerythrocytic piroplasm (black arrow) consistent with Theileria spp. infection. Parasites were detected in 2/15 (13.3%) infested cows; none were observed in smears from healthy controls. Scale bar = 10 μm.
3.5. The Average Variation in the Production of Milk
3.5.1. Weekly Trends in Milk Yield
Figure 6 presents the weekly monitoring of milk yield over an eight-week period in tick-infested and healthy (control) cows, with measurements taken independently during morning and afternoon milking sessions. In healthy cows, milk production remained stable throughout the study. Morning yields ranged from 11.21 L to 11.25 L, with an average of 11.23 ± 95% CL, while afternoon yields ranged from 11.29 L to 11.35 L, averaging 11.32 ± 95% CL. No significant weekly variation was observed. The relatively narrow range of yields in the control group (11.0–11.3 L) reflects standardized breed, feeding, and housing conditions, as well as the use of weekly group means, which reduces apparent variability compared to the tick-infested group.
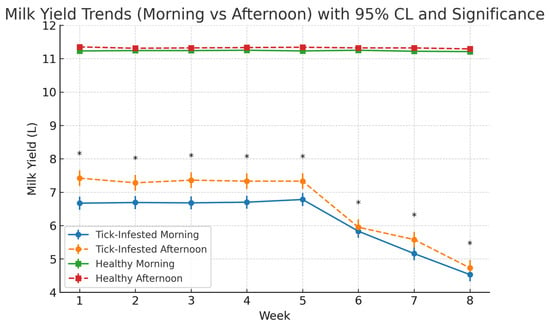
Figure 6.
Weekly milk yield (L) in tick-infested and healthy cows during morning and afternoon milking sessions over an 8-week period. Each point represents the mean milk yield per session per week (n = 15 cows per group). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Asterisks denote statistically significant differences between morning and afternoon yields within the tick-infested group for each week (p < 0.0001, paired t-test).
In contrast, tick-infested cows exhibited a progressive decline in milk yield beginning after week 5. Morning milk yield declined from 7.42 L in week 1 to 4.73 L by week 8 (overall mean: 6.62 ± 95% CL), while afternoon milk yield decreased from 6.67 L to 4.53 L over the same period (overall mean: 6.13 ± 95% CL) (Table 1). Weekly averages revealed a consistent diurnal pattern, with afternoon yields exceeding morning yields in both groups across all weeks. Paired t-tests confirmed these differences were statistically significant (p < 0.0001) in both the tick-infested group (t = 29.80–43.26) and the control group (t = 17.01–23.68). See Supplementary Table S8 for weekly group means of milk yield.”

Table 1.
Effect of tick infestation on milk yield and chemical composition in dairy cows over the eight-week study period. Values are presented as mean ± standard error (SE). Percentage differences are calculated relative to the healthy (control) group.
Linear regression models for the tick-infested group indicated strong linear declines in both morning (R2 = 0.71) and afternoon (R2 = 0.77) yields across the study period, showing that week of lactation explained a substantial proportion of the variance in milk yield. These findings suggest that progressive tick burden exerted a sustained and measurable negative influence on milk productivity in both milking sessions.
3.5.2. Effect of Tick Infection on Milk Components
Tick infestation had a significant impact on milk composition and SCC, as detailed in Table 1. Marked differences were observed between tick-infested and healthy cows across all measured parameters.
Milk calcium levels were significantly lower in infested cows (820.85 ± 2.25 mg/L) compared to healthy cows (1178.45 ± 2.66 mg/L), with the difference being highly significant (p < 0.0001). Similarly, potassium concentrations were substantially reduced in tick-infested cows (939.25 ± 6.68 mg/L) versus healthy controls (1587.36 ± 0.87 mg/L; p < 0.0001).
Protein content was significantly lower in the milk of tick-infested cows (1.34 ± 0.02%) than in healthy cows (3.81 ± 0.06%; p < 0.0001). A comparable pattern was observed for fat content, with infested cows yielding 1.15 ± 0.04% compared to 3.48 ± 0.09% in healthy animals (p < 0.0001).
In addition to these compositional changes, SCC was significantly elevated in tick-infested cows (580,000 ± 120,000 cells/mL) compared to healthy cows (310,000 ± 95,000 cells/mL; p < 0.01). The elevated SCC suggests ongoing inflammatory processes within the mammary gland, potentially indicating subclinical mastitis or a systemic immune response triggered by tick infestation.
Overall, these findings demonstrate that tick infestation negatively affects both the nutritional quality and hygienic status of milk. This is reflected not only in the reduced concentrations of essential minerals and macronutrients but also in elevated indicators of mammary inflammation (Table 1).
3.6. Serum Biochemical
The serum biochemical profile of tick-infested cows showed significant alterations compared to healthy controls, as presented in Table 2. Liver enzyme levels were markedly elevated in the infested group, with AST and gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) recorded at 140.5 ± 1.2 IU/L and 33.5 ± 1.1 IU/L, respectively, compared to 41.5 ± 1.3 IU/L and 13.1 ± 0.8 IU/L in the control group (p < 0.0001).

Table 2.
Serum biochemical parameters in tick-infested and healthy dairy cows (n = 15 per group). Values are presented as mean ± standard error (SE). Percentage differences are calculated relative to the healthy (control) group.
