Abstract
The apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii can potentially infect all warm-blooded animals, including birds, which, due to their high dispersal capabilities, are considered a significant candidate group of sentinel animals that reveal environmental contamination with this protozoan. In the present study, the serologic and molecular prevalences of T. gondii infection were determined in 333 corvids from Romania. Paired meat juice (n = 333) and heart samples (n = 244) were collected and analyzed using the modified agglutination test for antibodies, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for DNA, and SAG2 molecular marker sequencing for genotyping. The overall T. gondii antibodies prevalence was 19.5%, with 48.1% infected jackdaws, 72.8% rooks, 89.7% hooded crows, 77.5% magpies, and 42.9% jays. Of 244 heart samples analyzed with PCR amplification, only 3 (1.2%) resulted positive and were shown to belong to genotype III through the sequencing of the SAG2 amplicon. This is the first extensive study on T. gondii in crows from Romania.
1. Introduction
Toxoplasmosis, caused by the apicomplexan Toxoplasma gondii, is one of the most widespread zoonoses globally [1]. This obligate intracellular parasite can infect all species of mammals, including humans and birds [2], while its ability to infect cold-blooded animals remains unproven [3]. Birds, feeding either on the ground, potentially contaminated with T. gondii oocysts, or as raptors–carnivores on prey carrying tissue cysts, are a candidate group of sentinel animals able to reveal environmental contamination with T. gondii oocysts [4].
The infection of birds with T. gondii is widely reported; numerous species from at least 15 orders, namely Accipitriformes, Falconiformes, Galliformes, Passeriformes, Columbiformes, Anseriformes, Charadriiformes, Struthioniformes, Strigiformes, Sphenisciformes, Ciconiiformes [5,6], Apodiformes [7], Suliformes, Phaethontiformes [8], and Gruiformes [9], are confirmed intermediate hosts of this parasite. Regarding domestic Galliformes, even though T. gondii does not pose a direct health risk to chickens, they represent an essential food safety issue due to the transmission risk associated with chicken meat consumption [10]. Additionally, T. gondii-infected free-range chickens that died from other causes and remained in the environment may constitute a contamination source for a range of bird species.
Among wild birds, the passerine family Corvidae members, which include ravens, crows, magpies, jays, treepies, choughs, and nutcrackers, are distributed worldwide except the southern tip of South America and the polar ice caps [11]. They are generalist species widespread in various environments, from harsh mountainous regions to plain ecosystems, but they have adjusted and are thriving in anthropogenically modified areas [12].
Corvids are considered omnivorous, opportunistic feeders [13,14]; their diet includes plants, animals, and miscellaneous foods. This wide variety of corvid food sources makes them susceptible to infection with various infective elements from the environment, such as eggs, oocysts, larvae, or via intermediate hosts of many parasites. Of these, T. gondii oocysts are reported in all matrices worldwide, specifically in water sources, soil from greenhouses, vegetable gardens, public parks, and other urbanized areas, industrial and commercial land, woodland, grassland, or around rubbish dumps [15]. Concomitantly, all these environments represent favorable areas for corvids nesting and feeding, thus exposing them to infection with T. gondii oocysts. Furthermore, T. gondii cysts are reported in the tissues of many living or dead organisms that enter the diet of corvids. Carrion meat [16], small mammals [17], insects [18], small reptiles, amphibians, mollusks [3], birds’ eggs [19], or slaughterhouse leftovers [20] are all potential sources of infection for corvids.
Given this background, this study aimed to serologically and molecularly evaluate the prevalence of T. gondii infection in birds of the Corvidae family.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was performed on 333 corvids belonging to 5 species of the Corvidae family collected from all over Romania (Figure 1, Table 1). According to the Emergency Ordinance No. 7 of 6 March 2025, to amend and supplement Government Emergency Ordinance No. 57/2007 on the regime of protected natural areas, the conservation of natural habitats, and wild flora and fauna, the corvid species are not classified as protected species [21]. Therefore, most examined birds were hunted to combat the excessive number of resident corvids in certain areas or were found dead. The bird carcasses were collected, individually packaged, and frozen. The birds were identified based on morphological characters [22] and necropsied. During necropsy, the heart was collected and stored at −20 °C until processing. The meat juice samples obtained by freezing–thawing individual hearts were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 5 min and stored at −20 °C until examined.
