Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (Ilc2)-Deficient Mice Are Transcriptionally Constrained During Nippostrongylus brasiliensis Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. RNA Samples
2.3. RNA Analysis
2.4. Gene List Function and Pathway Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Expression, Gene Ontology, and Pathway Analysis
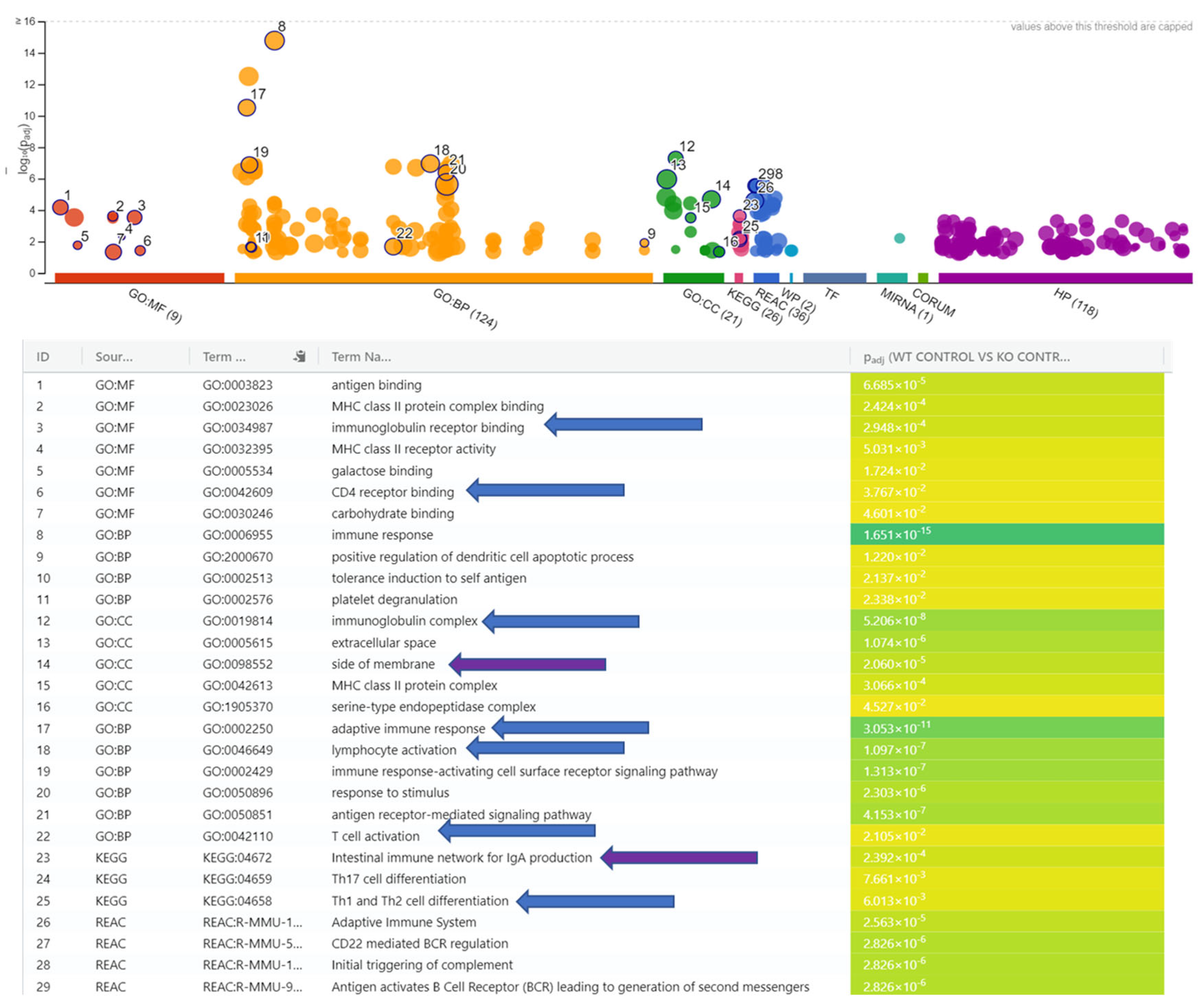
3.2. WT_Control vs. KO_Control
3.3. WT_Control vs. WT_NB_10dpi
3.4. KO_Control vs. KO_ NB_10dpi
4. Discussion
4.1. Mice Without Ilc2 Experience Downregulated Immunoglobulin Complex Immune Response and Transcriptional Regulators to N. brasiliensis Infection
4.2. RORα-Deficient Mice Show Differential Expression of Paralogs of Immune-Related Genes Expressed in Wild-Type Mice Infected with N. brasiliensis at 10 Dpi
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPI | days post-infection |
| NB | Nippostrongylus brasiliensis |
| ILC | innate lymphoid cell |
References
- Fricke, W.F.; Song, Y.; Wang, A.J.; Smith, A.; Grinchuk, V.; Mongodin, E.; Pei, C.; Ma, B.; Lu, N.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; et al. Type 2 immunity-dependent reduction of segmented filamentous bacteria in mice infected with the helminthic parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Microbiome 2015, 3, 40, Erratum in Microbiome 2015, 3, 77. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-015-0142-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filbey, K.; Bouchery, T.; Le Gros, G. The role of ILC2 in hookworm infection. Parasite Immunol. 2018, 40, e12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howitt, M.R.; Lavoie, S.; Michaud, M.; Blum, A.M.; Tran, S.V.; Weinstock, J.V.; Gallini, C.A.; Redding, K.; Margolskee, R.F.; Osborne, L.C.; et al. Tuft cells, taste-chemosensory cells, orchestrate parasite type 2 immunity in the gut. Science 2016, 351, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Taparowsky, E.J.; Kim, C.H. Retinoic Acid Differentially Regulates the Migration of Innate Lymphoid Cell Subsets to the Gut. Immunity 2015, 43, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delerive, P.; Monté, D.; Dubois, G.; Trottein, F.; Fruchart-Najib, J.; Mariani, J.; Fruchart, J.C.; Staels, B. The orphan nuclear receptor ROR alpha is a negative regulator of the inflammatory response. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haim-Vilmovsky, L.; Henriksson, J.; Walker, J.A.; Miao, Z.; Natan, E.; Kar, G.; Clare, S.; Barlow, J.L.; Charidemou, E.; Mamanova, L.; et al. Mapping Rora expression in resting and activated CD4+ T cells. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu-Li, J.