Similarly, renal function markers showed significant increases in tick-infested cows. Serum creatinine levels reached 8.0 ± 0.2 mg/dL and urea 32.2 ± 1.0 mg/dL, while in healthy controls these values were 0.9 ± 0.05 mg/dL and 14.0 ± 0.9 mg/dL, respectively (p < 0.0001).
Electrolyte balance was also affected. Mean serum calcium levels were significantly reduced in tick-infested cows (7.50 ± 0.9 mg/dL) compared to healthy animals (12.40 ± 0.6 mg/dL; p < 0.0001). In contrast, serum potassium levels were significantly lower in infested cows (2.44 ± 0.17 mmol/L) compared to the control group (4.45 ± 0.63 mmol/L; p < 0.0001).
These findings indicate that tick infestation induces marked metabolic disruptions, reflected by liver dysfunction, renal stress, and electrolyte imbalances (Table 2).
3.7. Hematological Results
The hematological profile further indicated systemic effects associated with tick infestation. WBC count was significantly elevated in tick-infested cows (25.5 ± 0.9 × 103/µL) compared to non-infested controls (17.6 ± 0.7 × 103/µL; p < 0.0001). A pronounced increase in red blood cell (RBC) count was observed in the infested group (19.1 ± 0.6 × 106/µL) versus controls (8.5 ± 0.5 × 106/µL; p < 0.0001).
Despite the elevated RBC count, severe anemia was evident in the infected cows, as reflected by a significantly reduced HGB concentration (3.0 ± 0.2 g/dL) compared to the control group (6.4 ± 0.3 g/dL; p < 0.0001). HCT was also slightly but significantly lower in the tick-infested cows (45.7 ± 0.5%) than in healthy controls (47.2 ± 0.4%; p < 0.0001) (Table 3).

Table 3.
Hematological parameters in tick-infested and healthy dairy cows (n = 15 per group). Values are presented as mean ± standard error (SE). Percentage differences are calculated relative to the healthy (control) group.
4. Discussion
Accurate morphological identification of Hyalomma species remains crucial for reliable species assignment in field-based tick surveillance. In this study, all adult ticks collected from dairy cattle in Hafar Al-Batin, Eastern Saudi Arabia, were morphologically identified as H. anatolicum based on standard taxonomic keys. Diagnostic features included a U-shaped genital aperture, prominent scapular grooves, pale annulated legs, well-defined coxal spurs, and festoons in female ticks, while male ticks exhibited cervical depressions, an ornamented scutum, and parallel adanal and subanal plates. These characteristics are consistent with classical morphological descriptions of H. anatolicum reported across the Middle East and North Africa [41,42,43].
Similar morphological profiles have been documented in regional studies: in the United Arab Emirates, H. anatolicum and H. dromedarii were distinguished by features such as genital aperture shape and coxal spur structure [43]; in Iraq, Al-Hamadan et al. [44] observed nearly identical morphological features in adult ticks from small ruminants; and in Iran, In Iran, Hosseini-Chegeni et al. [45] confirmed the diagnostic utility of ventral plate alignment and the prominence of the cervical (scapular) grooves for separating Hyalomma species. In Turkey, Aktaş et al. [46] (eastern Turkey) and Iça et al. [47] (central Anatolia) identified Hyalomma anatolicum from cattle using standard morphological keys coxae I, IV spur development, cervical (scapular) grooves, and the shape, alignment of the male adanal subanal plates (genital plate region).
Over 15 ixodid tick species have been recorded in Saudi Arabia, including H. arabicum, H. turanicum, and H. anatolicum [9,23,48]. In the present study, H. anatolicum was again identified as the dominant species, consistent with earlier reports highlighting its ecological adaptation to arid environments [49,50,51,52].
Geographic assignment to Hyalomma anatolicum is well supported for the Hafar Al-Batin sampling site. Although H. excavatum has not been specifically reported from Hafar Al-Batin, evidence from adjacent, ecologically comparable areas of Eastern Saudi Arabia indicates that it is rare or absent. In Al-Ahsa (Eastern Region), a large livestock survey (n = 5320 ticks) recorded H. anatolicum—including specimens historically designated as H. anatolicum excavatum—as >32% of collections and did not treat H. excavatum as a separate species [53]. A multi-province cattle study likewise found frequent H. anatolicum and H. impeltatum but only a single H. excavatum specimen [54], and camel collections in Riyadh Province showed H. excavatum constituted just 0.3% (1/296) compared with dominant H. anatolicum and H. dromedarii [5]. Region-wide species-distribution modelling also identifies H. dromedarii and H. anatolicum as the principal camel-associated Hyalomma in arid central/eastern Saudi Arabia [55]. Taken together, the established presence of H. anatolicum at Hafar Al-Batin and the consistent rarity of H. excavatum in comparable settings provide strong geographic support for assigning our material to H. anatolicum.
The use of PCR and sequencing to confirm morphological identification is a reliable method, as morphological features alone can often result in misidentification due to intraspecific variation. This is crucial because molecular confirmation improves morphological identification, which can be ambiguous due to intraspecific differences. A phylogenetic tree was constructed based on NJ analysis of the COI DNA sequence for the six study samples. Based on the generated phylogenetic tree, which revealed >99% sequence similarity (GenBank accessions: PQ613621–PQ613626) with H. anatolicum isolates from Turkey and China [56,57], and also H. excavatum.