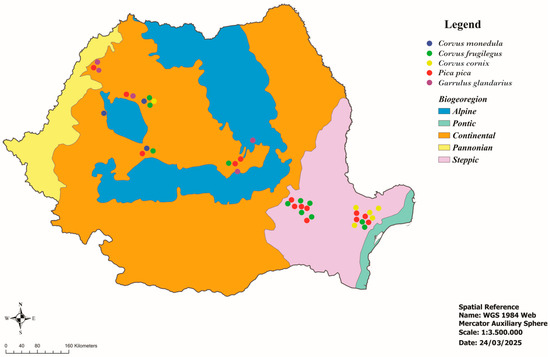
Figure 1.
Geographical location of the examined corvids.

Table 1.
Distribution of analyzed samples among five different corvid species.
Meat juice samples were analyzed using the modified agglutination test (MAT) to detect anti-T. gondii antibodies using formalin-fixed tachyzoites (RH strain) (supplied by the National Reference Centre on toxoplasmosis/Toxoplasma Biological Resource Center from Reims, France) as antigens. The protocol was performed according to Villena et al. [23]. Samples with a titer ≥ 1:24 were considered positive [5,24].
Genomic DNA was extracted from heart samples (n = 244) using the commercial ISOLATE II Genomic DNA Kit (Bioline, London, UK). The extraction protocol was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The extracted DNA was quantified with a NanoDrop 1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and stored at -20˚C until processing. DNA samples were analyzed using PCR for the detection of the 529 bp repetitive fragment using specific primers (Generi Biotech, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic), Tox4 (5′-CGCTGCAGGGAGGAAGACGAAAGTTG-3′) and Tox5 (5′-CGCTGCAGACACAGTGCATCTGG ATT-3′) [25]. For each reaction, amplification of DNA fragments was carried out in a final volume of 25 µL: 12.5 µL PCR Master Mix (2x Green PCR Master Mix, Rovalab, Teltow, Germany), 1 µL primer Tox4 (10 µM/µL), 1 µL primer Tox5 (10 µM/µL), 4 µL DNA and 6.5 µL ultrapure water. Positive (T. gondii RH strain) and negative (ultrapure water) controls were used in each set of reactions. The PCR inhibition was checked with serial dilution of selected PCR-negative samples (n = 10). Amplification was performed with a C1000TM Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, Berkeley, CA, USA). The amplification program was: 1 cycle of initial denaturation at 95 °C (1 min); 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C (15 s), annealing at 60 °C (15 s), and extension at 72 °C (10 s); 1 cycle of final extension at 72 °C (5 min). The PCR products were analyzed using electrophoresis in a 1.5% agarose gel stained with SYBR Safe DNA gel stain (Invitrogen, MA, USA) and visualized using the Gel Doc XR+ Gel Documentation System (Bio-Rad). The length of the amplified DNA fragments was estimated using a 100 bp molecular marker (O’GeneRuler 100 bp DNA Ladder, ready-to-use, Thermo Scientific). Positive DNA samples were amplified with primers specific for the SAG2 marker [26], purified using the commercial QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany), and sent for sequencing to Macrogen Europe (Amsterdam, The Netherlands). The obtained nucleotide sequences were compared with reference sequences from GenBank, using BLAST (Basic Local Alignments Tool) (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PROGRAM=blastn&PAGE_TYPE=BlastSearch&LINK_LOC=blasthome, accessed on 15 April 2025) analysis [27].
Statistical data processing was performed with Microsoft Excel and Epi Info programs [28]. Frequency, prevalence, and 95% confidence interval were calculated. Differences between prevalences were statistically analyzed using the Chi-square test. The p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
The overall prevalence of anti-T. gondii antibodies was 19.5% (65/333; 95% CI: 15.6–24.1) with MAT (Table 2). Depending on the species, the prevalence was 9.6% in jackdaw (5/52), 22.6% in rook (44/195), 28.2% in hooded crow (11/39), 12.5% in magpie (5/40), whereas no infected jays were found. The maximum dilution at which anti-T. gondii antibodies were detected was 1:192 in rooks (Table 3). The differences in seroprevalence recorded between corvid species were statistically significant (p = 0.0001).

Table 2.
Prevalence of T. gondii infection in corvids with MAT (≥1:24) and PCR.

Table 3.
Prevalence of T. gondii infection in corvids with MAT dilutions.
The molecular prevalence was lower, with T. gondii DNA detected in three (1.2%; 95% CI: 0.25–3.55) of the 244 heart samples analyzed. The positive samples originated from the rook (1/106), the hooded crow (1/39; MAT ≥ 1:24), and the magpie (1/40). Two of three PCR-positive samples originated from birds with antibody titers below the cut-off value (rook MAT ≥ 1:12, magpie MAT ≥ 1:6). The differences between the prevalences recorded by species were not statistically significant (p = 0.75).
Sequence analysis of the three SAG2 amplicons showed 100% homology to genotype III (VEG strain). The sequence was deposited in GenBank under the accession no. PV485377.