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Paul, W.E. Innate immunological function of TH2 cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.P.; Wilhelm, C.; Yang, Q.; Hall, J.A.; Bouladoux, N.; Boyd, A.; Nutman, T.B.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Wang, J.; Ramalingam, T.R.; et al. Adaptation of innate lymphoid cells to a micronutrient deficiency promotes type 2 barrier immunity. Science 2014, 343, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Kaller, M. MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and samples in a single report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenberg, D.; Gordon, A.; Von Kuster, G.; Coraor, N.; Taylor, J.; Nekrutenko, A.; Galaxy, T. Manipulation of FASTQ data with Galaxy. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1783–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.; Allen, J.E.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Bennett, R.; et al. Ensembl 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D988–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglott, D.; Ostell, J.; Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T. Entrez Gene: Gene-centered information at NCBI. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D52–D57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt, C. UniProt: The Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D523–D531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, E.M.; Laird, R.M.; Papillion, A.M.; Tatum, A.H.; Princiotta, M.F.; Hayes, S.M. Reduced B lymphoid kinase (Blk) expression enhances proinflammatory cytokine production and induces nephrosis in C57BL/6-lpr/lpr mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydar, D.; Gonzalez, R.; Garvy, B.A.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Thamban Chandrika, N.; Bocklage, T.J.; Feola, D.J. Myeloid arginase-1 controls excessive inflammation and modulates T cell responses in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. Immunobiology 2021, 226, 152034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, T.E.; Rückerl, D.; Logan, N.; Duncan, S.; Wynn, T.A.; Allen, J.E. Ym1 induces RELMα and rescues IL-4Rα deficiency in lung repair during nematode infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-196a/b Mitigate Renal Fibrosis by Targeting TGF-beta Receptor 2. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3006–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramura, T.; Nomura, T. Acute skin barrier disruption alters the secretion of lamellar bodies via the multilayered expression of ABCA12. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 100, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Osterburg, A.R.; Flury, J.; Huang, S.; McCormack, F.X.; Cormier, S.A.; Borchers, M.T. NKG2D Regulation of Lung Pathology and Dendritic Cell Function Following Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhan, R.; Han, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, R.; et al. TLR9 Regulates the NF-κB-NLRP3-IL-1β Pathway Negatively in Salmonella-Induced NKG2D-Mediated Intestinal Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.C.; Okumura, R.; Motooka, D.; Sasaki, R.; Nakamura, S.; Iida, T.; Takeda, K. Alleviation of colonic inflammation by Lypd8 in a mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease. Int. Immunol. 2021, 33, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ensembl_ID | log2(FC) | P-adj | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENSMUSG00000111709 | 2.49 | 7.62 × 10−11 | Gm3776 |
| ENSMUSG00000110275 | 2.36 | 1.70 × 10−9 | Gm5905 |
| ENSMUSG00000074196 | 1.46 | 1.49 × 10−2 | Clca4c-ps |
| ENSMUSG00000010142 | −1.19 | 2.38 × 10−2 | Tnfrsf13b |
| ENSMUSG00000067341 | −1.34 | 2.93 × 10−2 | H2-Eb2 |
| ENSMUSG00000041538 | −1.37 | 2.01 × 10−2 | H2-Ob |
| ENSMUSG00000051998 | −1.38 | 1.51 × 10−3 | Lax1 |
| ENSMUSG00000093894 | −1.39 | 4.95 × 10−2 | Ighv1-53 |
| ENSMUSG00000076939 | −1.39 | 4.58 × 10−2 | Iglv3 |
| ENSMUSG00000014453 | −1.45 | 2.01 × 10−2 | Blk |
| ENSMUSG00000024863 | −1.49 | 2.39 × 10−2 | Mbl2 |
| ENSMUSG00000026616 | −1.50 | 2.01 × 10−2 | Cr2 |
| ENSMUSG00000076613 | −1.53 | 1.60 × 10−3 | Ighg2b |
| ENSMUSG00000076614 | −1.53 | 1.20 × 10−2 | Ighg1 |
| ENSMUSG00000096715 | −1.55 | 8.14 × 10−3 | Igkv3-4 |
| ENSMUSG00000096499 | −1.57 | 1.20 × 10−2 | Ighv1-5 |
| ENSMUSG00000076594 | −1.62 | 6.66 × 10−3 | Igkv6-13 |
| ENSMUSG00000094335 | −1.62 | 1.19 × 10−3 | Igkv1-117 |
| ENSMUSG00000003379 | −1.64 | 1.23 × 10−3 | Cd79a |
| ENSMUSG00000094433 | −1.75 | 1.23 × 10−3 | Igkv5-43 |
| ENSMUSG00000076563 | −1.93 | 2.28 × 10−4 | Igkv5-48 |
| ENSMUSG00000095127 | −2.01 | 7.43 × 10−5 | Ighv1-82 |
| WT_CONTROL VS. WT_NB_10DPI | KO_CONTROL VS. KO_NB_10DPI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensembl_ID | log2(FC) | Gene Name | Ensembl_ID | log2(FC) | Gene Name | |
| ENSMUSG00000013653 | 4.25 | 1810065E05Rik | Overlapping DEGs between WT and KO at 10 dpi | ENSMUSG00000013653 | −0.95 | 1810065E05Rik |
| ENSMUSG00000050296 | 2.54 | Abca12 | ENSMUSG00000050296 | −0.98 | Abca12 | |
| ENSMUSG00000095649 | 2.02 | Gvin-ps3 | ENSMUSG00000095649 | −1.17 | Gvin-ps3 | |
| ENSMUSG00000071356 | 4.02 | Reg3b | ENSMUSG00000071356 | −0.99 | Reg3b | |
| ENSMUSG00000030017 | 3.34 | Reg3g | ENSMUSG00000030017 | −0.91 | Reg3g | |
| ENSMUSG00000025993 | 2.2 | Slc40a1 | ENSMUSG00000025993 | −1.41 | Slc40a1 | |