Although phylogenetic analysis revealed close similarities to both H. anatolicum and H. excavatum, morphological examination confirmed the specimens’ identity as H. anatolicum. Diagnostic features included big size, elongated body, long palps, brown scutum, eyes, bifid spurs on coxae I, and prominent leg annulations. These characteristics are compatible with established taxonomic keys. In the studies conducted by Abbasi et al. [58] (2017) and Ali et al. (2024) [59], they showed that males of H. anatolicum have large, equal coxa spurs, but H. excavatum has a distinct arch and raised ridges on the scutal caudal area. Furthermore, the collection sites are in the known endemic range of H. anatolicum in hot and dry climates of the Mediterranean, Middle East, Central Asia, and parts of Africa, with few records of H. excavatum in this area [60,61]. Key separating characters for H. anatolicum versus H. excavatum are summarized in Supplementary Table S9.
In the United Arab Emirates, both H. anatolicum and H. dromedarii have been identified using molecular markers such as COI and 16S rRNA genes, reinforcing the regional applicability of these loci for tick species confirmation [62]. Phylogenetic analysis in our study clearly clustered H. anatolicum distinctly from other Hyalomma species and from Rhipicephalus annulatus, demonstrating the specificity and robustness of the COI gene as a molecular marker for tick species discrimination. This finding aligns with previous studies confirming the efficacy of the COI gene in resolving phylogenetic relationships among ixodid ticks, including those of the Hyalomma and Rhipicephalus genera [63,64]. Similar integrative approaches have been successfully implemented in regional tick studies in Egypt, Lebanon, and Iraq, enhancing the reliability of species-level identification and supporting targeted vector control programs [65,66]. While such dual-method frameworks are well established in some MENA countries, national-scale surveillance systems remain under development in others, including Iraq, where molecular-based identification has been recently initiated using mitochondrial markers [67].
H. anatolicum is a recognized vector of Theileria annulata, the causative agent of tropical theileriosis—a disease of major economic importance in Saudi Arabia and other Arab countries [44,68]. Most prior molecular and parasitological surveys on Theileria infections have focused on the central and western regions of the country. For instance, a molecular study sampling cattle from Riyadh, Al-Kharj, Al-Hasa, and Al-Qassim reported 1.9% prevalence of T. annulata and 0.6% for T. ovis in 362 animals, with cattle in Riyadh showing the highest infection rates [54]. Additionally, older microscopy-based work documented Theileria spp. as one of the most common hemoparasites affecting cattle within central regions such as Qassim [69]. These findings collectively highlight both the fragmented nature of previous studies and the need for molecular surveys in eastern Saudi Arabia.
To our knowledge, this is the first report from Eastern Saudi Arabia linking tick infestation to both decreased milk yield and altered milk composition in dairy cows. Our data show a clear decline in production among tick-infested cows—from 7.42 L in week 1 to 4.73 L by week 8—while non-infested animals maintained a stable output. These findings align with previous studies reporting milk yield reductions of 25–40% in tick-infested cattle. For example, de Castro (1997) reported that heavy tick burdens in dairy cattle can substantially depress milk yield and overall productivity in developing-country systems [70], while Bondan. (2018) documented significant yield loss and udder damage associated with tick bites in Brazil [71]. Similarly, Norval et al. (1997) longitudinal studies from Zimbabwe reported consistent declines in milk yield under chronic tick infestation, with significant losses across lactation [72]. Although such quantitative studies are lacking in Saudi Arabia, our results provide new regional evidence of the economic impact of tick infestation in arid dairy production systems. Hurtado and Giraldo-Ríos (2018) [12] also emphasized the broader economic and health impact of ticks on ruminant productivity. Supporting this trend, Satti et al. (2021) [73] reported a significant burden of tick-borne diseases—such as anaplasmosis and babesiosis—on cattle health and productivity in Khartoum State, Sudan, underscoring regional similarities in the physiological and economic consequences of infestation.
The observed decline in milk production in tick-infested cows is likely multifactorial. These cows had visible tick infestations at the start of the experiment, as confirmed by veterinary examination, while control cows—though from the same free-grazing herd—were free of ticks. The initially lower milk yield in the infested group reflects early physiological impacts of tick burden. The sharper decline observed between weeks 5 and 8 is likely due to cumulative effects, including persistent blood loss, localized inflammation and skin lesions, chronic systemic inflammation, and stress-induced metabolic disruption. Although adult ticks were removed daily for monitoring, no acaricidal treatment was applied, and immature tick stages likely reattached, compounding the parasitic load in later weeks. Reduced feed intake, physiological stress, and metabolic imbalance, as described by Azambuja et al. (2020) [74], likely contributed to the observed yield loss. Notably, afternoon milk yields were consistently higher than morning values across all weeks, potentially reflecting diurnal variation in feed intake and energy metabolism [75,76]. These findings are consistent with studies that emphasize the detrimental impact of parasitic pressure on both milk yield and composition [77,78].
This study also provides the first documentation in Eastern Saudi Arabia of tick infestation impacting milk mineral composition. We observed substantial reductions in calcium (30.3%) and potassium (40.8%) levels in milk from infested cows. These results echo findings from Egypt, where Noha et al. (2024) reported significantly decreased calcium and zinc concentrations in milk from cattle infested with ticks and infected with blood parasites, compared to non-infested controls [79]. Calcium is essential for mammary gland function, and its depletion may reflect systemic metabolic stress or hormonal disruption [80]. Similar reductions in milk calcium have been reported in Pakistan and attributed to endocrine imbalance and udder dysfunction [81]. Potassium, a key regulator of osmotic balance and enzyme function, was also markedly reduced, likely due to inflammation-related electrolyte shifts [82]. These changes may impair milk quality and pose potential risks to consumer safety.