4. Discussion
Corvids are one of the most abundant and extensively studied and abundant groups of passerine birds worldwide [29]. The populations of the species incorporated in the present study include millions of adult specimens worldwide, with a stable trend (Table 4) [30,31]. The abundance of corvid populations, their varied diet and sedentarism, the synanthropization favorable to their development, and implicitly, their close contact with humans or domestic animals make these birds a possible reservoir of various pathogens, some with zoonotic potential, including the apicomplexan T. gondii. Multiple studies on the prevalence of infection in corvids have been conducted worldwide.

Table 4.
Populations of corvid species in this study.
In Asian countries, T. gondii infection is reported in several corvid species. In Iran, a molecular prevalence of 16.36% (9/55) was recorded by studying the brain tissue of hooded crows, revealing the same genotype III in eight isolates [32]. Through histopathological examination of brain tissue, T. gondii was identified in 3.8% of 125 rooks from the same country [33]. An increased molecular prevalence of 34% (34/100) was recorded from the brains of Eurasian magpies collected from Northwestern Iran; 5.9% of the isolates belonged to T. gondii genotype II and 94.1% to type III [34]. In Kazakhstan, the infection was histopathologically confirmed, recording a prevalence of 1.7% in carrion crows (Corvus corone) [35]. In Western Asia, the infection was reported in carrion crows from Turkey, with molecular prevalence determined from the brain tissue of 4.7%; still, the infection was not confirmed in the single magpie specimen analyzed [36]. In the same area, T. gondii seroprevalence was studied in crows in Israel to assess exposure to this pathogen in scavenger birds and their possible role in the epidemiology of toxoplasmosis [37]. Using MAT, 52 of the 122 examined crows (42.6%) were seropositive. By species, the infection was seroconfirmed in 48 of 101 carrion crows (47.5%), 2/5 (40%) jackdaws, and 2/16 (12.5%) house crows (Corvus splendens), a common bird of Asian origin currently spread in many parts of the world. PCR analysis of brain-extracted DNA from a crow was positive and identified as genotype II. The seroprevalence of T. gondii infection, determined by the latex agglutination test, was 35% in house crows in Pakistan; the higher seropositivity might be due to the scavenging of infected carrion [38].
The first report of T. gondii infection in corvids worldwide originated in New York State, USA [39]. Parasites were identified from the brain tissue of the American crow (Corvus brachyrhynchos) by intraperitoneal passages in mice. The strain isolated from this crow species was less pathogenic to mice than others and highly pathogenic to rabbits, while ducklings seemed refractory. However, the incidence of natural infection seems low (around 1%). More recently, however, infection in the same corvid species was not confirmed in Colorado, probably because only two specimens were examined [40]. T. gondii infection was also immunohistochemically diagnosed in the American native ‘Alala (Corvus hawaiiensis) species, the most endangered corvid in the world, in Hawaii [41]. Also, in America, the infection was studied in Mexico in the common raven (Corvus corax), one of the most widespread corvid species in the Northern Hemisphere; still, the infection was not serologically confirmed, probably due to the limited number of birds examined [42].
The majority of the studies on T. gondii infection in corvids were carried out on the European continent. In Western Europe, the infection was molecularly confirmed in Spain in magpies (5/33; 15.1%) and jays (5/23; 21.7%) from the brain and serologically with MAT in common ravens (91/113; 80.5%) but not in Eurasian jackdaws [4,24,43]. In Portugal, it was proven in carrion crows (1/3; 33.3%) [7], whereas in Italy, magpies (41/651; 6.3%) and hooded crows (4/120; 3.3%) were serologically and molecularly confirmed hosts, infected with either genotype II or III; in contrast, the rook and Eurasian jay did not reveal T. gondii infection [44,45]. In Central and Eastern Europe, studies of T. gondii parasitism in birds are generally scarce, and regarding crows, the infection was reported in only two countries. In the Czech Republic, jackdaws (1/5; 20.0%), rooks (89/495; 18.0%), and jays (1/43; 2.3%) were confirmed as T. gondii hosts [9]. In Serbia, molecular analysis of the hearts showed that 40% of rooks and 35.3% of hooded crows were infected with T. gondii, indicating substantial exposure to the parasite, and suggesting a high level of environmental oocyst contamination [46].
In Africa, although several studies on T. gondii infection in birds exist, they do not include corvids. However, it has been molecularly confirmed in bucerotids (Tockus leucomelas), columbids (Spilopelia senegalensis and Streptopelia semitorquata), and larids (Larus michahellis) [47,48].
