Characterization of Microbial Growth, Pathogen Presence, and Histamine Accumulation in Chilled Rainbow Trout and Mackerel Samples Collected from Romanian Markets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Total Viable Count
2.3. Pseudomonas/Aeromonas Count
2.4. Enumeration of the Enterobacteriaceae
2.5. Classical Isolation Protocol for Potential Pathogen Strains
2.5.1. Isolation of Salmonella spp.
2.5.2. Isolation of Listeria spp.
2.6. Microbial Population Isolation Using the VITEK® 2 Compact System
2.7. Mini Vidas Automated Analyzer for the Detection of Pathogenic Strains
2.8. Histamine Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.9. PCR Confirmation of Pathogen Strains
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
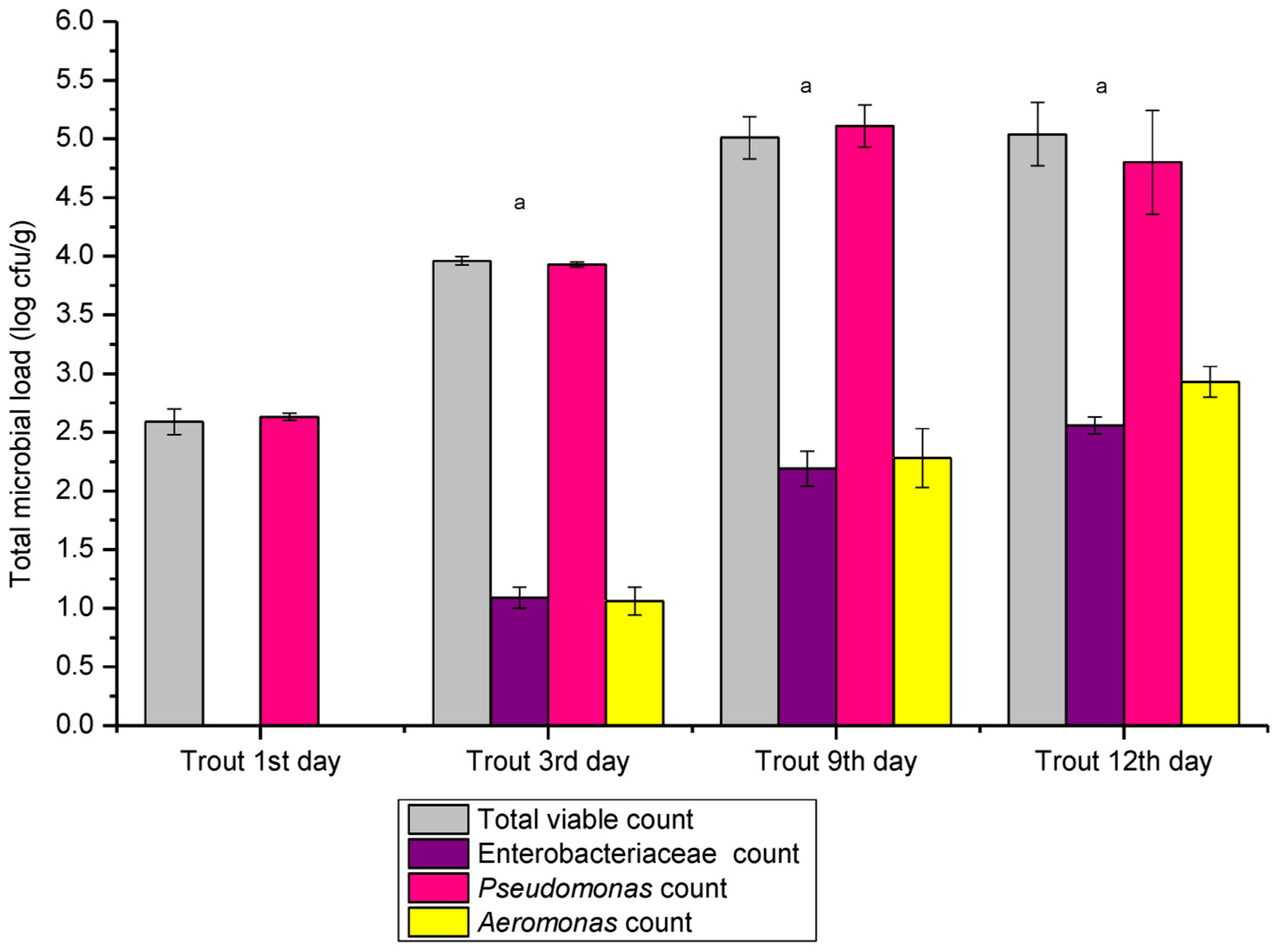
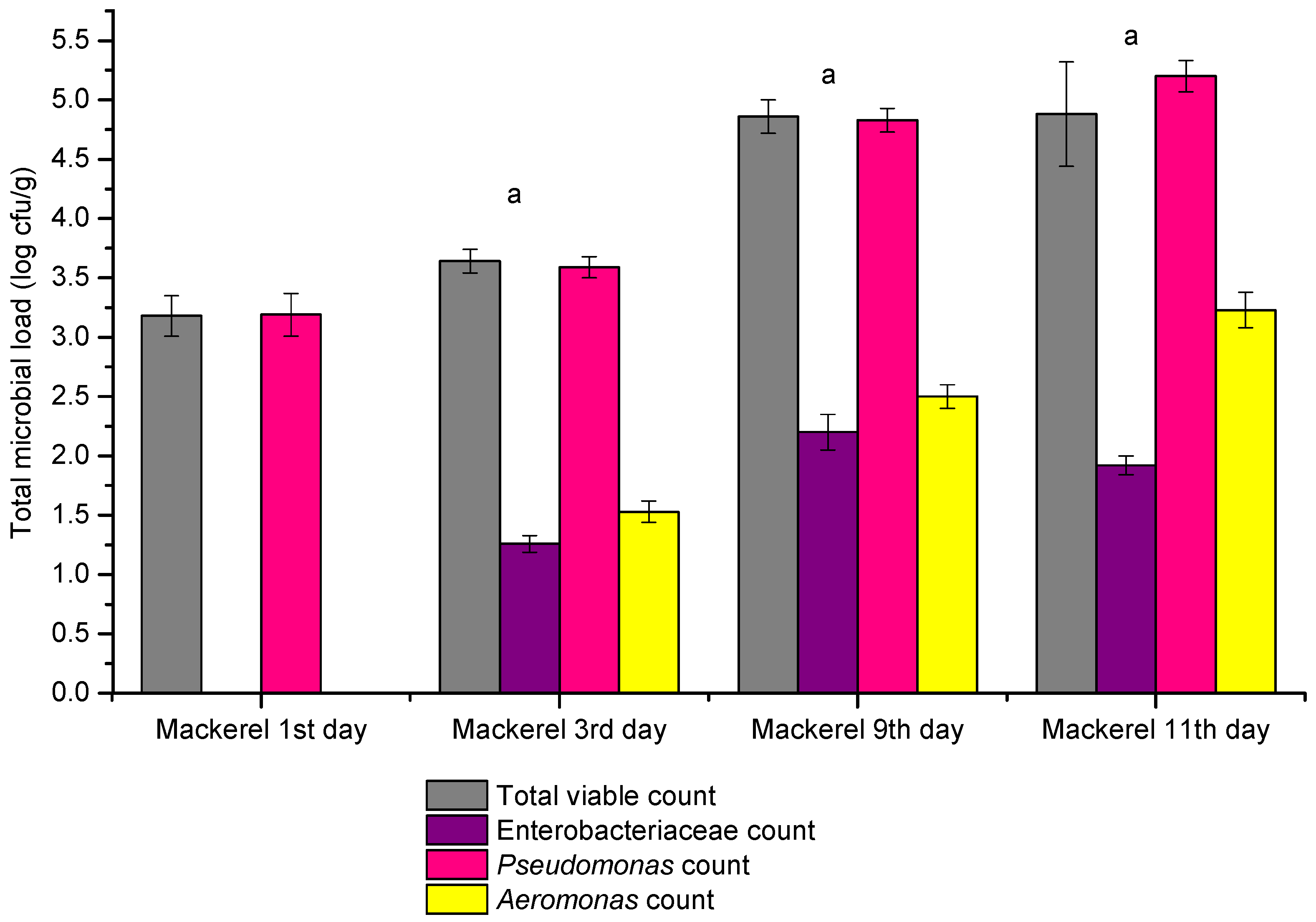
3.1. Results Total Viable Counts
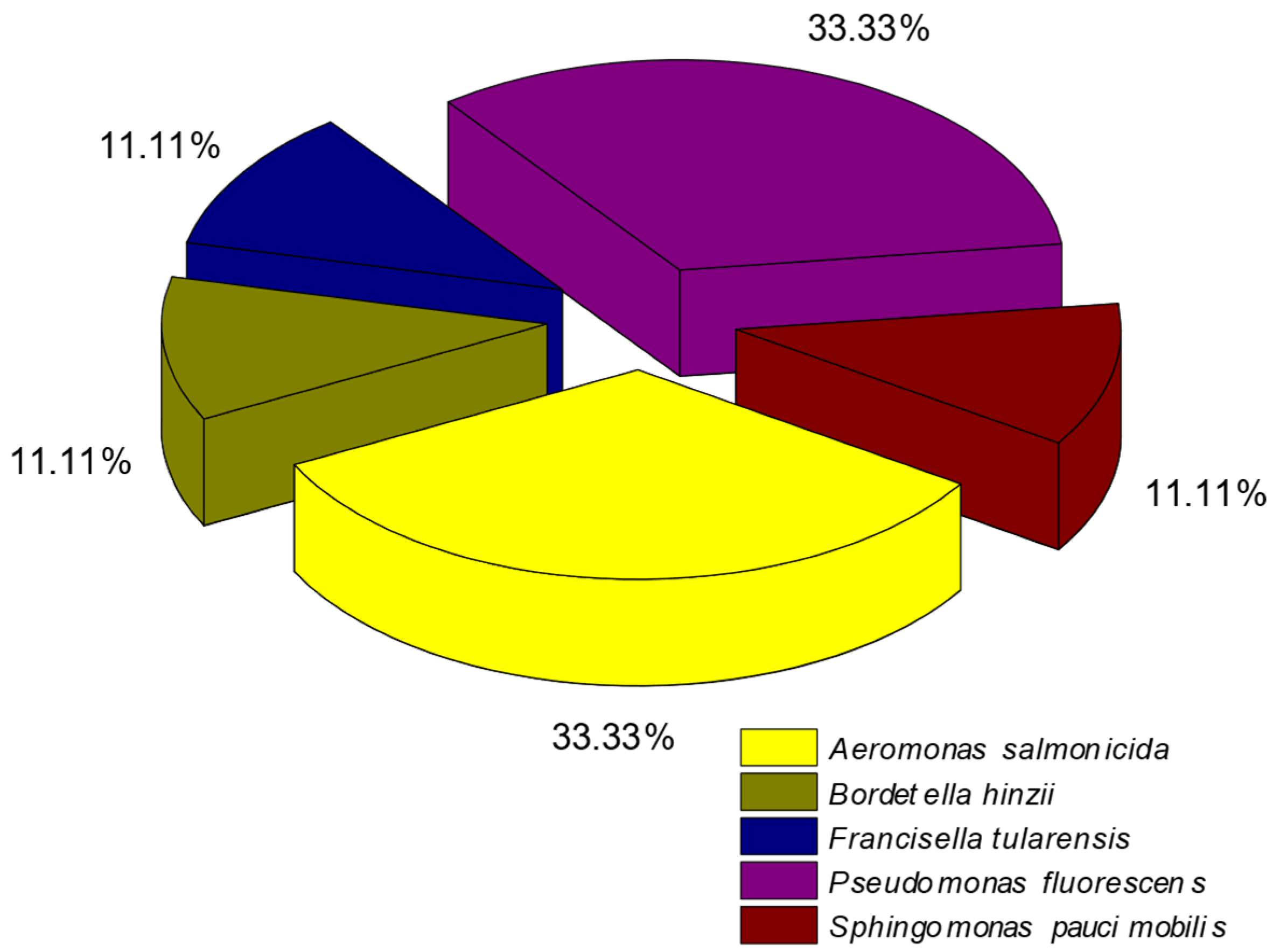
3.2. Microbial Diversity Characterisation
3.3. Pathogens Detection in Mackerel Samples
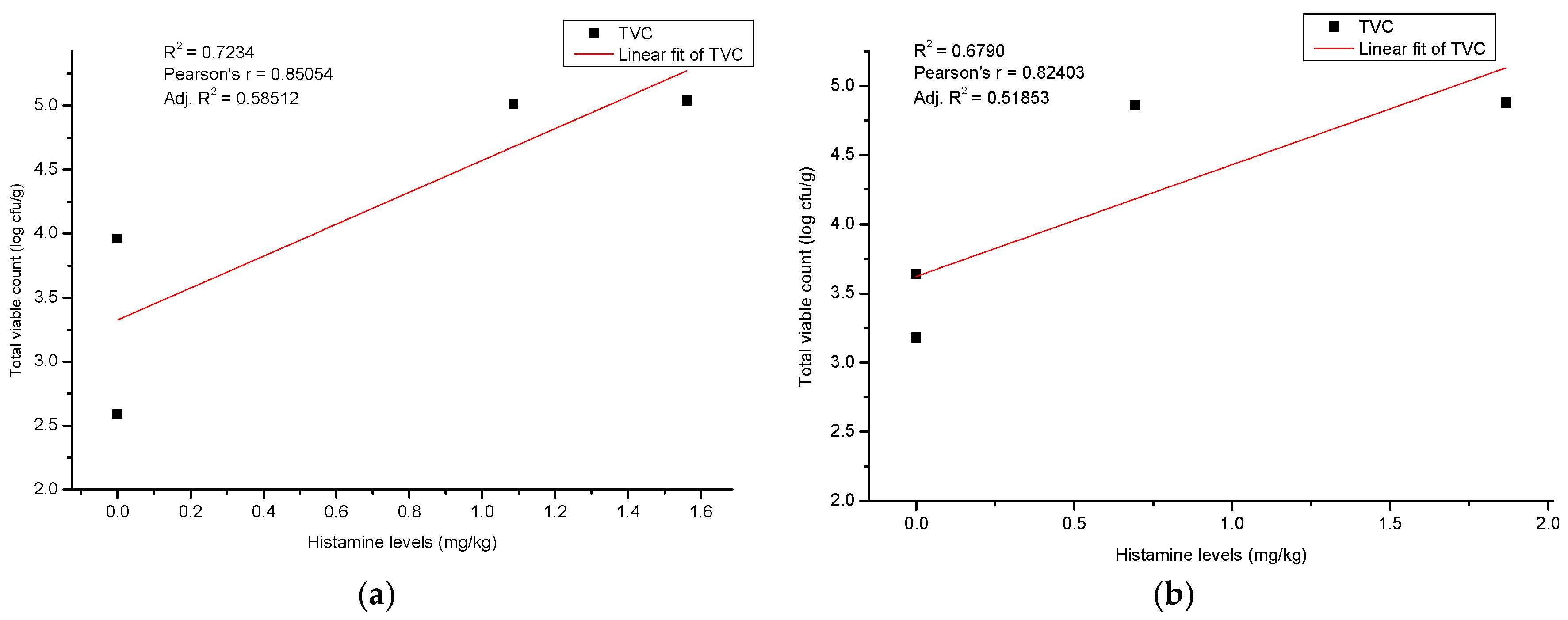
3.4. Histamine Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abisha, R.; Krishnani, K.K.; Sukhdhane, K.; Verma, A.K.; Brahmane, M.; Chadha, N.K. Sustainable Development of Climate-Resilient Aquaculture and Culture-Based Fisheries Through Adaptation of Abiotic Stresses: A Review. J. Water Clim. Change 2022, 13, 2671–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili Tilami, S.; Sampels, S. Nutritional Value of Fish: Lipids, Proteins, Vitamins, and Minerals. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquacult. 2017, 26, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pila, M.; Stanciuc, N.; Stanciu, S. Fisheries and Aquaculture in Romania: A Global Outlook on Sustainable Development. Sci. Pap. Ser. Manag. Econ. Eng. Agric. Rural Dev. 2023, 23, 517–522. [Google Scholar]
- Tahiluddin, A.; Maribao, I.; Amlani, M.; Sarri, J. A Review on Spoilage Microorganisms in Fresh and Processed Aquatic Food Products. Food Bull. 2022, 1, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, S.; Culloty, S.; Whooley, J.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The Gut Microbiota of Marine Fish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, N.C.; Wallgren, H.R.; Marbach, S.; Turner, J.W. Relationship between Rainfall, Fecal Pollution, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Microbial Diversity in an Urbanized Subtropical Bay. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e01229-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, T.E.; Thulsiraj, V.; Zimmer-Faust, A.G.; Dagit, R.; Krug, J.; Hanley, K.T.; Adamek, K.; Ebentier, D.L.; Torres, R.; Cobian, U.; et al. Long-Term Monitoring of Molecular Markers Can Distinguish Different Seasonal Patterns of Fecal Indicating Bacteria Sources. Water Res. 2015, 71, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.R.; Hoskins, G.E.; Hodgkiss, W. Aspects of the Characterization, Identification, and Ecology of the Bacterial Flora Associated with the Surface of Stream-Incubating Pacific Salmon (Oncorhynchus) Eggs. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 1971, 28, 1511–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolnick, D.I.; Snowberg, L.K.; Hirsch, P.E.; Lauber, C.L.; Knight, R.; Caporaso, J.G.; Svanbäck, R. Individuals’ Diet Diversity Influences Gut Microbial Diversity in Two Freshwater Fish (Threespine Stickleback and Eurasian Perch). Ecol. Lett. 2014, 17, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A.M. Environmental and Physiological Factors Shape the Gut Microbiota of Atlantic Salmon Parr (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2017, 467, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanch, A.; Alsina, M.; Simon, M.; Jofre, J. Determination of Bacteria Associated with Rearing Turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) Larvae. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 82, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, G.; Delbert, G.; Steven, R. Microbial Ecology of the Gastrointestinal Tract of Fish and the Potential Application of Prebiotics and Probiotics in Finfish Aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2005, 36, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthiayani, T.; Mahadeva Iyer, K. Quantitative and Qualitative Studies on the Bacterial Flora of Fresh Sardines. Fish. Technol. 1967, 4, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, A.M. Studies on the Microbiota of Fishes and the Factors Influencing Their Composition. Ph.D. Thesis, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ringø, E.; Sperstad, S.; Myklebust, R.; Refstie, S.; Krogdahl, Å. Characterisation of the Microbiota Associated with Intestine of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua L.). Aquaculture 2006, 261, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, C.; Nagar, S.; Lal, R.; Negi, R.K. Fish Gut Microbiome: Current Approaches and Future Perspectives. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G. Histamine Poisoning and Control Measures in Fish and Fishery Products. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giyatmi; Irianto, H.E. Chapter Ten-Enzymes in Fermented Fish. In Marine Enzymes Biotechnology: Production and Industrial Applications, Part III-Application of Marine Enzymes; Kim, S.-K., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 199–216. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, B. The Bacterial Microflora of Fish, Revised. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Qing, K.; Zhou, X.; Luo, Z. The Effects of Ventilation, Humidity, and Temperature on Bacterial Growth and Bacterial Genera Distribution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedane, T.D.; Agga, G.E.; Gutema, F.D. Hygienic Assessment of Fish Handling Practices Along Production and Supply Chain and Its Public Health Implications in Central Oromia, Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derome, N.; Gauthier, J.; Boutin, S.; Llewellyn, M. Bacterial Opportunistic Pathogens of Fish. In The Rasputin Effect: When Commensals and Symbionts Become Parasitic; Hurst, C., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoslavskij, A.; Terentjeva, M.; Eizenberga, I.; Valciņa, O.; Bartkevičs, V.; Bērziņš, A. Major Foodborne Pathogens in Fish and Fish Products: A Review. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.R.; da Costa, M.M.; de Carvalho Azevedo, V.A.; de Padua Pereira, U. Fish Pathogens: Infection and Biological Control. Fishes 2023, 8, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshath, A.A.; Rajan, A.P.; Vimal, S.; Prabhakaran, V.S.; Ganesan, R. Bacterial Pathogenesis in Various Fish Diseases: Recent Advances and Specific Challenges in Vaccine Development. Vaccines 2023, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Gao, R.; Huang, F.; Liang, B.; Guo, J.; Fan, L.; Wang, A.; Gao, S.-H. Occurrence, Transmission, and Risks Assessment of Pathogens in Aquatic Environments Accessible to Humans. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6579-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection, Enumeration and Serotyping of Salmonella. Part 1: Detection of Salmonella spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- ISO 11290-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Detection and Enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes and of Listeria spp. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- AOAC. Determination of Histamine by Liquid-Chromatographic Method, Following the EC Regulation No. 2073/2005/EC with Its Subsequent Amendments; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1998; Volume 81. [Google Scholar]
- Lerke, P.A.; Werner, S.B.; Taylor, S.L.; Guthertz, L.S. Scombroid Poisoning: Report of an Outbreak. West. J. Med. 1978, 129, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, H.A.; Yoshinaga, D.H.; Nip, W.K. Histamine Formation and Honeycombing During Decomposition of Skipjack Tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis), at Elevated Temperatures. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1981, 43, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mihaiu, L.; Lapusan, A.; Tanasuica, R.; Sobolu, R.; Mihaiu, R.; Oniga, O.; Mihaiu, M. First Study of Salmonella in Meat in Romania. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, M.N.; Ciupescu, L.M.; Dan, S.D.; Crisan-Reget, O.L.; Tabaran, A. Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Food Products in Romania. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gram, L. Spoilage of Three Senegalese Fish Species Stored in Ice and at Ambient Temperature. In Proceedings of the SEAFOOD 2000, Halifax, NS, Canada, 12–16 May 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gram, L.; Wedell-Neergaard, C.; Huss, H.H. The Bacteriology of Fresh and Spoiling Lake Victorian Nile Perch (Lates niloticus). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1990, 10, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICMSF (International Commission of Microbiological Specification for Food). Microorganisms in Food 2. Sampling for Microbiological Analysis: Principles and Specific Applications, 2nd ed.; University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1986; pp. 189–191. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, W.H.; Hammack, T.S. BAM Chapter 1: Food Sampling/Preparation of Sample Homogenate. In United States Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) Bacteriological Analytical Manual; United States Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjee, S.A.; Karim, M.E. Microbiological Quality Assessment of Frozen Fish and Fish Processing Materials from Bangladesh. Int. J. Food Sci. 2016, 2016, 8605689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renata, A.C. Escherichia coli in Seafood: A Brief Overview. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 450–454. [Google Scholar]