| ENSMUSG00000043705 | −3.82 | Capn13 | Gene paralogs between WT and KO at 10 dpi | ENSMUSG00000054083 | 0.91 | Capn12 |
| ENSMUSG00000069922 | −2.42 | Ces3a | ENSMUSG00000055730 | 0.94 | Ces2a | |
| ENSMUSG00000004267 | −2.04 | Eno2 | ENSMUSG00000060600 | 0.79 | Eno3 | |
| ENSMUSG00000013643 | 2.46 | Lypd8 | ENSMUSG00000026344 | 0.88 | Lypd1 | |
| ENSMUSG00000037145 | 2.9 | Lypd8l | ENSMUSG00000061068 | −0.87 | Mcpt4 | |
| ENSMUSG00000022227 | −2.38 | Mcpt1 | ENSMUSG00000045725 | 0.79 | Prr15 | |
| ENSMUSG00000022226 | −2.4 | Mcpt2 | ENSMUSG00000051079 | −0.94 | Rgs13 | |
| ENSMUSG00000043795 | −2.2 | Prr33 | ENSMUSG00000020641 | 0.77 | Rsad2 | |
| ENSMUSG00000079516 | 5.16 | Reg3a | ENSMUSG00000024818 | 0.97 | Slc25a45 | |
| ENSMUSG00000068341 | 2.47 | Reg3d | ENSMUSG00000070563 | −0.96 | Spaca4 | |
| ENSMUSG00000037627 | −3.95 | Rgs22 | ENSMUSG00000027801 | 0.88 | Tm4sf4 | |
| ENSMUSG00000038530 | −2.5 | Rgs4 | ENSMUSG00000056133 | 1.27 | Unc93a2 | |
| ENSMUSG00000039096 | −2.88 | Rsad1 | ||||
| ENSMUSG00000031633 | −2.02 | Slc25a4 | ||||
| ENSMUSG00000080316 | −2.35 | Spaca6 | ||||
| ENSMUSG00000038623 | −3.03 | Tm6sf1 | ||||
| ENSMUSG00000067049 | −2.3 | Unc93a | ||||
| Term Id | Term Description | # Genes | Enrichment Score | Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0061844 | Antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide | 14 | 6.63 | Mmp7, Xcl1, Reg3g, Ang, Defa21, Defa24, Gm15308, Dmbt1, Reg3b, Defa-rs1, Ccl28, Reg3a, Cxcl9, Rpl39 |
| GO:0050830 | Defense response to Gram-positive bacterium | 14 | 5.59 | Hck, Mmp7, Reg3g, Zg16, Hmgb2, Ang, Defa21, Defa24, Gm15308, Dmbt1, Lyz1, Reg3b, Defa-rs1, Rpl39 |
| GO:0050829 | Defense response to Gram-negative bacterium | 14 | 5.19 | Mmp7, Reg3g, Pycard, Serpine1, Nlrp10, Hmgb2, Defa21, Defa24, Gm15308, Dmbt1, Lyz1, Reg3b, Defa-rs1, Lypd8 |
| CL:36134 | Mixed, incl. defensin and protease inhibitors | 17 | 6.04 | Serpina1f, Ceacam10, Cercam, AY761184, Gm15315, Defa21, Gm14851, Gm10104, Defa24, Gm14850, Gm15308, Dmbt1, Def-rs1, Defa22, Gm15284, Lypd8, Gm15293 |
| CL:25609 | Cell wall disruption in other organisms, and Cobalamin (Cbl, vitamin B12) transport and metabolism | 3 | 8.42 | Reg3g, Reg3b, Reg3a |
| CL:36334 | Defensin/corticostatin family, and peptidyl-arginine ADP-ribosylation | 7 | 6.04 | Gm15315, Defa21, Gm14851, Defa24, Gm14850, Gm15284, Gm15293 |
| CL:16259 | Mixed, incl. macrophage proliferation and CD59 antigen, conserved site | 4 | 4.87 | Retnla, Mgl2, Chil3, Siglec5 |
| CL:25564 | Mixed, incl. activation of matrix metalloproteinases and cell wall disruption in other organisms | 6 | 6.86 | Reg3g, Klk1, Reg3d, Reg3b, Reg3a, Sycn |