Here, we report on T. gondii infection in corvids from Romania, revealing variable prevalences in all examined species. The differences with some of the previous studies may be due to the diagnostic method employed, i.e., serology, molecular testing, or histopathology. Among the serological methods, the most commonly used in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis are the indirect hemagglutination test (IHA), the immunofluorescence antibody test (IFAT), and the modified agglutination test (MAT). The literature has shown the MAT to be specific and sensitive for testing bird antibodies against T. gondii, with the additional advantages of not requiring special equipment or species-specific conjugates [5,49]. In molecular testing, false results may arise due to the type of tissue used for DNA extraction. The brain seems to be the predilection organ of T. gondii in mammals, as confirmed in pigs, sheep, and rodents [50,51,52]. It is followed by the heart, lungs, skeletal muscles, diaphragm, liver, and kidneys [53,54,55,56,57]. However, in birds, the heart, brain, or liver are equally considered predilection organs, as demonstrated in experimental or natural infections in gallinaceous and anseriforms [58,59,60,61]. Additionally, the inconsistency between the prevalence revealed using MAT and PCR is explainable by the different targets of these methods. The MAT detects specific IgG antibodies, which may persist for months or even years, suggesting prior exposure to the infection. In contrast, PCR detects the T. gondii DNA in tissues, where the parasite load can be low and not uniformly distributed.
Regardless of the methods and tissues used, the pooled prevalence of T. gondii infection in crows has been systematically reviewed and reached 25% with limits between 7 and 49%; this is amongst the highest values recorded in wild birds, exceeded only by owls (29%; 18–42%), gulls (29%; 12–49%), kestrels (25%; 20–30%), and hawks (25%; 15–36%) [6]. This increased prevalence of T. gondii in corvids is influenced by several risk factors. The data reported indicate that epidemiological variables, such as environmental conditions, diet, feeding behavior, and, implicitly, the trophic level to which they belong, age, sedentary habit, the crows’ population density, the season, habitat, and the density of animal, human, and feline populations in the area can influence the prevalence of T. gondii in wild birds [4,37,44,62,63,64]. Out of the mentioned factors, the environmental conditions, diet, and feeding behavior of corvids, combined with a high density of infected animal, human, and feline populations, could play a significant role in crow contamination. Numerous studies conducted in the last decade in Romania targeting humans, domestic definitive and intermediate hosts, as well as small wild mammals, most of which are food sources for opportunistic omnivorous corvids, support this hypothesis. Most national studies on toxoplasmosis were performed in the moist, warm, and low-altitude continental biogeographical region [65], including Central and North-Western Romania, where high prevalence levels are revealed (Figure 2 and Figure 3).
It is found that the high seroprevalence recorded in cats, the definitive host (62.9%) [66], correlates with the values in humans (35.9%) [67] and other intermediate hosts [68,69,70], including corvids. If the increased seroprevalence in humans is explained by the harmful eating habits of consuming less heat-sterilized animal products, the leading cause in domestic intermediate hosts could be the increased level of contamination of various environments (pastures, food storage) with T. gondii oocysts. In corvids, however, their omnivorousness and access to numerous contamination sources are likely the causes of the infection’s increased prevalence.
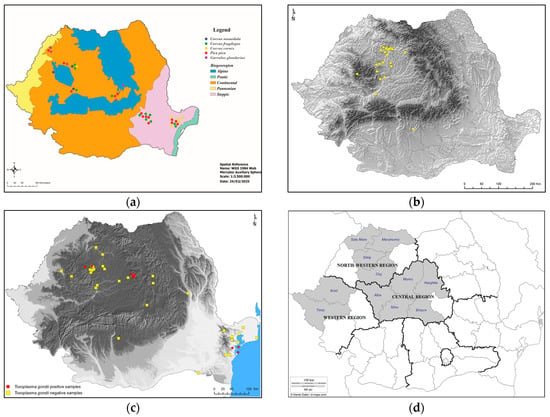
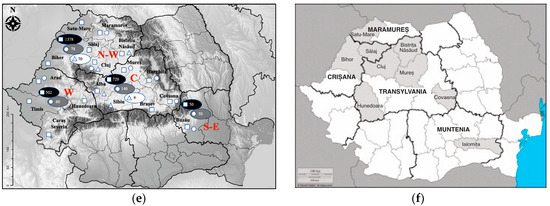
Figure 2.
Central and northwestern locations of most studies targeting T. gondii infection prevalence in definitive and intermediate hosts in Romania: (a) Crows—current study; (b) cats [66]; (c) small mammals [17]; (d) pigs [68]; (e) sheep (squares—counties of sheep origin; circles—counties of lambs origin; triangles—counties of sheep abortions origin; black ovals—total number of sheep per region; gray ovals—total number of lambs per region; white ovals—total number of sheep abortions per region) [69]; (f) goats [70].