Milk protein and fat contents were reduced by 64.8% and 66.9%, respectively, in tick-infested cows. These reductions support previous findings that parasitic stress—particularly due to ectoparasites like ticks can impair mammary gland metabolism and inhibit macronutrient synthesis in lactating animals. Such alterations in milk composition have critical implications for nutritional quality, consumer safety, and dairy product yield, especially in rural regions with limited veterinary infrastructure or quality control measures [83,84].
SCC was significantly elevated (mean = 580 × 103/mL) in infested cows compared to healthy controls (mean = 310 × 103/mL), representing an 87.1% increase. Elevated SCC is a well-recognized marker of subclinical mastitis and inflammation [17,18], and similar trends have been reported in cows exposed to ectoparasites [85]. The increase in SCC may result from immunosuppressive effects of tick-borne pathogens (Babesia, Anaplasma, Theileria) and associated secondary infections [86,87].
The marked alterations in serum biochemistry observed in tick-infested cows highlight the systemic physiological burden imposed by chronic parasitism. In our study, AST and GGT levels increased by 238% and 156%, respectively, relative to healthy controls. These enzymes are classical indicators of hepatocellular damage and biliary stress, suggesting significant liver involvement in response to the prolonged inflammatory insult induced by tick feeding. This aligns with previous reports by El-Tarabany et al. (2018), who observed elevated hepatic enzymes in Holstein cows infected with blood parasites, attributing these elevations to hepatic congestion and oxidative stress [84].
Moreover, serum urea and creatinine concentrations were significantly elevated (130% and 789%, respectively), strongly indicating compromised renal clearance or intensified protein catabolism. These findings are consistent with those of Saleem et al. (2020) in Pakistan, who reported increased urea and creatinine levels in Babesia-infected cattle, suggesting nephrotoxic effects due to systemic inflammation and hemolysis [88].
Importantly, we also observed significant electrolyte imbalances in tick-infested cows for which serum calcium and potassium were lower than in healthy controls (calcium: 7.50 ± 0.90 vs. 12.40 ± 0.60 mg/dL; potassium: 2.44 ± 0.17 vs. 4.45 ± 0.63 mmol/L). Hypocalcaemia and hypokalaemia in this context likely reflect mineral sequestration due to tissue injury, inflammation-induced loss, or impaired hormonal regulation (e.g., parathyroid hormone). A similar biochemical profile was reported by Goswami et al. (2024) in naturally tick-infested cows in northern India, where significant reductions in calcium and phosphorus levels were associated with parasitic burden [89].
Collectively, these biochemical changes provide valuable diagnostic insight into the multi-organ stress response elicited by ticks. They suggest that hepatic, renal, and metabolic pathways are profoundly impacted during chronic ectoparasitic infestations. Such findings underscore the importance of incorporating routine serum biochemistry into herd health surveillance, especially in regions with endemic tick exposure.
The haematological profile of tick-infested cows further underscores the systemic stress associated with prolonged ecto-parasitism. Notably, WBC counts were markedly elevated (25.50 ± 0.90 × 103/µL) compared to healthy controls, indicating a robust immune response to continuous tick exposure, blood loss, and potential pathogen transmission, such as Theileria or Babesia spp. This leukocytosis is consistent with the inflammatory state induced by parasitic infestation and is a common finding in tick-borne infections [89].
Interestingly, we also observed increased RBC counts (19.10 ± 0.60 × 106/µL), a less commonly reported feature. This may reflect compensatory erythrocytosis triggered by hypoxic stress, dehydration, or adrenergic stimulation due to inflammation. Similar trends were documented by Kim et al. (2024), who noted elevated RBC values in tick-infested cattle possibly due to splenic contraction and stress-induced haemoconcentration [90].
However, despite the elevated RBC count, HGB and HCT levels were significantly reduced (3.00 ± 0.20 g/dL and 45.70 ± 0.50%, respectively), indicating either non-functional erythrocytes, hemolysis, or anemia of chronic disease (ACD)—a condition commonly associated with parasitic infections, where inflammation suppresses erythropoiesis and iron utilization. These findings are consistent to report from Nazifi et al. (2012), these findings are consistent with reports of hemolytic anemia in bovine anaplasmosis and babesiosis conditions in which hemoglobin and hematocrit fall markedly, reflecting hemolysis and impaired erythropoiesis. [91].
Altogether, these haematological alterations reflect a complex physiological adaptation to parasitic pressure, characterized by immune activation, erythroid stress, and metabolic imbalance, reinforcing the need for early tick control to mitigate systemic pathology.
By integrating milk production parameters with hematological and biochemical indicators, this study offers a holistic assessment of the physiological burden imposed by tick infestation in dairy cattle. These results highlight the pressing need for holistic tick control strategies that encompass prudent use of acaricides, surveillance by veterinarians, specific mineral supplementation, and nutritional support. Implementing such measures is essential to reduce economic losses, safeguard animal welfare, and improve milk quality and safety in arid and semi-arid dairy systems.
5. Conclusions
This study confirms the presence of H. anatolicum in dairy cattle from Hafar Al-Batin, Eastern Saudi Arabia, through both morphological and molecular identification. Tick infestation significantly reduced milk yield and altered milk composition, highlighting its substantial impact on dairy productivity and cow health.
