Comparative IP-MS Reveals HSPA5 and HSPA8 Interacting with Hemagglutinin Protein to Promote the Replication of Influenza A Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Plasmids
2.3. Antibodies
2.4. Protein Immunoprecipitation
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. ShRNA Transfection
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Virus Infection
2.9. Virus Attachment and Internalization Assay
2.10. Real Time qPCR (RT-qPCR)
2.11. Immunofuorescence Assay
2.12. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.13. Gene Ontology
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
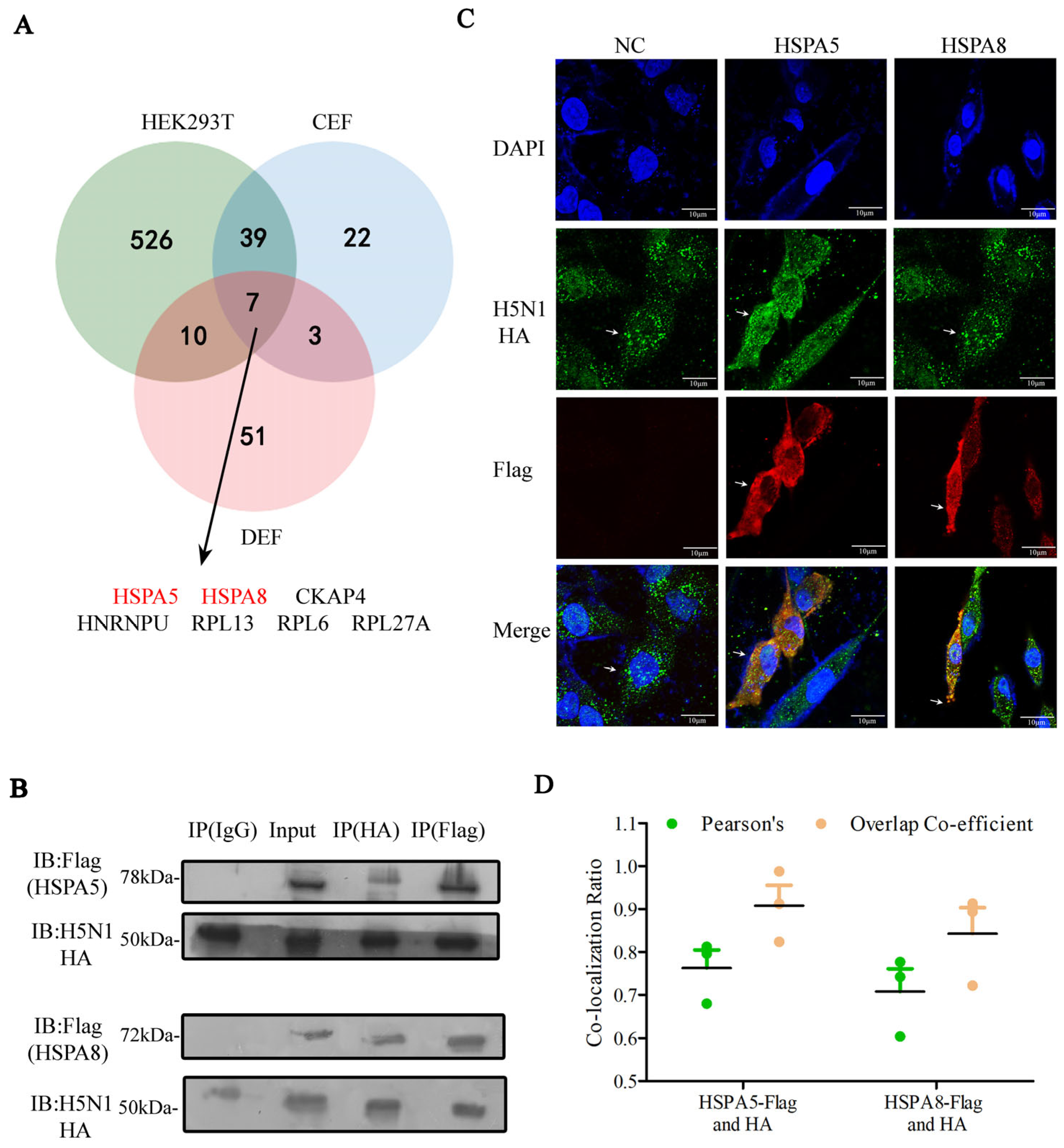
3.1. Identification of the Host Factors That Interacted with HA Protein of IAV and Plasmids
3.2. Functional Analysis of HA-Interacting Host Proteins
3.3. HSPA5 or HSPA8 Interacts with HA in Chicken, Duck and Human Cells
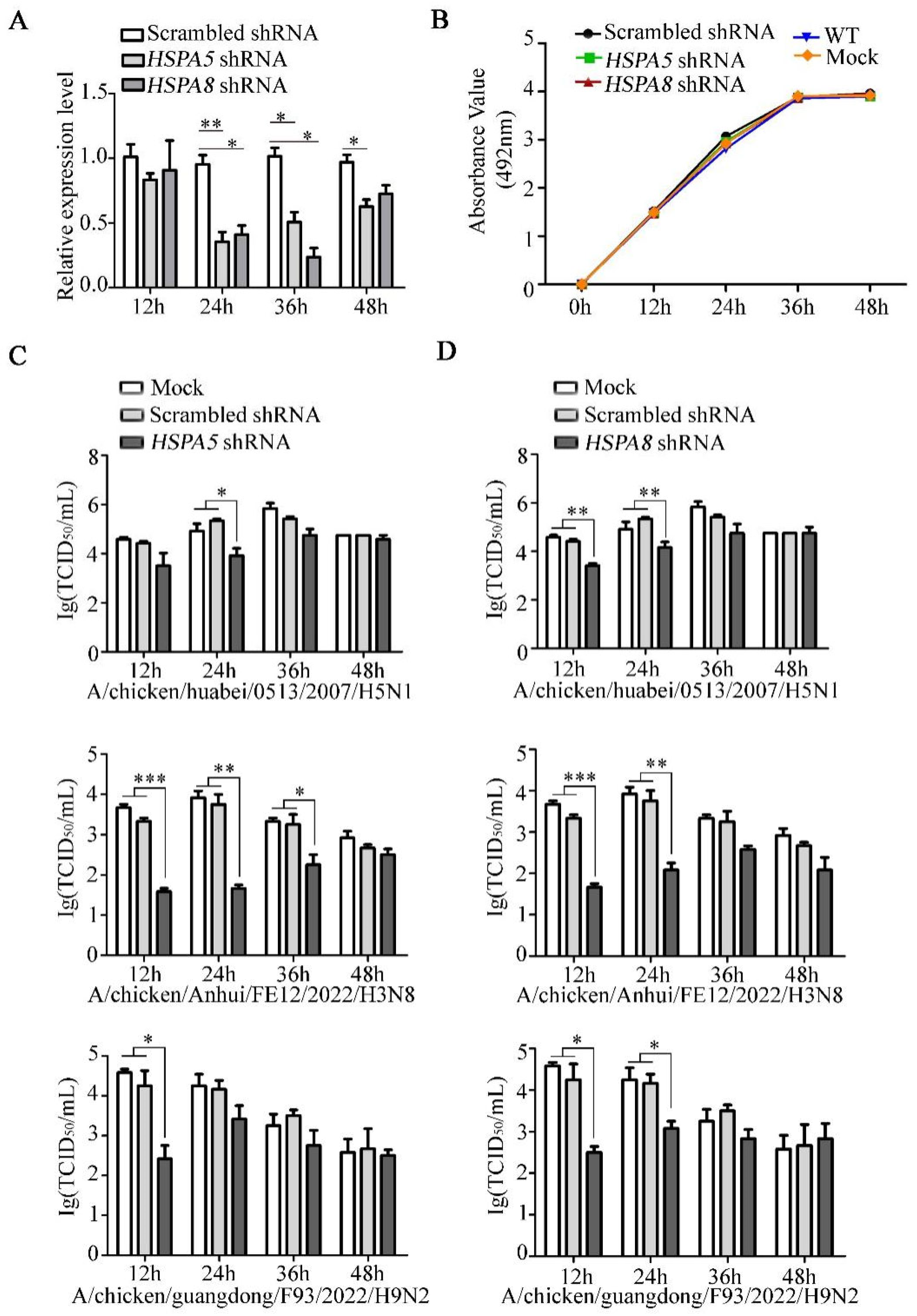
3.4. HSPA5 or HSPA8 Positively Regulate the IAV Replication
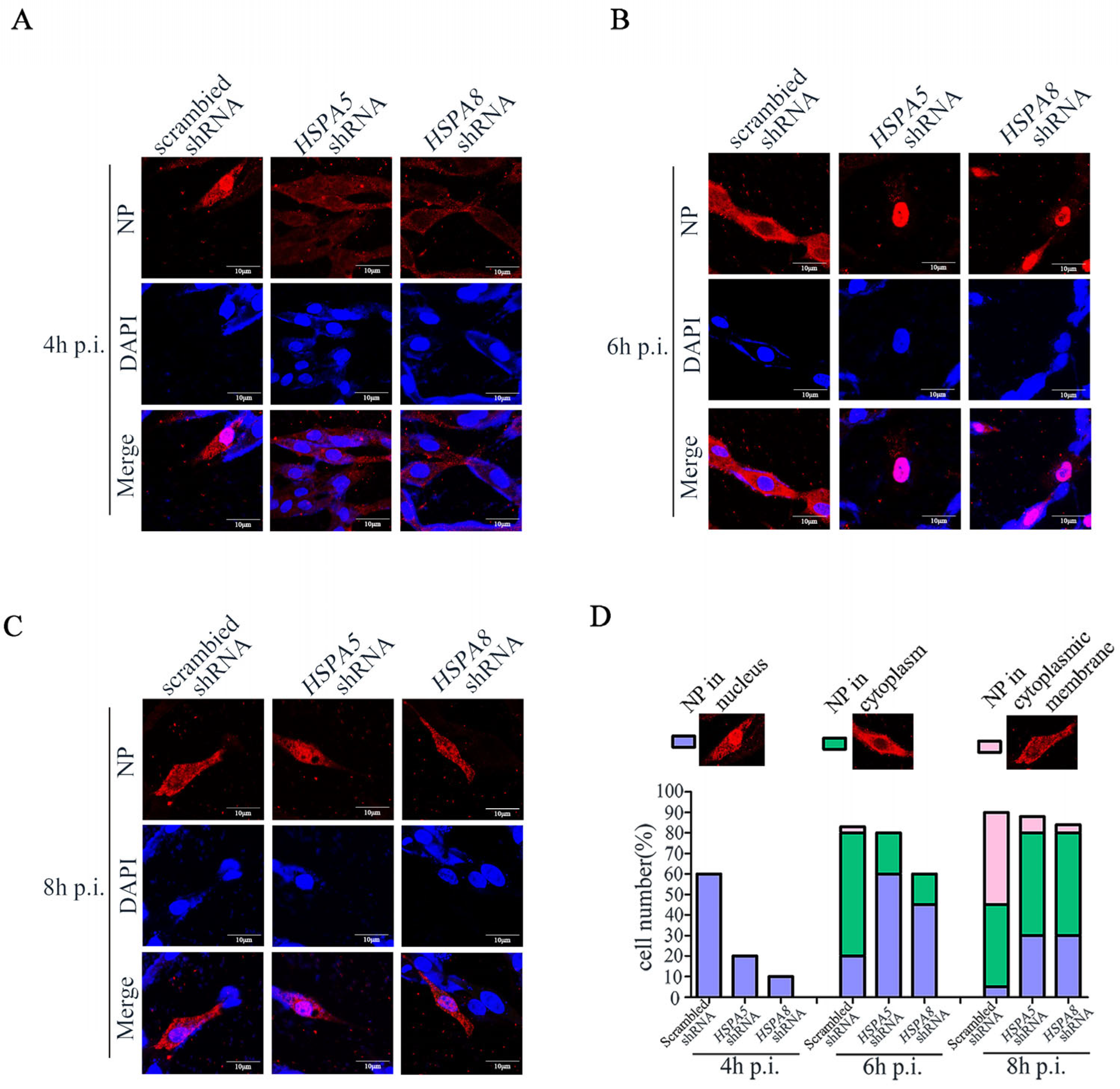
3.5. HSPA8 or HSPA5 Is Involved in the Early Stage of IAV Replication Cycle
3.6. HSPA8 or HSPA5 Promotes IAV Attachment and Internalization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pleschka, S. Overview of influenza viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 370, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hutchinson, E.C. Influenza Virus. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 809–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, E.F.; Tompkins, S.M. Fitness Determinants of Influenza A Viruses. Viruses 2023, 15, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, D.; Revol, R.; Östbye, H.; Wang, H.; Daniels, R. Influenza A Virus Cell Entry, Replication, Virion Assembly and Movement. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.P.; Gordon, M.L. An overview of influenza A virus genes, protein functions, and replication cycle highlighting important updates. Virus Genes 2022, 58, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eierhoff, T.; Hrincius, E.R.; Rescher, U.; Ludwig, S.; Ehrhardt, C. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) promotes uptake of influenza A viruses (IAV) into host cells. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Kong, F.; Li, Q.; Yan, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, L.; et al. The G Protein-Coupled Receptor FFAR2 Promotes Internalization during Influenza A Virus Entry. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01707-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, Y.; Nishide, S.; Ose, T.; Suzuki, T.; Kato, I.; Fukuhara, H.; Fujioka, M.; Horiuchi, K.; Satoh, A.O.; Nepal, P.; et al. A Sialylated Voltage-Dependent Ca(2+) Channel Binds Hemagglutinin and Mediates Influenza A Virus Entry into Mammalian Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 809–818.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Li, C.; Deng, G.; Shi, J.; Kong, H.; et al. Influenza virus uses mGluR2 as an endocytic receptor to enter cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 1764–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, N.S.; Moshkina, N.; Fenouil, R.; Gardner, T.J.; Aguirre, S.; Shah, P.S.; Zhao, N.; Manganaro, L.; Hultquist, J.F.; Noel, J.; et al. Targeting Viral Proteostasis Limits Influenza Virus, HIV, and Dengue Virus Infection. Immunity 2016, 44, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, M.; Wen, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G. Viral-Host Interactome Analysis Reveals Chicken STAU2 Interacts With Non-structural Protein 1 and Promotes the Replication of H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 590679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawakami, E.; Shoemaker, J.E.; Lopes, T.J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Tomita, Y.; Kozuka-Hata, H.; Gorai, T.; Kuwahara, T.; Takeda, E.; et al. Influenza virus-host interactome screen as a platform for antiviral drug development. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 16, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapira, S.D.; Gat-Viks, I.; Shum, B.O.; Dricot, A.; de Grace, M.M.; Wu, L.; Gupta, P.B.; Hao, T.; Silver, S.J.; Root, D.E.; et al. A physical and regulatory map of host-influenza interactions reveals pathways in H1N1 infection. Cell 2009, 139, 1255–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.M.; Chu, H.; Zhang, A.J.; Leung, L.H.; Sze, K.H.; Kao, R.Y.; Chik, K.K.; To, K.K.; Chan, J.F.; Chen, H.; et al. Hemagglutinin of influenza A virus binds specifically to cell surface nucleolin and plays a role in virus internalization. Virology 2016, 494, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, E.; Causse, S.; Baverel, V.; Dubrez, L.; Borges-Bonan, N.; Demidov, O.; Garrido, C. Endoplasmic Reticulum Chaperones in Viral Infection: Therapeutic Perspectives. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e0003521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongwichit, S.; Sornjai, W.; Jitobaom, K.; Greenwood, M.; Greenwood, M.P.; Hitakarun, A.; Wikan, N.; Murphy, D.; Smith, D.R. A functional interaction between GRP78 and Zika virus E protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricher, F.; Macri, C.; Ruff, M.; Muller, S. HSPA8/HSC70 chaperone protein: Structure, function, and chemical targeting. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1937–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Wei, Y.; Dong, C.; Pei, G.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, J.; Yao, Z.; Wang, Q. HSPA8 regulates anti-bacterial autophagy through liquid-liquid phase separation. Autophagy 2023, 19, 2702–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dores-Silva, P.R.; Cauvi, D.M.; Coto, A.L.S.; Silva, N.S.M.; Borges, J.C.; De Maio, A. Human heat shock cognate protein (HSC70/HSPA8) interacts with negatively charged phospholipids by a different mechanism than other HSP70s and brings HSP90 into membranes. Cell Stress Chaperones 2021, 26, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.S.; Mistry, B.; Haslam, S.M.; Barclay, W.S. Host and viral determinants of influenza A virus species specificity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Le Sage, V.; Nanni, A.V.; Snyder, D.J.; Cooper, V.S.; Lakdawala, S.S. Genome-wide analysis of influenza viral RNA and nucleoprotein association. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 8968–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Clohisey, S.M.; Chia, B.S.; Wang, B.; Cui, A.; Eisenhaure, T.; Schweitzer, L.D.; Hoover, P.; Parkinson, N.J.; Nachshon, A.; et al. Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies host dependency factors for influenza A virus infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmapalan, D. Influenza. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, K.M.; McGregor, M.J.; Bouhaddou, M.; Polacco, B.