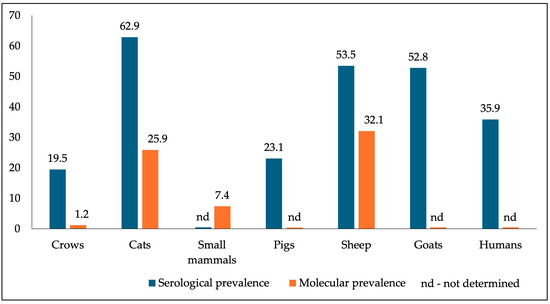
Figure 3.
The current study’s T. gondii infection sero- and molecular prevalence in crows corroborated with that reported in domestic definitive and intermediate hosts.
The comparative analysis of the T. gondii infection prevalence in corvids, worldwide and nationally detected, demonstrates a more or less pronounced heterogeneity, influenced by the previously mentioned factors. The direct role of these birds as sources of human contamination is almost non-existent. However, it is necessary to fill in the information gaps regarding the prevalence of T. gondii in bird populations globally, as some species are directly involved in public health. In addition, it is necessary to implement specific measures to prevent environmental contamination. Related to corvids, it is crucial to raise public awareness to collect the corpses of these birds, which can be a source of contamination for cats or other intermediate hosts. This will minimize the impact of T. gondii on environmental pollution and animal welfare [6].
5. Conclusions
Our findings, a high seroprevalence along with the detection of T. gondii DNA in a (limited) number of crows, support the idea that corvids, through their feeding habits and ecological interactions, are indeed sentinels. This suggests they may potentially contribute to the environmental circulation of T. gondii. To our knowledge, this is the first study describing T. gondii infection in corvids in Romania.
Overall, this work highlights the importance of the continuous surveillance of wild intermediate hosts. Increased public awareness about environmental contamination risks and targeted outreach campaigns are essential to reduce the impact of T. gondii on humans, domestic animals, and wildlife.
Future studies should focus on clarifying the epidemiological chains in which T. gondii is involved by standardizing surveillance techniques and diagnostic methods; this could improve our understanding of the parasite’s distribution and transmission dynamics in bird species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.C. and A.G.; methodology, A.B., Z.K., A.M.I., I.V., F.S. and S.d.C.; software, A.G.; validation, I.V., V.C. and A.B.; formal analysis, A.G.; investigation, A.B., Z.K. and A.M.I.; data curation, A.G. and I.V.; writing—original draft preparation, C.M.G.; writing—review and editing, C.M.G., A.G., F.S. and S.d.C.; visualization, A.G.; supervision, A.G.; project administration, V.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because it was conducted on dead birds collected from roadsides, legally hunted according to the Romanian laws, or humanely euthanized in private vet clinics before sending them to the Parasitic Diseases Department of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine in Cluj-Napoca due to the impossibility of rescuing them.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data may be shared and should be requested from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank everyone involved in providing the dead birds.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Agrawal, V.; Singh, A.; Singh, S.K. Parasites of the musculoskeletal system. In Developments in Microbiology, Organ-Specific Parasitic Diseases of Dogs and Cats; Rana, T., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 265–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeri, T.; Sarvi, S.; Daryani, A. Toxoplasma gondii in mollusks and cold-blooded animals: A systematic review. Parasitology 2021, 148, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezón, O.; Garcia-Bocanegra, I.; Molina-Lopez, R.; Marco, I.; Blanco, J.M.; Höfle, U.; Margalida, A.; Bach-Raich, E.; Darwich, L.; Echeverria, I.; et al. Seropositivity and risk factors associated with Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild birds from Spain. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. A review of toxoplasmosis in wild birds. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 106, 121–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, L.; Olfatifar, M.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Eslahi, A.V.; KarimiPourSaryazdi, A.; Taghipour, A.; Hamidianfar, N.; Badri, M.; Jokelainen, P. Global prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in birds: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2024, 25, e00350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.; Brandão, R.; Lopes, A.F.; Sargo, R.; Casero, M.; Nunes, C.; Silva, F.; Dubey, J.P.; Cardoso, L.; Lopes, A.P. Prevalence of Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in Different Wild Bird Species Admitted to Rehabilitation Centres in Portugal. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.D.; Valle, C.A.; Nieto-Claudin, A.; Fessl, B.; Lewbart, G.A.; Deresienski, D.; Bouazzi, L.; Zapata, S.; Villena, I.; Poulle, M.L. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Galapagos birds: Inference of risk factors associated with diet. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0287403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Literák, I.; Hejlicek, K.; Nezval, J.; Folk, C. Incidence of Toxoplasma gondii in populations of wild birds in the Czech Republic. Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, P.S.; Slutsker, L.; Dietz, V.; McCaig, L.F.; Bresee, J.S.; Shapiro, C.; Griffin, P.M.; Tauxe, R.V. Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1999, 5, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wascher, C.A.F. Corvids. In Encyclopedia of Animal Cognition and Behavior; Vonk, J., Shackelford, T.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Zeid, F.; Morelli, F.; Ibáñez-Álamo, J.D.; Díaz, M.; Reif, J.; Jokimäki, J.; Suhonen, J.; Kaisanlahti-Jokimäki, M.L.; Markó, G.; Bussière, R.; et al. Spatial Overlap and Habitat Selection of Corvid Species in European Cities. Animals 2023, 13, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyoak, D. A comparative study of the food of some British Corvidae. Bird Study 1968, 15, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, D.W.; Billerman, S.M.; Lovette, I.J. Crows, Jays, and Magpies (Corvidae), version 1.0. In Birds of the World; Billerman, S.M., Keeney, B.K., Rodewald, P.G., Schulenberg, T.S., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Ureña, N.M.; Chaudhry, U.; Calero Bernal, R.; Cano Alsua, S.; Messina, D.; Evangelista, F.; Betson, M.; Lalle, M.; Jokelainen, P.; Ortega Mora, L.M.; et al. Contamination of Soil, Water, Fresh Produce, and Bivalve Mollusks with Toxoplasma gondii Oocysts: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, S.; Wood, L.; Su, C.; Spriggs, M.; Brown, J.; Van Why, K.; Gerhold, R. Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in carnivorous wild birds in the eastern United States. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2021, 15, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmár, Z.; Sándor, A.D.; Balea, A.; Borşan, S.D.; Matei, I.A.; Ionică, A.M.; Gherman, C.M.; Mihalca, A.D.; Cozma-Petruț, A.; Mircean, V.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii in small mammals in Romania: The influence of host, season and sampling location. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percipalle, M.; Salvaggio, A.; Pitari, G.M.; Giunta, R.P.; Aparo, A.; Alfonzetti, T.; Marino, A.M.F. Edible Insects and Toxoplasma gondii: Is It Something We Need To Be Concerned About? J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, P.G.; Shukla, R.R.; Sekariah, P.C. Toxoplasma from the eggs of the domestic fowl (Gallus gallus). Science 1961, 133, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzer, S.; Basso, W.; Benavides Silván, J.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Maksimov, P.; Gethmann, J.; Conraths, F.J.; Schares, G. Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis in farm animals: Risk factors and economic impact. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guvernul României. Ministerul Dezvoltării Regionale și Administrației Publice. Portal Legislativ. Available online: https://legislatie.just.ro/Public/DetaliiDocumentAfis/295259 (accessed on 1 June 2025).
- Svensson, L.; Mullarney, K.; Zetterstrom, D.; Grant, P.J. Collins Bird Guide: The Most Complete Guide to the Birds of Britain and Europe; HarperCollins: London, UK, 1999; pp. 330–338. [Google Scholar]
- Villena, I.; Durand, B.; Aubert, D.; Blaga, R.; Geers, R.; Thomas, M.; Perret, C.; Alliot, A.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Thébault, A.; et al. New strategy for the survey of Toxoplasma gondii in meat for human consumption. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-López, R.; Cabezón, O.; Pabón, M.; Darwich, L.; Obón, E.; Lopez-Gatius, F.; Dubey, J.P.; Almería, S. High seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in the Common raven (Corvus corax) in the Northeast of Spain. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 93, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, W.L.; Vercammen, M.; De Braekeleer, J.; Verschueren, H. Identification of a 200- to 300-fold repetitive 529 bp DNA fragment in Toxoplasma gondii, and its use for diagnostic and quantitative PCR. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhang, X.; Dubey, J.P. Genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii by multilocus PCR-RFLP markers: A high resolution and simple method for identification of parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Library of Medicine. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Epi InfoTM. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/epiinfo/index.html (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Droege, G.; Töpfer, T. The Corvids Literature Database--500 years of ornithological research from a crow’s perspective. Database 2016, 2016, bav122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DataZone by BirdLife. Available online: https://datazone.birdlife.org (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Păsări Din România. Available online: https://pasaridinromania.sor.ro/web (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Abdoli, A.; Arbabi, M.; Pirestani, M.; Mirzaghavami, M.; Ghaffarifar, F.; Dalimi, A.; Sadraei, J. Molecular assessment of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in hooded crows (Corvus cornix) in Tehran, Iran. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 57, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslami, A.; Meshgi, B.; Rahbari, S.; Ghaemi, P.; Aghaebrahimi-Samani, R. Biodiversity and Prevalence of Parasites of Rook (Corvus frugilegus) in Iran. Iranian J. Parasitol. 2007, 2, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilifallah, M.; Sadraei, J.; Pirestani, M.; Kalantari, R. Molecular characterization and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in free-living animals in Iran: Effect of One Health. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2022, 36, 100808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, S.M. Toxoplasmosis of Birds in Kazakhstan; Nauka Publishing: Alma-Ata, Kazakhstan, 1976; 115p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Muz, M.N.; Orunç Kilinç, Ö.; İşler, C.T.; Altuğ, E.; Karakavuk, M. Molecular Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in Brain Tissues of Some Wild Birds. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2015, 21, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salant, H.; Hamburger, J.; King, R.; Baneth, G. Toxoplasma gondii prevalence in Israeli crows and Griffon vultures. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 191, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, A.; Ali, S.; Ahmed, H.; Simsek, S.; Rizwan, M.; Kaleem, I.; Gondal, M.A.; Shabbir, A.; Pervaiz, F.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Toxoplasma gondii in Wild Birds of Punjab Province, Pakistan. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, P.; Manwell, R.D. Toxoplasma from the crow, a new natural host. Exp. Parasitol. 1956, 5, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Felix, T.A.; Kwok, O.C. Serological and parasitological prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in wild birds from Colorado. J. Parasitol. 2010, 96, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work, T.M.; Massey, J.G.; Rideout, B.A.; Gardiner, C.H.; Ledig, D.B.; Kwok, O.C.; Dubey, J.P. Fatal toxoplasmosis in free-ranging endangered ‘Alala from Hawaii. J. Wildl. Dis. 2000, 36, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Esquivel, C.; Rajendran, C.; Ferreira, L.R.; Kwok, O.C.; Choudhary, S.; Alvarado-Esquivel, D.; Rodríguez-Peña, S.; Villena, I.; Dubey, J.P. Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in wild birds in Durango, Mexico. J. Parasitol. 2011, 97, 809–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, L.; Cabezón, O.; Echeverria, I.; Pabón, M.; Marco, I.; Molina-López, R.; Alarcia-Alejos, O.; López-Gatius, F.; Lavín, S.; Almería, S. Presence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum DNA in the brain of wild birds. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 183, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancianti, F.; Terracciano, G.; Sorichetti, C.; Vecchio, G.; Scarselli, D.; Perrucci, S. Epidemiologic Survey on Toxoplasma gondii and Trichinella pseudospiralis Infection in Corvids from Central Italy. Pathogens 2020, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardoni, S.; Rocchigiani, G.; Varvaro, I.; Altomonte, I.; Ceccherelli, R.; Mancianti, F. Serological and Molecular Investigation on Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Wild Birds. Pathogens 2019, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penezić, A.; Pantelić, I.; Uzelac, A.; Bogdanović, N.; Ćirović, D.; Klun, I. Synanthropic birds and rodents as indicators for Toxoplasma gondii oocyst contamination in urban and suburban environments. In Proceedings of the XIV European Multicolloquium of Parasitology, Wrocław, Poland, 26–30 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lukášová, R.; Kobédová, K.; Halajian, A.; Bártová, E.; Murat, J.B.; Rampedi, K.M.; Luus-Powell, W.J. Molecular detection of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in birds from South Africa. Acta Trop. 2018, 178, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, A.; Ramos, R.; Parra-Torres, Y.; Mercier, A.; Galal, L.; Pearce-Duvet, J.; Villena, I.; Montalvo, T.; González-Solís, J.; Hammouda, A.; et al. Exposure of yellow-legged gulls to Toxoplasma gondii along the Western Mediterranean coasts: Tales from a sentinel. Int. J. Parasitol. Parasites Wildl. 2019, 8, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yue, C.L.; Yuan, Z.G.; Lin, R.Q.; He, Y.; Yin, C.C.; Xu, M.J.; Song, H.Q.; Zhu, X.Q. Molecular and serological diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection in experimentally infected chickens. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 173, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juránková, J.; Basso, W.; Neumayerová, H.; Baláž, V.; Jánová, E.; Sidler, X.; Deplazes, P.; Koudela, B. Brain is the predilection site of Toxoplasma gondii in experimentally inoculated pigs as revealed by magnetic capture and real-time PCR. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juránková, J.; Basso, W.; Neumayerová, H.; Frencová, A.; Baláž, V.; Deplazes, P.; Koudela, B. Predilection sites for Toxoplasma gondii in sheep tissues revealed by magnetic capture and real-time PCR detection. Food Microbiol. 