Although limited by sample size and study duration, the findings provide important baseline data and emphasize the need for integrated tick management strategies. Future research should involve larger cohorts, molecular screening for co-infections, and analysis of tick genetic variation to better understand long-term effects.
Regional efforts should prioritize geospatial risk mapping and shared tick-pathogen databases to strengthen surveillance and control.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pathogens14090883/s1, Table S1: Regional Hyalomma distribution summary (Saudi Arabia & UAE); Table S2. Tick counts per cow, daily by week (Days 1–7 with weekly subtotal). (Tables S2.1week1 to S2.8_Week 8 &Table S2 in text.); Table S3. Tick counts—weekly totals per cow and grand total (n = 250 adult ticks); Table S4. Milk yield per cow, per-milking records (04:00 & 16:00) for Weeks 1–8 (tick-infested vs. healthy); Table S5. Chemical composition of milk (mean ± SE); Table S6. Serum biochemical parameters (mean ± SE); Table S7. Hematology parameters by week (mean ± SE); Table S8. Milk yield, weekly group means for Weeks 1–8 (04:00 vs. 16:00; mean ± SE); Table S9. Morphology comparison, H. anatolicum vs H. excavatum (key separating traits).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.-S. and E.A.-O.; methodology, M.A.-S.; software, M.A.-S.; validation, S.A. and N.A.; formal analysis, A.A.; investigation, E.A.-O.; resources, M.A.-S.; data curation, M.A.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.-S.; writing—review and editing, E.A.-O., I.O.A. and M.A.; visualization, M.A.; supervision, E.A.-O.; project administration, E.A.-O.; funding acquisition, E.A.-O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Scientific Research Ethics Committee, King Saud University, according to the ethical principles of human and animal research (Approval no. KSU-SE-23-100).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The final assembled sequences were added to the GenBank database with accession numbers [PQ613621-26].
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Ongoing Research Funding Program (ORF-2025-111), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- El-Alfy, E.-S.; Abbas, I.; Saleh, S.; Elseadawy, R.; Fereig, R.M.; Rizk, M.A.; Xuan, X. Tick-borne pathogens in camels: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence in dromedaries. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2024, 15, 102268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, N.; Muzaffar, S.B.; Al-Deeb, M.A. Ticks and tick-borne diseases of livestock in the Middle East and North Africa: A review. Insects 2021, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, G.; Singh, P.; Molla, M.; Yimer, Y.S.; Ewunetie, A.; Tadesse, T.Y.; Ayele, T.M.; Kefale, B. Nutraceuticals: A source of benefaction for neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 97, 105260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardakci, F.; Al-Subaie, S.H.M.; Badraoui, R.; Adnan, M.; Siddiqui, A.J. Molecular Characterization of Hard Ticks Infesting Camels in the Northern Region of Saudi Arabia Using the Barcoding Gene, Mitochondrial Cytochrome oxidase subunit I. Life 2023, 13, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanazi, A.D.; Nguyen, V.L.; Alyousif, M.S.; Manoj, R.R.; Alouffi, A.S.; Donato, R.; Sazmand, A.; Mendoza-Roldan, J.A.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Ticks and associated pathogens in camels (Camelus dromedarius) from Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Al-Ahmadi, B.M.; Ibrahim, R.; Alahmadi, S.; Gattan, H.; Shater, A.F.; Elshazly, H. Hard Ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) Infesting Arabian Camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Medina and Qassim, Saudi Arabia. J. Parasitol. 2023, 109, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Manjunathachar, H.V.; Ghosh, S. A review on Hyalomma species infestations on human and animals and progress on management strategies. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makwarela, T.G.; Nyangiwe, N.; Masebe, T.M.; Djikeng, A.; Nesengani, L.T.; Smith, R.M.; Mapholi, N.O. Morphological and molecular characterization of tick species infesting cattle in South Africa. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazi, A.D.; Al-Mohammed, H.I.; Alyousif, M.S.; Said, A.E.; Salim, B.; Abdel-Shafy, S.; Shaapan, R.M. Species diversity and seasonal distribution of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting mammalian hosts in various districts of Riyadh Province, Saudi Arabia. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, M.; Hassan, S.; Ahmed, S.; Salih, D. Prevalence of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) and Theileria annulata infection of cattle in Gezira State, Sudan. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2020, 10, e00148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbill, H.; Tanaka, T.; Karawia, D.; Rahman, S.; Zeb, J.; Sparagano, O.; Baruah, A. Morphological identification and molecular characterization of economically important ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from North and North–Western Egypt. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, O.J.B.; Giraldo-Ríos, C. Economic and health impact of the ticks in production animals. In Ticks and Tick-Borne Pathogens; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, A.M. Genetic Characterization of Hyalomma anatolicum (Ixodoidea: Ixodidae) in Babylon Province, Middle Iraq. SAR J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2023, 4, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, P.S.; Ahmed, M.; Ansari, A.S.; Gadahi, J.A.; Memon, S.B.; Tariq, M.; Laghari, Z.A.; Soomro, F.; Bhutto, B.; Mari, N.-U.-N. Molecular Identification of Hyalomma Ticks and Application of Bacillus thuringiensis Toxins as an Effective Biological Acaricide. J. Parasitol. Res. 2024, 2024, 9952738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogalska, A.; Momot, M.; Nogalski, Z. The mineral composition of milk from high-yielding dairy cows depending on the month of lactation and udder health. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoi, M.; Manuelian, C.L.; Penasa, M.; De Marchi, M. Effects of somatic cell score on milk yield and mid-infrared predicted composition and technological traits of Brown Swiss, Holstein Friesian, and Simmental cattle breeds. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schukken, Y.; Wilson, D.; Welcome, F.; Garrison-Tikofsky, L.; Gonzalez, R. Monitoring udder health and milk quality using somatic cell counts. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Hameed, A.; Ahmad, T. Prevalence of gastrointestinal parasites in buffalo and cow calves in rural areas of Toba Tek Singh, Pakistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2009, 19, 67–70. [Google Scholar]