| CL:25566 | Mixed, incl. Cobalamin (Cbl, vitamin B12) transport and metabolism and cell wall disruption in other organisms | 5 | 7.23 | Reg3g, Reg3d, Reg3b, Reg3a, Sycn |
| MMU-1462054 | Alpha-defensins | 12 | 6.44 | AY761184, Gm15315, Defa21, Gm14851, Gm10104, Defa24, Gm14850, Gm15308, Defa-rs1, Defa22, Gm15284, Gm15293 |
| MMU-6803157 | Antimicrobial peptides | 20 | 3.44 | Prtn3, Clu, Reg3g, Rnase2a, AY761184, Ear2, Gm15315, Defa21, Gm14851, Gm10104, Defa24, Gm14850, Gm15308, Reg3d, Reg3b, Def-ars1, Defa22, Gm15284, Reg3a, Gm15293 |
| MMU-211859 | Biological oxidations | 15 | 4.22 | Mgst1, Ptgis, Cyp46a1, Sult1c, Cyp2c55, Maoa, Fmo3, Aadac, Aldh1b1, Cyp3a59, Nr1h4, Cyp3a25, Ugt2b5, Ces3a, Ugt2b36 |
| BTO:0001485 | Muscular system | 27 | 2.47 | Cnn1, Srpk3, Casq1, Ckm, Serpinb9b, Timp1, Slc2a4, Tpm2, Itgb1bp2, Slc25a4, Pdlim3, Tagln, Fn1, Gja1, Cav3, Sgcg, Dysf, Dio2, Trdn, Tnnc2,Sgca, Nppa, Hspb7, Myh7, Tnnt2, Dtna, Tnnt3 |
| BTO:0006111 | M2 macrophage | 3 | 6.44 | Arg1, Retnla, Chil3 |
| KW-0211 | Defensin | 14 | 6.35 | Defb40, AY761184, Gm15315, Defa21, Gm14851, Gm10104, Defa24, Gm14850, Gm15308, Defa-rs1, Defa22, Gm15284, Gm15293, Defa2 |
| KW-0929 | Antimicrobial | 22 | 5.20 | Irg1, Reg3g, Defb40, AY761184, Gm15315, Defa21, Gm14851, Gm10104, Defa24, Chil1, Gm14850, Gm15308, Lyz1, Reg3b, Def-ars1, Defa22, Gm15284, Reg3a, Slpi, Gm15293, Defa2, Vgf |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fleming, D.S.; Liu, F.; Urban, J.F., Jr.; Li, R.W. Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (Ilc2)-Deficient Mice Are Transcriptionally Constrained During Nippostrongylus brasiliensis Infection. Pathogens 2025, 14, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060571
Fleming DS, Liu F, Urban JF Jr., Li RW. Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (Ilc2)-Deficient Mice Are Transcriptionally Constrained During Nippostrongylus brasiliensis Infection. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):571. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060571
Chicago/Turabian StyleFleming, Damarius S., Fang Liu, Joseph F. Urban, Jr., and Robert W. Li. 2025. "Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (Ilc2)-Deficient Mice Are Transcriptionally Constrained During Nippostrongylus brasiliensis Infection" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060571
APA StyleFleming, D. S., Liu, F., Urban, J. F., Jr., & Li, R. W. (2025). Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell (Ilc2)-Deficient Mice Are Transcriptionally Constrained During Nippostrongylus brasiliensis Infection. Pathogens, 14(6), 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060571