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Nguyen, T.T.; Newton, B.W.; Urbanowski, M.; Kim, H.; Williams, M.A.P.; et al. Proteomic and genetic analyses of influenza A viruses identify pan-viral host targets. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Andel, E.; Roosjen, M.; van der Zanden, S.; Lange, S.C.; Weijers, D.; Smulders, M.M.J.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Zuilhof, H.; Tijhaar, E.J. Highly Specific Protein Identification by Immunoprecipitation-Mass Spectrometry Using Antifouling Microbeads. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 23102–23116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.K.; Munro, J.B.; Shi, G.; Majdoul, S.; Compton, A.A.; Rein, A. Restriction of Influenza A Virus by SERINC5. mBio 2022, 13, e0292322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Eriksson, P.; Naguib, M.M.; Jax, E.; Sihlbom, C.; Olsson, B.M.; Lundkvist, Å.; Olsen, B.; Järhult, J.D.; Larson, G.; et al. Expression of influenza A virus glycan receptor candidates in mallard, chicken, and tufted duck. Glycobiology 2024, 34, cwad098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, A.; Webster, R.; Matrosovich, M. Differences between influenza virus receptors on target cells of duck and chicken. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Río-Bergé, C.; Cong, Y.; Reggiori, F. Getting on the right track: Interactions between viruses and the cytoskeletal motor proteins. Traffic 2023, 24, 114–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, Y.; Keusch, J.J.; Decamps, L.; Ho-Xuan, H.; Iketani, S.; Gut, H.; Kutay, U.; Helenius, A.; Yamauchi, Y. Influenza virus uses transportin 1 for vRNP debundling during cell entry. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubkowska, A.; Pluta, W.; Strońska, A.; Lalko, A. Role of Heat Shock Proteins (HSP70 and HSP90) in Viral Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachatoorian, R.; Ganapathy, E.; Ahmadieh, Y.; Wheatley, N.; Sundberg, C.; Jung, C.L.; Arumugaswami, V.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Dasgupta, A.; French, S.W. The NS5A-binding heat shock proteins HSC70 and HSP70 play distinct roles in the hepatitis C viral life cycle. Virology 2014, 454–455, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khachatoorian, R.; Riahi, R.; Ganapathy, E.; Shao, H.; Wheatley, N.M.; Sundberg, C.; Jung, C.L.; Ruchala, P.; Dasgupta, A.; Arumugaswami, V.; et al. Allosteric heat shock protein 70 inhibitors block hepatitis C virus assembly. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Song, D.; Li, H.; He, M.L. Stress proteins: The biological functions in virus infection, present and challenges for target-based antiviral drug development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, R.; Kuroda, K.; Yoshida, R.; Tsuda, Y.; Fujikura, D.; Miyamoto, H.; Kajihara, M.; Kida, H.; Takada, A. Heat shock protein 70 modulates influenza A virus polymerase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7599–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, U.C.; Bagchi, P.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Dutta, D.; Chawla-Sarkar, M. Cell death regulation during influenza A virus infection by matrix (M1) protein: A model of viral control over the cellular survival pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Ning, M.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Pu, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Huang, Y. Comparative IP-MS Reveals HSPA5 and HSPA8 Interacting with Hemagglutinin Protein to Promote the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Pathogens 2025, 14, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060535
Feng X, Ning M, Chen B, Li X, Sun H, Pu J, Liu J, Wang N, Huang Y. Comparative IP-MS Reveals HSPA5 and HSPA8 Interacting with Hemagglutinin Protein to Promote the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Pathogens. 2025; 14(6):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060535
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xingwei, Mengfei Ning, Bin Chen, Xuan Li, Honglei Sun, Juan Pu, Jinhua Liu, Na Wang, and Yinhua Huang. 2025. "Comparative IP-MS Reveals HSPA5 and HSPA8 Interacting with Hemagglutinin Protein to Promote the Replication of Influenza A Virus" Pathogens 14, no. 6: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060535
APA StyleFeng, X., Ning, M., Chen, B., Li, X., Sun, H., Pu, J., Liu, J., Wang, N., & Huang, Y. (2025). Comparative IP-MS Reveals HSPA5 and HSPA8 Interacting with Hemagglutinin Protein to Promote the Replication of Influenza A Virus. Pathogens, 14(6), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens14060535