- Perveen, N.; Bin Muzaffar, S.; Al-Deeb, M.A. Population dynamics of Hyalomma dromedarii on camels in the United Arab Emirates. Insects 2020, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, K.; Weakley, M.; Do, T.; Mir, S. Current and future molecular diagnostics of tick-borne diseases in cattle. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpy, L. Les espèces iraniennes du genre Hæmaphysalis Koch, 1844: Identité d’Hæmaphysalis cholodkovskyi Ole-nev, 1928 et d’H. cinnabarina var. cretica Senevet et Caminopetros, 1936. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 1938, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Bouattour, A.; Camicas, J.; Walker, A.R. Ticks of Domestic Animals in the Mediterranean Region: A Guide to Identification of Species; University of Zaragoza: Zaragoza, Spain, 2004; 131p. [Google Scholar]
- Diab, F.; Al-Khalifa, M.; Al-Asgah, N.; Hussein, H.; Khalil, G. Ticks (Acari: Argasidae, Ixodidae) infesting livestock in Saudi Arabia. Fauna Arab. 2006, 22, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shabbani, A.H.; Al-Fatlawi, M.A. Morphological and genotypical identification of Hyalomma anatolicum isolated from cattle in Al-Daghara city, Al-Qadisiyah province, Iraq. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 37, 683–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binetruy, F.; Dupraz, M.; Buysse, M.; Duron, O. Surface sterilization methods impact measures of internal microbial diversity in ticks. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Fingerle, V.; Noll, M. Analysis of tick surface decontamination methods. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Feldman, B.F.; Zinkl, J.G.; Jain, N.C. Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology, 5th ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Ames, IA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Soulsby, E.J.L. Helminths, Arthropods and Protozoa of Domesticated Animals, 7th ed.; Baillière Tindall: London, UK, 1982; 809p. [Google Scholar]
- Garaniya, N.; Ramani, H.; Golakiya, B. Comparative Study of Nutrients Profile of Cow Milk at Different Lactation: A Case Study of Gir Cow Milk. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, 118027. [Google Scholar]
- Monardes, H.G.; Moore, R.K.; Corrigan, B.; Rioux, Y. Preservation and storage mechanisms for raw milk samples for use in milk-recording schemes. J. Food Prot. 1996, 59, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björn, M.; Nischwitz, V. ICP-MS for the analysis at the nanoscale—A tutorial review. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1432–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg, B.; Soder, K.; Pereira, A.; Standish, R.; Brito, A. Production, milk fatty acid profile, and nutrient utilization in grazing dairy cows supplemented with ground flaxseed. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1294–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, B.; Green, M. Use and interpretation of somatic cell count data in dairy cows. Practice 2005, 27, 310–315. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, D.J.; Wardrop, K. Drug-induced blood cell disorders. In Schalm’s Veterinary Hematology, 6th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.B.; Yahya, A.; Aloqab, Z.; AlHudhaifi, A.; Alateef, A.A.; Morshed, A.; Qasem, A.; Al-Awlaqi, M.; Alshahari, S.; Mohammed, N. Determination of reference intervals for common liver function tests among healthy adults. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandic-Havelka, A.; Nilsen, T.; Sunde, K.; Norell, M.; Hansson, L.O.; Larsson, A. Turbidimetric Determination of Fecal Calprotectin Using Two Table Top Chemistry Analyzers: Mindray BS-200E and Cobas® c111. Clin. Lab. 2017, 63, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Yepes, F.A.; Behling-Kelly, E.; Caixeta, L.S.; Tikofsky, L.; Parrish, L.; Heaton, K.N. Evaluation of a point-of-care calcium device in bovine plasma and serum. JDS Commun. 2023, 4, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimeski, G.; Badrick, T.; St John, A. Ion selective electrodes (ISEs) and interferences—A review. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.T.D.; Alves, M.L.; Spada, J.C.P.; Leonel, J.A.F.; Vioti, G.; Benassi, J.C.; Carregaro, V.M.L.; Alves-Martin, M.F.; Starke-Buzetti, W.A.; Oliveira, T.M.F.S. Feline leishmaniosis: Hematological and biochemical analysis. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2023, 32, e003823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omer, S.A.; Alsuwaid, D.F.; Mohammed, O.B. Molecular characterization of ticks and tick-borne piroplasms from cattle and camel in Hofuf, eastern Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2023–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalifa, M.; Hussein, H.; Diab, F.; Khalil, G. Blood parasites of livestock in certain regions in Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2009, 16, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Deeb, M.A.; Muzaffar, S.B. Prevalence, distribution on host’s body, and chemical control of camel ticks Hyalomma dromedarii in the United Arab Emirates. Vet. World 2020, 13, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hamadan, N.; Mohammad, J.; Amin, B. Molecular identification and phylogenetic study of ticks (Ixodidae) isolated from small ruminants in Duhok Governorate, Iraq. Basrah J. Vet. Res. 2021, 20, 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini-Chegeni, A.; Hosseini, R.; Tavakoli, M.; Telmadarraiy, Z.; Abdigoudarzi, M. The Iranian Hyalomma (Acari: Ixodidae) with a key to the identification of male species. Persian J. Acarol. 2013, 2, 503–529. [Google Scholar]