2015, 52, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P. Tissue cyst tropism in Toxoplasma gondii: A comparison of tissue cyst formation in organs of cats, and rodents fed oocysts. Parasitology 1997, 115, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opsteegh, M.; Langelaar, M.; Sprong, H.; den Hartog, L.; De Craeye, S.; Bokken, G.; Ajzenberg, D.; Kijlstra, A.; van der Giessen, J. Direct detection and genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii in meat samples using magnetic capture and PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juránková, J.; Opsteegh, M.; Neumayerová, H.; Kovařčík, K.; Frencová, A.; Baláž, V.; Volf, J.; Koudela, B. Quantification of Toxoplasma gondii in tissue samples of experimentally infected goats by magnetic capture and real-time PCR. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Sharma, S.P. Parasitemia and tissue infection in sheep fed Toxoplasma gondii oocysts. J. Parasitol. 1980, 66, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirata, I.W. Comparison of Toxoplasma gondii Cysts Predilection in the Heart and Diaphragm of Pig in Bali. J. Sain Vet. 2014, 32, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Aubert, D.; Escotte-Binet, S.; Durand, B.; Robert, C.; Geers, R.; Alliot, A.; Belbis, G.; Villena, I.; Blaga, R. Anatomical distribution of Toxoplasma gondii in naturally and experimentally infected lambs. Parasite 2022, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lehmann, T.; Lautner, F.; Kwok, O.C.; Gamble, H.R. Toxoplasmosis in sentinel chickens (Gallus domesticus) in New England farms: Seroconversion, distribution of tissue cysts in brain, heart, and skeletal muscle by bioassay in mice and cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 214, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangoura, B.; Zöller, B.; Koethe, M.; Ludewig, M.; Pott, S.; Fehlhaber, K.; Straubinger, R.K.; Daugschies, A. Experimental Toxoplasma gondii oocyst infections in turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo). Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 196, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zöller, B.; Koethe, M.; Ludewig, M.; Pott, S.; Daugschies, A.; Straubinger, R.K.; Fehlhaber, K.; Bangoura, B. Tissue tropism of Toxoplasma gondii in turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) after parenteral infection. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S.A.; Huyvaert, K.P.; Bailey, L.L.; Iqbal, A.; Su, C.; Dixon, B.R.; Alisauskas, R.T.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Jenkins, E.J. Multi-scale occupancy approach to estimate Toxoplasma gondii prevalence and detection probability in tissues: An application and guide for field sampling. Int. J. Parasitol. 2016, 46, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.G.; Lapen, D.R.; Mitchell, G.W.; Provencher, J.F.; Wilson, S. Interaction of diet and habitat predicts Toxoplasma gondii infection rates in wild birds at a global scale. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonso, E.; Lemoine, M.; Poulle, M.L.; Ravat, M.C.; Romand, S.; Thulliez, P.; Villena, I.; Aubert, D.; Rabilloud, M.; Riche, B.; et al. Spatial distribution of soil contamination by Toxoplasma gondii in relation to cat defecation behaviour in an urban area. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C. Parasite zoonoses and wildlife: One Health, spillover and human activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerburg, B.G.; Kijlstra, A. Changing climate—Changing pathogens: Toxoplasma gondii in north-western Europe. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Györke, A.; Balea, A.; Borșan, S.; Su, C.; Jiang, T.; Magdaș, C.; Mărcuțan, D.; Blaga, R.; Mircean, V.; Villena, I.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii genotypes and frequency in domestic cats from Romania. BMC Vet. Res. 2024, 20, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmár, Z.; Briciu, V.; Ieremia, A.; Lupșe, M.; Ionică, A.M. Seroprevalence of IgG Antibodies Against Toxoplasma Gondii Among Hospitalized Patients from Northwestern Romania. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference On Infectious Disease Dynamics, Bologna, Italy, 12 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Paştiu, A.I.; Györke, A.; Blaga, R.; Mircean, V.; Rosenthal, B.M.; Cozma, V. In Romania, exposure to Toxoplasma gondii occurs twice as often in swine raised for familial consumption as in hunted wild boar, but occurs rarely, if ever, among fattening pigs raised in confinement. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paștiu, A.I.; Mircean, V.; Mercier, A.; Passebosc-Faure, K.; Plault, N.; Dardé, M.L.; Blaga, R.; Villena, I.; Pusta, D.L.; Cozma-Petruț, A.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii infection in sheep from Romania. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovu, A.; Györke, A.; Mircean, V.; Gavrea, R.; Cozma, V. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in dairy goats from Romania. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).