- Kuley, E.; Durmus, M.; Balikci, E.; Ucar, Y.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ozogul, F. Fish Spoilage Bacterial Growth and Their Biogenic Amine Accumulation: Inhibitory Effects of Olive By-Products. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, K.C.A.; Akbar, J.B.; Nurul Lyana, M.S.; Faizul, H.N.; Isma Yanti, M.N.; Irwandi, J.; Bulbul, M. Comparative Study on Spoilage and Pathogenic Bacteria in Selected Commercial Marine and Freshwater Fishes. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 298–304. [Google Scholar]
- Altinok, I.; Kayis, S.; Capkin, E. Pseudomonas putida Infection in Rainbow Trout. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy, B.; Kodjo, A.; Laurent, F. Prospective Nationwide Study of Aeromonas Infections in France. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Dey, S.; Kadam, S.; Kalal, S.; Jali, S.; Koley, H.; Sinha, R.; Nag, D.; Kholkute, S.D.; Roy, S. Isolation of NMD-1-Producing Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas putida from a Paediatric Case of Acute Gastroenteritis, India. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 5, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.Y.; Abukamar, M.; Anand, D. Nosocomial Pseudomonas putida Meningitis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Oman Med. J. 2017, 32, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershman, M.D.; Kennedy, D.J.; Noble-Wang, J.; Kim, C. Multistate Outbreak of Pseudomonas fluorescens Bloodstream Infection after Exposure to Contaminated Heparinized Saline Flush Prepared by a Compounding Pharmacy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Z. Bacteria: Pseudomonas. Encycl. Food Saf. 2014, 1, 490–500. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Tung, M.C.; Tu, C.; Chang, C.D.; Tsai, S.S. Enzootics of Visceral Granulomas Associated with Francisella-Like Organism Infection in Tilapia (Oreochromis spp.). Aquaculture 2006, 254, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.B.; Mikalsen, J.; Rode, M.; Alfjorden, A.; Hoel, E.; Straum-Lie, K.; Haldorsen, R.; Colquhoun, D.J. A Novel Systemic Granulomatous Inflammatory Disease in Farmed Atlantic Cod, Gadus morhua L., Associated with a Bacterium Belonging to the Genus Francisella. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, P.J.; Markey, B.K.; Carter, M.E.; Donnelly, W.J.; Leonard, F.C. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Disease; Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 2002; pp. 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Pechous, R.D.; McCarthy, T.R.; Zahrt, T.C. Working Toward the Future: Insights into Francisella tularensis Pathogenesis and Vaccine Development. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 684–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.; Forsman, M. Chapter 31: Francisella. Handbook of Foodborne Diseases. In Food Microbiology; Liu, D., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Keukeleire, S.; De Bel, A.; Jansen, Y.; Janssens, M.; Wauters, G.; Piérard, D. Yersinia ruckeri, an Unusual Microorganism Isolated from a Human Wound Infection. New Microbes New Infect. 2014, 2, 134–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Yersinia ruckeri, the Causative Agent of Enteric Redmouth Disease in Fish. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Agency). The Community Summary Report on Trends and Sources of Zoonoses, Zoonotic Agents, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Foodborne Outbreaks in the European Union in 2006. EFSA J. 2007, 130, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugapriya, S.; Senthilmurugan, T.; Thayumanavan, T. Genetic Diversity Among Yersinia enterocolitica Isolated from Chicken and Fish in and Around Coimbatore City, India. Iran. J. Public Health 2014, 43, 835–844. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Yersinia enterocolitica as a Cause of Septicemia in Crucian Carp (Carassius carassius). Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2016, 15, 402–414. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, M.P.; Adley, C.C. Sphingomonas paucimobilis: A Persistent Gram-Negative Nosocomial Infectious Organism. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 75, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, J.P.; Burd, E.M. Chapter 238: Other Gram-Negative and Gram-Variable Bacilli. In Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 2667–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, M.P.; Pembroke, J.T. Brevundimonas spp: Emerging global opportunistic pathogens. Virulence 2018, 9, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kawamura, Y.; Fujiwara, N.; Naka, T.; Liu, H.; Huang, X.; Kobayashi, K.; Ezaki, T. Sphingomonas yabuuchiae sp. nov. and Brevundimonas nasdae sp. nov., isolated from the Russian space laboratory Mir. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Choi, N.-S.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Yoon, J.-H.; Song, J.J. Brevundimonas naejangsanensis sp. nov., a proteolytic bacterium isolated from soil, and reclassification of Mycoplana bullata into the genus Brevundimonas as Brevundimonas bullata comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavelu, S.; Zavros, Y.; Merchant, J.L. Acinetobacter lwoffii infection and gastritis. Microbes Infect. 2003, 5, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuntas, F.; Yildiz, O.; Eser, B.; Gundogan, K.; Sumerkan, B.; Cetin, M. Catheter-related bacteremia due to Kocuria rosea in a patient undergoing peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. BMC Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.S.; Wong, C.L.; Lai, K.T.; Chan, E.C.; Yam, W.C.; Chan, A.C. Kocuria kristinae infection associated with acute cholecystitis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.J.; Leber, A. 140-Enterobacter, Cronobacter, and Pantoea Species. In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 824–827. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, M.; Kerr, K.G. Microbiological and Clinical Aspects of Infection Associated with Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.; Paydar, M.; Ismail, S.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Radmehr, B.; Abedini, A. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and virulotyping of Listeria species and Listeria monocytogenes isolated from open-air fish markets. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakar, D.; Borah, P.; Das, L.; Mathipi, V.; Sailo, C.V.; Dutta, R.; Deka, N.K.; Kumar, N.S. Prevalence and Virulent Gene Profiling of Listeria monocytogenes from Fish and Meat Samples from Aizawl, Mizoram. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, H.; Al-Ashmawy, M.; Soliman, A.M.; Elbediwi, M.; Sabeq, I.; Yousef, M.; Algammal, A.M.; Hiott, L.M.; Berrang, M.E.; Frye, J.G.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of Listeria innocua recovered from retail milk and dairy products in Egypt. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1160244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on microbiological criteria for foodstuffs. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2005, 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, G.C.; Summers, G.; Winchester, R.V.; Wong, R.J. Histamine and Histidine in New Zealand Marine Fish and Shellfish Species, Particularly Kahawai (Arripis trutta). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1995, 4, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). Application of Risk Assessment in the Fish Industry; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004; 63p. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, A.A.; Karkalas, J.; Roy, R.N.; Williams, C.S. The Occurrence of Non-volatile Amines in Chilled-stored Rainbow Trout (Salmo irideus). Food Chem. 1988, 27, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; An, H.; Price, R.J. Histamine Formation and Bacterial Spoilage of Albacore Harvest off the U.S Northwest Coast. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, L.; Olley, J. Histamine Fish Poisoning Revisited. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silviu, V.; Tabaran, A.; Crişan Reget, O.L.; Duma, M.N.; Panait, L.C.; Dan, S.D. Characterization of Microbial Growth, Pathogen Presence, and Histamine Accumulation in Chilled Rainbow Trout and Mackerel Samples Collected from Romanian Markets. Pathogens 2025, 14, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060580
Silviu V, Tabaran A, Crişan Reget OL, Duma MN, Panait LC, Dan SD. Characterization of Microbial Growth, Pathogen Presence, and Histamine Accumulation in Chilled Rainbow Trout and Mackerel Samples Collected from Romanian Markets. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060580
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilviu, Vida, Alexandra Tabaran, Oana Lucia Crişan Reget, Mihaela Niculina Duma, Luciana Cătălina Panait, and Sorin Daniel Dan. 2025. "Characterization of Microbial Growth, Pathogen Presence, and Histamine Accumulation in Chilled Rainbow Trout and Mackerel Samples Collected from Romanian Markets" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060580
APA StyleSilviu, V., Tabaran, A., Crişan Reget, O. L., Duma, M. N., Panait, L. C., & Dan, S. D. (2025). Characterization of Microbial Growth, Pathogen Presence, and Histamine Accumulation in Chilled Rainbow Trout and Mackerel Samples Collected from Romanian Markets. Pathogens, 14(6), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060580