- Aktaş, M.; Dumanlı, N.; Angın, M. Cattle infestation by Hyalomma ticks and prevalence of Theileria in Hyalomma species in the east of Turkey. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 119, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iça, A.; Vatansever, Z.; Yıldırım, A.; Düzlü, Ö.; İnci, A. Detection of Theileria and Babesia species in ticks collected from cattle. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 148, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shammery, K.A.; Fetoh, B.; Alshammari, A.M. Differentiation between common tick species using molecular biology techniques in Saudi Arabia. J. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 73, 305–307. [Google Scholar]
- Perveen, N.; Muzaffar, S.B.; Al-Deeb, M.A. Prevalence, Distribution, and Molecular Record of Four Hard Ticks from Livestock in the United Arab Emirates. Insects 2021, 12, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yijun, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.; Liu, G.; Luo, J.; Guan, G.; Ren, Q.; Yin, H. Insight into Hyalomma anatolicum biology by comparative genomics analyses. Int. J. Parasitol. 2024, 54, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallatah, S.; Ghallab, E.; Khater, E. Phylogenetic diversity and DNA barcoding of the camel tick Hyalomma dromedarii (Acari: Ixodidae) of the Eastern region of Saudi Arabia. Trop. Biomed. 2019, 36, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El Kammah, K.M.; Oyoun, L.; El Kady, G.; Shafy, S.A. Investigation of blood parasites in livestock infested with argasid and ixodid ticks in Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2001, 31, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Marri, T.M.; Abdally, M.H.; Abdally, H.M.; Al-Jabr, O.A. Incidence and prevalence of hard ticks in ruminants of Al-Ahsa Oasis Region, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. World Vet. J. 2020, 10, 276–285. [Google Scholar]
- Alanazi, A.D.; Abdulaziz, S.A.; Mohammad, Y.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Hend, H.A.M.A.; Ahmad, M.A.; Bassma, S.M.E.; Sobhy, A.-S.; Muslimah, N.A.; Khan, A.; et al. Tick burden and molecular detection of tick-borne pathogens in cattle from four regions of Saudi Arabia. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, N.; Muzaffar, S.B.; Jaradat, A.; Sparagano, O.A.E.; Willingham, A.L. Camel tick species distribution in Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates using MaxEnt modelling. Parasitology 2024, 151, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Lv, J.; Li, F.; Li, K.; He, B.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Johnson, N.; Lin, X. Identification and molecular analysis of ixodid ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting domestic animals and tick-borne pathogens at the Tarim Basin of Southern Xinjiang, China. Korean J. Parasitol. 2020, 58, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olcay, H.; Ays, N.O. Distribution and phylogeny of Hyalomma ticks (Acari:Ixodidae) in Turkey. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 73, 501–519. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, F.; Abbasi, I.H.R.; Nissa, T.F.; Bhutto, Z.A.; Arain, M.A.; Soomro, R.N.; Siyal, F.A.; Fazlani, S.A. Epidemiological study of tick infestation in buffalo of various regions of district Khairpur, Pakistan. Vet. World 2017, 10, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ali, S.; Ahmad, A.S.; Ashraf, K.; Khan, J.A.; Rashid, M.I. Insights into the involvement of male Hyalomma anatolicum ticks in transmitting Anaplasma marginale, lumpy skin disease virus and Theileria annulata. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Fatlawi, M.; Ali, M.; Albayati, H. Morphological and phylogenetic study of Hyalomma anatolicum in Al-Najaf, Iraq. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 32, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Hussain, S.; Yu, A.; Varga, C.; De Leo, G.A.; Smith, R.L. Geographical epidemiology of Hyalomma anatolicum and Rhipicephalus microplus in Pakistan: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e030944239178282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and tick-borne diseases: A One Health perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafy, S.; Allam, N.A.; Mediannikov, O.; Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Molecular detection of spotted fever group rickettsiae associated with ixodid ticks in Egypt. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2012, 12, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, J.; Song, B.; Khan, M.A.; Senbill, H.; Aziz, M.U.; Hussain, S.; Díaz Sánchez, A.A.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; Alzahrani, A.; Alshehri, M.; et al. Genetic diversity of tick-borne zoonotic pathogens in ixodid ticks collected from small ruminants in Northern Pakistan. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2024, 124, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaja, M.F.; Tempesta, M.; Bayan, A.; Vesco, G.; Greco, G.; Torina, A.; Blanda, V.; La Russa, F.; Scimeca, S.; Lelli, R. Diversity and distribution of ticks from domestic ruminants in Lebanon. Vet. Ital. 2017, 53, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hamadan, H.Z.; Al-Khafaji, A.M.; Mero, W.M.; Al-Attar, M.A.A. Molecular identification of hard ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) infesting cattle in Iraq using mitochondrial 12S and 16S rRNA genes. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, A.; Bakheit, M.; Mohamed, A.E.; Zweygarth, E. High infection rates of the tick Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum with Trypanosoma theileri. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2004, 71, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.I.; Gabr, H.S.; Abdel-Shafy, S.; Hammad, K.M.; Mokhtar, M.M. Prevalence of tick-vectors of Theileria annulata infesting the one-humped camels in Giza, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EI-Metenawy, T.M. Prevalence of Theileria spp. in cattle in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia—Microscopy survey. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 99, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, J.J. Sustainable tick and tick-borne disease control in livestock improvement in developing countries. Vet. Parasitol. 1997, 71, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondan, C.; Folchini, J.A.; Noro, M.; Quadros, D.L.; Machado, K.M.; González, F.H.D. Milk composition of Holstein cows: A retrospective study. Ciência Rural. 2018, 48, e20180123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norval, R.A.I.; Sutherst, R.W.; Gibson, J.D.; Kerr, J.D.; Thorne, L.M.; Ellenhauge, A. The effects of the brown ear-tick, Rhipicephalus appendiculatus, on milk production in dairy cattle. Med. Vet. Entomol. 1997, 11, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satti, R.A.; Awadelkareem, E.A.; Suganuma, K.; Salim, B.; Inoue, N.; Xuan, X.; Rehan, S.; Mossaad, E. Cattle anaplasmosis and babesiosis: Major tick-borne diseases affecting the cattle industry in Khartoum State, Sudan. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2021, 26, 100–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azambuja, R.C.; Rodrigues, P.F.; Menezes, L.M.; Costa, R.F.; Teixeira, B.B.; Mendonça, F.S.; Suñé, R.W.; Silveira, I.D.; Cardoso, F.F. Milk Production and Constituents of Beef Cows with Different Breed Compositions. Res.Sq. 2020. Preprint Version 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addo, S.O.; Bentil, R.E.; Mosore, M.-T.; Behene, E.; Adinkrah, J.; Tagoe, J.; Yeboah, C.; Baako, B.O.A.; Atibila, D.; Kwarteng, S.A. Risk factors affecting the feeding site predilection of ticks on cattle in Ghana. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2024, 92, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paucar-Quishpe, V.; Pérez-Otáñez, X.; Rodríguez-Hidalgo, R.; Pérez-Escalante, C.; Cepeda-Bastidas, D.; Grijalva, J.; Enríquez, S.; Arciniegas-Ortega, S.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Ron-Garrido, L. Farmers’ adoption, knowledge, and perceptions of tick control measures on dairy farms in subtropical areas of continental Ecuador. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 5023240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, H.; Rizwan, H.M.; Younus, M.; Farid, M.U.; Naeem, M.A.; Ali Taseer, M.S.; Asghar, M.; Sargison, N.; Opara, M. Parasite control strategies: Trace elements and minerals. In Parasitism and Parasitic Control in Animals; CIBA: Basle, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Radostits, O.M.; Gay, C.; Hinchcliff, K.W.; Constable, P.D. A textbook of the diseases of cattle, horses, sheep, pigs and goats. Vet. Med. 2007, 10, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Noha, N.Y.; Fadwa, A.E.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Mahmoud, F.A. Impact of tick infestation and blood parasites on milk minerals, production, and reproductive performance in dairy cattle. Egypt. Vet. Med. Soc. Parasitol. J. 2024, 18, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, N.; Kirmani, M.A. Milk fever in dairy cows: A systematic review. Res. J. Biol. 2021, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, S.; Budachetri, K.; Mukherjee, N.; Williams, J.; Kausar, A.; Hassan, M.J.; Adamson, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Apanskevich, D.; Arijo, A. A study of ticks and tick-borne livestock pathogens in Pakistan. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, N.; Davis, R.; De Witt, M. An estimate of the economic effects of cattle tick (Boophilus microplus) infestation on Queensland dairy farms. Aust. Vet. J. 2001, 79, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dank, M.; Holzhauer, M.; Veldhuis, A.; Frankena, K. Association between Dictyocaulus viviparus status and milk production parameters in Dutch dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 7741–7747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Tarabany, M.S.; Atta, M.A.; El-Tarabany, A.A. Impact of heat stress on health and performance of dairy animals: A review Impact parasitic infection on milk yield, composition, and oxidative stress biomarkers in Holstein dairy cows. Livest. Sci. 2018, 216, 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Tsioulpas, A.; Grandison, A.; Lewis, M. Changes in physical properties of bovine milk from the colostrum period to early lactation. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 5012–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, P.; Roy, R.K.; Kumari, R.R.; Kumar, A.; Sarma, K.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, M. Mixed infection of tick-borne haemo-parasites in water buffalo and associated pathological responses and treatment. Indian. J. Anim. Res. 2022, 56, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumon, S.M.R.; Parvin, M.S.; Ehsan, M.A.; Islam, M.T. Dynamics of somatic cell count and intramammary infection in lactating dairy cows. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2020, 7, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Akhtar, T.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.F.; Shakoori, A.R. Hematobiochemical alterations in crossbred cattle naturally infected with babesiosis. Pak. J. Zool. 2020, 52, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, R.; Arora, N.; Mrigesh, M.; Arya, D. Impact of tick infestation on haematological and biochemical profiles in cattle: A comparative study. Int. J. Adv. Biochem. Res. 2024, 8, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ku, J.-Y.; Jung, Y.; Lim, Y.-H.; Ji, M.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Cho, H.-C.; Choi, K.-S.; Park, J. Evaluation of haematological parameters in haemolytic anaemia caused by tick-borne pathogens in grazing cattle. Vet. Med. Sci. 2024, 10, e1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazifi, S.; Razavi, S.M.; Kaviani, F.; Rakhshandehroo, E. Acute phase response in cattle infected with Anaplasma marginale. Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 155, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).